Chronic Inflammation and Wound Healing
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
When does chronic inflammation occur?
After repeated episodes of acute inflammation that fails to eliminate inciting stimulus
What types of cells will we see in chronic inflammation?
Mononuclear (plasma, lymphocytes, macrophages)
Fibroblasts
What are some causes of Chronic inflammation?
Persistant infection of microorganisms
Prolonged toxic exposures
Autoimmune rxns
Persistent inj
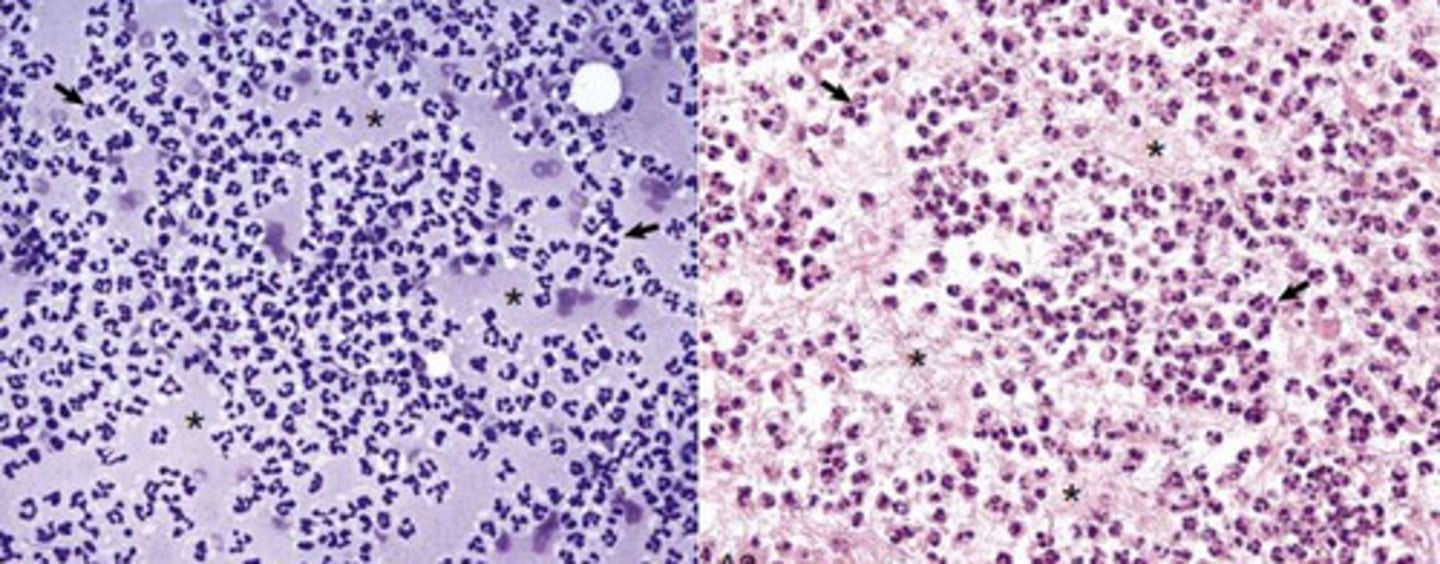
What kind of inflammation is this?
Acute - neutrophils and edema
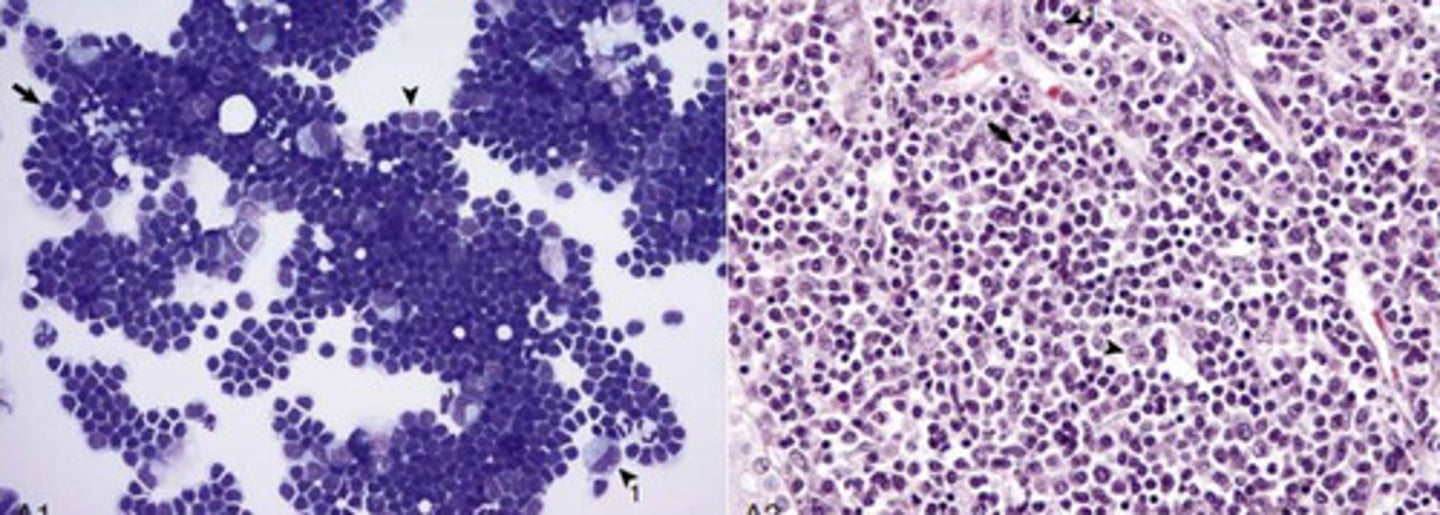
What kind of inflammation is this?
Chronic - lymphocytes and macrophages
Name a few benefits of Chronic inflamation?
Wall off antigens
Can prevent exaggerated immune response
What are ways Chronic inflammation can be harmful?
Take up space, displacing tissue
affects function of tissue
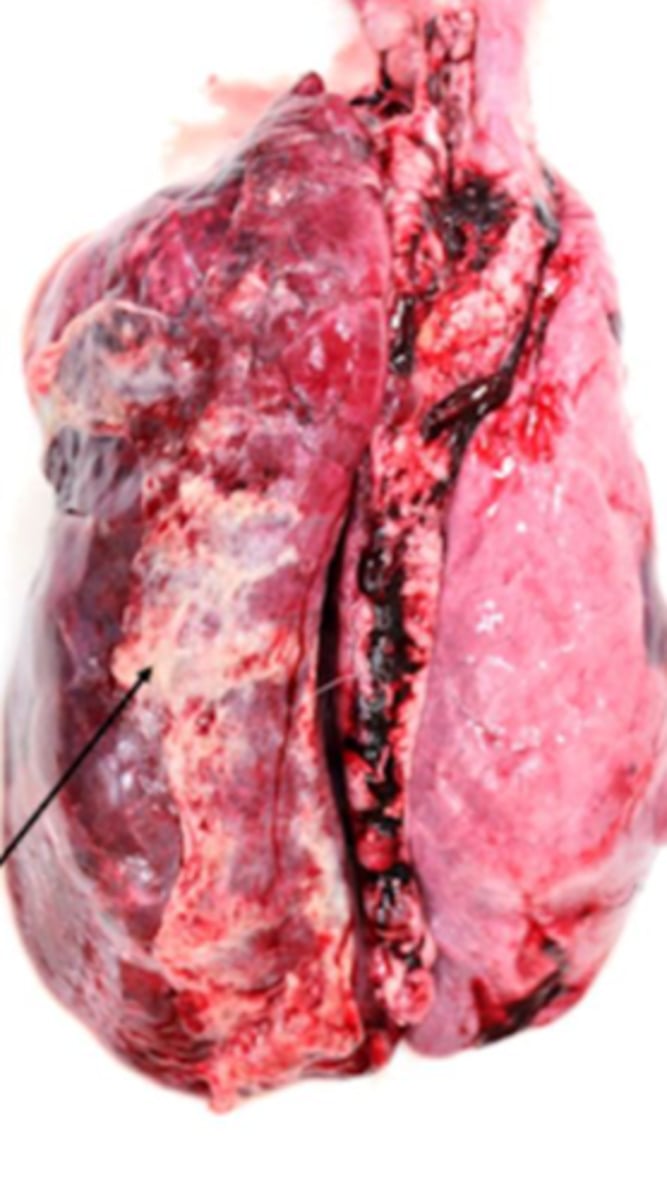
What kind of inflammation is present?
