Edexcel IAL Biology A-Level = Gas Exchange and Membrane Transport
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Why do large multicellular organisms require specialised exchange surfaces?
1. small surface area to volume ratio
2. diffusion insufficient to provide all cells with the required oxygen and nutrients, and to remove all waste products
3. exchange surface increase rate of diffusion and shorten diffusion distance
how is surface area to volume ratio calculated?
ratio = surface area / volume
3 properties of an efficient exchange surface
1. large surface area to volume ratio
2. small diffusion distance
3. large concentration difference
How does diffusion distance affect the rate of diffusion?
the greater the diffusion distance, the further the molecules must travel
hence slower rate of diffusion
How does the concentration gradient affect the rate of diffusion?
the steeper the concentration gradient the faster the rate of diffusion
as area with high concentrations have many more particles in a certain volume and so there is a much greater chance of each particle moving to the less concentrated area
how does surface area to volume ratio affect the rate of diffusion?
the larger the surface area to volume ratio the faster the rate of diffusion
because as size of surface area increase, more molecules can diffuse across the surface thus diffusion rate increase
however as volume increase, there is a greater distance that molecule need to diffuse through, thus lowering rate of diffusion
How can the rate of diffusion be calculated?
Using Fick's law:
rate of diffusion ∝ (surface area x concentration gradient) / thickness of membrane
named the parts of the mammalian respiratory system
1. Trachea
2. Bronchus
3. Bronchiole
4. Diaphragm
5. Alveolus
6. Ribs
7. Intercostal muscles
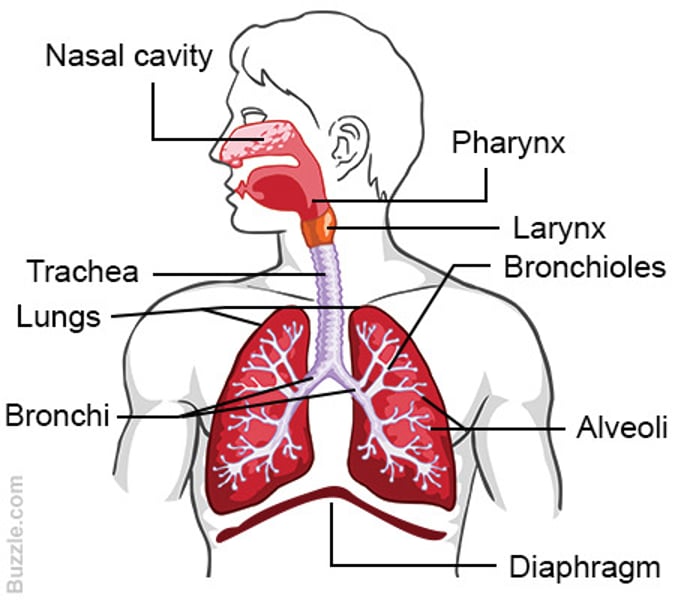
Describe the trachea and its function in the mammalian gaseous exchange system.
1. wide tube supported by c-shaped cartilage to keep the air passage open during pressure changes
2. lined by ciliated epithelium cells which move mucus. produced by goblet cells, towards the throat to be swallowed, preventing lung infections
3. carrier air to bronchi
Describe the bronchi and their function in the mammalian gaseous exchange system.
1. supported by rings of cartilage and are lined by ciliated epithelium cells and goblet cell
2. they are narrower and there are 2 of them, one for each lung
3. they allow the passage of air into the bronchioles
Describe the bronchioles and their function in the mammalian gaseous exchange system.
1. narrower than the bronchi
2. do not need to be kept open by cartilage therefore mostly have only smooth muscle and elastic fibres so that they can contract and relax easily during ventilation
3. allow passage of air into the alveoli
Describe the alveoli and their function in the mammalian gaseous exchange system.
1. mini air sacs, lined with epithelium cells
2. site of gas exchange
3. walls only one cell thick, covered with a network of capillaries, 300 million in each lungs
explain the process of inspiration and the changes that occur throughout the thorax
1. external intercostal muscle contract while internal relax, pulling ribs up and out
2,. diaphragm contracts + flattens
3. volume of the thorax increase
4. air pressure outside lungs is therefore higher than air pressure inside, so air moves in to rebalance
explain the process of expiration and the changes that occur throughout the thorax
1. external intercostal muscle relax while internal contract, pulling ribs down and in
2,. diaphragm relaxes + return to its dome-like shape
3. volume of the thorax decrease
4. air pressure inside lungs is therefore higher than air pressure outside, so air moves out to rebalance
describe the structure and components of a typical cell membrane
contain a phospholipid bilayer which is studded with various protein.
they also typically contain cholesterol which sits in the hydrophobic portion of membrane to regulate fluidity
other molecules like glycoprotein and glycolipids may protrude from the membrane
5 function of cell membrane
1. act as selectively permeable barriers
2. contain receptors used for communication
3. site of chemical reaction
4. allow for signal transduction
5. used for transport and uptake of substance
What is the fluid mosaic model?
