Physiology final modules 15/16 and turning point/hw
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
1
New cards
immune
__*Overall Function of _________system*__
Defend against pathogens like a virus and microbes like a bacteria or fungal cell. Also remove foreign bodies and destroy cancer cells within the body
\
mast cells are innate, come into contact first
\
broke apart pathogen = antigen
2
New cards
myeloid
leukocytes: White blood cells
***- Are able to leave circulatory system***
-Two groups
-________& Other:
-__Macrophages:__ Found in almost all organs and tissues, Located where they encounter pathogens/particles trying to enter the body
-__Dendritic__: Process phagocytized pathogens, Main ***antigen-presenting cell*** to T cells
-__Mast__: release histamine, Help stimulate ***innate*** immune response
***- Are able to leave circulatory system***
-Two groups
-________& Other:
-__Macrophages:__ Found in almost all organs and tissues, Located where they encounter pathogens/particles trying to enter the body
-__Dendritic__: Process phagocytized pathogens, Main ***antigen-presenting cell*** to T cells
-__Mast__: release histamine, Help stimulate ***innate*** immune response
3
New cards
lymphoid
leukocytes: White blood cells
***- Are able to leave circulatory system***
-Two groups
\-_____
-lymphocytes recognize cells in adaptive immune responses
Some lymphocytes circulating in the blood, but most are housed in the Lymphoid organs
***- Are able to leave circulatory system***
-Two groups
\-_____
-lymphocytes recognize cells in adaptive immune responses
Some lymphocytes circulating in the blood, but most are housed in the Lymphoid organs
4
New cards
bone marrow
Primary Lymphoid organs: lymphocyte development, cells are not activated by specific antigen yet
\-***____*** ***___________– produces B cells***
\-Thymus – produces T Cells
5
New cards
activation
\-Secondary Lymphoid Organs: ***___________***
\-Mainly: Spleen, Lymph nodes, Tonsils
\-All lymphocytes are descended from cells that matured in the primary organs
\-Mainly: Spleen, Lymph nodes, Tonsils
\-All lymphocytes are descended from cells that matured in the primary organs
6
New cards
innate, adaptive
•Two categories:
•**________:** inherited general defense
•**________:** cells change throughout lifetime to combat pathogen
•Terminology: Antigen, pathogen, foreign invader
7
New cards
pamps
innate is not specific
\-These defenses recognize some ***general*** signature marking the invader as foreign first line
\-Toll-like receptors – **(_______ , pathogen associated molecular patterns, unique to invaders)**
\*how i know its not my cell!
\-These defenses recognize some ***general*** signature marking the invader as foreign first line
\-Toll-like receptors – **(_______ , pathogen associated molecular patterns, unique to invaders)**
\*how i know its not my cell!
8
New cards
fever
innate immune response
Does not require memory, or past exposure – its inherited!
The nonspecific defenses may include: (for attack)
Physical barriers
***_____(symptom… increase temp increase cell activity)***
***Phagocytosis***
Interferons
9
New cards
lymphocytes
adaptive immune defense
-**_________**recognize specific foreign molecules called antigens.
10
New cards
antigens
adaptive immune defenses
-_____: stack of “paper”
\-stimulate production of specific antibodies (bind)
-are proteins or polysaccharides
-any molecule the host does not recognize as ‘self’
-_____: stack of “paper”
\-stimulate production of specific antibodies (bind)
-are proteins or polysaccharides
-any molecule the host does not recognize as ‘self’
11
New cards
lymphocyte
3 stages of adaptive immune response
1\. __Encounter and recognition__: Each lymphocyte presents a receptor for a specific antigen
\-l***ymphocyte _________determined during development***
\-Once the specific antigen is recognized, it is bound to its lymphocyte
1\. __Encounter and recognition__: Each lymphocyte presents a receptor for a specific antigen
\-l***ymphocyte _________determined during development***
\-Once the specific antigen is recognized, it is bound to its lymphocyte
12
New cards
activation
3 stages of adaptive immune response cont
2\. Lymphocyte ____________ :__ once antigen is bound, lymphocyte undergoes rapid mitotic division
-Some lymphocytes are used in attacking antigens, the rest are stored (memory cells)
2\. Lymphocyte ____________ :__ once antigen is bound, lymphocyte undergoes rapid mitotic division
-Some lymphocytes are used in attacking antigens, the rest are stored (memory cells)
13
New cards
attack
3 stages of adaptive immune response cont
3\. __________ is launched
***B cells*** differentiate to ***plasma cells*** and dump antibodies into circulation
\-Cytotoxic T cells directly attack antigen
3\. __________ is launched
***B cells*** differentiate to ***plasma cells*** and dump antibodies into circulation
\-Cytotoxic T cells directly attack antigen
14
New cards
b
lymphocyte cells:
__ cells: mature in bone marrow, ***differentiate into plasma cells to secrete antibodies***
-remain at the location of activation and send plasma cells to travel through your body looking for specific antigens
-triggers an ***Antibody-mediated responses***: targets are bacteria, viruses, toxins
-ONLY ONE type of antibody per plasma cell meaning one receptor unique to binding with that antigen
\-The human body therefore has to have lots to code for lots of different antigens
__ cells: mature in bone marrow, ***differentiate into plasma cells to secrete antibodies***
-remain at the location of activation and send plasma cells to travel through your body looking for specific antigens
-triggers an ***Antibody-mediated responses***: targets are bacteria, viruses, toxins
-ONLY ONE type of antibody per plasma cell meaning one receptor unique to binding with that antigen
\-The human body therefore has to have lots to code for lots of different antigens
15
New cards
antibodies
_______: blood → interstitial fluid → cells/bind
Link the microbe to phagocytes. They do not do the killing themselves, they recognize!