Acute - fibrin
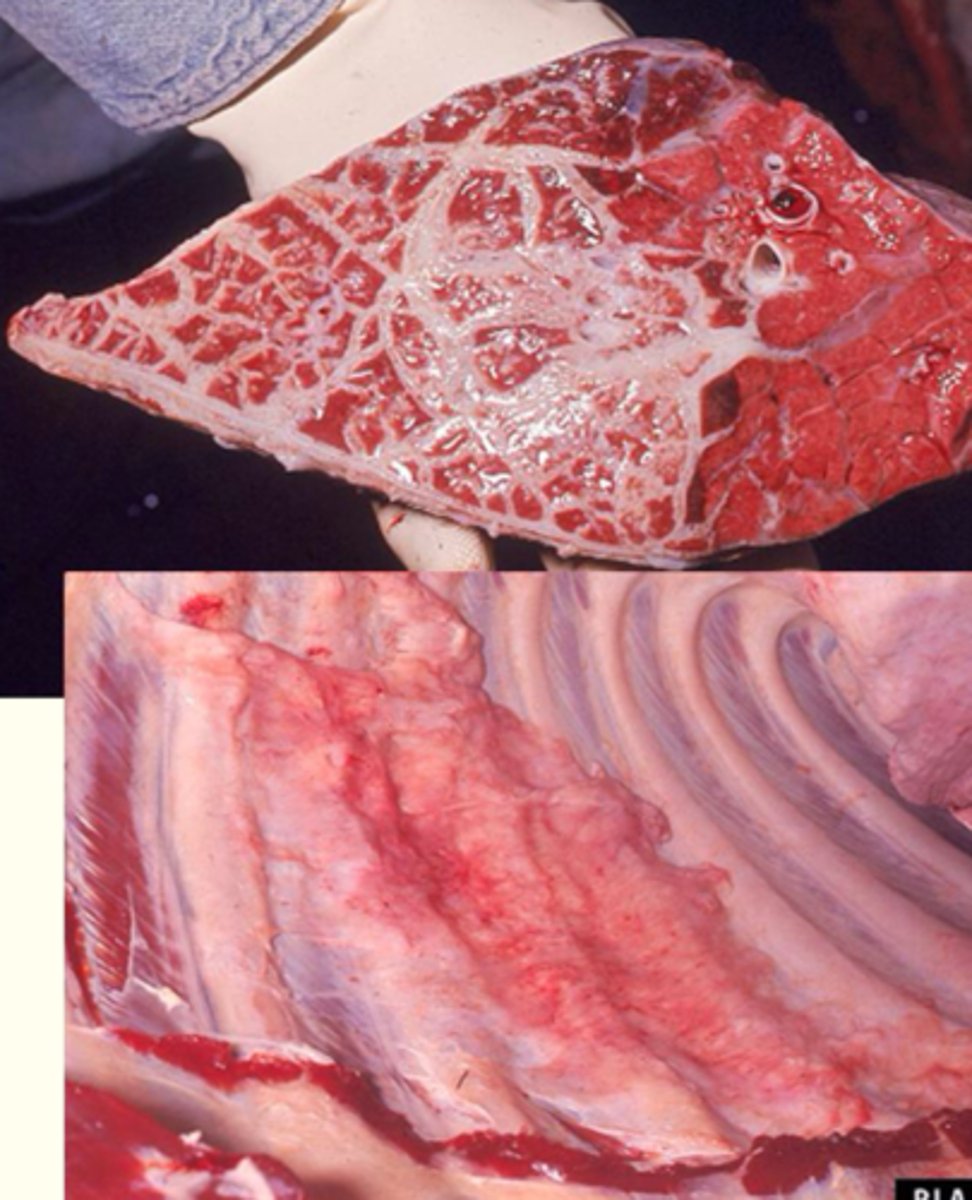
What kind of inflammation is present?
Chronic - Fiberous attachment to wall
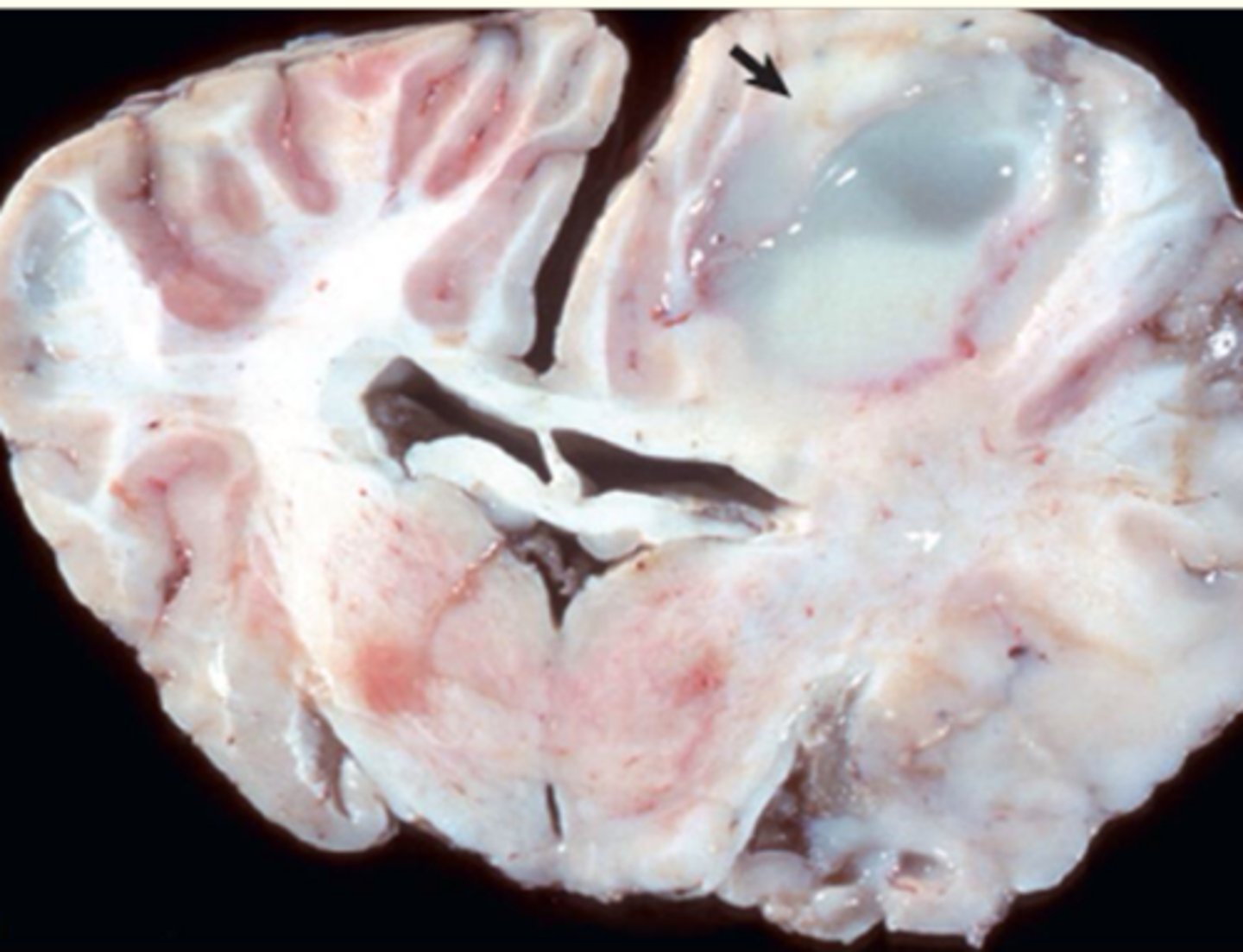
What is this an example of?
Abscess
How does an abscess form?
Enzymes from neutrophils will liquify tissue and neutrophils to form pus
What is the enzymes neutrophils release to form an abscess?
Myeloperoxidase
What are the two forms of abscess?
Septic - bacteria
Steril - no bacteria
What can happen to an abscess that makes it need to be lanced and unable to be penetrated w/ antibiotics?
The thin CT around the abbess will form a fibrous capsule to wall it off
What types of cells will we see in a granuloma?
