Bio 101L Fetal Pig Dissection Quiz
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
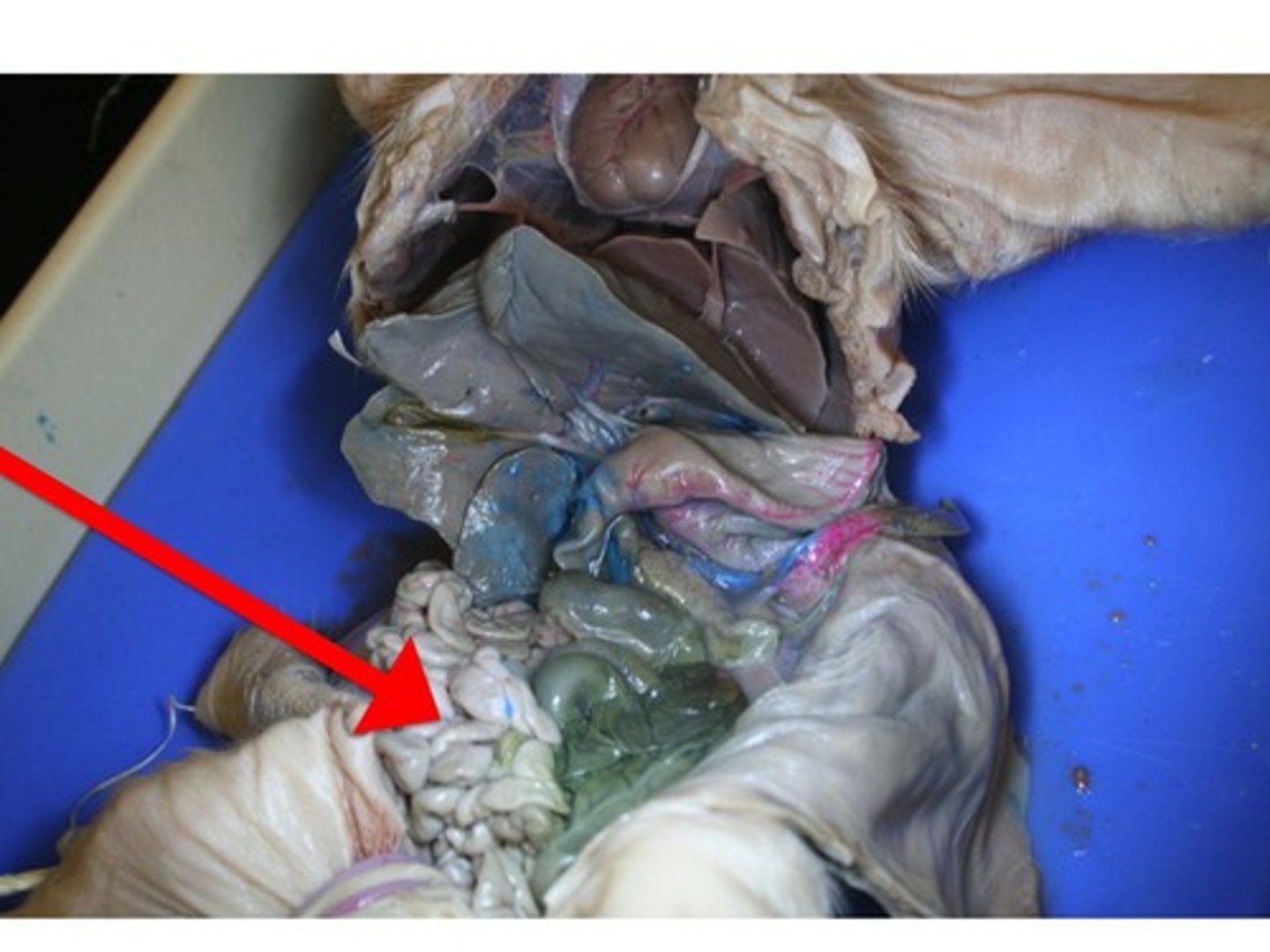
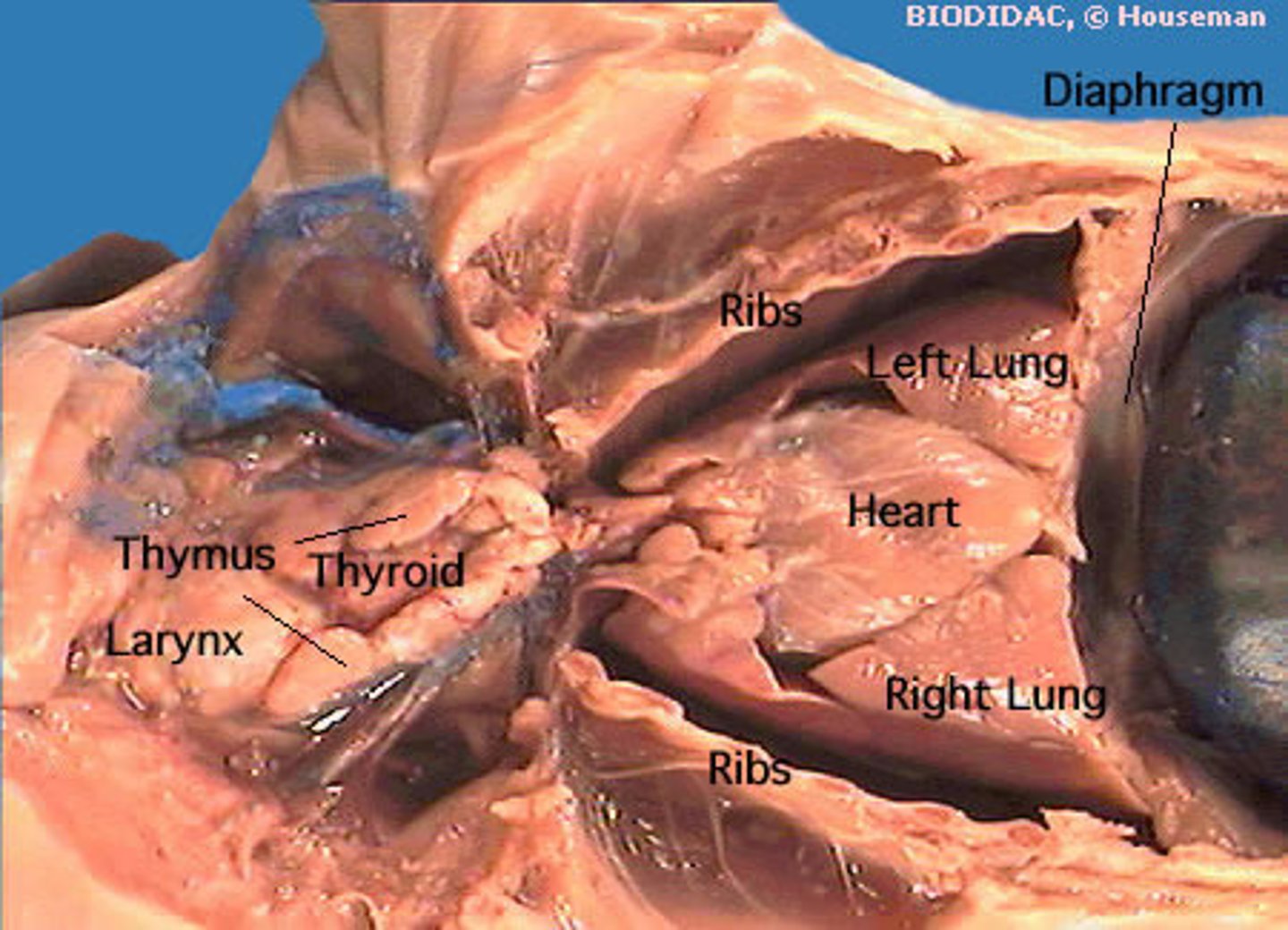
Diaphragm
attaches to the body and separates the abdominal cavity from the lungs and heart
Small Intestine
- usually on the right side of the pig
- looks sort of like a brain
Gall Bladder
- on the pig's right side, under the liver and stomach
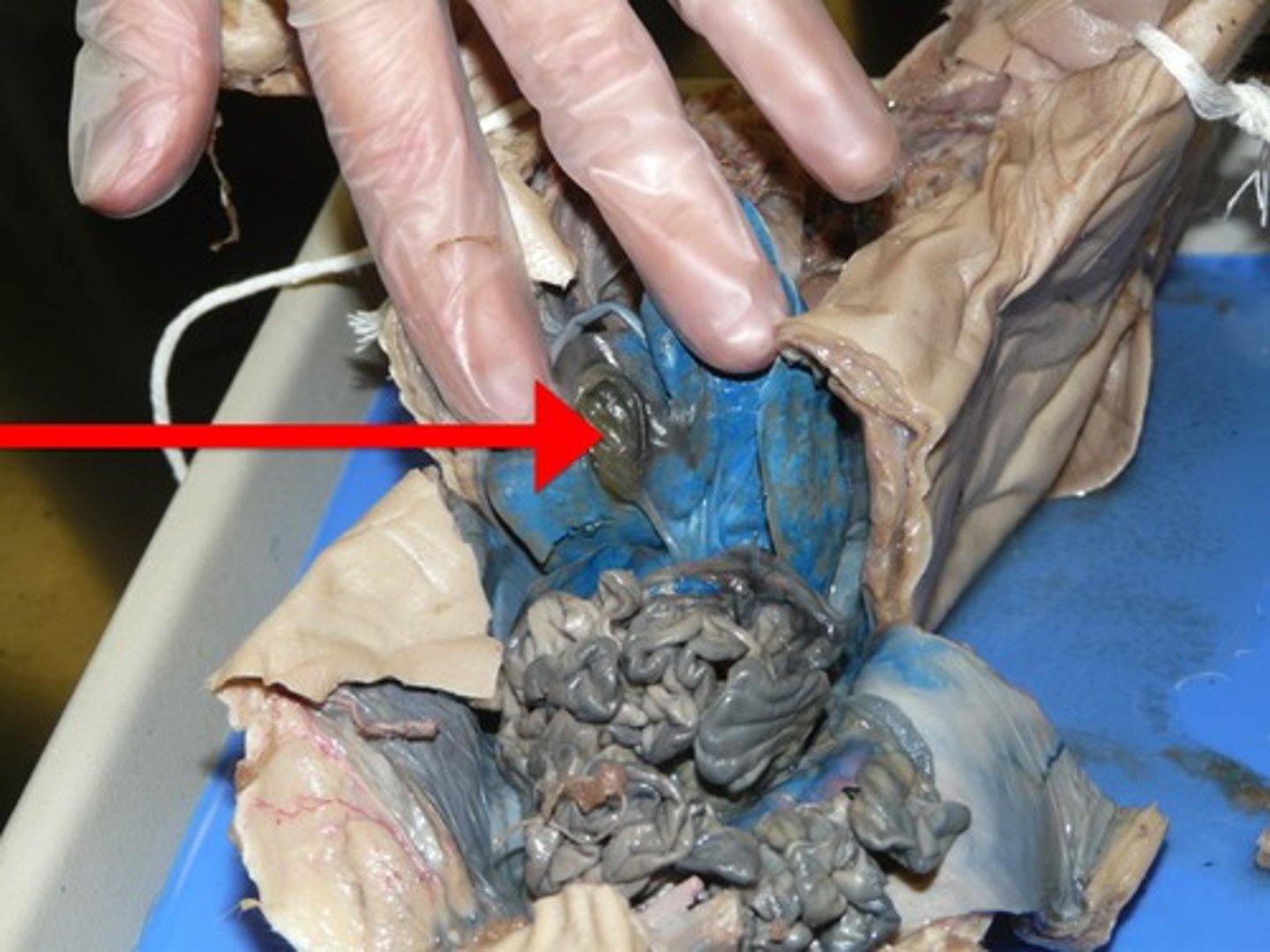
Duodenum
This duct leads to which structure?
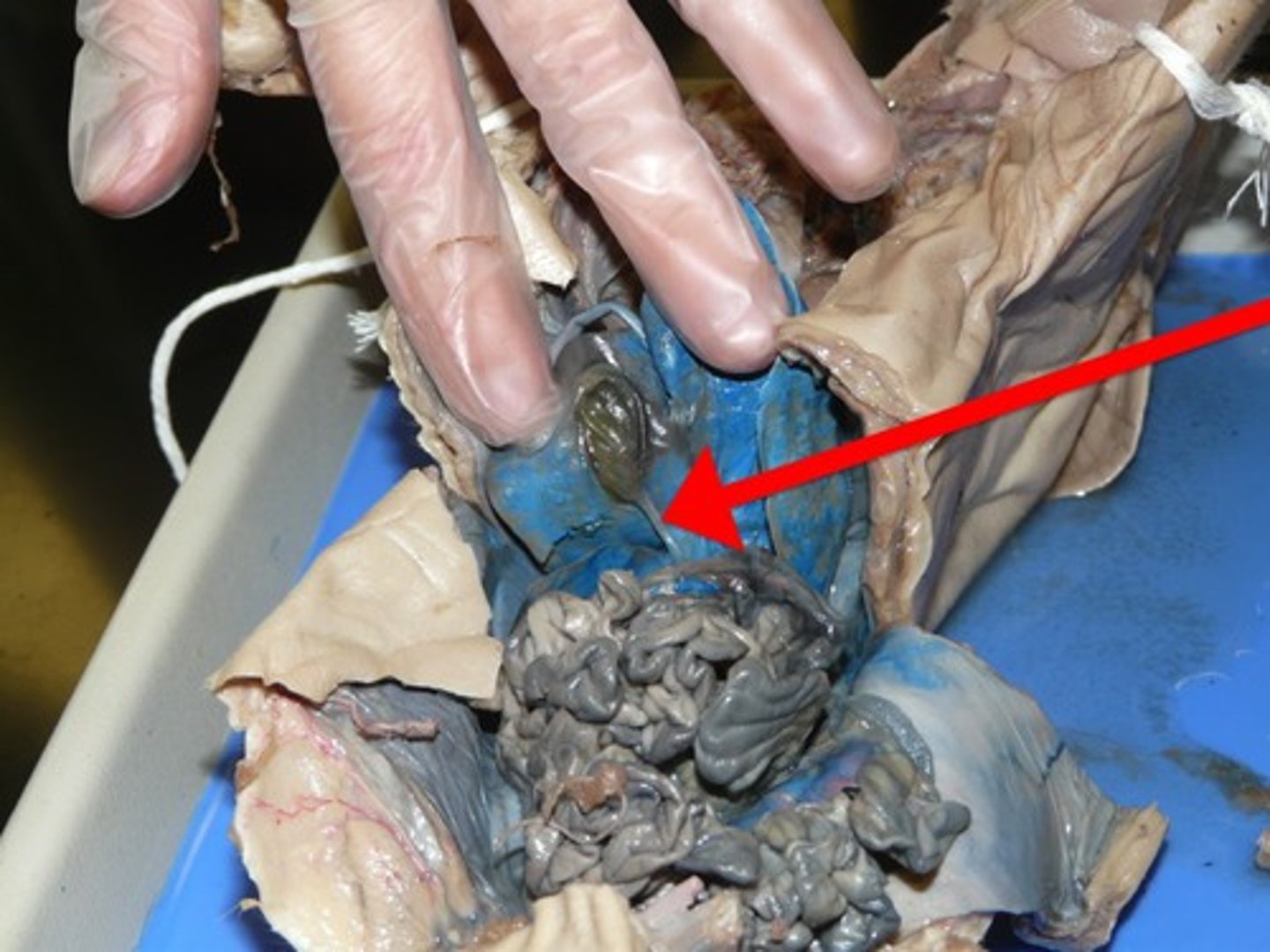
duodenum
- the first loop of the small intestine
- food goes through the ________ via the stomach TO the small intestine
Spleen
- on the pig's left side, next to the stomach
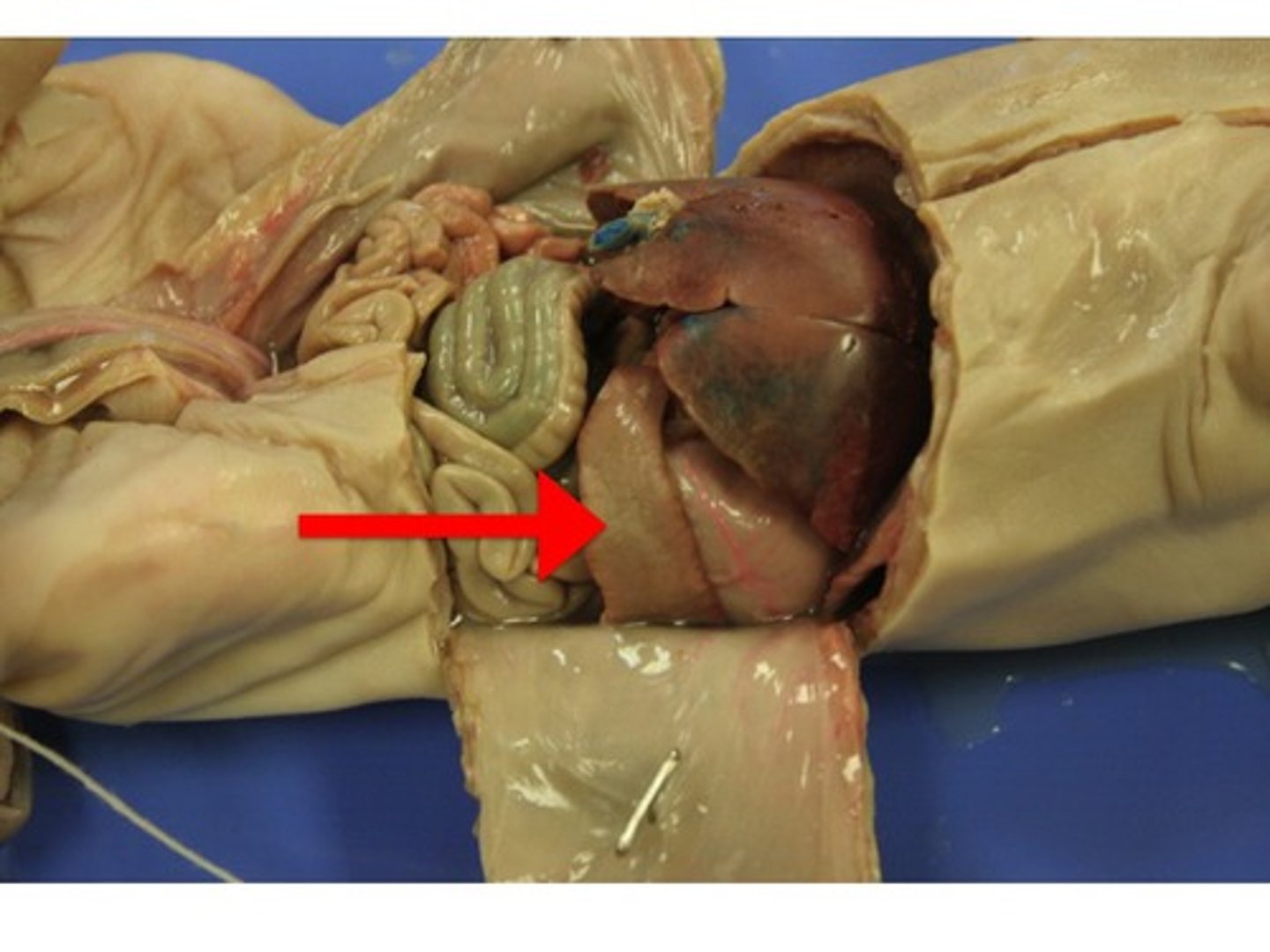
Liver
- large brownish-red organ just posterior to the diaphragm
