Kisner Chapter 10
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Overstretching, overexertion, overuse of soft tissue
Strain
This term is frequently used to refer specifically to some degree of disruption of the musculotendinous unit
Strain
Severe stress, stretch, or tear of soft tissues, such as joint capsule, ligament, tendon, or muscle
This term is frequently used to refer specifically to injury of a ligament
Sprain
True or False:
A sprain is less severe than a strain
False:
Other way around
True or False:
An incomplete or partial dislocation of the boney partners is called dislocation
False:
Subluxation ung sagot
True or False:
Displacement of a part, usually the boney partners in a joint, resulting in loss of the anatomical relationship is called dislocation
True
True or False:
If a rupture or tear is complete, pain is experienced in the region of the breach when the muscle is stretched or when it contracts
False:
Incomplete or partial lng may pain, walang pain complete
the general term that refers to chronic tendon pathology
Tendinopathy
inflammation of the synovial membrane covering a tendon
Tenosynovitis
inflammation of a tendon
Tendinitis
inflammation with thickening of a tendon sheath
Tenovaginitis
degeneration of the tendon due to repetitive microtrauma.
Tendinosis
True or False:
In tendinitis there may be resulting scarring or calcium deposits
True
Inflammation of a synovial membrane; an excess of normal synovial fluid in a joint or tendon sheath.
Synovitis
Bleeding into a joint, usually due to severe trauma
Hemarthrosis
Ballooning of a wall of a joint capsule or tendon sheath, arises due to trauma or RA
Ganglion
Bruising from a direct blow, resulting in capillary rupture, bleeding, edema, and inflammatory response
Contusion
Cumulative trauma disorders, repetitive strain injury
Overuse syndrome
Loss of function of a tissue or region.
Dysfunction
Mechanical loss of normal joint play in synovial joints, commonly causes loss of function and pain
Joint dysfuction
Adaptive shortening of skin, fascia, muscle, or a joint capsule that prevents normal mobility or flexibility of that structure
Contracture
Abnormal adherence of collagen fibers to surrounding structured during immobilization
Adhesions
Prolonged contraction of a muscle response to painful stimulus.
Reflex muscle guarding
Prolonged contraction of a muscle in response to the local circulatory and metabolic changes that occur when a muscle is in a continued state of contraction
Intrinsic muscle spasm
A decrease in strength of muscle contraction. May be the result of a systemic chemical or local lesion of a nerve of the central, peripheral or neuromuscular junction
Muscle weakness
Increased interstitial pressure in a closed nonexpanding myofascial compartment that compromises the function of the blood vessels muscles and nerves .
Myofascial compartment syndrome
If myofascial compatment syndrome is not given intervention it can result in what?
Ischemia and Irreversible muscle loss
Identify Which Grade of severity of tissue injury:
Near-complete or complete tear or avulsion of the tissue (tendon or ligament) with severe pain
Mild pain at the time of injury or within the first 24 hours
Moderate pain that requires stopping the activity
Identify Which Grade of severity of tissue injury:
Grade 3
Grade 1
Grade 2
True or False:
Mild swelling, local tenderness, and pain occur when the tissue is stressed in a Grade 1 tissue injury
True
True or False:
When the injury is to ligaments, some of the fibers are torn, resulting in some increased joint mobility in a Grade 1 tissue injury
False:
Grade 2 dapat
True or False:
In a grade 2 tissue injury palpation may reveal a defect. A torn ligament results in instability of the joint.
False:
Palpation identifying a defect only observed in grade 3 injuries
Enumerate the signs of inflammation:
swelling
redness
heat
pain at rest
loss of function
True or False:
In the acute phase when testing for ROM movement is painful and the patient usually guards against the motion before completion of the range is possible
True
How long does the acute stage last?
