Biology topic 6
1/168
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
169 Terms
Forensics
The application of scientific knowledge to legal matters, as in the investigation of crime
Fingerprints
Impressions left by the friction ridges of a human finger
Development of fingerprints
mostly formed between weeks 6-10 of foetal life
Raised portions of the epidermis
Movement of baby in the womb, speed of growth affect the fingerprint pattern
Detecting fingerprints
carbon,aluminium or magnetic iron powder (sticks to grease)
Ninhydrin (becomes purple with amino acids in sweat)
Superglue vapour
Dental records
Teach survive longer than other parts of the body, unique
Methods used to identify a body
ID papers
Fingerprints
Skeletal records
Dental records
DNA profiling
Non-coding DNA
Doesn’t code for proteins
About 99% of the genome
Short tandem repeats
non-coding DNA
Usually 3-7 bases long and repeated
Make up 3% of the human genome
Likely involved in chromatin folding and transcription regulation
STR locations
same locus on both homologous chromosomes
Number of STRs at a locus can vary
Inherited like genes
DNA profiling
also used in parentage testing, genealogical and medical research
Developed by Alec Jeffreys in 1984
uses STRs
DNA profiling steps
obtain DNA sample
Create fragments
Separate fragments
Visualise fragments
DNA samples
cheek cells from swabbing
White blood cells from blood sample
Restriction enzymes
= enzymes that cut DNA at specific recognition sites
discovered by Werner Arber in 1970
Found in bacteria
More than 600 available commercially
PCR
Polymerase chain reaction
Amplifies DNA
DNA primer
Short DNA sequences complementary to the DNA either side of the STR
Step 1 of PCR : denaturation
DNA strands separated (denatured) (hydrogen bonds are broken)
95°C for 1min
Step 2 of PCR: annealing
Small primers anneal at the start and end of STR sequence via complementary base pairing
55°C for 2 mins
Step 3 of PCR: extension
Taq DNA polymerase synthesises complementary DNA strands using free nucleotides(dNTPs)
70°C for 2 mins
Why is Taq polymerase used in PCR?
Thermostable so can withstand temperature changes
dNTPs
Deoxynucleotide triphosphates
Used in PCR
Amplifaication in PCR
steps 1-3 are repeated for 25-30 cycles
In every cycle more DNA is present to act as a template - increases exponentially
Performed by PCR machine/thermal cycler
Gel electrophoresis
a method of separating DNA fragments according to size in an agarose gel by applying an electric field
Step 1 of gel electrophoresis: preparing the gel
mix agarose and buffer
Microwave to melt agarose
Cool and pour into mole
Remove comb when gel has set
Step 2 of gel electrophoresis: loading the gel
the gel is put into a tank with buffer
DNA samples are loaded into the wells with a pipette
Step 3 of gel electrophoresis: running the gel
Electrodes attached - cathode near wells, anode on opposite side because DNA is negatively charged
Staying the DNA directly in gel electrophoresis
can be stained using ethidium bromide and visualised under a UV lamp
Most commonly used dye
Inserts itself between the base pairs in the double helix
Glows in UV light
Evidence for time of death
body temperature
Rigor mortis
Decomposition
Entomology and succession
how to measure core body temperature?
