Deformational Plagiocephaly and Craniosynostosis: Cranial Remolding - Professional Issues Lecture
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
130 Terms
Infant vs Adult Cranium
Growth of the neurocranium (skull) and viscerocranium (face) occurs at different rates. Important to note when addressing facial asymmetry.
Neurocranium - most significant growth occurs before 1 year of age
Viscerocranium - growth occurs very slowly over the first 10 years of life
At birth the skill comprises about 1/3 of body (big head)
The infant face is only about 1/8 of the skill, compared with ½ of the adult.
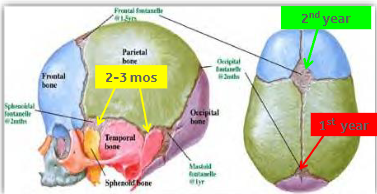
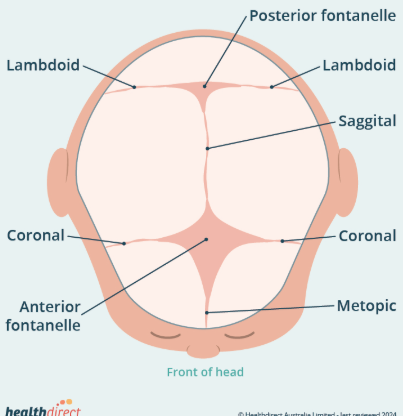
Fontanel
An opening in the skill where the boney plates come together. Incomplete ossification - Allows for rapid stretching and deformation of the cranium as the brain expands faster then the surrounding bone can grow.
Lateral fontanels (4) - obliterated within the first 2-3 months
Posterior fontanel (1) - within the 1st year
Anterior fontanel (1) - middle of the 2nd year
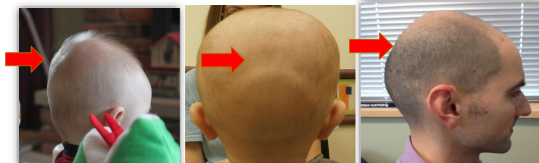
Posterior Fontanel
Commonly referred to as a divot, hole, flat spot, ridge, etc.
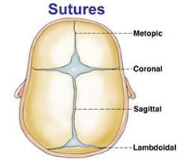
Sutures
Definition - Fibrous joints (Sharpey fibers) that bind the individual bones of the skill, allowing for movement (birth process) and flexibility (rapid and continued brain growth).
Time of suture closure varies widely (infancy to adulthood) can lead to delayed ossification.
Metopic suture union starts in the first year and is completed by the 8th year.
Other than metopic suture, all sutures should remain open during infancy and childhood
If closed prematurely that is called Craniosynostosis.
Intentional Cranial Deformation
artificial deformation of infant craniums has been practiced of many years
all of these cultures appreciated that early and persistent application of pressure to the cranium within the first year of life resulted in permanent alterations of skull shape.

Artificial Deformation
Head flattening or head binding is a form of body alteration in which the skull of a human is intentionally deformed.
done by distorting the normal growth of a child’s skull by applying external forces.
Normal Growth Patterns
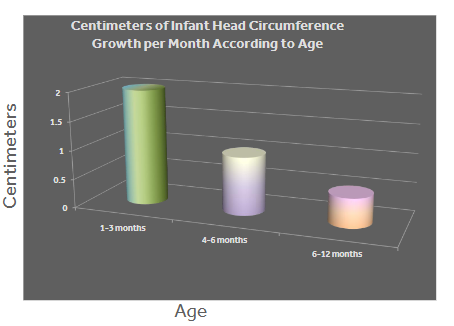
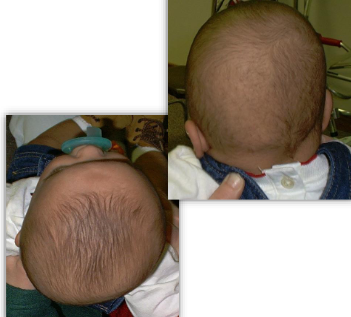
Unintentional Cranial Deformation - Deformational Plagiocephaly
Disease or physiological disruption that creates an imbalance in the static or dynamic modeling process, resulting in physical impairment of the individual.
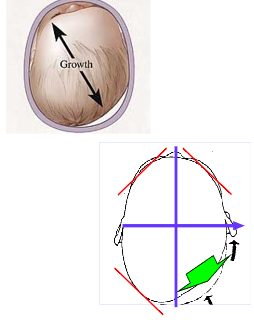
Goal of Treatment for Unintentional Cranial Deformation
To correct unintentional cranial deformation - to achieve symmetry
Cranial Remolding Orthosis (CRO)
intentional reformation
the product of the passive control of the normal vectors of infantile neurocranial growth through external restrictions
a redirection of growth
Will it Correct on its Own?