Lymphocytes,
multinucleated giant cells (macrophages)
epithelial macrophages
eosinophils
fibroblasts
endothelial proliferation
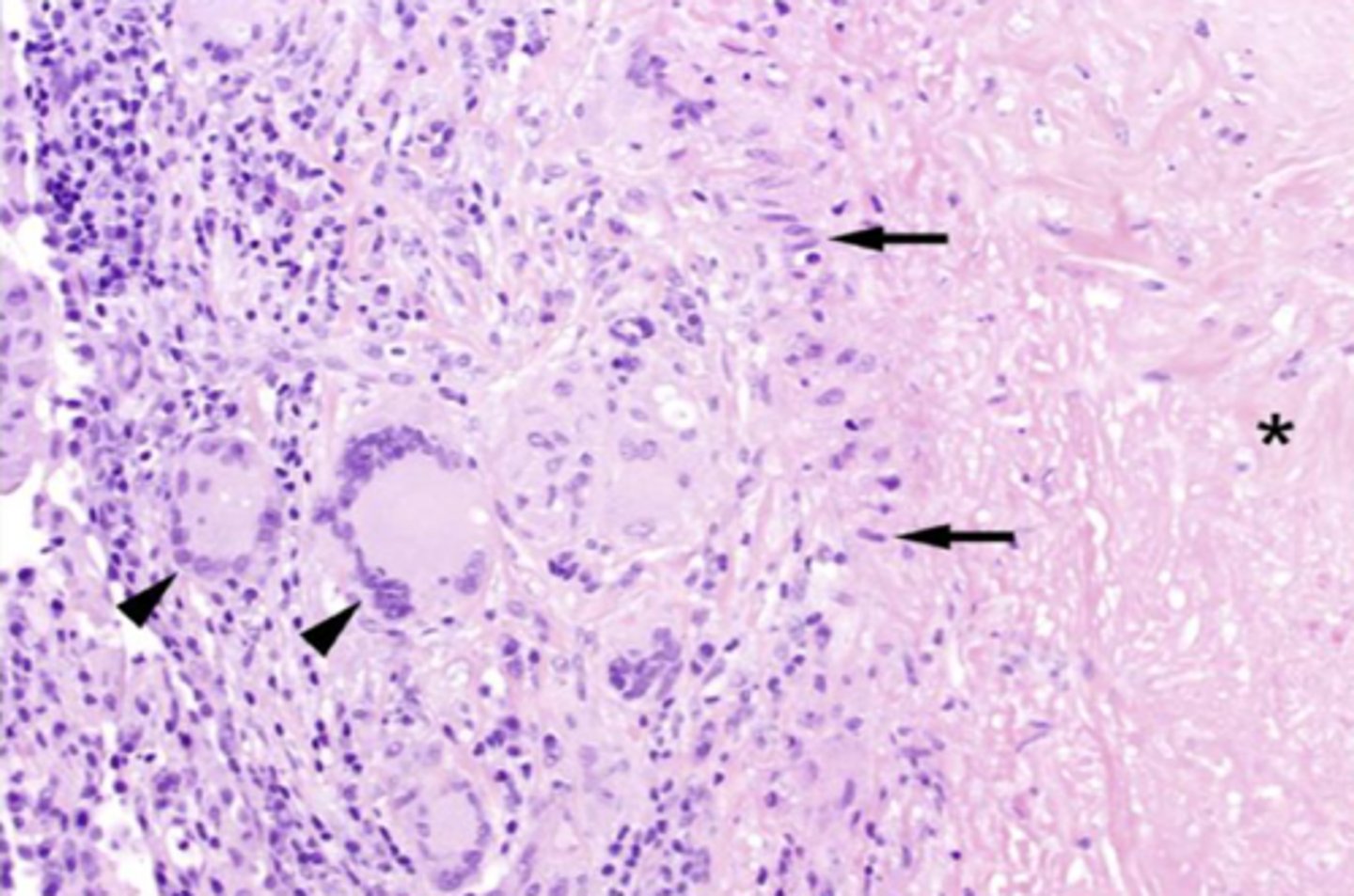
What cells are dictated by the arrows(full arrows) and what are their jobs?
Epithelioid macrophages
- Secrete cell mediators
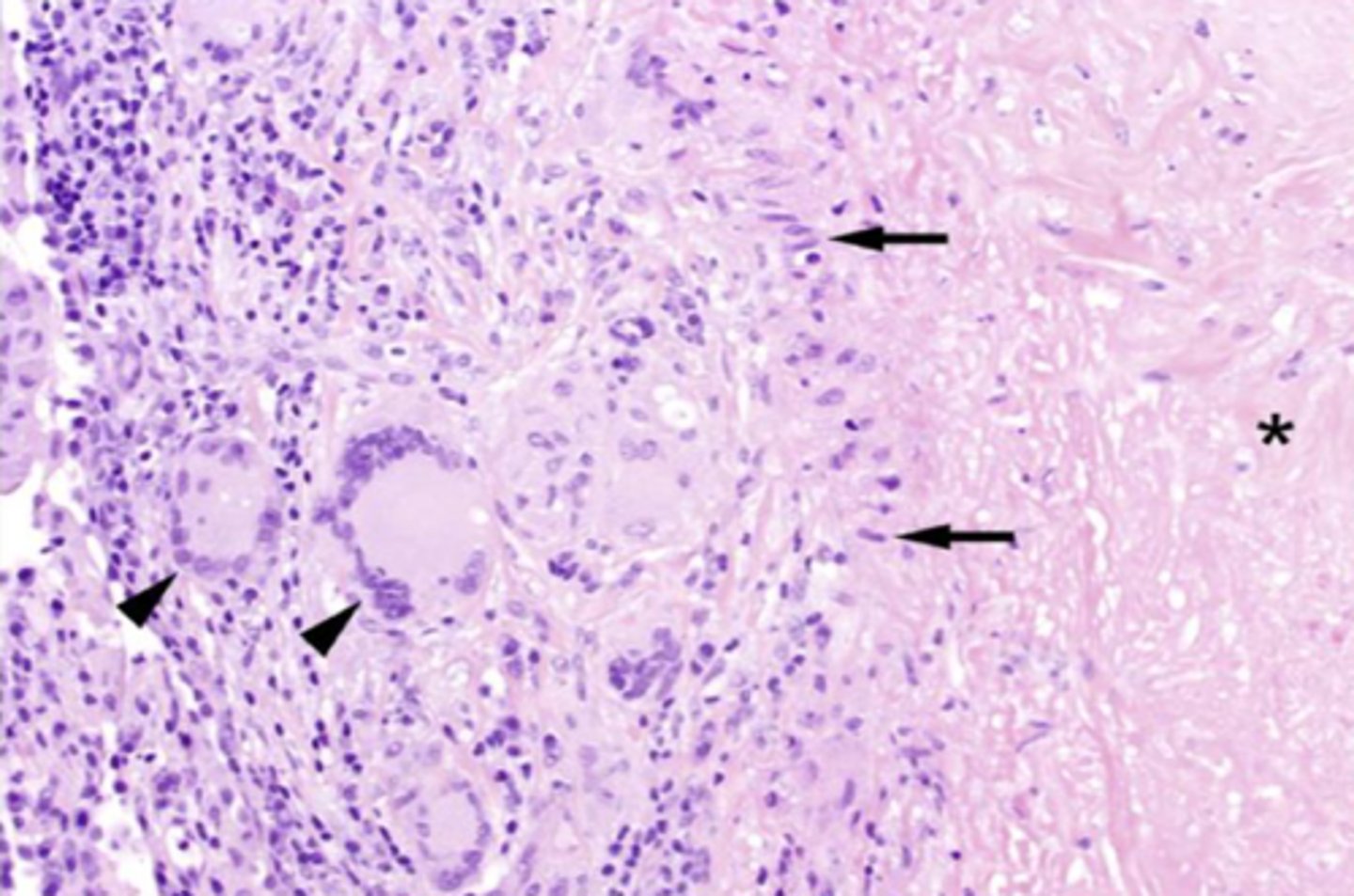
What are the cells dictated by the arrow heads and what are their function?
Multinucleated giant cells
-remove/ sequester foreign material
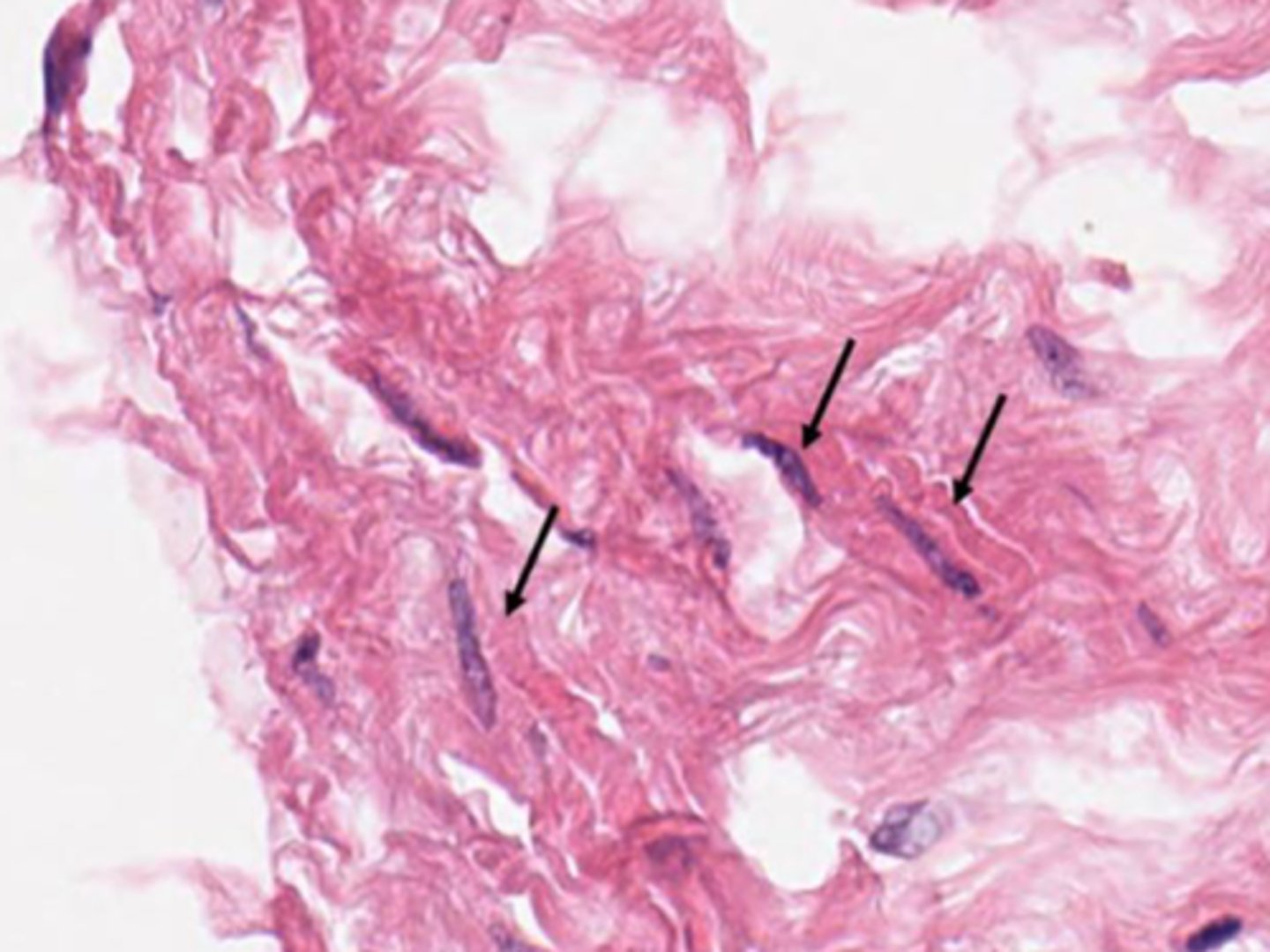
What are the arrows pointing to? What does it do?
