early diverging fungal lineages
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
what is the only genus in the phylum rozellomycota (cryptomycota)
rozella (monogeneric phylum, 27 described species)
how was cryptomycota first described and later confirmed as rozella
first from eDNA, in 2011, FiSH experiments at university of Exeter linked eDNA to pond-dredge rozella species
what is the life cycle of rozella’s multinucleate plasmodium
it cleaves in uninucleate zoospores or forms a multi-layered wall and encysts as a resting spore
when does rozella produce chitin
only in the resting spores (otherwise non chitinous)
what organisms does rozella parasitize
chytrids and blastocladiomycota (as an asexual endoparasite)
how does rozella obtain nutrients
phagotrophically (engulfing), unlike most fungi which are osmotrophic
synapomorphy
syn = shared, apo = derived, morphy = character (feature). unite a clade and differentiates from other clades.
ex: hair, live birth, lactation → shared w/ everything in mammalia
how many genera and species of microsporidia are described
about 150 genera and around 1200 species
what were microsporidia previously considered to be
protists
what is the infective stage of microsporidia
a multinucleate sporoplasm injected into the host
what process do sporoplasm nuclei undergo inside the host
merogony (binary fission producing meronts)
what do microsporidia meronts transition into
sporonts, which have cell walls and polar tubes
where can merogony occur in microsporidia infections
in parasitophorous vacuoles, parasite secreted envelopes or within the host’s endoplasmic reticulum
what kind of parasites are microsporidia
obligate chitinous endoparasites, mostly of arthropods
what is notable about microsporidia’s cell structure
they have very few organelles
what is the infective structure of microsporidia that initiates infection
the spore, which germinates and injects the sporoplasm through a polar tubule into the host cell
what happens after the sporoplasm enters the host cell
the nuclei undergo merogany (binary fission, producing meronts)
what is the difference between enterocytozoon bieneusi and ecephalitozoon spp. proliferation
e. bieneusi proliferates the host cytosol
encephalitozoon spp. proliferate in a parasitophorous vacuole
what stage follows merogony in microsporidia
sporogony - formation of sporonts with cell walls and polar tubes
what is the final stage of microsporidia intracellular development
release of mature spores from the host cell, which can infect new cells
which microsporidia species are associated with intestinal infections in humans
enterocytozoon bieneusi and encephalitozoon intestinalis
which encephalitozoon species can infect multiple organs
encephalitozoon hellem and encephalitozoon cuniculi
aphelida
parasites of algae
phagotrophic plasmodial injection
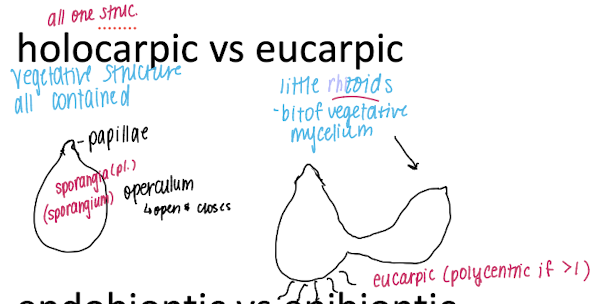
holocarpic vs eucarpic
holocarpic = vegetative structure all contained
eucaropic = little rhizoids, bit of vegetative mycelium
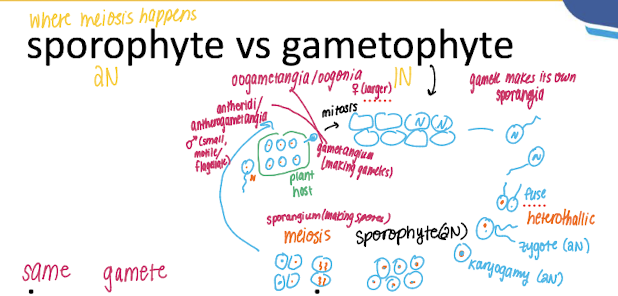
sporophyte vs gametophyte
endobiontic vs epibiontic
endo = lives inside host
epi = sits on top
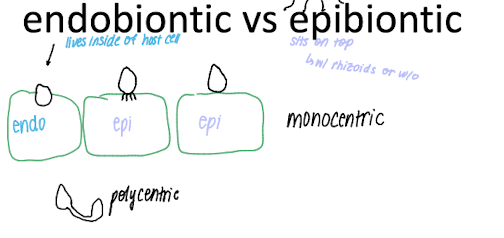
monocentric vs polycentric
mono = one of them
poly = multiples and connected by mycelium network
isogamous vs anisogamous
iso = same, gamous = gamete
ani = different gamous
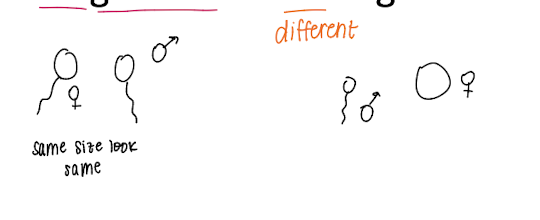
heterothallic vs homothallic
hetero = different mating types
homo = mate with themselves
physodermatales
order in blastocladiomycota
plant pathogens
mostly asexual
do meiosis seasonally
blastocladiales
order in blastocladiomycota
parasites on algae and arthropods
alternation of generations
allomyces
genus in blastocladiales
alternation of generations
aquatic fungi
oogamy
large female gamete is immotile, while the small male gamete is mobile