Basic Principles of deformation of reformation depends on -
pliability of the tissues
stage of development
duration of deforming force
Not treating can see positive or negative effects.
Theory of Cranial Remolding
Restrain the growth of the normal shape of the cranium by only allowing growth in the deformed areas. Providing the skull a symmetrical and/or proportional environment during rapid periods of growth.
Control the growth during the final stages of rapid cranial growth, 4-6 months of age.
Bone responds to
mechanical demand
force magnitude
rate of application
mode of load
frequency of load
Modeling Considerations
time of onset
duration of deforming forces
degree of severity
diagnosis/etiology
remaining growth
health of physiologic structures
developmental level
associated conditions
Principles of Orthotic Intervention
provide total contact in the areas where growth is to be curbed.
allow space in the areas where growth is desired.
passively controls the direction of cranial growth, not the overall magnitude.
there is a critical window of opportunity, specifically between 4-6 months of age, when the skull is most actively growing.
Clinical Documentation - What Information to Collect?
Gather Accurate & Comprehensive Information -
birth history
developmental observations
clinical evaluation of head deformity
Congenital Muscular Torticollis (CMT)
parent/caregiver education topics
thorough craniofacial evaluation
anthropometric cranial measurements
Clinical Documentation - Birth History
weeks gestation
NICU stay
single vs multiple - where they twins, quadruplets, etc.?
vaginal vs cesarean birth
deformity noted by parent ‘at birth’
other congenital anomalies or medical conditions

Clinical Documentation - Developmental Observations
Developmental Milestones
what skills does the infant have?
are delays present?
currently, what’s your infant’s sleep preference
Does the child have appropriate head control, neck strength, and posture?
Can they sit independently at appropriate milestone?
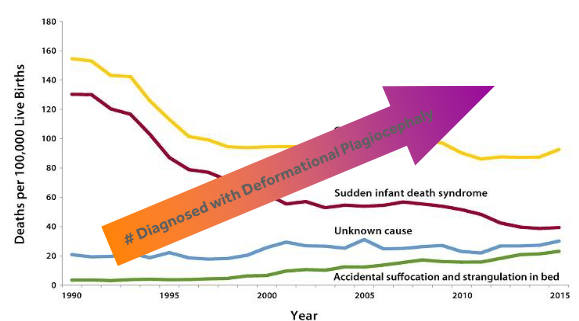
What is the significance of the “Back to Sleep” Program?
This program aimed to reduce the risk of SIDS and other sleep related deaths by encouraging parents to place their babies on their backs for every sleep.
Succeeded in reduction of sleep related deaths and SIDS.
Important to note that the number of infants diagnosed with deformational plagiocephaly increased as the risk for SIDS and sleep related deaths decreased.
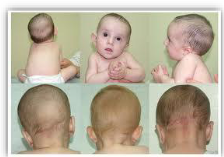
Clinical Documentation - Congenital Muscular Torticollis (CMT)
3rd most common congenital musculoskeletal anomaly
may subsequently result in DP and facial asymmetry
the sternocleidomastoid (SCM) muscle is affected
cervical muscle imbalance -
affected side is tight and shortened
opposite side is elongated and weak
identified 0-8 weeks of life
Deformational Plagiocephaly (DP) -
90% of DP cases have CMT
Early, proper identification is critical
Clinical Presentation of Congenital Muscular Torticollis (CMT)
head laterally flexes to the affected side
chin rotates away from the affected side
patient presents with limited ROM, both in flexion of head and neck
Right SCM is more common than left.
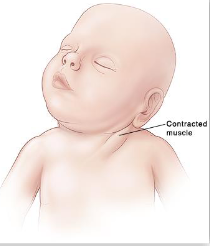
Treatment of Congenital Muscular Torticollis (CMT)
physical therapy is the first line of treatment -
positioning
handling
stretching
surgery reserved only for severe, non-responsive cases
multidisciplinary approach when couples with DP
treated as a separate condition

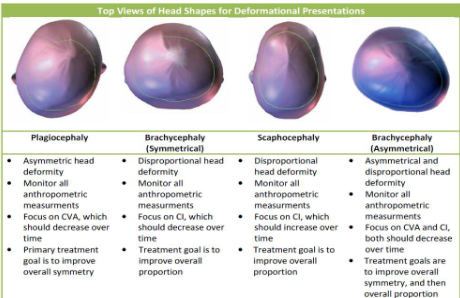
Evaluation of Head Deformity
This table shows the different possible abnormal head shapes and the characteristics of each.
