Human Sexuality Exam 2
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Sex & Gender, Fertility, Pregnancy & Childbirth
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
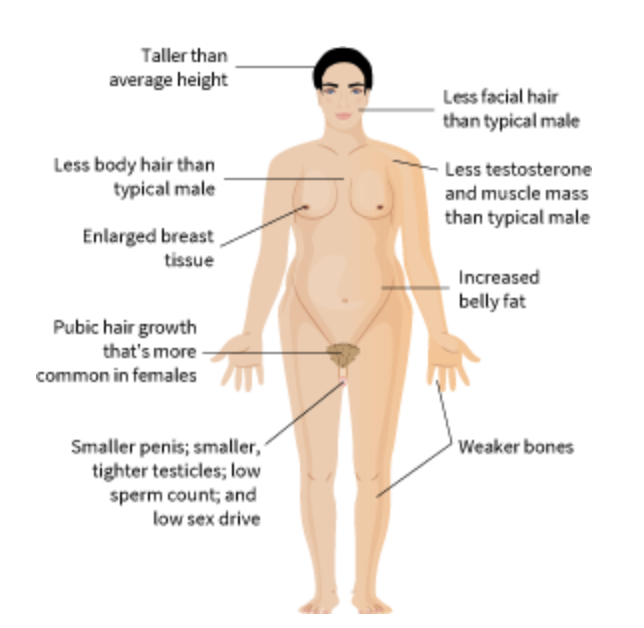
Klinefelter's syndrome
|
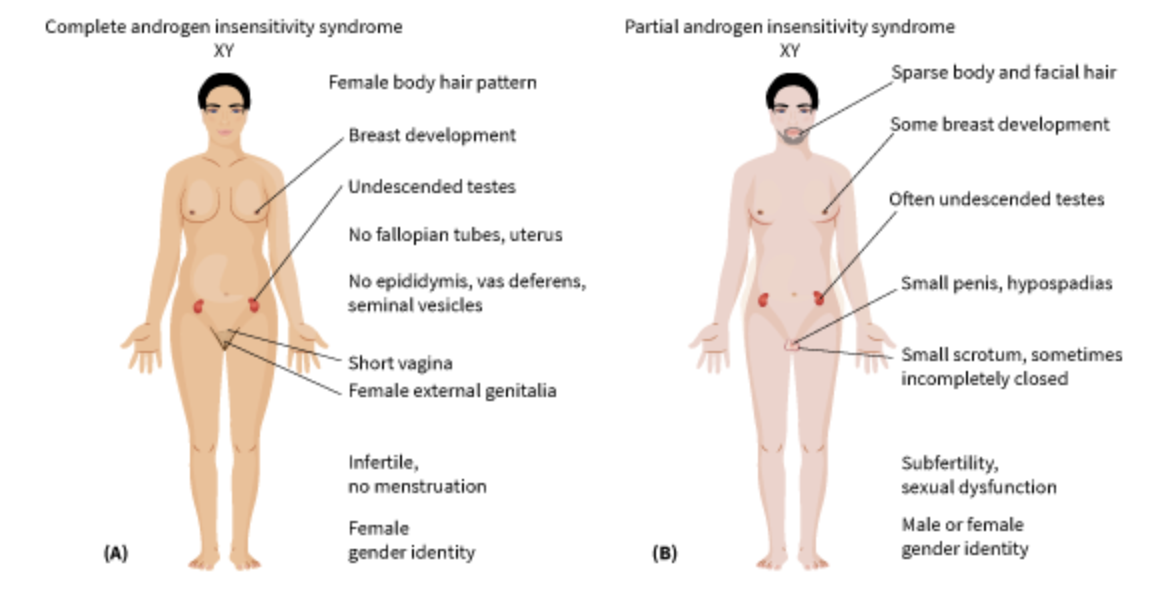
Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome
1 in 13,000 XY fetuses; tissues in the XY fetus do not respond to testosterone. Child typically has a very shallow vaginal pouch, a clitoris, a non-cyclic hormone status, and testes that never descend. Detected when a seemingly typical adolescent female does not start menstruating at the standard age of puberty
