M-Lec 6: G6 - Four Stages of Modernization
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Modernization
A complex process of societal, technological, and cultural transformation from traditional ways to more contemporary ones.
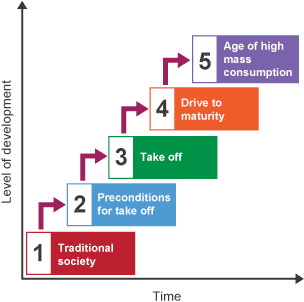
Model of Economic Growth
A theory model by Walt Rostow that outlines the 5 stages that countries progress through to achieve modernization and development.
Walt Rostow
An economist who developed the theory model of economic growth.
Traditional Society
The first stage of the model is where a community is deeply rooted in the past, governed by long-standing customs, habits, and beliefs rather than by future-oriented goals or modern innovations.
Preconditions for Take-Off
The second stage of modernization is where there are economic shifts such as agricultural production surplus, infrastructure growth from investments of tradeways, the rise of local entrepreneurship, colonization, and improvements in social.
Take-Off
The third stage of modernization is where a society begins rapid economic growth and moves away from traditional practices toward industrialization and modernization.
Drive to Maturity
The fourth stage of modernization is where there is a period of prolonged economic growth and diversification, innovations spread anywhere, there is deep involvement in global trade and finance, and living standards rise.
High Mass Consumption
The fifth and final stage of modernization is characterized by a surplus of goods and services, high disposable income, and a shift from heavy industry to a service- and consumer-driven economy.
Pre-colonial societies in Asia, Africa, and Latin America
Example of Traditional Society.
19th-century Philippines under Spanish/American rule, when ports were opened to international trade.
Example of Preconditions for Take-Off
Meiji (late 1800s)
A period in Japan where Western industrial practices were adopted. An example of preconditions for takeoff.
Industrial Revolution (late 18th-19th century)
A period happened in Great Britain where factories, steam engines, and railways emerged. An example of takeoff.
Japan
A country after WWII where they experienced rapid industrial rebuilding with the help of US aid and technology. An example of takeoff.
South Korea
A country where, during the 1960s-1980s, they experienced a transition from agrarian to industrial powerhouse. An example of takeoff.
Germany and Japan
2 countries where, after the 1950s, they rebuilt and became industrial giants. An example of driving to maturity.
United States
A country that entered an age of high mass consumption after World War II.
Western Europe
A certain part of a continent where they entered an age of high mass consumption.
Singapore
An ASEAN country where they are now in age of high mass consumption.
Eurocentric
A term describing that all countries must follow the Western path.
Gulf State
A state where they leapfrog or skip stages because of oil wealth.