Bio Chapter 6 -- Exam 2
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
anchored membrane proteins
Proteins that are covalently attached to fatty acids or toher lipid groups. Held in associatin with the membrane.
fluid mosaic model
The model describing cell membranes as a fluid bilayer of phospholipids with embedded proteins, mosaic because it is made up of many different types of moecules, and fluid because the components can move freely.
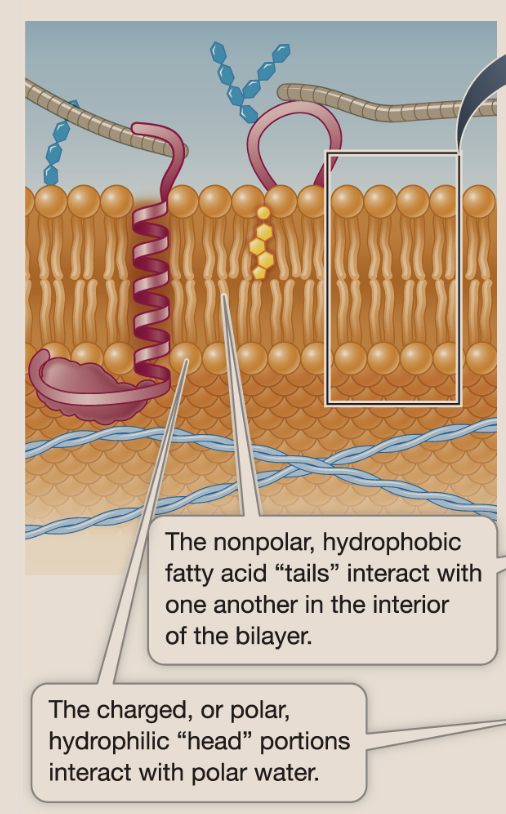
glycolipid
A carbohydrate covenlently bonded to a lipid. The carbohydrate serves as the recognition signal for the interactinos between cells.
glycoprotein
one or more short carbohydrate chains covalently bonded to a protein. The bound carbs are oligosaccharides —often function in cell recognition and adhesion.
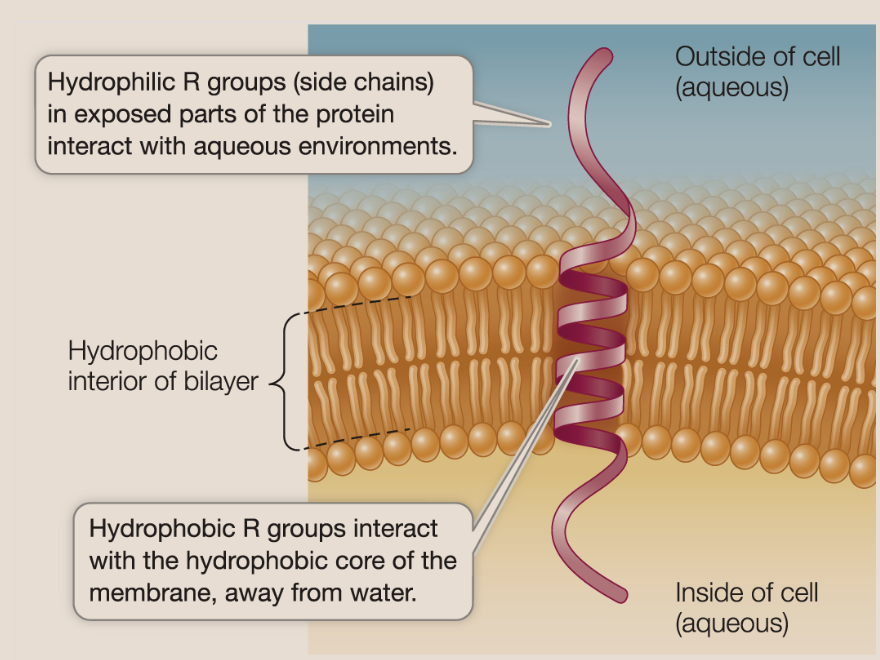
integral membrane proteins
Proteins that are at least partly embedded within the lipid bilayer and often span the entire membrane — must have hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions
—
peripheral membrane proteins
Proteins that are loosely associated with the membrane surface and can be easily removed. They lack the hydrophobic groups and are not embedded. They just interact with the heads of the membrane proteins.