Travel the fluids of the body – circulatory and lymphatic systems to find pathogens
Link the microbe to phagocytes. They do not do the killing themselves, they recognize!
Travel the fluids of the body – circulatory and lymphatic systems to find pathogens
16
New cards
t cells
lymphocytes cells :
__ ___
* mature in the thymus
* Receptors again are unique to one antigen
* There are 3 Types
* Cell-mediated, Need ***MHC & antigen*** to bind
__ ___
* mature in the thymus
* Receptors again are unique to one antigen
* There are 3 Types
* Cell-mediated, Need ***MHC & antigen*** to bind
17
New cards
cytotoxic
3 types of t cells:
***_____*** travel to targets and kill it by binding to the antigen and secreting chemicals
\- Can occur to body’s own cells that are infected or cancerous
***_____*** travel to targets and kill it by binding to the antigen and secreting chemicals
\- Can occur to body’s own cells that are infected or cancerous
18
New cards
helper
3 types of t cells
-***_________***assists the functions and activation of B cells through direct contact, assists cytotoxic T cells through helping other immune cells to help cytotoxic cells
-Without helper cells, the B and T cells could not function adequately
(communication is cell to cell through cytokine protein)
-***_________***assists the functions and activation of B cells through direct contact, assists cytotoxic T cells through helping other immune cells to help cytotoxic cells
-Without helper cells, the B and T cells could not function adequately
(communication is cell to cell through cytokine protein)
19
New cards
regulatory
***______:*** ***inhibits B and cytotoxic T cells***
* Destroys own proteins, suppress inappropriate responses & prevent autoimmune diseases
* People with autoimmune disease may have problems with the Regulatory T functioning correctly (destroy when job is done… autoimmune is pathophys)
20
New cards
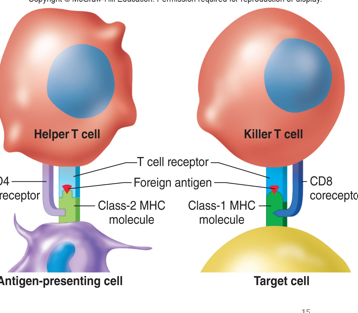
nucleated
•Major Histocompatibility complex molecules (MHC)
\-T Cell, MHC & Antigen Relationship
•There are two classes of MHC molecules:
**Class I MHC** are expressed on the surface of all *_______ cells*.
21
New cards
macrophages, b
**Class II MHC** are expressed on the surface of _____, activated _ cells, and dendritic cells (antigen presenting cells).
22
New cards
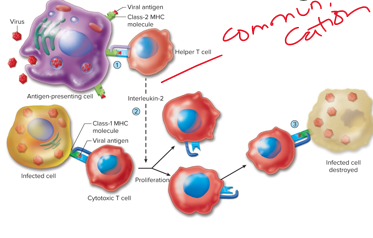
cytotoxic, kill
class 1 mhc protein on ______ t cells
\-antigens are located intracellularly.
\-T cell is focused on destruction of body’s own cells that are infected with viruses or cancerous
\-Viruses cause host cell to manufacture viral proteins
\-Cancerous cell has genes altered that are coding for proteins not normally found in the body
\-***T cell ____ the cell***
\-antigens are located intracellularly.
\-T cell is focused on destruction of body’s own cells that are infected with viruses or cancerous
\-Viruses cause host cell to manufacture viral proteins
\-Cancerous cell has genes altered that are coding for proteins not normally found in the body
\-***T cell ____ the cell***
23
New cards
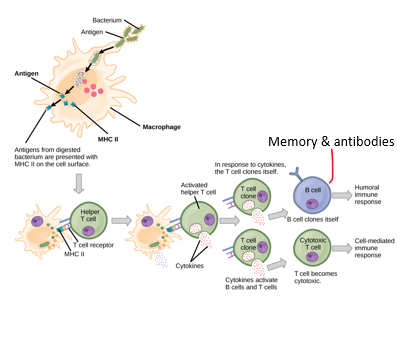
helper, antigen, vesicle, foreign
class 2 mhc proteins on _____ t cells
1\._______ is phagocytized by ***antigen presenting cell*** in a nonspecific response & broken down
2\. Antigen fragments bind to MHC II
3\. Vesicle presents ***MHC antigen complex*** on the surface of antigen presenting cell
4\. T cell now recognizes antigen
as foreign
1\._______ is phagocytized by ***antigen presenting cell*** in a nonspecific response & broken down
2\. Antigen fragments bind to MHC II
3\. Vesicle presents ***MHC antigen complex*** on the surface of antigen presenting cell
4\. T cell now recognizes antigen
as foreign
24
New cards
symptoms
__Antibodies__ \n Reminder: B cells differentiate into plasma cells which secrete antibodies
-**primary immune response: (1st exposure)**
-After first contact with antigen a slow production of antibodies occurs, including ***production of memory cells***
\-Generally takes 10–17 days to occur after exposure
-_________of illness occurs during these days
-**primary immune response: (1st exposure)**
-After first contact with antigen a slow production of antibodies occurs, including ***production of memory cells***
\-Generally takes 10–17 days to occur after exposure
-_________of illness occurs during these days
25
New cards
quick
antibodies
\-**secondary immune response: (all other exposures)**
\-Next contact with that antigen produces _______ production and action of the antibodies
-Takes Hours–7 days to occur
-***Occurs due to memory cells***
\-**secondary immune response: (all other exposures)**
\-Next contact with that antigen produces _______ production and action of the antibodies
-Takes Hours–7 days to occur
-***Occurs due to memory cells***
26
New cards
mast
steps in response to a wound: local inflammation
-Chemical mediators (**_______cells** producing histamine) dilate vessels in infected/damaged area. At these locations the membranes of the capillaries/venules become permeable to proteins
\-This allows increased blood flow and increased proteins participating in the inflammation
-The vasodilation and protein permeability causes increased fluid-edema, which is the swelling
-Chemical mediators (**_______cells** producing histamine) dilate vessels in infected/damaged area. At these locations the membranes of the capillaries/venules become permeable to proteins
\-This allows increased blood flow and increased proteins participating in the inflammation
