Introduction: Artificial Intelligence for Everyone
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Definition of Artificial intelligence (AI)
Ability of a machine to learn patterns and make predictions.
Computer systems designed to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence
Tasks AI can do
Understand Language
Recognize Images
Make Predictions
Play Games
Drive Cars
What is not AI
Traditional Rule-Based Systems
Simple Automation Tools
Mechanical Devices
Basic Sensors
Evolution of AI: 1950
"Computing Machinery and Intelligence" - Alan Turing’s paper
Turing test/”Imitation Test"
Evolution of AI: 1956
Dartmouth Conference - John McCarthy; birthplace of AI as a field
"Artificial Intelligence" - coined by John McCarthy
Evolution of AI: 1960s - 1970s
Progress in AI research
Expert systems
Early neural networks
Exploration of symbolic reasoning & problem solving
Evolution of AI: 1980s - 1990s
Mixed optimism and skepticism
Led to "AI winter"
Evolution of AI: 2000s onwards
Resurgence of interest & progress
Advancements in
computing power
data availability
algorithmic innovation
Narrow AI
Single tasks
predicting purchases
Planning schedules
consumer application
Siri
Can handle specific tasks effectively; lacks broader understanding.
Broad AI
Midpoint
More versatile; handles a wider range of related tasks
Businesses
General AI
Can perform tasks at the same intellectual level as humans
Artificial Superintelligence (ASI), self aware machines
Aren’t there yet
Data Science
Data inputs
numerical
alphabetical
alphanumeric
collection, analysis, and interpretation of large volumes of data; extract insights
Using
statistical methods
machine learning algorithms
data visualization
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Processes text and speech inputs; enable computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language.
Tasks
language translation
text summarization
speech recognition
Computer Vision
Deals with visual data inputs; enables computers to interpret and understand visual information.
Tasks
object detection
image classification
facial recognition
Applications
autonomous vehicles
medical imaging
augmented reality
Structured Data
Organized
rows and columns
names, dates, addresses, and stock prices
Straightforward to analyze and manipulate
Unstructured data
Lacks specific organization
Examples
images
text documents
customer comments
Extraction requires specialized tools and techniques.
Semi-structured data
Metadata to identify certain characteristics and organize data into fields
Ex: social media video with hashtags
Unstructured data

Semi-Structured data

Structured data
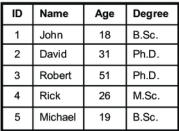
Natural Language Understanding (NLU)
Understanding the meaning of human language
Semantic analysis
Sentiment analysis
Named Entity recognition
Example: Spam filters
Natural Language Generation (NLG)
Generates human language
Takes structured data as input and turns it into coherent and readable text or speech
Data-to-text transformation; automatic report generation
Pixels
Grid of tiny colored dots
Represents a tiny portion of the image
Contains information about its color and intensity
Resolution
Total number of pixels along the width and height of the image
Ex: 1920x1080 px.
1920 pixels horizontally
1080 pixels vertically
AI in cv
Computers convert them into numbers
Each image divided into a series of numbers that represent the color and intensity of each pixel
Allows AI algorithms to process the image mathematically and extract info.
Cognitive Computing
mimic the way the human brain works in processing information and making decisions
Examples
IBM Watson
Microsoft Cognitive service
Extends trad. AI’s capabilities using CV, NLP, DS
Machine learning
Enables computers to learn from data and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed.
Deep learning
Imitates the human brain in processing data and creating patterns for use in decision making
Structure of the neurons and their connections
Permits a machine to train itself to perform a task
Applications
Aerospace and defence: Identifying objects from satellites
Medical research: Automatically detect cancer cells
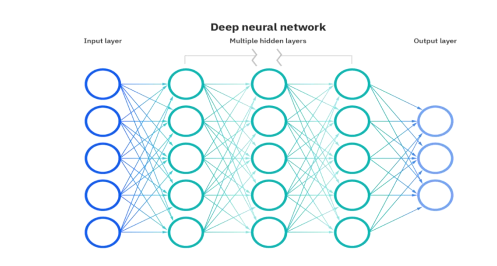
Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs)
Core heart and concept of Machine Learning
Mimic biological neurons
node layers
containing an input layer
one or multiple hidden layers
an output layer.
Deep Neural Network.
Number of Layers including the Input and Output Layer is more than three
MACHINE LEARNING
Less accurate
Trains on CPU
Divides the tasks into sub-tasks, solves them individually and finally combines the results
Can train on less data
Less time to train
DEEP LEARNING
Requires large datasets
Highly accurate
Longer to train
Requires GPU
Solves problem end to end
Supervised learning
Trained on labelled data
Input data is accompanied by the correct output
Learns based on example input-output pairs given
Goal: Model to make predictions on unseen data
Example
linear regression
logistic regression
Neural networks
Unsupervised Learning
Trains on unlabelled data
input data is not accompanied by the correct output
Finds hidden patterns or structure in the input data without explicit guidance
Goal: Discover inherent structures or relationships
Example
k-means clustering
hierarchical clustering
Reinforcement Learning
Interacting with an environment to maximize cumulative rewards
trial and error; receives feedback, rewards and penalties
Goal: learn a policy or strategy; make a sequence of decisions over time
Example
Q-learning
deep Q-networks (DQN)
BENEFITS
Increased efficiency and productivity
Improved decision-making
Enhanced innovation and creativity
Progress in science and healthcare
LIMITATIONS
Job displacement
Ethical considerations
Lack of explainability
Data privacy and security