NU 456 Quality Control (pt 1)
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What is quality control? How is performance measured? What action is taken?
-Activities that are used to evaluate, monitor, or regulate services rendered to consumers
-Performance is measured against
predetermined standards.
-Action is taken to correct discrepancies
between these standards and actual
performance
What is a standard? Why do organizations and professions set standards? How is it determined if standards are met? What happens if standards are not met?
- Predetermined baseline condition or level of excellence that constitutes a model to be followed and practiced
-Each organization and profession must set standards and objectives to guide individual practitioners in performing safe and
effective care.
-Information is collected to determine whether the standard has been met.
-Educational or corrective action is taken if the criterion has not been met.
What are the hallmarks of effective quality control programs and what does it require? (3)
-process is ongoing (continuous)
Requires
-Support from top-level administration
-Commitment by the
organization in terms of fiscal and human resources
-Quality goals reflect search for excellence rather than minimums.
What is the definition of quality control according to the WHO?
"change in the health of an individual,
group of people, or population that is
attributable to an intervention or
series of interventions."
In quality control, the quality and cost targets heathcare organizations are trying to improve: (7)
-Mortality
-Readmission
-Safety of care
-Effectiveness of care
-Patient experience
-Timeliness of care
-Efficient use of medical imaging
What is the joint commission (JCAHO)?
Joint Commission standards are the basis of an objective evaluation process that can help health care organizations measure, assess, and improve performance. The standards focus on important patient, individual, or resident care and organization functions that are essential to providing safe,
high quality care. The Joint Commission’s state-of-the-art standards set expectations for organization performance that are reasonable, achievable, and survey-able.
Surveys occur about once every 36 months
What is the leap frog group?
-"giant leaps for patient safety"
-collects data from publicly available sources
-places each measure into one of the 2 domains: each accounting for 50% of the overall score
What are process measures? What are structural measures? What are outcome measures?
-process measures: represent how often a hospital gives patients recommended treatment for a given medical condition or procedure
-structural measures: represent the environment in which patients receive care
-outcomes measures: represent what happens to a patient while receiving care
What are examples of process and structural measures?
-"Responsiveness of hospital staff" how long it takes for a staff member to respond when patients request help.
-strong nursing leadership and engagement
-computerized physician order entry systems to prevent medication errors
-safe medication administration
-hand hygiene policies
-the right staffing for the ICU
What are examples of outcome measures?
-infections, including: central line-associated bloodstream infections, catheter-associated urinary tract infections, surgical site
infections for colon surgery, MRSA and C. diff.
-falls and trauma, very severe pressure ulcers
-preventable complications from surgery such as foreign objects retained in the body and accidental punctures or lacerations
What is the MA Bureau of Healthcare Safety and Quality? Which groups are included in this (4)?
-Responsible for the oversight of
Massachusetts health care facilities to
ensure patients receive quality care in
a safe setting.
-Division of healthcare facility
licensure and certification
-OEMS
-Division of Quality Improvement
-Committees, Councils and Working
groups
Why was the LEAN Six Sigma developed? What is the focus of the six sigma? What is the focus of the LEAN?
-It was developed in the late 20th century, drawing from the quality control methods
pioneered by Motorola and the lean manufacturing techniques developed by Toyota.
-six sigma: focused on quality and consistency through process improvement and variation reduction
-LEAN: focused on efficiency, minimization of waste, errors and delays
What is the Lean Six Sigma? What framework is used?
-Follows a systematic
approach to process
improvement, incorporating
key steps to achieve
operational excellence.
