Cell Biology Exam 1
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
What makes up a single deoxyribonucleotide?
A molecule of the 5-carbon sugar deoxyribose, a nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group
If you want to see the smallest detail on the outside of a cell, what is the best type of microscope to use?
Scanning electron microscope
What are membrane bound compartments within cells?
organelles
Where are organelles found?
in all plant and animal cells
is the nucleus an organelle?
yes
what is true for organelles?
they can have different pH and other environmental features from the cytoplasm
What is present in plant cells but NOT in animal cells?
Chloroplast and Central vacuole
What chemical bond results from sharing of electrons so they orbit both atoms in the bond?
covalent bonds
What are the charges of THR (Threonine), TYR (Tyrosine), SER (serine), GLN (Glutamine), ASN (Asparagine)?
uncharged polar amino acids
what are the charges of ALA (Alanine), GLY (Glycine), VAL (valine), LEU (leucine), ILE (Isoleucine), PRO (Proline), PHE (Phenylalanine), MET (Methionine), TRP (Tryptophan), CYS (Cystine)?
nonpolar amino acids
what are the charges of ARG (Arginine), LYS (Lysine), and HIS (Histidine)?
positively charged polar amino acids (basic)
most enzymes are?
proteins
what type of catalytic activity do enzymes have?
they are catalysts
how do enzymes bind their substrate?
using the active site
how are some enzymes regulated?
using a regulatory molecule and an allosteric site
what happens according to the induced fit model for enzyme activity?
the substrate binding to the enzyme active site causes a shape change allowing the enzyme to better interact with the substrate
When GTP is bound, the protein is
activated
When GDP is bound, the protein is
inactivated
why are enzymes called catalysts of biochemical reactions?
because they reduce the activation energy of a reaction
what is an example of a fibrous protein?
fibroin
what is an example of a globular protein?
hemoglobin
T/F: the binding site for a ligand or substrate is formed from adjacent amino acids in the polypeptide chain
false
what is an enzyme that breaks down proteins called?
protease
what is an enzyme that breaks down nucleic acids is called a?
nuclease
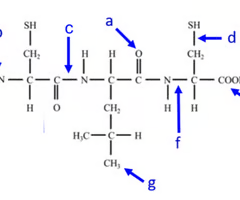
where is the carboxyl end of the polypeptide?
e
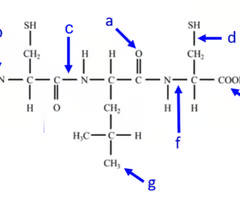
Where is the amino acid end of the polypeptide?
b
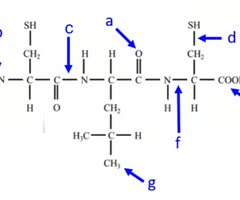
where is the peptide bond located?
c
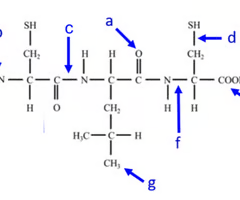
how many amino acids are chained together here?
3
what is a cell?
the fundamental unit of life and basic structure (lowest level of organization that can perform all activities required for life)
what are nucleotides?
building blocks for DNA and RNA
what are the building blocks for proteins?
Amino acids
what carries genetic information?
DNA
what is replication?
the process of DNA synthesis
what is transcription?
RNA synthesis
what is translation?
protein synthesis
what is transmission electron microscopy?
electrons are transmitted through the interior of the specimen
what is scanning electron microscopy?
when the surface of a specimen is scanned by detecting electrons deflected from the outer surface
bacteria and archaea are?
prokaryotes
what do prokaryotes lack?
membrane bound organelles, nucleus
what is something prokaryotes have that eukaryotes lack?
cell wall
what is a plant cell wall made up of?
cellulose
what is brightfield light microscopy?
differential interference contrast
what is rough ER?
flattened form of endoplasmic reticulum
what is the smooth ER?
tubular form of ER
what does the rough ER do?
protein synthesis
what does the smooth ER do?
site of lipid synthesis and membrane assembly
what does the golgi apparatus do?
receives and modifies molecules from the ER and sends them in or out of the cell
where are sugars added to proteins?
golgi apparatus
what do lysosomes do?
digest biomolecules
what transports components throughout cells?
small vesicles
what is responsible for muscle contraction?
actin
what type of bond receives and gives electrons between adjacent atoms?
ionic bond
what is a hydrogen bond?
weak bonds between a slight positive hydrogen and slight negative atom
what is a polar covalent bond
the sharing of atoms between two molecules where one atom is more electronegative, so the sharing is unequal (slight +/-).
what is the amino acid formula?
amino groups, alpha carbon atom, carboxyl group, r side chain
what charge do ASP (Aspartic acid), and GLU (glutamic acid have?
(acidic) negative charge
what is the structure of a nucleotide?
a five-sugar base attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base
what bases are different in RNA and DNA?
Thymine (DNA) and Uracil (RNA)
what are the functions of proteins?
catalyze chemical reactions, provide structural support, regulate membrane permeability
how do amino acids chain together
within a protein, linked by peptide bonds
what is primary structure?
amino acid sequence
what is secondary structure?
folding into alpha helix and beta sheets
what is tertiary structure?
3D folding of a single polypeptide chain
what is quaternary structure?
multiple polypeptides forming
what are cofactors?
protein components needed for protein function
what is another word for ligand?
substrate
what are globular proteins?
folded into compact tertiary sstructures
what are fibrous proteins
extensive regions of secondary structures that are given a highly ordered repetitive structured
what are allosteric proteins?
can cause shape change and can either help site function or prevent it
what is a protein domain
locally folded unit of a tertiary structure with a specific function
what does kinase do?
adds phosphotase
what does phosphotase do?
removes phosphate group
cut the py
cytosine, uracil, thymine = pyrimidine
GA the pur
guanine, adenine= purine
what is a nucleoside
a base covalently bonded to sugar with no phosphate group
what direction are 5’ and 3’
antiparallel
where does binding occur?
3’ OH
what is the difference between RNA and DNA nucleotides?
RIBOSE sugar (RNA) and DEOXYRIBOSE sugar (DNA)
what are chromosomes
proteins with a single molecule of DNA
what is a genome?
information contained within the organism’s DNA
what type of DNA has circular chromosomes?
prokaryotic
what is an RNA and DNA hybrid
r loop
what is the process of prokaryotic RNA transcription
binding, initiation, elongation, termination
what does RNA polymerase do?
copies DNA sequence into RNA sequence
what is the promoter
where RNA polymerase first binds
what is the terminator
the end of transcription region
what type of bond holds together beta plated sheets
hydrogen bonds
why are enzymes catalysts of biochemical reactions
they reduce the activation energy of a reaction
where does a competitive inhibitor bind to an enzyme?
active site
what is the +1 site of a gene
where the first nucleotide of RNA is encoded
the enzyme that synthesizes most mRNA in prokaryotes is
RNA polymerase (no number)
the enzyme that synthesizes most mRNA in eukaryotes is
RNA polymerase II