Unit 4 -- Consumers, Producers, and the Efficiency of Markets
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Welfare economics
the study of how the allocation of resources affects economic well-being
Well-being
the happiness or satisfaction with life as reported by individuals
Allocative efficiency
resource allocation where the value of the output by sellers matches the value placed on that output by buyers:
- Buyers and sellers receive benefits from taking part in the market.
- The equilibrium in a market maximizes the total welfare of buyers and sellers.
Willingness to pay
the maximum amount that a buyer will pay for a good - measures how much the buyer values the good or service
Consumer surplus
the amount a buyer is willing to pay for a good minus the amount the buyer actually pays for it
What does CS look like with a linear demand curve?
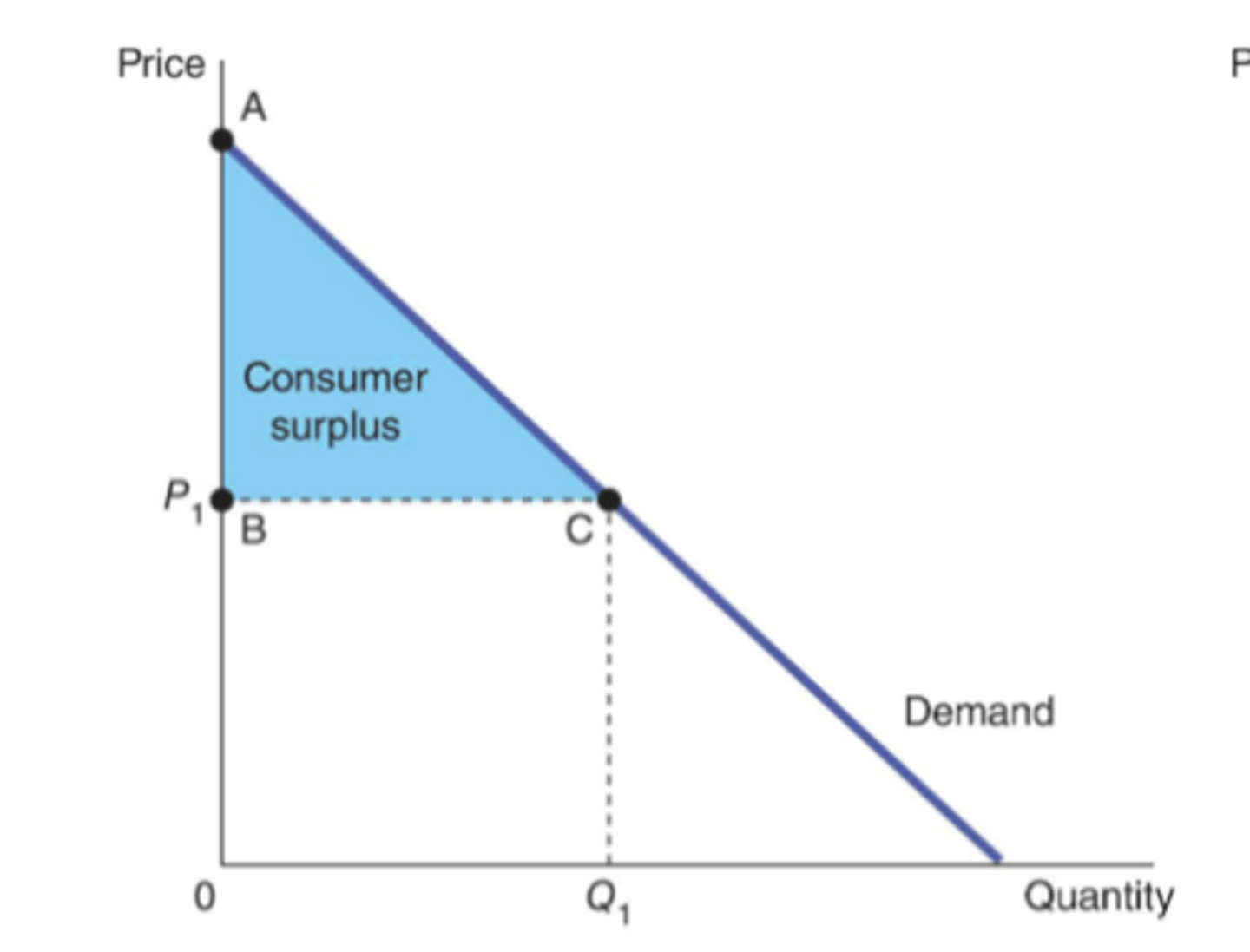
What would CS look like if price dropped?