phospholipids
The primary structural components of cell membranes consist of a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails. Heads are the external portion of the membrane, while the nonpolar fatty acid tails make up the middle.
lipid bilayer — two rows of phospholipids
the saturated chains allows closer packing of the tails, but the unsaturated fatty acis make for a less dense, more fluid packing
transmembrane domains
the domains of the transmembrane protein that extends through the bilayer
transmembrane protein
An integral protein that extends all the way through the phospholipid bilayer and protrudes on both sides.
cell adhesion
one ways that cells arrage themselves in grousp — The binding of cells to other cells or to the extracellular matrix — the connection between the two cells is strengthened
This occurs only through the interactions between the carbohydrates that are parts of glycolipids and glycoproteins
cell junctions
Specialized structures that connect adjacent cells and allow communication or adhesion
cell recognition
one of the two ways cells arrenge themselves — one cell recognizes and binds to antoher cell of a certain type
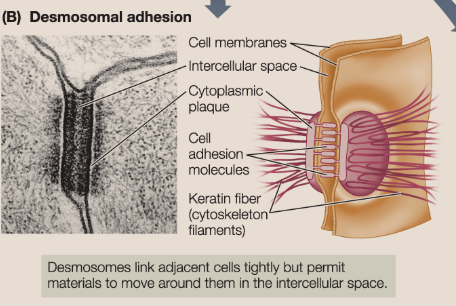
Desmosomes
act to hold neighboring cells firmly together — acting like spot welds or rivets.
Materials can still move around unlike the tight junctions, but it provides mechanical stability for tissues like skin.
gap junctions
Channels that run between membrane pores in adjacent cells, allowing substances to pass inbetween cells. Examples are muccles and the rapid transport of ions required to fire them.
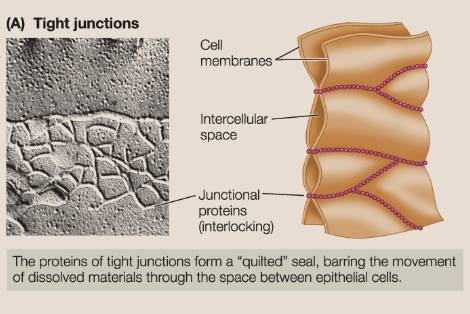
tight junctions
Sealing junctions prevent material from passing between cells. They also maintain distinct faces of a cell within a tissue by restricting the migration of membrane proteins over the cell surface from one face to another
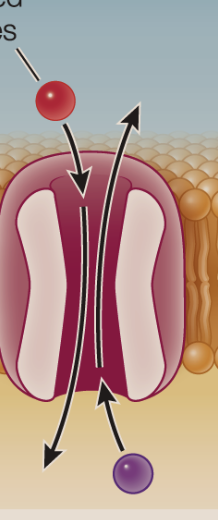
active transport
The movement of substances across membranes against their concentration gradient using energy — driven by energy
aquaporins
Specialized channel proteins that facilitate the rapid transport of water across membranes
carrier proteins
Transport proteins that undergo conformational changes to move specific substances across membranes — bind sith substances and speed up their diffusion across the bilayer
channel proteins
Transport proteins that form channels along the membrane that allows specific ions or molecules to pass through membranes. Think tunnels where only one thing can pass.