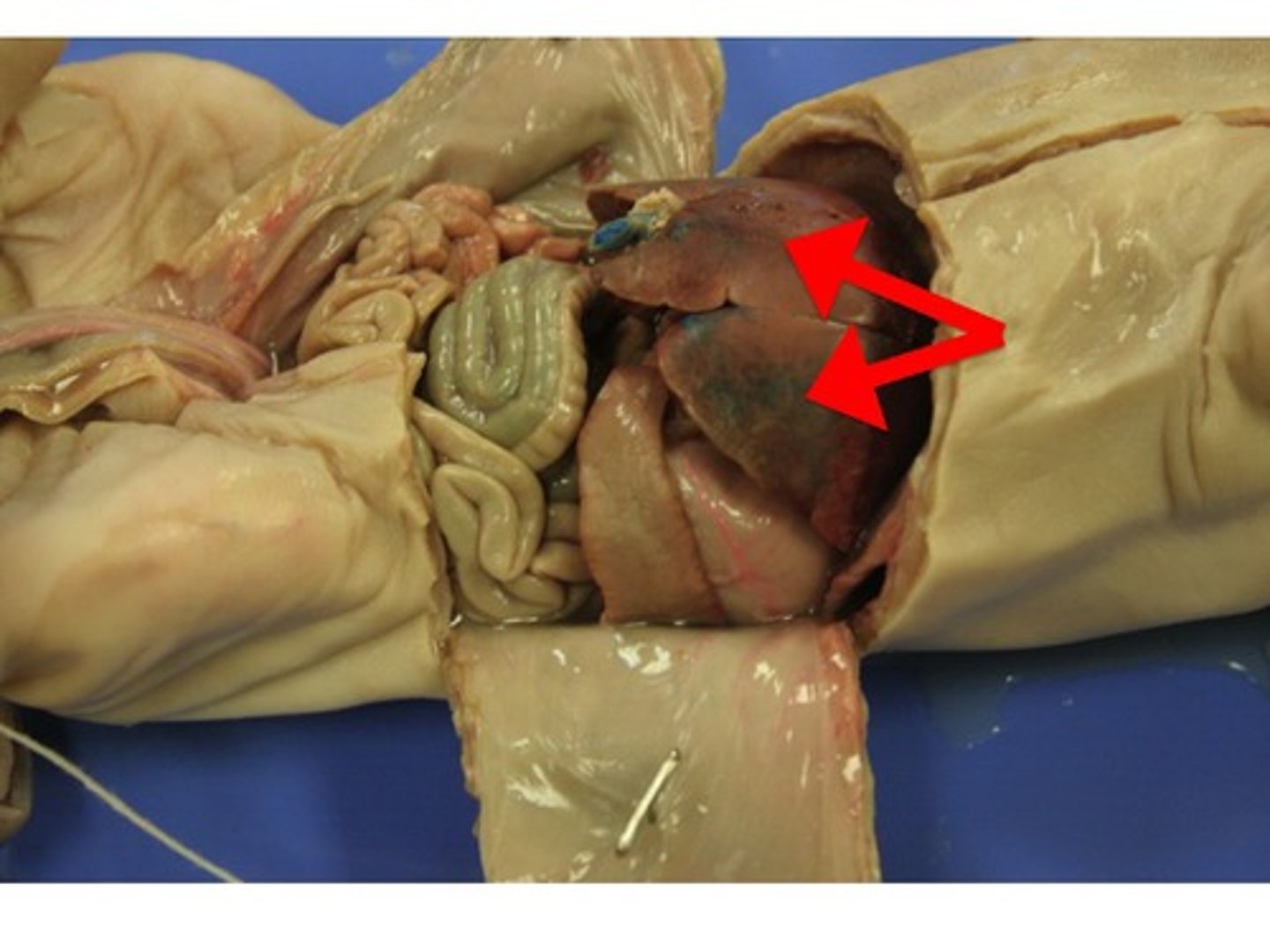
Stomach
- below the liver
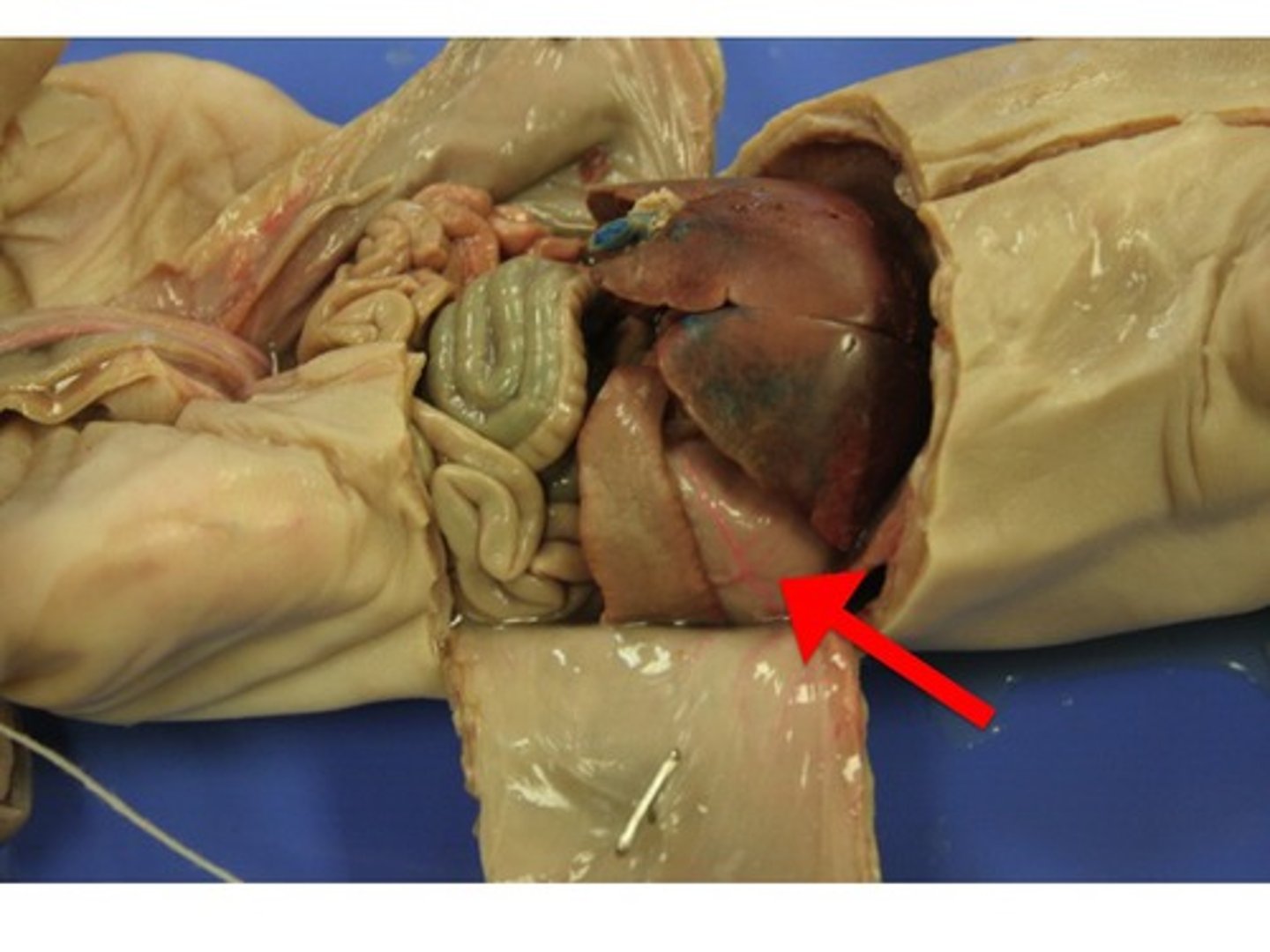
pyloric region
- lower part of the stomach
- separated from the small intestine by the pyloric sphincter
pyloric sphincter
- circular muscle which prevents backflow of contents from the intestine to the stomach
- just point to the end of the stomach
Pancreas
- below the stomach
- lowkey looks like a brain
- white organ between the stomach and the duodenum
- held in place by the mesentery membrane
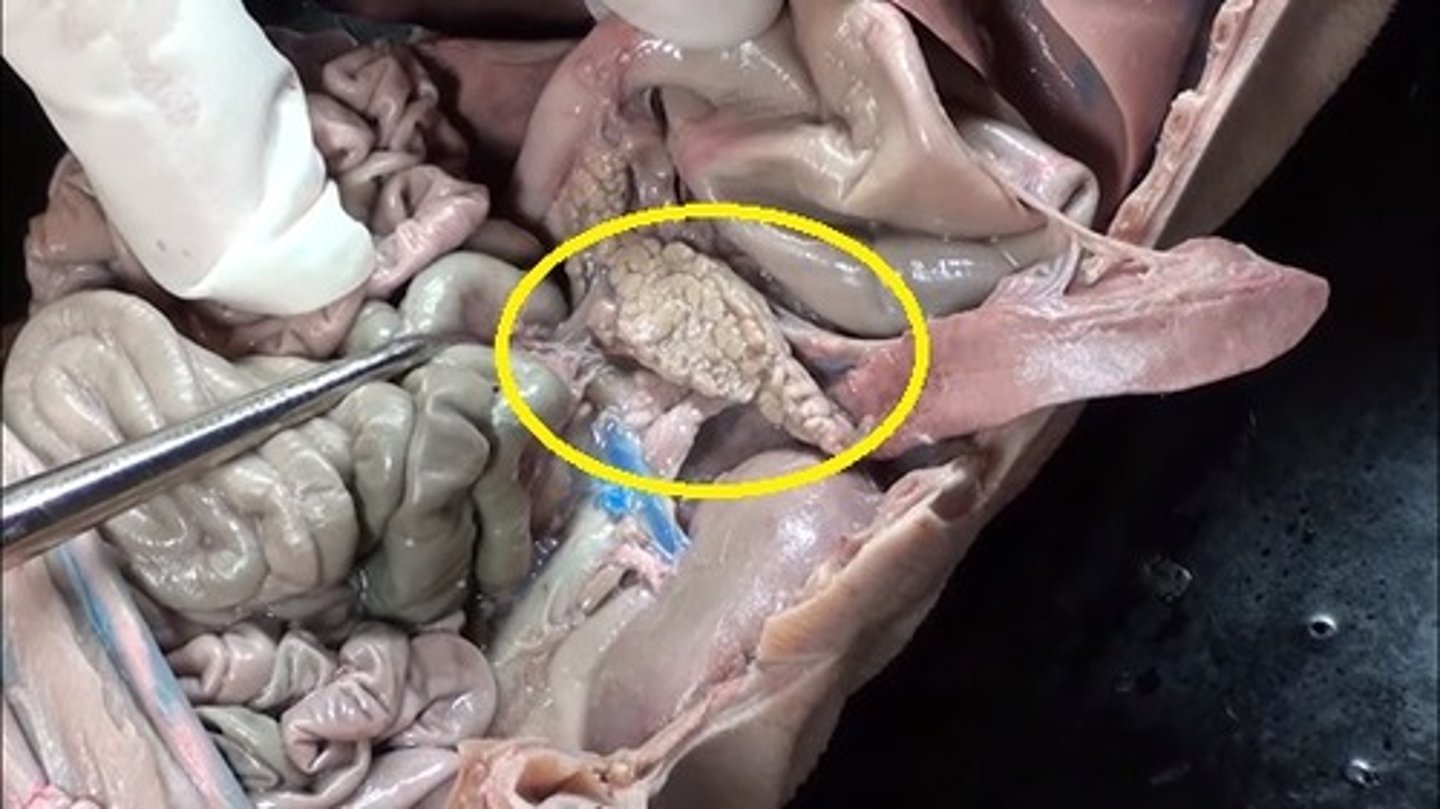
mesentery membrane
- holds the pancreas in place
- part of the peritoneum
peritoneum
- lines the abdominal cavity
- covers the kidneys
Heart
- wrapped in the lungs, above the liver
- located in the thoracic cavity
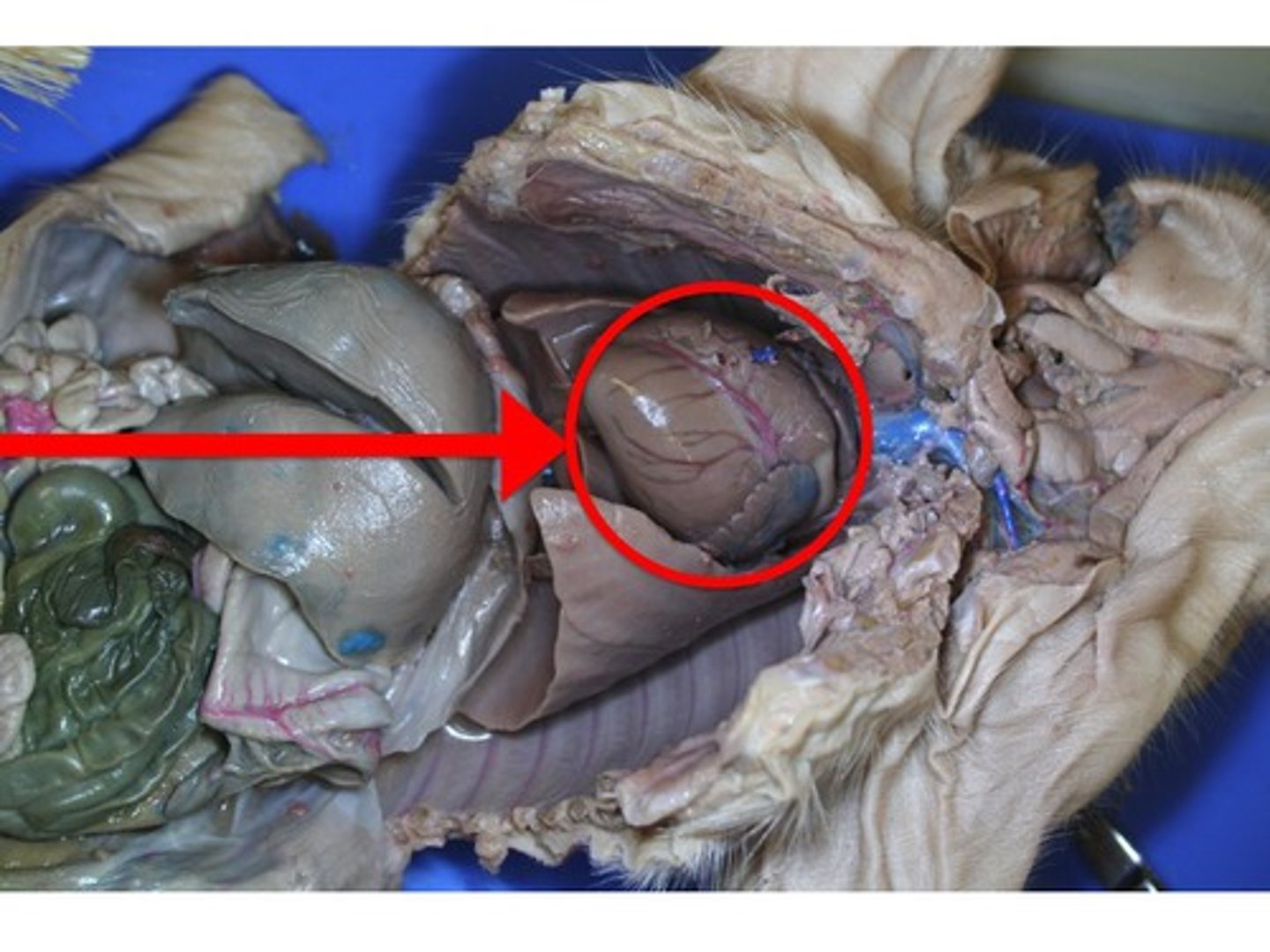
Lungs
- flaps that surround the heart
