Week 8 Neuroanatomy
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Functions of cerebellum
Voluntary smooth coordinated movement
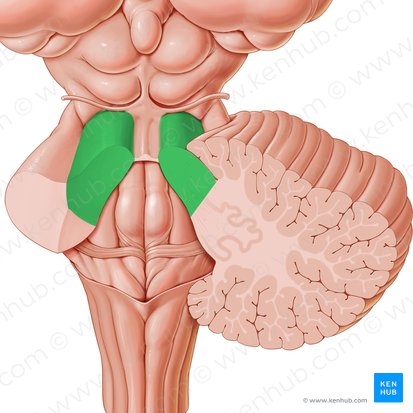
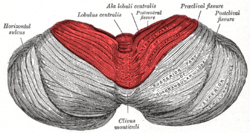
Anterior lobe
Paleocerebellum
paleocerebellum
spinal cerebellum
posterior lobe
neocerebellum
neocerebellum
cerebral cerebellum
flocculonodular lobe
archicerebellum
archicerebellum
vestibular lobe
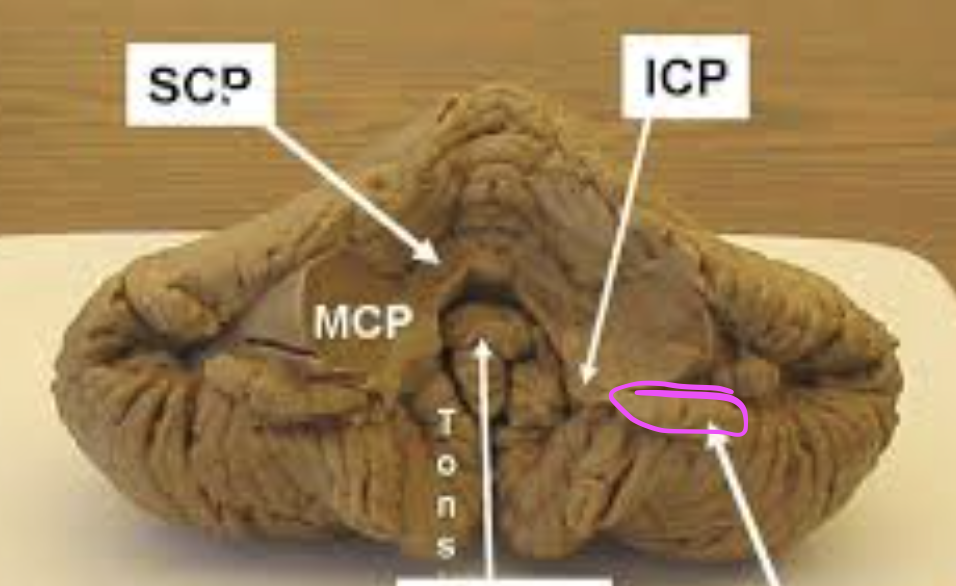
Superior cerebellar peduncle
brachium conjunctivum, connects the cerebellum to the midbrain. Although it contains a limited number of input fibers, its most abundant and most important components are output fibers.
middle cerebellar peduncle
brachium pontis, is the largest peduncle and connects the basilar part of the pons to the cerebellum. Its fibers are entirely input.
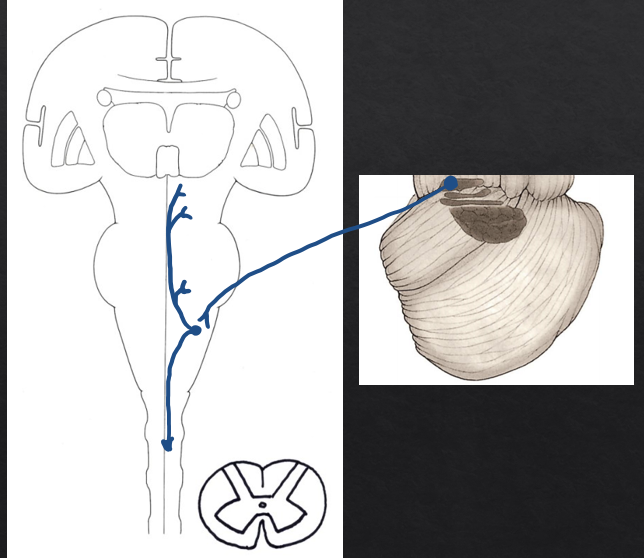
inferior cerebellar peduncle
arches dorsally from the dorsolateral surface of the medulla. Its composition is chiefly input fibers, although it does contain some output fibers. It consists of a large lateral part, the restiform body, and a small medial part, the juxtarestiform body.