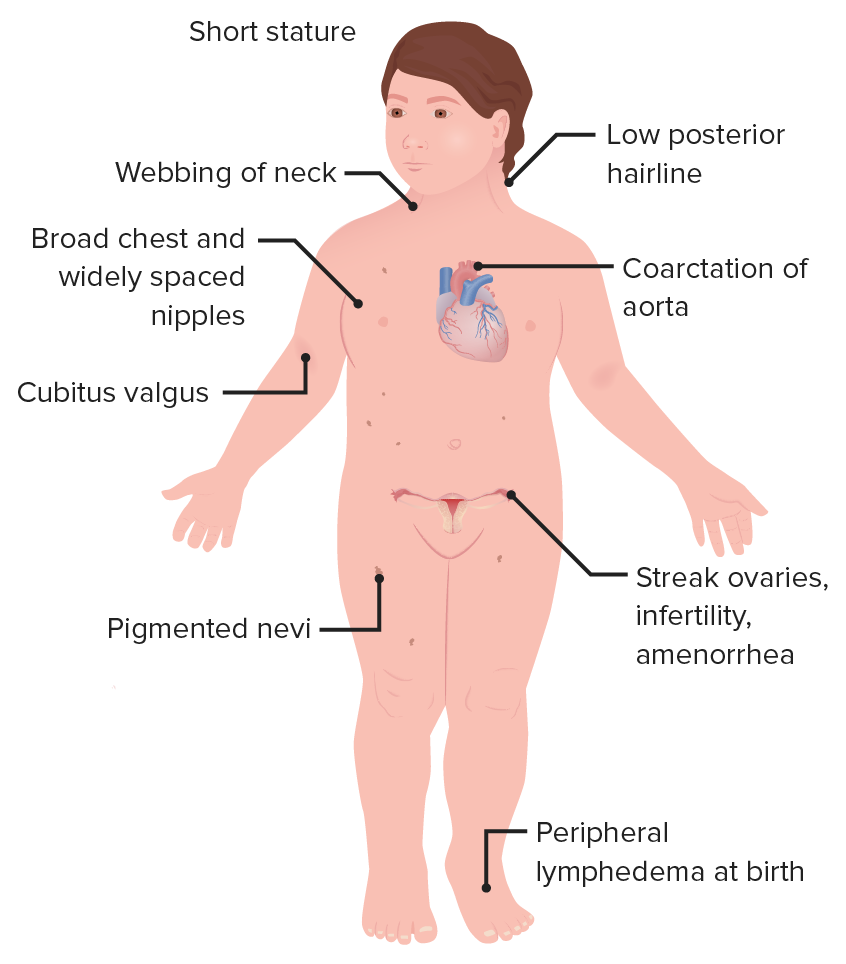
Turner syndrome
1 in 2,000 - 2,500; having one X chromosome— genotype XO. Look female and identify as women, infertile and often only develop menstrual cycles with hormonal therapies. does not cause intellectual impairment
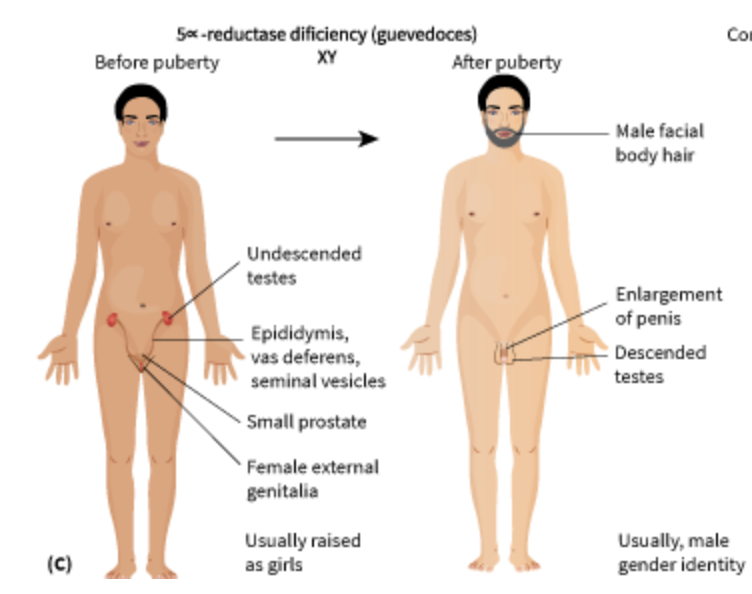
5-alpha reductase deficiency
affects sexual development before birth and during puberty in people with XY (typically male) chromosomes. Usually appears/born like a girl in childhood but develops male secondary characteristics during puberty. Deficiency in a hormone called dihydrotestosterone. Most are also infertile.
