MCQ 10 - possibilities for correcting myopia, hypermetropia, astigmatism and strabismus by optical lenses
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
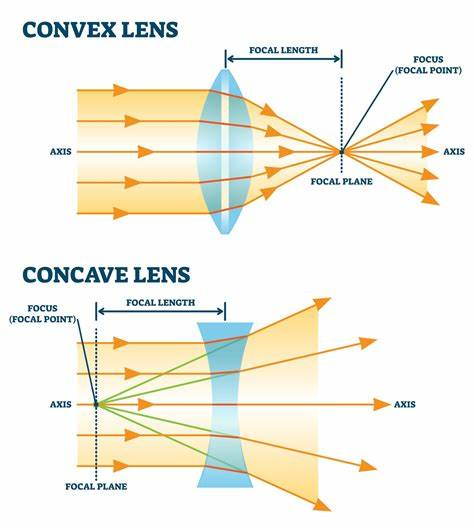
269. What type of lens is used for correction of near (short)-sightedness?
a. Cylindrical
b. Convex
c. Concave
c. Concave
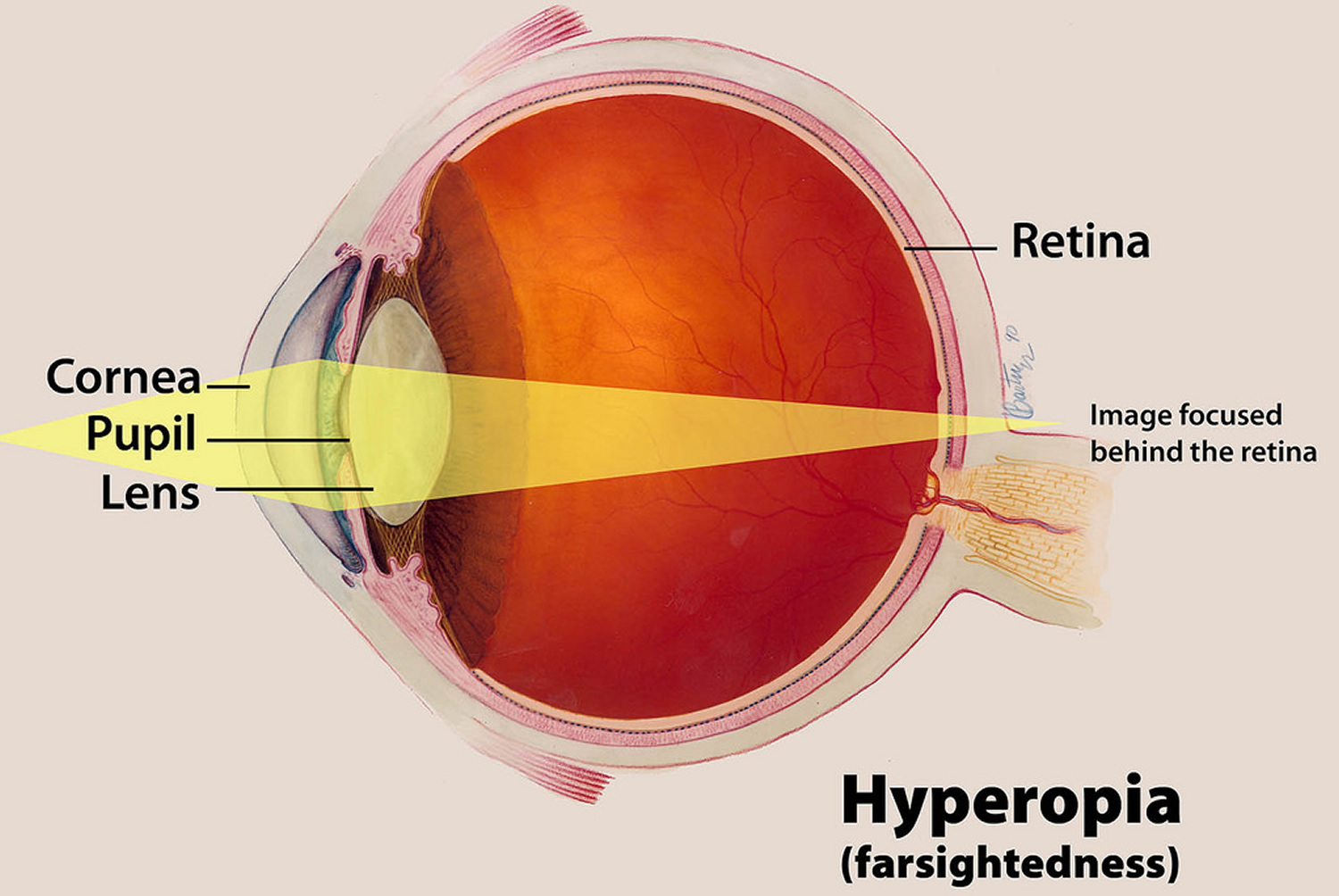
270. Where is the image formation in farsightedness (hyperopia)?
a. On the retina
b. Before the retina
c. Behind the retina
c. Behind the retina
271. What type of refractive condition (or conditions) of the eye are corrected with sphero- cylindrical lens with parameters: +2.5 Sph, +0.5 Cyl 1200
a. Astigmatism
b. Hyperopia and Astigmatism
c. Hyperopia and Strabismus
b. Hyperopia and Astigmatism
272. Which of the following refractive errors of the eye is characterized by greater than normal focusing power?
a. Myopia
b. Strabismus
c. Hyperopia
a. Myopia
273. What type of lenses are uses for correction of Myopia?
a. Convergent spherical lenses
b. Divergent spherical lenses
c. Conical
b. Divergent spherical lenses
274. What type of lens is used to correct Hyperopia?
a. Convergent spherical
b. Retinoscopic
c. Divergent spherical
a. Convergent spherical
275. What types of lens are used for correction of astigmatism?
a. Divergent spherical
b. Convergent conical
c. Cylindrical
c. Cylindrical
276. The human eye is most sensitive to what color (wavelength) of light?
a. Red
b. Green (yellow)
c. Blue
b. Green (yellow)
The human eye is most sensitive to green light with a wavelength of 555 nm 1. This is because green light stimulates two of the three types of cones, L and M, almost equally
L- red
M- green
S- blue
(Long, Medium, Short wavelengths)
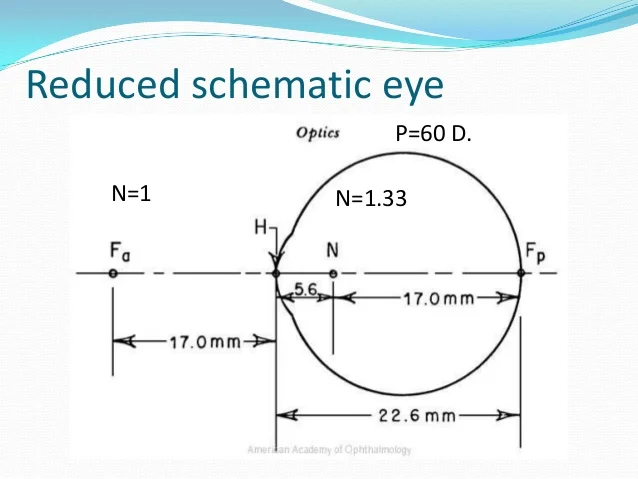
277. What does the term “reduced eye” mean?