fibroblasts - produces collagen and ECM as well as cytokines and chemokins
How are nodular granulomas arranged and what lymphocyte is associated with them?
Arranged in discrete masses/ Nodules - well demarcated- central necrosis
-TH1
Lepromatous granulomas are arranged how? What lymphocyte is associated w/ them?
Dispersed in sheets of cells at random. - white to gray/ non caseating
-TH2
What are two common examples of nodular granulomas?
Mycobacterium
Coccidioides (valley fever)
What are the stages of nodular granulomas?
1. Immune cells flood site,
2. Thin fibers CT forms and Macrophages start walling off,
3. Dense layer of macrophages and caseated center calcified outer ring
4. capsule formation
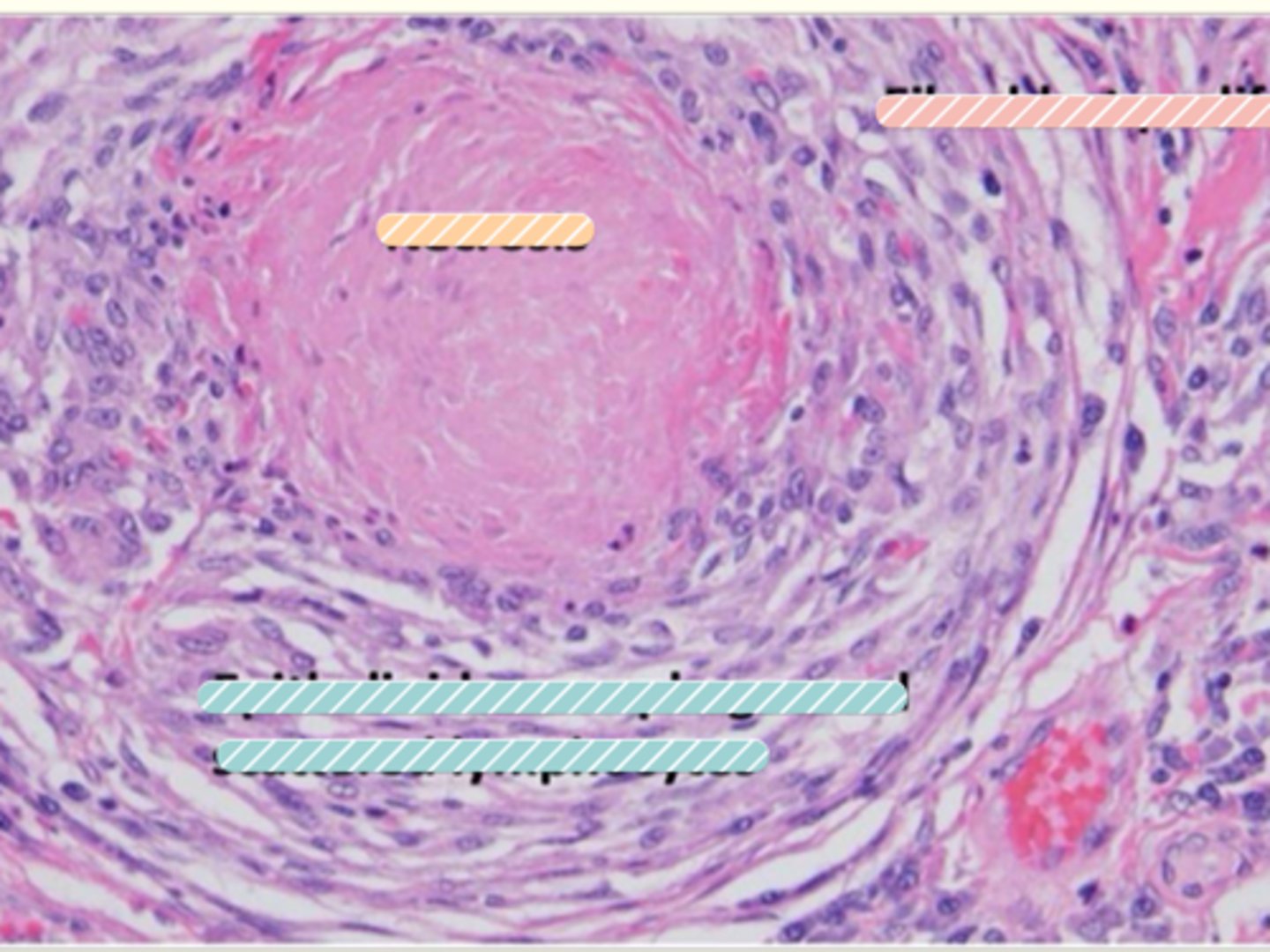
What do we find in the inner most region of a nodular granuloma?
Macrophages
Giant multinucleated cells
Caseating necrosis
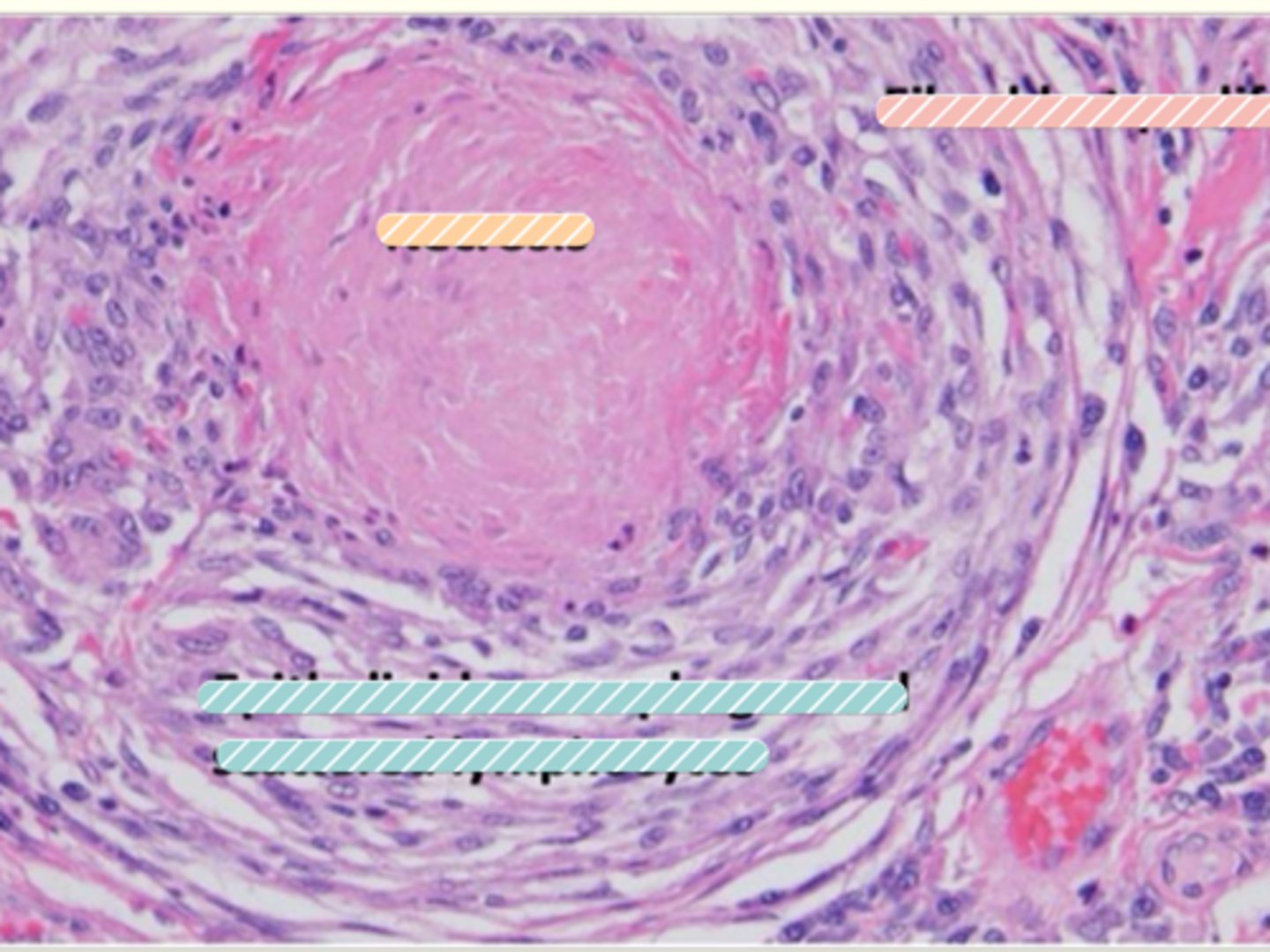
What do we find in the middle of a nodular granuloma?