- found in two pleural cavities on either side of the pericardial cavity (all within the thoracic cavity)
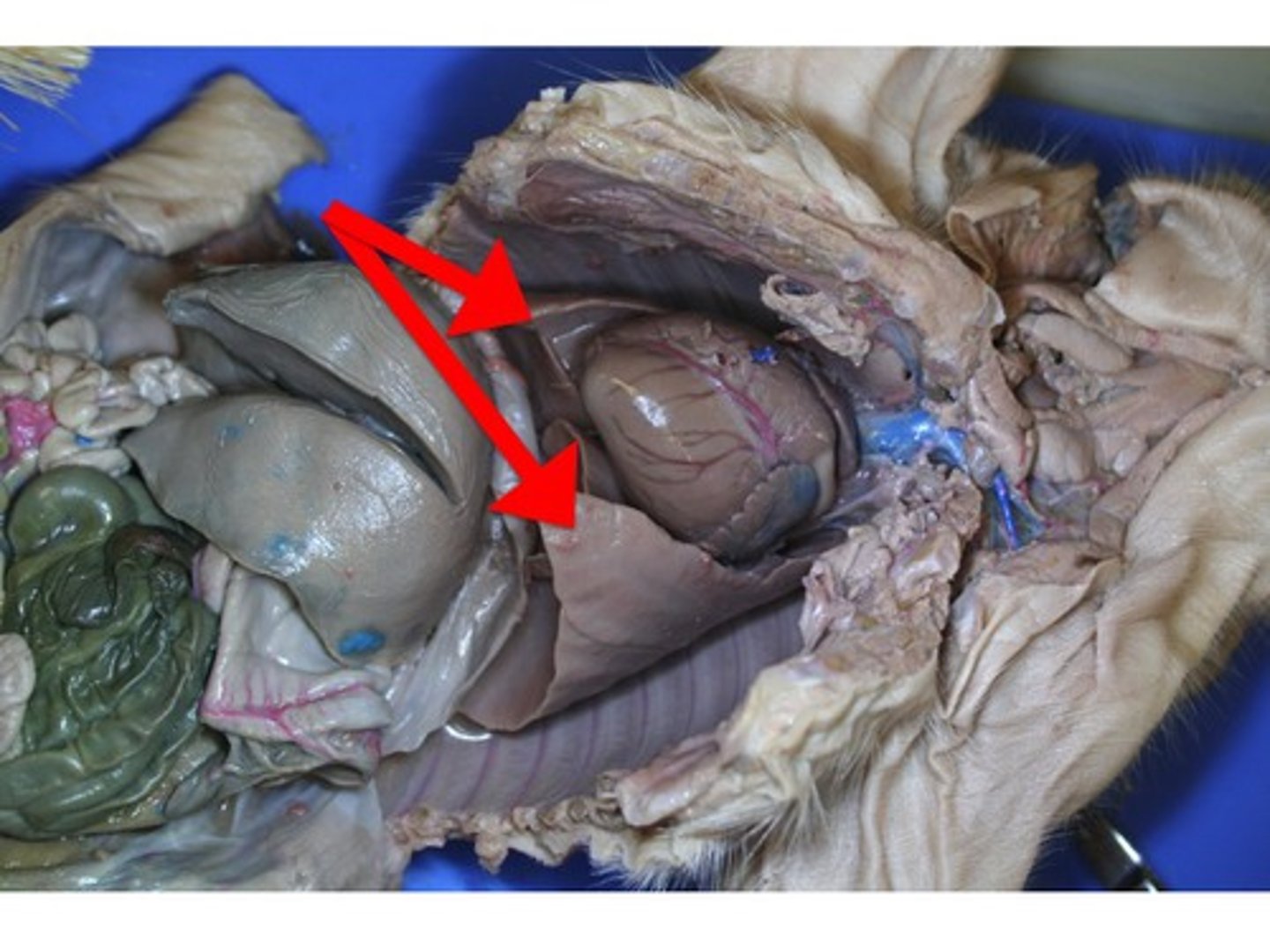
pleural cavities and the pericardial cavity
where the lungs are found
Systematic aorta
- under the pulmonary trunk
- arises from the left ventricle and eventually branches to carry blood to all parts of the body
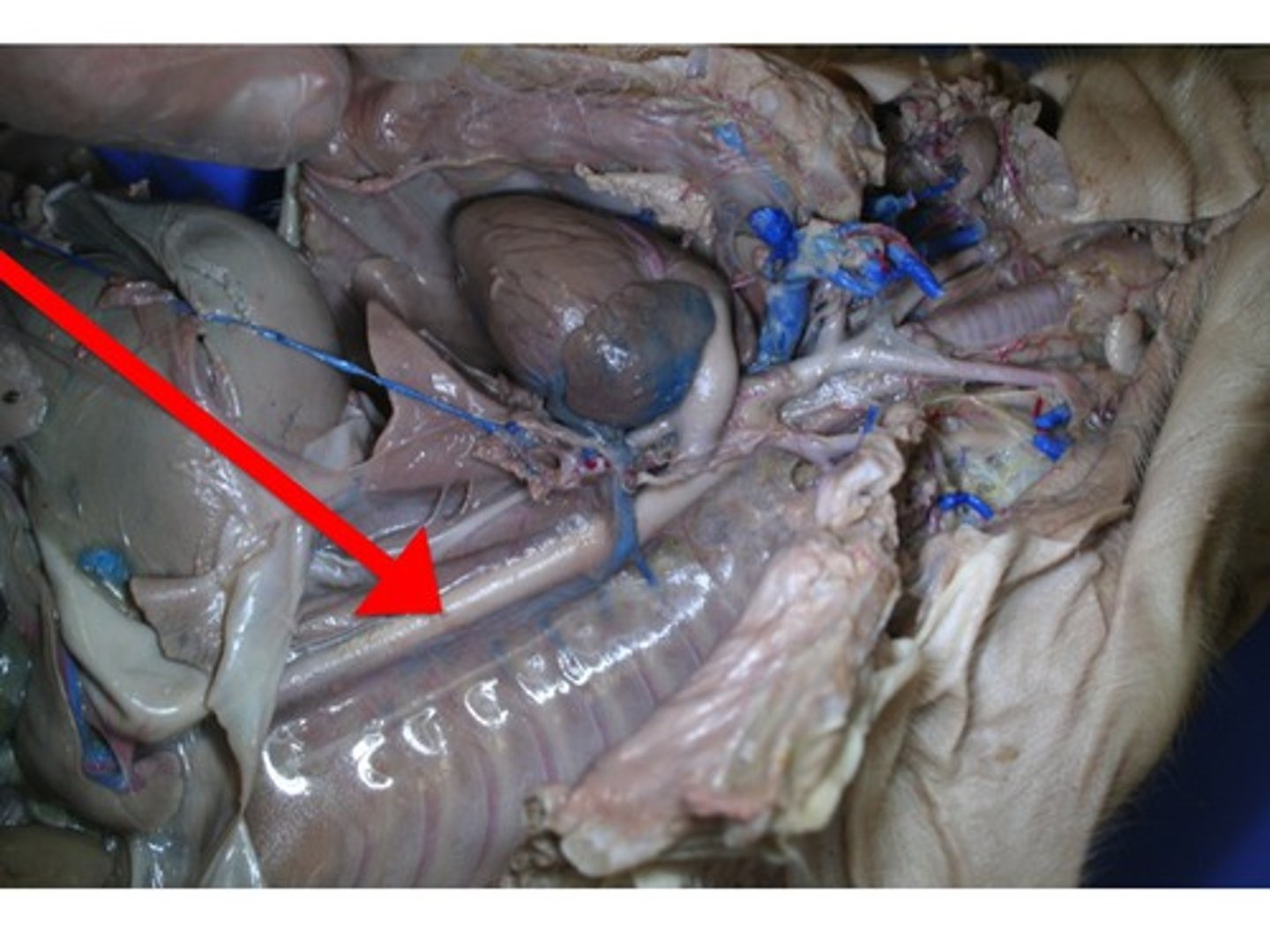
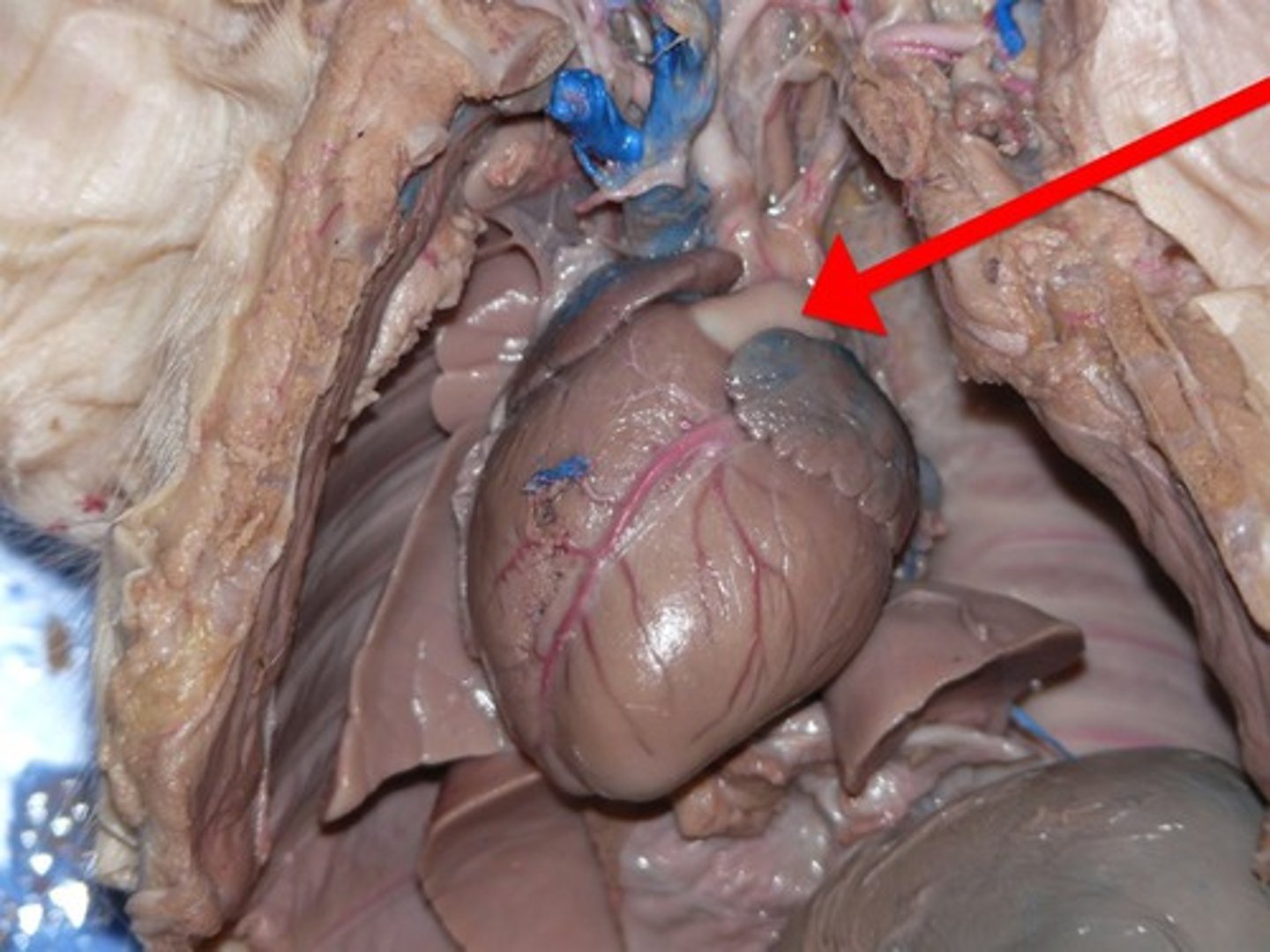
Pulmonary
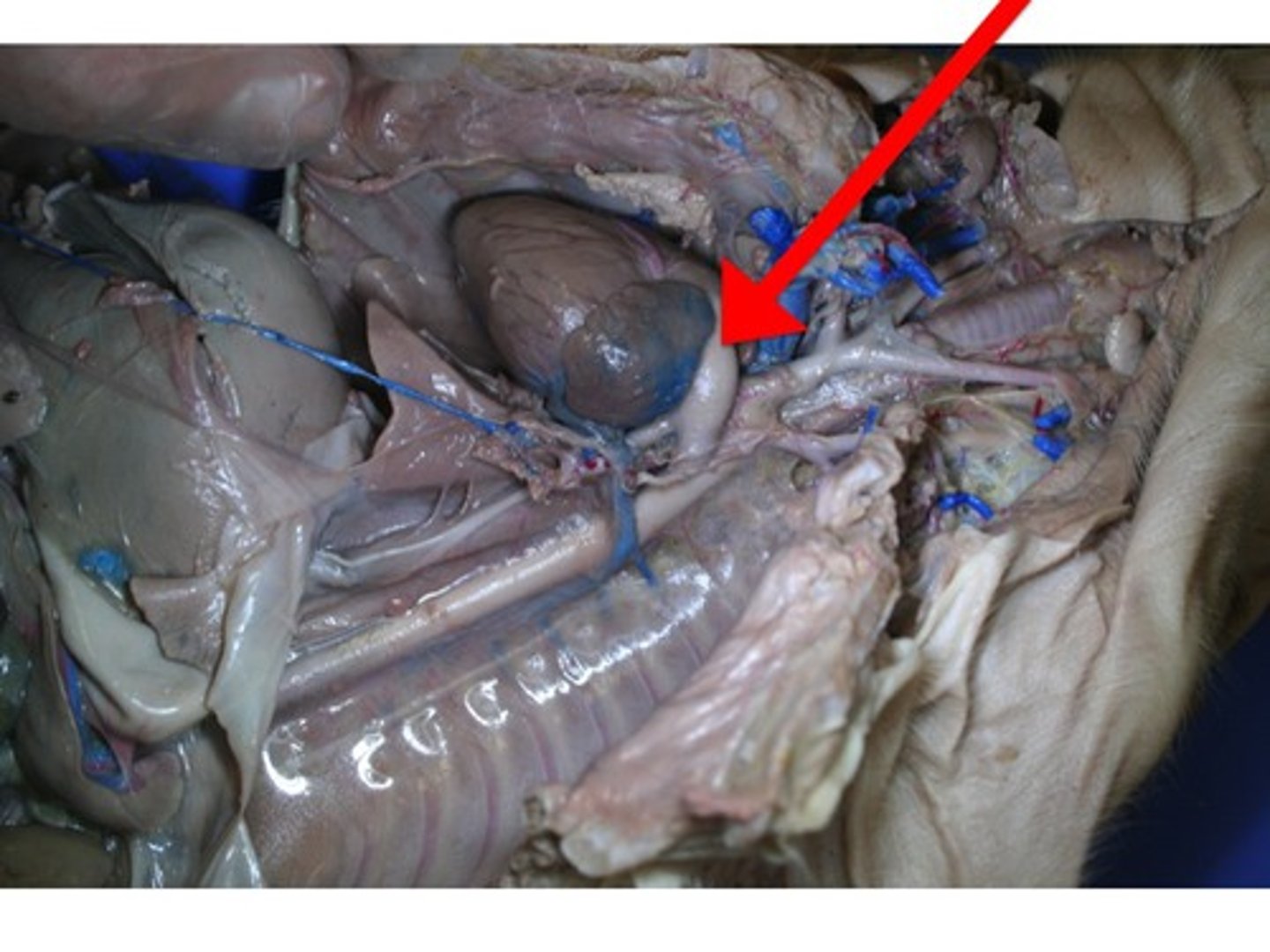
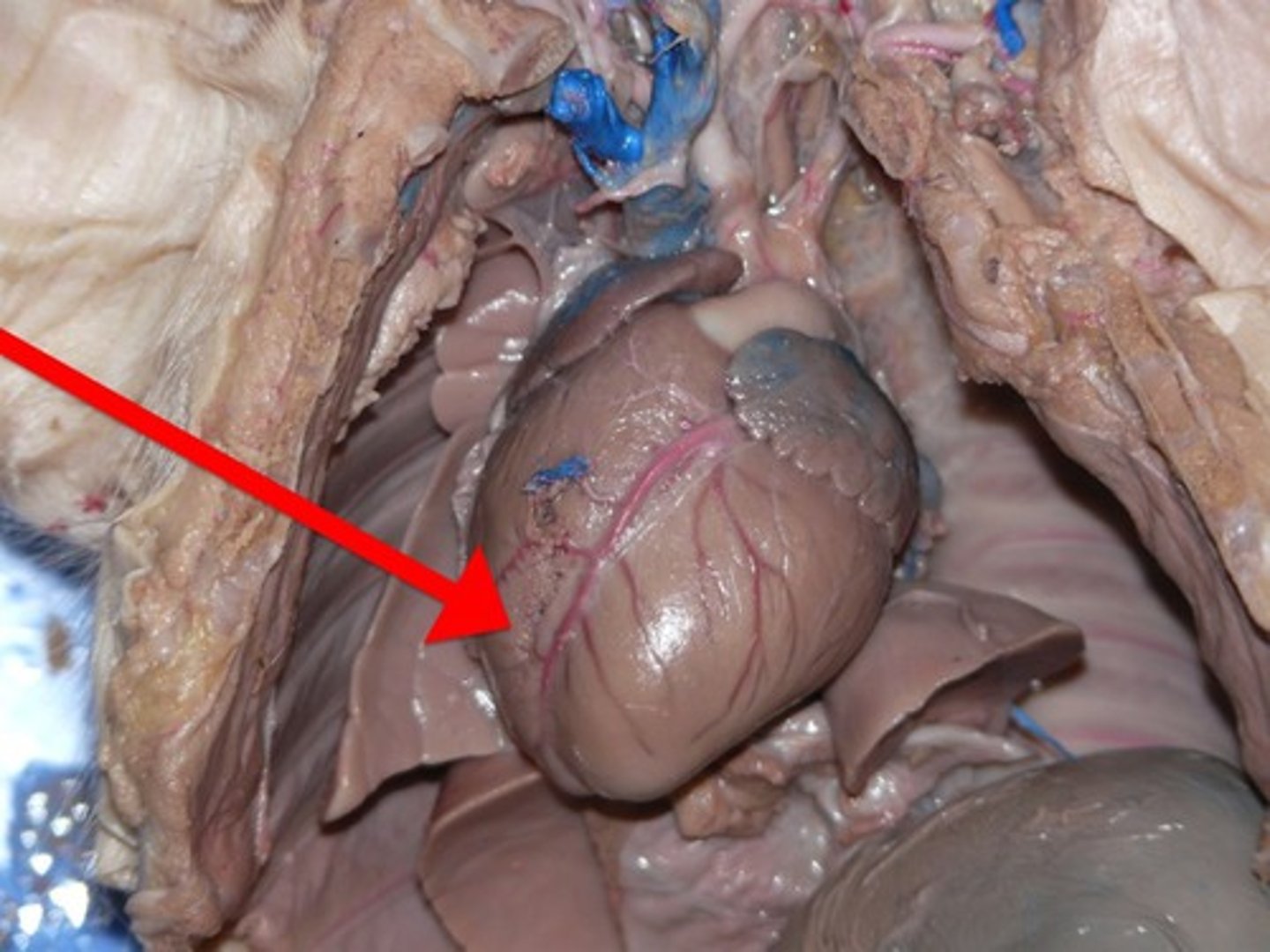
Coronary Artery
- boundary between the two ventricles
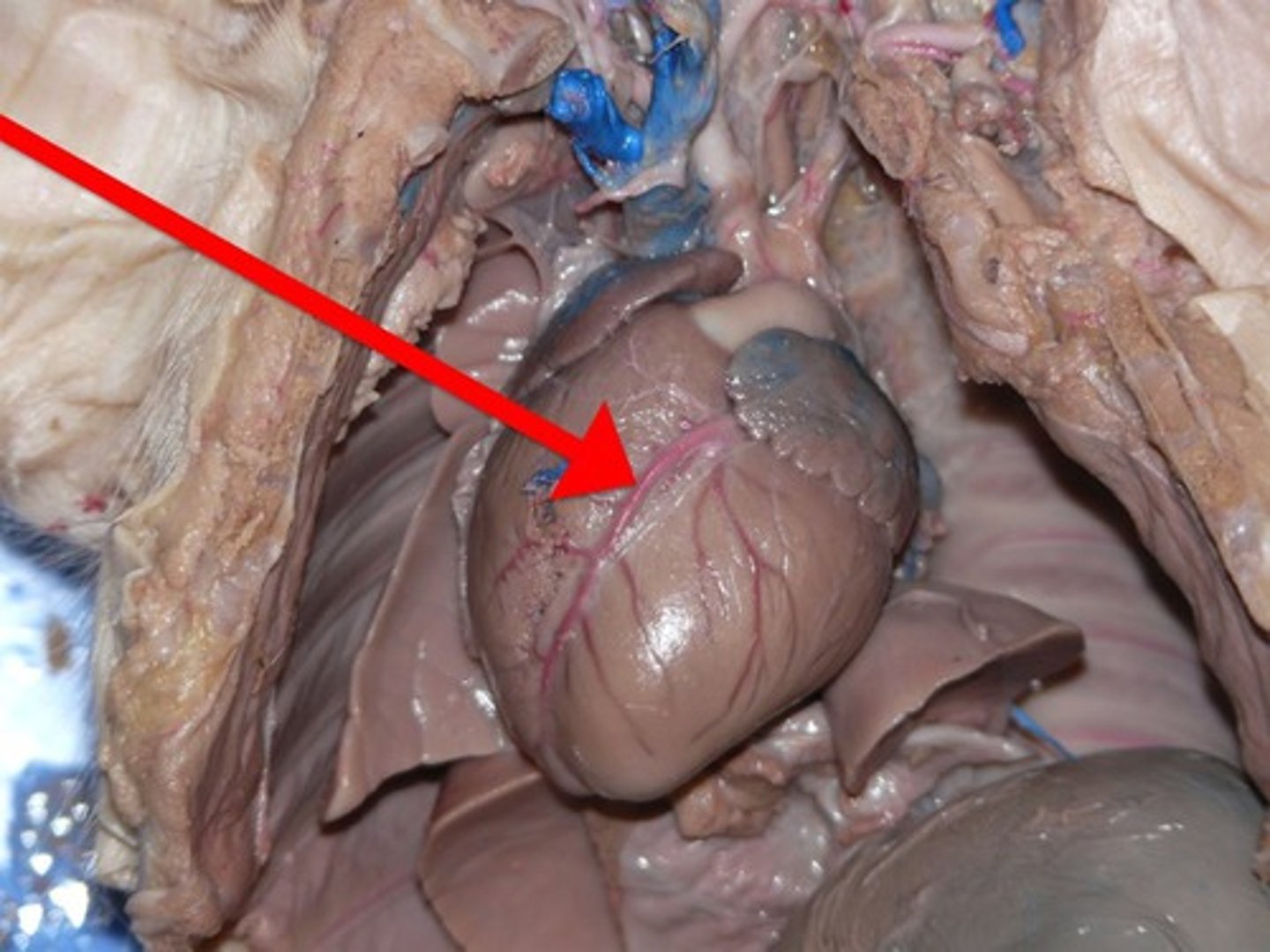
Left Atrium
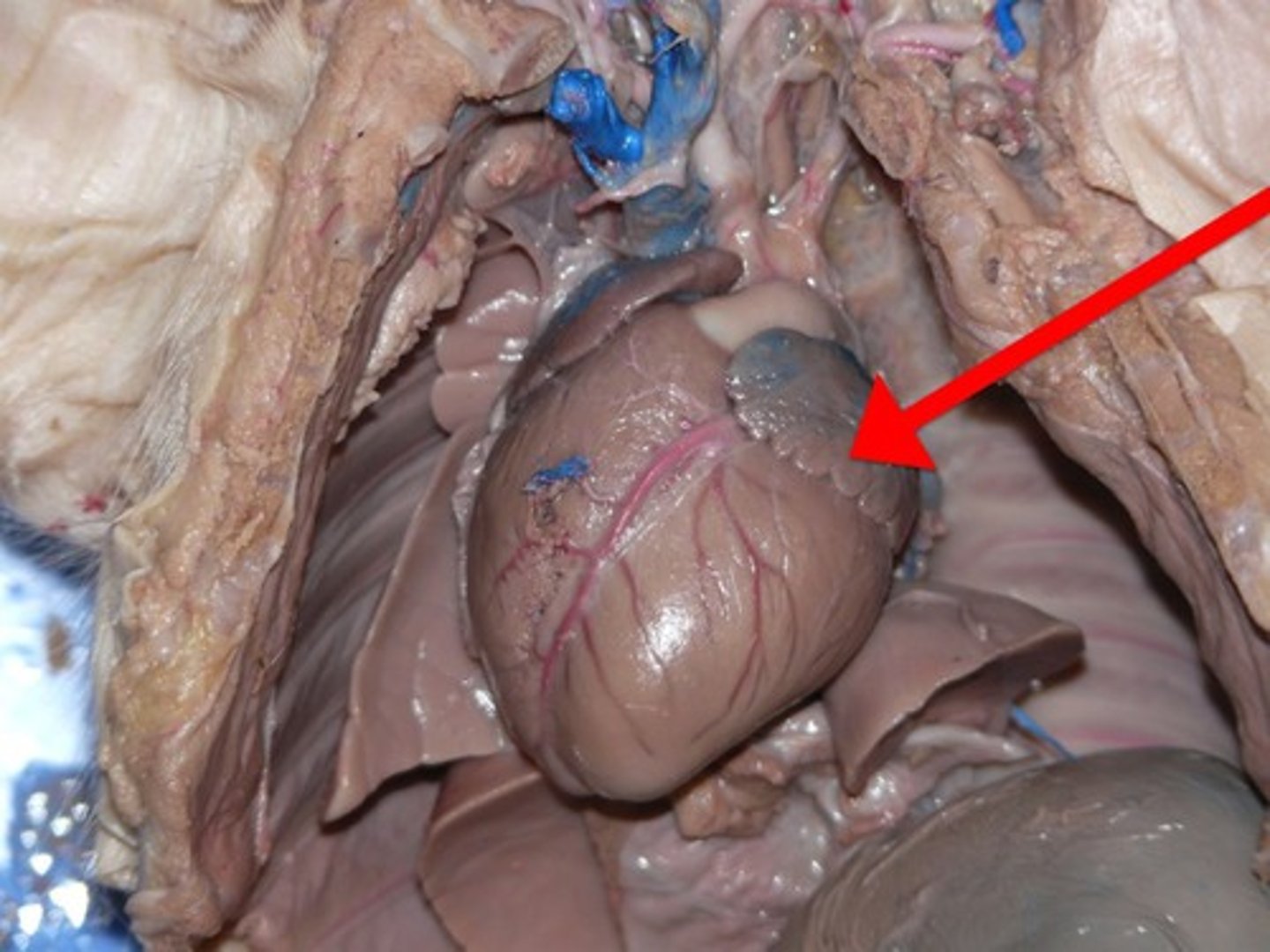
Left Ventricle
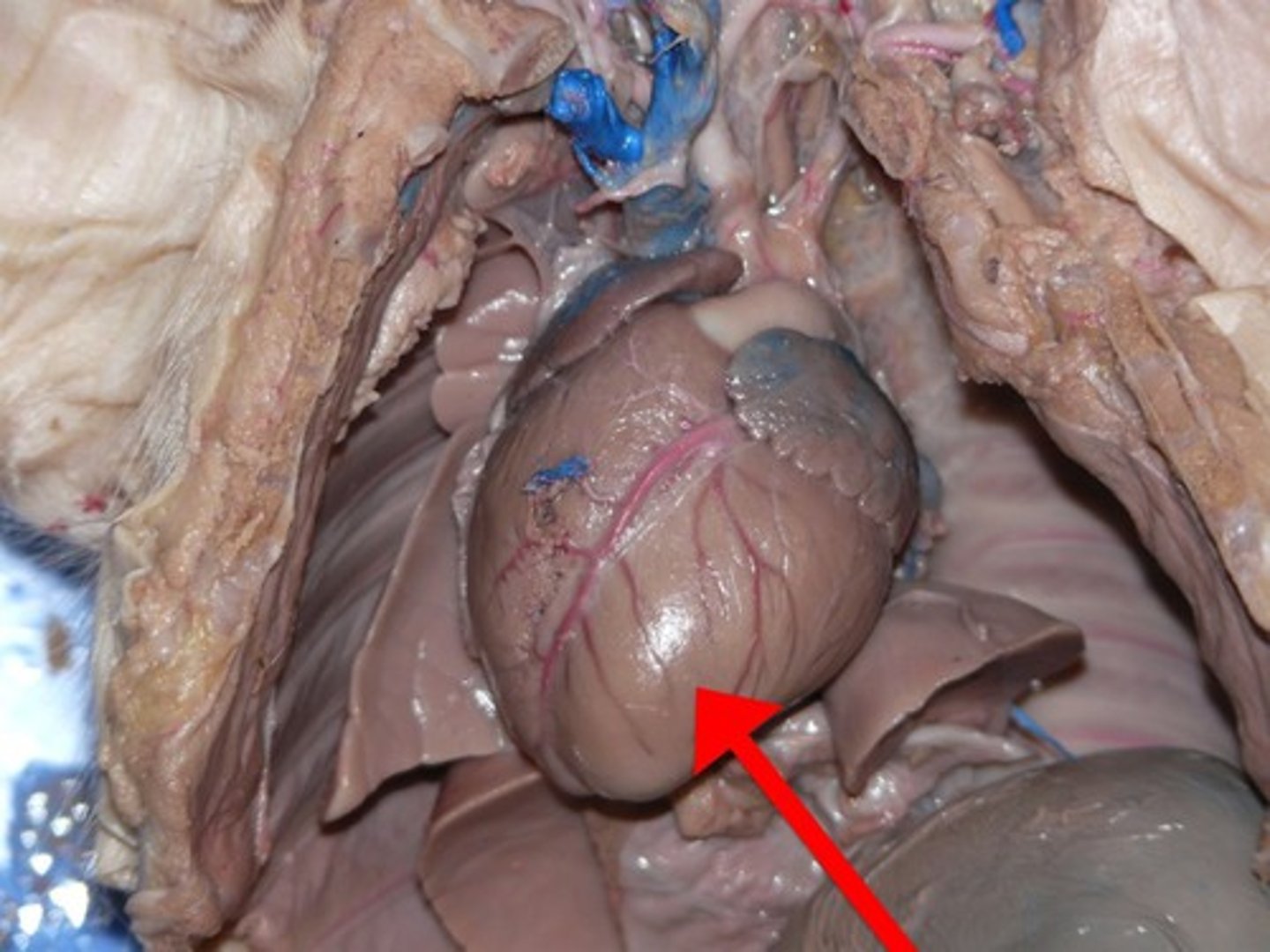
Right Ventricle
Pulmonary artery
- whiteish tube near the top of the heart
- 3 branches
