BIOL 2402 Final Exam Practice Questions
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Which of the following are required to produce biochemical energy?
A. Glucose.
B. Oxygen.
C. ATP.
D. CO2
E. Both A and B.
F. All of the above.
E. Both A and B. (Glucose & Oxygen)
During digestion, the milk sugar lactose is broken down into simple sugars galactose and glucose. What type of reaction is this?
A. Catabolic.
B. Anabolic.
C. Cellular respiration.
D. All of the above.
A. Catabolic.
Which of the following produces CO2?
A. Glycolysis.
B. The Krebs cycle.
C.Oxidative phosphorylation.
D. Glycogenesis.
E. All of the above.
B. The Krebs cycle.
Which of the following uses O2?
A. Glycolysis.
B. The Krebs cycle.
C. Oxidative phosphorylation.
D. Glycogenesis.
E. All of the above.
C. Oxidative phosphorylation.
Oxygen is crucial to ATP production because:
A. It is a highly efficient electron donor.
B. ATP synthase bonds with oxygen.
C. It is converted to H20 during electron transport.
D. It is required for glycolysis.
C. It is converted to H20 during electron transport.
Insulin is a peptide hormone. Where are insulin receptors found?
A. The plasma membrane of target cells.
B. The cytosol of target cells.
C. The cytosol of all body cells.
D. All of the above.
A. The plasma membrane of target cells.
Under normal conditions, high blood glucose levels will stimulate:
A) Glucose release by the liver.
B) Insulin release.
C) Glucagon release.
D) Both A and C.
B) Insulin release.
A patient has repeated high blood glucose and normal insulin levels. The patient is:
A) Hypoglycemic.
B) Type 1 diabetic.
C) Type 2 diabetic.
D) Normal.
C) Type 2 diabetic.
_______ is required for oxygen to be carried by the blood.
A) Carbon dioxide.
B) Plasma.
C) Calcium.
D) Iron.
D) Iron.
EPO is produced by the kidneys. Where are the target cells for EPO located?
A. Skeletal muscle.
B. Red bone marrow.
C. All tissues of the body.
D. Both A and B.
B. Red bone marrow
A patient has a hematocrit level of 42%. One month later, he has a hematocrit of 51%. What is the most likely explanation?
A. He is taking EPO injections.
B. Anemia.
C. Hyposecretion of EPO.
D. These are normal levels.
E. Can’t tell from the data given
A. He is taking EPO injections.
Which chamber of the heart receives oxygenated blood from the pulmonary circulation:
A) Right atrium
B) Left atrium
C) Right ventricle
D) Left ventricle
B) Left atrium
Blood in the aorta has just come from:
A) The vena cava
B) The right ventricle
C) The left ventricle
D) The systemic circulation
C) The left ventricle
_______ pumps blood to the pulmonary circulation:
A) Right atrium
B) Left atrium
C) Right ventricle
D) Left ventricle
C) Right ventricle
Which part of the ECG represents depolarization at the sinoatrial (SA) node:
A) P wave
B) QRS complex
C) T wave
D) All of the above
A) P wave
Which part of the ECG represents the opening of voltage-gated sodium (Na+) channels at the ventricles:
A. P wave
B. QRS complex
C. T wave
D. All of the above
B. QRS complex
Which of the following blood pressure readings would be indicative of hypertension?
A) 120/80 in a 30-year-old man
B) 140/90 in a 70-year-old woman
C) 170/96 in a 50-year-old man
D) 110/60 in a 20-year-old woman
C) 170/96 in a 50-year-old man
Which of the following blood vessels supplies the head and arms with oxygenated blood?
A) Common carotid artery.
B) Brachiocephalic trunk.
C) Common iliac artery.
D) Radial vein.
B) Brachiocephalic trunk.
Which of the following blood vessels has the highest blood pressure?
A. Subclavian artery.
B. Radial artery.
C. Femoral vein.
D. Inferior vena cava.
A. Subclavian artery.
Dan is given a shot of epinephrine, which increases heart rate and contraction of vascular smooth muscle. What effect does this have on blood pressure?
A. Blood pressure remains the same.
B. Blood pressure increases.
C. Blood pressure decreases.
D. Can’t tell from the data given
B. Blood pressure increases.
A patient with overproduction of albumin and other plasma proteins may have
A) Low MAP.
B) Extremely low hydrostatic pressure.
C) Edema.
D) High osmotic/oncotic pressure.
D) High osmotic/oncotic pressure.
In a capillary, the hydrostatic pressure outward is 37 mm Hg, while the osmotic pressure inward is 26 mm Hg. As a result, which is occurring?
