Chem Quantum Numbers
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
did pard
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Quantum Set
[3,1,0,+1/2] Describes the possible locations of e-
![<p>[3,1,0,+1/2] Describes the possible locations of e-</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ca51271e-f264-4558-b517-38e7e231ace0.png)
Principle Quantum Number
[3,1,0,+1/2] # → is energy level ‘n’ (1,2,3,4, → 7) can not be 0
![<p>[<span style="color: red;"><strong>3</strong></span>,1,0,+1/2] # → is energy level ‘n’ (1,2,3,4, → 7) can not be 0</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d592804f-4d42-4ddc-b95a-db011015f21c.jpg)
QM Model
[3,1,0,+1/2] 2nd Quan # → L, describes the shape of sublevel
l=0 → s (spherical)
l=1 → p (dumbbell shaped)
l=2 → d (clover shaped)
l=3 → f (complex shape)
![<p>[3,<span style="color: red;"><strong><span>1</span></strong></span>,0,+1/2] 2nd Quan # → L, describes the shape of sublevel </p><p>l=0 → s (spherical)</p><p>l=1 → p (dumbbell shaped)</p><p>l=2 → d (clover shaped)</p><p>l=3 → f (complex shape)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8f8ad077-3667-40ef-b97f-f8ef236cce59.jpg)