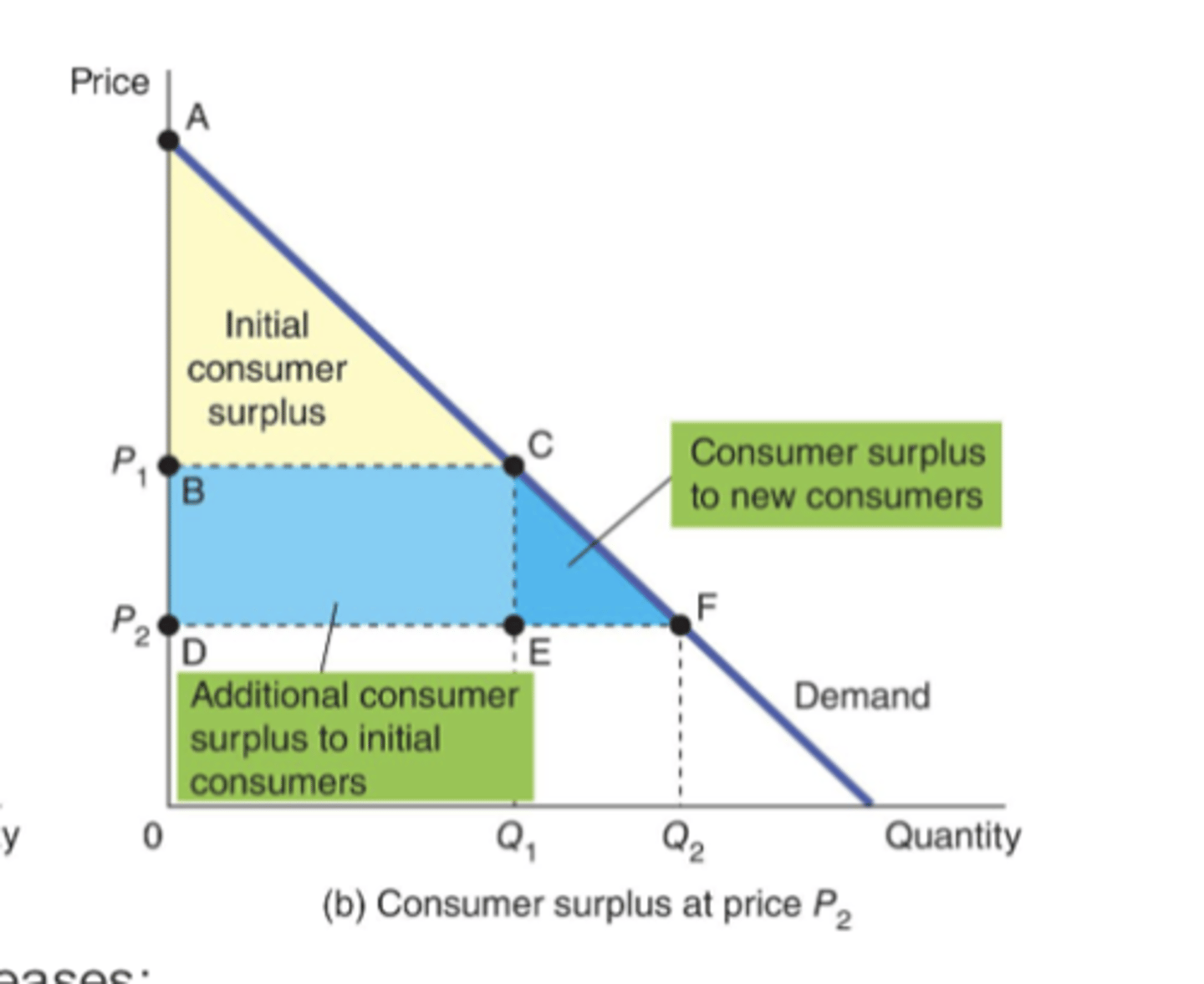
What does CS measure?
measures the benefit that buyers receive from a good as thebuyers themselves perceive it.
