Semmelweis Entrance Exam Medicine Biology
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
153 Terms
What are carbohydrates and lipids?
Organic compounds that are mostly composed of three types of atom; carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
What do carbohydrates do?
provide energy, in the form of sugars like glucose and fructose, but they also make up structures like cellulose, which form the cell wall of plant cells
What type of carbohydrate is the most important source of energy?
mono-, di- and poly-saccharides
What are mono and disaccharides?
polar and soluble in water
What are polysaccharides?
Macromolecules resulting from polymerisation (condensation) of sugars and are not soluble in water
Examples of monosaccharides
ribose, glucose, fructose, galactose
What forms a disaccharide?
two monosaccharides linked together by condensation reactions with glycosidic bonds releasing one H2O molecule
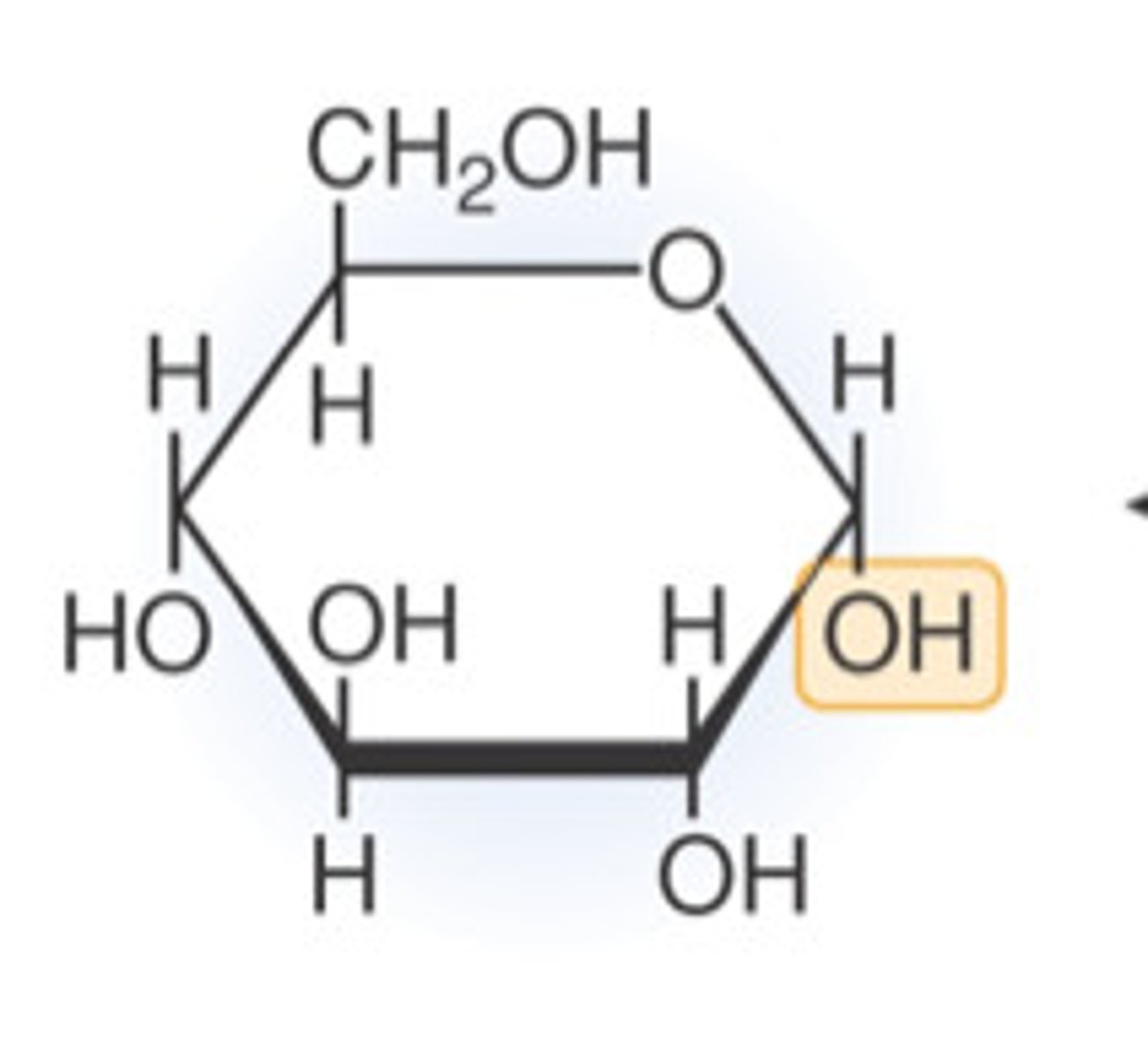
Alpha glucose structure
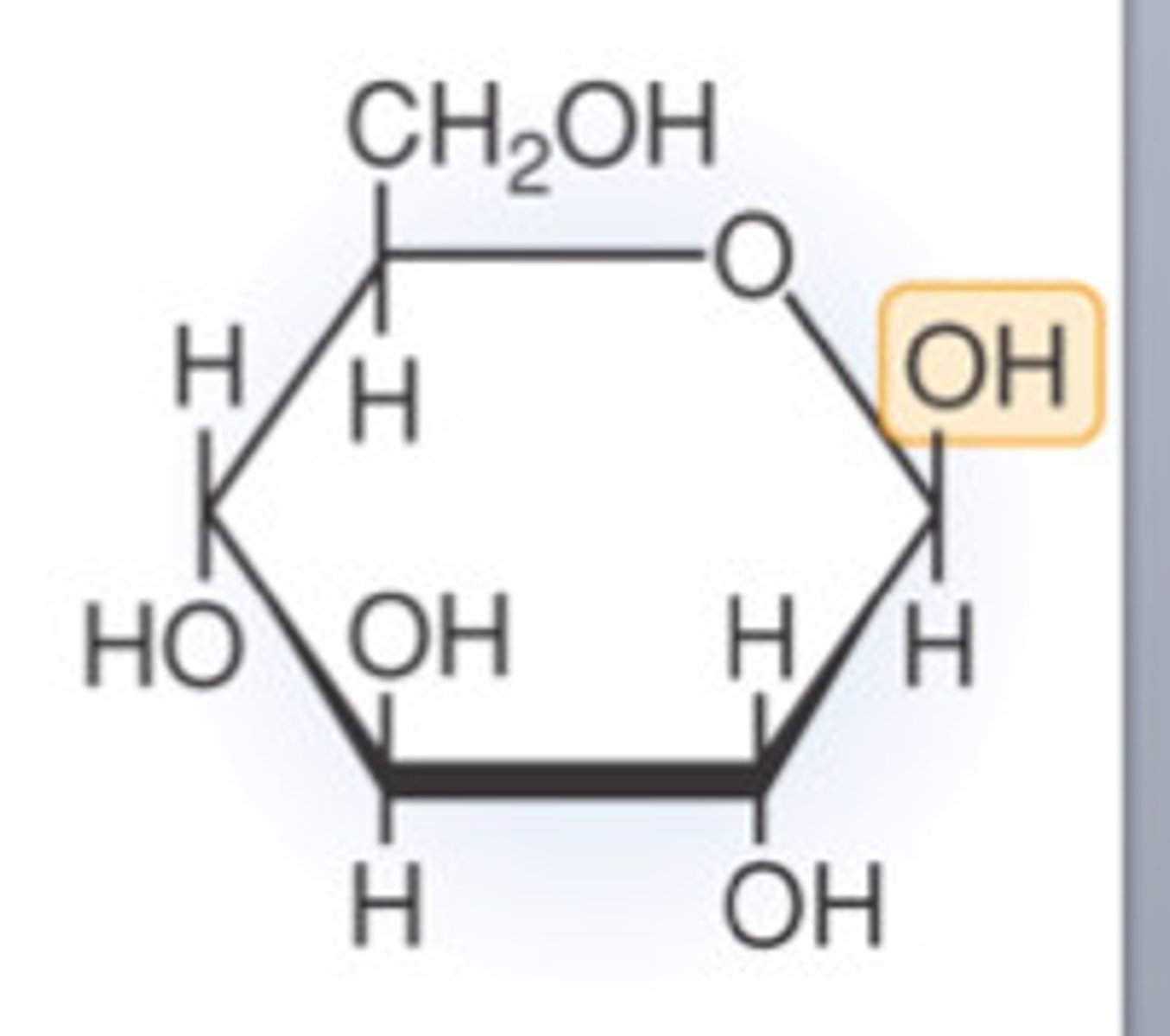
Beta glucose structure
Examples of Polysaccharides
cellulose, glycogen and starch
Monomer of Sucrose
glucose and fructose
monomer of maltose
glucose and glucose
monomer of lactose
glucose and galactose
monomer of starch
glucose
monomer of glycogen
glucose
monomer of cellulose
glucose
In animals, what carbohydrate stores energy?
