Management Theory: Historical and Contemporary Perspectives: CH 2
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
Management Theory
Study of principles guiding managerial practices.
Classical Viewpoint
Focus on efficiency and scientific management methods.
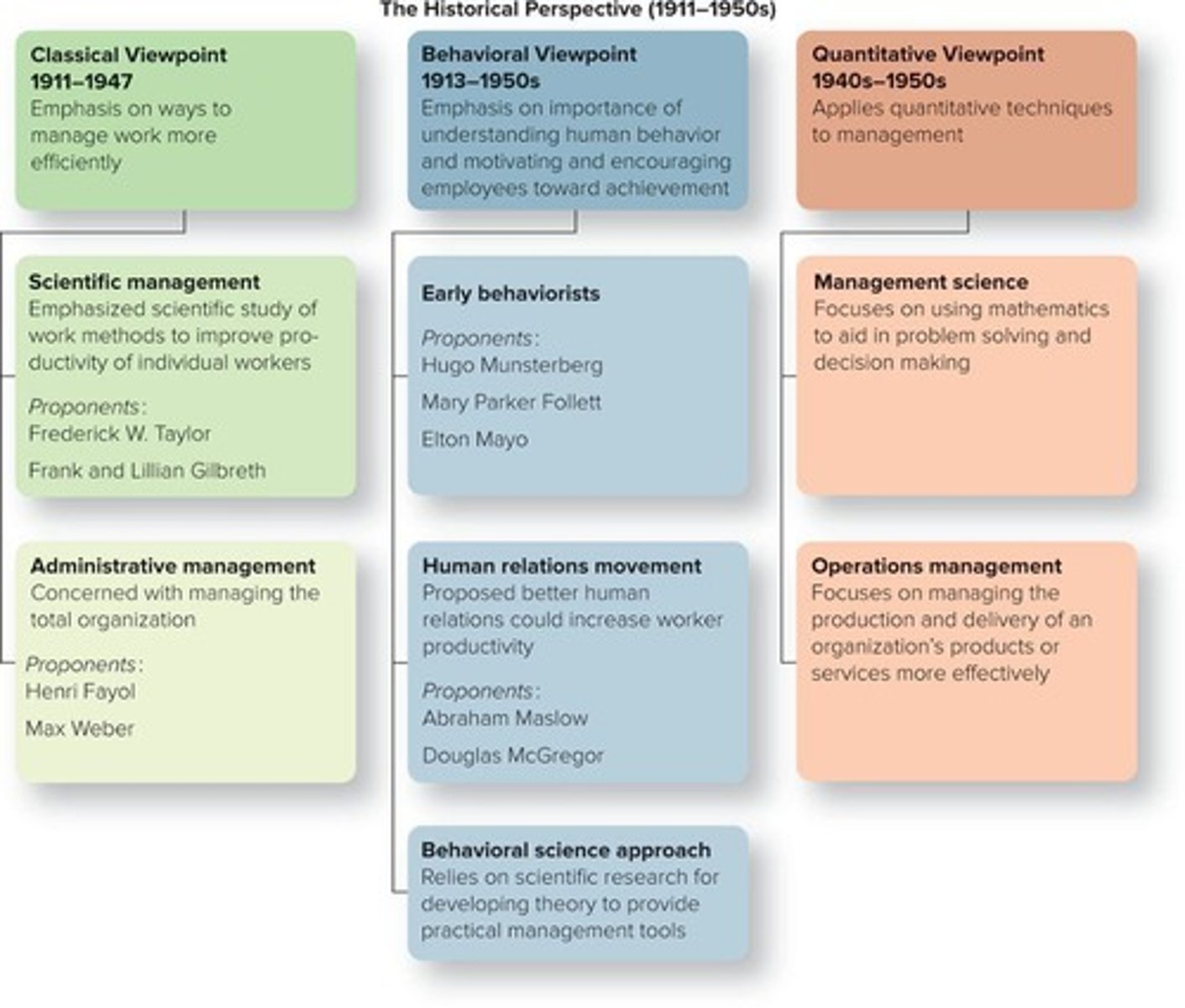
Scientific Management
Improving productivity through scientific study of tasks.