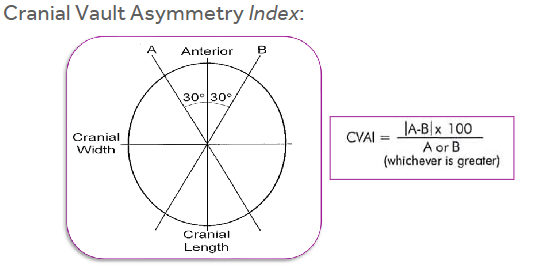
CI - a width to length ratio to determine asymmetry of head shape
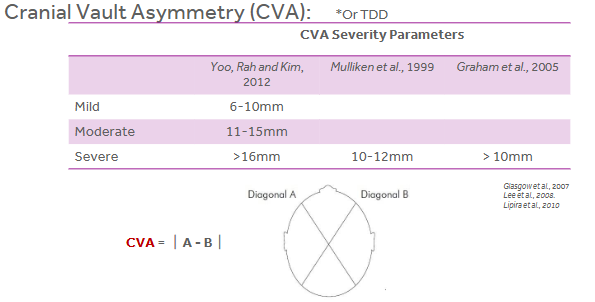
Cranial Vault Asymmetry (CVA) or Transcranial Diagonal Differential (TTD) - two diagonal measurements taken 30 degrees off of midline compared through subtracting the two.
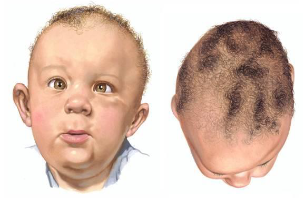
Deformational Plagiocephaly (DP) - Evaluation
Asymmetric
unilateral occipital flattening
ipsilateral forehead bossing
ipsilateral anterior ear shift
contralateral occipital prominence
contralateral forehead flattening
associated with congenital muscular torticollis ~90%
What is the goal of treatment with Deformational Plagiocephaly (DP)?
improve overall symmetry
Deformational Brachycephaly - Evaluation
Disproportionate - width
bilateral occipital flattening
increased cranial width
decreased cranial vault height
bilateral frontal bossing
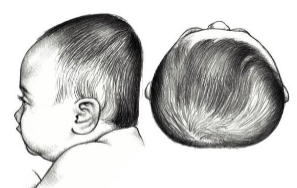
What is the goal of treatment of Deformational Brachycephaly?
reduce disproportion
Deformational Asymmetric Brachycephaly (DAB) - Evaluation
Asymmetric and disproportionate -
combined asymmetric and disproportional deformity
MOST COMMON TYPE
hybrid of DP and DB
bilateral occipital flattening, with increased flattening on one side crossing midline
prominences at the posterior parietal and the lateral parietal
frontal asymmetry and/or bossing may be present
facial asymmetry may be present
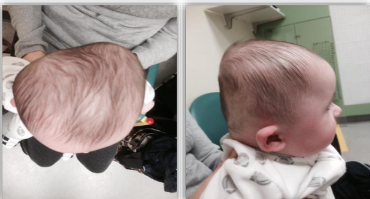
What is the goal of treatment for Deformational Asymmetric Brachycephaly (DAB)?
reduce asymmetry then reduce disproportion
Deformational Scaphocephaly (DS)
Disproportionate - Length
increased cranial length
decreased cranial width
occipital protuberance
frontal protuberance/bossing
asymmetry may be present
least common infant skull deformation
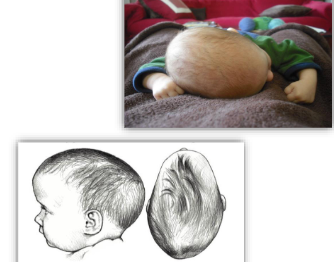
What is the goal of the treatment of Deformational Scaphocephaly (DS)?
increase disproportion
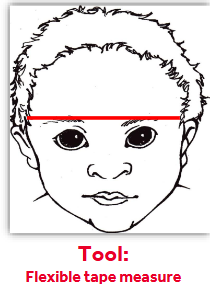
Anthropometric Measurements - Circumference
taken at eyebrow level
head in neutral position
horizontal to floor
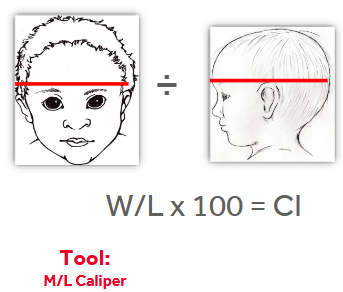
Anthropometric Measurements - Cephalic Index (CI)
Cranial Width - at widest dimension
Cranial Length - at longest dimension
Cephalic Index (CI) = Width / Length x 100
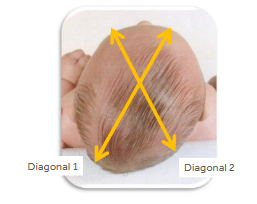
Anthropometric Measurements - Transcranial Diagonal Differential (TDD)
Diagonal 1 - right anterior quadrant to left posterior quadrant
Diagonal 2 - left anterior quadrant to right posterior quadrant
30 degrees off of midline
TDD = D1-D2
Tool - M/L Caliper
Anthropometric Measurements - Cranial Base Asymmetry
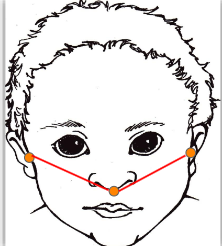
Tragions - point just anterior to ear
Subnasion - point at the center of the tip of the nose
length of right tragion to subnasion
difference between right and left
measures ear asymmetry
Tool - Facial Caliper or Tape Measure
Anthropometric Measurements - Orbitotragial Depth
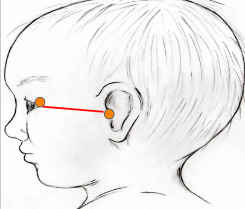
Tragion
Excanthion - point just lateral to the eye
length of right tragion to excanthion
length of left tragion to excanthion
difference between right and left
measure orbit depth asymmetry
Tool - Facial Caliper or Tape Measure
Anthropometric Measurements
Analysis of measurements determines which head shape classification you are treating.