macrophages
Epithelioid macrophages
Giant multinucleated cells
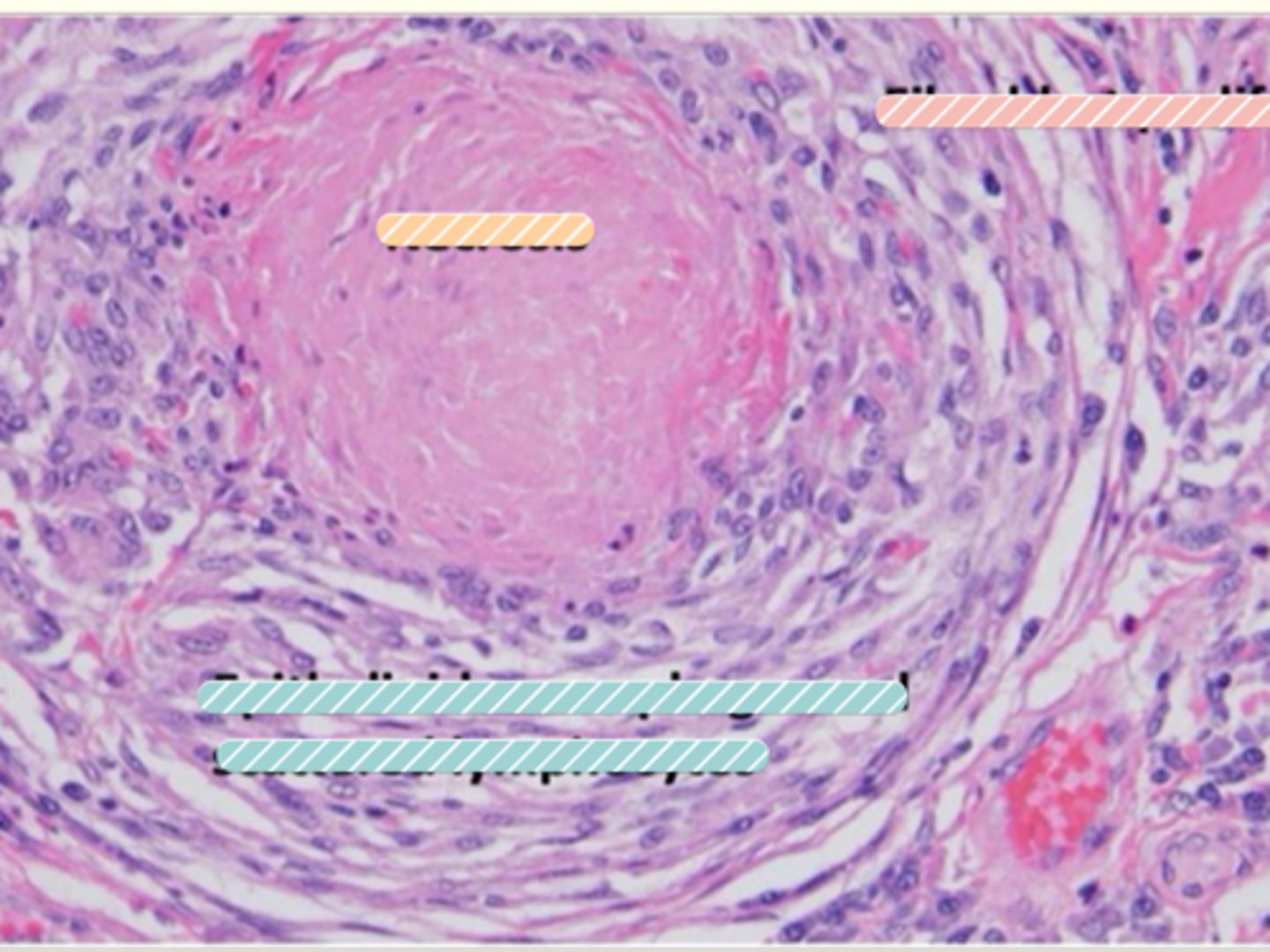
What do we find on the outside of a nodular granuloma?
Lymphocytes,
plasma cells
Fibroblasts
Fiberous capsule
What is an example of Lepromatous granuloma?
Johne's dz - affects lamina proprietor of ileum
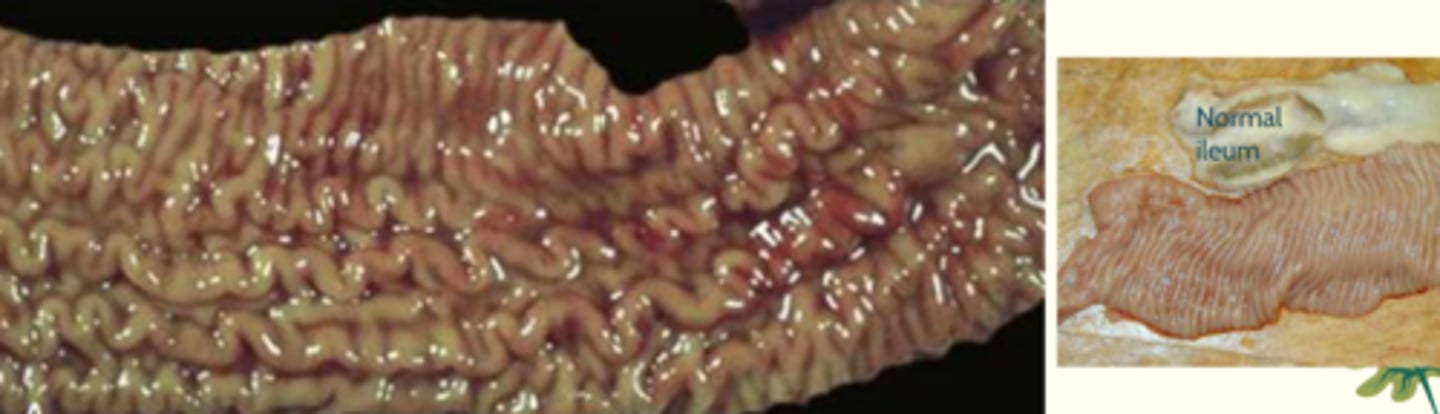
What kind of granuloma is this? What is the dz?