glycogen
What jobs do carbohydrates have other than storing energy?
structural components
What differs the polysaccharides all made up of glucose?
they differ in the arrangement of glucose molecules and position of the glycosidic bonds
Starch arrangement
amylopectin branched, amylose linear
What is galactose?
a sugar in milk
What is fructose?
a sugar found in fruit and honey
Main characteristic of lipids?
little to no affinity to water, mostly hydrophobic
What are the simple forms of lipids?
fat, oil and wax
What are lipids characteristics in different solvents?
they are non-polar and insoluble in water, but soluble in organic solvents
What are triglycerides?
the main group of lipids. They are formed by condensation reactions between one glycerol and three fatty acids, creating ester bonds
What are the main types of triglycerides?
fats and oils. Fats are solid and oil liquid at room temp
What are fatty acids?
carboxylic acids, possessing a -COOH functional group
What are the two basic forms of fatty acids?
saturated and unsaturated
What differs saturated from unsaturated fatty acids?
Unsaturated fatty acids have double bonds; a monounsaturated having one, whereas a polyunsaturated having multiple
What are cis and trans isomers?
cis having the double bond elements on the same side, trans on opposite
Benefit of lipids over carbohydrates?
Lipids have a higher energy content and can act as thermal insulators
What is the primary protein structure?
the number and sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide
What is the secondary protein structure?
Beta pleated sheet and alpha helix. Hydrogen bonds between polypeptides form these structures
What is the tertiary protein structure?
three dimensional conformation. Forms when a polypeptide folds up after translation. Stabilized by intramolecular bonds between amino acids and polypeptides
What is the quaternary protein structure?
linking two or more polypeptides to form a single protein
What is the basic structure of DNA?
it is composed of three parts, a pentose sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base
Difference in structure between DNA and RNA
RNA contains a ribose sugar instead of deoxyribose and is also single stranded as well as having Uracil as a base instead of thymine
What are the two double helix strands held together by?
hydrogen bonds
What are hydrogen bonds?
a special type of dipole-dipole attraction between molecules, not a covalent bond to a hydrogen atom. It results from the attractive force between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a very electronegative atom such as a N, O, or F atom and another very electronegative atom
Why is DNA antiparallel?
so that the paired bases can face each other
what is mRNA?
Messenger RNA: Encodes amino acid sequence of a polypeptide
What is tRNA?
transfer RNA. It carries amino acids around during translation.
What is rRNA?
Ribosomal RNA. with ribosomal proteins, makes up the ribosomes, the organelles that translate the mRNA
what is snRNA?
small nuclear RNA. with proteins, forms complexes that are used in RNA processing in eukaryotes
What are enzymes?
biological catalysts. They are globular proteins that can speed up a biochemical reaction. Alternative pathway
What is glycolysis?
the breakdown of glucose by enzymes, releasing energy and pyruvic acid.
What is the kreb's cycle?
second stage of cellular respiration, in which pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of energy-extracting reactions
What is the mechanism of ATP production in the mitochondria?
located in the inner mitochondrial membrane, allows the protons to diffuse back across the membrane to the matrix. ATP synthase uses the energy that the protons release as they diffuse down the concentration gradient to produce ATP
What is the net yield of ATP in cellular respiration?
38 total
2 in glycolysis
2 in Krebs's cycle
34 in chemiosmosis (electron transport chain)
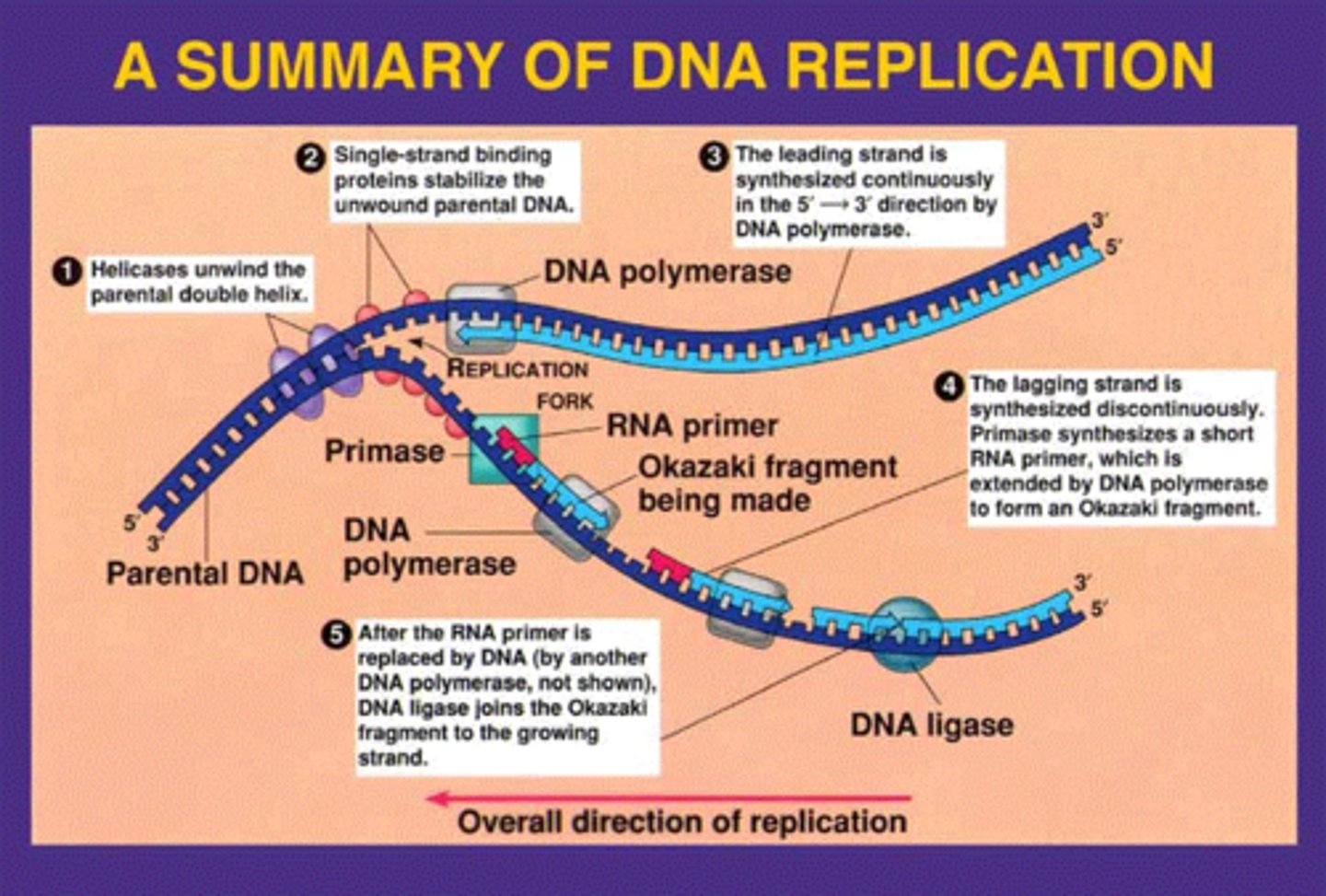
What is DNA replication?
the process of copying DNA
What is DNA transcription?
the organic process whereby the DNA sequence in a gene is copied into mRNA
What is translation?
the decoding of an mRNA message into amino acids which ultimately form protein
what are the stages of transcription?