Frederick W. Taylor
Pioneer of scientific management principles.
Gilbreths
Developed motion study techniques to enhance efficiency.
Motion Studies
Analysis of tasks to eliminate unnecessary movements.
Administrative Management
Management focused on overall organizational structure.
Henri Fayol
Identified major management functions: planning, organizing.
Max Weber
Proposed bureaucracy as an ideal organizational structure.
Bureaucracy
Rational organization with clear hierarchy and rules.
Hierarchy of Authority
Structured levels of management within an organization.
Formal Rules
Established guidelines governing organizational behavior.
Division of Labor
Specialization of tasks to improve efficiency.
Impersonality
Objective treatment of employees in bureaucratic systems.
Merit-Based Careers
Promotion based on performance and qualifications.
Behavioral Viewpoint
Focus on understanding employee motivation and behavior.
Quantitative Approaches
Use of mathematical models for problem-solving.
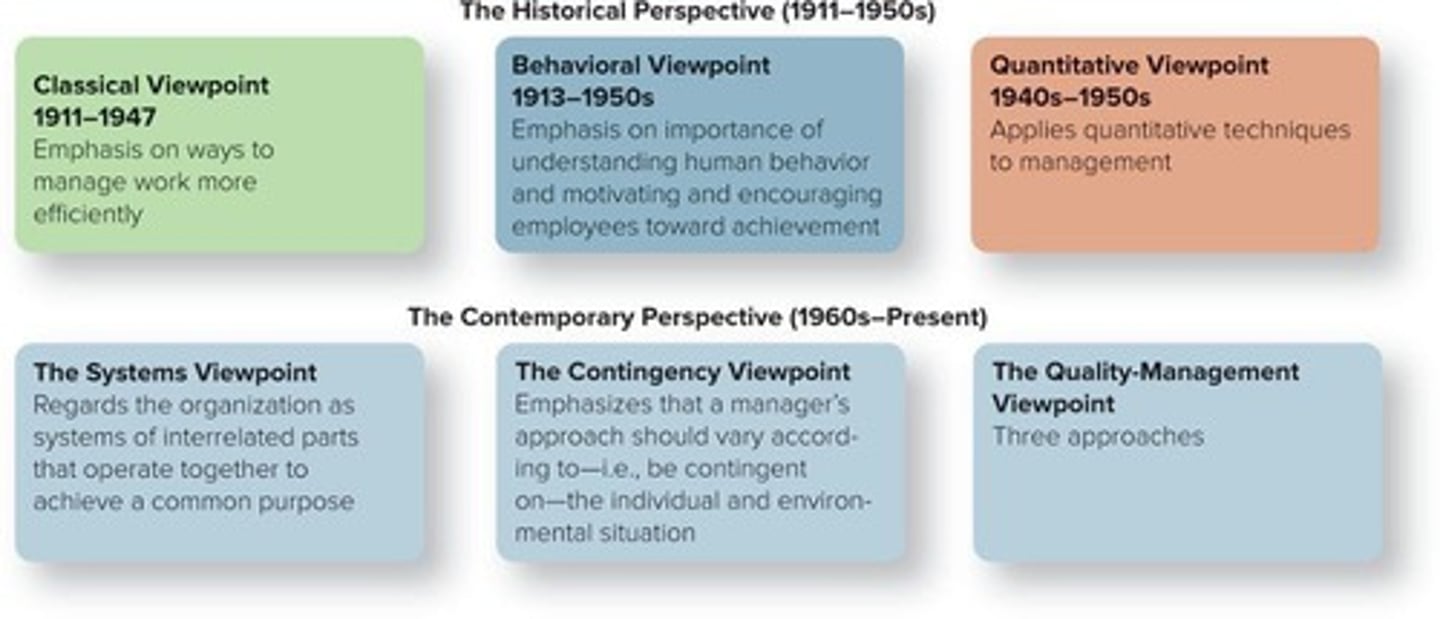
Systems Viewpoint
Holistic approach considering interrelated organizational components.