-The vasodilation and protein permeability causes increased fluid-edema, which is the swelling
27
New cards
neutrophil
steps in response to a wound:
-***________***(a type of myeloid cell) enters the inflamed area (macrophages innate)
-First to arrive
-This is an example of the leukocytes moving out of the circulatory system
-***________***(a type of myeloid cell) enters the inflamed area (macrophages innate)
-First to arrive
-This is an example of the leukocytes moving out of the circulatory system
28
New cards
chemotaxis
steps in response to a wound
-***_______***(multistage process of cells moving and adhering in the injured area)
-One neutrophil is attached to endothelial cells, chemoattractants (messengers) act on the neutrophil and another adhesion molecule attaches to endothelial cell allowing neutrophils to begin collecting
-***_______***(multistage process of cells moving and adhering in the injured area)
-One neutrophil is attached to endothelial cells, chemoattractants (messengers) act on the neutrophil and another adhesion molecule attaches to endothelial cell allowing neutrophils to begin collecting
29
New cards
diapedesis
steps in response to a wound
\-Next, ***_________***(where the neutrophil squeezes itself into the interstitial fluid), there it migrates to the site of damage.
\-Next, ***_________***(where the neutrophil squeezes itself into the interstitial fluid), there it migrates to the site of damage.
30
New cards
engulfing
steps in response to a wound: _______
-Once present at the damage site, the cells destroy the bacteria by **phagocytosis** The microbe that is engulfed is enclosed in a sac and known as a phagosome in the cell
-The ***lysosome*** of the cell will connect with the phagosomes to break down the microbe
(neutrophil / phagocytic cell communicate)
-Once present at the damage site, the cells destroy the bacteria by **phagocytosis** The microbe that is engulfed is enclosed in a sac and known as a phagosome in the cell
-The ***lysosome*** of the cell will connect with the phagosomes to break down the microbe
(neutrophil / phagocytic cell communicate)
31
New cards
skeletal
steps in response to a wound - last step
\-To repair the tissue in the final stage of this process, cell division may occur depending on location.
\-_______muscles cells do not divide
\-if there is a scar, the repair work was imperfect
\-To repair the tissue in the final stage of this process, cell division may occur depending on location.
\-_______muscles cells do not divide
\-if there is a scar, the repair work was imperfect
32
New cards
active immunity, vaccination
•**_______** **____________ refers to** resistance to infection due to contact with microorganisms and toxins or antigens
•**_________** is the introduction of a microorganism or its antigens which induces an immune response including production of memory cells
•Forms vaccines come in: inactivated pathogens, antigenically similar but less harmful, genetically engineered
33
New cards
passive
\-**__________ immunity:** Transfer of ***antibodies*** from one person to another (wanes over time) such as:
-A mother to fetus or baby because antibodies pass in the placenta and breast milk.
-Intravenous for autoimmune or cancer patients
-5 major classes: IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, IgM
-A varying amino acid sequence to give us millions of unique immunoglobulins each capable of combining with a specific antigen.
34
New cards
C
\
Lymphocytes include all of the following EXCEPT:
A
Cytotoxic T cells
B
B cells
C
Neutrophils
D
Helper T cells
Lymphocytes include all of the following EXCEPT:
A
Cytotoxic T cells
B
B cells
C
Neutrophils
D
Helper T cells
35
New cards
A
\
All T cells are lymphocytes but not all lymphocytes are T cells.
A
True
B
False
All T cells are lymphocytes but not all lymphocytes are T cells.
A
True
B
False
36
New cards
A
\
Which organ system is primarily involved in regulation of plasma and blood volume?
A
the urinary system
B
the digestive system
C
the lymphatic system
Which organ system is primarily involved in regulation of plasma and blood volume?
A
the urinary system
B
the digestive system
C
the lymphatic system
37
New cards
A
\
The concentration of K+ is higher inside the cell than outside the cell.
A
True
B
False
The concentration of K+ is higher inside the cell than outside the cell.
A
True
B
False
38
New cards
B
\
The vascular link between the hypothalamus and the __________ is called the hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal system.
A
posterior pituitary
B
anterior pituitary
C
thalamus
The vascular link between the hypothalamus and the __________ is called the hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal system.
A
posterior pituitary
B
anterior pituitary
C
thalamus
39
New cards
regulatory
**________** release cytokines to inhibit immune cells from attacking its own tissues and prevent Autoimmune diseases.
40
New cards
class 2 mhc, class 1 mhc
\
________ are expressed on macrophages, dendritic cells and B cells.
\
________ are expressed on macrophages, dendritic cells and B cells.
________ are expressed on macrophages, dendritic cells and B cells.
\
________ are expressed on macrophages, dendritic cells and B cells.
41
New cards
false
true/ false?
class 2 mhc are required for B cell activation by a foreign antigen
class 2 mhc are required for B cell activation by a foreign antigen
42
New cards
innate
innate or adaptive immunity?
toll-like receptor
toll-like receptor
43
New cards
b cells
\
What leukocyte differentiates into memory cells?