concentration gradient
The difference in concentration of a substance across a space or membrane
diffusion
The passive movement of molecules from areas of high concentration to low concentration — toward a state of equilibrium
facilitated diffusion
Passive transport of molecules across membranes with the help of channel or carrier proteins
hypertonic
a hypertonic solution has a higher concentration of solutes compared to another solution
hypotonic
a hypotonic solution has a lower concentration of solutes compared to another solution
ion channels
Membrane proteins that allow specific ions to pass through the membrane — often gated, opening either in response to ligand, light or voltage
isotonic
Having the same concentration of solutes as another solution
ligand
A molecule that binds specifically to a receptor or other protein
osmosis
The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane — passive process with no energy use
passive transport
The movement of substances across membranes without the input of cellular energy
selective permeability
The property of membranes that allows some substances to pass while blocking others. Specific proteins on the membrane can also act to increase or decrease the permebility of the membrane.
antiporter
A transport protein that moves two different ions or molecules in opposite directions, one into the cell and one out of the cell
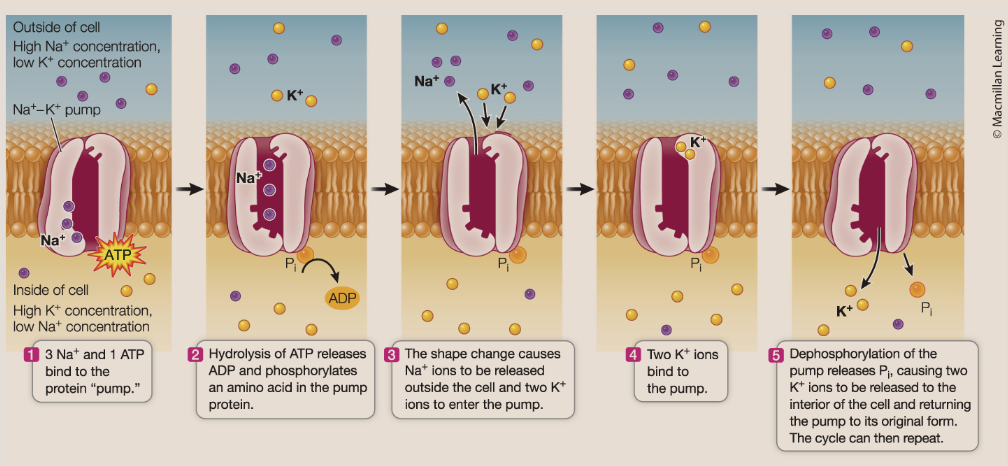
sodium–potassium (Na+−K+) pump
An active transport protein that maintains concentration gradients by pumping Na+ out and K+ into cells — this is an integral membrance glycoprotein. Thsi is a from of primary active transport— also an antiporter
symporter
A active transport protein that moves two different substances in the same direction across a membrane
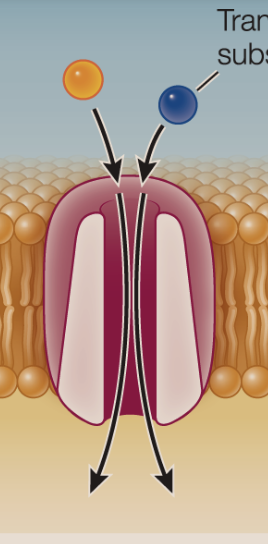
uniporter
A active transport protein that moves only one type of ion or molecule across a membrane in one direction.
phagocytosis
The process by which cells engulf large particles or other cells — used by white blood cells to eat viruses. The food vacule that forms or phagosome usually fuses with a lysosome, so the contents can be properly digested
pinocytosis
The process by which cells take in small droplets of extracellular fluid by membrane invagination — vesicles still frm, however they are smaller and the process operates to bring fluids and dissolved substances into the cell.
receptor-mediated endocytosis
A selective form of endocytosis where specific molecules bind to receptors on the cell surface triggering the process of endocytosis to engulf.