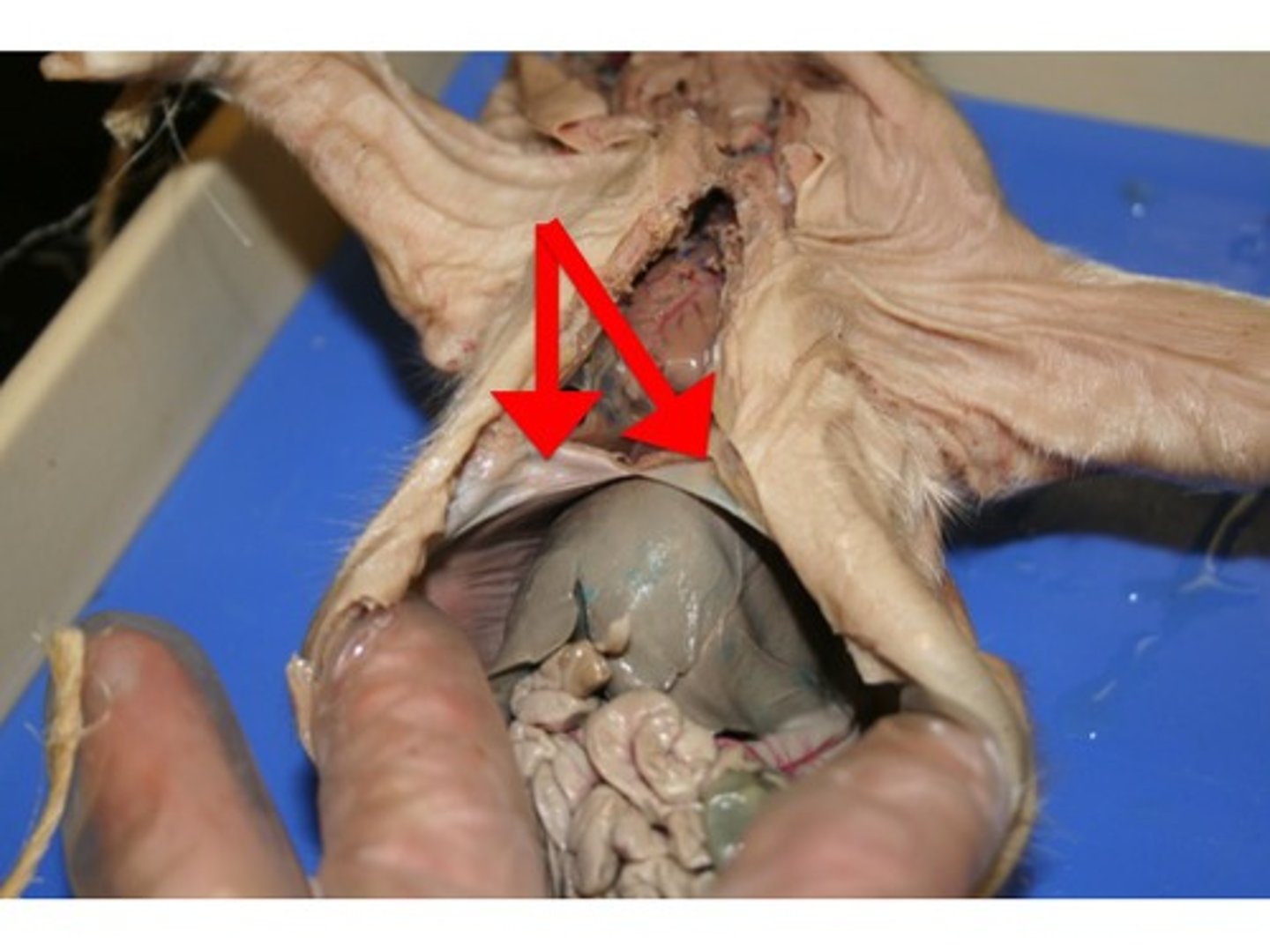
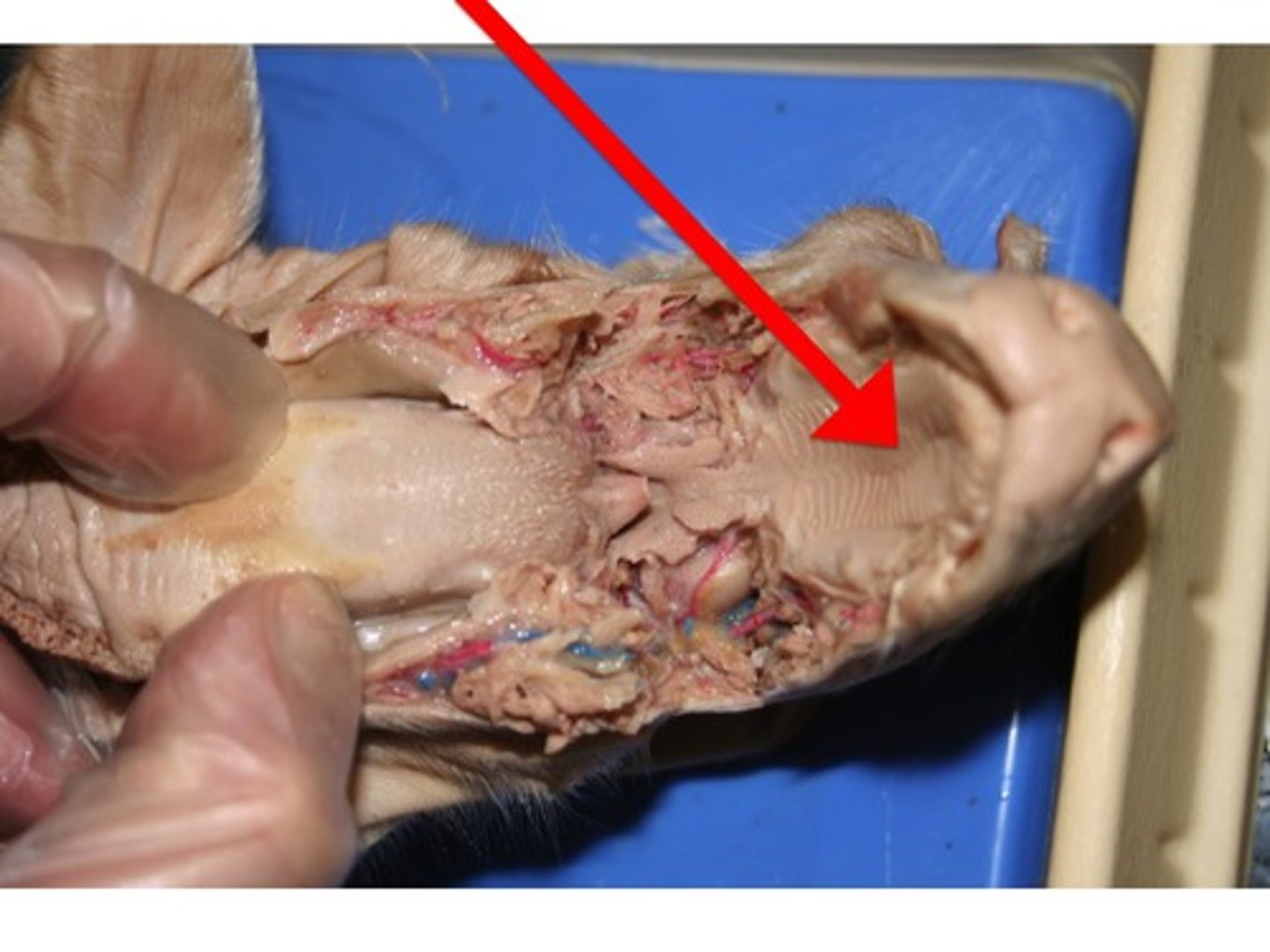
Soft Palette
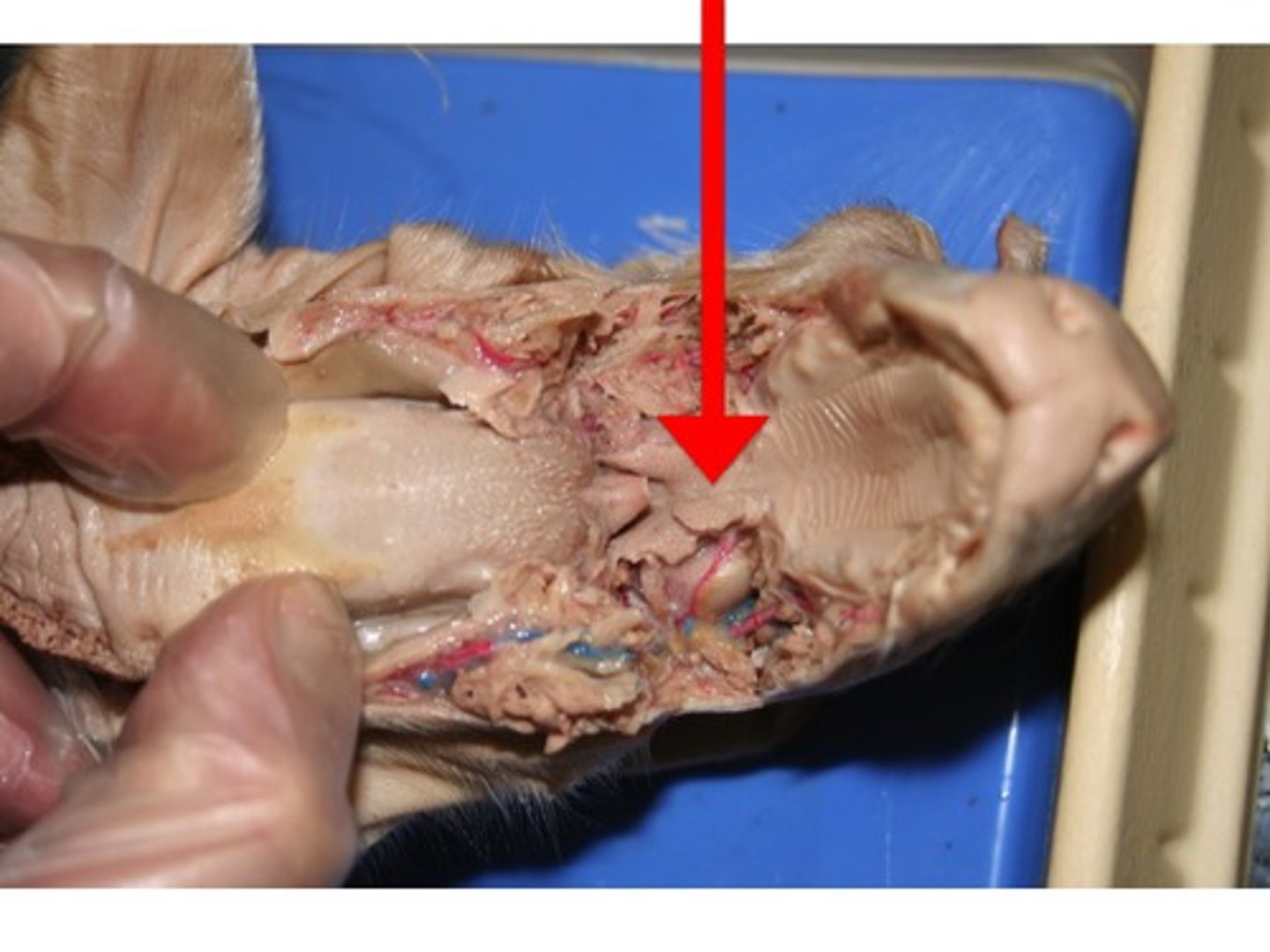
Nares
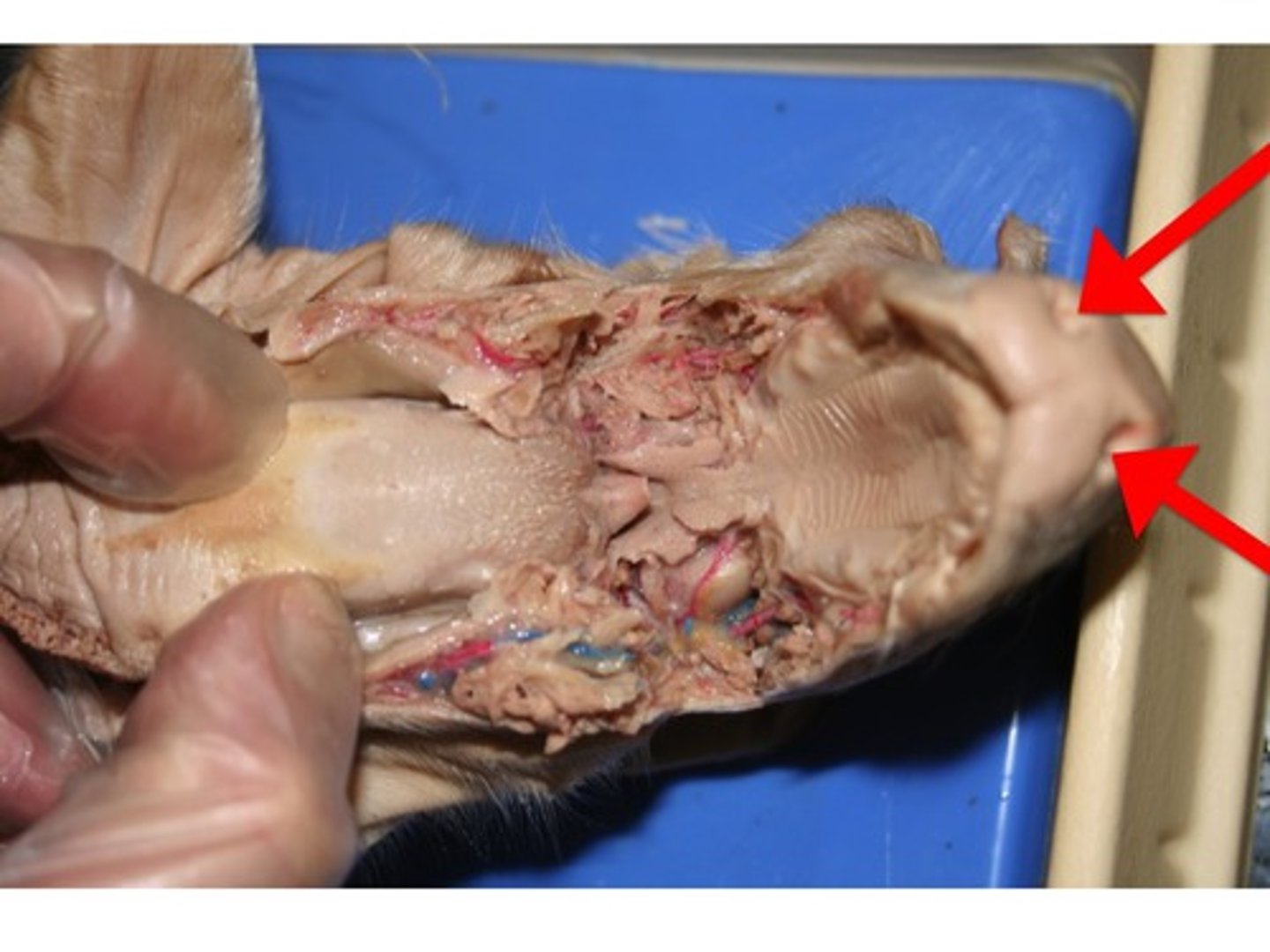
Epiglottis
- at the back of the mouthing the pharynx
- designed to keep the respiratory and digestive systems separate
- activated during swallowing to cover the glottis
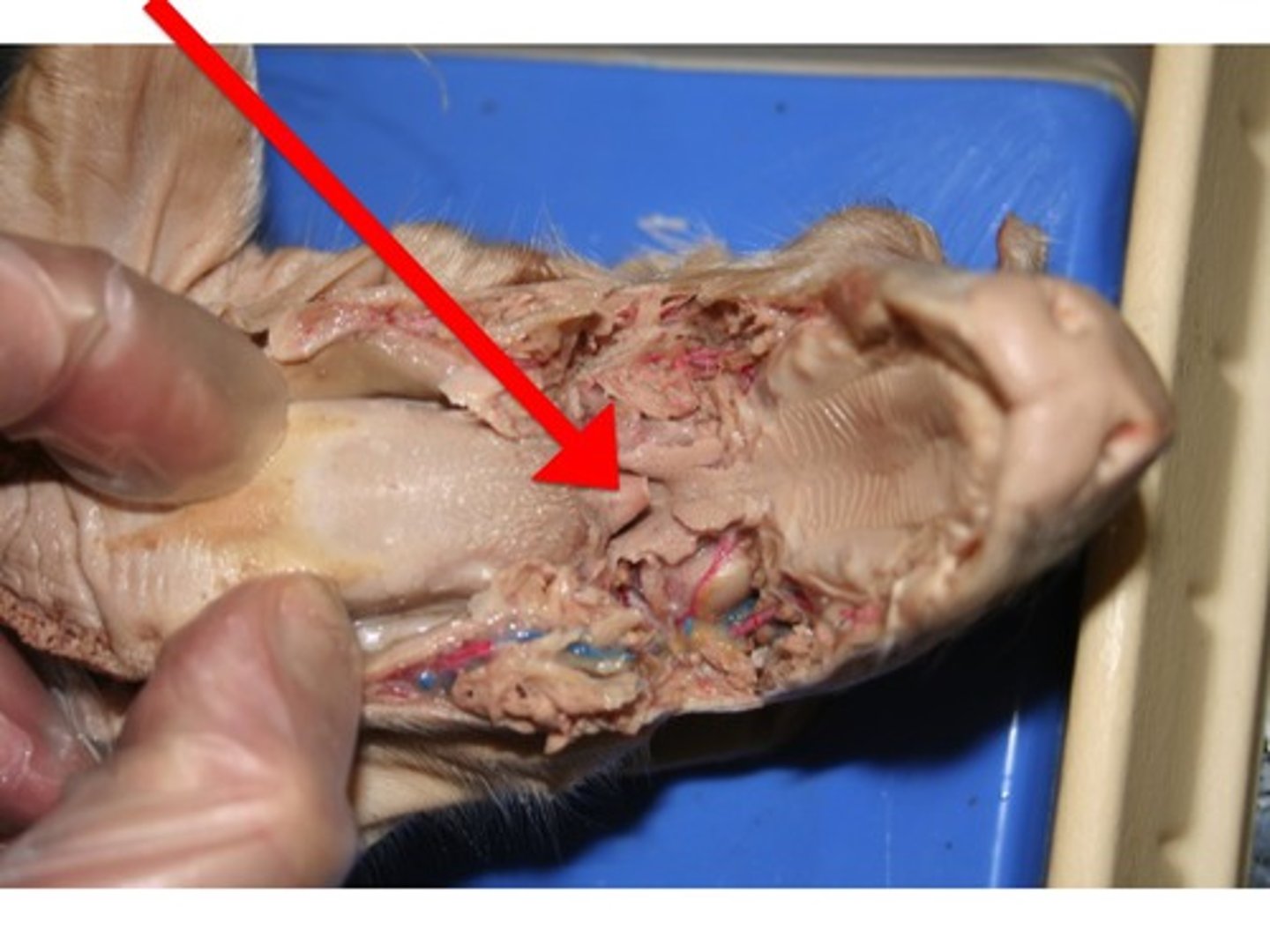
glottis
- opening into the respiratory system that the epiglottis covers during swallowing
Hard Palette
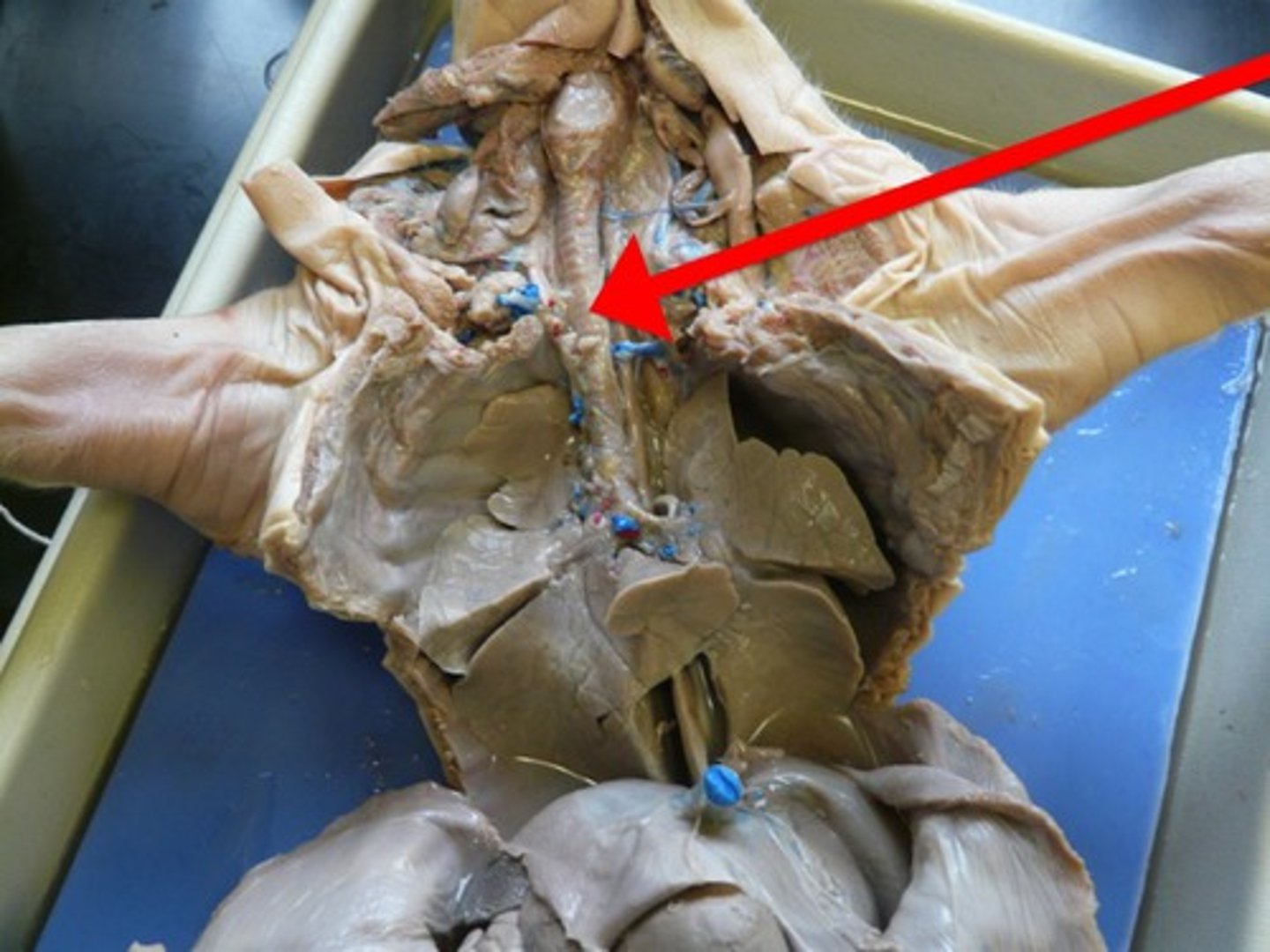
Trachea
- leads into the larynx (voice box)
- thicker/bigger tube on MY left of the esophagus
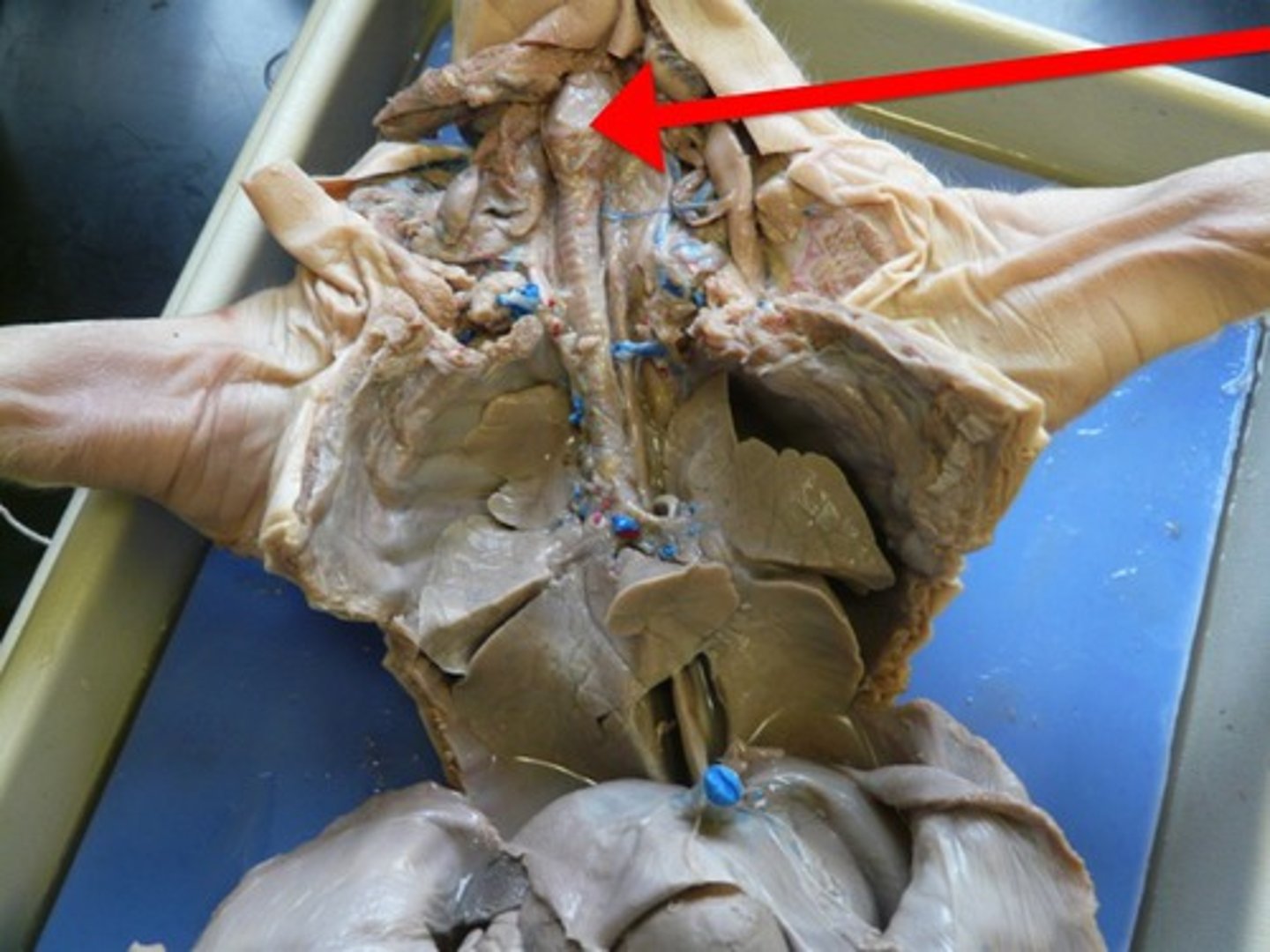
Larynx
- voice box
- top of the trachea
- oval shape at top of tube
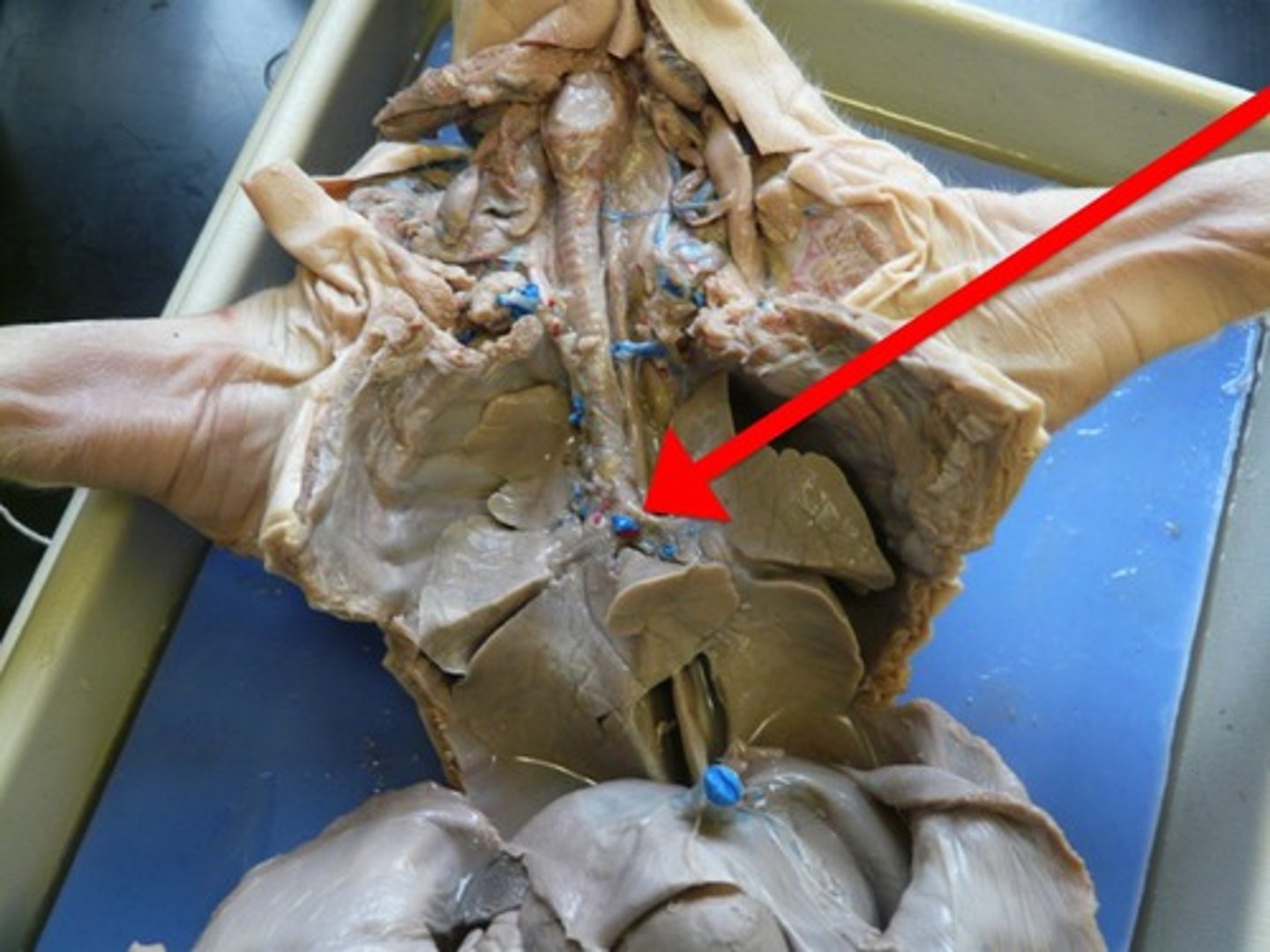
Primary Bronchi
Male
Is this pig male or female?