What leukocyte differentiates into memory cells?
44
New cards
specific
\
Antibodies moving through circulation are looking for a specific/nonspecific antigen to bind to.
Antibodies moving through circulation are looking for a specific/nonspecific antigen to bind to.
45
New cards
True
\
Antigen presenting cells act as "flags" to combine MHC complexes with antigens or pathogenic organisms and present them to B and T cells. (T/F)
Antigen presenting cells act as "flags" to combine MHC complexes with antigens or pathogenic organisms and present them to B and T cells. (T/F)
46
New cards
\
Luteal Phase
B.
High estrogen and progesterone; low FSH and LH
B.
High estrogen and progesterone; low FSH and LH
Ovulation
A.
LH surge
A.
LH surge
Luteal Phase
B.
High estrogen and progesterone; low FSH and LH
B.
High estrogen and progesterone; low FSH and LH
Ovulation
A.
LH surge
A.
LH surge
47
New cards
memory
\
_________ b cells differentiate during an initial immune response but remain dormant until being activated during a subsequent exposure to an antigen are called:
_________ b cells differentiate during an initial immune response but remain dormant until being activated during a subsequent exposure to an antigen are called:
48
New cards
cytokine
Protein messengers that allow the immune system cells to communicate are called:
49
New cards
macrophages
The first line of immune system defense present in the respiratory system are:
50
New cards
true
Adaptive immune responses differ from innate immune responses in that the adaptive response is mediated by lymphocytes. (T/F)
51
New cards
bladder
\
Which of the following is not part of the 'sperm journey' from development through ejaculation? (Which structure does the sperm NOT travel through?)
Which of the following is not part of the 'sperm journey' from development through ejaculation? (Which structure does the sperm NOT travel through?)
52
New cards
proliferative
The follicular phase of the ovaries corresponds to the ________ phase of the endometrium.
53
New cards
one, zygote, morula, blastocyst
\
Reviewing the slide in the Reproductive chapter titled, "Migration". Fertilization occurs between one 'egg' or ovum and ____ sperm. After fertilization, the fertilized ovum is first called a ______. Approximately 72 hours later it gets a new name, a _____ and finally as implantation occurs it is called a ______.
Reviewing the slide in the Reproductive chapter titled, "Migration". Fertilization occurs between one 'egg' or ovum and ____ sperm. After fertilization, the fertilized ovum is first called a ______. Approximately 72 hours later it gets a new name, a _____ and finally as implantation occurs it is called a ______.
54
New cards
menstrual phase
which phase?
low estrogen and progesterone
\
\
low estrogen and progesterone
\
\
55
New cards
follicular phase
which phase
\
increasing estrogen; low LH and low progesterone
\
\
increasing estrogen; low LH and low progesterone
\
56
New cards
luteal phase
what phase?
High estrogen and progesterone; low FSH and LH
High estrogen and progesterone; low FSH and LH
57
New cards
ovulation
which phase?
LH surge
LH surge
58
New cards
oxytocin and prostaglandins
Uterine contractions are stimulated by
59
New cards
progesterone
hormone
stimulates milk production
stimulates milk production
60
New cards
prolactin
hormone
stimulates milk production
stimulates milk production
61
New cards
estradiol
hormone
allows for growth and branching
allows for growth and branching
62
New cards
oxytocin
Hormone
allows for milk ejection reflex
allows for milk ejection reflex
63
New cards
germ
•_______cells: formed within gonads – testes or ovaries
•Function: Sexual reproduction where genes from two individuals randomly combine to continue the next generation
•There are many hormones involved in Reproduction- it is very much tied to the endocrine system!
64
New cards
hypothalamo
endocrine involvement w/reproductive
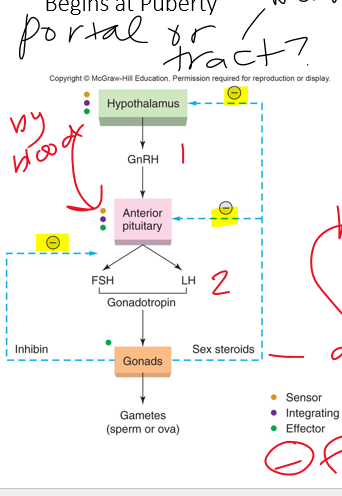
•Regulatory hormones released into ______-hypophyseal portal
\-negative feedback
(tract is for nervous)
•Regulatory hormones released into ______-hypophyseal portal
\-negative feedback
(tract is for nervous)
65
New cards
fsh, lh
•Both male and female have ___ *&* __that stimulates gonads for spermatogenesis or oogenesis
•Gonads secrete testosterone, estradiol, progesterone
•Development of duct systems are controlled by ***gonadal*** (testes or ovaries) hormones
\
cascade
•Gonads secrete testosterone, estradiol, progesterone
•Development of duct systems are controlled by ***gonadal*** (testes or ovaries) hormones
\
cascade
66
New cards
male
this is the _______ reproductive system
67
New cards
scrotum
testes
•__**_________**__: outpouching of the abdominal wall divided into two sacs for the testes. The descent of the testes into these sacs is crucial for normal sperm production.
•__**_________**__: outpouching of the abdominal wall divided into two sacs for the testes. The descent of the testes into these sacs is crucial for normal sperm production.
