Foundations of Genetics – Vocabulary Flashcards
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
40 vocabulary flashcards summarizing key terms, theories, scientists, and molecular concepts from the genetics lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Genetics
The scientific study of heredity and the variation of inherited characteristics.
Heredity
the passing on of physical or mental characteristics genetically from one generation to another.
Variation
tendency of offspring to vary from their parents.
Preformation
Theory which stated that the sperm of fertilized egg contains a complete miniature adult known as homunculus.
Homunculus
A sperm containing a miniature adult; perfect in proportion and fully formed.
Epigenesis
the theory, now generally held, than an embryo develop progressively. From an undifferentiated egg cell.
Cell Theory
(proposed by Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann in 1830)
States that all organisms are composed of basic structural units called (?)
Spontaneous Generation
life came from non-living matter. Disproved by Louis Pasteur.
1859
Theory of Evolution on “The Origin of Species” and Theory on "Pangenesis"
Pangenesis
Darwin’s hypothesis that hereditary “gemmules” from all body parts collect in the gametes.
Alfred Russel Wallace
proposed the theory on natural selection which is based on the observation of the population.
1866: Gregor Johann Mendel
conducted a decade long series of experiment involving pea plants. and published a paper showing how traits were passed from generation to generation in pea plants.
Chromosome Theory of Inheritance
explains how genetic information is transmitted from generation to generation.
Mitosis
Chromosomes are copied and distributed so that each daughter cell receives a diploid set of chromosomes identical to parent cell.
Meiosis
Cell produced by meiosis receive only one chromosome from each pair, and the resulting number of chromosomes is called haploid number.
Walther Flemming
in 1878 chromosome was identified which was initially coined as “chromatin”
Friedrich Miescher
discovered DNA through pus/white blood cells.
Rosalind Franklin
Produced X-ray diffraction images crucial to elucidating DNA’s double-helix structure.
James Watson & Francis Crick
Discovered the helical structure in 1953 bridging from the works of Dr. Franklin.
Honorable Mention: Dr. Franklin! hell yeah
basically, the discovery was made by those ppl BUT it was only possible bc of my dawg Dr. Franklin, specifically bc of her X-RAY diffractions.
Yeah, James and Francis discovered it by combining their research w hers.
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
a long, ladder-like molecule that “twist” to form a double helix.
RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)
Single-stranded nucleic acid involved in gene expression and protein synthesis.
note: ts isn’t actually included, i js added it kasi may meaning yung DNA and wala ‘to, hell yeah
Nucleotides
Each linear strand of the helix is made up of subunits called nucleotides.
Each nucleotide consists of:
Nitrogenous base group
Phosphate group
Sugar group
Mutation
any heritable change in the DNA sequence and are the source of all genetic variation.
Transcription
A process in which the nucleotide sequence in one strand of DNA is used to construct a complementary RNA sequence.
Translation
synthesis of RNA to amino acids which forms proteins.
Proteins
End product of gene expression
Molecules with the potential for enormous structural diversity serve as the mainstay of biological systems.
Amino Acid
the building blocks of proteins.
Catalytic Proteins (Enzymes)
Represent the largest class of proteins.
They enhance the reaction rates a million fold.
Regulatory Proteins (Hormones)
polypeptides and small proteins found in relatively lower concentrations in animal kingdom but play highly important regulatory role in maintaining order in complex metabolic reactions.
Protective Proteins (Antibodies)
Protein combined with protein and other substances fight against certain diseases.
Example includes: Immunoglobulin
Sickle-Cell Anemia
Genetic disorder caused by a mutation in the β-globin gene leading to abnormal hemoglobin and sickle-shaped red blood cells.
if u ain’t reading allat js know they’re caused by a mutant form of hemoglobin 🙏
note: the sentence including the yellow-colored text lang yung word for word. the sentence above it is a generated description using the rest of the bullets included, so it’s still based on ur paper.
Hemoglobin
Oxygen-transport protein composed of α-globin and β-globin polypeptide chains.
A protein made up of a-globin and b-globin (each encoded by a different gene)
note: the sentence including the yellow-colored text lang yung word for word. the sentence above it is a generated description using the rest of the bullets included, so it’s still based on ur paper.
Restriction Endonuclease
Bacterial enzyme that cuts DNA at specific sequences; tool for DNA cloning.
js gonna include this too:
DNA fragments-> vectors -> reproduce recombinant DNA molecules.
Recombinant DNA
DNA molecules formed by laboratory joining of genetic material from different organisms.
Transgenic Organism
is created from the transfer of heritable traits across species using recombinant DNA technology.
Dolly the Sheep (my bb)
First mammal cloned (1996) by nuclear transfer.
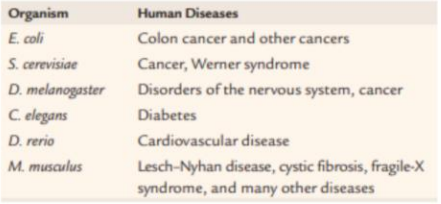
Model Genetic Organism
an organism used for the study basic biological processes.
Other model organisms
hell yeah