—the recpetor proteins here are often coated pits that create slight depressions that form into a coated vesicle of the ligand and receptors. From here it goes to fuse with a lysosome and start digestion.
receptor proteins
Membrane proteins that bind to specific signaling molecules and initiate cellular responses
phospholipid bilayer
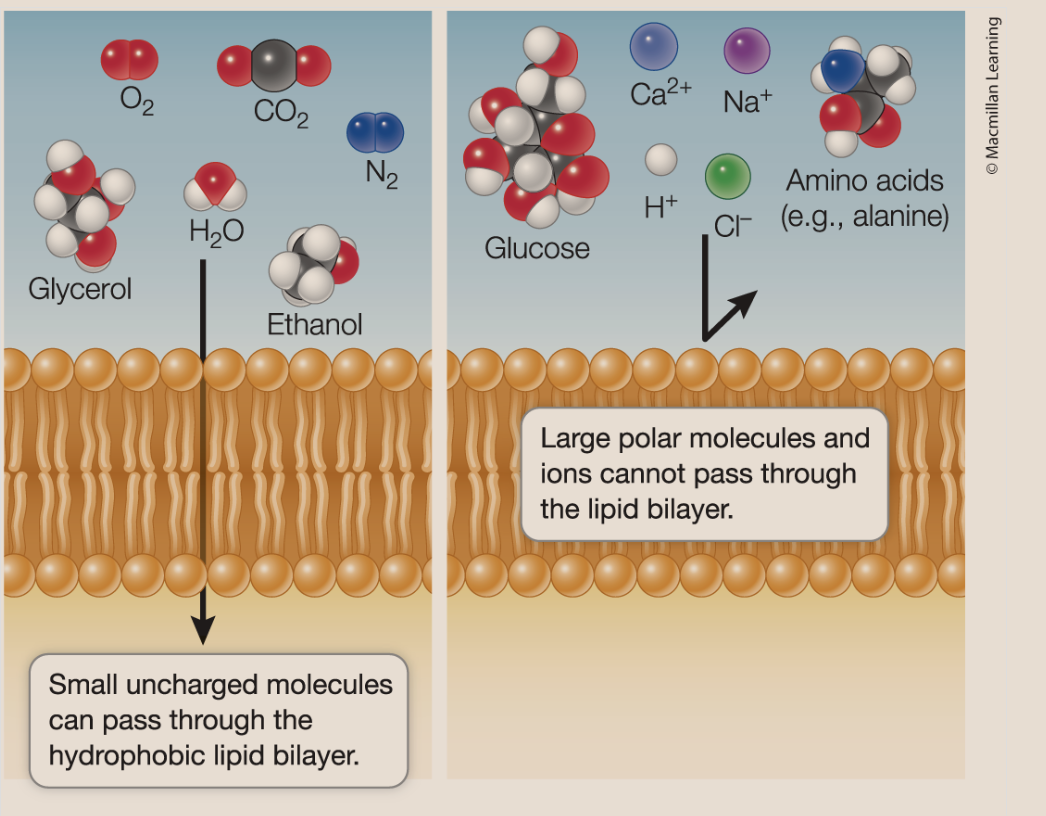
lipids establish the integrity of the membrane —create a barrier of phospholipids the oppose the rapid transport og hydrophilic materials like polar molceules and ions
— serves as a “lake” where transmembrane proteins float
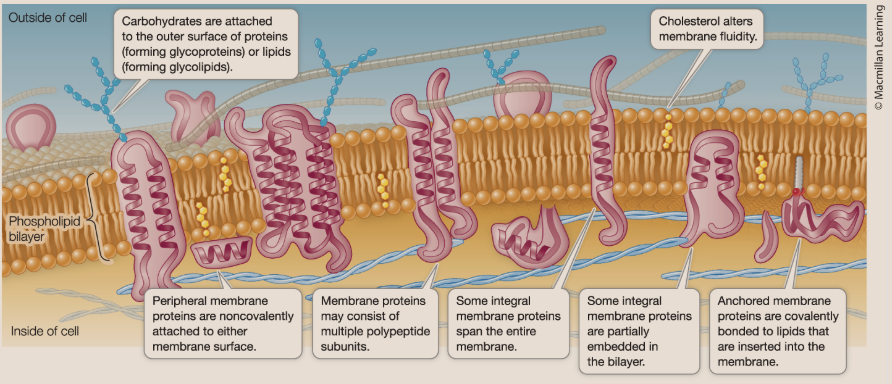
Importance of Cholesterol
Cholesterol moduates the membrane fluidity—the hydroxyl end of the cholesterol interacts with the polar heads and the nonpolar rings of the hydrocarbon chain exist in the interior — imbeded
fluidity is essential for lateral and vertical movement across the celular membrane
factors affecting membrane fluidity
Lipid Composition— Cholesterol and long chain, saturated fatty acids pack tightly— the more cholesterol the more fluid, the less cholesterol, the less fluid
Temperature— molecules move more slowely and fluidity decreases at reduced temperatures — so some animals or organisms change the lipid composition by replacing saturated bilayers with shorted unsaturated bilayers.