a. Simple model of the eye, based on one equivalent lens with optical power of 60 dpt
b. Simple model of the eye, using liquid substance and glass body
c. Simple model of the eye, representing only the cornea and retina
a. Simple model of the eye, based on one equivalent lens with optical power of 60 dpt
278. Myopia is a refractive eye condition where:
a. The image is focused before the retina due to greater than normal optical power of the eye
b. The image is focused before the retina due to lesser than normal optical power of the eye
c. The image is focused behind the retina due to insufficient optical power of the eye
a. The image is focused before the retina due to greater than normal optical power of the eye
Myopia is an ocular disorder in which the optical power of the eye is too strong for the corresponding axial length
279. Spherical lenses are:
a. Sections of spheres
b. Sections of cylinders
c. Sections of cones
a. Sections of spheres
280. Fish eyes are remarkably similar to human eyes. One significant difference is the shape of crystalline lens. In fish they are denser and more spherical. This adaptation can be contributed to:
a. The high pressure under water
b. The speed of light under water
c. The need to collect light from wider angles
b. The speed of light under water
Water is denser than air, so light travels slower underwater. When underwater, the light passing through the eye must be refracted enough to focus on the fovea. When light travels into the eye underwater, it doesn’t get refracted very much. This is because the densities of the vitreous humor and water are very similar. That is the job of the lens; the lens, being denser, refracts the light more, thereby focusing it. The lens, being quite round, makes light pass through it for a longer distance, refracting it more. This makes light converge at the right point.