Using Cephalic Index (CI)
Using Cranial Vault Asymmetry (CVA) or (TDD)
Circumference, M/L, A/P, transcranial distance A and transcranial distance B, MUST be taken at each appointment.
Measurements help to direct clinical decisions.
Positive feedback for parents/caregivers.
Cranial Base and Orbitotragial Asymmetry measurements to be taken at initial, mid-treatment, and final evaluation.
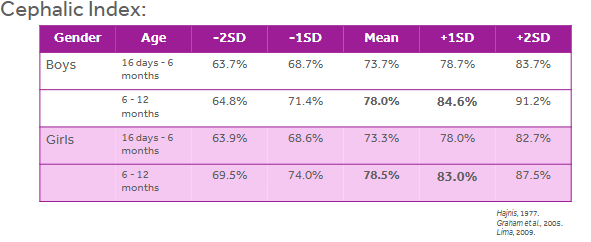
Cephalic Index Measurement Scale
Cranial Vault Asymmetry (CVA) or (TDD) Scale
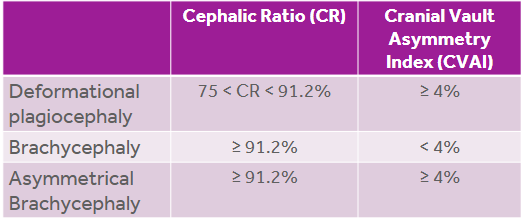
Guidelines used for Classifying Infants requiring treatment with a cranial remolding orthosis (CRO)
Determining Severity using Scales
Rating scale based on visual assessment criteria - Argenta Scale
Rating scale based on quantitative assessments - Hutchinson Scale
Rating scale based on visual and quantitative criteria - Plagiocephaly Severity Scale by Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta (CHOA)
Argenta Scale for Plagiocephaly
Rating scale based on visual assessment criteria.
Posterior Lateral Cranial Asymmetry
Type I - Posterior Asymmetry
Type II - Ear Malpositions
Type III - Frontal Asymmetry
Type IV - Facial Asymmetry
Type V - Temporal Bossing or Posterior Vertical Growth
Argenta Scale for Brachycephaly
Rating scale based on visual assessment criteria
Posterior only Cranial Asymmetry
Type I - Central posterior flattening
Type II - Widening of posterior skull
Type III - Temporal bossing or posterior vertical growth
Hutchinson Scale
Rating scale based on quantitative assessments -
SVA for lateral Plagiocephalic shape
CI for posterior only Brachiocephalic shape
Standards remains to be established across disciplines.
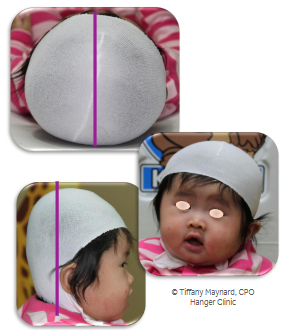
Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta Plagiocephaly Severity Scale
This is the most commonly used scale for assessing asymmetry.
Cranial Technologies - DOC Band
FIRST company to be cleared by FDA in 1998.
fabricates remolding and post-op cranial orthoses
low profile design
thermoplastic, side-opening design
fabricates from a scan
Digital Surface Imaging (DSI) - acquires the image in a fraction of a second, allowing for movement.
no lasers are involved in the process
Orthomerica - STARband
SECOND company to be cleared by FDA in 2000.
