BIS183 Lecture 15 - Protein-Protein Interactions I
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Why are we interested in protein-protein interactions?
Protein complexes (multiple working together)
transcription factors
Enzyme complexes
Sense of how the proteome is organized
Receptor-ligand pairs
Yeast Two Hybrid Methodology
Two hybrid proteins - takes advantage of TF modularity
DNA Binding Domain
Activating Domain
Bait
Protein of interest + GAL4 DBD
Prey
Protein Y + GAL4 AD
Introduce Bait and prey
Look for expression of reporters
HIS3 - Helps grow on media lacking HIS3
LACZ - turns blue in presence of LAC Z substrate
What does autoactivation look like in Y2H assay?
BAIT alone (Protein of interest +DBD) is sufficient to drive trxn of a reporter
due to Yeast protein + AD complex interactions
BAD → if bait strain results in autoactivation, cannot be used
What are the 4 different results possible for Y2H Assay
1) Reporter construct alone
HIS3 - no growth
LACZ - white
2) Bait alone
HIS3 - no growth
LACZ - white
3) Bait + Prey - Interact
HIS3 - no growth
LACZ - white
4) Bait + Prey - DON’T interact
no growth
white
Describe the Permissive and Binary aspects of Y2H
Permissive
Grows yeast on media containing HIS (media regularly DOESN’T contain HIS) → lets yeast survive and Bait + prey successfully introduced for yeast
Binary
Only test interaction between one protein and another protein
Can’t test more than two at once
How can “Guilt by Association” be used to infer protein function in Y2H Assay?
Look at the trxn of associated proteins
Guilt by Association
proteins interact with each other
in clustering methods → look at similar transcripts
Proteins that interact with each other may have similar function in the body
Quesitons regarding the validation of networks and Overalp between two studies
How much overlap do you think there was between these studies?
Look at the overlap between bait and prey in studies
17% overlap
How do you determine what a “true” or real interaction is?
Must determine if interactions occur in vivo or in cell
What do you think the best way is to biologically validate a protein-protein interaction in a study? 6 things
1) Literature (previous reports)
2) MIPS - Munich Infor center for Genes and Protein