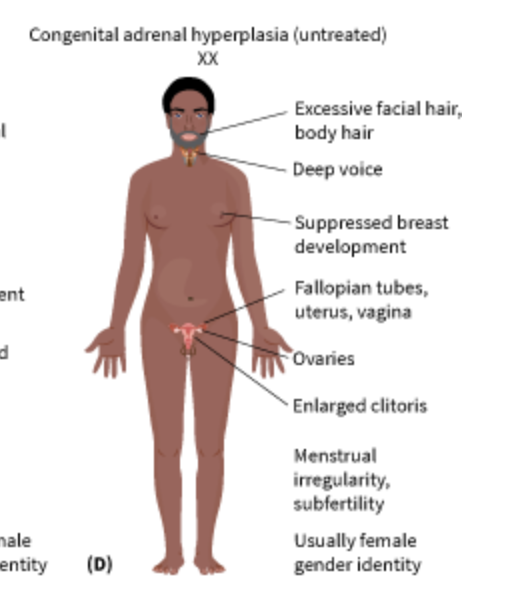
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH)
1 in 13,000; overabundance of male hormones that cause the clitoris to become enlarged and a partially fused labia and infertility.
Gender identity
how someone personally defines their own gender; used to describe people who do not “match” their assigned sex
Gender expressions
how a person communicates their sense of their own gender to the world. All the traits, characteristics, apparel, mannerisms, etc. Most commonly seen thorugh name, pronouns, clothing, hair, behavior, voice, body characteristics.
Sexuality/Sexual Identity
All the aspects of our bodies and personalities that construct how we and others understand ourselves as sexual beings.
Leptin
Hormone that signals the beginning of puberty; secreted by fat cells.
Kisspeptin
A neurotransmitter involved in puberty that triggers the release of GnRH
Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH)
Causes the pituitary to release gonadotropins which causes the gonads in both males and females to begin producing massive amounts of sex steroids like androgens and estrogen.
Dr Money’s idea about gender identity
Said that gender identity is malleable and is simply a learned response to one’s environment.
Refractory Period
the delay most men experience after ejaculating once; lasts from 15 minutes to 24 hours.
Chivers, Seto and Blanchards Research
women showed genital response to erotica featuring men (hetero and gay porn) and women (lesbian porn).
Social Role Theory
acknowledges the importance of biology. Attempts to blend evolutionary and social constructionist perspectives with the idea of embedded social roles.
men —> more likely to provide for family
women —> more likely to assume domestic and childcare reponsiblities
Social Learning Theory
Shows how norms surrounding gender are instilled and reinforced. Most children learn from an early age that they are expected to behave in ways that are consistent with the stereotypes that exist for their gender.
Cognitive Development Theory
borrowed from Piaget; states that children progress through somewhat predictable stages in terms of how they conceptualize gender. Changes as they mature.
Gender Schema Theory
Children learn gender roles from their culture like the messages, ideas, and stereotypes put forth by their culture.
First type of Gender Gap
boys tend to perform higher on math achievement tests than girls
Second type of Gender Gap
The vast differences in pay and job opportunities available to men compared to women.
Stereotype Threat
the risk of confirming negative stereotypes about an individual.s racial, ethnic, gender, or cultural group which can lead to high cognitive load and reduce one’s academic focus and performance
Different cultures have historically recognized gender fluidity and transgender identities
Native American cultures recognized “two-spirited” people with unique spiritual roles
Releasing Factor (GnRH)
Released by the hypothalamus and stimulates the pituitary
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Released by the pituitary and stimulates testosterone production in interstitial cells of testes and estrogen production in ovaries; both men and women
Gonadotropins
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Released by the pituitary and stimulates sperm production in seminiferous tubule of testes and ripening of follicles in ovaries; both males and females
Gonadotropins
Sex steroids
work to stimulate many bodily tissues, including the uterus, the penis, and hair follicles.
Include: testosterone, estrogen, and progesterone
Follicular Phase
Phase 1: GnRH is steadily released from the hypothalamus and stimulates the pituitary to release LH and FSH. LH causes the ovaries to produce estrogen. Rising estrogen levels in the female body cause the uterine lining (the endometrium) to thicken in preparation for a potential pregnancy.
Ovulation
Phase 2: always occurs about two weeks prior to the start of a women's menstrual period. Estrogen levels will exceed this set point, causing the hypothalamus to begin pulsing the release of GnRH.