4 to 6 days
Read this table I think its important
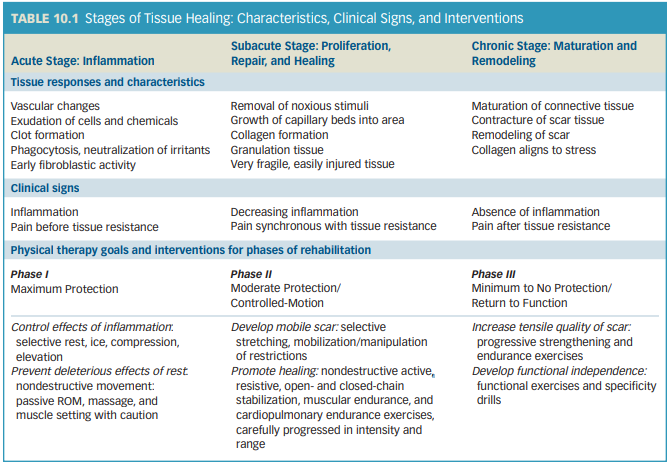
During this phase testing ROM, the patient may experience pain synchronous with encountering tissue resistance at the end of the available ROM.
Which phase of tissue healing is described?
Subacute Stage
Pain occurs only when the newly developing tissue is stressed beyond its tolerance or when tight tissue is stressed
What can we expect when performing MMT during the subacute phase?
Muscles may be weak or have limited function
How long does the subacute phase usually last?
10-17 days
14-21 days after onset of injury
How long does the subacute phase last in tissues with limited circulation (i.e tendons)
6 weeks
True or False:
During the chronic stage, connective tissue continues to strengthen and remodel in responses to stresses applied to it.
True
How long does the chronic stage last?
6 months to 1 year
This is a state of prolonged inflammation when the injured tissue is beyond its ability to repair.
Chronic inflammation
True or False:
In chronic inflammation, there are symptoms of increased pain, swelling and muscle guarding that last more than several hours after activity
True
True or False:
In chronic inflammation, there is increased feelings of stiffness after rest, loss of ROM 12 hours after activity, and progressively greater stiffness of the tissue as long as the irritation persists.
False:
Loss of ROM 24 hours after activity
During the first 48 hours after insult to soft tissue, __________ changes predominate.
Vascular changes
Refer to Box 10.1 for the management guidelines during the acute phase:
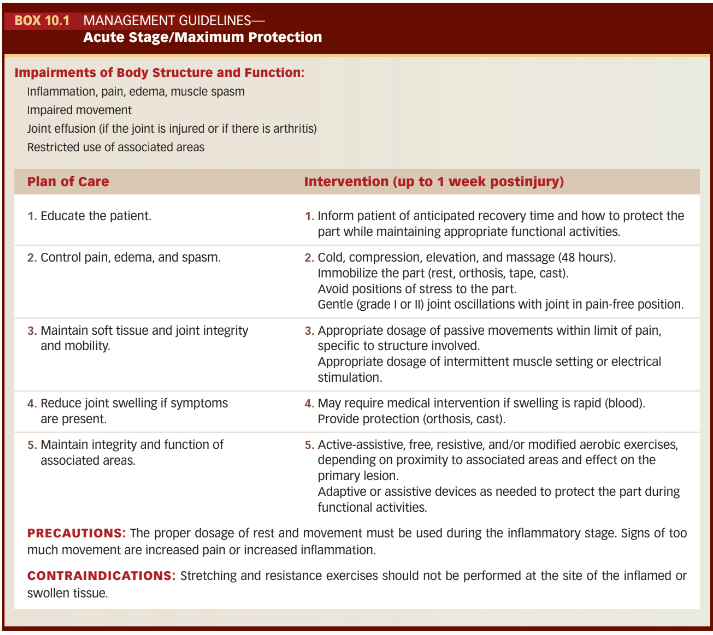
To minimize the musculoskeletal pain and promote healing, protection of the part affected is necessary during the first __________ hours
24-48 hours
True or False:
To influence the development of an organized scar, begin treatment during the acute stage, when tolerated, with carefully controlled active movements.
False:
Passive movements not active
These types of movements are directed to the structure involved to prevent abnormal adherence of the developing fibrils to surrounding tissue to avoid future disruption of the scar.
Tissue-specific movement
True or False:
The intensity of the movement should be gentile enough so the fibrils are not detached from the site of healing
True
True or False:
Active movement is contraindicated in neighboring regions of the injured area.