flocculonodular lobe
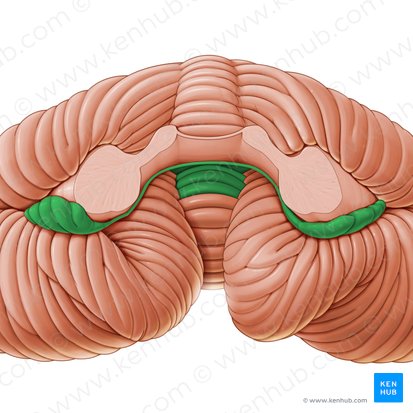
flocculus
nodulus
anterior lobe
posterior lobe
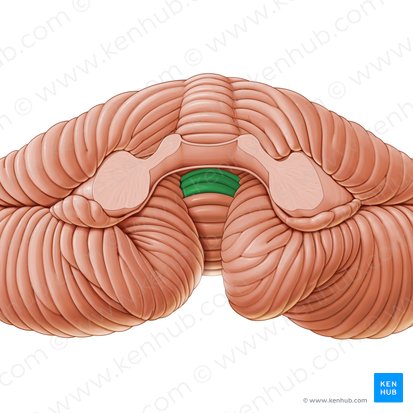
vermis
folium
ridges and Gyri in the cerebellum
primary fissure
posterolateral fissure
fastigial nuclei
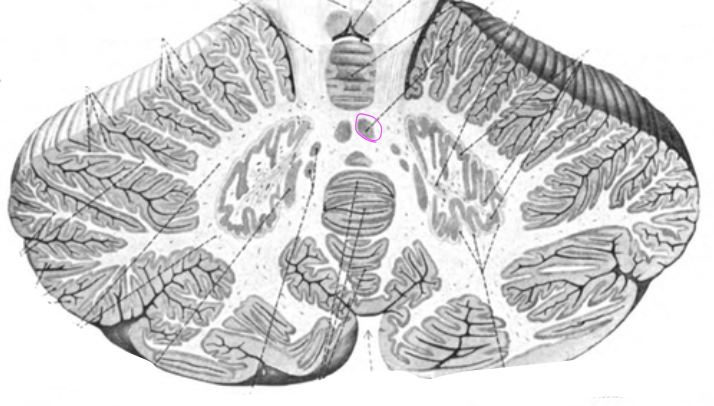
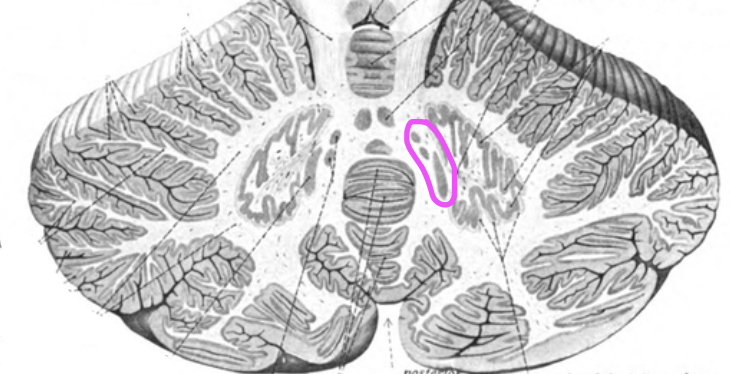
Interposed nuclei
Emboliform and globus nuclei
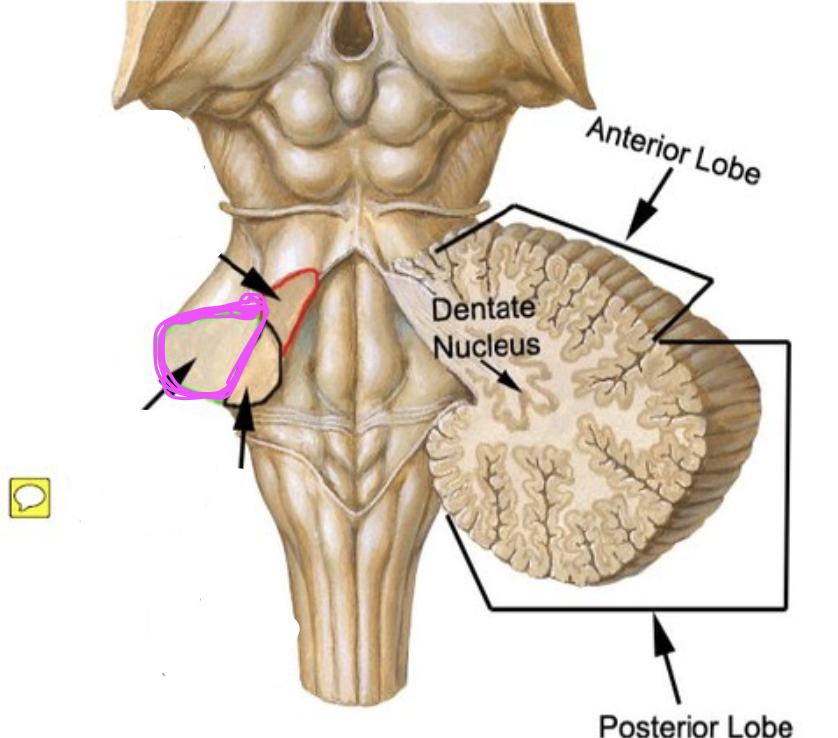
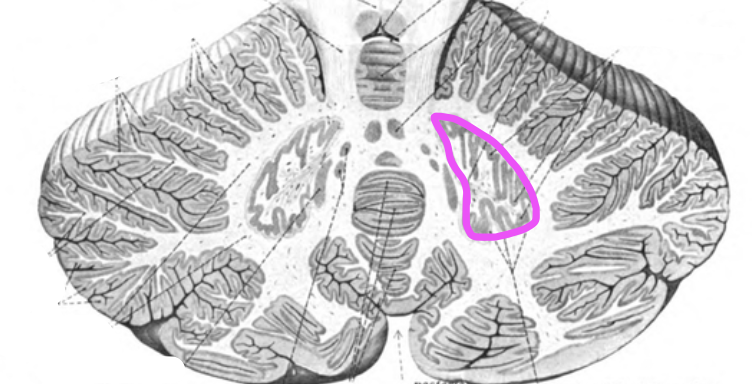
dentate nuclei
Functions of posterior lobe
Upper extremities, precise coordinated movement
posterior lobe syndrome
intentional tremor, perpendicular movement to intended, dysmetria
inputs to posterior lobe