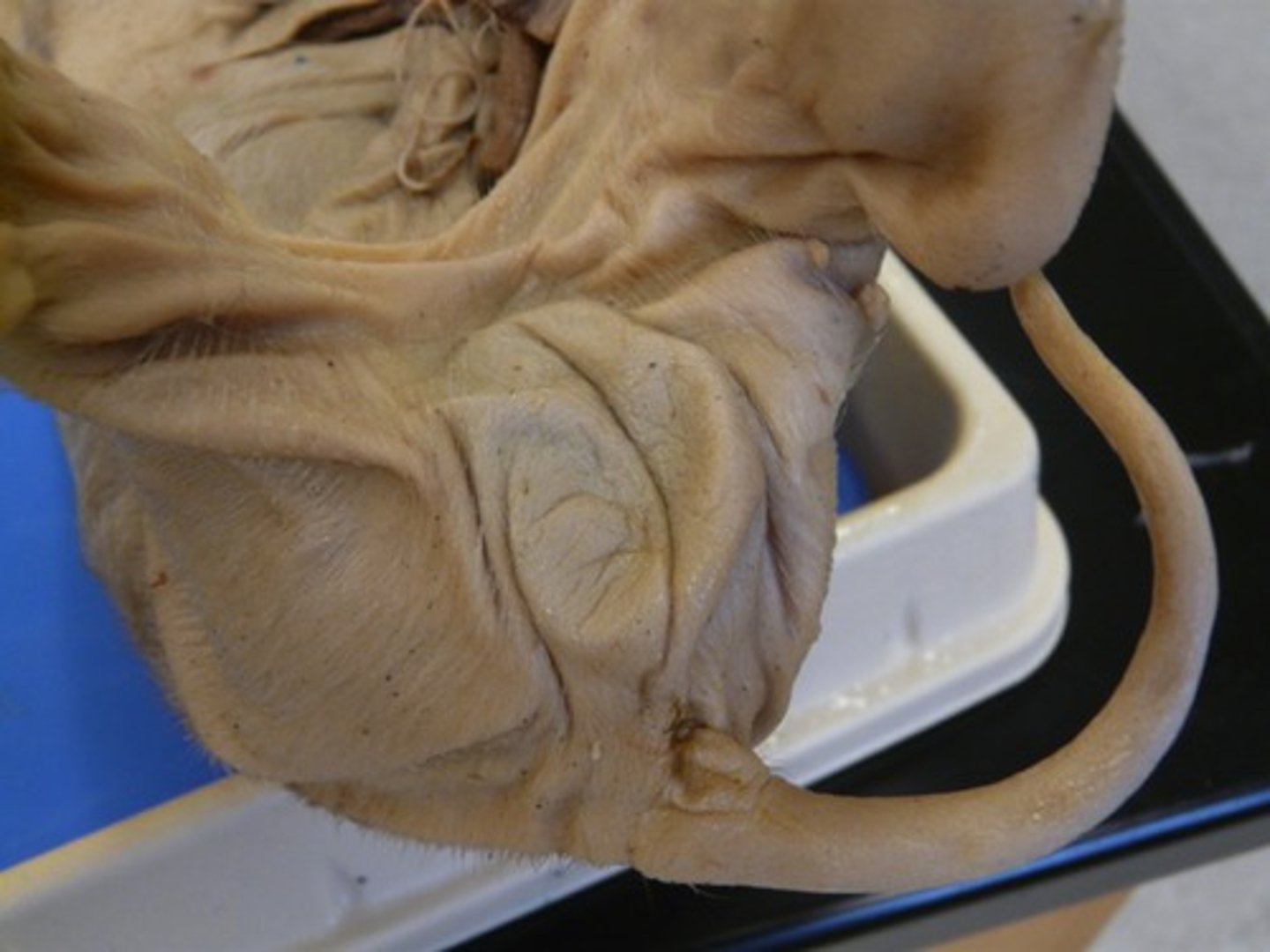
Pinna
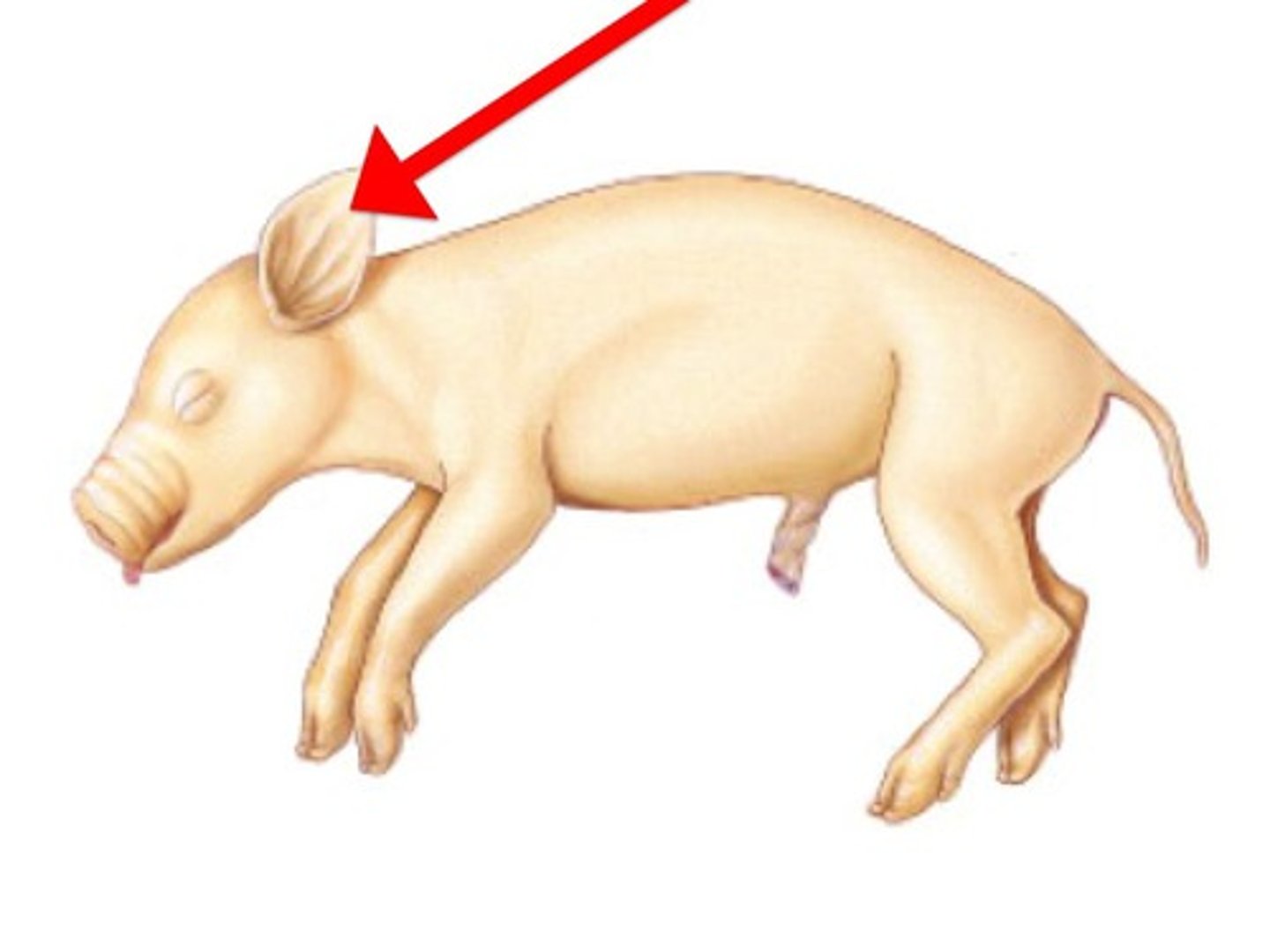
Umbilical cord
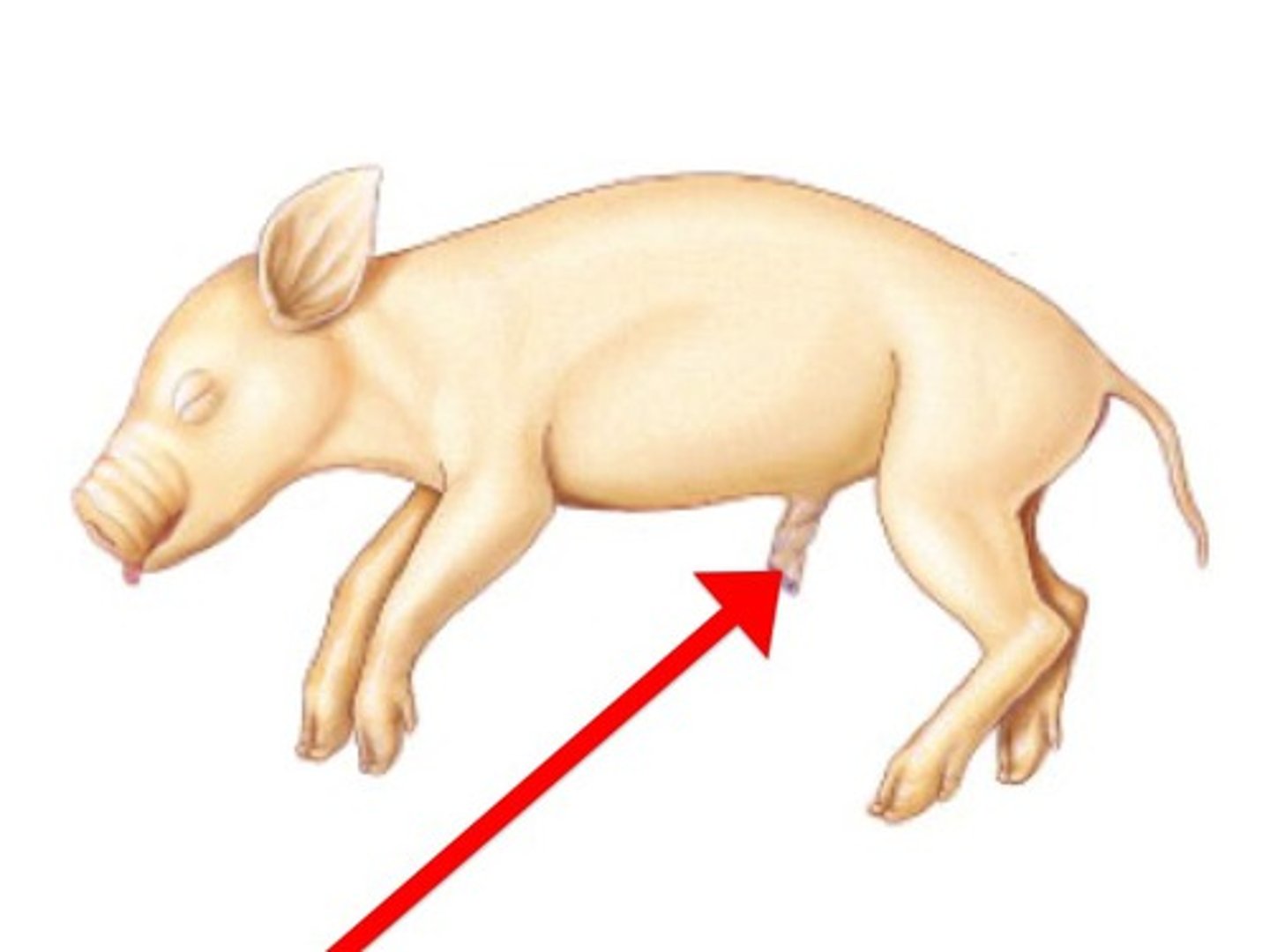
Urinary Bladder
- between the urinary arteries
- the ureter flow into it
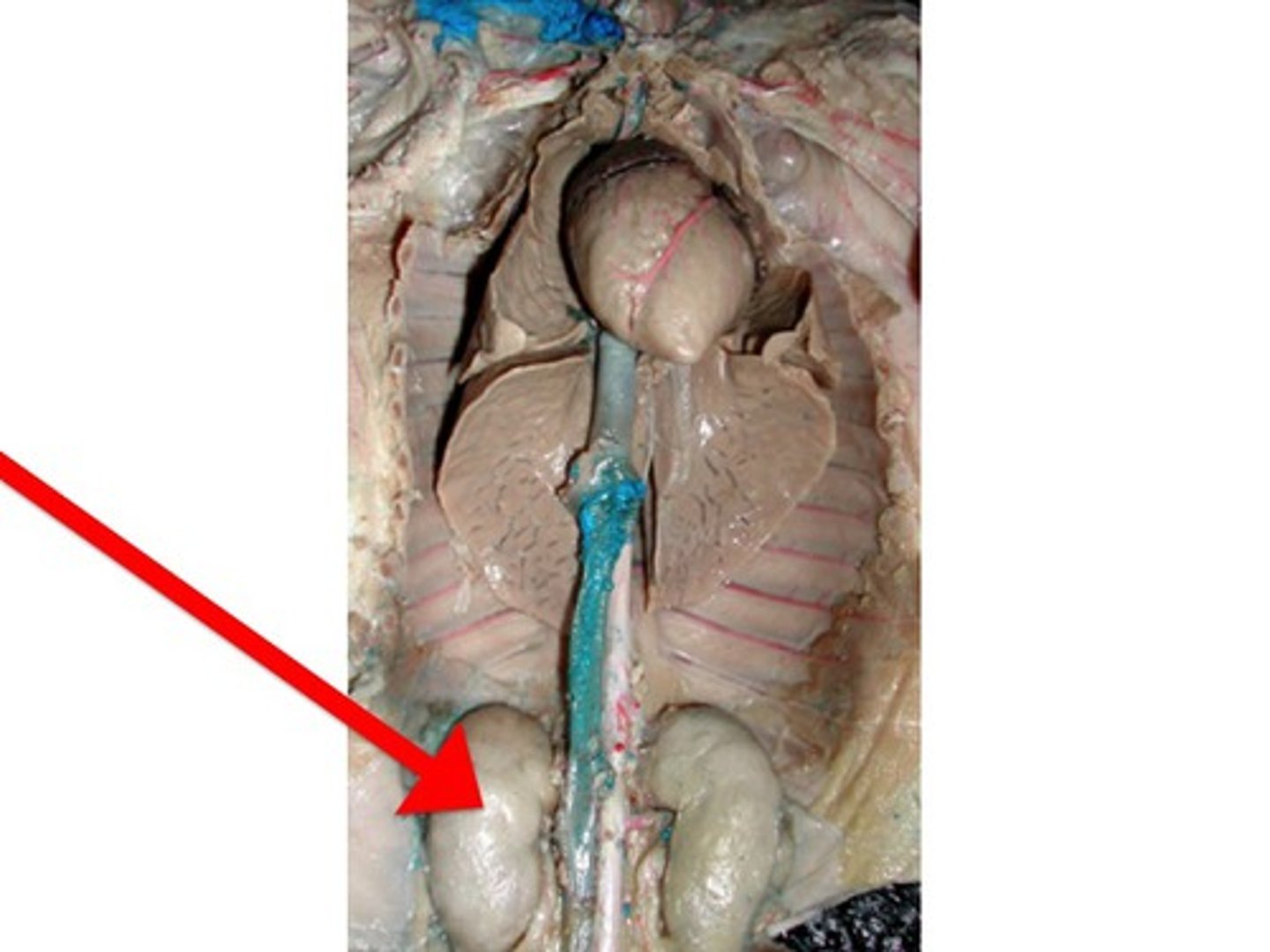
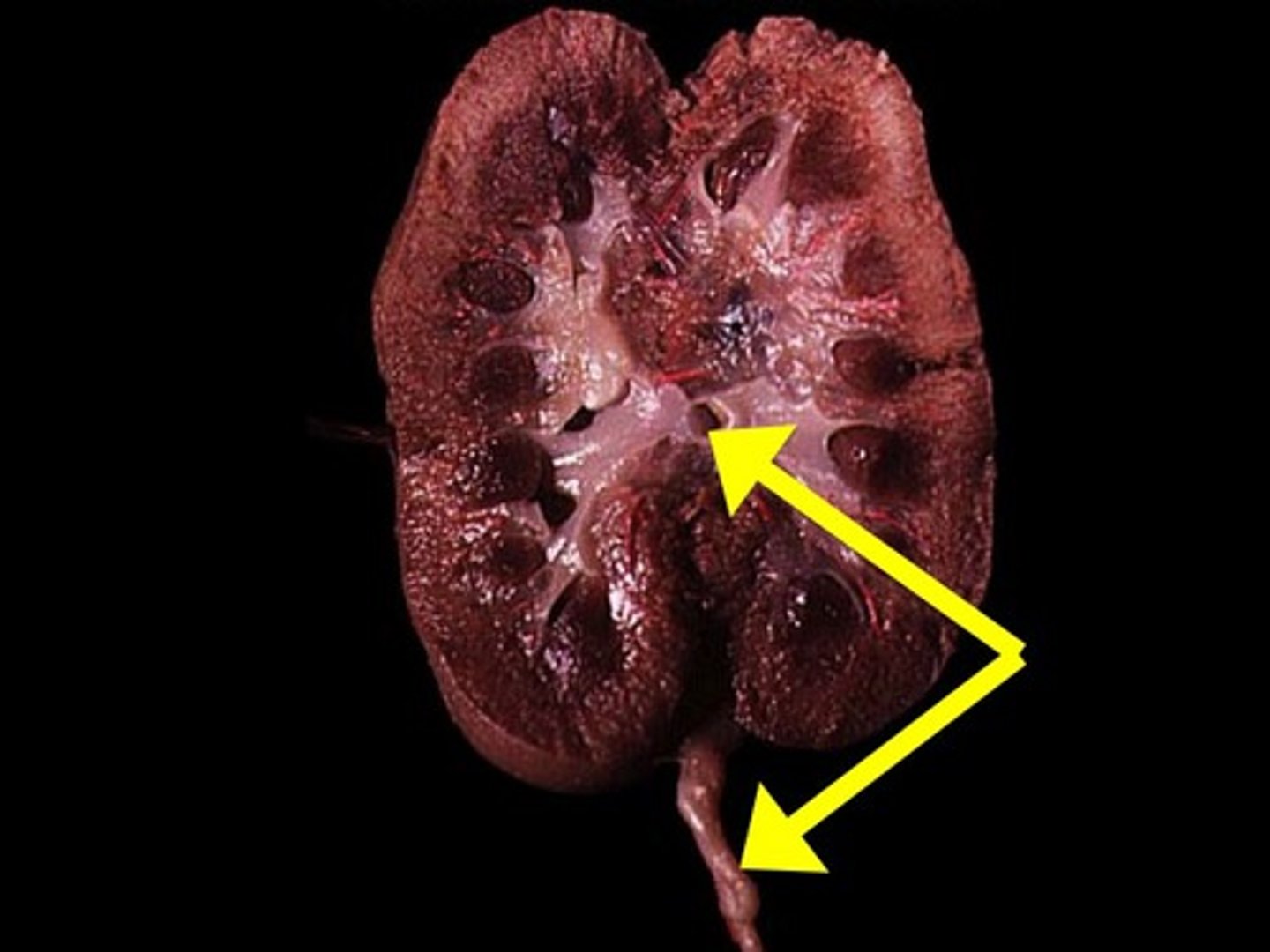
Kidney
- sort of underneath the intestines
- two of them
- bumps near the spinal cord
Transverse
The blue line separates the pig along this body plane.
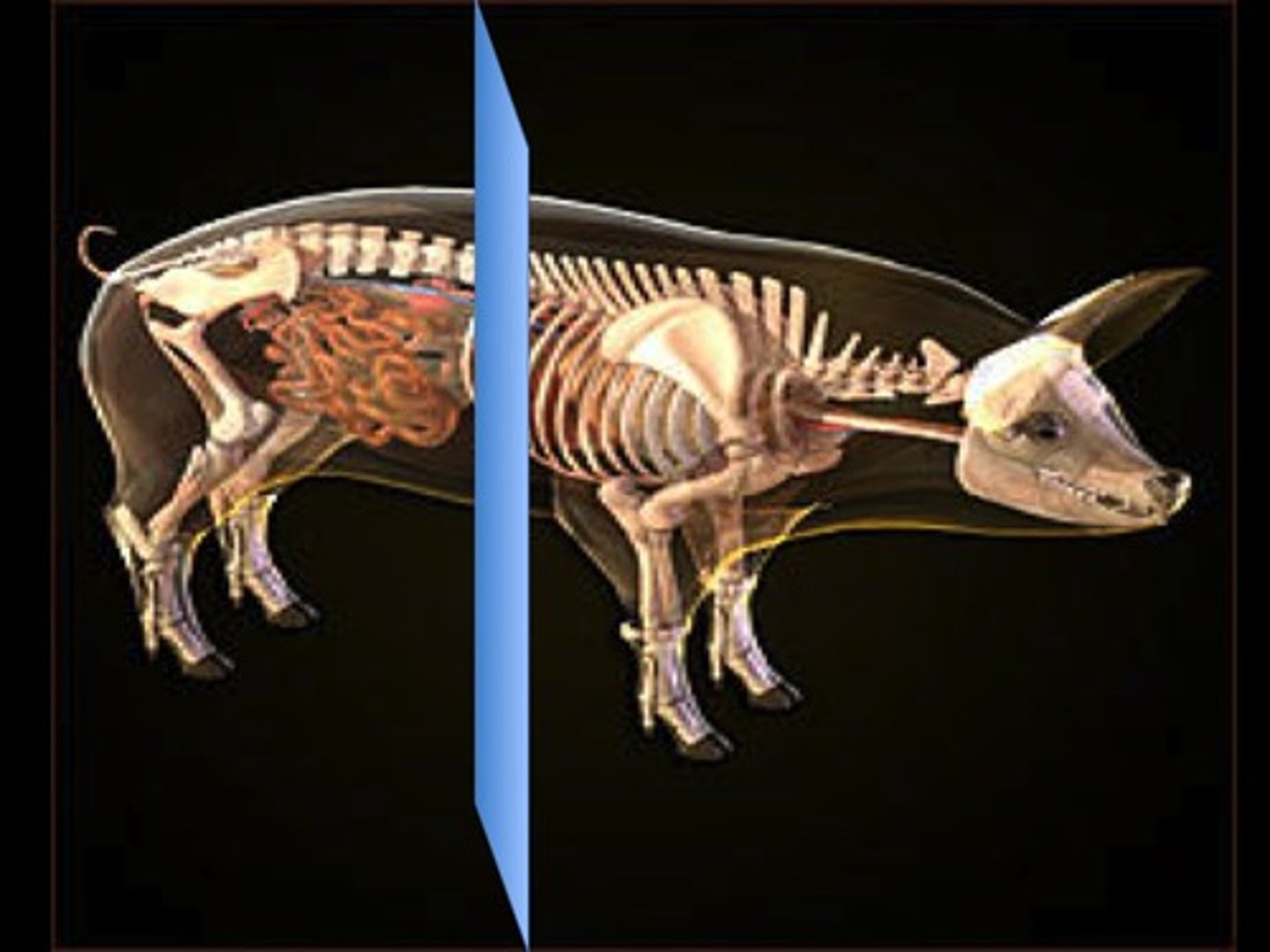

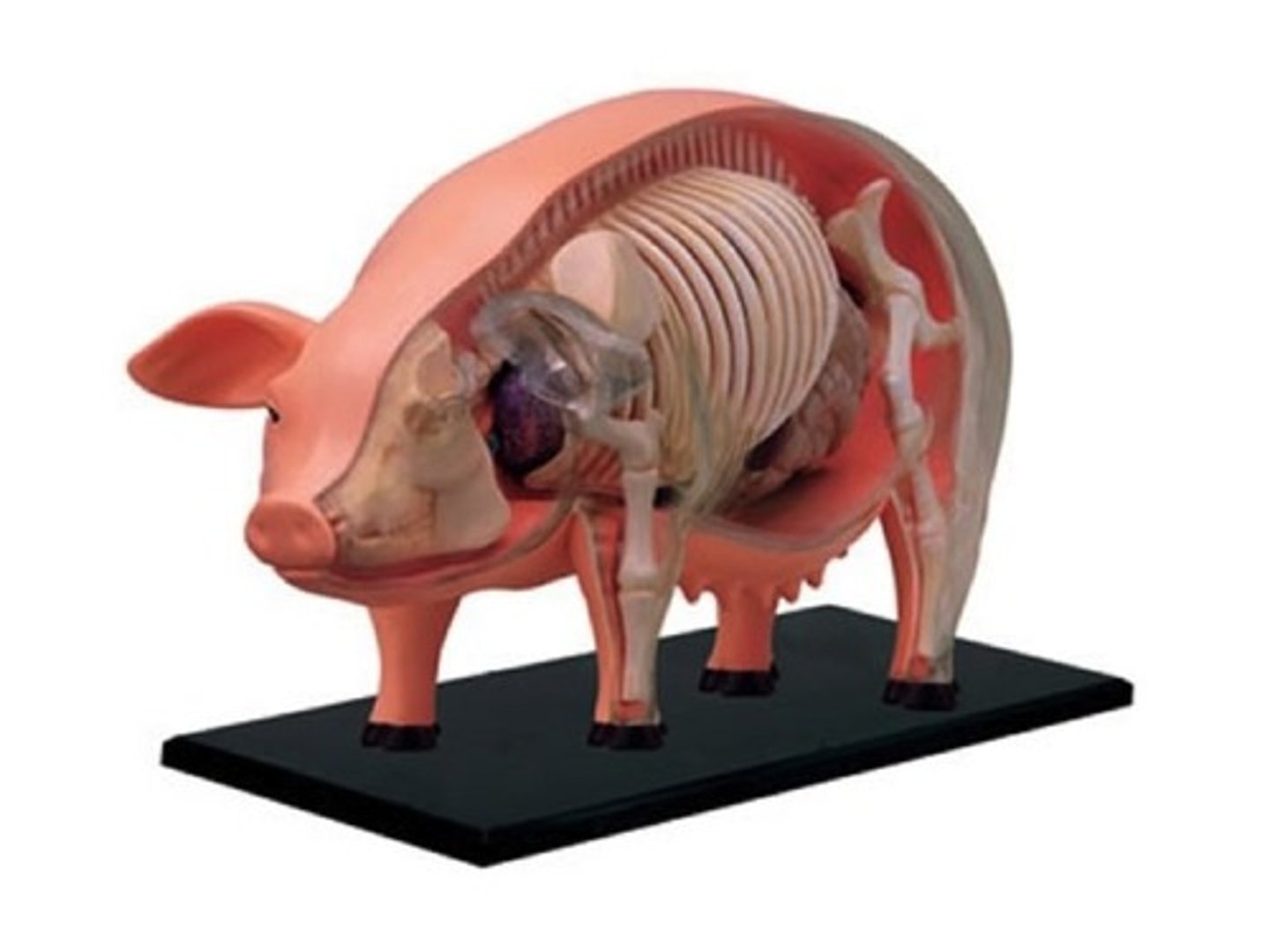
Sagittal
This skin was cut through this body plane to reveal internal structures like the skeleton.