68
New cards
seminiferous
testes: male sperm from
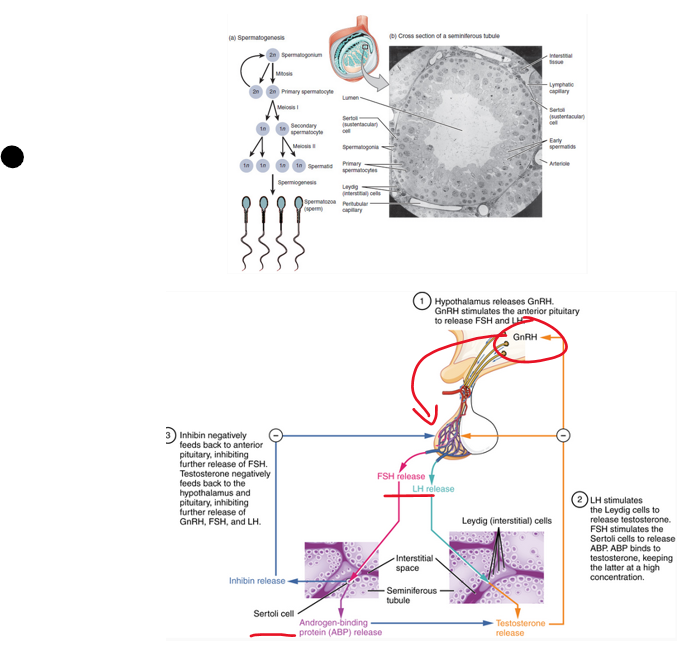
•__**_________tubules**__ spermatogenesis site
•__**_________tubules**__ spermatogenesis site
69
New cards
sertoli
_________cells - seminiferous tubule
•Stimulated by FSH (follicle stimulating hormone)
•Supporting cells of ***germ cells***
•Cells form a ring (Sertoli cell barrier) -an arrangement ideal for the conditions necessary for germ cell development
•Stimulated by FSH (follicle stimulating hormone)
•Supporting cells of ***germ cells***
•Cells form a ring (Sertoli cell barrier) -an arrangement ideal for the conditions necessary for germ cell development
70
New cards
leydig
_______ cells - seminiferous tubule
•Stimulated by LH (luteinizing hormone)
•Synthesize and releases ***testosterone***
•Testosterone has many functions
•Stimulated by LH (luteinizing hormone)
•Synthesize and releases ***testosterone***
•Testosterone has many functions
71
New cards
Decreases
leydig cells
•__________ GnRH secretion via an action on the hypothalamus
•Required for initiation and maintenance of spermatogenesis (acts via Sertoli cells)
\-secondary sex characterists from testerone
•__________ GnRH secretion via an action on the hypothalamus
•Required for initiation and maintenance of spermatogenesis (acts via Sertoli cells)
\-secondary sex characterists from testerone
72
New cards
vas deferens
sperm journey (sperm + fluid = semen)
An efferent duct system drains the **rete testis** into **epididymis.** Smooth Muscle contractions in the epididymis move fluid through to the **__ ________** to be ejaculated.
An efferent duct system drains the **rete testis** into **epididymis.** Smooth Muscle contractions in the epididymis move fluid through to the **__ ________** to be ejaculated.
73
New cards
urine
During ejaculation: sphincter to bladder is closed so sperm cannot enter and _______ cannot get out
74
New cards
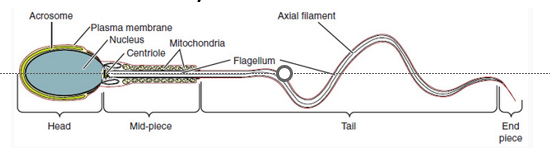
acrosome, mito
sperm
•Head consists of nucleus with the ***DNA*** and a tip covered by the helmet
•**_________(helmet)** protein filled vesicle containing enzymes used in *fertilization*
•**Midpiece**: full of _____(energy)
•**Tail**: flagellum (transportation)
300 min produced in seminiferous tubule each day
•Head consists of nucleus with the ***DNA*** and a tip covered by the helmet
•**_________(helmet)** protein filled vesicle containing enzymes used in *fertilization*
•**Midpiece**: full of _____(energy)
•**Tail**: flagellum (transportation)
300 min produced in seminiferous tubule each day
75
New cards
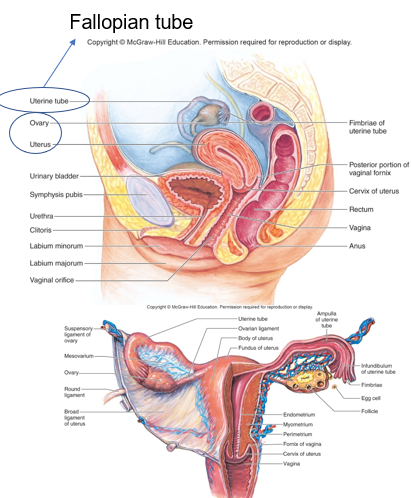
uterus
________ is the source of menstrual flow where fetus develops in pregnancy
76
New cards
oogenesis
________
•At birth the ovaries have all the eggs they will ever have, only a few hundred will be ovulated, the other few million will degenerate at some point until a women reaches menopause (50’s)
