PBL Case 7: TBI
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
WIDE SPREAD SHARING + RETRACTION of AXONS are common with what type of head injury
diffuse axonal injury (DAI)
what OUTCOME MEASURE for a patient with a TBI would be indicative of someone with the BEST REHAB POTENTIAL
Rancho Level VI
what are 3 SIGNS that indicate a TBI patient is NOT TOLERATING TREATMENT WELL
1. elevated HR
2. increased respiratory rate
3. falling BP
your TBI patient is currently a LEVEL 2 on the Rancho Scale. what would be your PRIMARY THERAPY GOAL at this time
maintain ROM of all major joints
you are assessing cognitive status on a patient status post TBI. what would be the BEST WAY to ASSESS "ABSTRACT" REASONING ABILITY
interpreting meaning of the phrase "a rolling stone gathers no moss"
what are 6 PATIENT ASSETS that play a POSITIVE ROLE in the recovery of a TBI patient
1. pre-admission/pre-injury independence + activity level (PLOF)
2. strong family support
3. pre-injury social history
- no alcohol/smoking history
- active lifestyle
4. resting vitals within functional limits
5. preserved functional strength
- able to sit with balance + stand with assistance
- no paralysis/hemiparesis noted
6. improved in Rancho Level
(suggestive possible cognitive improvements over time)
what are 9 PATIENT LIABILITIES that play a NEGATIVE ROLE in the recovery of a TBI patient
1. patient age
- advance age = impact healing, slow neuroplasticity + increase risk of complications
2. cognitive impairment
- Rancho Level
- unable to follow more than one-step commands
3. TBI classification (mild/moderate/severe TBI)
4. musculoskeletal damage to dominant side
5. postural + balance deficits
6. orthostatic hypotension
7. skin concerns
8. limited ROM
9. additional lines (catheter + G-tube)
- require additional nursing care
- increased risk of infection
what are 6 FACTORS why a patient requires MAXIMAL ASSIST of 2 PEOPLE to STAND but appears to have relatively NORMAL MOTOR STRENGTH
1. cognitive impairments (Rancho Level IV)
2. fear
3. poor postural control
4. agitation
5. inability to follow commands
6. impulsivity
what are 5 STRATEGIES to help a patient overcome the reason for needing MAXIMAL ASSIST of 2 PEOPLE to STAND while having relatively NORMAL MOTOR STRENGTH
1. implement repetition
2. structured + quiet low-stimulus environment
3. consistent verbal cues + tactile input
4. incorporate visual prompts
5. incorporate graded exposure to upright posture to reduce fear
what are 12 TESTS + MEASURES/OUTCOME MEASURE that are commonly used in patients with MILD TBI
1. immediate post-concussion assessment + cognitive testing
2. standardized assessment of concussion
3. vestibular positional tests
4. sensory organization test
5. balance error scoring system
6. dynamic gait index (DGI)
7. functional gait assessment (FGA)
8. high-level mobility assessment tool
9. post-concussion scale-revised
10. sport concussion assessment tool post-concussion symptom scale
11. dizziness handicap inventory
12. activities-specific balance confidence scale
what are 8 AREAS for a PT to EXAMINE + INTERVENE in patients with a MILD TBI
1. patient education
2. activity intolerance