A. Filtration.
B. Reabsorption.
C. Edema.
D. All of the above.
A. Filtration.
Which of the following act(s) as the first line of defense against foreign pathogens?
A) Skin
B) Antibodies
C) Complement proteins
D) Both a and c
A) Skin
Why does a secondary immune response produce antibodies faster than a primary immune response?
A) New antigens are recognized more quickly.
B) Memory T cells.
C) Memory B cells.
D) Antibodies from the primary response remain in the blood.
C) Memory B cells.
Antibody titer is highest :
A) When the pathogen enters the body.
B) 7-10 days after the first exposure.
C) 2-3 days after the second exposure.
D) Before the pathogen enters the body
C) 2-3 days after the second exposure.
Which of the following has the highest oxygen pressure:
A. The pulmonary veins.
B. The pulmonary arteries.
C. The tissues of the body.
D. The alveoli.
D. The alveoli.
Which of the following has the highest carbon dioxide pressure:
A. The pulmonary veins.
B. The pulmonary arteries.
C. The tissues of the body.
D. The alveoli.
C. The tissues of the body.
During inspiration:
A) Intrapulmonary pressure goes down.
B) The volume of the lungs decreases.
C) Intrapulmonary pressure stays the same.
D) The volume of the lungs increases.
E) Both A and D.
E) Both A and D.
During inspiration, how does the air pressure within the lungs (PPUL) change?
A) Decreased lung volume causes an increase in PPUL.
B) Increased lung volume causes an increase in PPUL.
C) Increased lung volume causes a decrease in PPUL.
D) PPUL decreases, causing lung volume to increase.
C) Increased lung volume causes a decrease in PPUL.
Fully-oxygenated arterial blood enters a capillary bed, where it encounters high CO2, inducing a right-shift of the hemoglobin dissociation curve. This results in:
A) Increased oxygen binding by hemoglobin.
B) Decreased oxygen binding by hemoglobin.
C) No change in oxygen binding.
D) Can’t tell from the data given.
B) Decreased oxygen binding by hemoglobin.
In which location will hemoglobin have the weakest affinity for O2?
A) Blood leaving the systemic capillaries of the tissues (PO2 = 40 mm Hg).
B) Blood leaving the pulmonary capillaries of the alveoli (PO2 = 100 mm Hg).
C) Blood in the systemic veins (PO2 = 40 mm Hg).
D) Both A and C.
D) Both A and C. (Blood leaving the systemic capillaries of the tissues (PO2 = 40 mm Hg) & Blood in the systemic veins (PO2 = 40 mm Hg)
Where does chemical digestion of food begin?
A) The stomach
B) The esophagus
C) The mouth
D) The liver
C) The mouth
Which of the following is most responsible for absorption of nutrients?
A. The stomach
B. The small intestine
C. The esophagus
D. The large intestine
B. The small intestine
What is the correct sequence as food moves through the GI tract?
A) Stomach, pyloric valve, duodenum, jejeunum, ileum
B) Gastroesophageal sphincter, duodenum, stomach, pyloric valve
C) Stomach, ileum, pyloric sphincter, ileocecal valve
D) None of the above are correct.
A) Stomach, pyloric valve, duodenum, jejeunum, ileum
Impurities begin to be filtered out of the blood at:
A. The nephron loop
B. The glomerulus
C. The proximal convoluted tubule
D. The distal convoluted tubule
B. The glomerulus
The nephrons of the kidneys continuously filter the blood, producing ~180 L of filtrate per day. How much of this filtrate is excreted as urine?
A. 100%
B. More than 95%
C. 50%
D. Less than 1%
D. Less than 1%
Tubular reabsorption moves water :
A. From the nephron to the blood.
B. From the kidneys to the bladder.
C. From the major calyx to the renal pelvis.
D. From the blood to the nephron.
A. From the nephron to the blood.
Release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) by the pituitary causes:
A. Increased aquaporins in the PCT
B. Increased aquaporins in the collecting duct.
C. Decreased tubular reabsorption
D. All of the above
B. Increased aquaporins in the collecting duct.
In humans, how many chromosomes do diploid somatic cells have?
A. 23
B. 46
C. 2
D. Can’t tell from the data given.
B. 46
Which of the following activates both spermatogenesis (in males) and ovulation (in females):
A) Luteinizing hormone (LH).
B) Progesterone.
C) Testosterone.
D) Both B and C.
A) Luteinizing hormone (LH).
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is produced by:
A) The anterior pituitary gland.