(Corticopontine fibers) Association cortex→ internal capsule/ crus cerebri → Pontine nuclei
(Pontocerebellar fibers) Pontine nuclei→ transverse pontocerebellar fibers/middle cerebellar peduncle→ Dentate nucleus
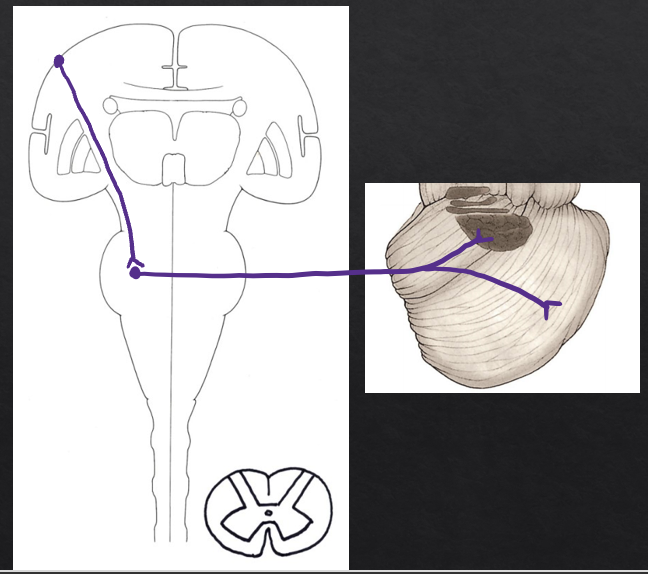
outputs to posterior lobe
(Dentatothalamic fibers) Dentate nucleus→ Superior cerebellar peduncle and decussation→ Thalamus
(Thalamocortical fibers) Thalamus→ internal capsule→ Motor cortex
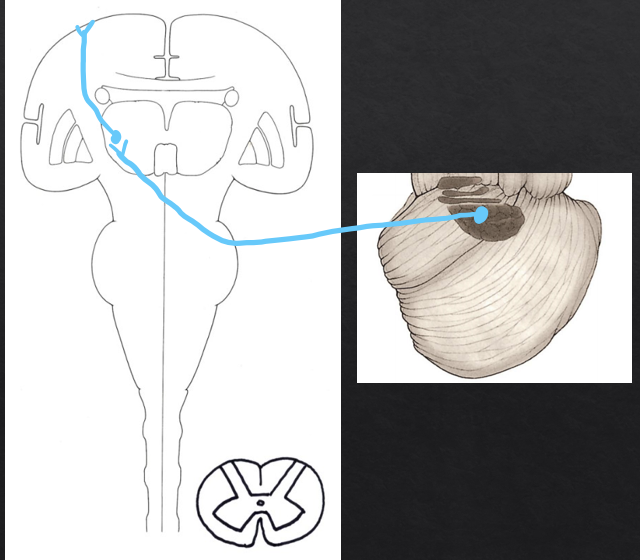
Functions of anterior lobe
Axial and lower extremity movements (gait and station)
anterior lobe syndrome
Loss of coordination in lower limbs (Heel-shin test)
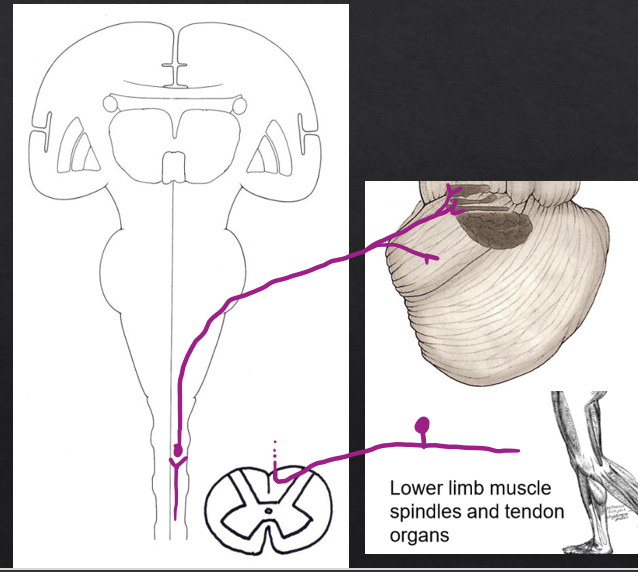
inputs to the anterior lobe from the lower limb