- The methodology typically
involves a structured
framework, often referred to
as DMAIC
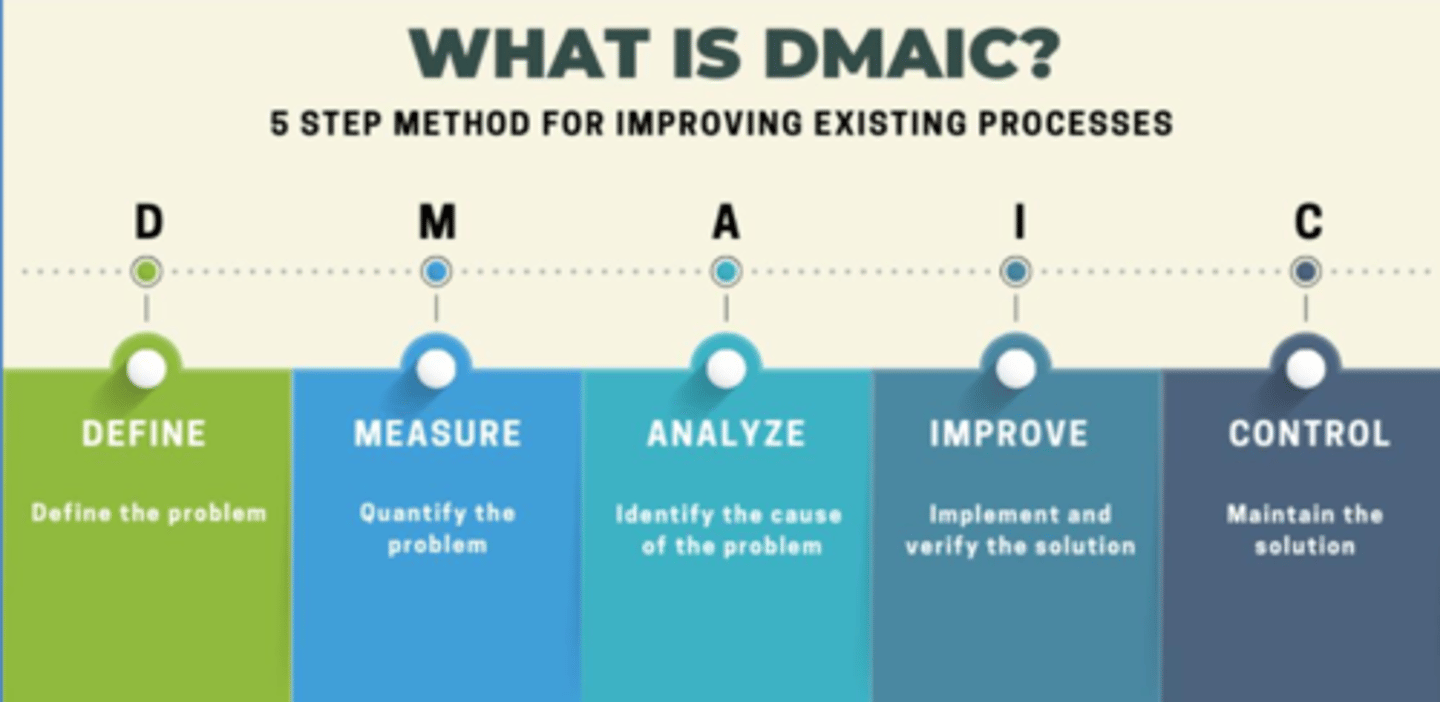
What is DMAIC?
Define: define the problem
Measure: quantify the problem
Analyze: identify the cause of the problem
Improve: implement and verify the solution
Control: maintain the solution
What is the Massachusetts Health Policy Commission? What methods do they use? What is their goal? What do they ensure?
-Independent state agency working to improve the affordability of health
care for all residents of the Commonwealth.
-Through data-driven analysis, actionable policy insights to reduce healthcare costs
-Seeks to improve health care delivery, lower costs, and reduce health disparities
-Ensures patient access to needed health care by safeguarding the rights of health insurance consumers and patients regarding coverage and care
decisions by health plans and certain provider organizations
What are the key responsibilities of the MA health policy commission? (pt 1) (4)
-Setting the health care cost growth benchmark
-Assessing and enforcing provider and payer performance relative to the health care cost growth benchmark
-Analyzing the impact of health care market mergers, acquisitions, and other transactions on cost, quality, access, and equity
-Collecting and disseminating key information about the structure and functioning of Massachusetts health care providers through the Registration of Provider Organizations
What are the key responsibilities of the MA health policy commission? (pt 2) (4)
-Evaluating the pricing and value of certain prescription drugs
-Creating care delivery standards for Accountable Care Organizations
-Investing in innovative care models
-Administering independent external reviews of insurer medical necessity denials and risk-based provider organization decisions, as well as open enrollment waivers
What is the National Healthcare Quality and Disparities Reports (NHQDR)? How are quality measures compared?
-The NHQDR provides a unique set of AHRQ data tools to assist in focusing efforts on identifying areas for improvement in the delivery of healthcare in the United States.
-Quality measures are compared with achievable benchmarks derived from the top-performing states.