Exam II - Depth Perception
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Depth perception
the ability to appreciate depth in visual space. The visual ability to perceive the world in 3D. Mostly binocular, but can be monocular if there are depth cues present.
Pictorial depth cues
depth cues such as relative size, linear perspective, and texture that can be presented in 2D representation such as a photograph or painting. Allows for monocular depth perception.
Relative size
an important depth cue when viewing a scene that includes objects whose size can be compared to each other.

Size constancy
pictorial depth cue involving judging an objects distance based on its typical size. Ie) a plane in the sky is seen as far away because we know planes are typically large.
Linear perspective
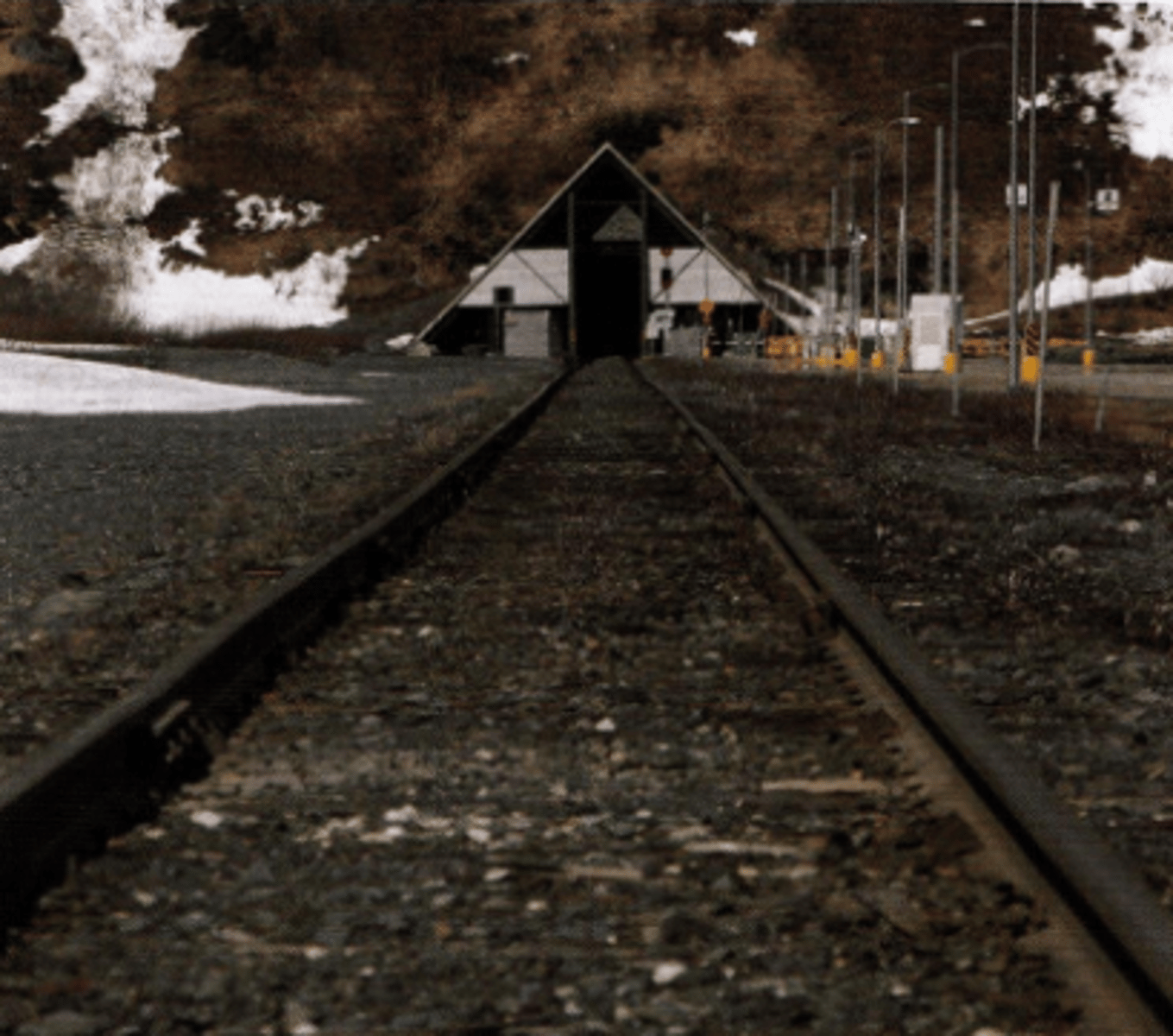
pictorial depth cue where the retinal image size of a linear object creates a perception of depth. Ie) railroad track has a smaller retinal image size in the background than the foreground

Texture gradient