Quality-Management Viewpoint
Focus on continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
Learning Organization
An organization that facilitates continuous learning.
Positive Results
Outcomes achieved through effective management practices.
Historical Perspective
Study of past management theories and practices.
Contemporary Perspective
Modern approaches to management in current organizations.
Classical Viewpoint
Views humans as cogs in a machine.
Scientific Management
Focuses on improving productivity through work methods.
Behavioral Viewpoint
Emphasizes understanding human behavior in management.
Early Behaviorism
Foundation of industrial psychology and employee motivation.
Hugo Munsterberg
Father of Industrial Psychology, studied job suitability.
Mary Parker Follett
Advocated for community-based organizational operations.
Elton Mayo
Led studies showing attention increases worker productivity.
Hawthorne Effect
Increased productivity from attention and care from managers.
Human Relations Movement
Improves productivity through better human relations.
Abraham Maslow
Pioneered the concept of Hierarchy of Needs.
Douglas McGregor
Developed Theory X and Theory Y on worker attitudes.
Theory X
Pessimistic view of workers as irresponsible and lazy.
Theory Y
Optimistic view of workers as responsible and creative.
Behavioral Science
Uses research to develop theories on human behavior.
Quantitative Viewpoint
Applies quantitative techniques in management practices.
Management Science
Focuses on using mathematical models for decision-making.
Behavioral Science Disciplines
Includes psychology, sociology, anthropology, and economics.
Motivating Employees
Understanding behavior to enhance employee achievement.
Conflict Resolution
Managers and workers discuss to find mutual solutions.
Facilitator Role
Managers guide rather than control knowledgeable workers.
Employee Welfare
Attention from managers improves overall employee productivity.
Job Suitability
Matching individuals to jobs based on psychological conditions.
Management Science
Uses mathematics for problem solving and decision making.
Operations Management
Manages production and delivery of products or services.
Work Scheduling
Planning work tasks to optimize efficiency.
Production Planning