(primary sensory neuron) Dorsal root ganglia (L and S)→ gracile tract→ dorsal thoracic nucleus of Clarke
(Secondary neuron) Dorsal thoracic nucleus of clarke→ Dorsal spinocerebellar tract/ inferior cerebellar peduncle→ Fastigial nucleus/interposed nuclei
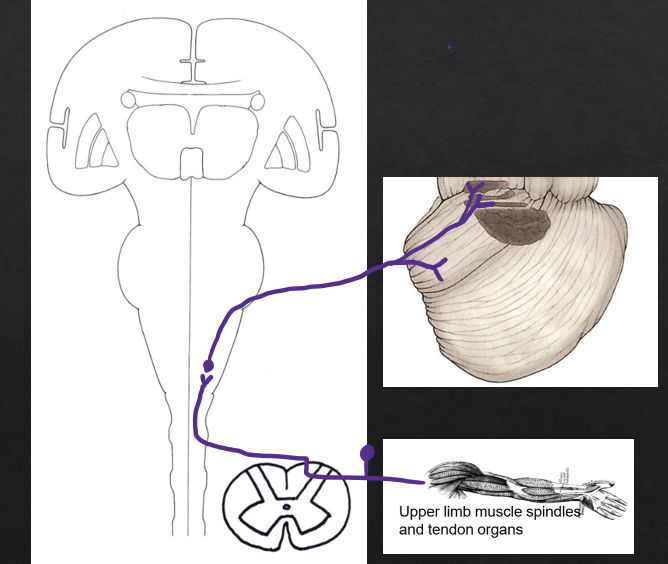
inputs to anterior lobe from upper limb
(Primary sensory neuron) Dorsal root ganglion (C)→ cuneate tract→ accessory cuneate nucleus
(Secondary neuron) Accessory cuneate nucleus→ inferior cerebellar peduncle→ Fastigial nucleus/ interposed nucleus
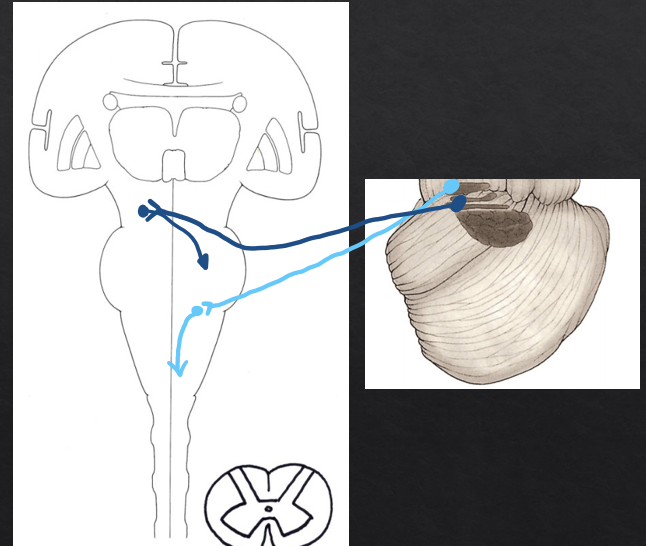
outputs from the anterior lobe
(output 1) Fastigial nucleus→ Inferior cerebellar peduncle→ vestibular nuclei