Lepromatous granuloma
Johne's dz
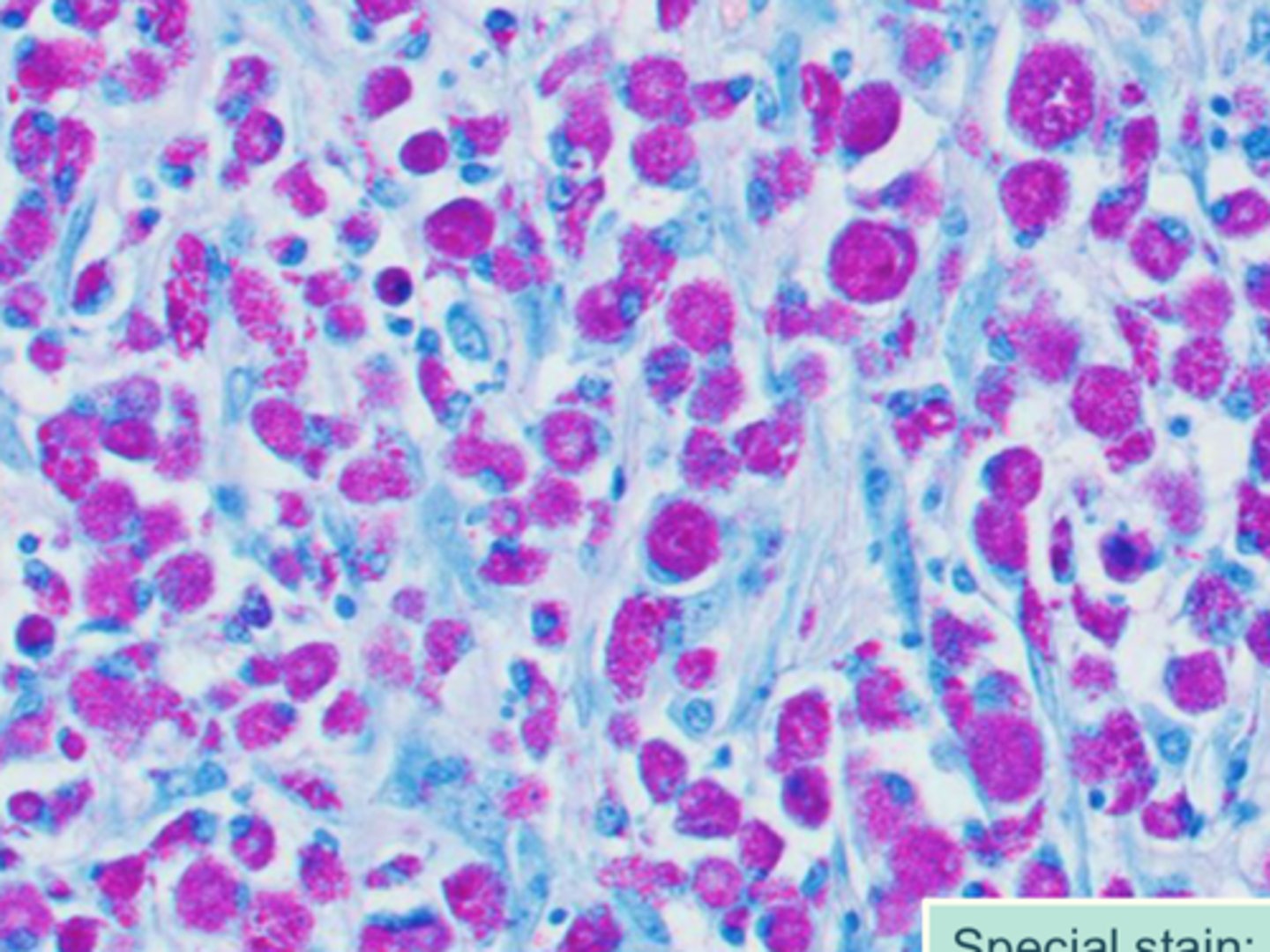
What kind of granuloma is this? What is this special stain showing?
Lepromatous granuloma
acid-fast showing bacteria (pink)
What are eosinophilic granulomas?
Dense infiltrates of eosinophils that are chronic in natures
What cells will we see present in a Eosinophilic granuloma?
Eosinophils
Macrophages
Multinucleated Giant cells
Collagen
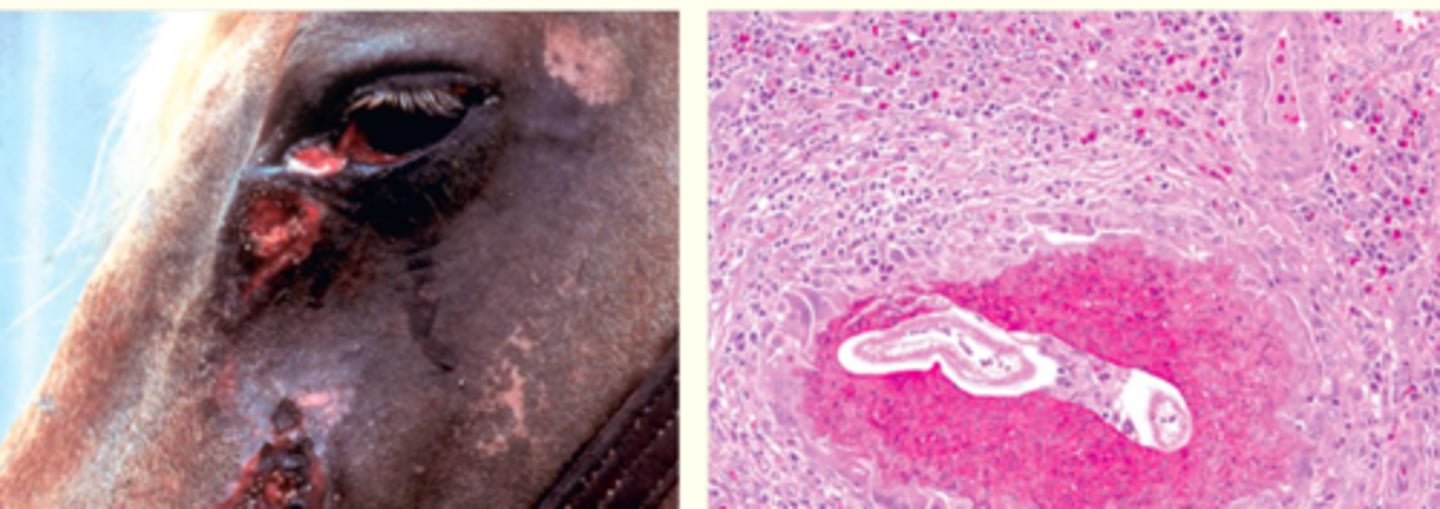
What is the pathology?
Cutaneous habronemiasis causing a eosinophilic granuloma
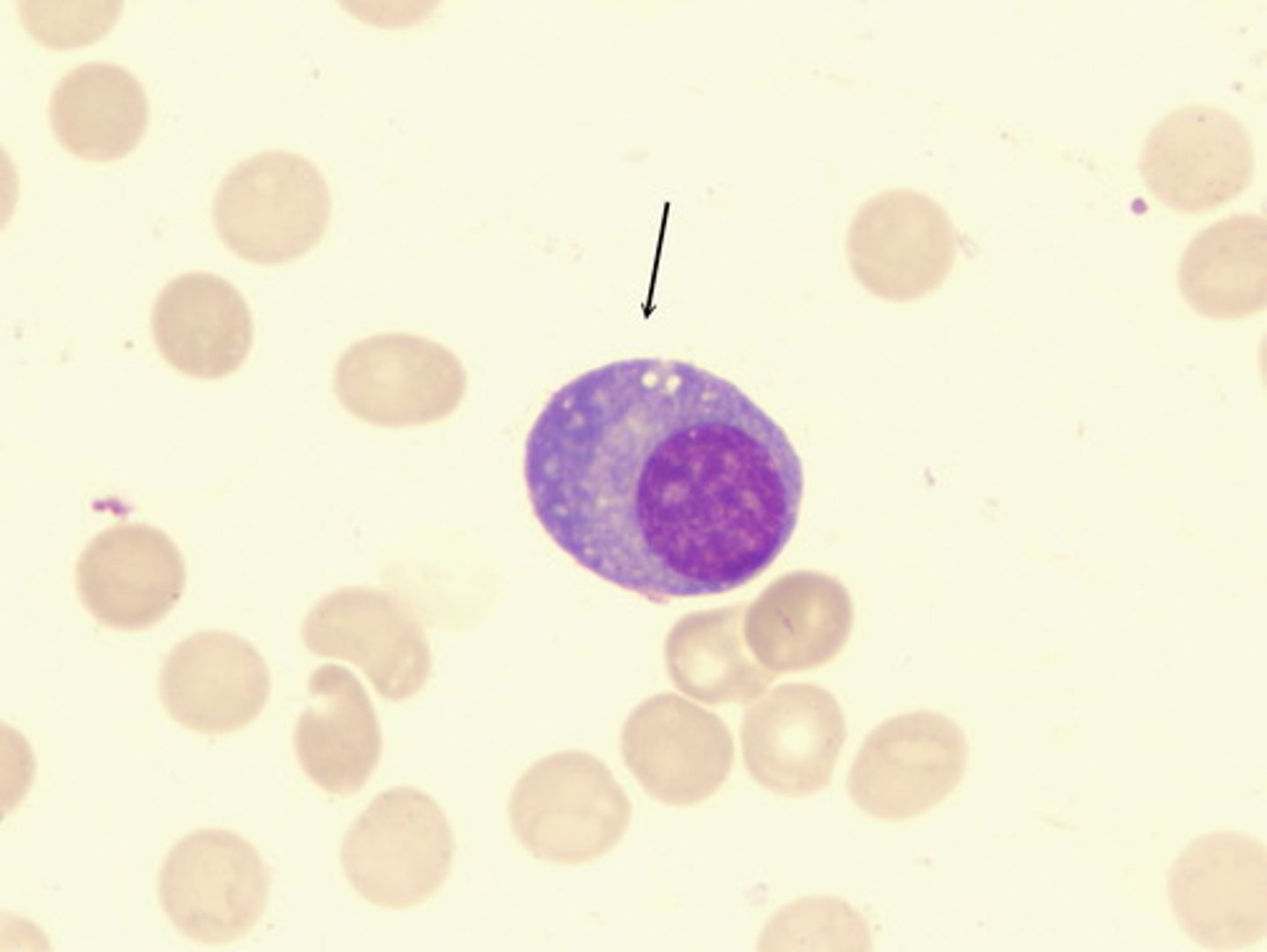
Identify the type of lymphocyte?