3. vestibular dysfunction
4. high-level balance dysfunction
5. post-traumatic headache
6. temporomandibular disorder
7. attention + dual-task performance
8. participation in exercise
what are 18 ELEMENTS of the EXAMINATION for a TBI patient
1. aerobic capacity/endurance
2. arousal, attention + cognition
3. behavioral status
4. cranial nerve integrity
5. gait, locomotion + balance
6. integumentary integrity
7. joint integrity + mobility
8. motor function (motor control + learning)
9. muscle performance (strength, power + endurance)
10. neuromotor development + sensory integration
11. pain
12. posture
13. ROM
14. reflex integrity
15. self-care + ADL skills
16. sensory integrity
17. ventilation + respiration/gas exchange
18. work/leisure/community reintegration
what are 8 OUTCOME MEASURES used for assessing the AROUSAL, ATTENTION + COGNITION of a TBI patient
1. coma recovery scale-revised
2. disorders of consciousness sale
3. rancho los amigos levels of cognitive functioning
4. moss attention rating scale
5. test of everyday attention
6. trail making test part B
7. Galveston orientation + amnesia test
8. orientation log
what are 3 OUTCOME MEASURES used for assessing the BEHAVIORAL STATUS of a TBI patient
1. supervision rating scale
2. neurobehavioral rating scale-revised
3. agitated behavior scale
what are 7 OUTCOME MEASURES used for assessing GAIT, LOCOMOTION + BALANCE of a TBI patient
1. BERG balance scale
2. community balance + mobility scale
3. high-level mobility assessment tool
4. rancho los amigos OGA system
5. 10 meter walk test
6. 6MWT
7. modified walking + remembering test
what are 2 OUTCOME MEASURES used for assessing SELF-CARE + ADL SKILLS of a TBI patient
1. functional independence measure (FIM)
2. functional assessment measure
what are 2 OUTCOME MEASURES used for assessing WORK/LEISURE/COMMUNITY REINTEGRATION of a TBI patient
1. mayo-portland adaptability inventory
2. community integration questionnaire
what are 2 PRIMITIVE REFLEXES that arise following a TBI
1. ATNR
2. STLR
Asymmetrical Tonic Neck Reflex (ATNR)
Trigger: turning head to one side
Response:
- extension of arm + leg on face side
- flexion of arm + leg on skull side
Impact:
1. difficulty with bilateral tasks
2. interferes with bed mobility (rolling + bridging)
3. can cause unintentional UE/LE extension
4. can cause loss of balance during gait/transfers
5. maintain head in midline + avoid passive head turning during tasks
what TRIGGERS the ATNR
turning head to one side
what are the 2 RESPONSES of the ATNR when triggered
1. extension of arm + leg on face side
2. flexion of arm + leg on skull side
what are 4 WAYS the presence of an ABNORMAL ATNR can influence treatment of a TBI patient
1. difficulty with bilateral tasks
2. interferes with bed mobility (rolling + bridging)
3. can cause unintentional UE/LE extension
4. can cause loss of balance during gait/transfers
in the presence of an ABNORMAL ATNR what should be maintained + avoided
Maintain: head in midline
Avoid: passive head turning during tasks
Symmetrical Tonic Labyrinthine Reflex (STLR)
Trigger: head position relative to gravity (flexion/extension)
Response:
1. head extended = increased extensor tone in trunk + limbs
2. head flexed = increased flexor tone in trunk + limbs
Impact:
1. poor transfers (supine to sit, sit to stand)
2. exaggerated extension/flexion tone depending on head position
3. can result in loss of:
- balance
- postural instability
- unintended movement patterns during mobility
4. limit extreme head flexion/extension + facilitate trunk control in midline
what TRIGGERS the STLR
head position relative to gravity (flexion/extension)
what are the 2 RESPONSES of the STLR when triggered
1. head extended = increased extensor tone in trunk + limbs
2. head flexed = increased flexor tone in trunk + limbs
what are 3 WAYS the presence of an ABNORMAL STLR can influence treatment of a TBI patient
1. poor transfers (supine to sit, sit to stand)
2. exaggerated extension/flexion tone depending on head position
3. can result in loss of:
- balance
- postural instability
- unintended movement patterns during mobility
in the presence of an ABNORMAL STLR what should be limited + facilitaed
Limited: extreme head flexion/extension
Facilitate: trunk control in midline
what are 5 MINIMUM QUALIFICATIONS for being ACCEPTED into an INPATIENT REHAB FACILITY
1. patient needs to be medically stable enough to participate in therapy + manage potential complications arising during rehab
2. patient must have a condition necessitating an intensive program
3. patient must be able to handle 3 hours of therapy per day at least 5 days/week (PT, OT, SLP)
4. patient will make measurable functional improvement
5. patient must be able + willing to actively participate in intensive therapy
how does MEDICARE REIMBURSE for INPATIENT REHABILITATION
1. medicare uses IRF-PAI to classify patients into payment groups
2. facilities then get reimbursement based on the diagnosis, severity + patient's functional status
how long will a TBI PATIENT stay in an INPATIENT REHAB SETTING
2 weeks (13-15 days)
how long can a patient RECEIVE SKILLED NURSING CARE under MEDICARE
1. days 1-20 100% covered by Medicare part A
2. days 21-100 Medicare requires a daily co-payment
3. once 100 days are reached within a benefit period Medicare no longer covers SNF care
- patient would have to have a 60-day well-period before process restarts
what is a TBI (Traumatic Brain Injury)
is an alteration in brain function or other evidence of brain pathology caused by an external force
what are 4 ETIOLOGICAL FACTORS associated with TBIs
1. falls
2. motor vehicle/traffic accidents
3. struck by/against events
4. assaults
what are the 3 DIFFERENT AGE LEVELS that TBIs PEAK at
1st peak: early childhood (1-2 years)
2nd peak: late adolescence + early adulthood (15-24 years)
3rd peak: elderly population
what is the 1st TBI PEAK (early childhood) related to
child abuse
what is the 2nd TBI PEAK (late adolescence + early adulthood) related to
risk-taking behaviors
what is the 3rd TBI PEAK (elderly population) related to
falls
what is the PATHOPHYSIOLOGY of TBIs
brain damage results from external forces that cause brain tissue to make direct contact with an object, rapid acceleration/deceleration forces or blast waves from an explosion