STARband (thermoplastic)
remolding cranial orthosis
side opening or bi-valve
STARlight (Surlyn)
remolding cranial orthosis
side opening or bi-valve
STARlight PRO (Surlyn)
post-op cranial orthosis
bi-valve
STARband 3D
STARScanner
SmartSoc
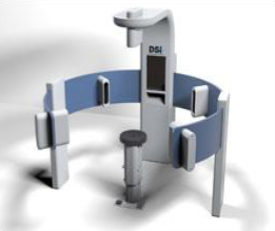
Orthomerica - SmartSoc
SmartSoc 3D Capturing System
used to manufacture the STARband and STARlight
works off of a smartphone Iphone or Android
allows movement
portable system
MCU Report
FDA Regulation
1998 - cranial remolding orthoses were reclassified as a Class II Medical Device
all cranial remolding orthoses must be manufactured by a 510(k) approved manufacturer
post manufacture modifications must be limited to minor adjustments in order to remain compliant
this made it illegal for anyone who was not granted FDA clearance to fabricate the orthoses
The Two Kinds of Family/Parent Personalities
Well-Informed and educated
want to start the process right away
need additional research to prove efficacy of treatment
Lack of previous research or education on process
be clear and concise in the way you provide information
provide written information for them to refer back to
be aware of what parents may see or read on the internet, specifically in Facebook groups or research articles.
Distractions in the Treatment Room
Distraction Gadgets and Toys
KEY is movement and lights
this keeps the baby distracted for measuring and scanning
have disinfectant wipes or spray available to clean your toys and gadgets!
Scanner in the Treatment Room
Be thoughtful when choosing a spot for your scanner unit so that family can see
live feed if possible

Baby Seat in the Treatment Room
Bumbo Floor Seat
Mamas and Papas Baby Snug
A device WITH a seat strap

Treatment Tools
ML Gauge
Flexible tape measure
Distraction gadgets
Sharpies
Lipstick or chalk
Pen/paper
Anatomy of infant skull
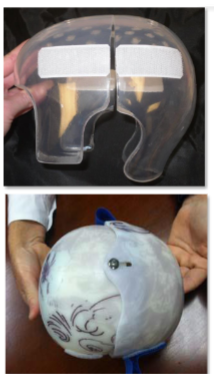
Craniosynostosis
Condition where the bones of a baby’s skull fuse together too early, before the brain is fully developed.
Cranial Vault Reconstruction
typically performed by plastic surgeon at 9 months old
removal of the skull at the equator, reshaping each individual piece
Endoscopic Craniectomy
typically preformed prior to 4 months of age, by a neurosurgeon with assistance from a plastic surgeon
removal of the premature suture(s)
Post operative Cranial Remolding Orthosis
Timeline of Endoscopic Craniectomy
Receive Rx and notes for physician
Day 1 - pre-operative consult, evaluation, scan
Day 2 - surgery
Day 3 - discharged
Day 4 - post-operative scan
Day 6-10 - patient seen for fit and delivery
Timeline of a Smaller Segment of Bone (Endoscopic Craniectomy)
receive Rx and notes for physician
Day 1 - pre-operative consult, evaluation, pre-op scan
Day 2 - surgery
Day 3 - discharged
Day 2-5 - patient for fit and delivery
CRO Designs
Traditional Surlyn
1/4” Surlyn
Fishmouth design, with lay over Velcro
Correction within orthosis