Determining production levels and timelines.
Facilities Location
Choosing sites for production and operations.
Optimum Inventory Levels
Ideal stock levels to meet demand without excess.
Closed Systems
Organizations with minimal environmental interaction.
Open Systems
Organizations interacting continuously with their environment.
Synergy
Combined efforts producing greater results than individual parts.
Complexity Theory
Studies networks of interdependent parts in systems.
Contingency Viewpoint
Management approach varies based on situation and context.
Evidence-Based Management
Uses best evidence for rational decision making.
Quality
Total ability to meet customer needs.
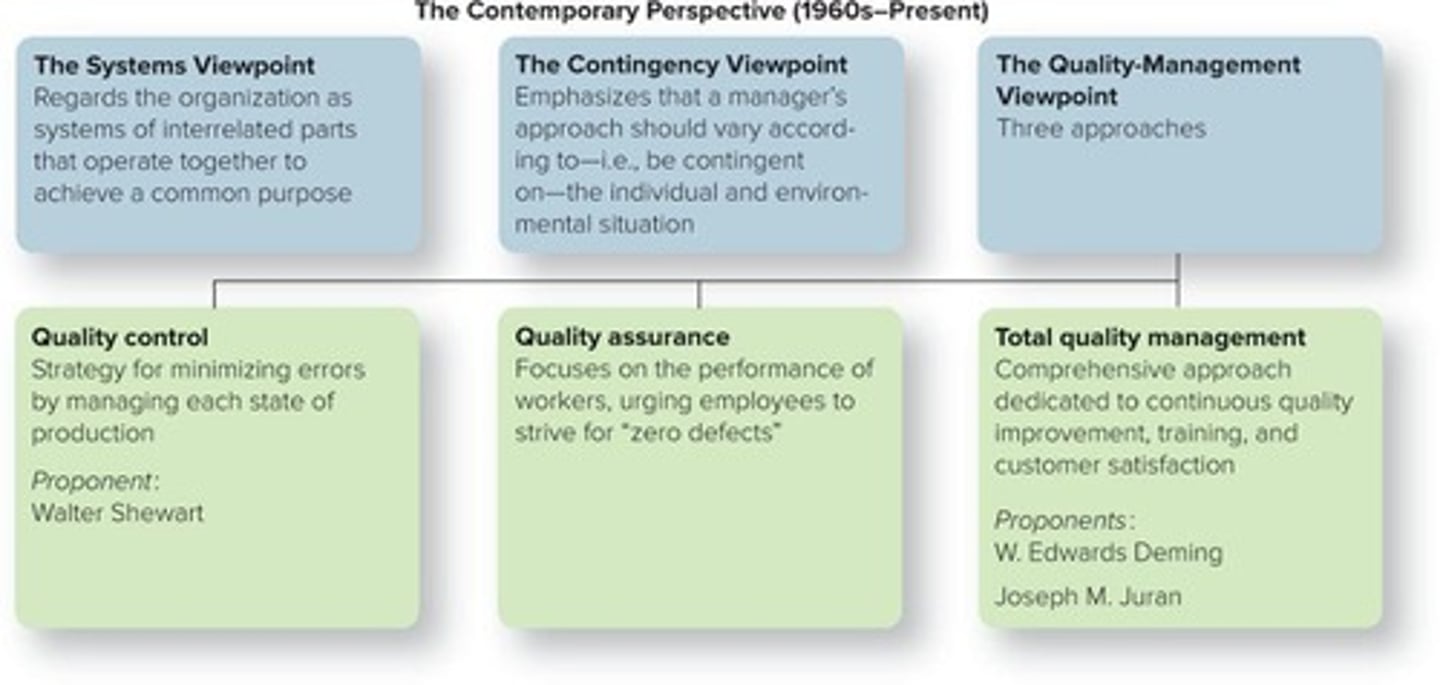
Quality Control
Minimizes errors by managing production stages.
Quality Assurance
Focuses on performance to achieve zero defects.
Total Quality Management (TQM)
Continuous improvement and customer satisfaction focus.
Learning Organization
Actively creates and transfers knowledge internally.
Commitment to Learning
Building a culture focused on continuous learning.
Generating Ideas with Impact
Creating significant and actionable ideas.
Generalizing Ideas with Impact
Applying impactful ideas across the organization.
Historical Perspective
Management theories from 1911 to 1950s.
Classical Viewpoint
Focus on efficient work management techniques.
Behavioral Viewpoint
Focus on understanding and motivating employee behavior.
Quantitative Viewpoint
Uses quantitative techniques for management decision-making.
Systems Viewpoint
Views organization as interrelated parts achieving common goals.
Contingency Viewpoint
Manager's approach varies based on situation and individual.
Quality Management Viewpoint
Focuses on continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
Classical Viewpoint
Emphasizes efficient work management methods.
Scientific Management
Improves productivity through scientific study of work methods.
Administrative Management
Focuses on managing the total organization effectively.
Human Relations Movement
Better relations can enhance worker productivity.
Behavioral Science Approach
Uses research to develop practical management theories.
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
Pyramid of human needs from basic to self-fulfillment.