•No more ovulation due to no more eggs
•At birth the ovaries have all the eggs they will ever have, only a few hundred will be ovulated, the other few million will degenerate at some point until a women reaches menopause (50’s)
•No more ovulation due to no more eggs
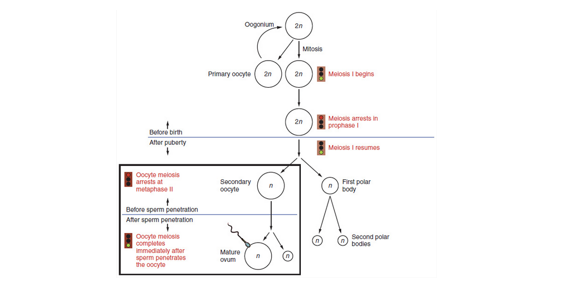
77
New cards
granulosa
•Oocyte or Eggs exist in follicles in the ovaries
•Begin as primordial follicles surrounded by ***________ cells***
•Granulose cells differentiate into layers
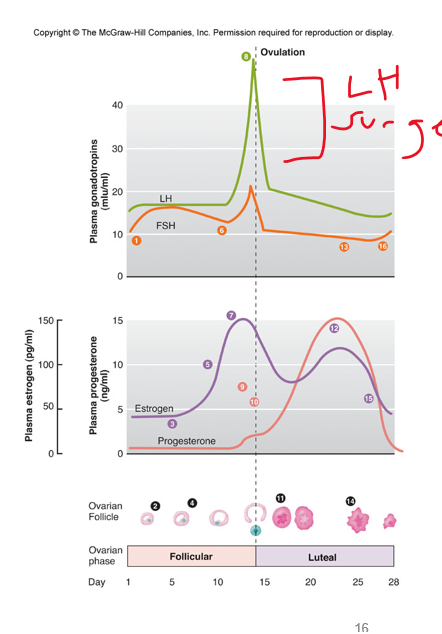
•Influenced by FSH (cause)
•At a point during the cycle one dominant follicle continues to develop (day 1-14) , others regress (becomes egg)
•The oocyte undergoes a first meiotic division and is then called a ***secondary oocyte (day 14)***
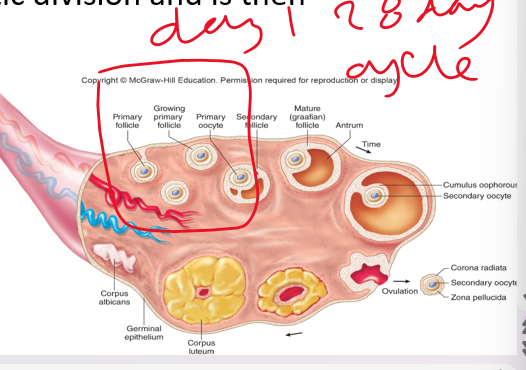
78
New cards
ovulation
\
•**_________**: Occurs when the walls of the follicle and ovary rupture due to enzymatic digestion, the secondary oocyte is carried out of the ovary
Occurs on about ***day 14*** of the ovarian cycle
•More than one oocyte can be ovulated at one time, but usually just one (twins)
•**_________**: Occurs when the walls of the follicle and ovary rupture due to enzymatic digestion, the secondary oocyte is carried out of the ovary
Occurs on about ***day 14*** of the ovarian cycle
•More than one oocyte can be ovulated at one time, but usually just one (twins)
79
New cards
corpus luteum
headed to fallopian tube OR
•Empty follicle becomes ____ ________
•Loss leads to menstruation
•Empty follicle becomes ____ ________
•Loss leads to menstruation
80
New cards
estradiol
•***______***is released by granulosa cells during follicular phase and then during the luteal phase by the corpus luteum
81
New cards
progesterone
•***_________***is released by both, mainly corpus luteum
egg (ovum) is currently in fallopian tubes ready to be fertilized
egg (ovum) is currently in fallopian tubes ready to be fertilized
82
New cards
ok
ok
83
New cards
gnrh
control of OVARIAN functions
•Depends on the secretion of ***_______***, (1st from hypothalamus to ovaries) hypothalamic neuro-endocrine cells.
•Follicular growth and estradiol dependent on FSH
•Ovulation depends on LH
•Depends on the secretion of ***_______***, (1st from hypothalamus to ovaries) hypothalamic neuro-endocrine cells.
•Follicular growth and estradiol dependent on FSH
•Ovulation depends on LH
84
New cards
endometrium
endometrial (menstrual) cycle aka uterine part
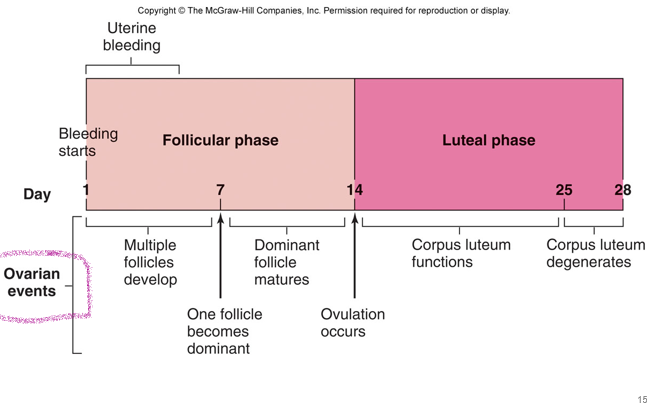
•First few days result in menstrual flow or ***_________ degeneration***
•This includes endometrial arterioles dilating, hemorrhaging (the loss of blood) along with endometrial debris
•Due to withdrawal of estrogens or steroids
•First few days result in menstrual flow or ***_________ degeneration***
