Exam 3 patho: Renal Disorders
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Kidney function
filter and reabsorbs → maintain pH and fluid balance
Kidney Structure – Nephron
Glomerulus
Proximal convoluted tubule
Loop of Henle
Distil convoluted tubule
Collecting tubule
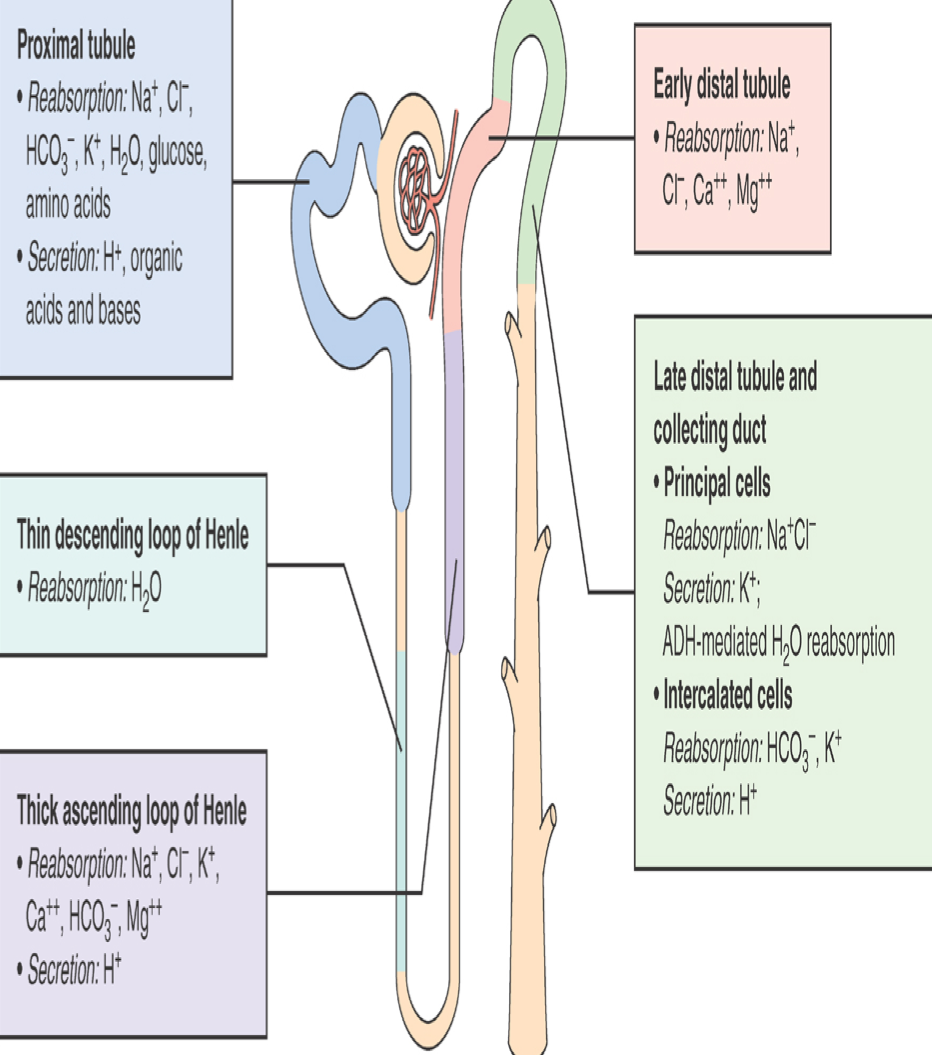
Maintenance via…
Lab tests to assess renal function
BUN
Creatinine
BUN/Cr ratio
GFR
Urinalysis
BUN test and high vs low BUN
A blood test that measures the amount of urea nitrogen in the blood
Urea nitrogen is a waste product produced when your liver breaks down protein
High BUN: May indicate kidney problems, dehydration, or a high-protein die
Low BUN: May be due to liver damage, malnutrition, or overhydration
Purpose of creatinine test
Creatinine is a product of muscle metabolism, and higher levels in the blood indicates that the kidneys are not functioning well bc they are not filtering out the creatinine
True indicator of kidney function
GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate)
the volume of blood filtered by the kidneys per minute, indicating their ability to remove waste products
Urinalysis
Measures:
Specific gravity
Casts
Presence of proteins
Specific Gravity of Urine
measure of the concentration of dissolved particles in urine, reflecting the kidney's ability to concentrate or dilute urine
Higher SG indicates more particles in the urine, signaling that someone has kidney disease
Age related changes due to renal cells not working as efficiently
Decreased GFR
Tubular transport under stress less efficient
Drug elimination decreases —> toxic reactions
Renal activation of Vit. D
Causes of Glomerular Disease
Immunologic
Non immunologic
Hereditary mechanisms
Immunologic conditions that cause Glomerular Disease (2)
Post Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis
Systemic Lupus Erythematous Glomerulonephritis
Nonimmunologic conditions that cause Glomerular Disease
Diabetes
Hypertension
Drug/Chemical Toxicity
Hereditary condition that causes Glomerular Disease
Alport Syndrome
type of progressive kidney disease
What is the result of glomerulus disease?