Bivalve Design
Copolymer
Bi-valve design, with lay over Velcro
Lined
Total Contact, minimal correction
ALL correction principles are the same despite what design is being used.
Clinical Appearance of Craniosynostosis- Sagittal Suture
ridged ossification of sagittal suture and anterior fontanel
long head - boat or football shaped
bitemporal and biparietal narrowing
frontal bossing and sloping occiput - occipital cupping
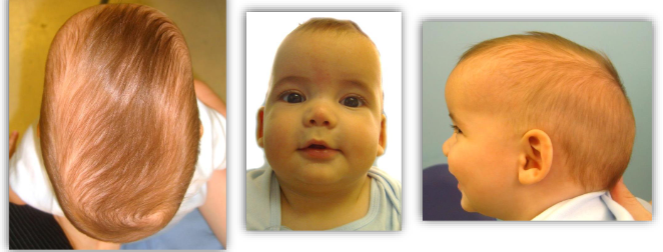
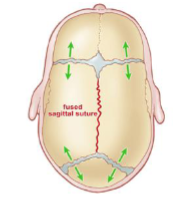
Synostotic Sagittal vs Deformational Scaphocephaly
Sagittal Synostosis is the most common synostosis
premature fusion of the sagittal suture
severe (bilateral) frontal and occipital bossing
posterior cranium narrows
no facial asymmetry
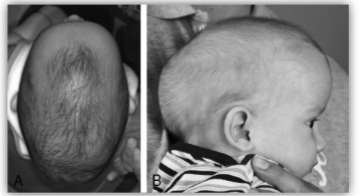
Clinical Appearance of Craniosynostosis - Unicoronal Suture
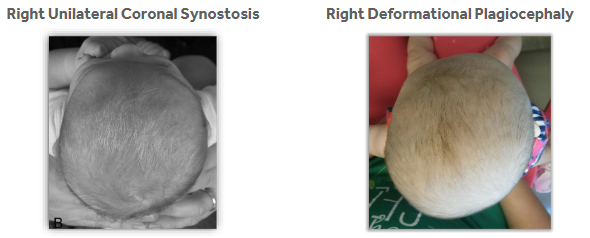
ridged ossification of affected coronal suture
frontal bone asymmetry
superior orbit/sphenoid asymmetry, eye appears larger on effected side
frontal bossing of non-affected side
root of nose deviates to non-affected side
Right Unilateral Coronal Synostosis vs. Right Deformational Plagiocephaly
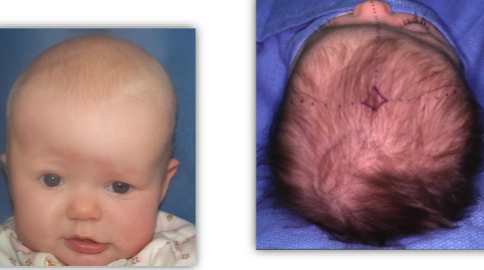
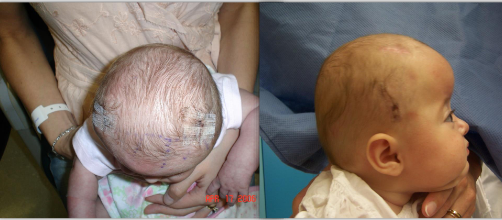
Clinical Appearance of Craniosynostosis - Bicoronal Suture
Ridged ossification of both coronal sutures
tall forehead
bi-parietal widening, brachycephalic
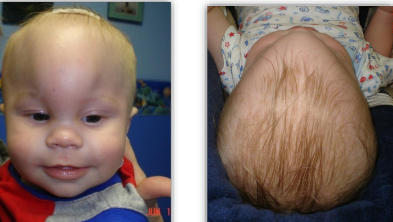
Clinical Appearance of Craniosynostosis - Metopic Suture
ridged ossification of metopic suture
midline frontal bossing
bitemporal narrowing
trigonalcephaly - triangular shape of the head
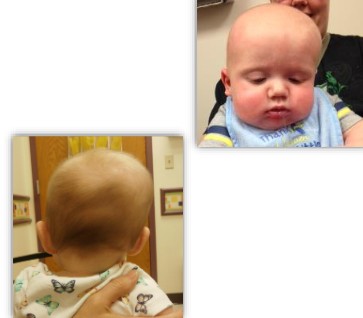
Clinical Appearance of Craniosynostosis - Lambdoid Suture
impressive unilateral posterior flattening without anterior bossing
ear is positioned close to the area of flattening
mastoid prominence on the same side of closed suture
opposite side parietal bossing
Lambdoid = Trapezoid
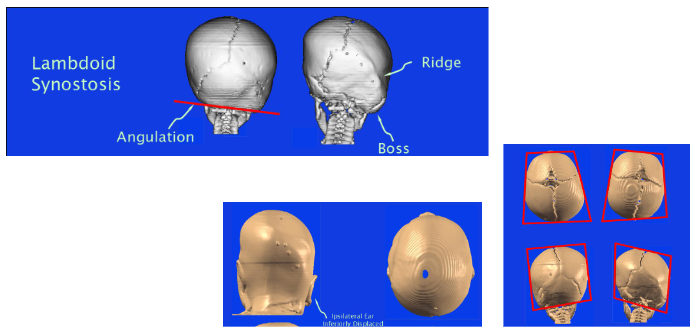
Unilateral Lambdoid Synostosis
impressive unilateral posterior flattening without anterior bossing
ear is positioned close to the area of flattening
mastoid prominence on the same side of closed suture
opposite side parietal bossing
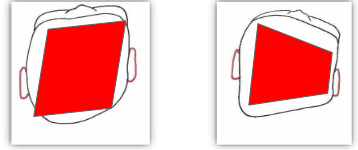
Deformational Plagiocephaly
unilateral posterior flattening with anterior frontal bossing on the same side as the posterior flattening
ear move away from the area of flattening
from a proximal view - “parallelogram-shaped” head
Craniosynostosis must be ______ ______.
ruled out
Is imaging necessary for Craniosynostosis?
nope, you can see or feel the abnormalities of the bony structures
Follow-up
Following Fit/Delivery
1 week post delivery
4 two week follow ups
3 week follow ups until completion
Evaluate fit, are principles of correction being followed
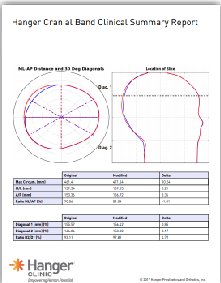
Review anthropometric measurements, every appointment.