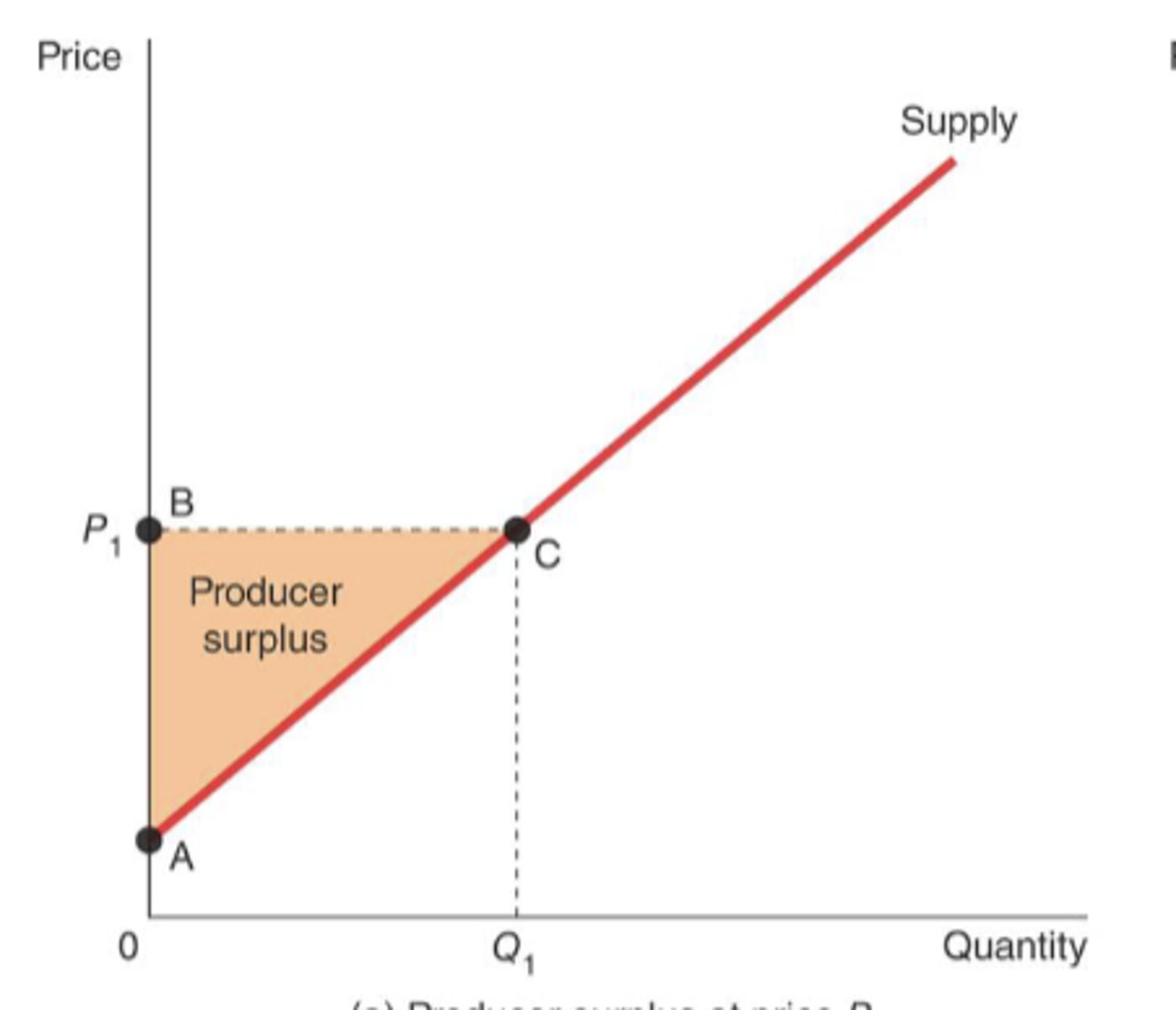
Producer surplus
the amount a seller is paid for a good minus the seller's cost of providing it -- measures the benefit to sellers participating in a market
Cost
the value of everything a seller must give up to produce a good
What does PS look like with a linear supply curve?
