Chapter 2: Ozone Hole
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
1 DU is ___mm
0.01mm
1 atm = _____Pa pressure
101325 Pa
What is the size and location of the ozone hole?
220 DU or lower, Antarctica region
The active forms of chlorine related to the ozone hole are __ and __
Cl and CLO
the inactive forms of chlorine are __ and ____
HCl and ClONO2
each chlorine atom destroys about __ ozone molecules per day during the ____
50, sping
chemical reactions that lead ultimately to zone destruction occur in a thin aqueous layer present at the surface of _______ (PSC) in the form of ___ crystals
polar stratospheric clouds, ice
Write the reaction for gaseous chlorine nitrate (ClONO2) with water to produce hypochlorous acid and HNO3
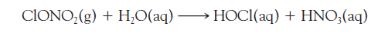
In the aqueous layer, gaseous hydrogen chloride dissolves and forms ions. Write this reaction
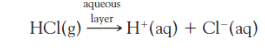
write the first route of how molecular chlorine can be produced:
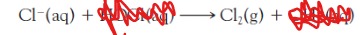
HOCl (aq), OH-
write the second route of how molecular chlorine, Cl2 can be produced
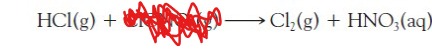
ClONO2 (g)
most of the ozone hole destruction occurs via mechanism ____
II
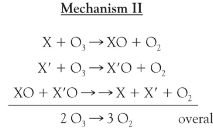
Question: A minor route for ozone destruction in the ozone hole involves Mechanism II with bromine as X and chlorine as X ́ (or vice-versa). The ClO and BrO free radical molecules produced in these processes then collide with each other and rearrange their atoms to eventually yield O2 and atomic chlorine and bromine. Write out the mechanism for this process and add up the steps to determine the overall reaction.
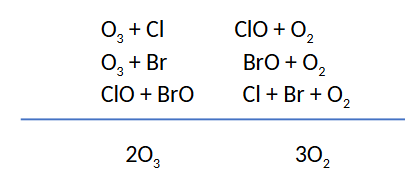
The next four card will be about why Mechanism I does not cause ozone hole destruction because it requires ____ oxygen, without a ____ concentration of ____ oxygen, ____(O3) cannot be destroyed.
atomic, high, ozone
in the region where the polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs) form and ____ is activated, the concentration of ___ oxygen atoms is small
chlorine, free
Few atoms are produced there on account of the scarcity of ___ light that is required to dissociate O2
UV-C
also, any atomic oxygen atoms produced in this way immediately collide with the ___ O2 molecules to form ozone, O3
abundant
CFCs, HFCs, HCFCs, HBFCs and Halons cause _____
ozone destruction
what is the CFC code of CCl2F2?

what is the CFC code for C2Cl3F3

deduce the code numbers for CH3CCl3

To find the chemical formula given the number/code, first add __ to the abc number, to obtain a 3-digit def number, where d is the # of __ atoms, e is the number of __ atoms, and f is the number of __ atoms
the formula for the number of Cl atoms is?

What is the chemical formula for CFC-11?

What is the chemical formula of CFC-12?

Halons are ____carbons, not hydrofluorocarbons, which means no ___ atoms and at least one __ atom
fluorocarbons, hydrogens, bromine
What is the Halon nomenclature for C2F4Br2?

The increase in stratospheric chlorine is due to the use and release of _____ carbons, which are compounds that contain ___, ___, and ___ which are commonly called CFCs
chlorofluorocarbons, chlorine, fluorine, and carbon
CFCs have no ____ sink, so all molecules of them eventually rise to the ____
tropospheric sink, stratosphere
CFC molecules eventually migrate to the ___ and ___ parts of the stratosphere where the UV-C light _____ decomposes them, thereby releasing ___ atoms.
middle and upper, photochemically, chlorine
CFCs do not absorb sunlight with wavelengths greater than ___ nm, and generally require ___ nm or less for photolysis
290, 220
CFCs must rise to the mid-___ before decomposing since ___ light does not penetrate to lower altitudes
stratosphere, UV-C
At what chlorine level does the Antarctic ozone hole appear?
3 ppb
What are the favorable characteristics of CFC
nontoxic, nonreactive, nonflammable
Which UV light is required to photolysis of CFC?
UV-C light
Explain why stratospheric bromine destroys more ozone than chlorine.
Bromine remains in the radical forms Br and BrO, since the inactive forms HBr and BrONO2 are efficiently decomposed photochemically by sunlight
The action of chlorine reduced Antarctica ozone by about ____%
50%
Temperate zone encompasses between the ____ zones and the ___ zones.
tropical, polar
The size of the ozone hole is comparable with _____.
north america