False:
Active movement is appropriate in neighboring regions to maintain integrity in uninjured tissue and to aid in circulation and lymphatic flow
True or False:
Stretching is contraindicated during the acute phase
True
Which grades of joint mobilization are beneficial during the acute stage?
Grades 1 and 2
Gentle isometric muscle contractions performed intermittently and at a very low intensity so as not to cause pain or joint compression is called what?
Muscle Setting
True or False:
Massages can be applied to the injured tissue during the acute phase
True
When treating tendinous lesions with massage, a gentle dosage is applied ________ to the fibers to smooth roughened surfaces or to maintain mobility of the tendon in its sheath.
Transverse to the fibers
When applying massage to a tendon should it be kept taut or slack?
taut
When treating muscle lesions with massage, is the muscle kept in shortened or lengthened position?
shortened
Interventions for associated areas
ROM, Resistance exercises and Functional activities
Fibroblasts are present in tremendous numbers by which day during the injury
Fourth Day
Continues to be large in number until the 21st day
Myofibroblastic activity which causes scar shrinkage begins at which day
5th day
Wound closure in muscles and skin usually takes how long?
5-8 days
Wound closure in tendons and ligaments take how long?
3 to 6 weeks
Refer to box 10.2 for management guidelines during the subacute phase

Signs of excessive stress with exercise or activities (for patient education)

There is a predominance of fibroblasts that are easily remodeled from day ______ to day _____
Day 21 to 60
Healing with progressively increasing tensile quality in the injured tissue may continue for how long?
12 to 18 months
Immature collagen molecules can be easily remodeled with gentle and persistent treatment until how many weeks pass”?
10 weeks
At how many weeks does the scar become unresponsive to remodeling?
14 weeks
Refer to box 10.4 for management guidelines of the chronic stage
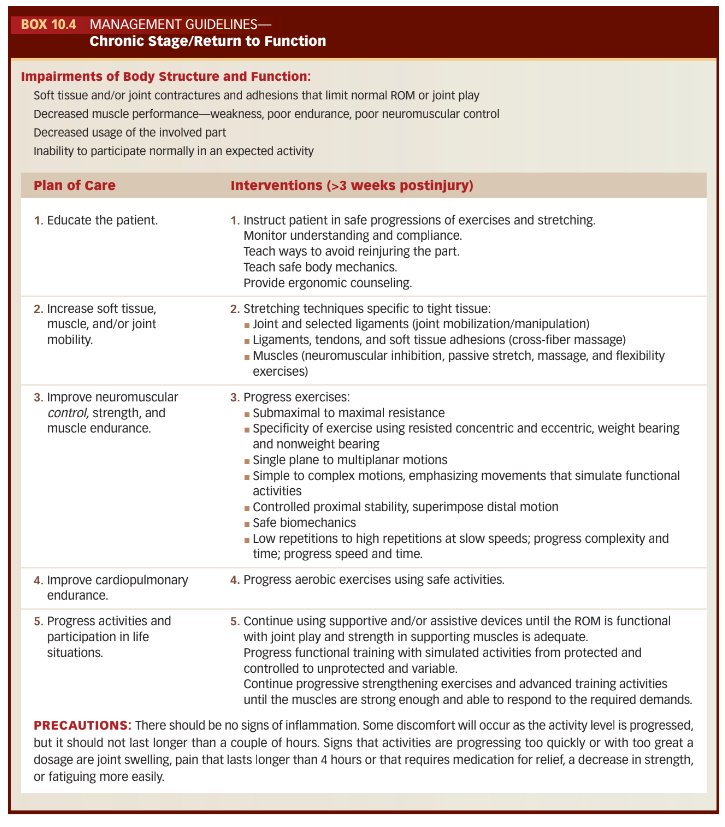
A muscle grade of what is required for discontinuation of the use of ambulatory devices?
Grade 4/5
True or False:
We can progress the intensity of stretching so long as no signs of increased irritation persist beyond 12 hours
False:
24 hours not 12
True or False:
We treat chronic inflammation the same as an acute condition.
True
Refer to box 10.5 for management guidelines for chronic inflammation