The three types of membrane Proteins
Integral proteins, peripheral proteins, and achored proteins
homotypic vs. heterotypic
describes the binding of cells — either the same molecule sticks out of both cells which fit together and bind to one another (Homo)
or different molecules bind together on different cells (hetero) — which is caused by an affinity on the groups of the molecules.
the three types of cell junctions the connect adjacent cells
Tight Junctions
Desmosomes
Gap Junctions
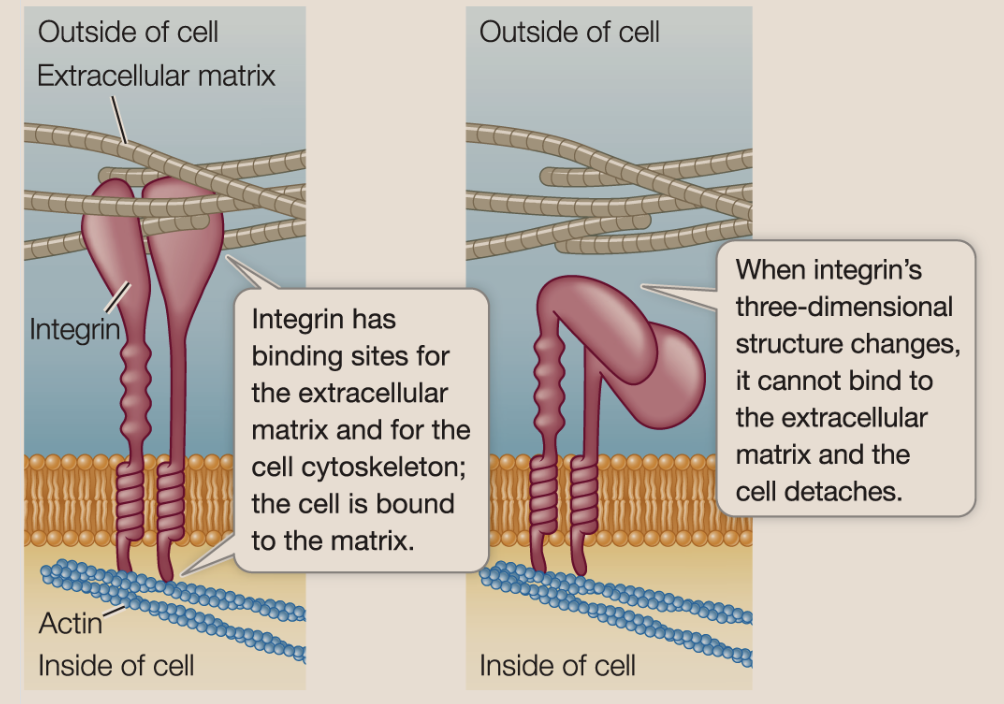
integrin
A transmembrane protein that often mediates the attachment of the cell to the extracellular matrix. The protein can be activated or deactivated to promote stability and movement. The binding between the protein and the extracellular matrix is noncovalent and reversible
simple diffusion
smal molceules pass through the phospholipid bilayer — if a molcule is small a
nd hydrophobic, it can pass
gated ion channel