Initiation, elongation, termination
How does DNA replication occur?
what is the nucleus
A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction
What are chromosomes?
Chromosomes are long, thin strings composed of DNA and proteins which carry genes.
What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum?
Modifies, packages, and transports proteins
What is the function of the golgi apparatus?
sorts and modifies proteins that have arrived from the rough ER
What is the function of ribosomes?
protein synthesis by translating mRNA
What is the cytoskeleton?
a microscopic network of protein filaments and tubules in the cytoplasm of many living cells, giving them shape and coherence.
What is exocytosis?
a process by which the contents of a cell vacuole are released to the exterior through fusion of the vacuole membrane with the cell membrane.
What is endocytosis?
the taking in of matter by a living cell by invagination of its membrane to form a vacuole
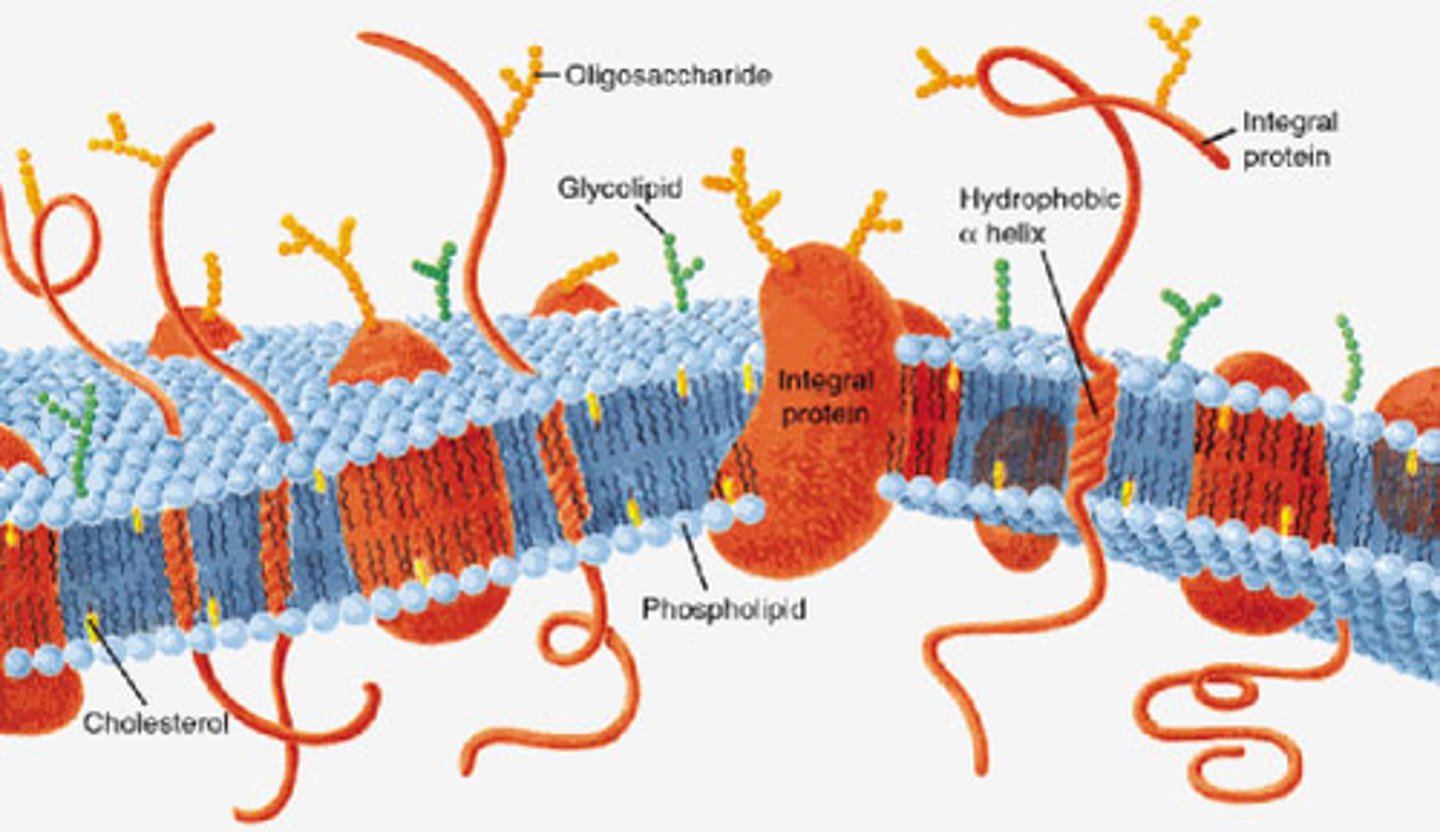
What is the function of a cell membrane?
The cell membrane regulates what enters and leaves the cell and also protects and supports the cell
Cell membrane diagram
Describe the process of mitosis
- Start with: Diploid, 2N
- Interphase: DNA replication = Dipoid, 4N
- Prophase: Condensation of chromatin,
appearance of sister chromatids
- Metaphase: Sister chromatids align
- Anaphase: Sister chromatids separate,
centromeres divide
- Telophase and Cytokinesis: Two identical,
diploid, daughter cells: Diploid, 2N
Describe the process of meiosis
When a cell divides to form gametes:
1. Copies of the genetic information are made
2. The cell divides twice to form four gametes, each with a single set of chromosomes
3. All gametes are genetically different from each other
Gametes join at fertilisation to restore the normal number of chromosomes. The new cell divides by mitosis. The number of cells increases. As the embryo develops, cells differentiate.
When does crossing over occur?
prophase I of meiosis
When does recombination occur in meiosis?
during prophase I, when homologous chromosomes line up in pairs and swap segments of DNA.
What is the structure of prokaryotic cells?
