Chapter 12: Cognitive Development in Middle Childhood
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Concrete operational stage
The period of cognitive development between ages 7-12
Characterized by the active and appropriate use of logic to concrete problems
For 2 years before moving firmly into the COS, children flip back and forth between COS and POS
Ex: they can answer a question correctly but can’t articulate how
Decentering
The ability to take multiple aspects of a situation into account
Reversibility
The notion that processes transforming a stimulus can be reversed, returning it to its original form
ex: understanding that a ball of clay that has been stretched can return to a ball
Limitation of concrete operational thinking
Children are tied to physical reality and cannot understand truly abstract or hypothetical questions
Memory
The ability to encode, store, and retrieve information
Sensory memory
The initial, momentary storage of information that lasts only an instant
It records an exact replica of the stimulus
Short-term memory (aka working memory)
Information is stored for 15-25 seconds
Improves significantly during middle childhood
Part of the reason young children struggle with conservation may be due to memory limitations
Long-term memory
Information is stored relatively permanently, although it may be difficult to retrieve
Metamemory
An understanding about the processes that underlie memory that emerges and improves during middle childhood
Control strategies
Conscious, intentionally used tactics to improve cognitive processing
Ex: school-age children are aware that rehearsal is a useful strategy and increasingly employ it over the course of middle childhood
They progressively make more effort to organize material into coherent patterns, use mnemonics, organization, and cognitive elaboration
Zone of proximal development
The level at which a child can almost, but not quite, understand or perform a task
According to Vygotsky, education should…
Focus on activities that involve interactions with others
Cooperative learning
Children work together in groups to achieve a common goal
Benefit from others’ insights and can be kept on track by their peers
Reciprocal teaching
A technique to reach reading comprehension strategies in which students are taught to skim a passage, ask questions about the central point, summarize it, then predict what happens next
Over the course of middle childhood, the use of ___ and ___ increases
Passive voice (the dog was walked by John) and conditional sentences
Syntax
The rules that indicate how words and phrases can be combined to form sentences
Children’s understanding grows through middle childhood
Intonation
School-aged children have difficulty decoding sentences that depend on intonation
Ex: “George gave a book to David, and he gave one to Bill” vs “George gave a book to David, and he gave one to Bill”
Pragmatics
The rules governing the use of language to communicate in a given social setting
Increases with middle childhood, especially in regard to give-and-take conversation
Metalinguistic awareness
An understanding of one’s own use of language which becomes more explicit during middle childhood
Helps children achieve comprehension when information is fuzzy or incomplete
Ex: preschoolers rarely ask for clarification when they’re confused because they blame themselves for not understanding. 7/8 year olds realize that miscommunication goes both ways
Children use “self-talk” to…
Regulate their own behavior and increase self-control
Benefits of bilingualism:
Greater cognitive flexibility
Ability to solve problems with greater creativity and versatility
Associated with higher self-esteem in minority students
US schools are experiencing a return to…
The 3 R’s reading, writing, and arithmetic, individual accountability
Emotional intelligence
The set of skills that underlie the accurate assessment, evaluation, expression, and regulation of emotions
Delaying a child’s entry into school…
Dores not provide an advantage and may be harmful

Reading stage 0
Birth - 1st grade
Children learn the prerecs for reading: identifying letters, writing their names, reading familiar words (ex: stop on a stop sign)

Reading stage 1
1st - 2nd grade
Phonological recoding skills
Sounding out words, names of letters, sounds of lettters

Reading stage 2
2nd - 3rd grade
Read aloud with fluency but not much attention to the meaning of the words