Magnetic Quantum Number
[3,1,0,+1/2] What orbital the e- is in the sublevel
s → 0
p → -1,0,+1
d → -2,-1,0,+1,+2
f → -3,-2,-1,0,+1,+2,+3
![<p>[3,1,<span style="color: red;"><strong><span>0</span></strong></span>,+1/2] What orbital the e- is in the sublevel</p><p>s → 0 </p><p>p → -1,<span style="color: red;"><strong>0</strong></span>,+1</p><p>d → -2,-1,0,+1,+2</p><p>f → -3,-2,-1,0,+1,+2,+3</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/48ec53dd-6176-41b0-9e89-c368601dcec2.png)
Electron Spin
[3,1,0,+1/2 ] shows what spin the electron is spinning, can only be -1/2 or +1/2
![<p>[3,1,0,<span style="color: red;"><strong><span>+1/2</span></strong></span> ] shows what spin the electron is spinning, can only be -1/2 or +1/2 </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ca4ef6af-4309-446f-b57a-77659ba6897a.png)
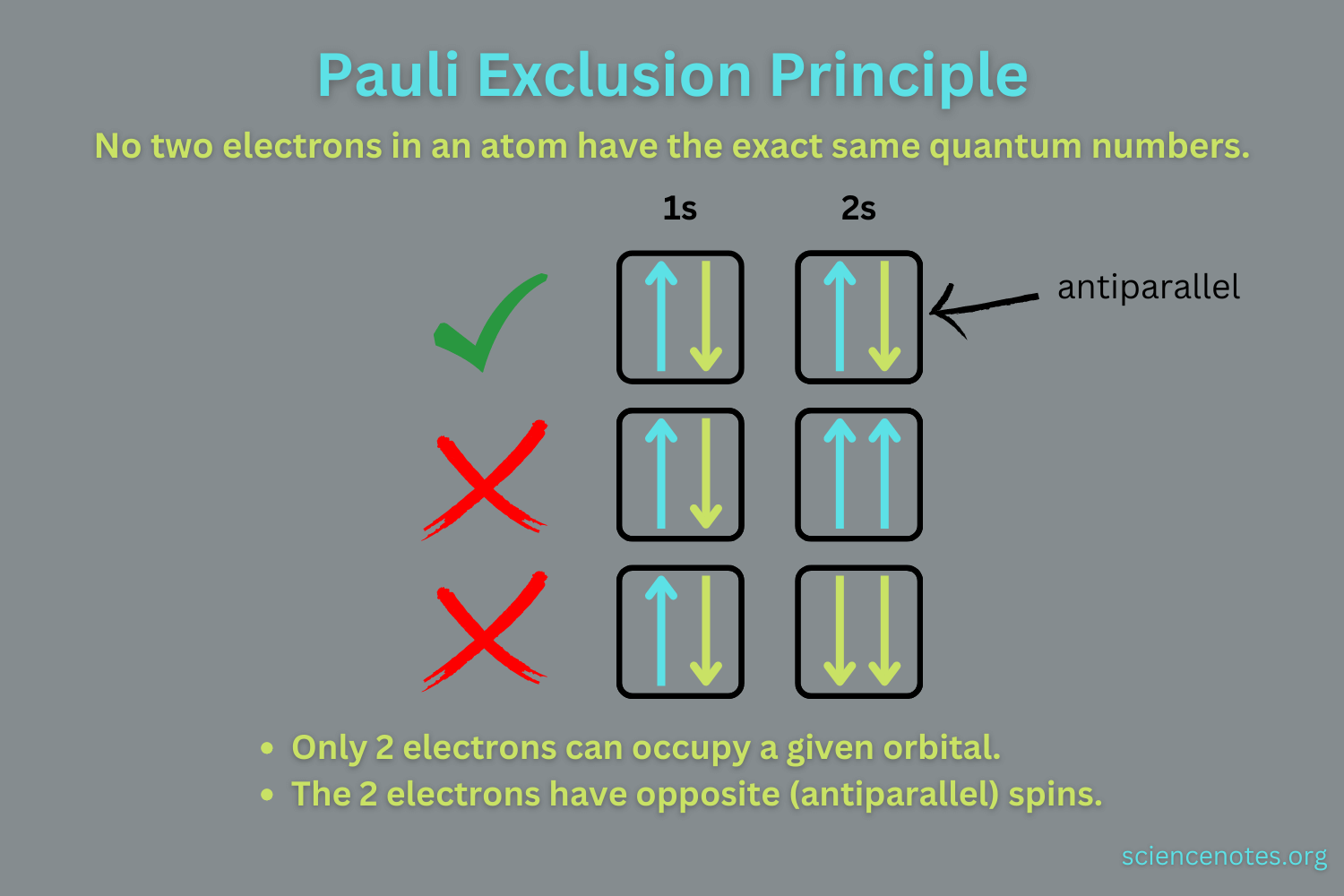
Orbital Occupancy
Each orbital can only have two electrons. To fill, they need to have opposite spin.
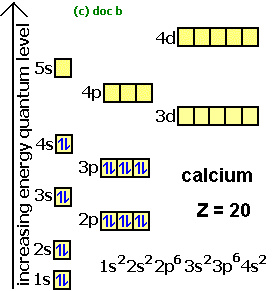