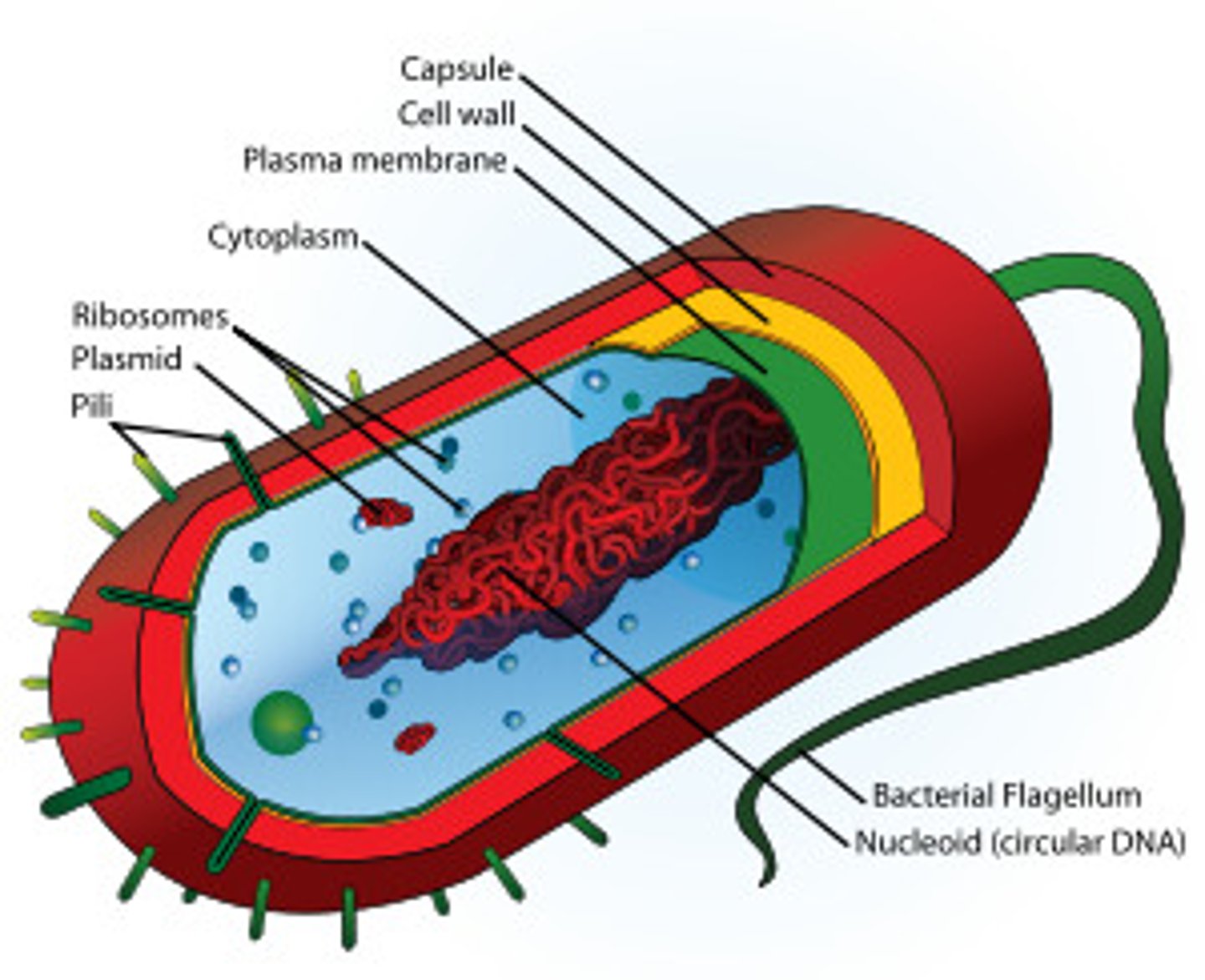
Example of prokaryotic cell
E. coli
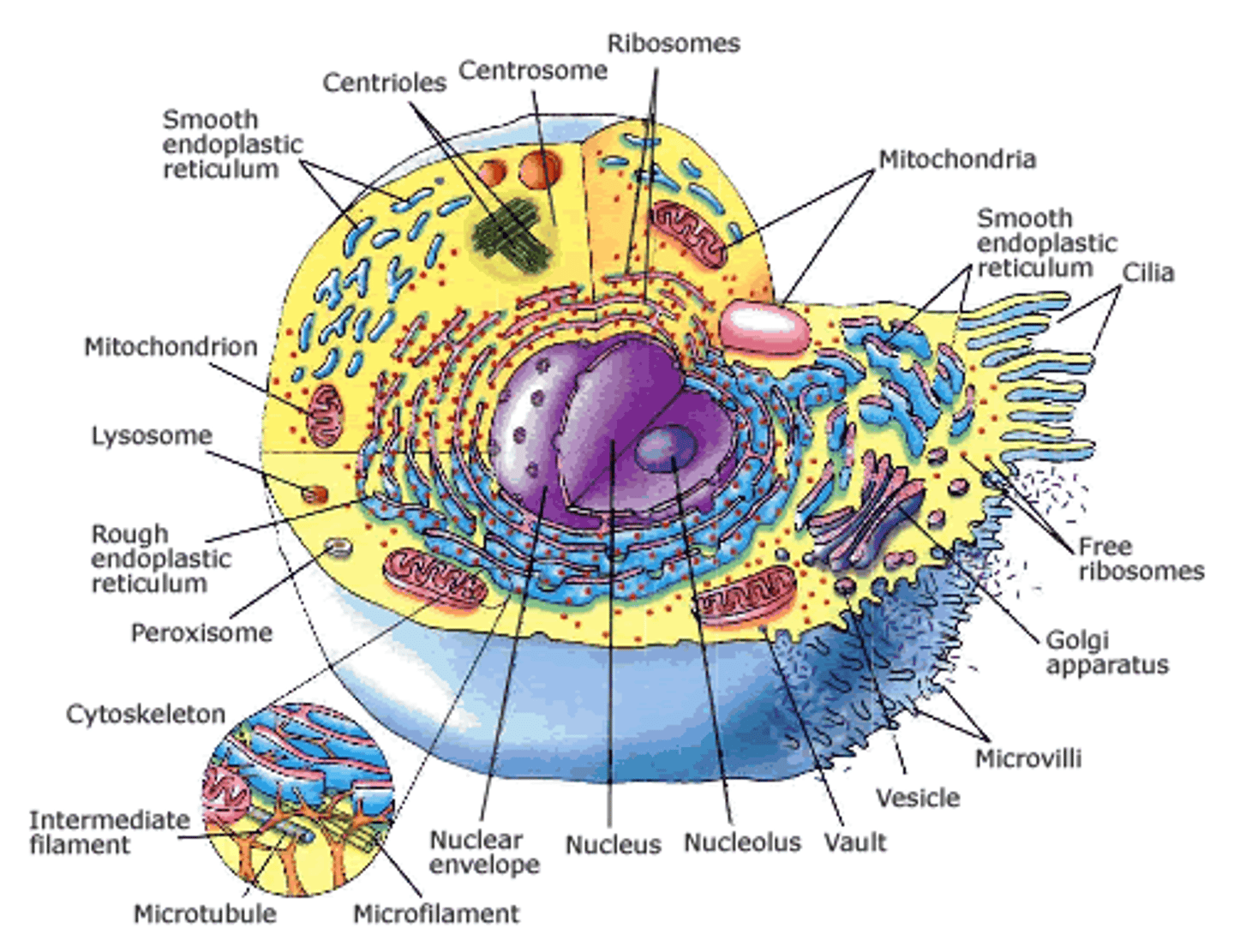
Example of eukaryotic cell
plant and animal cells
What is the structure of eukaryotic cells?