long thermoprobe via rectum or abdominal stab
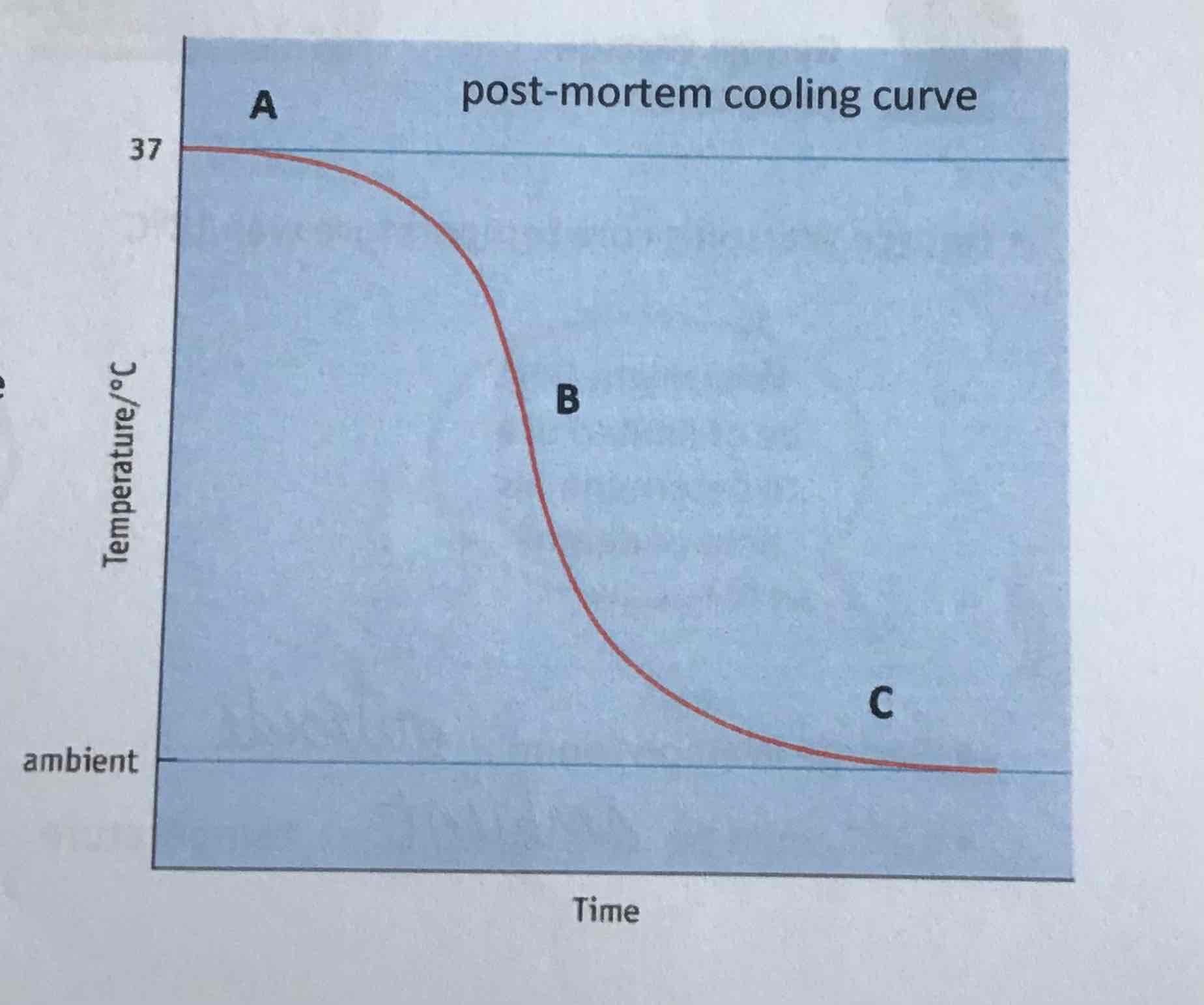
point A on curve
sigmoid curve
plateau, 30-60 mins
metabolic reactions not fully stopped yet
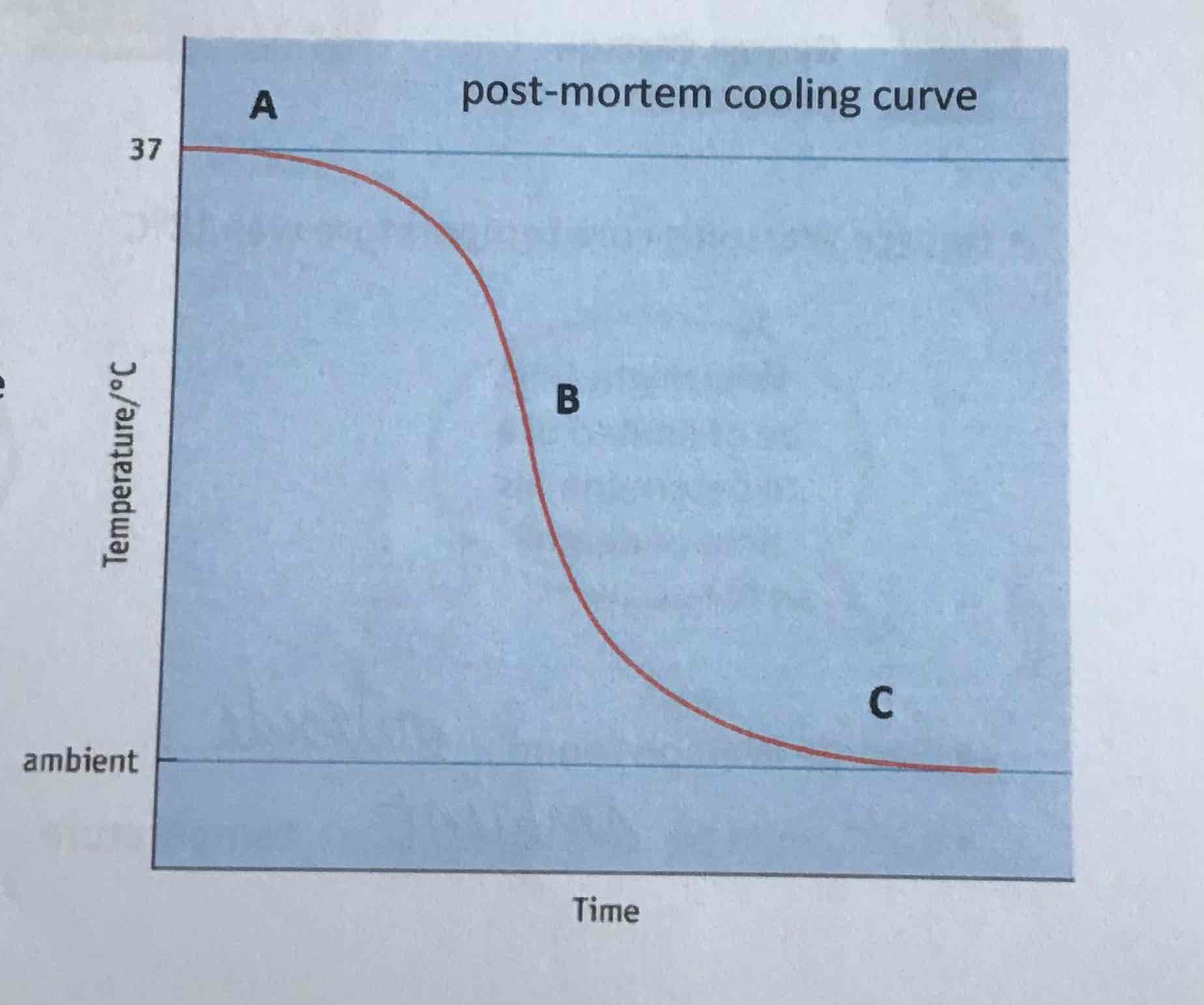
point B on curve
linear decline of temperature can be used to estimate time of death (approx -1.5C/h)
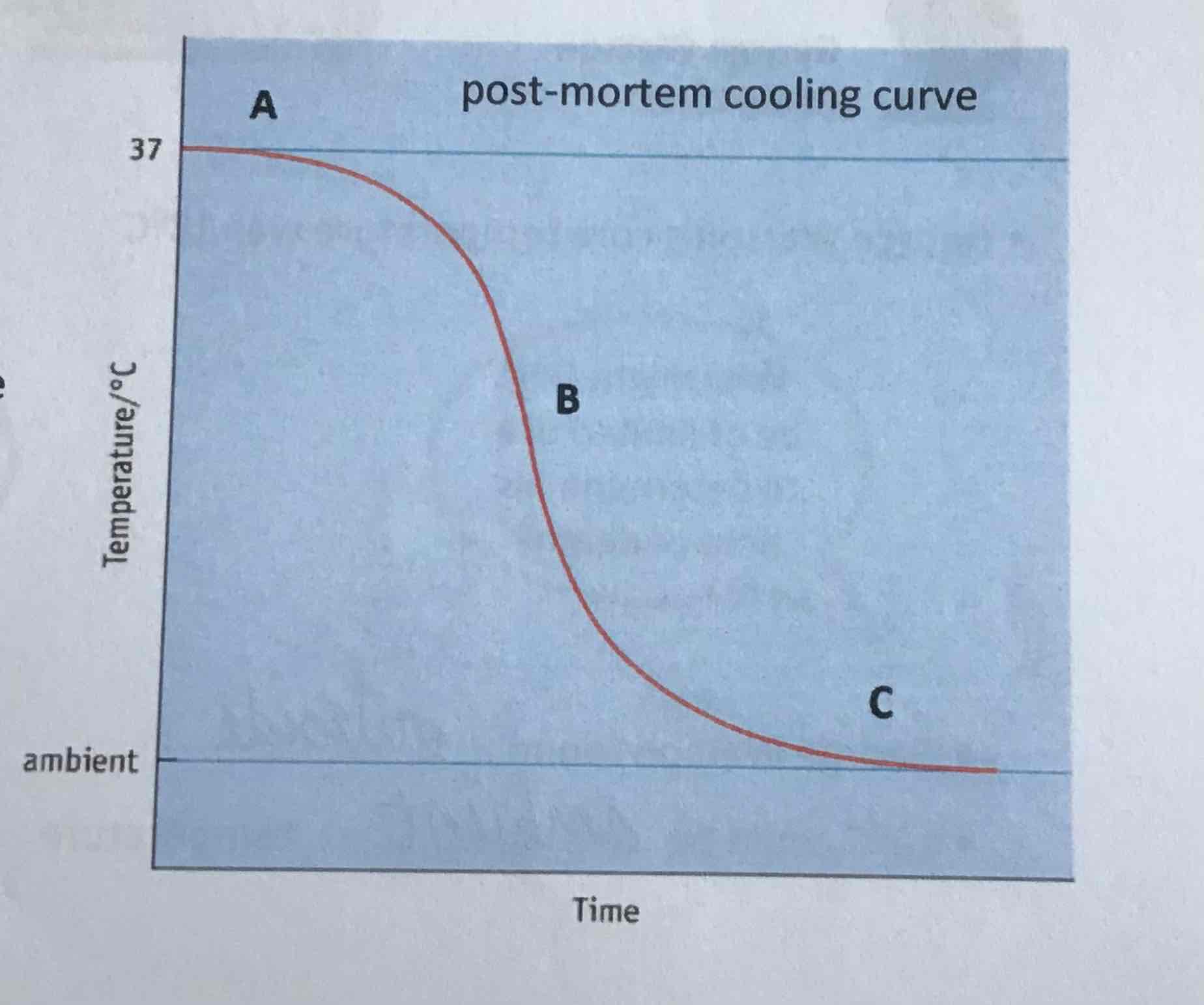
point C on curve
body temperature reaches ambient (environmental) temperature
factors that affect initial body temperature
fever
hypothermia
factors that affect post-mortem cooling
environmental temperature
air movement (wind)
humidity/ body found in water
body size, SA/vol ratio
fat composition
body location
clothing
how factors affect post mortem cooling
greater temperature gradient and wind, quicker cooling
higher humidity, slower cooling
a body in water will cool quicker due to the large temperature gradient
small body cools quicker due to high SA/vol ratio
high fat composition and clothing will insulate a body
rigor mortis
after death, muscles first relax, then stiffen and then relax again
rigor mortis steps
1) death: muscles become starved of oxygen —> aerobic respiration stops
2) respiration becomes anaerobic —> produces lactic acid
3) pH falls, inhibiting enzymes —> anaerobic respiration stops
4) ATP is no longer produced —>myosin and actin permanently fixed in contracted state
why does rigor mortis stop after about 36 hours?