a channel protein that opens when a stimulus causes a change in the 3D shape of the channel. — usually from the stimulus of a binding chemical signal (ligand )
active transport
movement of molecules or ions against a gradient using an input of energy —usually ATP
works wither through a uniporter, symporter, or antiporter
active transport is directional — only happens one way
primary vs. secondary active transport
primary — involves the direct hydrolysis of ATP — provides the energy for transport
secondary — does not use ATP directly, but instead uses an ion concentraion gradient established by primary active transport to work
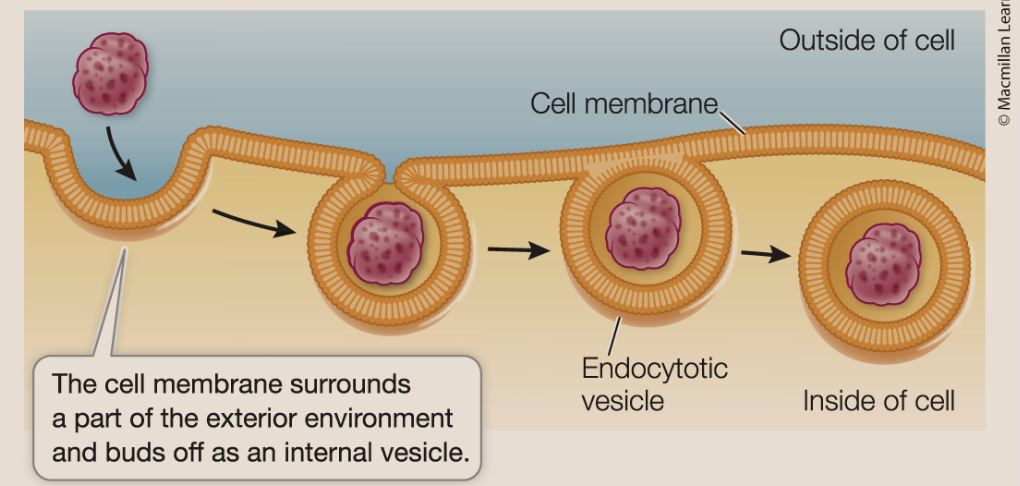
Endocytosis
term for a group of processes that bring small molecules, macromolecules, and large particles, and even small cells, into the eukaryotic cell.
3 types: phagocytosis, pinocytosis, and receptor mediated endocytosis
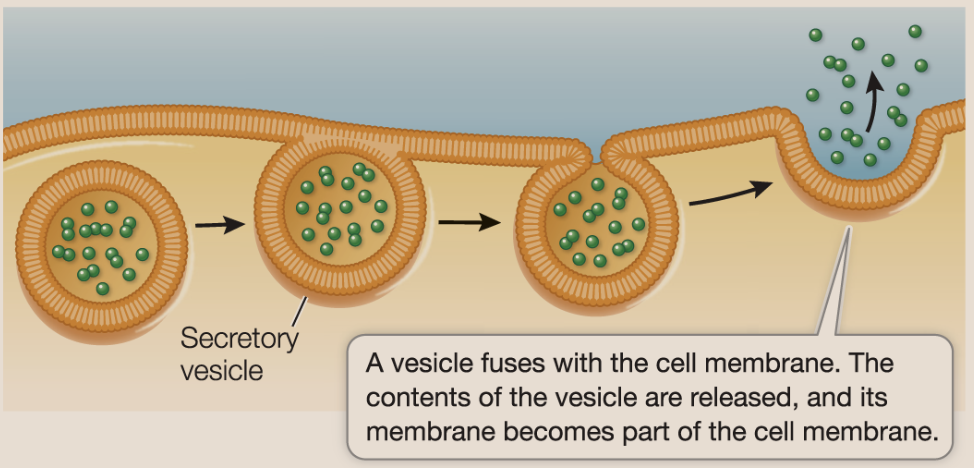
Exocytosis
process by which materials or waste packaged in vesicles are secreted in the extracellular space. This is dont pretty much in a reverse to endocytosis.