Rescan for new orthosis, with physician’s orders.
Utilize the Cranial Report.
2-3 CRO’s until a year old.
Evidence Based Care of Child with Deformational Plagiocephaly: Part 1 Flannery & Looman
importance of repositioning and education prior to 4 months when patient gains head control
torticollis needs to be identified and treated as it limits repositioning
classification of head shape deformities - determining brachycephalic
crucial to be clinically trained in ruling out craniosynostosis
Evidence Based Care of Child with Deformational Plagiocephaly: Part 2 Flannery & Looman
systematic review of literature to identify best practice in management of plagiocephaly
American Academic of Pediatrics recommends at least 6-8 weeks of repositioning prior to considering CRO treatment
multidisciplinary approach provides best outcomes for patients and families
no evidence that CRO treatment causes harm and is most effective if begun by 6 months of age
Orthotic Management of Deformational Plagiocephaly - Lin et.al.
Clinical Practice Guidelines are based on this systematic review
statements taken from the literature and rated on a Likert scale by 30 high volume cranial orthotists
total of 54 consensus statements are present in Appendix A of the article
created algorithm to aide clinicians in knowing when to initiate treatment based on severity and age
RCT: Helmet Therapy in Infants with Positional Skull Deformation - Van wijk et.al.
frequently referred to as the BMJ study or the Dutch study
findings suggested no difference between treatment with a CRO and natural course (no treatment)
patients with torticollis were excluded from this study
cannot be reproduced due to lack of standards, consistency between treating orthotists, and unknown education level
CHINSTRAP IS NOT COOL
Clinical Practice Guidelines
Standard Definition - systematically developed statements to assist practitioner and patient decisions about appropriate health care for specific circumstances
provide guidance to novice clinicians
respect the expertise of established clinicians
establishing boundaries (stay within these lines)
ensure comprehensive considerations
Findings in Research
Fifty four best practice statements were identified, along with several clinical algorithms.
defined in 4 categories
diagnosis
presentation and severity
initiating treatment
management principles
Clinical Practice Guidelines - Diagnosis
Recommendation - Craniosynostosis should be ruled out during the initial evaluation of a patient with an atypical head shape.
radiologic imaging is generally unnecessary
craniofacial specialists (neurosurgeon, cranial orthotist, pediatric physical therapist, etc.) should be consulted when moderate to severe deformation is observed
lambdoid synostosis is rare, but should be ruled out
when in doubt, refer to craniofacial clinic and/or neurosurgeon
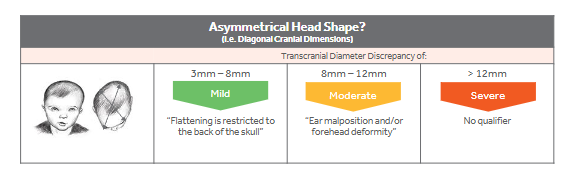
Clinical Practice Guidelines - Presentation and Severity of Plagiocephaly
Recommendation - The severity of plagiocephaly is a product of anthropometric measurements, ear malposition, and forehead symmetry
Objective - Transcranial Diagonal Differential (TDD)
Subjective - Ear Malposition and forehead symmetry
Collectively - Mild, Moderate, and Severe definitions
Plagiocephaly - Presentation and Severity
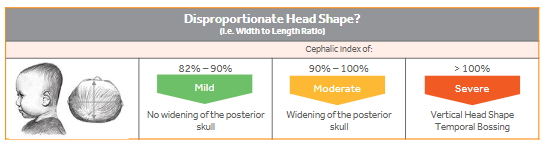
Clinical Practice Guidelines - Presentation and Severity of Brachycephaly
Recommendation - the severity of brachycephaly is the product of anthropometric measurement, skull widening and temporal bossing
Objective - Cephalic Index (CI)
Subjective - Posterior skull widening, temporal bossing & vertical head shape (cranial sloping)
Brachycephaly - Presentation and Severity
Clinical Practice Guidelines - Initiating Treatment
Recommendation - Ideally, the treatment should begin between 4 and 6 months, depending upon the severity of the presentation.
When to start treatment :
Severe - at 4 months old
Moderate - at 5 months old
Mild - 6 months old at the family’s discretion
Basic Orthotic Strategies
Directed growth of the cranial sutures -
total contact over areas of prominence
void/space over areas of flattening
structured follow-up program
monitored cranial growth
ongoing adjustments as needed
monitor post-treatment to prevent regression
Initial Fitting Considerations - Before seeing pt
ALWAYS REMOVE CRO FROM BAG PRIOR TO FAMILY COMING IN.