The lens is a transparent biconvex structure in most land vertebrate eyes. Along with the cornea, aqueous and vitreous humours it refracts light, focusing it onto the retina.
281. The eye receptors responsible for color vision are:
a. Visual cortex
b. Cone cells
c. Rod cells
b. Cone cells
282. There are three types of color sensitive cone cells in the retina. Two types overlap significantly in their spectral sensitivity, and one does not overlap much with the other two. Which are the two overlapping colors?
a. Blue and green
b. Blue and red
c. Green and red
c. Green and red
The spectral sensitivities of the red and green cones in human eyes overlap because they are both sensitive to light in the yellow-green region of the spectrum
283. The native optical power (in diopters) of the human eye is about:
a. 7 dpt
b. 0.5 dpt
c. 70 dpt
c. 70 dpt
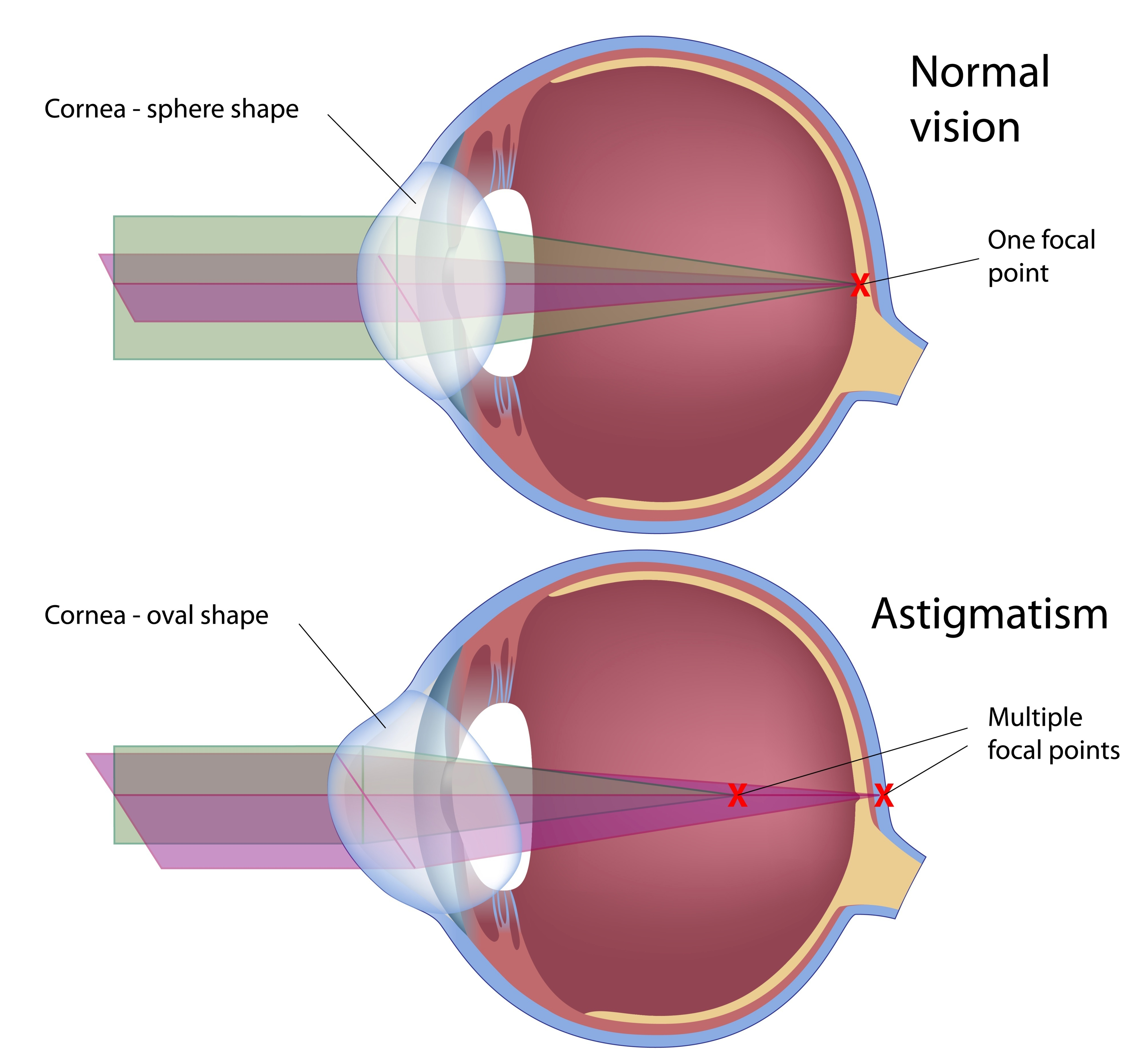
284. Astigmatism is a refractive defect of the eye, where:
a. There are irregularities in the curvature of the iris
b. There is a mismatch between the anatomical and optical axes of the eye
c. There are irregularities in the curvature of the cornea or crystalline lens
c. There are irregularities in the curvature of the cornea or crystalline lens
cornea - transparent front part of eye covering iris, pupil and anterior chamber
285. About 2/3 of the total optical power of the human eye is due to refraction in the cornea.This is because:
a. The difference between the refractive indices (n) of air and the cornea is greater compared to the other refractive elements of the eye
b. The cornea has the greatest surface curvature