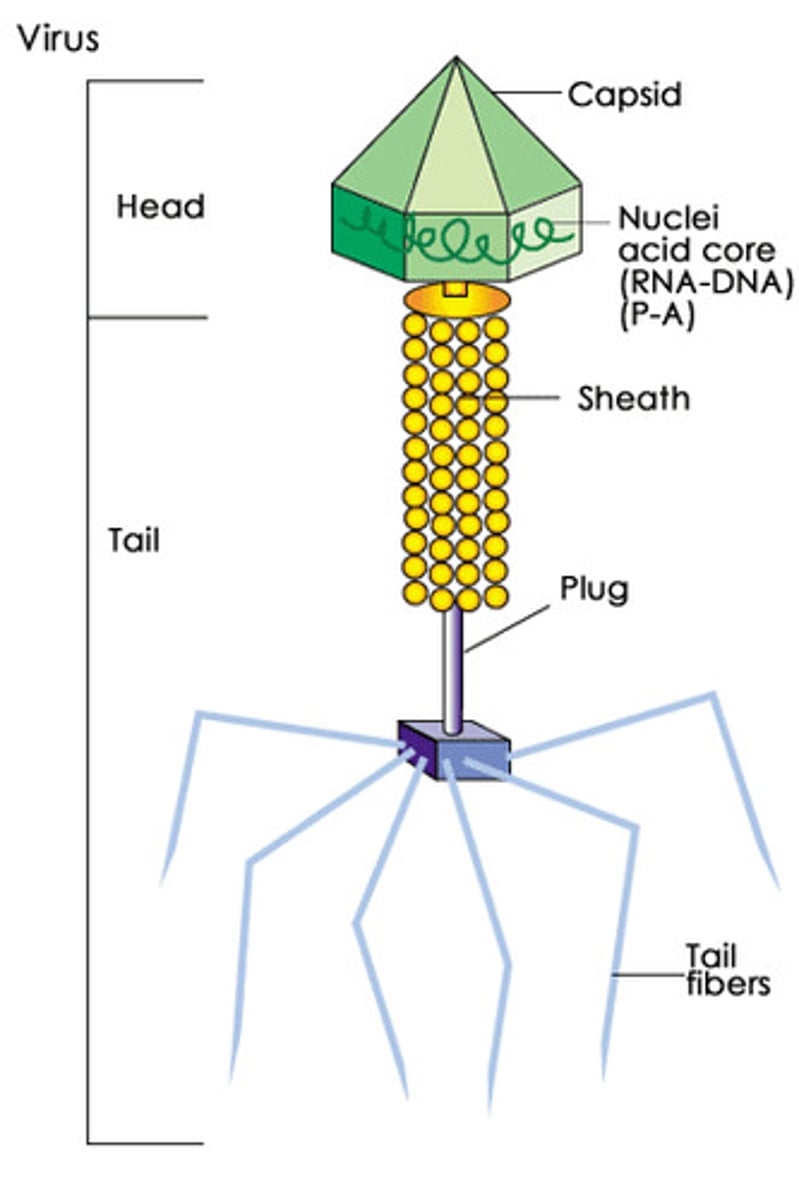
What is the structure of a virus?
A typical virus is composed of a core of DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coat
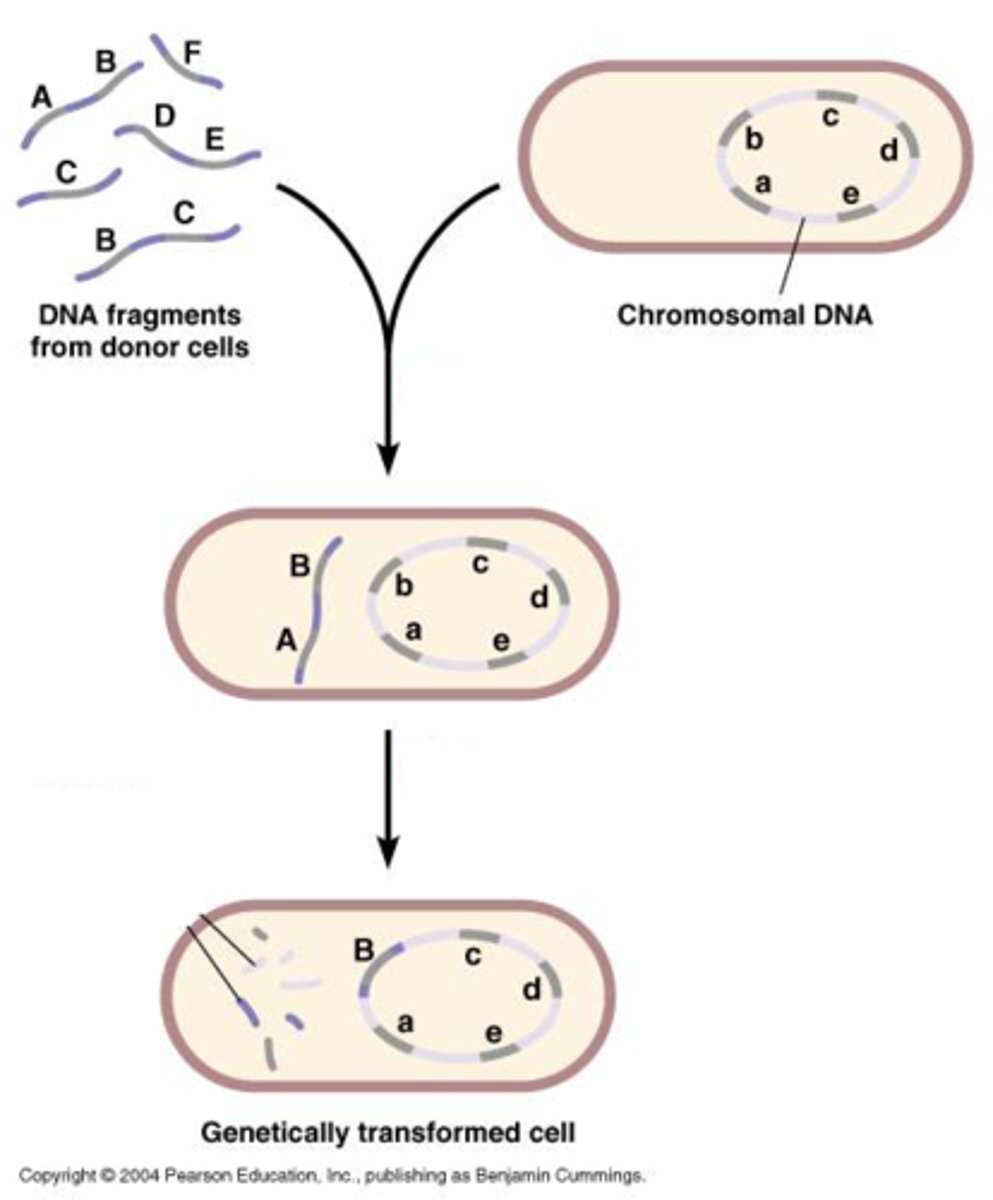
What is transformation?