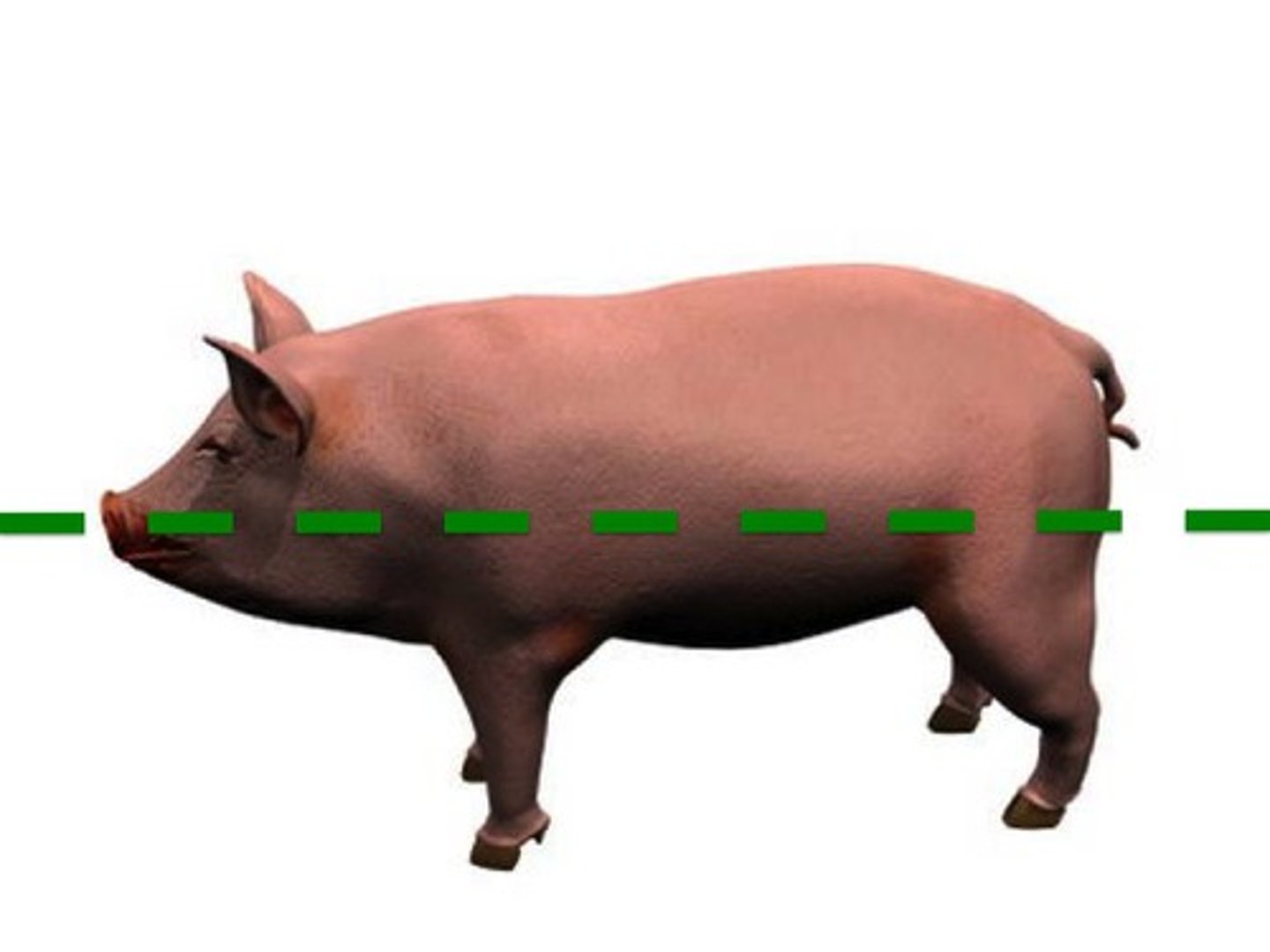
Frontal
The dashed green line separates the pig into two sections along this body plane.
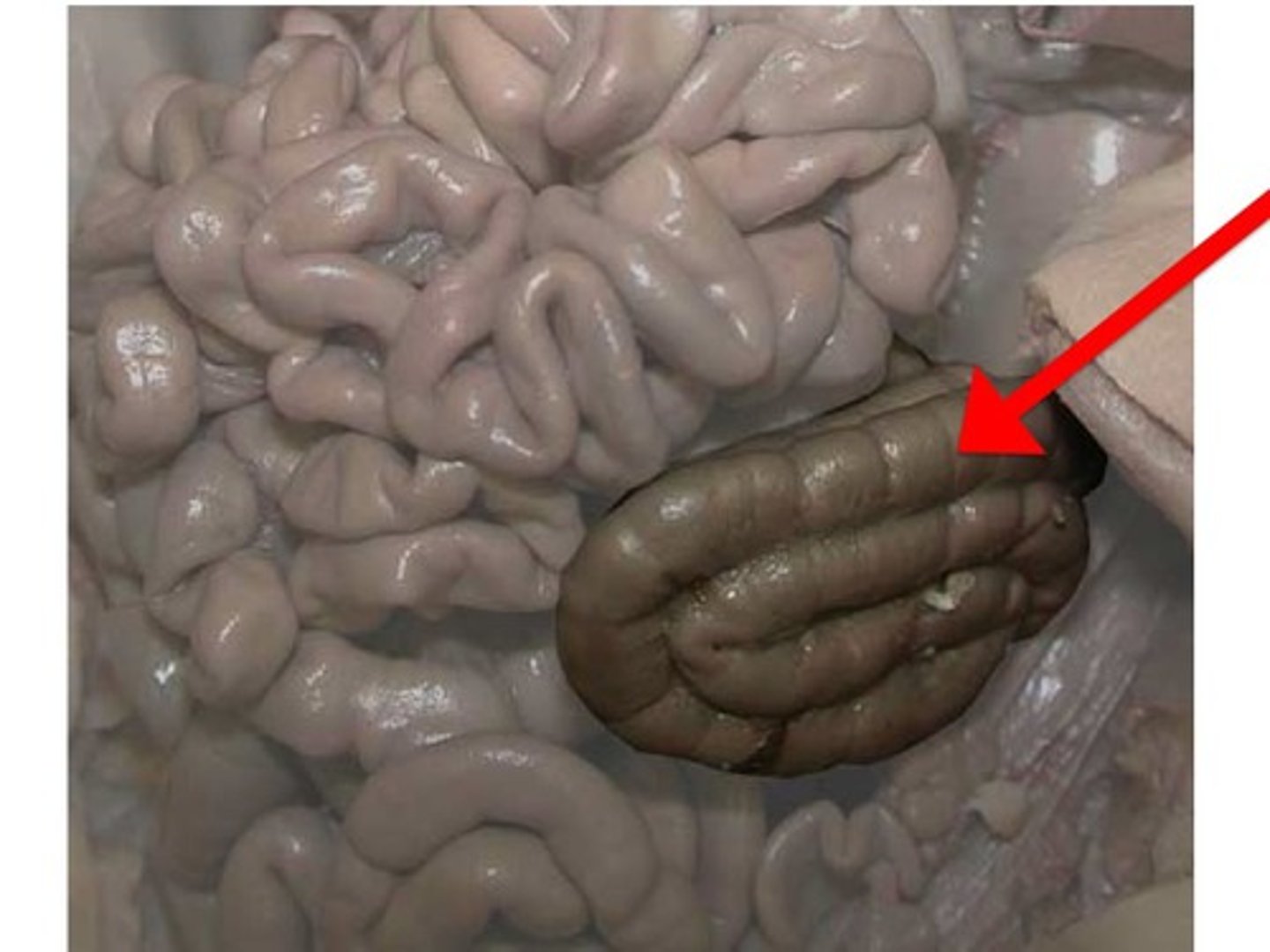
Large Intestine
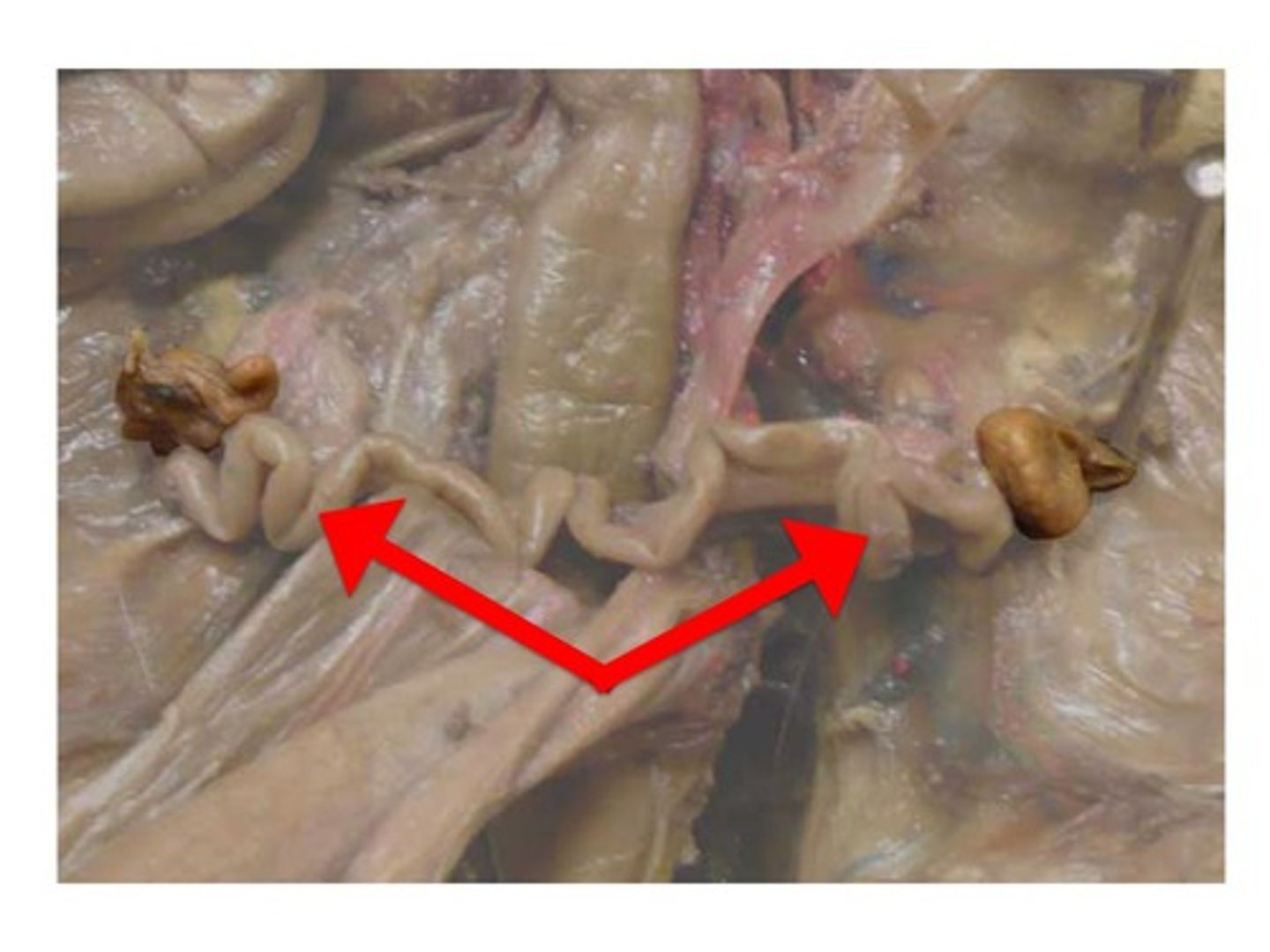
Ovaries
- two small balls on either side of what looks like a squiggly tube (oviduct/fallopian tube)
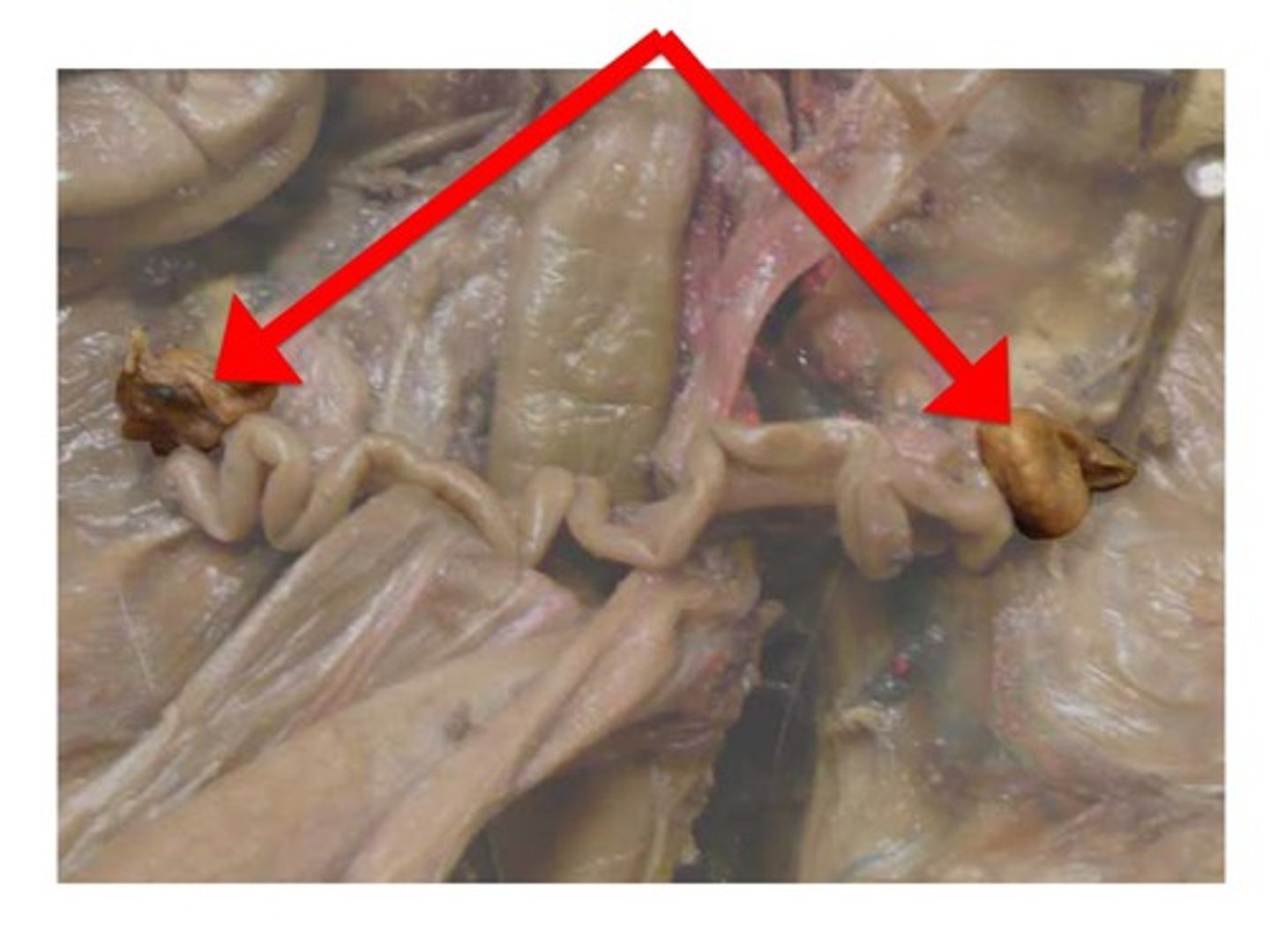
Uterine Horns
- oviduct merges into this
- curvy tubes between the ovaries
Rectum
- connected to the end of the large intestine and goes to the anus
- looks like a thick tube that goes from the large intestine (aka descending colon) to the ass

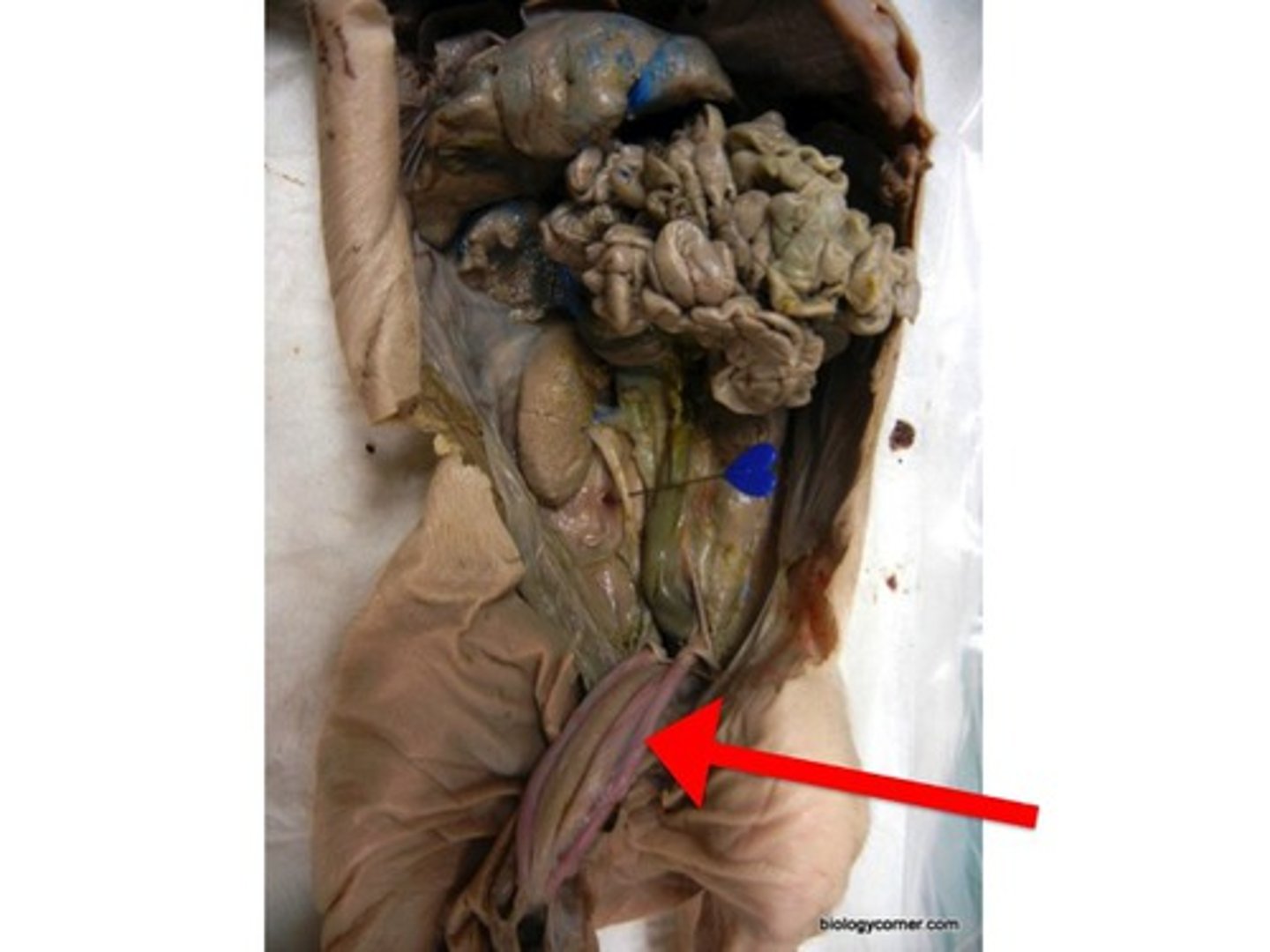
anus
where the insides of a pig exit (hole)
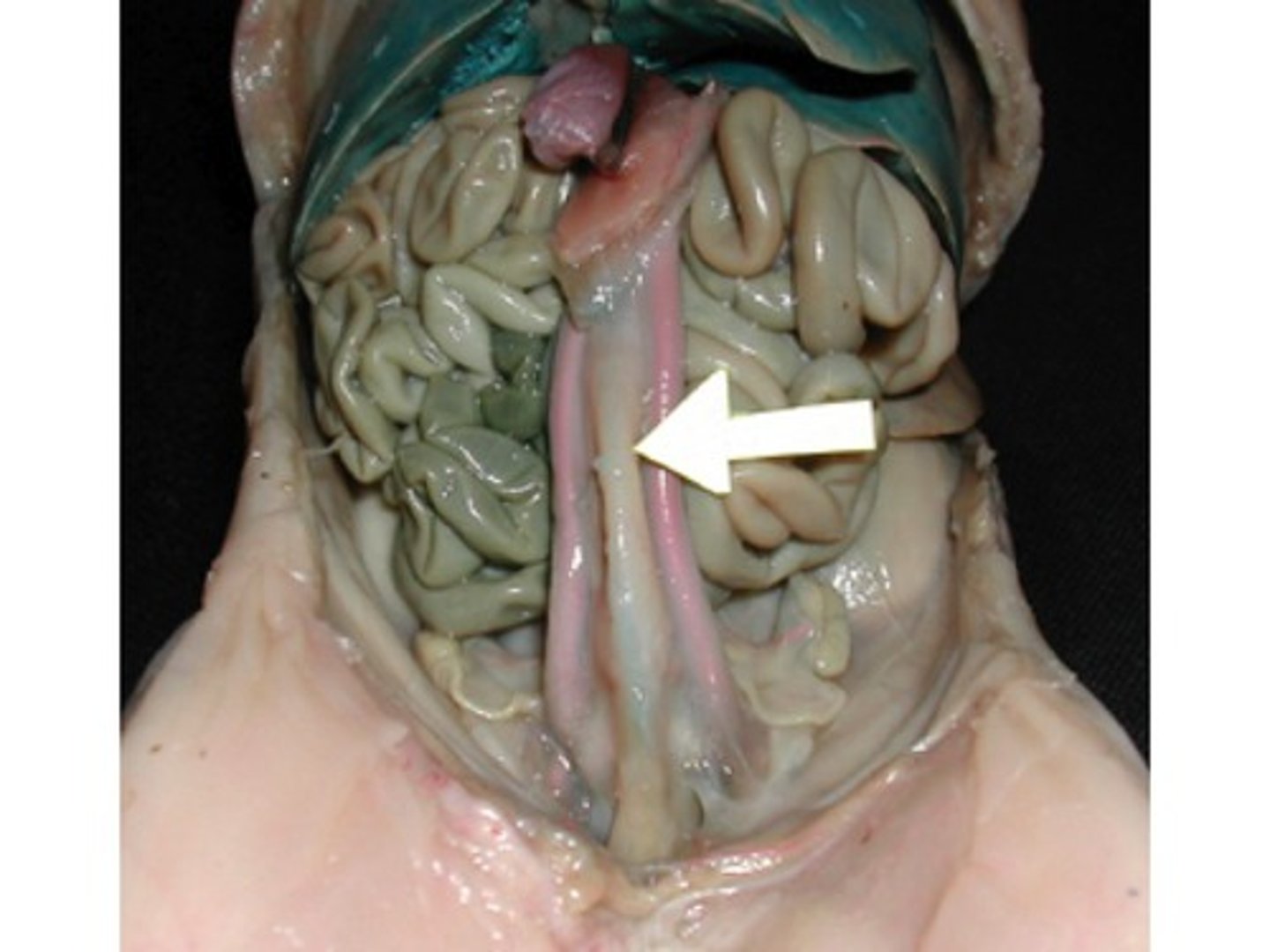
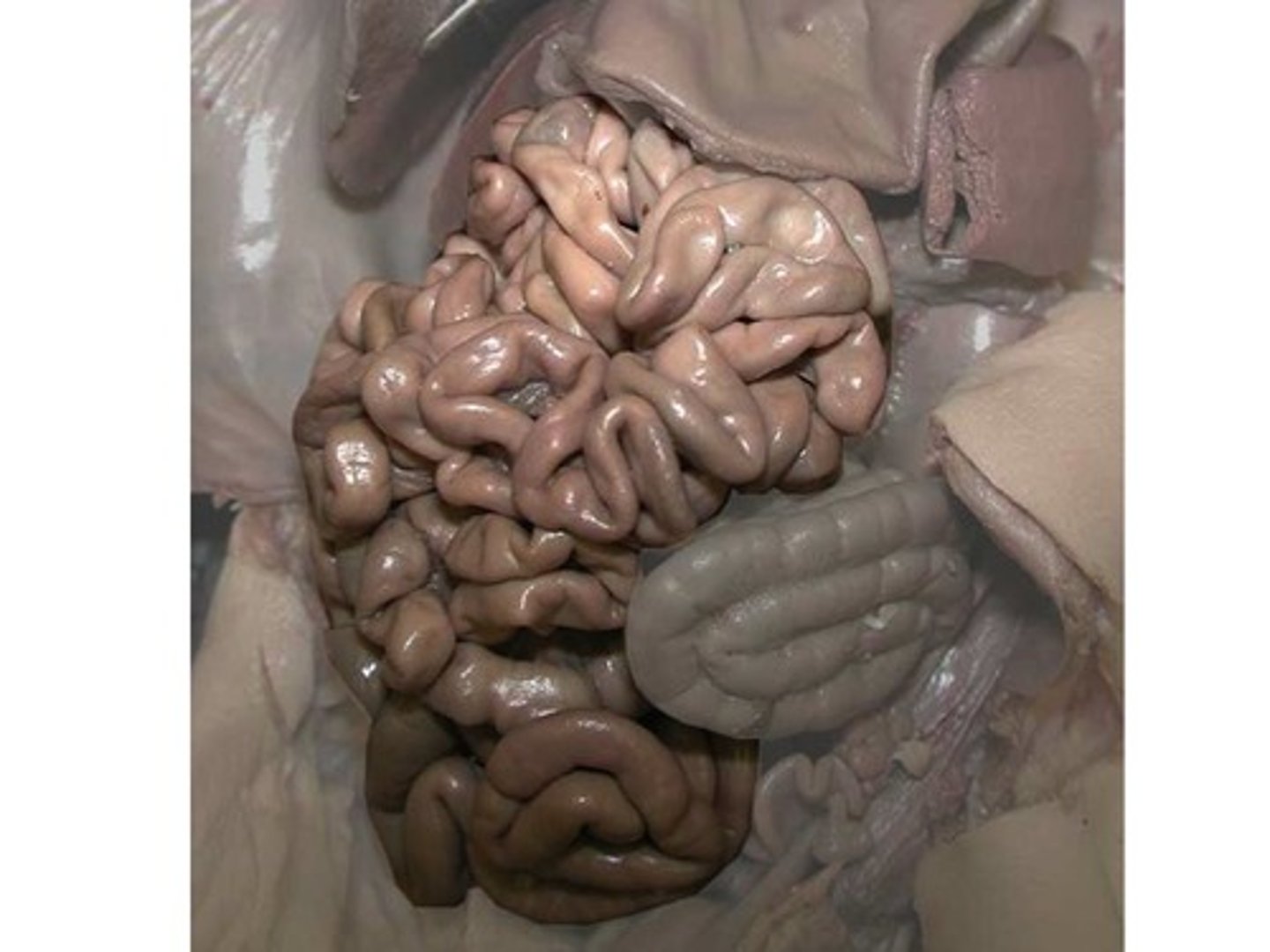
Small Intestine
Which organ is standing out in this photo?(background organs have been lightened)
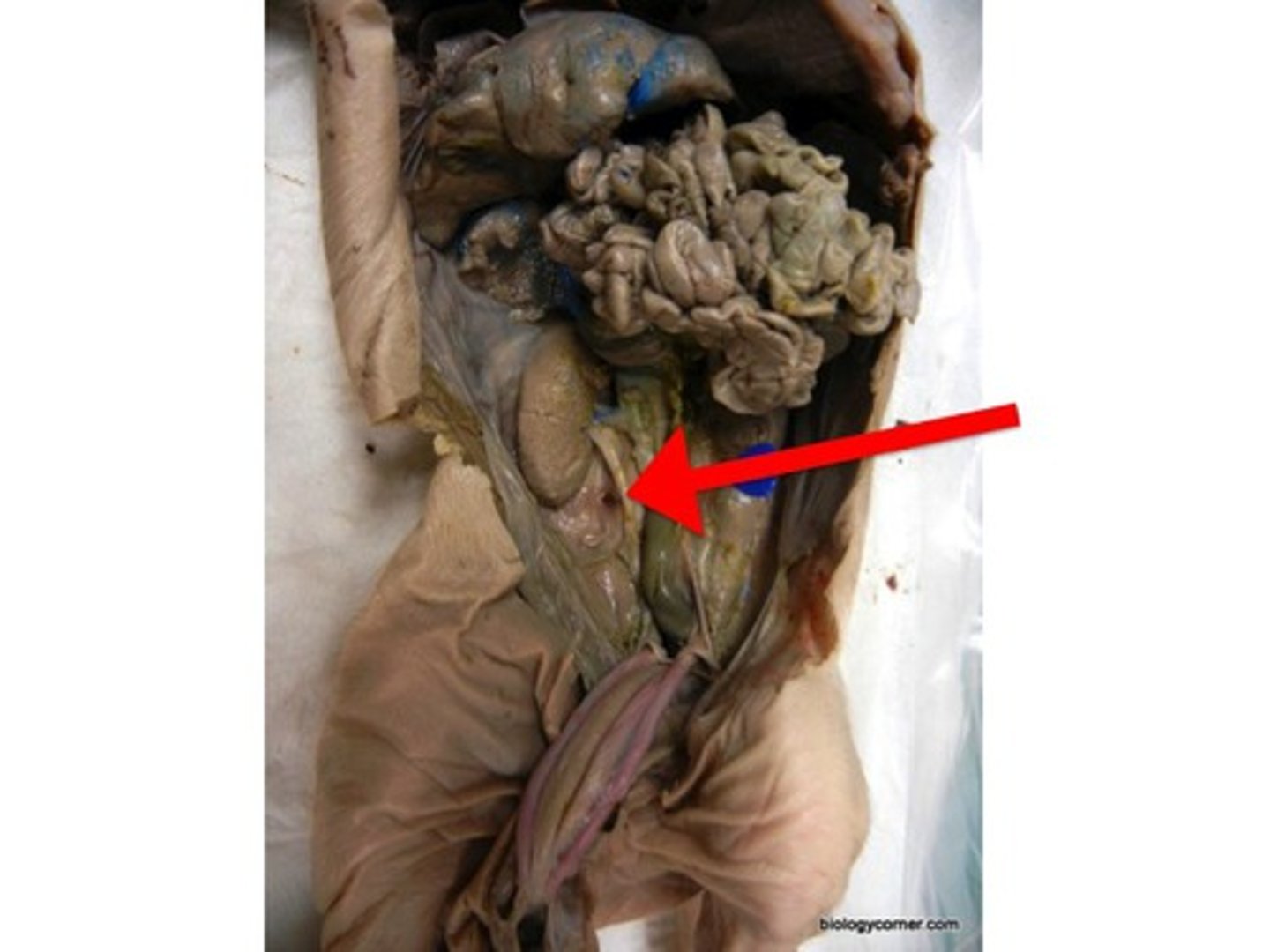
Umbilical Artery

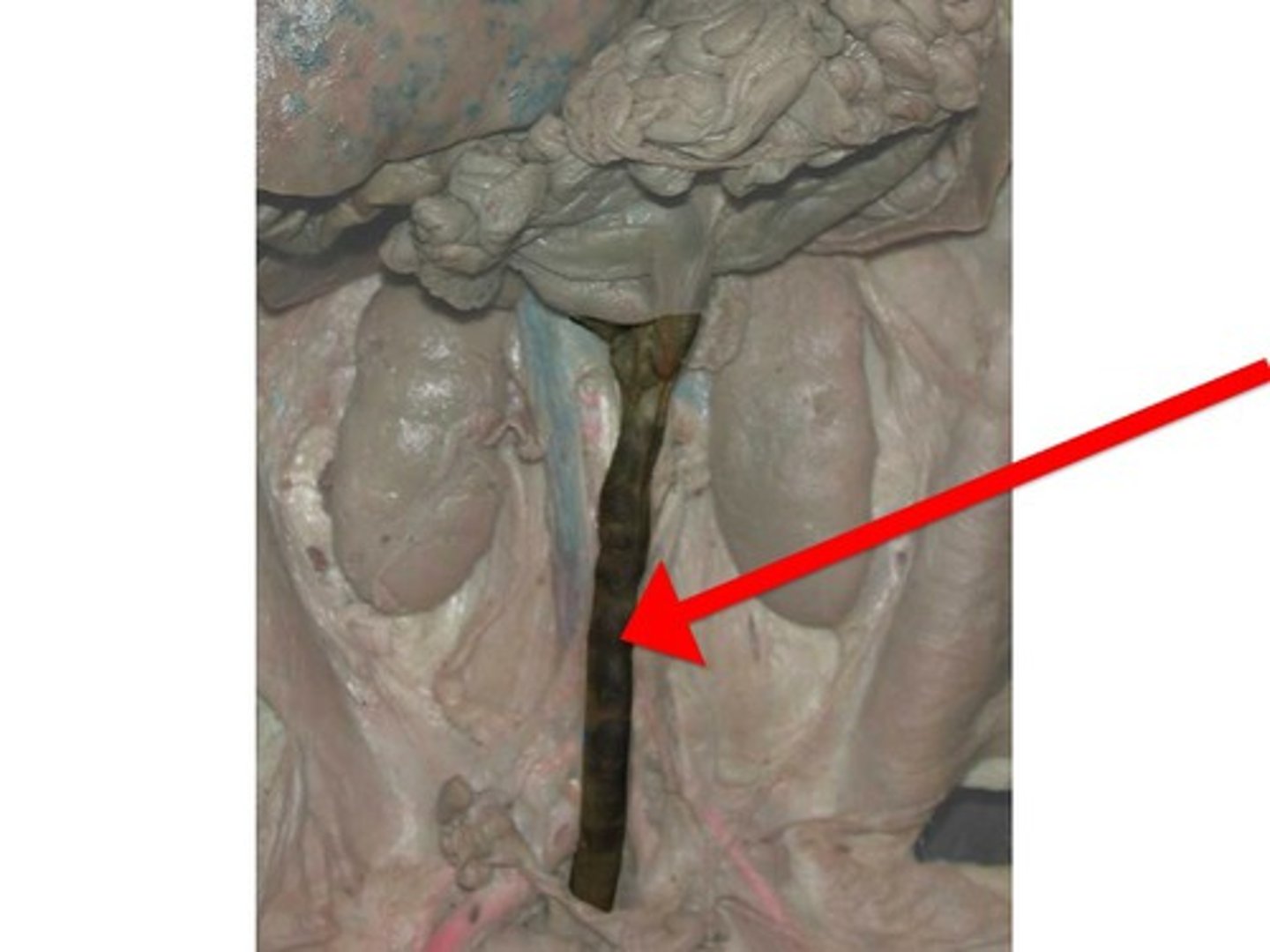
Ureter
- leads from the kidney to the urinary bladder
- the testes and ovaries lie over/cover the __________s so to see them you will have to dissect them
- looks like a tube that comes from the kidneys/adrenal gland near the middle of the body
Testes

Renal Cortex
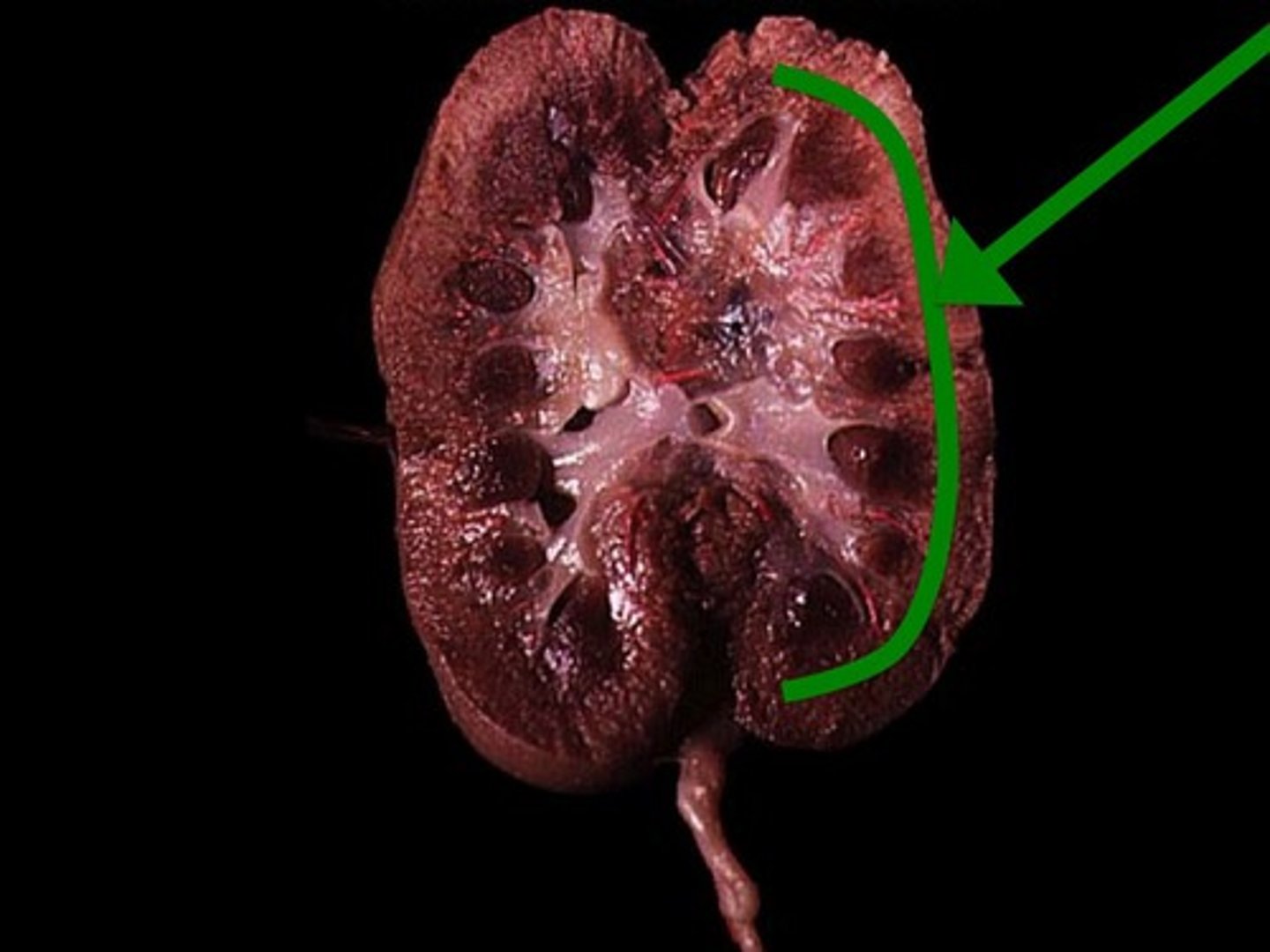
Renal Medulla
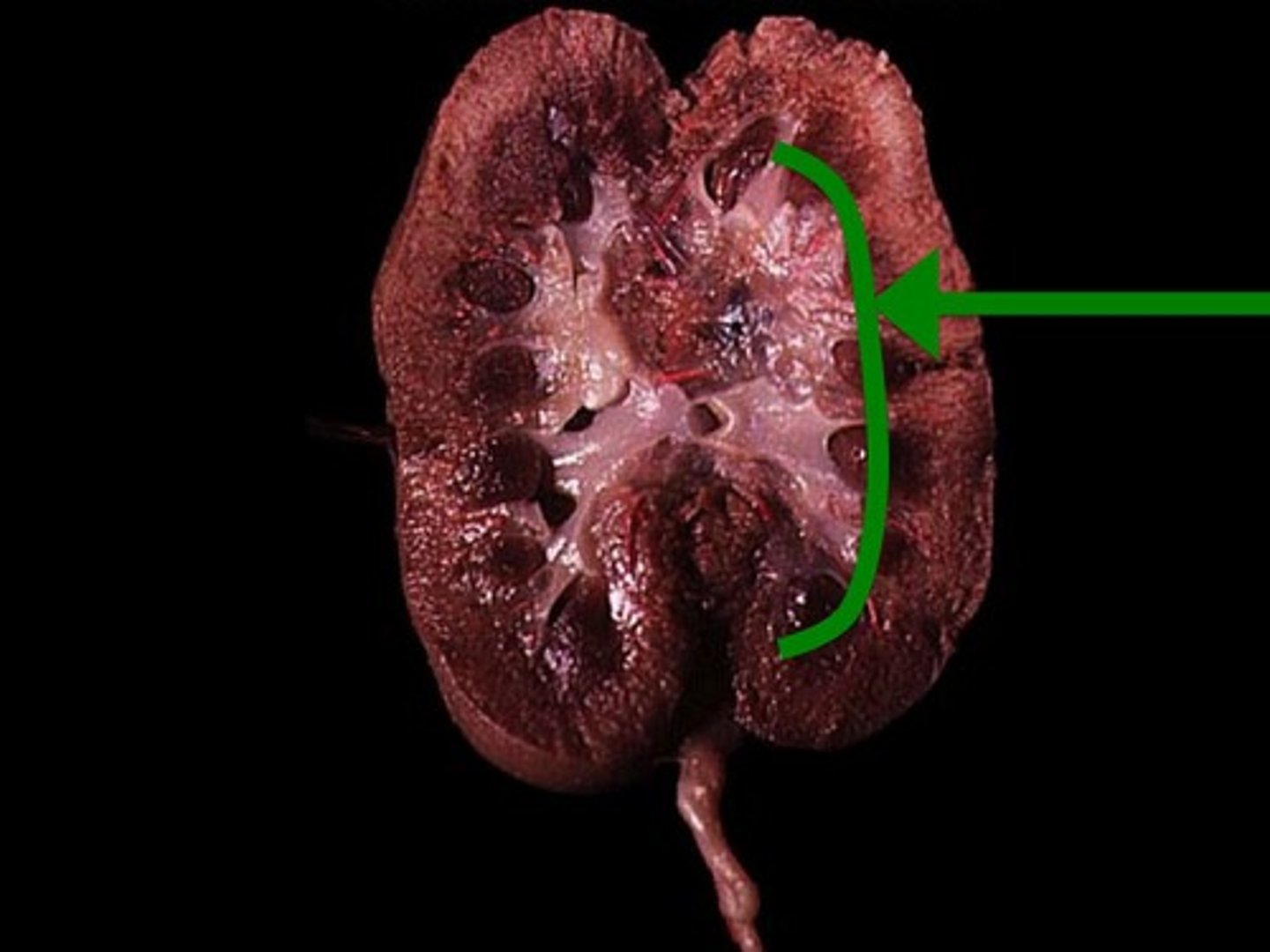
Renal Pyramid
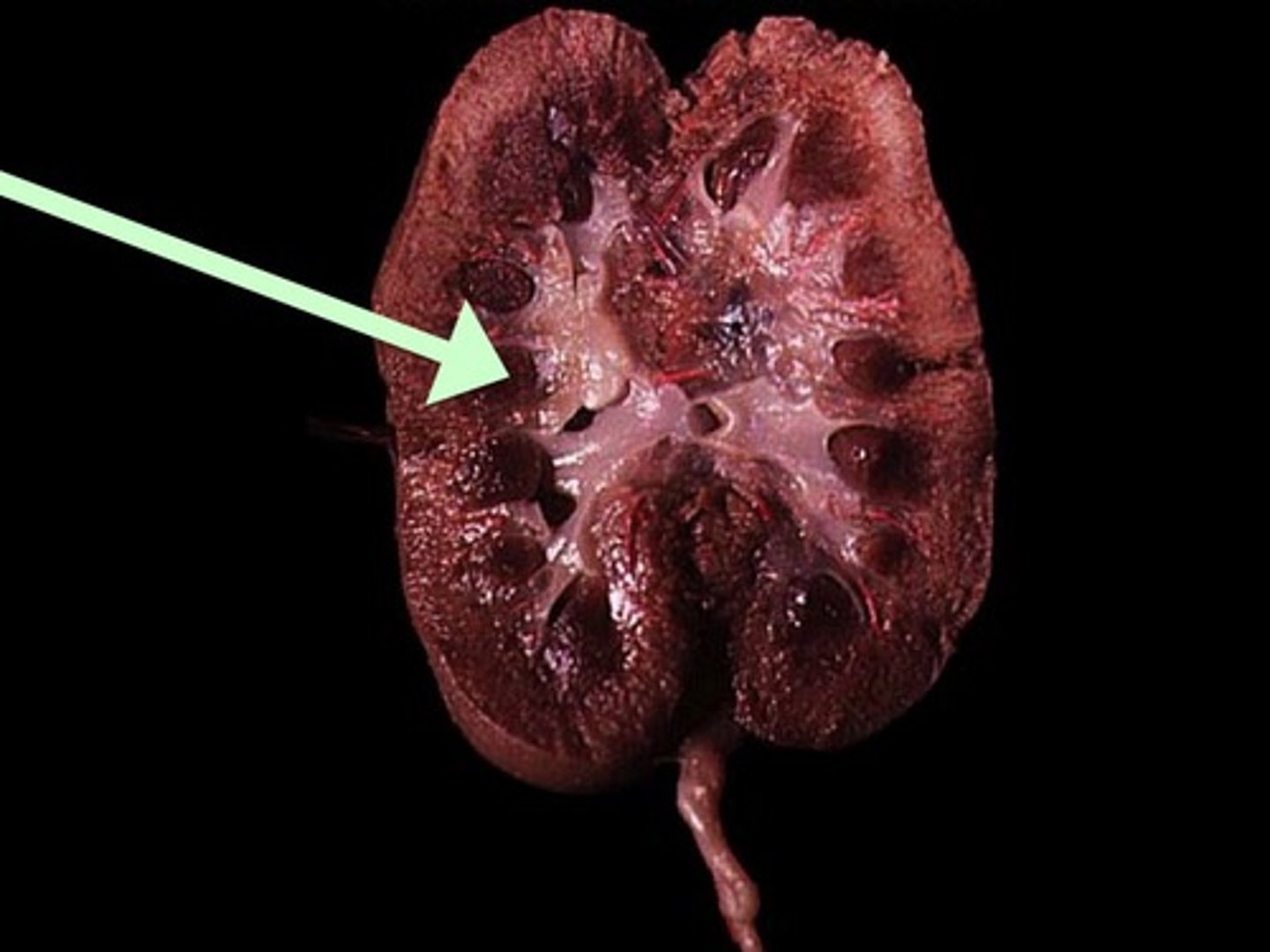
Renal Column
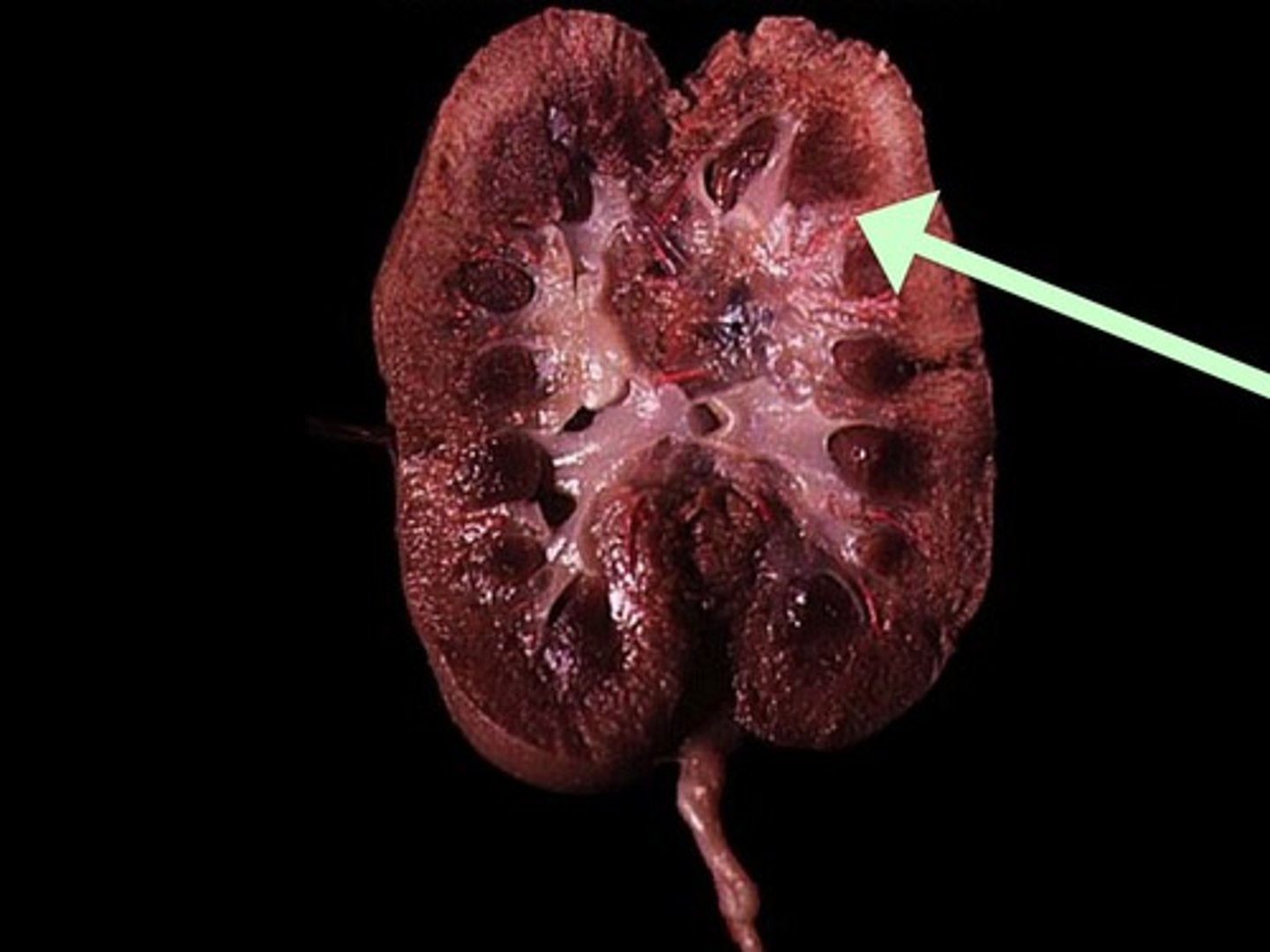
Renal Pelvis
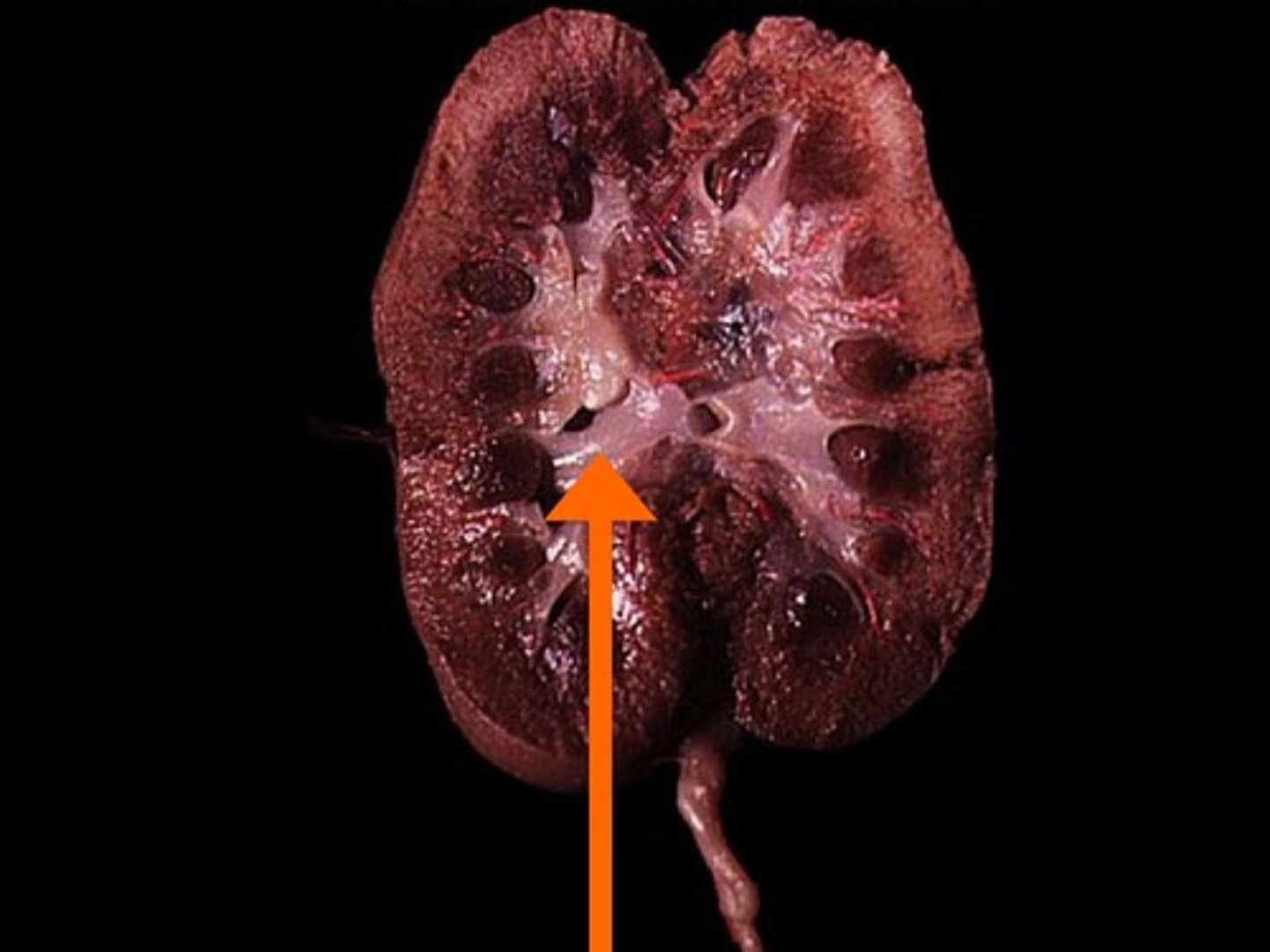
Ureter
cranial
- head
- towards the head or part of the animal that points forward or meets the environment first
caudal
- tail
- opposite the cranial side of the animal
dorsal
the side of the pig that faces the sky
(think of where the _______ fin on a dolphin is located)
ventral
side of the pig that faces the ground
proximal