Reading stage 3
4th - 8th grade
Reading is a means to an end (way to learn), information can only be understood from 1 perspective
Reading stage 4
8th grade+
Process information that reflects multiple povs
Code-based approaches to reading
The belief that reading should be taught by presenting the basic skills that underlie it
Emphasizes phonics and that reading consists of processing words’ individual components, combining them into words, then using the words to derive meaning
Strongest option for teaching reading
Whole-language approach to reading
The view of reading as a natural process (like oral language) and that is should be taught through exposure to complete writings
Encouraged to make guesses about word meaning via context
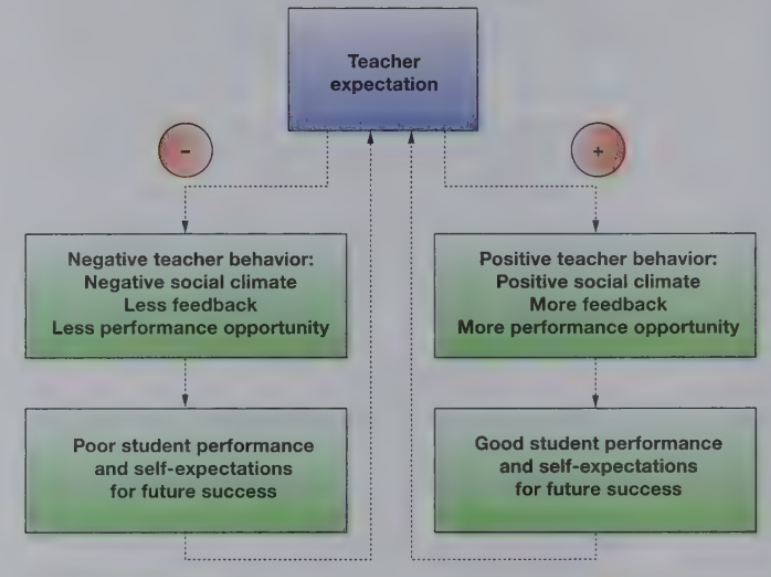
Teacher expectancy effect
The phenomenon whereby an educator’s expectations for a given child actually bring about the expected behavior
Expectations are transmitted via complex verbal and nonverbal cues
Multicultural education
Education in which the goal is to help students from minority cultures develop competence in the culture of the majority group while maintaining positive group identities that build on their original cultures
Cultural assimilation model
The view of American society as a melting pot in which all cultures are amalgamated into a unique, unified American culture
Accepted until the early 1970’s
Pluralistic society model
The concept that American society is made up of diverse, coequal cultures that should preserve their individual features
Charter schools
Independently ran public schools that families can voluntarily choose for their children
Often small and sometimes have a particular focus (arts, sciences, a language, etc)
Intelligence
The capacity to understand the world, think with rationality, and use resources effectively when faced with challenges
Alfred Binet
Linked intelligence test scores to a mental age and school success
Defined intelligence as that which his test measured
Mental age
The typical intelligence level found for people of a given chronological age
Intelligence quotient
A score that expresses the ratio between a person’s mental and chronological age
Higher IQ is connected to finishing more years of school, but is not linked to income and life success
Not the primary measure of intelligence
Tend to be biased in favor of white, upper and middle class students
Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scale
An oral test that varies according to the person’s age
Ex: children are asked about everyday activities while older people are asked to explain proverbs
Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children
A test for children that provides separate measures of verbal and performance (nonverbal) skills as well as a total score
Ex: understanding a passage vs copying a complex design
Kaufman Assessment Battery for Children
An intelligence test that measures children’s ability to integrate different stimuli simultaneously and use step-by-step thinking
It is more equitable to children with English as a second language
Fluid intelligence
Intelligence that reflects information-processing capabilities, reasoning, and memory
Ex: categorizing a series of letters or remembering a set of numbers
Crystallized intelligence
The accumulation of information, skills, and strategies learned through experience and people can apply in problem-solving situations
Ex: solve a puzzle or mystery
Henry Gardner’s 8 types of intelligence
Naturalist, intrapersonal, interpersonal, spatial, linguistic, logical mathematical, bodily kinesthetic, musical
Naturalist intelligence
The ability to identify and classify patterns in nature
Intrapersonal intelligence
Knowledge of the internal aspects of oneself and access to one’s own feelings and emotions
Interpersonal intelligence
Skills in interacting with others, such as sensitivity to the moods, temperaments, motivations, and intentions of others
Spatial intelligence
Skills involving spatial configurations, such as those used by artists and architects
Vygotsky’s view of intelligence
It must be looked at through the lens of culture because it manifests differently in different cultures
Triarchic theory of intelligence
The belief that intelligence consists of 3 aspects of information processing: the componential, experiential, and contextual
Componential: how efficiently information is processed and analyzed
Experiential: comparing new vs old material and relating them
Contextual: ways of dealing with the demands of everyday environment
Developed by Robert Sternberg