(output 2) interposed nuclei→ Superior cerebellar peduncle and decussation→ red nucleus
functions of flocculonodular lobe
Eye, Neck, and trunk movement
flocculondodular lobe syndrome
Trunkal Ataxia
inputs to flocculonodular lobe
(primary sensory neuron) Vestibular apparatus of the inner ear→ CN VIII→ Vestibular nuclei
(secondary neuron) Vestibular nuclei→ Inferior cerebellar peduncle→ Fastigial nucleus
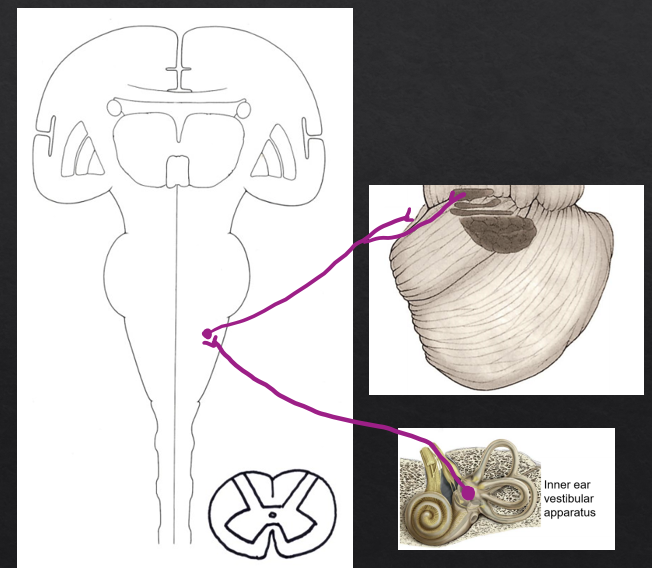
outputs from the flocculondular lobe
(fastigiobulbar projection) Fastigial nucleus→Inferior cerebellar peduncle→ Vestibular nuclei
(vestibulospinal and vestibuloocular projections) Vestibular nuclei→ Medial longitudinal fasciculus→ CN III, IV, VI nuclei and medial motor nucleus in spinal cord.