anything in the pig that is more towards the middle
distal
anything more toward the outside or further away from the point of reference
urogenital papilla
- females have this
- the small bud-like protrusion, just ventral to the anus
- when you pick up the pig, lift its tail to see
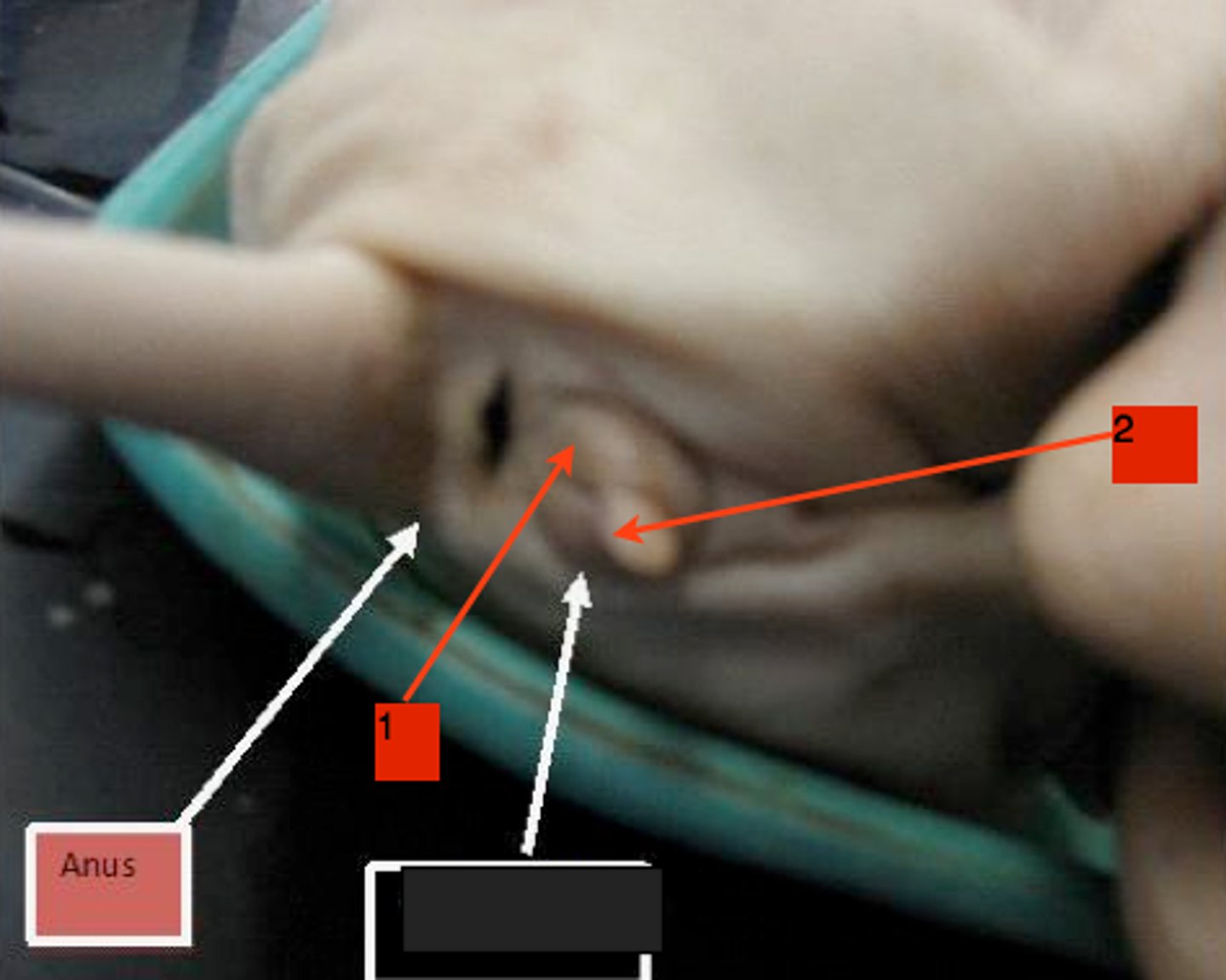
scrotum
- a little more ventral than the where the urogenital papilla would be
- near the hind legs
- area where the skin looks thin and puffy, forming two slightly rounded patches
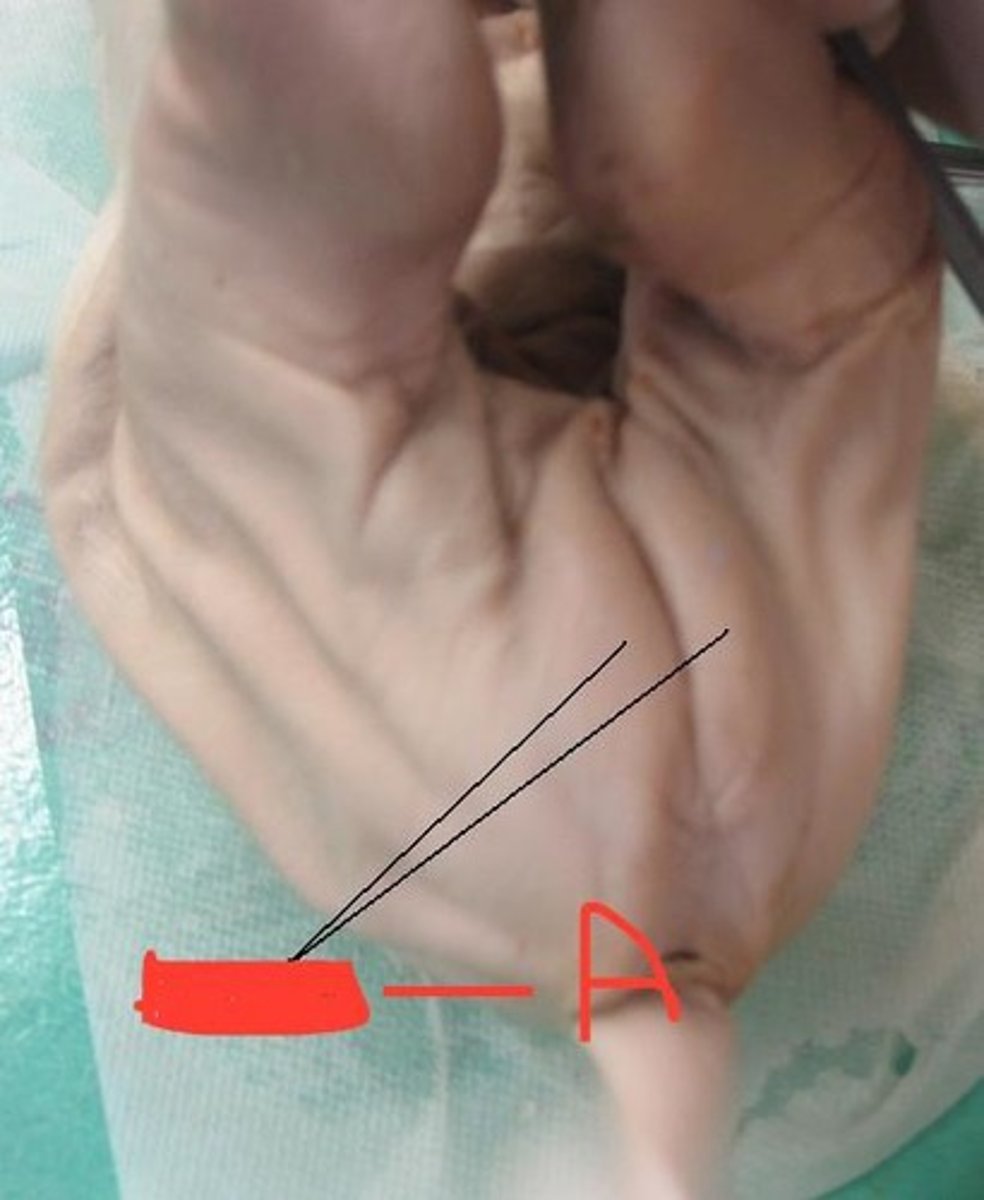
male urogenital opening
- small mound just posterior to the umbilical cord on the ventral side (male)
**on a female, it is located near the anus!!
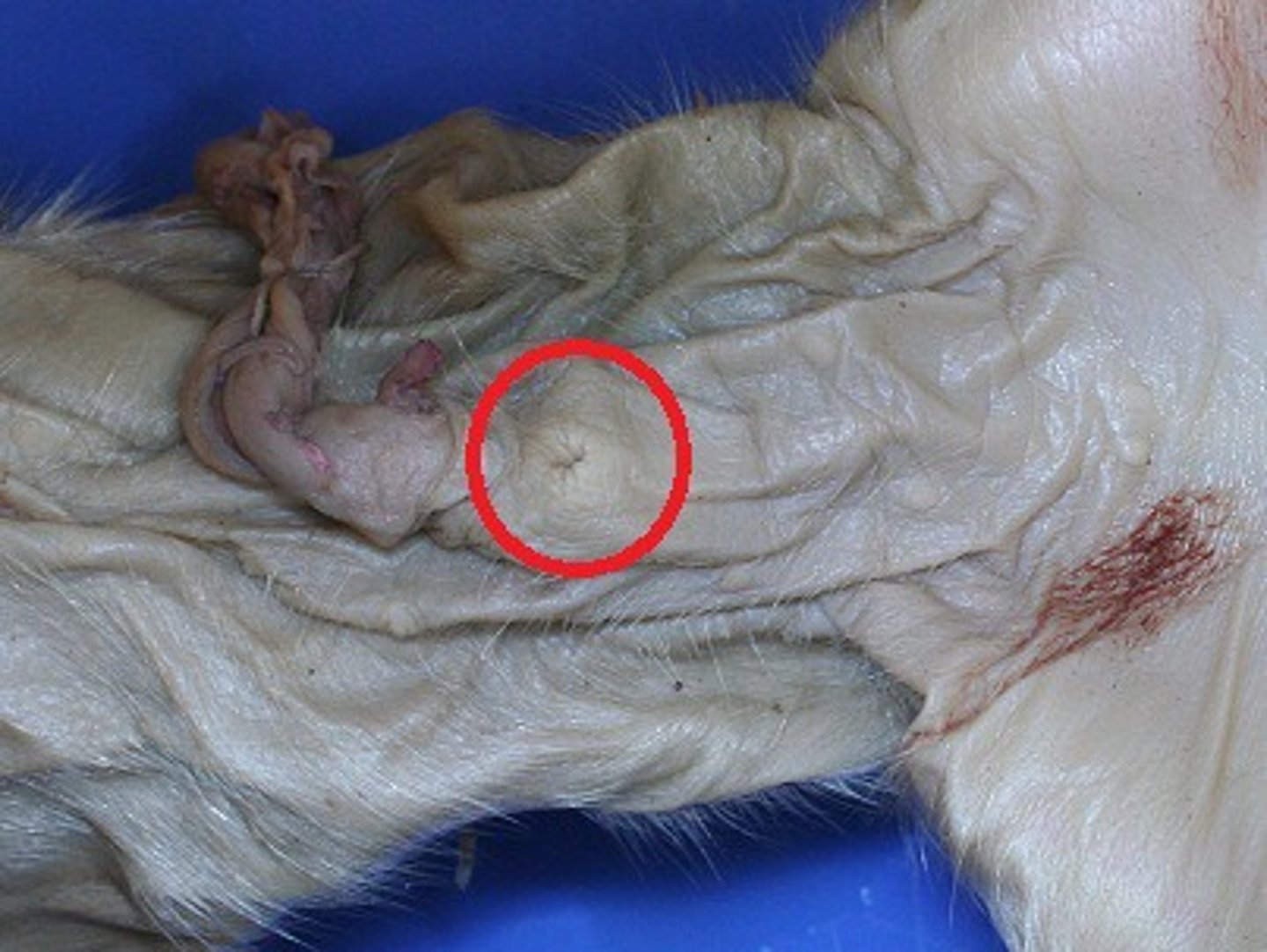
epitrichium
- filmy, white layer of waxy material peeling off of the pig
- it's the layer of the epidermis sloughed off as more is produced
nipples
- two parallel line down the ventral side (called the milk lines)
pig umbilical vein
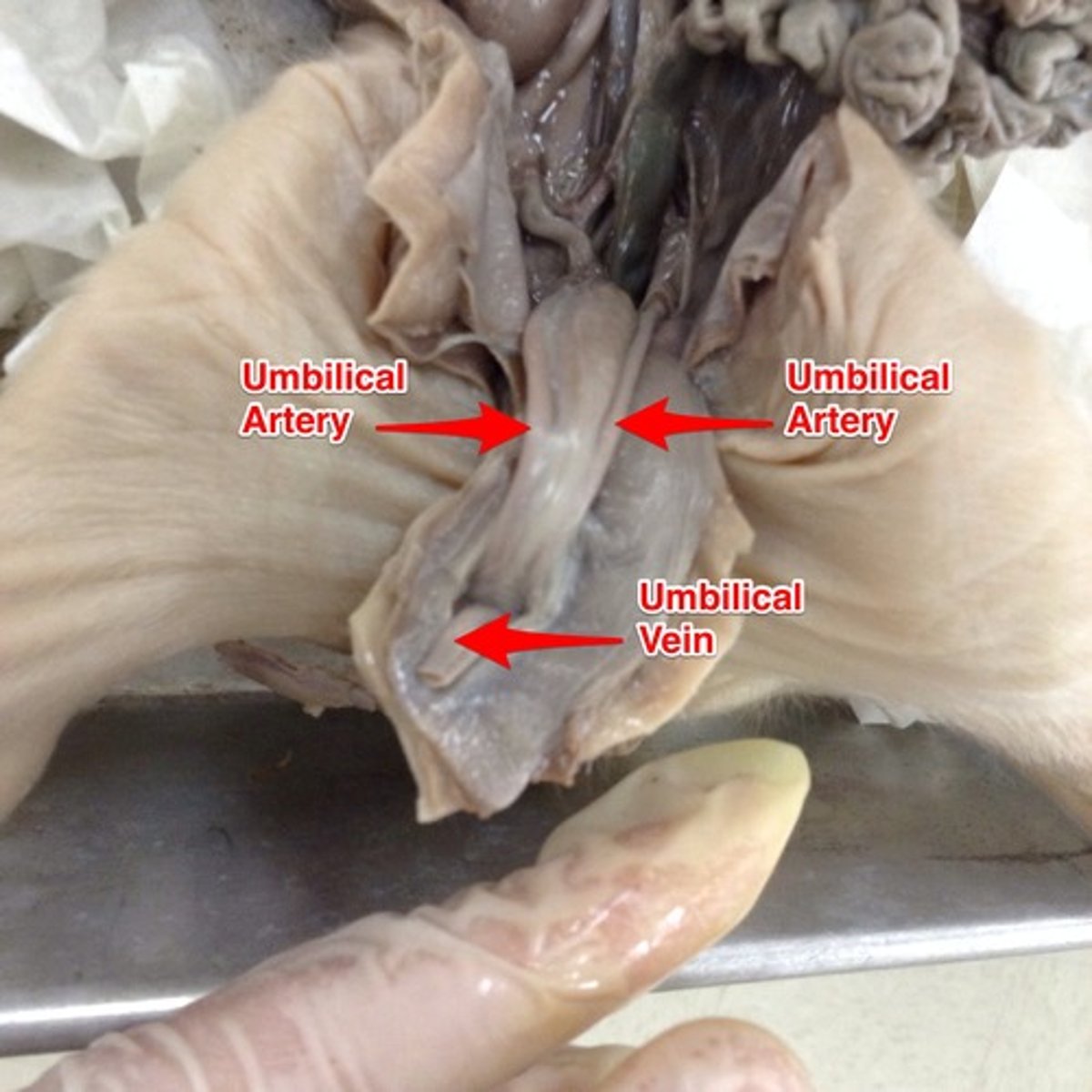
allantoic stalk
- part/area of the pig that the umbilical arteries and veins and urinary bladder go into
thoracic cavity
chest area/section of the pig
abdominal cavity
area between feet/legs
sternum
- breastplate
meconium
- inside the stomach
- greenish black material formed mostly from amniotic fluid and sloughed-off cells, that fills the digestive system
caecum pig
- blind sac
- at the junction of the large intestine (colon) and the small intestine
pharynx
cavity at the back of the mouth
esophagus pig
- the smaller tube on MY right of the trachea, below the larynx
bronchioles pig
- the many small tubes inside the lungs that lead from the alveoli
- within the lungs
alveoli
- small terminal sacs where the O2 and CO2 exchange occurs
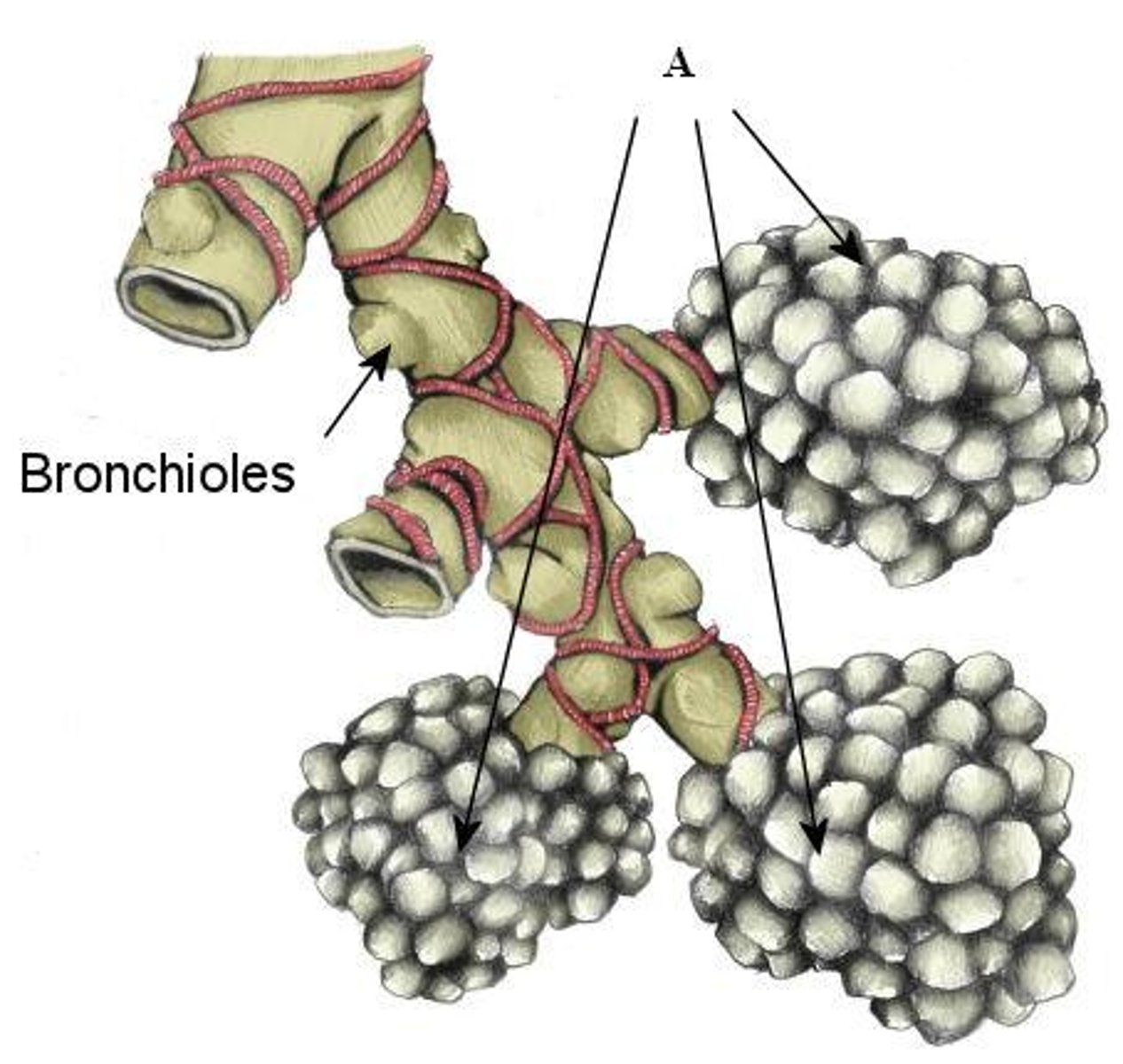
bronchus
- leads into each lung