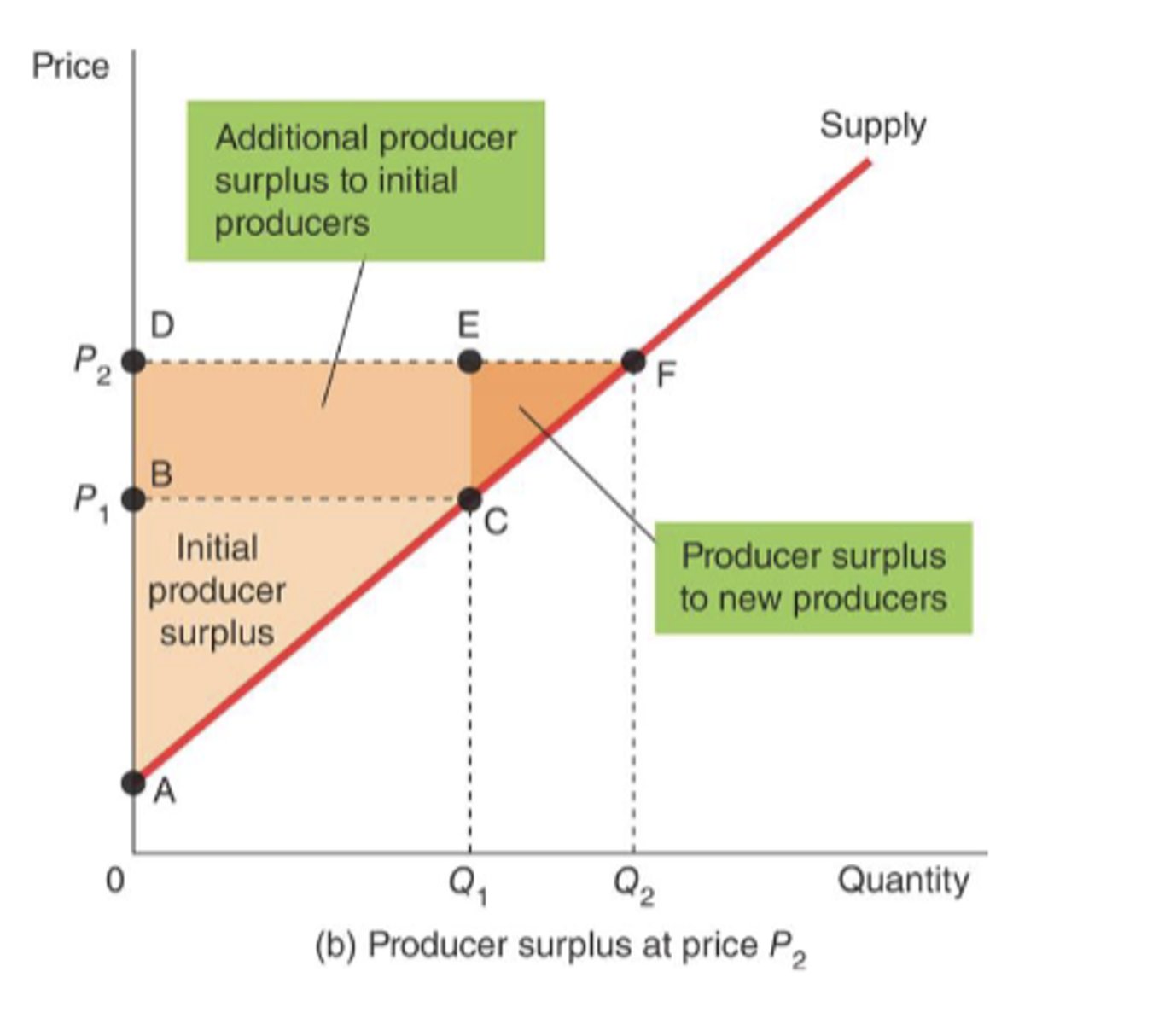
What would happen to PS if there was an increase in price?
Is the allocation of resources determined by free markets inany way desirable?