uptake of DNA from environment
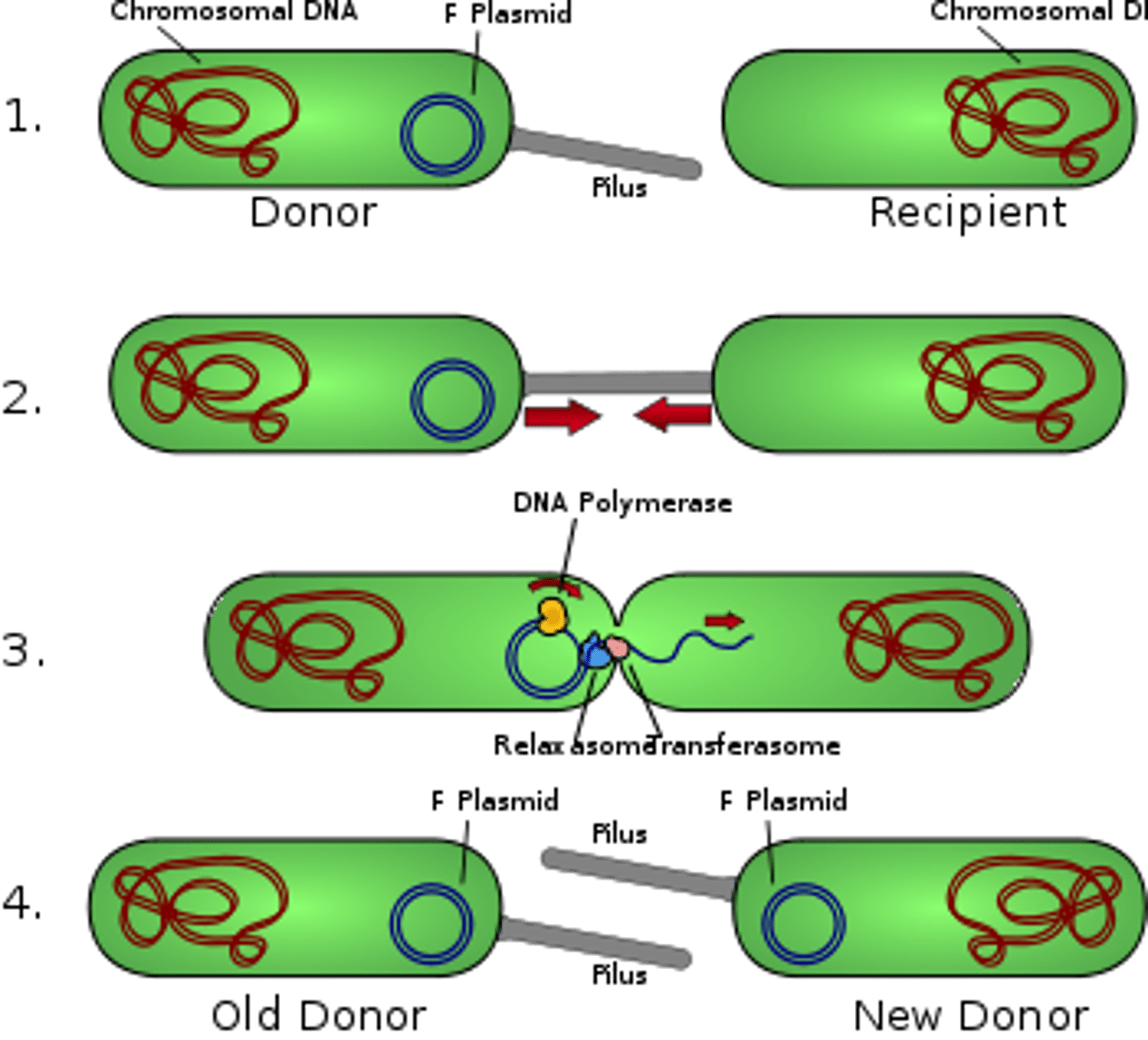
What is conjugation?
A process in which 2 organisms exchange genetic material
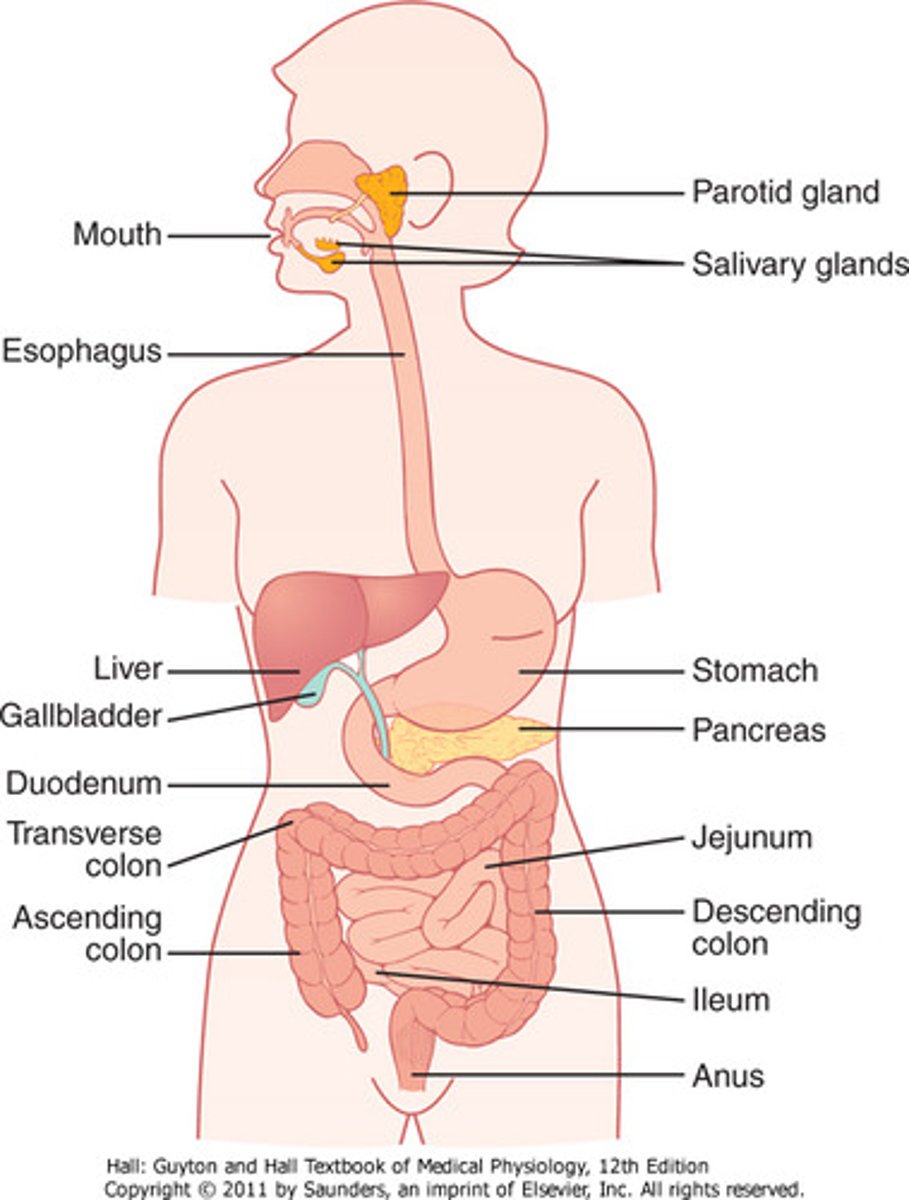
What are all the parts to the digestive system?
How does absorption occur?
diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, active transport
How does absorption work?
- food molecules are absorbed into the blood or the lymph. To be absorbed in the body the molecules need to pass into the capillaries or the villus. Fats absorb into the lymph
- Substances to be absorbed move from the lumen into the epithelial villi
- Amino acids and monosaccharides move from the villi into capillaries and monoglycerides move into the lacteals
What are some of the digestive enzymes?