c. The difference between the density (ρ) of the air and the cornea is greater compared to the other optical elements of the eye
a. The difference between the refractive indices (n) of air and the cornea is greater compared to the other refractive elements of the eye
286. The image formation in the human eye is similar to:
a. Image formation with concave lens
b. Image formation with convex lens
c. Image formation with convex mirror
b. Image formation with convex lens
(or conCAVE mirror)
287. The optimal distance from the (uncorrected) eye, for the formation of clear image is:
a. 15 cm
b. 20 cm
c. 25 cm
c. 25 cm
The optimal distance of 25 cm is known as the least distance of distinct vision. It is the minimum distance at which the lens of an uncorrected eye can focus on an object without any strain
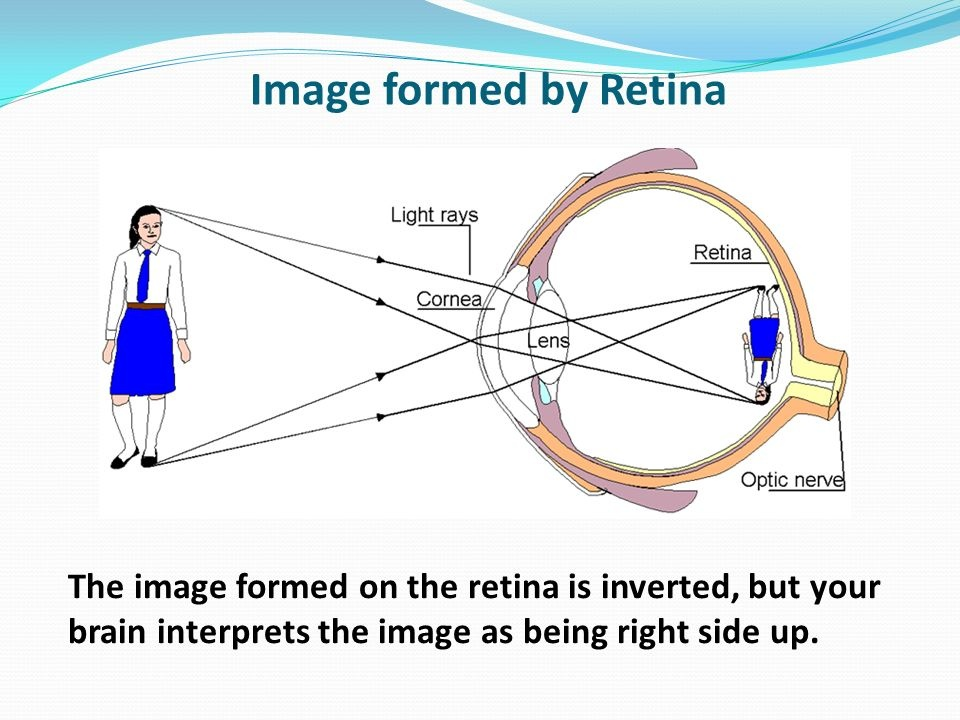
288. What type of image is formed on the retina of the human eye?
a. Erect, reduced, and real
b. Erect, identical, and real
c. Inverted, reduced, and real
c. Inverted, reduced, and real
289. If narrow beam of red light passes through glass prism, on the screen behind it there will be:
a. Narrow red line
b. Dispersion pattern
c. Interference pattern
a. Narrow red line
290. If narrow beam of white light passes through a glass prism, the image on the screen behind it will be:
a. Narrow white line
b. Dispersion pattern
c. Dark spot
b. Dispersion pattern
291. How can the eye recognize the difference between blue and green?
a. By the speed of the wave
b. By the frequency of the wave
c. By the amplitude of the wave
b. By the frequency of the wave