decomposition - lysosomes break down and release enzymes that break down cells
factors that affect the onset of rigor mortis
temperature
O2 availability
manner of death
decomposition
digestion of cells resulting in the breakdown of tissues and release of carbon and minerals (e.g. nitrate and phosphate)
five stages of decomposition
fresh, initial decay
bloating, putrefaction
active decay
advanced decay
dry remains
fresh, initial decay
0 to 3 days after death
autolysis
anaerobic bacteria in gut start to digest tissues and release gasses (start of putrefaction)
bloating/putrefaction
3 to 10 days after death
increased gas production by bacterial activity causes swelling of tissues and putrid odour
breakdown of haemoglobin leads to venous marbling and green discolouration of abdomen
active decay / black putrefaction
10 to 20 days after death
discolouration of skin - turns purple then black
tissues start to soften and liquefy
flesh looks creamy
loss of fluid and deflation of body
advanced decay
20 to 50 days after death
majority of internal tissue lost
body starts to dry out
dry remains
50 - 365 days after death
soft tissues lost leaving skin, bone and cartilage
autolysis
self-digestion of cells
starts 4 mins after death
when respiration stops, lysosomes release digestive enzymes which digest cell components
digestive enzymes secreted into gut
putrefaction
digestion of proteins and tissues by anaerobic bacteria
putrefaction in detail
as proteins are broken down, gases are produced and secreted by anaerobic bacteria ( which cause putrid odour)
gases diffuse to other parts of the body, leading to bloating of torso and then limbs
increased pressure weakens and separates tissues
factors that affect decomposition rate
weather
exposure
temperature
succession
insects arrive on a corpse in a predictable sequence based on the stage of decomposition
forensic entomology
study of insects and other small invertebrates in criminal investigations
fresh/initial decay entomology
0 to 3 days after death
anaerobic bacteria
blow flies arrive within minutes of death and lay eggs around wounds and body openings
24h later, eggs hatch and larvae (maggots) feed on body tissue
blating/putrefaction entomology
3 to 10 days after death
young blow fly larvae feed on body
other fly species (e.g. flesh flies) arrive
beetles (e.g. rove and carrion beetles) arrive and feed on fly eggs and larvae
active decay entomology
10 to 20 days after death
blow fly larvae are the dominant larvae
parasitoid wasps and scavenger flies arrive
beetles are the dominant adult insects present
advanced decay entomology
20 to 50 days after death
as body dries out, blow fly larvae are no longer able to eat tough tissue so migrate away
beetles remain - can chew through skin and ligaments
dry remains entomology
50 - 365 days after death
mites and moth larvae feed on hair until only bones left
how does a forensic entomologist determine time of death?
take samples of larvae
take temperature of environment
keep maggots to determine species
kill maggots to determine age
factors that affect succession of insects
location
temperature of surroundings
presence of drugs
circular DNA of bacteria
genetic code (not associated with proteins)
plasmid
small loop of DNA
food granules
glycogen granules, lipid droplets
mesosome
infolding of cell membrane, possible site of respiratopn
cell wall of bacteria
made of peptidoglycan (polypeptide + polysaccharide)
capsule
slime layer on surface for protection and to prevent dehydration
pili
thin protein tubes, allow bacteria to adhere to surfaces
flagellum
hollow cylindrical tail-like structure, rotates to move cell
bacterial cell wall structure
made of peptidoglycan - polysaccharides held together by oligopeptide crosslinks
Gram staining
crystal violet stain turns Gram-positive bacteria blue-violet
safarin turns Gram-negative bacteria pink
Gram-positive bacterial cell wall
thick layer of peptidoglycan
one cell membrane
Gram-negative bacterial cell wall
thin layer of peptidoglycan
cell membrane and another outer membrane
Gram positive bacteria
blue violet stain due to crystal violet
more susceptible to lysozyme and antibiotics
tend to live on skin
Gram negative bacteria
pink stain due to safranin
tend to live in wet areas because susceptible to drying out
how do bacteria reproduce?