Plasma cell
Give an example of Lymphoplasmacytic inflammation?
IBD
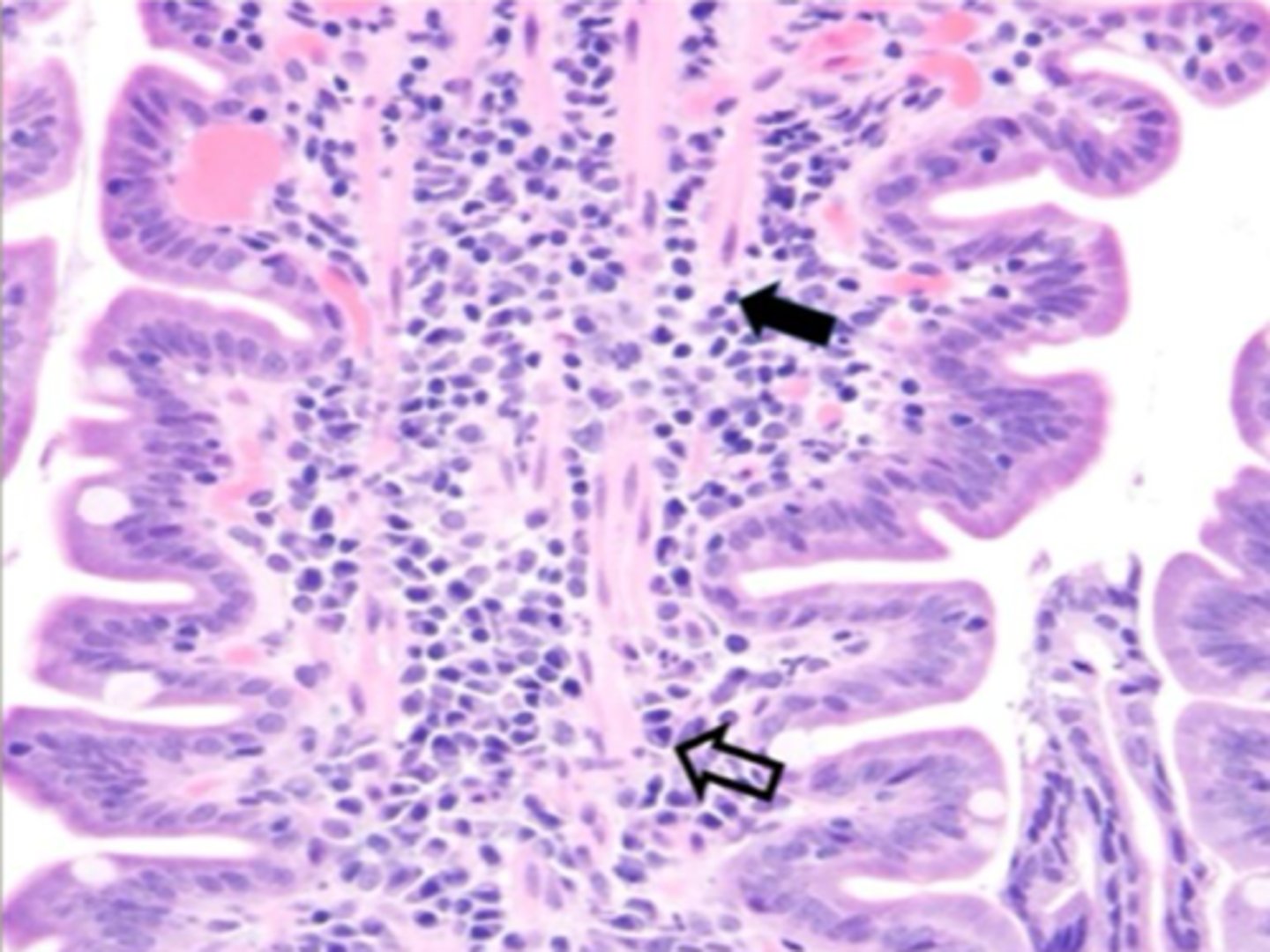
What is this an example of?
IBD Lymphoplasmacytic inflammation
What is chronic active inflammation?
Same cellular components as chronic inflammation but also has acute inflammatory response
What is an example of chronic active inflammation?
Feline infectious peritonitis
What does FIP look like on histopathology?
Pyogranulomatous vasculitis
What does FIP look like grossly?
Multifocal grey-tan slightly raised foci that follows vascular structures
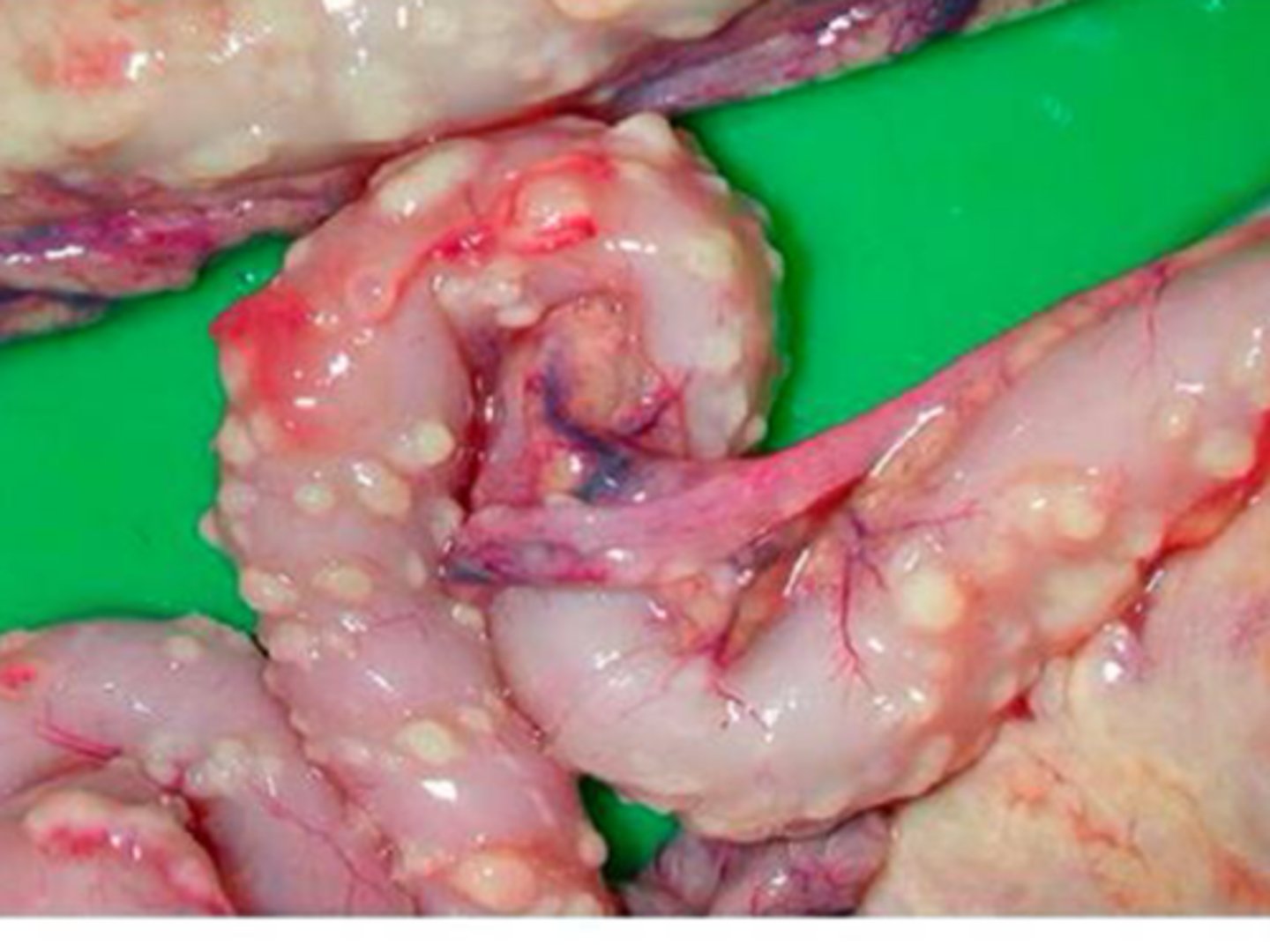
What is this an example of?