pictorial depth cue where densely packed object produce smaller retinal image sizes and are perceived as more distant. Ie) distant bricks appear more densely packed than bricks in the foreground
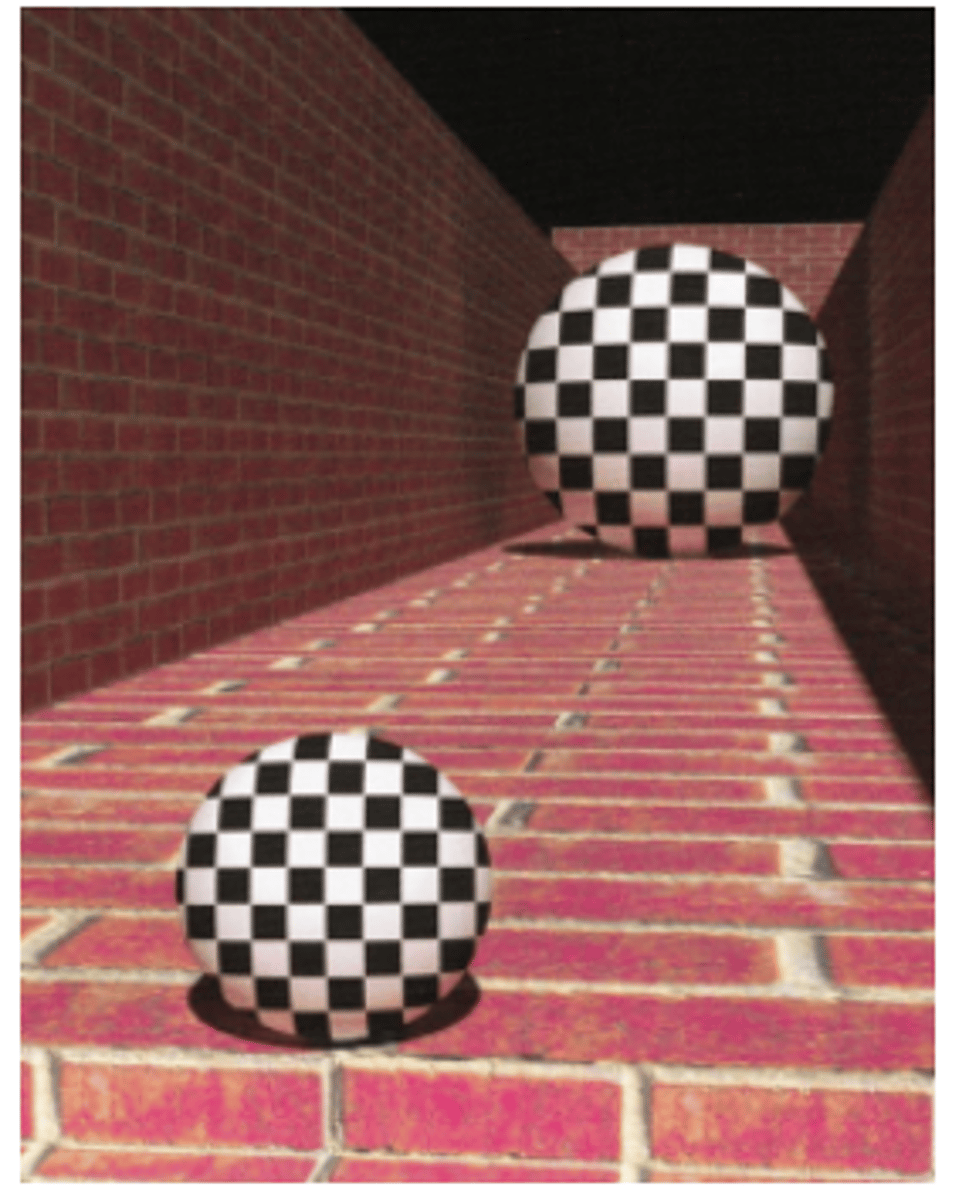
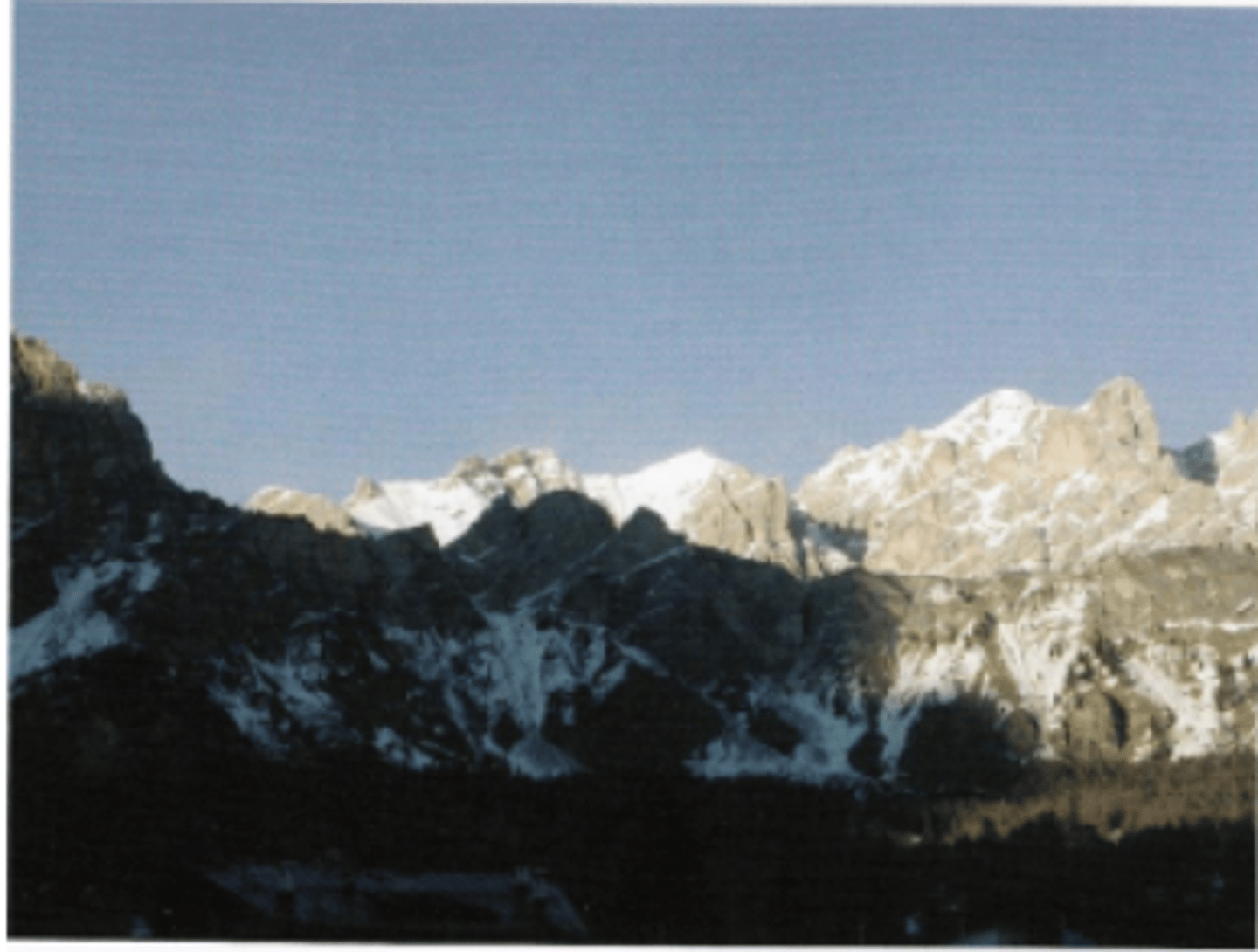
Interposition
pictorial depth cue that occurs when the view of a scene is partially obstructed. Objects overlying other objects in a scene are viewed as being closer. Ie) house in front of the mountains.

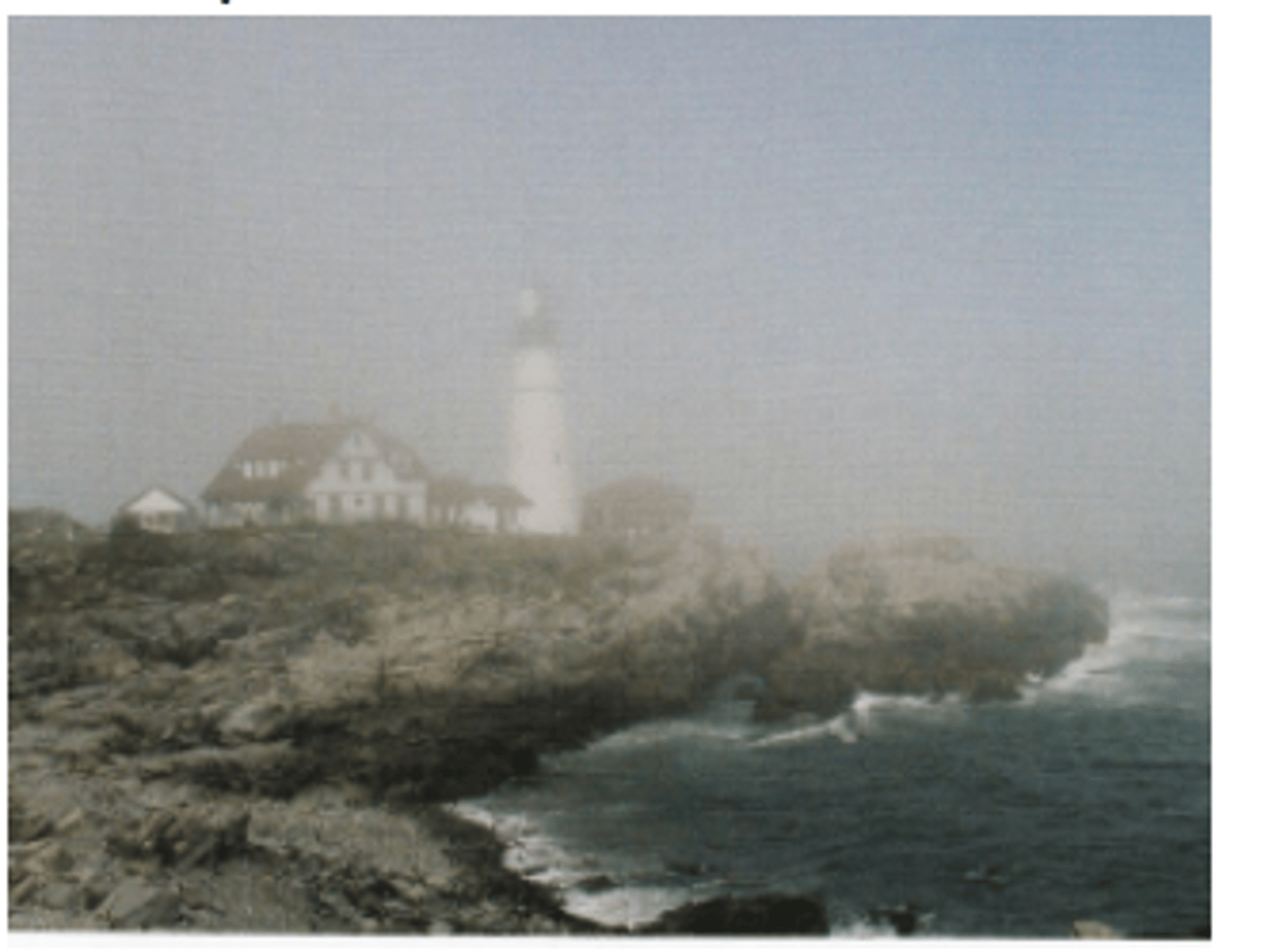
Clarity (ariel perspective)
pictorial depth cue where unobstructed objects, objects with more clarity, in photographs appear as closer than those obscured by haze.

Shading
pictorial depth cue where shadow is interpreted as falling behind the object creating a sense of depth.

Kinetic depth effect
the illusion that a 2 dimension object has dimension when moving. Occurs due to looming
Looming
rapid expansion or shrinking in the size of a given image that is responsible for the kinetic depth effect.
Angular declination below the horizon
the angle formed by an object with the horizon making the observer able to judge distance without pictorial depth cues.
Motion parallax