•This includes endometrial arterioles dilating, hemorrhaging (the loss of blood) along with endometrial debris
•Due to withdrawal of estrogens or steroids
85
New cards
proliferative
endometrial (menstrual) cycle
•***________phase*** the endometrium thickens due to estradiol beginning to increase
(day 6-14)
•***________phase*** the endometrium thickens due to estradiol beginning to increase
(day 6-14)
86
New cards
secretory
endometrial (menstrual) cycle
•Next, ovulation occurs and from ovulation to the onset of the next cycle is termed **_________ phase**
•Next, ovulation occurs and from ovulation to the onset of the next cycle is termed **_________ phase**
87
New cards
all together
\
\
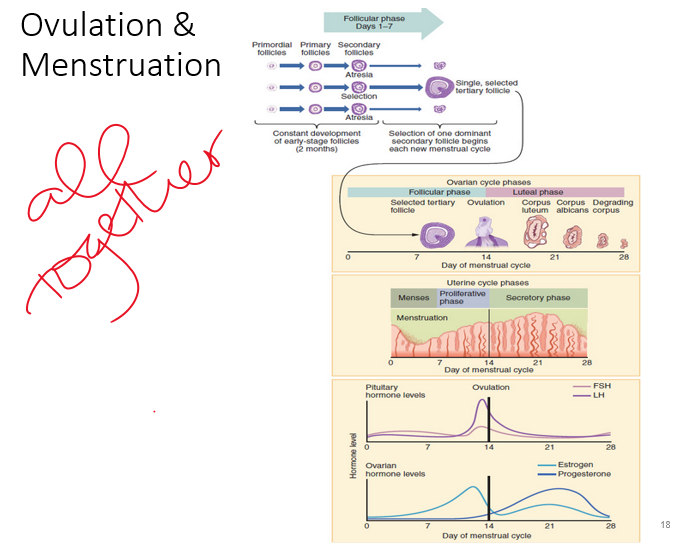
88
New cards
estrogen
sperm transport
•Sperm become activated and survive in cervical mucus for a short time due to ***_________*** that induces changes to the mucus pH
•Large amounts of death occurs
•Sperm moves via its own ***flagella and uterine contractions***
•Sperm become activated and survive in cervical mucus for a short time due to ***_________*** that induces changes to the mucus pH
•Large amounts of death occurs
•Sperm moves via its own ***flagella and uterine contractions***
89
New cards
fertilization
__________:
•Upon entry into the vagina, sperm are capable of fertilizing an ovum (egg) up to 6 days.
•The ovum is only viable up to 48 hours
•Upon entry into the vagina, sperm are capable of fertilizing an ovum (egg) up to 6 days.
•The ovum is only viable up to 48 hours
90
New cards
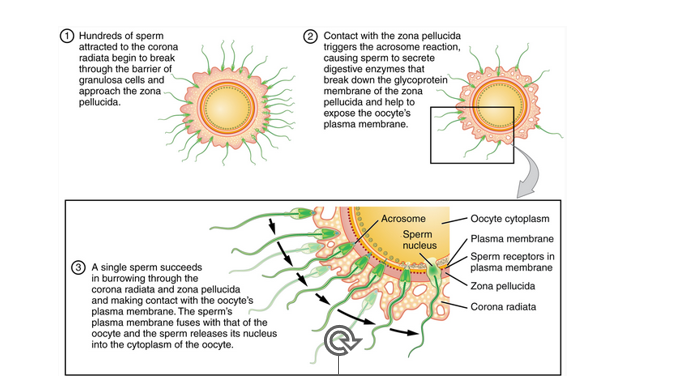
pellucida
fertilization
•Begins when sperm and ovum fuse
•The sperm head must break through the **zona ______** to fuse with the membrane. The sperm head is then released into the cytosol of the ovum
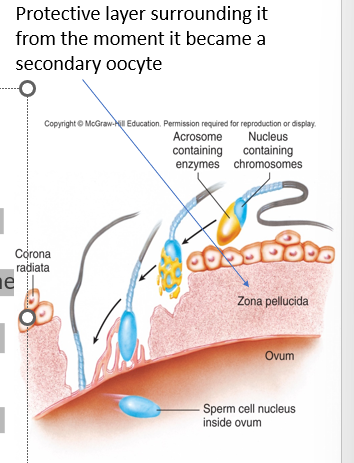
91
New cards
zygote
fertilization
•As soon as this fusion happens many changes occur to ensure survival of the **_____** including:
•Changes in membrane potential to prevent further entry of sperm by hardening the zona pellucida and using **enzymes** to inactivate sperm binding sites
•As soon as this fusion happens many changes occur to ensure survival of the **_____** including:
•Changes in membrane potential to prevent further entry of sperm by hardening the zona pellucida and using **enzymes** to inactivate sperm binding sites
92
New cards
fallopian tube
migration
Ovum movement is slow, fertilization must occur here in the ______ ________
Approx 4-6 Days later implantation in the uterus occurs
\
ovulation 14 | implantation 21
Ovum movement is slow, fertilization must occur here in the ______ ________
Approx 4-6 Days later implantation in the uterus occurs
\
ovulation 14 | implantation 21
93
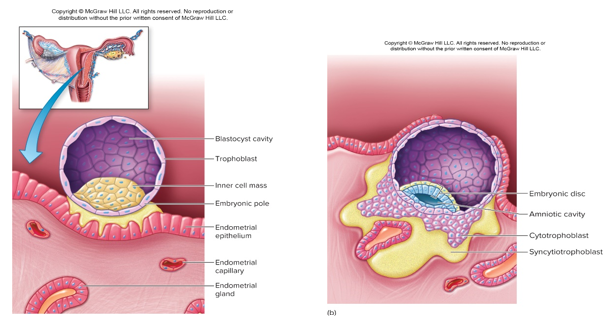
New cards
hcg
•early development, implantation and placentation
