Chem test protons
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Alpha Decay
When a nucleus decays, emits alpha particle = 2 protons + 2 neutrons
Ernest Ruthuford
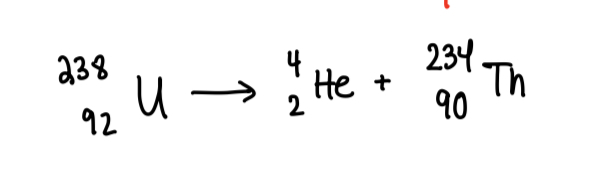
Beta decay
Electron is ejected from nucleus. Neutron converts to proton, extra negative charge is ejected
Ernest ruthuford
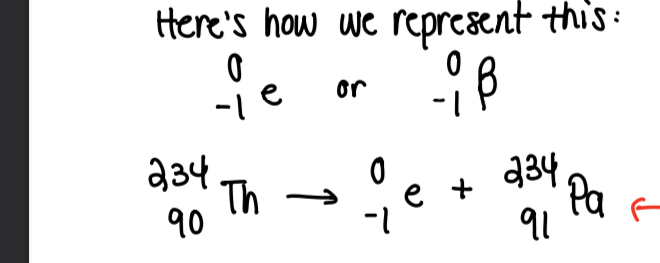
Gamma radiation
Energy being emitted. Happens all the time

Location of proton, neutron and electron
Proton- nucleus
Neutron- nucleus
Electrons- outside of nucleus
What is Democritus known for
The point where matter could not be cut into any smaller pieces
What are three tenets to Daltons theory
All substances are made of atoms
All atoms of the same element are alike + have same mass/ atoms of different elements are different+ have different matter
Atoms join together to form compounds, always consisting of same kind of atom in the same ratio
Daltons theory falls short where
Too simple; don’t include subatomic particles
What did Thomson theorize
He was the first to theorize the presence of electrons
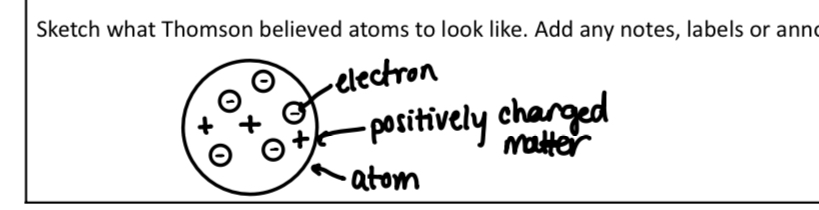
Explain Thomson’s “cathode Ray experiment”
Particles were deflected away from negative charged
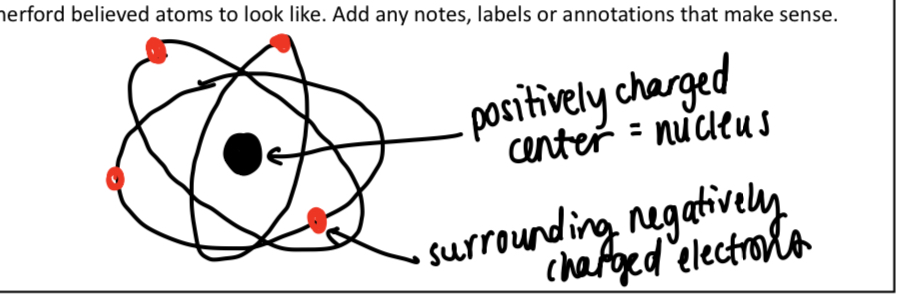
What did Rutherford discover
The nucleus
Explain Rutherford’s “gold foil experiment”
Fired stream of alpha particles at sheet of pure gold
Assumed the alpha particles would pass through( surprisingly didn’t happen)
Some of the alpha particles were deflected, positive charge must be concentrated
What Rutherford thought atoms look like
What does quantized mean
Only specific values are allowed
Bohr’s model is what
Electrons on outside and nucleus is on the inside
How did Bohr model include quantization in his atomic theory
Suggested that electrons could orbit nucleus in specific orbits or shells. Can’t be located between shells
What is the Quantum mechanical model
Electrons act like particles and waves
Can identify where an electron has a high probability of being found
Electron clouds-location of electrons
What is an isotope
Atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different number of neutrons
Valence electron
Electrons found in the outermost shell or the highest energy level
The octet rule
Adams tend to gain/lose or share electrons to achieve a full outer shell, which usually means eight valence electrons
Formation of ions
An ion is an atom that has gained or lost one or more electron resulting in a net elect charge
cation- a positively charged ion when it loses an electron
anion- a negatively charged iron when it gains one or more electron
Where are metals, nonmetals, metalloids
Properties of metals and nonmetals
Metals- high melting point, solid at room tem except for mercury, ductile and malleable, magnet, can react with acid
Nonmetals- insulator, brittle, dull
What is the law of definite proportions?
A chemical compound always contains the same elements in the exact same proportion by mass, regardless of the amount of source of the compound
My ass about 11% of hydrogen and 89% oxygen
What is the law of multiple proportions
Adams combine and whole number ratios supporting Dalton’s atomic theory