3) Mine available transcription datasets is protein transcripts found in same time + place
4) If proteins are found in the same cells (AD or Tag proteins)
5) Determine if proteins physically interact → Affinity Purification
6) Function → genetics
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the Y2H Assay
Advantages
Sensitivity
overproduction of proteins in yeast
Detects weaks interactions
Flexibility
Large number of variable inserts can be examined at once
Disadvantages
Labor and material intensive
Array based Y2H - need efficient elaborate pooling and deconvolution schemes
False positive (in assay, but not in vivo), false negative (not in assay, but in vivo)
Exmaples of False negatives in Y2H
Real interactions are missed
Failures in nuclear localization
Membrane proteins and secretory proteins not amenable to system
Autoactivation
Improper folding
Missing cofactors
Missing post-translational modifications
Differences in vector systems
Examples fo False Positives in Y2H
Non-relevant interaction - overexpression
Autoactivation
Describe the steps for Tandem Affinity Purification
Purpose: to extract on the Protein of interest, IP-based purification tech to study P=P interactions
1) Bait protein
Creates complex containing:
Protein
CaBP - Cal modulin binding protein (binds CA²+)
TEV Cleavage Site Protease (Enable cleavage by TEV protease)
Protein A (Able to be recognized by Igv beads)
2) Introduce construct into cells
In vitro - translate protein _incubate protein with a protein cocktail from lysed cells
3) Bait protein forms complex with other cellular protein
Identify other protein so your bait interacts with (advantage - proteins are found within one complex)
4) Cell extract, pass over column with IgG beads
5) Cleave complex with TEV protease
Very pure (two tandem purifications)
reduced chance of pulling down non-specific proteins
6) Trypsin digestion of protein complex - break protein to small pieces
7) Mass spectrometry analysis - ID the proteins, list of proteins with which your bait has complexed
COMPLEX; in vivo interactions
Help us better understand the proteome
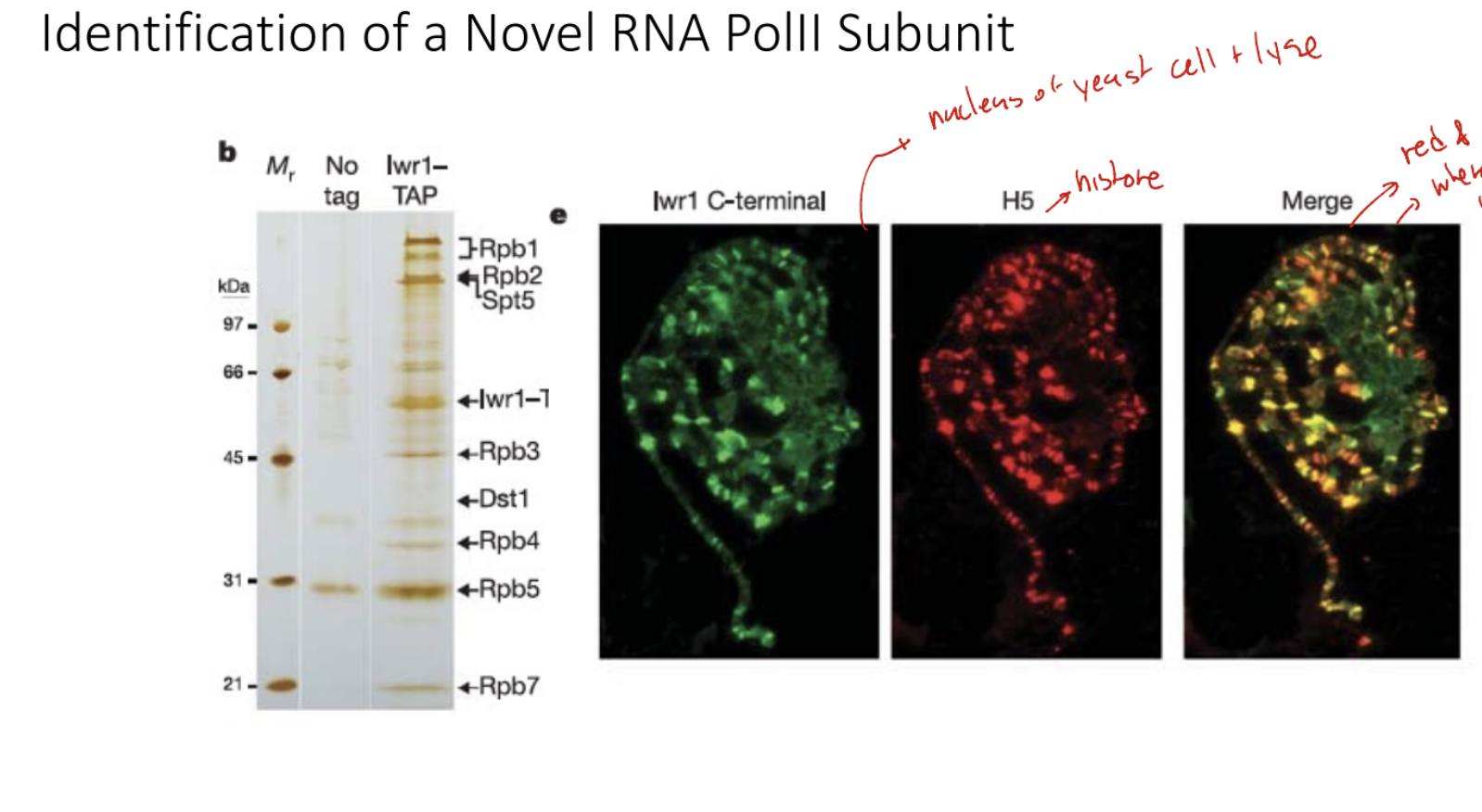
Describe the Identification of Novel RNA Pol II Subunit
Top row - Tagged subunit protein with TAP
Column (y-axis) - proteins that interact with IWR protein
Rpb → RNA polymerase binding