In theory, free market economies usually do not have long term vast shortages
1. Incentives exist for producers and consumers to change their behavior which moves the market to equilibrium.
2. The market mechanism leads to efficient outcomes.
3. Consumers are maximizing utility and producers are maximizing profits and producing at minimum average cost
Total surplus
consumer surplus + producer surplus
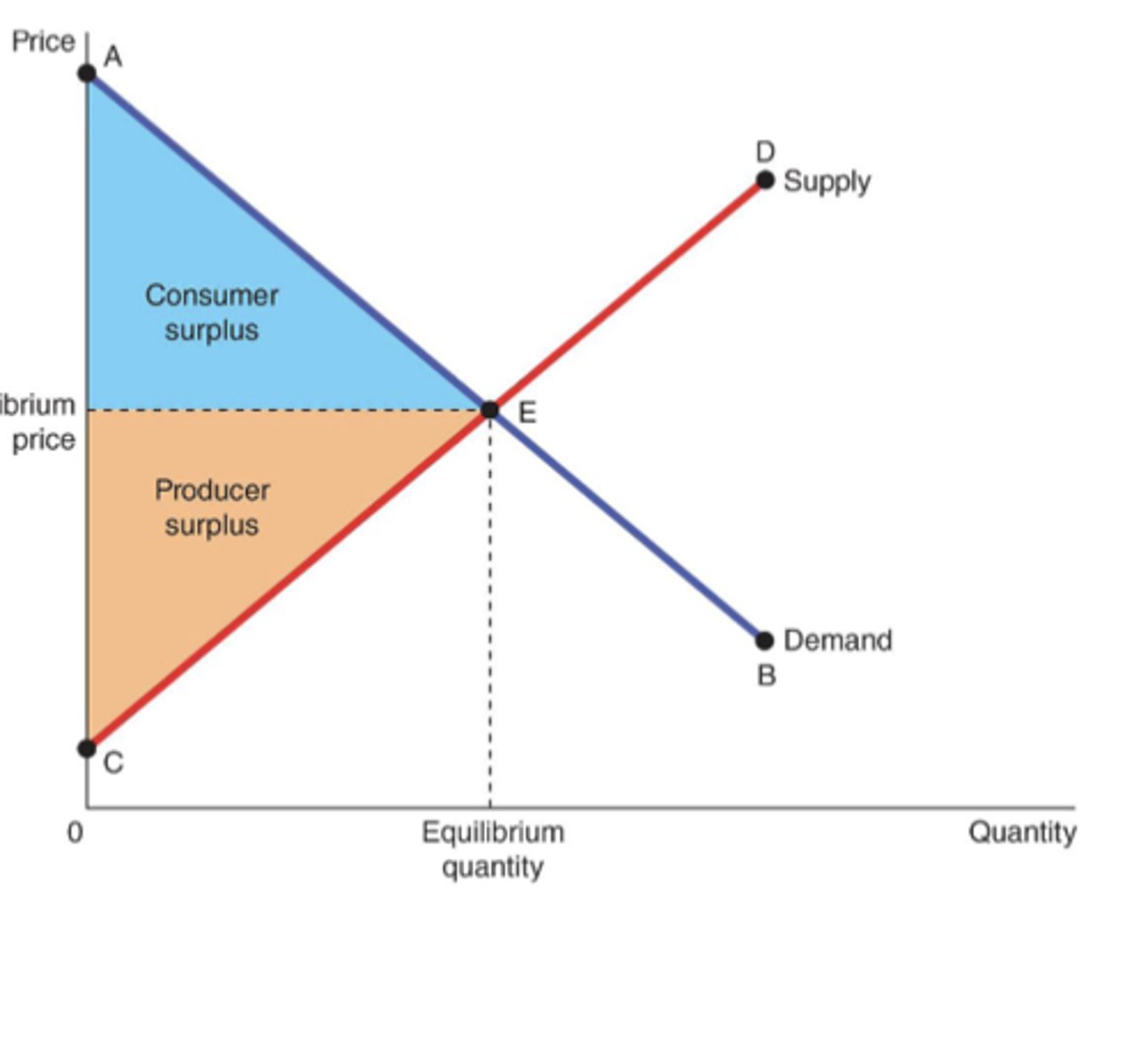
Three Insights Concerning Market Outcomes
1. Free markets allocate the supply of goods to the buyers who value them most highly, as measured by their willingness to pay.
2. Free markets allocate the demand for goods to the sellers who can produce them at least cost.
3. Free markets produce the quantity of goods that maximizes the sum of consumer and producer surplus.