- bronchioles join together to form the larger ___________
adrenal gland
- spongy tissue located as a cap on a kidney
- part of the endocrine system
- located at the top, behind the kidneys
urethra
- the opening of the bladder to the outside atmosphere
- beside the vagina inside the girl pig
-
vas deferens (sperm duct)
- originates at the testis
- looks kinda like an artery/vein
- find the testis and then follow upward until you get to the urinary bladder (it connects to it)
epididymis
- coiled set of tubules that surrounds the testis
gubernaculum
- the tough ligament that pulls the testis to join the scrotal sac
scrotal sac
- to the right of the urethra and penis (male pig)
- droopy sac
penis
- urogenital duct made up of the ________ and the urethra running through it
- skin
oviduct
- near the ovaries
- connects to the horns of the uterus
pericardium
- Lucent membrane that covers the heart
thymus pig
- spongy tissue anterior to the heart
- part of the immune system
- in the throat of the pig
- on either side of the thyroid
atria
- smaller sections of the heart at the top
- the right _____ is on the left side and vice versa
ventricles
- the larger sections of the heart at the bottom
- the right _______ is on the left side and vice versa
aortic arch
- the curve of the aorta
- looks like an indent right above the pulmonary artery
precaval vein
- under the heart
- enters the right atrium
- drains the upper part of the body
postcaval vein
- under the heart
- enters the right atrium
- drains the lower part of the body
foramen ovale
- located between the two atria allowing some blood flowing into the right atrium to be shunted to the left atrium without being sent to the lungs
ductus arteriosus
- the connection between the pulmonary artery and the systematic trunk near the point of emergence from the heart