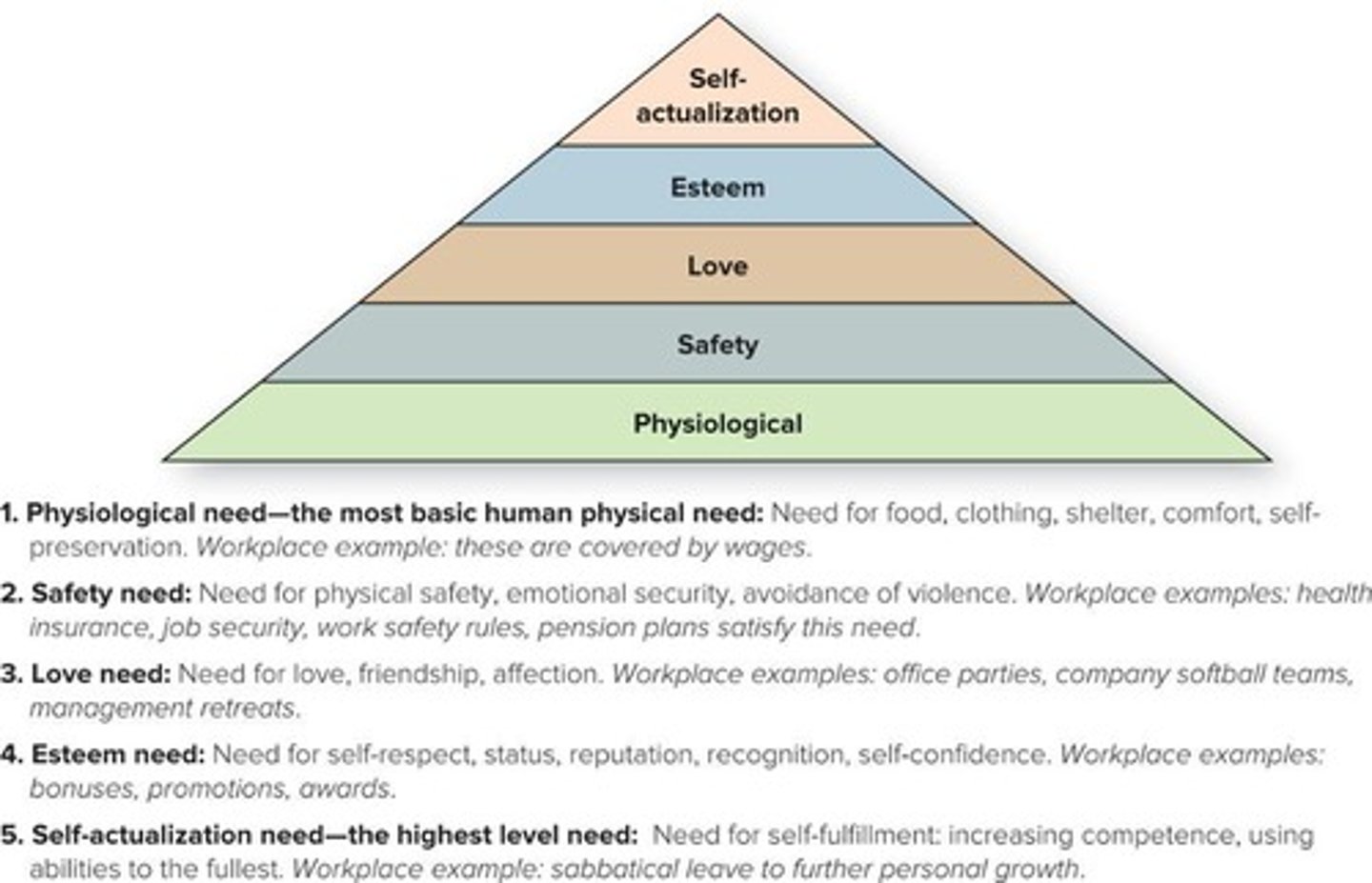
Physiological Need
Basic needs for food, shelter, and self-preservation.
Safety Need
Need for physical safety and emotional security.
Love Need
Need for affection, friendship, and social connections.
Esteem Need
Need for self-respect and recognition from others.
Self-Actualization Need
Need for personal growth and fulfillment of potential.
Quality Control
Minimizes errors by managing production processes.
Quality Assurance
Encourages striving for zero defects in performance.
Total Quality Management
Comprehensive approach for continuous quality improvement.
Management Science
Applies mathematics to solve management problems.
Operations Management
Manages production and delivery of products/services.
Early Behaviorists
Pioneers in understanding human behavior in organizations.
Proponents of Management Theories
Key figures advocating specific management approaches.