Cervical mucus changes to be hospitable to sperm by becoming alkaline, copious, watery, elastic, slippery, and akin to raw egg whites. At the same time, the cervix softens and rises within the vaginal canal
Luteal
Phase 3: always lasts for 14 days; most regular and predictable part of the menstrual cycle. LH stimulates the corpus luteum to secrete estrogen and progesterone.
Cervical mucus turns "hostile," meaning that it becomes less stretchy and more dry and acidic.
Premenstrual
Phase 4: "late luteal phase." The corpus luteum degenerates, causing progesterone and estrogen levels to decline. Prostaglandins begin causing the myometrium to contract, causing menstrual cramping. This can also sometimes cause bloating
Destructive
Phase 5: progesterone, estrogen, FSH, and LH are all low.
Causes the endometrial lining, which had been growing thicker and richer throughout the month, to break down and exit the body through the vagina.
Premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
physical and emotional changes that occur in the premenstrual (late luteal) phase of a female's menstrual cycle.
Symptoms include: tension/anxiety, sadness, mood swings, aches, altered appetite, or food cravings and cramps.
Physical symptoms include: bloating, fatigue, irritability, tender breasts, acne, and mood changes.
Which of the following hormones corresponds to the most likely physiological cause of PMS symptoms?
Decreased estrogen: carbohydrate metabolism, intensified craving for sweets
The Calendar Method
uses the calendar of a woman's monthly cycle to track the days during which she is most likely to be ovulating
Cervical Mucus Method
mucus transforms from being hostile (dry, tacky) to friendly (wet, slippery) to fertile (very stretchy and clear, like raw egg white), and finally back to hostile again after ovulation occurs. A very effective way to estimate the timing of ovulation.
Extremely effective, especially if used in conjunction with tracking cervical mucus.
Cervical Changes
The cervical is is hard and closed (similar in touch to the tip of one's nose) when fertility is low and soft and open (similar in feel to partly opened lips) when fertility is high.
Basal Body Temperature
can be measured with a special thermometer and rises and falls in a predictable pattern that aligns with ovulation.
Prior to ovulation, temperature is relatively low (below 98.0F)
At the end of the cycle, when progesterone falls, body temperature returns to its original cooler state.
grandmother hypothesis
the cessation of the menstrual cycle while a female is at full physical capacity allows her to devote precious time and resources (namely food and knowledge) to their adult children, which in turn allows them to be better parents
Andropause
male menopause; declining sperm counts, declining ejaculate volume, and increased likelihood of having erectile disorder
Testosterone supplementation for males
It is effective only in males who show below normal levels of testosterone, and even then it still carries risks.
human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
the hormone that is secreted as the embryo implants in the uterus. Pregnancy tests measure this.
Hegar's signs
softening of the uterus and changes in the color of the cervix, vagina, and labia
hypotension
One of the most serious risks during childbirth that involves a sudden drop in maternal blood pressure
pruritus
a generalized itching sensation on the skin that is a common side effects of an epidural
lochia
dark bloody discharge expelled from the vagina for several days after birth
quickening
In the early part of the second trimester, the pregnant female will begin to feel kicks from her fetus.
The First Trimester
where pregnancy symptoms first appear, like: Breast tenderness and exhaustion, backaches, constipation, heartburn, frequent urination, food cravings, and food aversions, all of which result from changing levels of hormones and physical changes in the mother's body due to the developing pregnancy
Can greatly interfere with the mother's libido
Zygote
A single fertilized cell (ovum)
Blastocyst
Is multi-celled and contains an inner cell mass
Inner Cell Mass
The group of cells that will develop into an embryo
Trophoblast
The outer membrane that will develop into the placenta
Blastocoele
The fluid surrounding the inner cell mass.
The Second Trimester
The most enjoyable trimester of pregnancy. Morning sickness disappears, energy is plentiful, and she begins to look and feel more pregnant.
Quickening can happen
chemical pregnancy
blastocyst implants and causes hCG levels to rise, but spontaneously aborts before an ultrasound can even detect a fetal heartbeat.
Account for 50–75% of all miscarriages
The Third Trimester
Most females continue to feel good for the majority of the third trimester. Dramatic changes will occur in the mother's body like dramatic enlargement of the uterus causes even more pressure on the female's internal organs.
Can lead to:
shortness of breath, indigestion, back pain, constipation, hemorrhoids, frequent urination, heartburn, and urine leakage.
Braxton-Hicks contractions
The uterus practicing and preparing itself for labor and delivery; typically become more frequent and strong during the last few weeks of pregnancy