B) The testes.
C) The corpus luteum.
D) None of the above.
D) None of the above. (Trophoblasts make hCG)
Hemoglobin b is a protein that works to carry oxygen in erythrocytes. The gene encoding the hemoglobin b protein is found:
A. Only in the red bone marrow.
B. On Chromosome 11 of all cells in the body.
C. In the cytoplasm of all cells in the body.
D. None of the above.
B. On Chromosome 11 of all cells in the body.
Which of the following determines the direction of gas movement in the respiratory system?
A. Solubility in water.
B. Partial pressure gradient.
C. Temperature.
D. Molecular weight and size of the molecule.
B. Partial pressure gradient.
Which of the following has the highest CO2 pressure?
A. Alveoli
B. Blood plasma
C. Erythrocytes
D. Skeletal muscle
D. Skeletal muscle
Which of the following is false regarding a right-shift of the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve?
A. It reflects decreased affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen.
B. It is often referred to as the Bohr effect.
C. It can be caused by increased temperature.
D. It can be caused by increased pH.
D. It can be caused by increased pH.
Which of the following has the greatest stimulating effect on the respiratory centers in the brain?
A. Oxygen
B. Carbon dioxide
C. Calcium
D. Willpower
B. Carbon dioxide
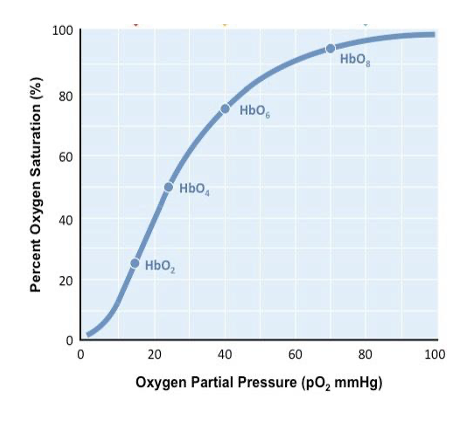
In the pulmonary capillaries, the pO2 of the blood is 100 mm Hg. When the blood travels to the systemic capillaries, the pO2 falls to 40 mm Hg. What is hemoglobin’s oxygen saturation?
A. 10%.
B. 40%.
C. 75%.
D. 98%.
C. 75%.
What are the major inputs and outputs of glycolysis?
Inputs: Glucose
Outputs: 2 Pyruvic acid, 2 NADH + H, 2 ATP
What are the major inputs and outputs of the Krebs cycle?
Inputs: Pyruvic acid & fatty acids.
Outputs: NADH, FADH 2, ATP, CO2
What are the major inputs and outputs of oxidative phosphorylation?
Inputs: NADH, FADH2, Oxygen
Outputs: ATP, H20
What is formed during cellular respiration after electrons are passed down the electron transport chain?
A. Oxygen
B. Carbon dioxide
C. Water
D. NADH
E. All of the above.
C. Water
Percothrin is a drug that binds to the F1F0 ATP synthase and prevents protons (H+) from diffusing through the enzyme complex. What effect does percothrin have on ATP production by ATP synthase?
A. ATP production stops.
B. ATP production increases.
C. No effect. Protons have nothing to do with ATP synthesis.
D. No effect. ATP synthase will rotate faster.
A. ATP production stops.
Blood in the common carotid artery has just come from:
A. The jugular vein
B. The axillary artery
C. The brachiocephalic trunk
D. The aortic arch
E. None of the above.
D. The aortic arch
As blood moves through a capillary from the arteriolar end to the venous end, the hydrostatic pressure (HPc) drops. What happens to osmotic pressure within the capillary (OPc) as the blood moves through the capillary?
A. Osmotic pressure drops as well.
B. Osmotic pressure increases.
C. Osmotic pressure remains the same.
D. Can’t tell from the data given.
C. Osmotic pressure remains the same.
Within a capillary, the hydrostatic pressure (HPc) is 30 mm Hg and the osmotic pressure of the interstitial fluid (OPif) is 4 mm Hg. Outside the capillary, the osmotic pressure of the capillary (OPc) is 25 mm Hg, and the hydrostatic pressure of the interstitial fluid (HPif) is 0 mm Hg. What is the net filtration pressure, and will it result in filtration or reabsorption?
NFP = (HPc + OPif) – (HPif + OPc)
A. 51 mm Hg, filtration
B. 9 mm Hg, filtration.
C. 55 mm Hg, reabsorption
D. -9 mm Hg, reabsorption
E. Can’t tell from the data given.
B. 9 mm Hg, filtration.