regarding TBI PATHOPHYSIOLOGY, what are the 3 CATEGORIES that brain tissue damage is classified under
1. primary injury (primary TBI)
2. secondary injury
3. blast injury
what is a PRIMARY INJURY due to
direct trauma to parenchyma
what does a SECONDARY INJURY result from
cascade of biochemical, cellular + molecular events that evolve over time due to initial injury + injury-related hypoxia, edema + elevated ICP
what does a PRIMARY TBI result from
1. brain tissue coming into contact with an object (bony skull/external object creating a penetrating injury)
OR
2. rapid acceleration/deceleration of brain
what is the PREDOMINANT MECHANISM of INJURY in SEVERE to MODERATE TBIs
diffuse axonal injury (DAI)
what is DIFFUSE AXONAL INJURY (DAI) common in (2)
1. high-speed motor vehicle accidents
2. some sports-related TBIs
how does BLAST INJURY lead to BRAIN DAMAGE
explosive device detonates = transient shock waves produced causing brain damage
what are the 3 TYPES of BLAST INJURIES
1. primary blast injury
2. secondary blast injury
3. tertiary blast injury
what does a PRIMARY BLAST INJURY result from
direct effect of blast overpressure on brain
what does a SECONDARY BLAST INJURY result from
shrapnel + other objects being hurled at individual
when does a TERTIARY BLAST INJURY occur
when victim is flung backwards + strikes an object
what can BLAST-RELATED BRAIN INJURY result in (5)
1. edema
2. contusion
3. DAI
4. hematomas
5. hemorrhage
what are 4 NEUROMUSCULAR IMPAIRMENTS associated with a TBI
1. paresis
2. abnormal tone
3. motor function
4. postural control
what are 6 COGNITIVE IMPAIRMENTS associated with a TBI
1. arousal level
2. attention
3. concentration
4. memory
5. learning
6. executive functions
what are 7 NEUROBEHAVIORAL IMPAIRMENTS associated with a TBI
1. agitation/aggression
2. disinhibition
3. apathy
4. emotional lability
5. mental inflexibility
6. impulsivity
7. irritability
what are 10 SECONDARY IMPAIRMENTS + CONCOMITANT INJURIES associated with a TBI
1. DVTs
2. heterotopic ossification
3. pressure ulcer
4. pneumonia
5. chronic pain
6. contractures
7. decreased endurance
8. muscle atrophy
9. fracture
10. peripheral nerve damage
Characteristics of Mild TBI
Level of Consciousness (LOC): 0-30 minutes
Alteration of Consciousness (AOC): brief >24 hrs
PTA: 0-1 days
Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS): 13-15
Neuroimaging: normal
what is the LEVEL of CONSCIOUSNESS associated with a MILD TBI
0-30 minutes
what is the ALTERATION of CONSCIOUSNESS associated with a MILD TBI
brief >24 hrs
what is the PTA associated with a MILD TBI
0-1 days
what is the GLASGOW COMA SCALE associated with a MILD TBI
13-15
is the NEUROIMAGING for a MILD TBI considered to be NORMAL/ABNORMAL
normal neuroimaging
Characteristics of Moderate TBI
Level of Consciousness (LOC): >30 minutes + <24 hrs
Alteration of Consciousness (AOC): >24 hrs
PTA: >1 + <7 days
Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS): 9-12
Neuroimaging: normal/abnormal
what is the LEVEL of CONSCIOUSNESS associated with a MODERATE TBI
>30 minutes + <24 hrs
what is the ALTERATION of CONSCIOUSNESS associated with a MODERATE TBI
>24 hrs
what is the PTA associated with a MODERATE TBI