Initial contact stimulates rapid trophoblast proliferation, this is what stimulates the hormone ***____*** in the mother. This hormone maintains the endometrium until the placenta takes over. **Corpus luteum does not regress (estrogen)**
•Endometrial cells provide fuel first few weeks until placenta takes over this function and steroid hormone secretion
•Implantation occurs around 21 of a typical cycle
94
New cards
blood
at 8-8 weeks (prenatal) pregnancy can be detected b/c of hcg
____ tests accurate earliest
____ tests accurate earliest
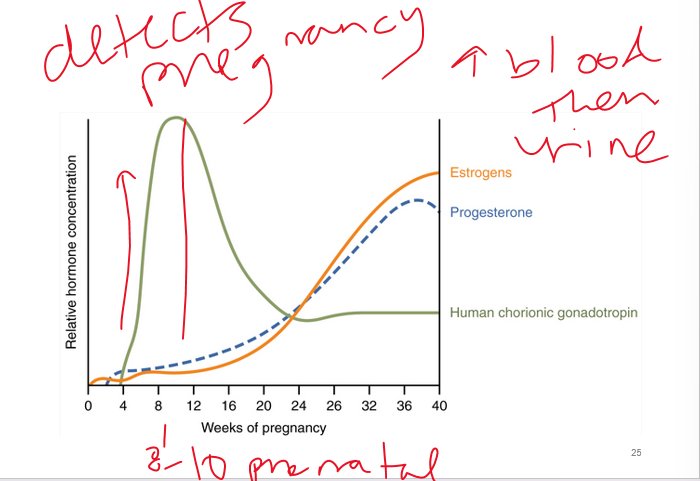
95
New cards
mixing
blood supply:
•Umbilical arteries and veins to the fetus are housed in the ***umbilical cord***
•Waste moves from ***fetus to maternal blood***
•Nutrients, hormones and growth factors move from maternal blood to fetus
•There is no mixing of the blood, just ***_________ of materials between bloodstreams***
•Umbilical arteries and veins to the fetus are housed in the ***umbilical cord***
•Waste moves from ***fetus to maternal blood***
•Nutrients, hormones and growth factors move from maternal blood to fetus
•There is no mixing of the blood, just ***_________ of materials between bloodstreams***
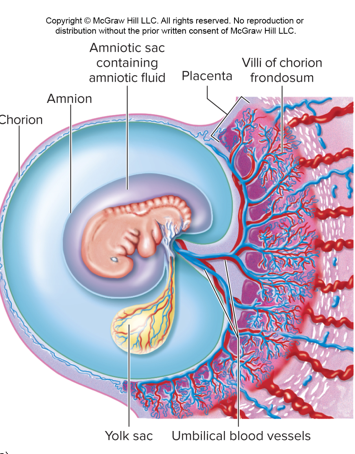
96
New cards
partuition:
•All the events near the end of the 40 week pregnancy including delivery
•Oxytocin and prostaglandins (fatty acid produced in several locations for regulation) stimulate contractions
•All the events near the end of the 40 week pregnancy including delivery
•Oxytocin and prostaglandins (fatty acid produced in several locations for regulation) stimulate contractions
97
New cards
adrenal
parturition
•Starts: ***Activation of fetal _________ cortex***
•Delivery stems from ***strong rhythmic contractions of myometrium***
•Ca2+ channels for muscle contraction are stimulated by oxytocin and prostaglandins (inc # and strength)
•Starts: ***Activation of fetal _________ cortex***
•Delivery stems from ***strong rhythmic contractions of myometrium***
•Ca2+ channels for muscle contraction are stimulated by oxytocin and prostaglandins (inc # and strength)
98
New cards
amniotic sac
•***__________ _______*** surrounding baby ruptures and flows through the vagina
\-no more oxytocin changes
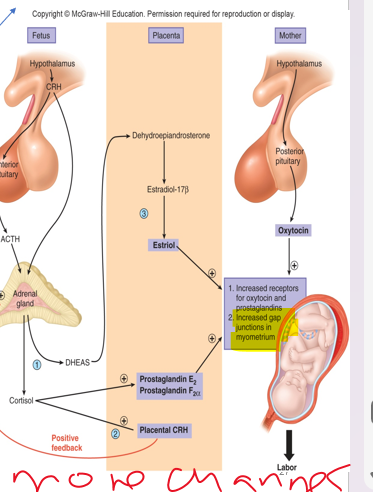
99
New cards
10
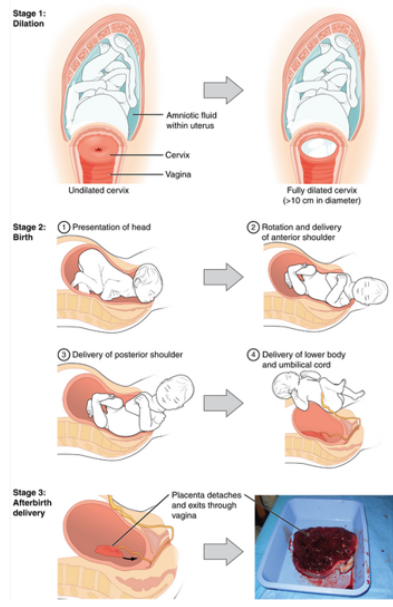
parturition
•As contractions increase in intensity and frequency, the cervix is forced to dilate to a maximum of **__ cm**
•Mother can increase abdominal pressure to add to contractions to deliver the baby
•Afterbirth is the delivery of the ***placenta*** as blood flow has stopped and it detaches
•As contractions increase in intensity and frequency, the cervix is forced to dilate to a maximum of **__ cm**
•Mother can increase abdominal pressure to add to contractions to deliver the baby
•Afterbirth is the delivery of the ***placenta*** as blood flow has stopped and it detaches