FIP
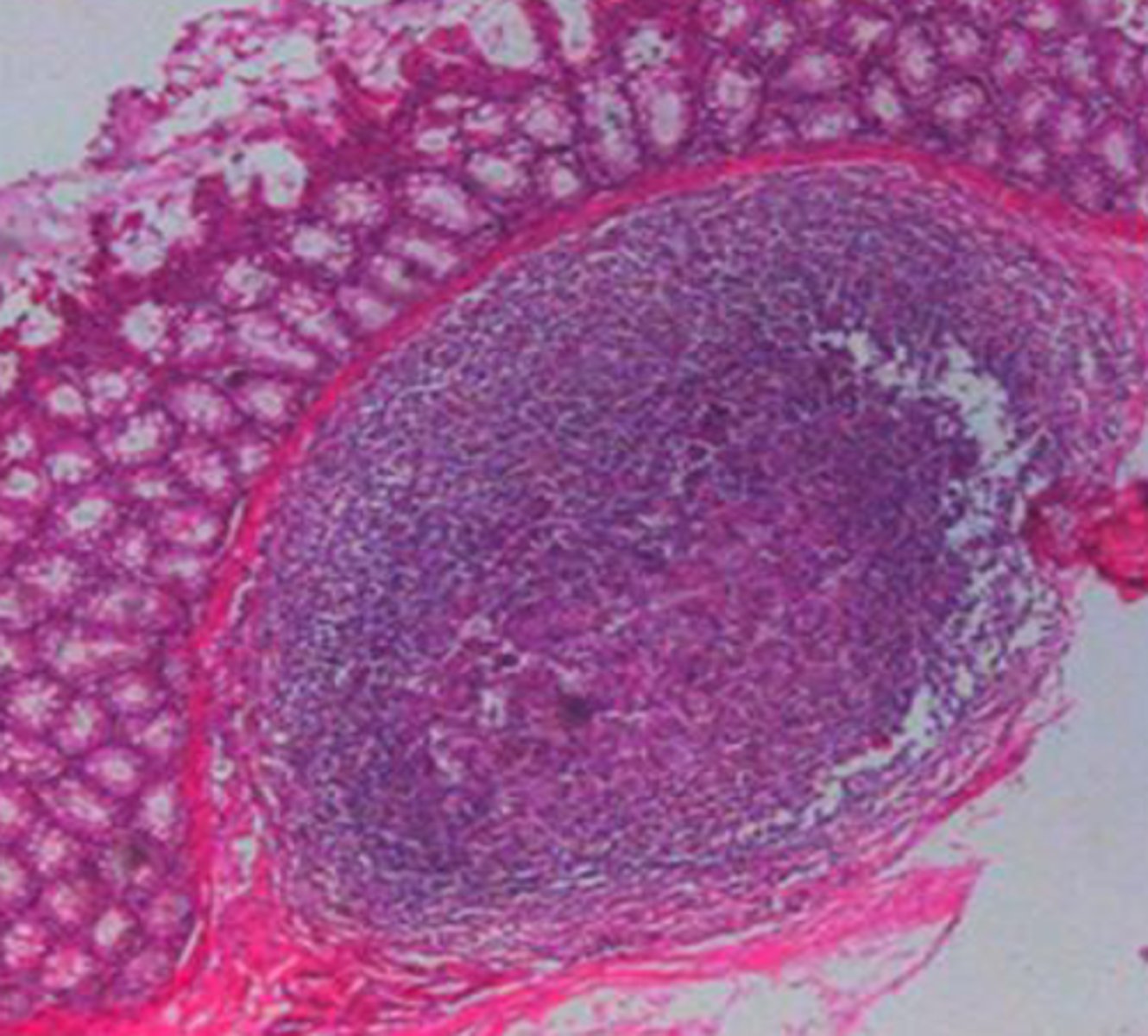
What is the pathology?
FIP
What is the infection pathway of FIP?
Fecal oral of Feline enteric coronavirus, infects enterocytes and mutates and replicates in macrophages - disseminates based on hosts immune response
If the host has a weak immune system what will we see w/ FIP?
Delayed type IV hypersensitivity dry form (no effusion)
If we see no immune system in an FIP host what will we see?
Wet form, hypersensitivity III response - effusive
What are some things chronic inflammation and neoplasia have in common?
Increased cell division, reduced immune surveillance
What is an example of Chronic inflammation leading to neoplasia?
Feline inj site sarcoma
How does Feline inj site sarcoma occur?
Neoplastic transformation of fibroblasts/ CT
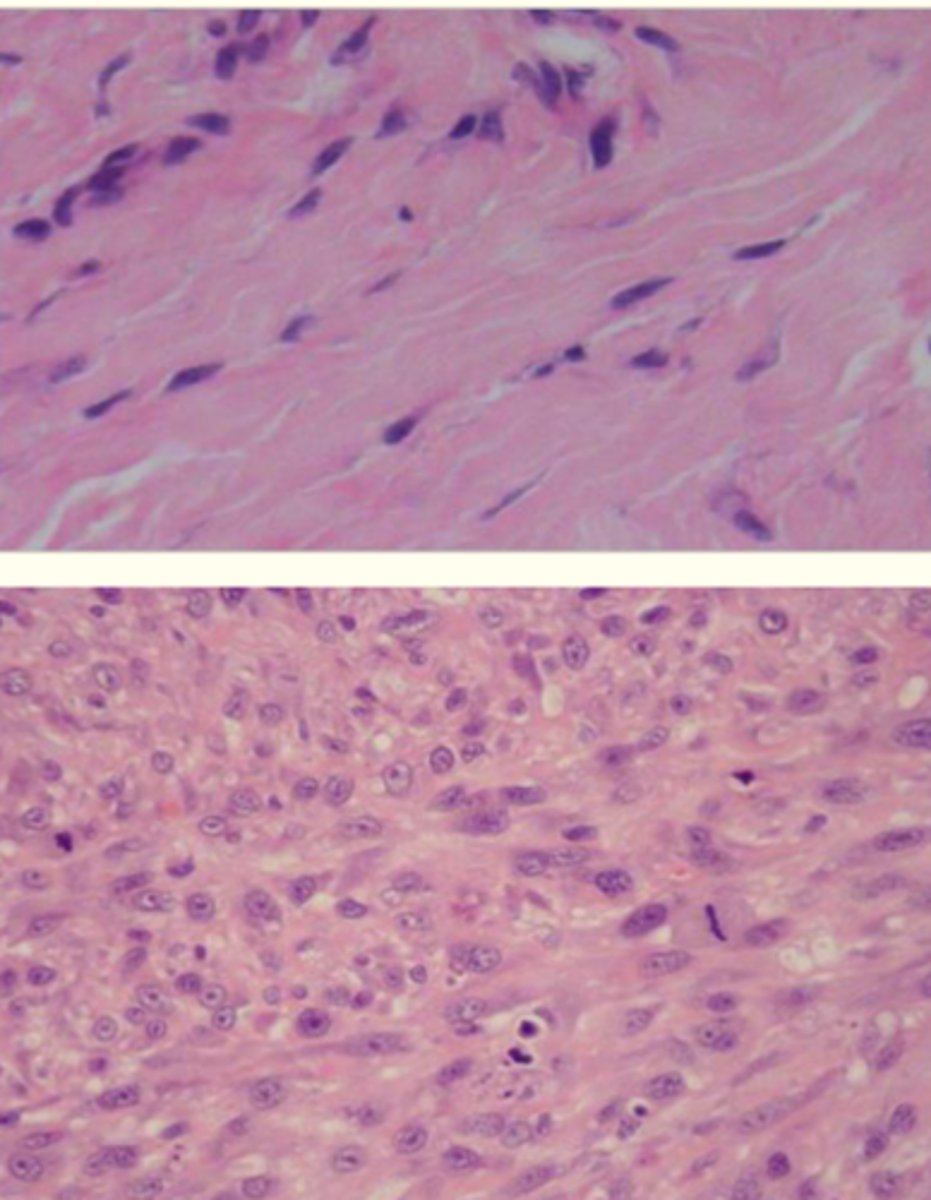
What is the photo displaying?
Feline inj site sarcoma
What are the post inj stages?
Hemostasis
Acute inflammation
Proliferation - granulation tissue, angiogenesis and epithelialization
Remodeling
In the maturation of wound healing what will we see?
Collagen will switch from type 3 to type 1
What is a the most critical growth factor in wound healing?
TGF-b
What is the difference between primary intention and secondary intention healing?
Primary - quick healing, little scar tissue
Secondary - long healing, gap/ infected, disorganized, lots of scaring
What is granulation tissue?
Exposed CT forming on a healing wound that bleeds easy,
What is proud flesh?
Over growth of granulation tissue inhibiting healing (horses)
Healthy granulation tissue will be?
Pink/red
Granular/nodular surface
Bleeds easy
Poor granulation tissue will be?
Dark in color,
Indicative of poor perfusion
ischemia
infection
Granulation tissue will restore ____ integrity but not alway ___ integrity?
Structural
Functional