review order form
correct color
seam on correct side
were my directions follows
utilize the CDC Provided Overlays
what type of head shape
what movement should i expect
where should redness be
where should the void be
Initial Fitting Considerations - Fitting the helmet
the CRO should NOT fit intimately at initial visit
verify sufficient contact over prominent areas (with slight blanching)
try not to apply and remove the CRO more than 3 times during the initial fitting
allow the infant to wear the CRO for at least 30 minutes during the initial fitting
allow the infant to wear the CRO for at least 30 minutes to check skin tolerance and overall fit
allow the infant to play and lay down with CRO donned to verify the security of the initial fit

Fitting Process - Pre-Fit
room/tool readiness
sharpie, tape measure, ML stick, distraction devices, etc.
patient positioning
on parent’s lap, faced outward, extended out to knee, holding infant’s torso
position the orthosis
kneel in front of patient
spread opening from plastic as wide as possible (never Velcro/chafe)
center the CRO on infant’s head using the midline of the forehead as a guide
do not secure Velcro strap
assess and mark initial trim lines
Fitting Process - Establishing Initial Trim Lines
Lateral Edges -
lateral trims should extend to the end of the infant’s earlobe
clear infant’s peripheral vision
check to make sure all lateral extensions are making total contact
ear trims should be very close to the ears (<1cm away)
keep them smaller than you think
Posterior Edge -
it should capture the entire occipital area, extending inferior to the occiput bone and end just proximal to C7
the infant should be able to extend their head, even in a prone position, without any interference from the posterior-distal/lateral edges
Anterior Edge -
the trimlines around the face are verified and trimmed LAST
anterior trim lines should extend just proximal to the brow (< 1 cm)
‘Square-off’ around radius of anterior trim (around eyes)
Fitting Process - Evaluate the Side Opening
The side opening should be fully come together and close
if there is gapping, the infant may have had a cranial growth spurt since the scan (see troubleshooting)
The Velcro strap is used merely to secure the CRO
verify that the opening is on the correct side
Fitting Process - Evaluate the Proximal Opening
roughly 50-60% of the width and length of the head
should not extend below the crown of the head
a larger proximal opening will ease the donning process, but must be considered relative to the overall skull deformity
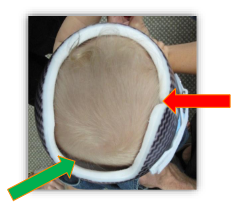
Fitting Process - Evaluate Areas of Total Contact/Relief
slight blanching is observed over areas of total contact where skull growth is unwanted
voids are observed over the flattened areas where skull growth is encourage
there design modifications promote more symmetrical and/or proportional skull growth
Fitting Process - Finalize the Initial Fitting
refit the CRO on the infant and demonstrate proper donning and doffing techniques to the parent
parents turn! they must also practice
re-assess the final fit and all trim lines
anterior, posterior, laterals, and superior
review the wearing schedule
review the cleaning schedule
schedule follow up appointment
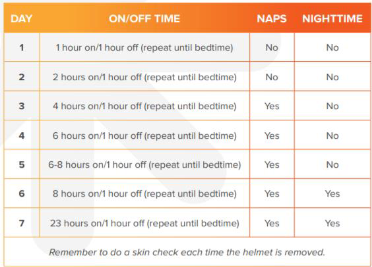
Hanger Wear Schedule
Hanger Cleaning Instructions

Caregiver Education at Delivery
redness or discoloration
blanching or pink areas are normal and expected in areas of total contact
you should never see any discoloration in areas of void/space and will need to remove material immediately if it occurs
when redness occurs, if it does not dissipate within 60 minutes after removing orthosis - stop wearing CRO and call office asap
because the CRO does not fit intimately, there may be some slight movement initially (especially when laying against a surface)
clean daily, but do not clean 24 hrs before each visit
initial infant reactions and adjustment periods may vary for each patient
increased head perspiration is common the first 2-3 weeks
will eventually subside as infant acclimates
subsequent itching of head due to increased moisture
perspiration may persist in summer months or for infant’s who are ‘sweaters’ (clothe lightly and corn starch use)
dress accordingly
remove CRO if infant has a fever
can re-apply once fever has reduced and normal body temperature maintained (without Tylenol management)
Recommended Tools
urethane arbor
Tycro wheel
conical sanding arbor
sanding drum
keep cranial tools separate from your day to day tools
prevents harsh materials from coming into contact with the sensitive skin of the infant
Follow-up Guidelines
The purpose of a structured follow-up schedule
stay ahead of growth in desired areas
prevent unnecessary skin irritation
maximize improvements to cranial symmetry and/or proportion
Ongoing adjustments
strategically remove material to encourage growth
strategically relieve areas to reduce pressure
strategically add padding to resist rotation/translation
Patient follow-up with a cranial remolding orthosis is more critical than ANY other orthosis you will fit.
Cranial remolding orthoses are the ONLY orthosis that is classified as a Class II medical device by the FDA.
When to Remove Foam?
when voids have been filled
when max head circumference has been reached
areas of redness