Energy Levels
n - 1 = s → 2e-
n - 2 = s, p → 8e-
n - 3 = s, p, d → 18e-
n - 4 = s, p, d, f → 32e-
4-7 = 32e-
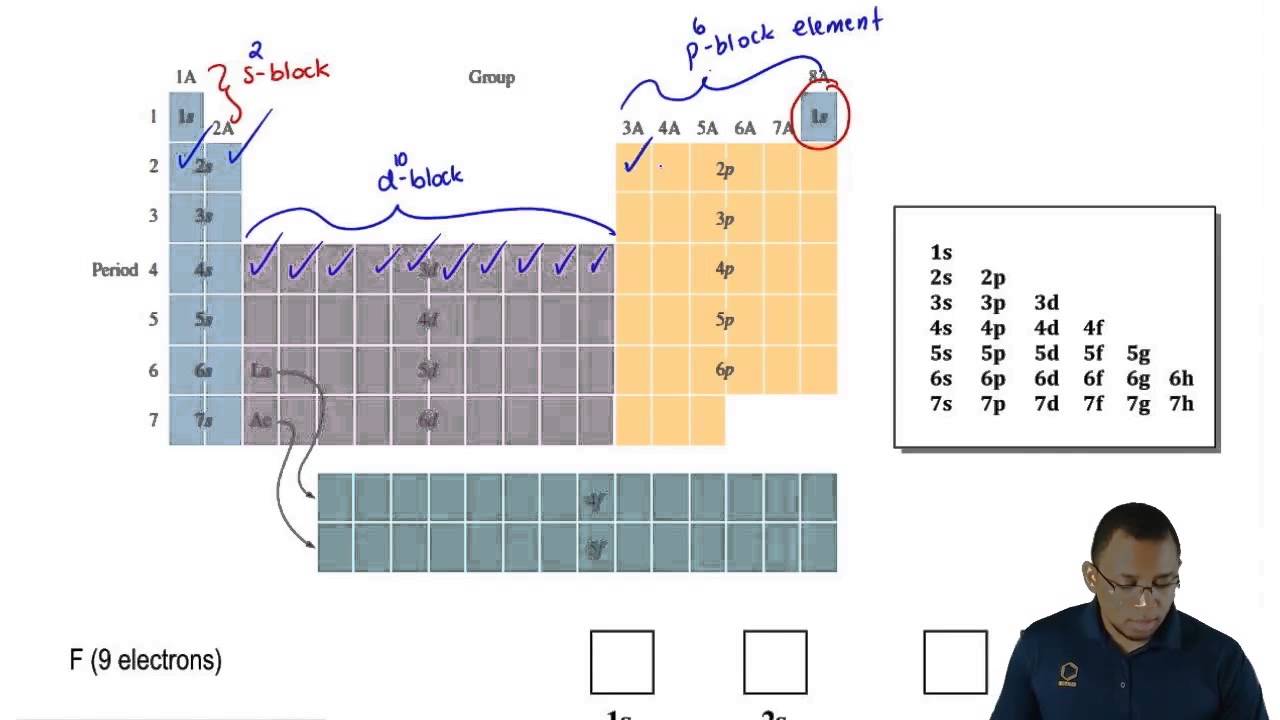
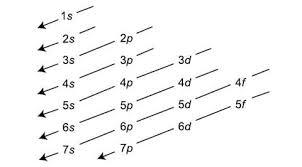
Written Sublevel Occupancy
1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, ect.
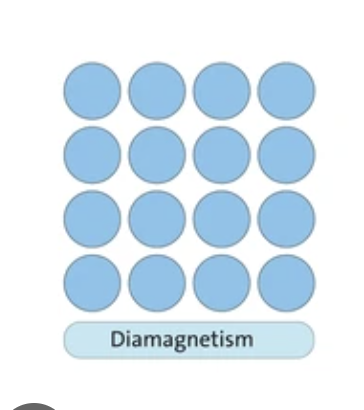
Diamagnetism
All electrons are pared, there is no net spin. All electron spin gets canciled out by eachother.
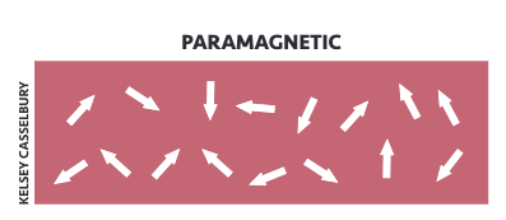
Paramagnetism
Electron spins are randomly oriented
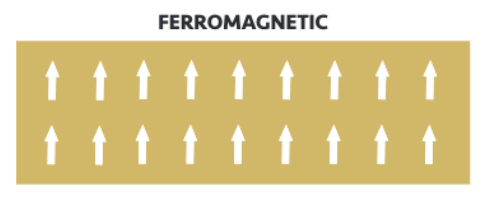
Ferromagnetism
Electron spins are parallel
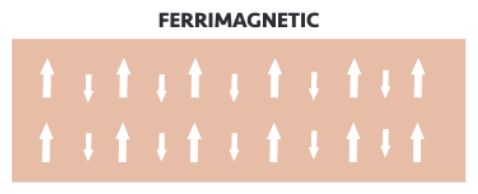
Ferrimagnetism
Electron spins are parallel and an opposite directions, but don't cancel each other out.
Aufbau’s Rule
Electrons fill atomic orbitals from the lowest energy level to the highest
Pauli Exclusion Rule
States that no two electrons in an atom can have identical spins
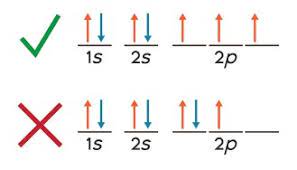
Hund’s Rule
electrons in a sub level will singly occupy each orbital with parallel spins before any orbital is doubly occupied