>1 + <7 days
what is the GLASGOW COMA SCALE associated with a MODERATE TBI
9-12
what are the NEUROIMAGING results associated with a MODERATE TBI
normal/abnormal
Characteristics of Severe TBI
Level of Consciousness (LOC): >24 hrs
Alteration of Consciousness (AOC): >24 hrs
PTA: >7 days
Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS): <9
Neuroimaging: normal/abnormal
what is the LEVEL of CONSCIOUSNESS associated with a SEVERE TBI
>24 hrs
what is the ALTERATION of CONSCIOUSNESS associated with a SEVERE TBI
>24 hrs
what is the PTA associated with a SEVERE TBI
>7 days
what is the GLASGOW COMA SCALE associated with a SEVERE TBI
<9
what are the NEUROIMAGING results associated with a SEVERE TBI
normal/abnormal
what are 12 PHARMACOLOGICAL TREATMENT OPTIONS for TBIs
1. diuretics
1. anticonvulsants
3. electrolytes
4. NMDA receptor antagonists
5. barbiturates
6. calcium channel blockers
7. stimulants
8. dopamine agonists
9. SSRIs
10. antipsychotics
11. muscle relaxers
12. pain relievers
what are 7 SURGICAL TREATMENT OPTIONS for TBIs
1. craniotomy
2. decompressive craniectomy
3. Burr hole surgery
4. skull fracture repair
5. shunt placement
6. intracranial pressure monitoring
7. placement of an EVD
what are 5 GUIDELINES for the MEDICAL TREATMENT of TBI PAITENT
1. SBP should be above 90 mmHg
2. O2 saturation should be above 90%
3. patient's neck should be stabilized with a collar + head elevated 30 degrees
4. complete neurological examination performed
5. continuously monitor patient
what is INCREASED ICP
is an increase in pressure around the brain
what are 11 CAUSES of INCREASED ICP
1. increased CSF production
2. impaired/blocked CSF drainage
3. brain swelling
4. hematomas
5. high BP
6. low sodium levels
7. TBI
8. ischmeia/hypoxia of brain
9. tumors
10. infections (meningitis/encephalitis)
11. hydrocephalus
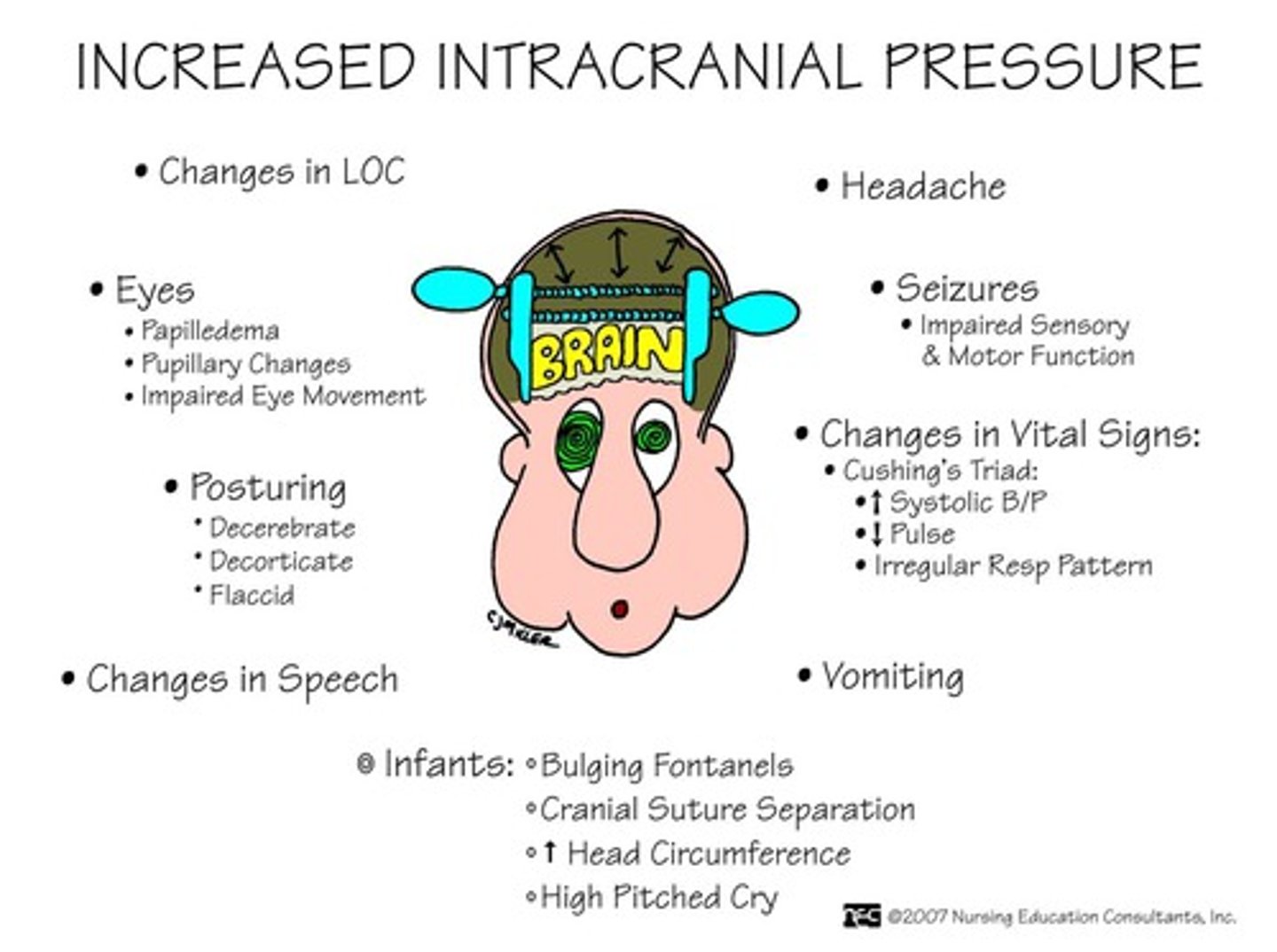
what are 7 SIGNS + SYMPTOMS associated with INCREASED ICP
1. severe headache
2. nausea + vomiting
3. drowsiness/confusion
4. vision changes (blurred vision/double vision)
5. seizures
6. loss of consciousness
7. posturing (decerebrate, decorticate + flaccid)
what does the GEGENHALTEN NATURE refer to
involuntary resistance to passive movement
what is the GEGENHALTEN NATURE classified as
form of hypertonia
what does a TOTAL SCORE of 3 on the GLASGOW COMA SCALE indicate
totally unresponsive
what does a TOTAL SCORE of <8 on the GLASGOW COMA SCALE indicate
comatose
what does a TOTAL SCORE of 15 on the GLASGOW COMA SCALE indicate
best response
what are the 8 RANCHO LOS AMIGOS LEVELS of COGNITIVE FUNCTIONING
1. no response (Level I)
2. generalized response (Level II)
3. localized response (Level III)
4. confused-agitated (Level IV)
5. confused-inappropriate (Level V)
6. confused-appropriate (Level VI)
7. automatic-appropriate (Level VII)
8. purposeful-appropriate (Level VIII)
what does LEVEL 1 on the RANCHO LOS AMIGOS LOCF mean
no response
what are 2 FEATURES of LEVEL 1 (No Response) on the RANCHO LOS AMIGOD LOCF
1. patient appears to be in a deep sleep
2. completely unresponsive to any stimuli
what does LEVEL 2 on the RANCHO LOS AMIGOS LOCF mean
generalized response