a kinetic molecular depth cue that results when a moving observer fixates on an object while noticing the relative motion of surrounding object. This provides information regarding the relative distance of these objects.
MTV5
area of the brain shown to encode motion parallax by processing binocular disparity and motion
against, with
Motion parallax is used to determine the distance of objects while performing monocular ophthalmoscopy. Objects that are closer than the fixation point it will show _______ motion, if the object is further than the fixation point it will show ____ motion.
weak cue
Accommodation is a _____ to depth perception.
Stereopsis
the perception of depth that is produce by retinal disparity. An important contributor to depth perception at near distance, but is less important for viewing far objects.
Uncrossed disparity
images form nasal to the foveas signaling that an object is farther than fixation.
Crossed disparity
images form temporal to the foveas signaling that an object is closer than fixation.
diplopia
Retinal disparity that is too large to all for fusion will result in...
Perceptual constancy
the tendency to see familiar objects as having standard shape, size, color, or location regardless of changes in the angel of perspective, distance, or lighting.
Size illusion
occurs when judgments of distance are erroneous, such as viewing a flat picture, and size constancy fails.
Emmert's law
the perceived size of an object producing a retinal image of a give fixed size is proportional to its perceived distance. Ie) moon illusion
Moon illusion
when viewed on the horizon, the moon appears larger than when viewed overhead even though the angular subtense is the same under both conditions.
Muller-lyer illusion
illusion where two lines of equal size appear different due to their endings. Suggested to be encoded early in stages of cortical processing.
3-40 arc seconds
Stereoacuity is measured on a scale of
Anisometropia and strabismus
two disorders of binocular vision that can cause reduced stereoacuity due to decreased development of binocular cortical neurons.
Monovision
a common clinical practice where one eye is corrected for distance and the other for near. Can cause a reduction of stereopsis, but monocular cues still function.