Ineffective filtering
What is the most common side effect of glomerular disease that helps with diagnosis?
Oliguria
3 types of glomerular damage
Proliferative
Sclerotic
Membranous
Proliferative glomerular damage
Number of cells increase
Describes the hypercellular inflammatory process involving infiltrating leukocytes or WBCs & proliferation of glomerular cells
Sclerotic glomerular damage
Increaed amount of extracellular material
Membranous glomerular damage
Increase in thickness of glomerular capillary
abnormal thickening of the glomerular basement membrane
Systemic disease glom disease (4)
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Glomerulonephritis
Long term
Hypertensive Glomerular Disease
Makes filtration difficult
Less BF to glomerulus —> decrease in GMR —> not enough BF to cells —> cells atrophy
Sclerotic changes to renal arterioles & small arteries
Diabetic Glomerulonephritis
Diabetic Glomerulosclerosis
Lots of buildup and thickening of the meninges matrix, which affect filtration. This reduces the SA of filtration, leading to decreased filtration
high glucose in BS? will cause sugars to be pulled into the BS
Pores open up, allowing albumin to leak out into the urine filtrate — protein in urine
The nephron will try to pull back the albumin, which puts a lot strain on the kidneys
End up with microalbuminuria
Microalbuminuria Disease
a condition characterized by the presence of small amounts of albumin in the urine
a key indicator of early diabetic nephropathy
Acute infection of glomerulonephritis — Group A beta hemolytic streptococci
an immune-mediated inflammatory response triggered by a streptococcal infection
Antigen-Antibody are now in the kidneys and causes the kidneys to inflame
Symptoms of Acute Post Infectious Glomerulonephritis
Inflammation = decreased BF —> causes decreased GFR
Can lead to scarring
Capillary permeability will increase
Allows for RBCs to leak out into the urine — dark urine
Other proteins leak out of kidney into urine
Na+ and H2O retention that is not being filtered
‣ Swelling as a result
Isotemia
Isotemia
medical condition characterized by abnormally high levels of nitrogen-containing compounds, like urea and creatinine, in the blood
Increase BUN and creatinine bc it’s not filtered out
What is Acute Pyelonephritis and why does it occur?
Bacterial infection of kidney parenchyma and renal pelvis
Occurs after a UTI
The infection went up the ureters into the kidney
Risk factors for acute pyelonephritis
Anything that can lead to a UTI, such as:
Pregnant women
Inserting anything in body (e.g. catheter)
Obstruction of outflow of urine
When urine sits it will collect more organisms and cause infection
Symptoms of acute pyelonephritis
Kidney inflammation
Fever
Chills
Acute pyelonephritis can lead to _____ of the kidneys, eventually leading to…
Scarring of the kidneys because it is acute
Can lead to chronic pyelonephritis
Chronic Pyelonephritis
Persistent/recurring infection and scarring
chronic obstruction prevents elimination of bacteria
Chronic obstruction (pyelonephritis) leads to… (3 steps)
Progressive inflammation and fibrosis of interstitial spaces btwn tubules
Tubule destruction
Leads to impaired ability to concentrate urine —> may develop CKD
What can occur because of tubule scarring?
Acid-base balance is off
Impairs ability to filter blood
Polyuria
Can lead to hyperkalemia
Drug related nephropathies — substances can damage kidneys by…(4)
Decreasing blood flow
Obstructing urine flow
Direct damage to tubulointerstitial structures
Illicit drug abuse
When administering drugs to someone with nephropathies, you must be mindful of… (3)
Age
Existing renal function
Hydration
Symptoms of obstructive kidney disorders
Recurrent UTI
Pain
Urine output
oliguria, polyuria, nocturia
Most common cause of OKD
Nephrothilitis or kidney stones
Supersaturation of salt in urine results in:
Crystalize to form large crystals
High or low pH can cause…
Kidney stones
obstruct the urethra and they cannot pee
Types of kidney stones
Calcium
Struvite
Uric acid
Cystine
Calcium kidney stone
Most common
Renal calculi (kidney stones) cascade of events (formation is not definite)
Supersaturation of one or more salts in urine
Precipitation of salts from liquid to solid state
Growth through crystallization or aggregation
Calcium stones
Large amounts in BS will filter out and end up in urine and create stones
Struvite stones — “staghorn” stones
Cause: bacteria (urease enzyme)
Produce ammonia ions
Increase phosphate levels in urine
Produces large stones
Uric acid stones
Cystine stones
Due to a genetic disorder
Childhood kidney stones
Clinical manifestations of kidney stones
Severe pain
Nausea/vomiting
Hematuria can occur
kidney stones pain renal colic and non-renal colic
Renal colic: stabbing pain
Non-colicky: dull pain but still very painful
Treatments for kidney stones
Pain relief
Stones pass spontaneously
Large stones and struvite stones require lithrotripsy or surgery