-typsinogen and chymotrypsin (breaks down proteins)
-amylase breaks down starches and sugars
-lipase breaks down fats
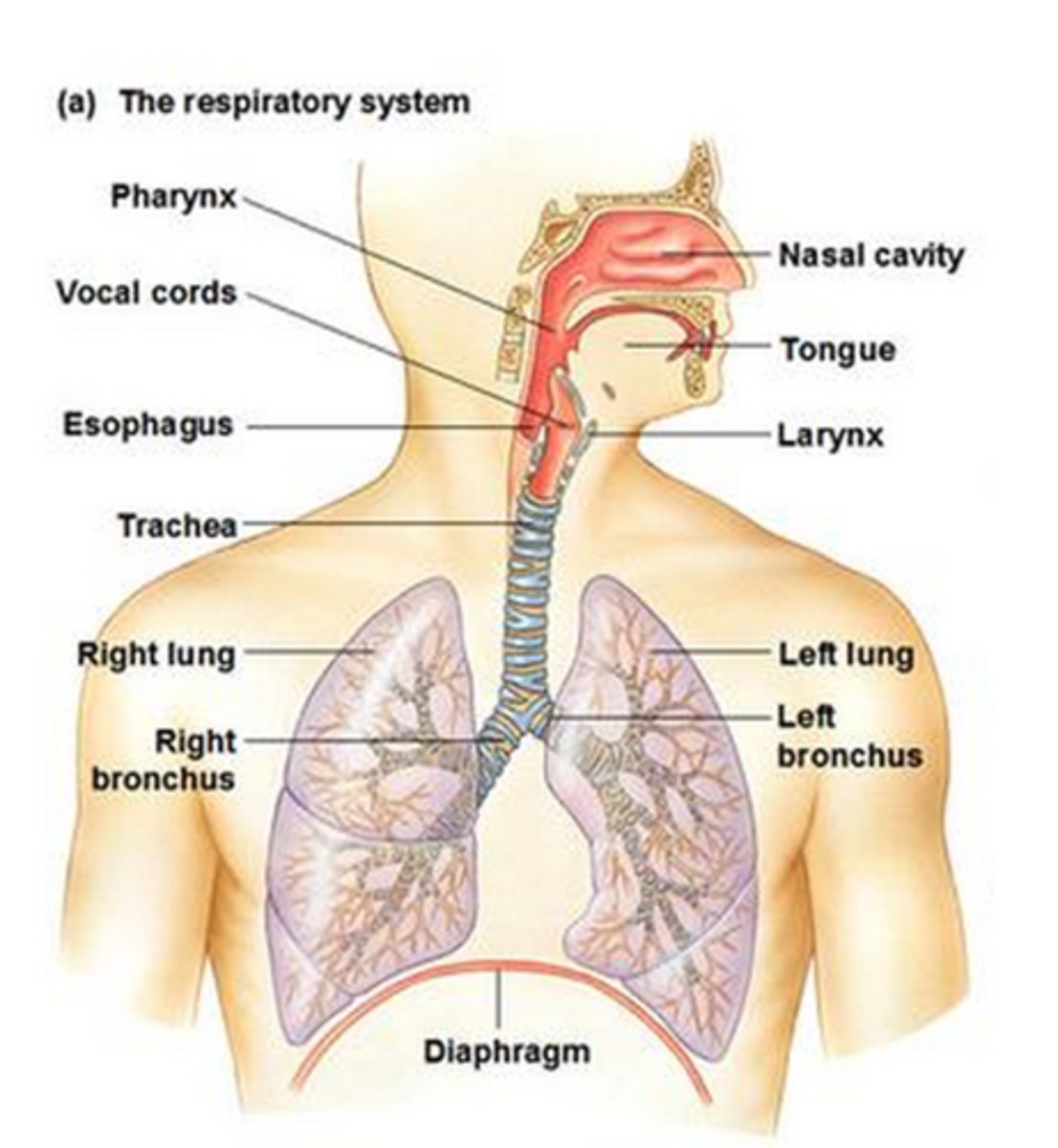
What are the parts of the respiratory system?
What are the mechanisms of inhalation and exhalation?
When you inhale, the diaphragm contracts and moves downward. Through exhalation air leaves the lungs and the diaphragm relaxes
How does the oxygen and CO2 exchange in the lungs occur?
Gas exchange is the delivery of oxygen from the lungs to the bloodstream, and the elimination of carbon dioxide from the bloodstream to the lungs. The walls of the alveoli share a membrane with the capillaries in which oxygen and carbon dioxide move freely between the respiratory system and the bloodstream
What are the parts of the excretory system?
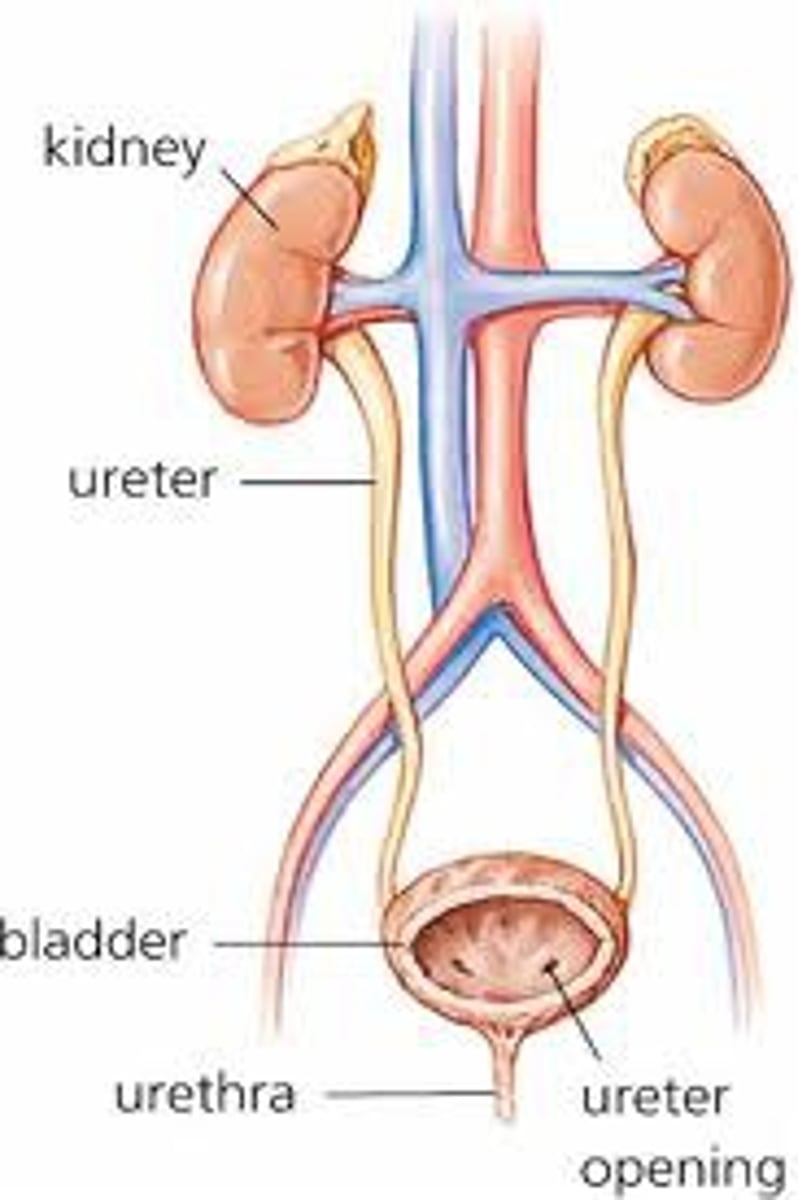
What are the parts of the circulatory system?