what are 3 FEATURES of LEVEL 2 (Generalized Response) on the RANCHO LOS AMIGOD LOCF
1. patient reacts inconsistently + non-purposefully to stimuli in a nonspecific manner
2. responses are limited + often the same regardless of stimulus presented
3. responses may be:
- physiological changes
- gross body movements
- vocalization
what does LEVEL 3 on the RANCHO LOS AMIGOS LOCF mean
localized response
what are 3 FEATURES of LEVEL 3 (Localized Response) on the RANCHO LOS AMIGOD LOCF
1. patients reacts specifically but inconsistently to stimuli
2. responses directly related to type of stimulus presented
3. may follow simple commands (closing eyes/squeezing hand) in an inconsistent, delayed manner
what does LEVEL 4 on the RANCHO LOS AMIGOS LOCF mean
confused-agitated
what are 9 FEATURES of LEVEL 4 (Confused-Agitated) on the RANCHO LOS AMIGOD LOCF
1. patient in heightened state of activity
2. bizarre + nonpurposeful behavior relative to immediate environment
3. doesn't discriminate among people/objects
4. unable to cooperate directly with treatment efforts
5. verbalizations frequently incoherent/inappropriate to environment
6. confabulation may be present
7. gross attention to environmental is very brief
8. selective attention often nonexistent
9. patient lacks short + long-term recall
what does LEVEL 5 on the RANCHO LOS AMIGOS LOCF mean
confused-inappropriate
what are 10 FEATURES of LEVEL 5 (Confused-Inappropriate) on the RANCHO LOS AMIGOD LOCF
1. patient able to response to simple commands fairly consistently
2. response non-purposeful, random/fragmented with increased complexity of commands or lack of any external structure
3. demonstrates gross attention to environment
4. highly distractible + lacks ability to focus attention on a specific task
5. with structure, maybe able to converse on a social automatic level for short periods of time
6. verbalization often inappropriate + confabulatory
7. memory severely impaired
8. often shows inappropriate use of objects
9. may perform perviously learned tasks with structure
10. unable to learn new information
what does LEVEL 6 on the RANCHO LOS AMIGOS LOCF mean
confused-appropriate
what are 6 FEATURES of LEVEL 6 (Confused-Appropriate) on the RANCHO LOS AMIGOD LOCF
1. patient shows goal-directed behavior
2. dependent on external input/direction
3. follows simple directions consistently
4. shows carryover for relearned tasks (self-care)
5. responses incorrect due to memory problems but appropriate to situation
6. past memories show more depth + detail than recent memory
what does LEVEL 7 on the RANCHO LOS AMIGOS LOCF mean
automatic-appropriate
what are 7 FEATURES of LEVEL 7 (Automatic-Appropriate) on the RANCHO LOS AMIGOD LOCF
1. patient appears appropriate + oriented within hospital + home settings
2. goes through daily routine automatically but frequent robot-like
3. patient shows minimal to no confusion
4. has shallow recall of activities
5. shows carryover for new learning but at a decreased rate
6. with structure able to initiate social/recreational activities
7. judgement remains impaired
what does LEVEL 8 on the RANCHO LOS AMIGOS LOCF mean
purposeful-appropriate