In this model, a flexible layer made of lipid molecules is mixed with large protein molecules that act as channels.
what are intrinsic proteins
Proteins found within the phospholipid bilayer. Includes channel and carrier proteins
outline the functions of intrinsic proteins
- Structural support
- Carry water-soluble molecules across the phospholipid bilayer
- Form ion channels to enable active transport
what are extrinsic proteins
Proteins found at the edges of the phospholipid bilayer
outline the functions of extrinsic proteins
- Receptors
- Act as antigens, enabling cell recognition
- Help cells adhere to each other
what is meant by the term compartmentalisation in biology?
compartmentalisation is the separation of areas within cells which allows for the localisation of enzymes and molecules so that separate areas can carry out specific function
What is the glycocalyx?
A glycoprotein and glycolipid coating surrounding the cell membrane of some cells
state 3 factors that affect the permeability of the plasma membrane
1. amount of unsaturated fatty acids
2. temperature
3. amount of cholesterol present
describe how varying temperature affect membrane permeability
1. temperature increases, molecules have more kinetic energy and so move around more, creating gaps in membrane
2. as temperature increases past a certain point, the proteins in membrane become denatured, disrupting the membrane
describe the structure of cholesterol
1. 4 carbon rings with a side chain
2. Steroid backbone
3. Hydrocarbon tail (thus hydrophobic)
4. Stored in the phospholipid bilayer
describe the function of cholesterol
Cholesterol regulates membrane fluidity.
At high temperatures, it stabilises the membrane and at low temperatures, it keeps the phospholipids apart which allows the membrane to remain fluid
how does the amount of unsaturated fatty acids affect membrane permeability
- unsaturation causes a bend in the fatty acid tails
- this means they cannot pack as tightly together which allows more substance to pass through the membrane so the membrane is more permeable
how do organic solvents affect membrane fluidity
Organic solvents can disrupt or even dissolve the membrane, making it more fluid
Define osmosis
The passive movement of water molecules from a region of high water potential to a region of lower water potential (down a water potential gradient) through a semi-permeable membrane
what is water potential
Measure of the tendency of water molecules to diffuse from one region to another
what unit is water potential measured in?
kilopascals (kPa)
What is the water potential of pure water?
0 kPa
Define diffusion
The random molecular motion by which matter is transported from a region of higher concentration to one of lower concentration without the use of energy
Define facilitated diffusion
The net movement of substances from a high concentration to a lower concentration (down their concentration gradient) through transport proteins without the use of energy.
define active transport
The movement of substances from a low concentration to a high concentration against a concentration gradient, through carrier proteins with the use of energy in the form of ATP
what are the 2 mechanisms of bulk transport
endocytosis and exocytosis
Define endocytosis
The bulk uptake of substances into a cell by invagination of the membrane to form a vesicle. Uses energy in the form of ATP
State 2 types of endocytosis
phagocytosis and pinocytosis
What is pinocytosis?
The bulk uptake of liquids into the cell using energy in the form of ATP.
What is phagocytosis?
The bulk uptake of solids into the cell using energy in the form of ATP
Define exocytosis
The bulk transport of substances out of a cell via a vesicle that fuses with the plasma membrane. Uses energy in the form of ATP
what are the 2 difference between carrier proteins and channel proteins?
channel proteins provide hydrophilic passage for molecules to passively diffuse through
carrier proteins can transport substances across a membrane through conformational changes which an be either passive or active.
Why does oxygen diffuse from the alveoli into the blood?
Oxygen concentration is higher in the alveoli than in the blood, so it moves into the capillaries by diffusion.
How is oxygen transported in the blood?
Oxygen binds to haemoglobin in red blood cells, forming oxyhaemoglobin, and is carried to body tissues.
Why does carbon dioxide move from the blood into the alveoli?
Carbon dioxide concentration is higher in the blood than in the alveoli, so it diffuses into the alveoli to be exhaled.
How is carbon dioxide transported in the blood?
About 70% is carried as bicarbonate ions, 20% binds to haemoglobin (carbaminohaemoglobin), and 10% dissolves in plasma.
Why must alveoli be moist for gas exchange?
Oxygen dissolves in the moisture, allowing it to diffuse more easily into the blood.
Where can goblet cells be found in the respiratory system?
Goblet cells are scattered throughout the ciliated epithelium in the trachea and bronchi, but usually not in the bronchioles.
Where is smooth muscle found in the respiratory system?
In the walls of the trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles.
Function of smooth muscle
It regulates air flow by relaxing when more air is needed and constricting when less is needed.
What are elastic fibers and where are they located in the respiratory system?
Elastic fibers, also known as elastin, are found in the lining of the airways and in the walls of the alveoli. They help the airways and alveoli recoil to their original shape after stretching during inhalation.