asexual reproduction by binary fission
vertical gene transfer
how do bacteria cause illness?
endotoxins (in outer layer of Gram negative bacteria) cause vomiting, diarrhoea, fever
exotoxins (soluble proteins released by metabolism) have a toxic effect on cells, inhibit neurotransmitters
viruses
submicroscopic infectious agents that replicate inside living cells
general structure of viruses
0.002-0.3 micrometres
50x smaller than average bacteria
many morphologies
protein coat (capsid) made of repeating protein units (capsomeres)
genome (RNA or DNA, double or single stranded)
genetic material linear or circular
helical structure of viruses
e.g. tobacco mosaic
RNA bound to protein helix by interactions between negative RNA and positive proteins
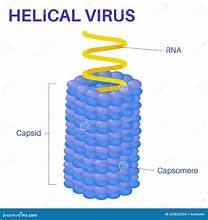
polyhedral virus structure
e.g. adenovirus

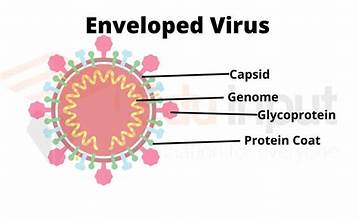
enveloped virus structure
e.g. influenza and COVID-19
surrounded by host cell membrane studded with viral proteins
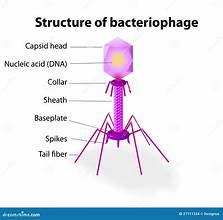
complex virus structure
e.g. bacteriophages
how do viruses cause illness?
destruction of host cell during lysis
hijack host cell’s protein synthesis so slow down host cell’s metabolism
produce toxins
methods of disease transmission
skin to skin
droplet infection
blood to blood
sexually transmitted
stool to mouth
maternal transmission
food borne
waterborne
animal borne
immune system
a host defence system comprising many biological structures and processes that protect against disease
humoral
molecules that circulate in the blood
cell mediated
cell to cell contact
non-specific (innate) immune system
non-antigen specific
immediate maximum response
no memory cells made
specific (adaptive) immune system
antigen specific
lag time between exposure and maximum response
memory cells are made following exposure
anatomical barriers to infection
mouth, nose and eyes - chemical lysozyme
skin - physical - keratin, chemical - sebum, biological - microbiome
ears chemical - earwax
airways - ciliated cells
stomach - stomach acid
gut - microbiome
vagina - acidic secretions
anatomical immunity of non-specific IS
physical factors
chemical factors
biological factors
humoral components of non-specific IS
complement
cytokines
coagulation
cell-mediated components of non-specific IS
phagocytosis
inflammation
how does lysozyme work?
hydrolyses bonds in peptidoglycan which causes lysing of bacterial cells due to osmotic shock
complement system
enhances the ability of antibodies and phagocytic calls to clear microbes and damaged cells from an organism - circulate in blood as precursors
examples of the complement system
lysis - bind to and lyse target cells
chemotaxis - attraction of phagocytes to sites of infection
opsonisation - opsonise (mark) bacteria for digestion by phagocytes
inflammation - stimulate mast cells to release histamine
cytokines
small proteins that initiate changes in gene expression
interferon
cytokine
produced by virus infected cells
induces virus resistance in uninfected cells
mast cells and histamine in inflammation
mast cells release histamine in response to a bacterial infection leading to inflammation
vasodilation —> increased blood supply (redness and heat)
increased vascular permeability (endothelial cells contract) —> swelling (oedema) and pain
more white blood cells arrive to clear bacteria
phagocytosis
engulf and digest bacteria
phagocytic cells
neutrophils
monocytes and macrophages
neutrophils
multilobed nucleus
70% of leucocytes
produce free radicals to break down bacterial DNA and proteins
activate specific IS