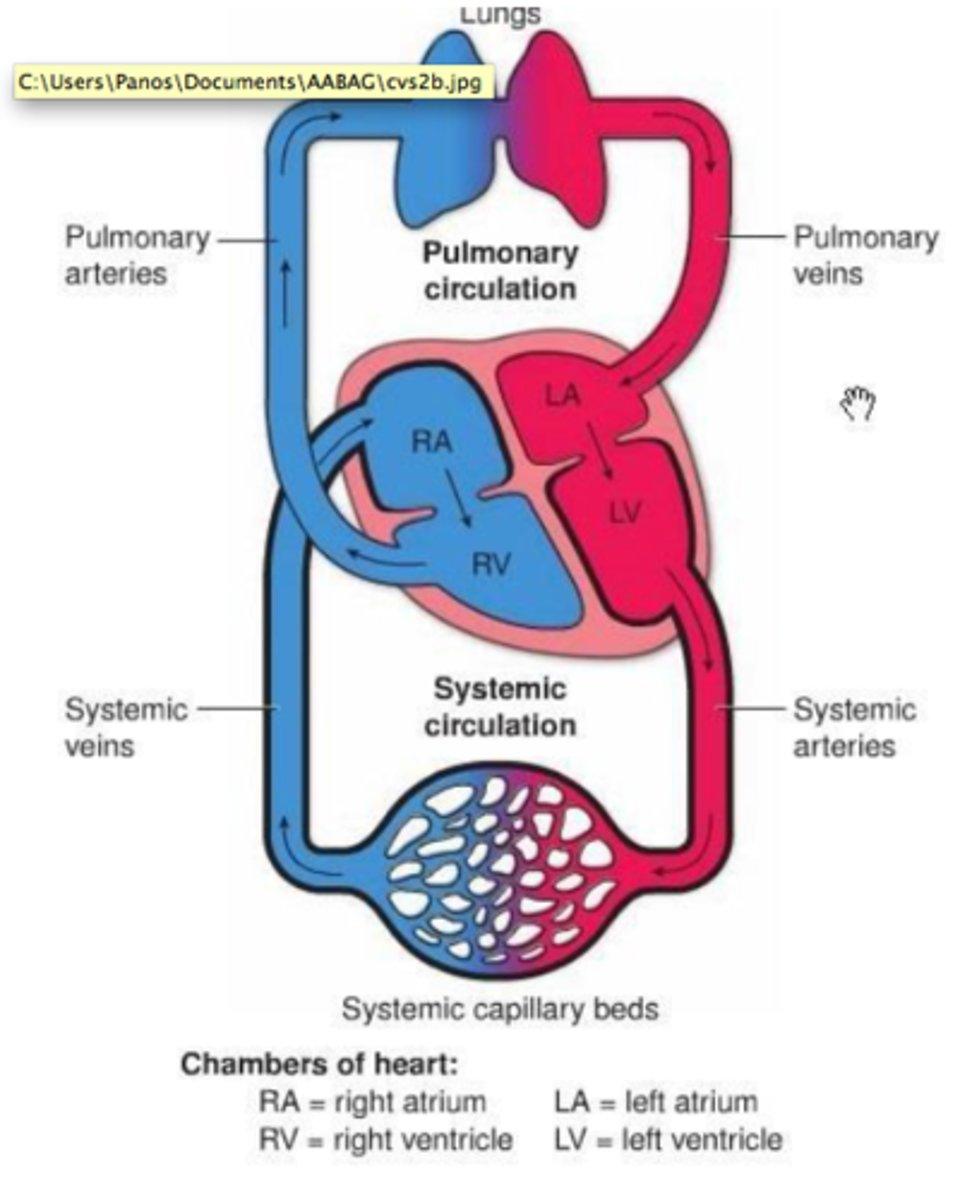
What is the function of the heart?
The heart is the most powerful muscle in the body, pumping 4,000 gallons of blood a day
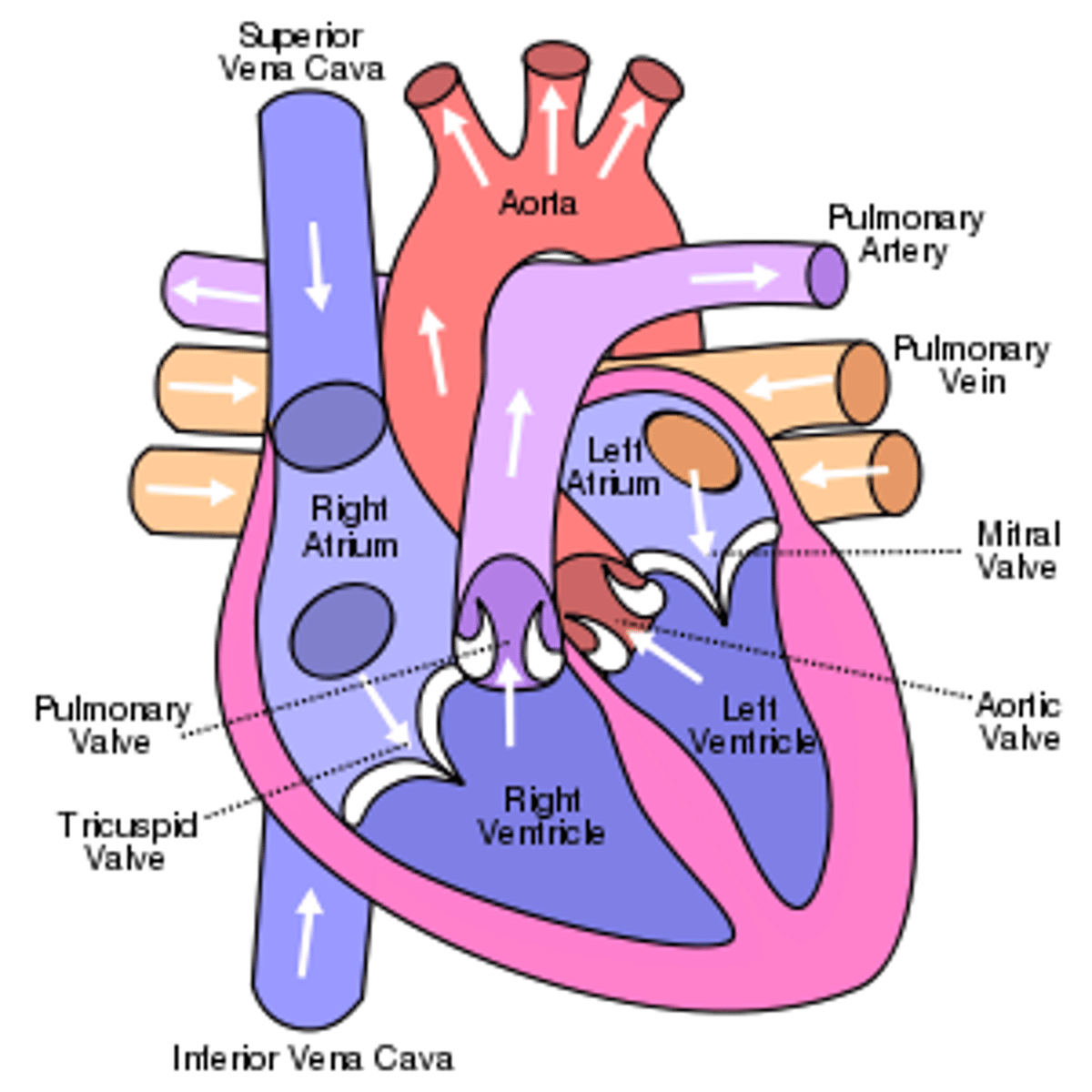
What is the structure of the heart?
What is blood?
fluid connective tissue
What does blood contain?
Nutrients such as glucose, antibodies, carbon dioxide, heat, oxygen, urea and hormones
What are the different cell types?
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic
What is the process of cellular immune response?
the immune system's third line of defense, involving the attack of pathogens by T cells
What are the three lines of defense?
First line: Natural barriers: Skin and mucous membranes
Second line: Inflammation
Third line: Adaptive (acquired) immunity
How does blood clotting occur?
Clotting seals damaged vessels to prevent pathogenic entry
- Injured cells and platelets release clotting factors
- These factors convert prothrombin into thrombin
- Thrombin converts fibrinogen (soluble) into fibrin (insoluble)
- Fibrin forms a mesh of fibres that block the injured site - Clotting factors also cause platelets to become sticky and form a solid plug (called a clot), sealing the wound - This process of events is called a coagulation cascade
- Clot formation in coronary arteries lead to heart attacks
What is innate immunity?
Nonspecific protection against foreign substances indiscriminantly
All cells but lymphocytes
What is the humoral immune response?
The humoral immune response targets pathogens circulating in "humors," or extracellular fluids, such as blood and lymph. Antibodies target invading pathogens for destruction via multiple defense mechanisms, including neutralization, opsonization, and activation of the complement system. Patients that are impaired in the production of antibodies suffer from severe and frequent infections by common pathogens and unusual pathogens
What are muscles?
tissues or fibers that cause movement of body parts and organs
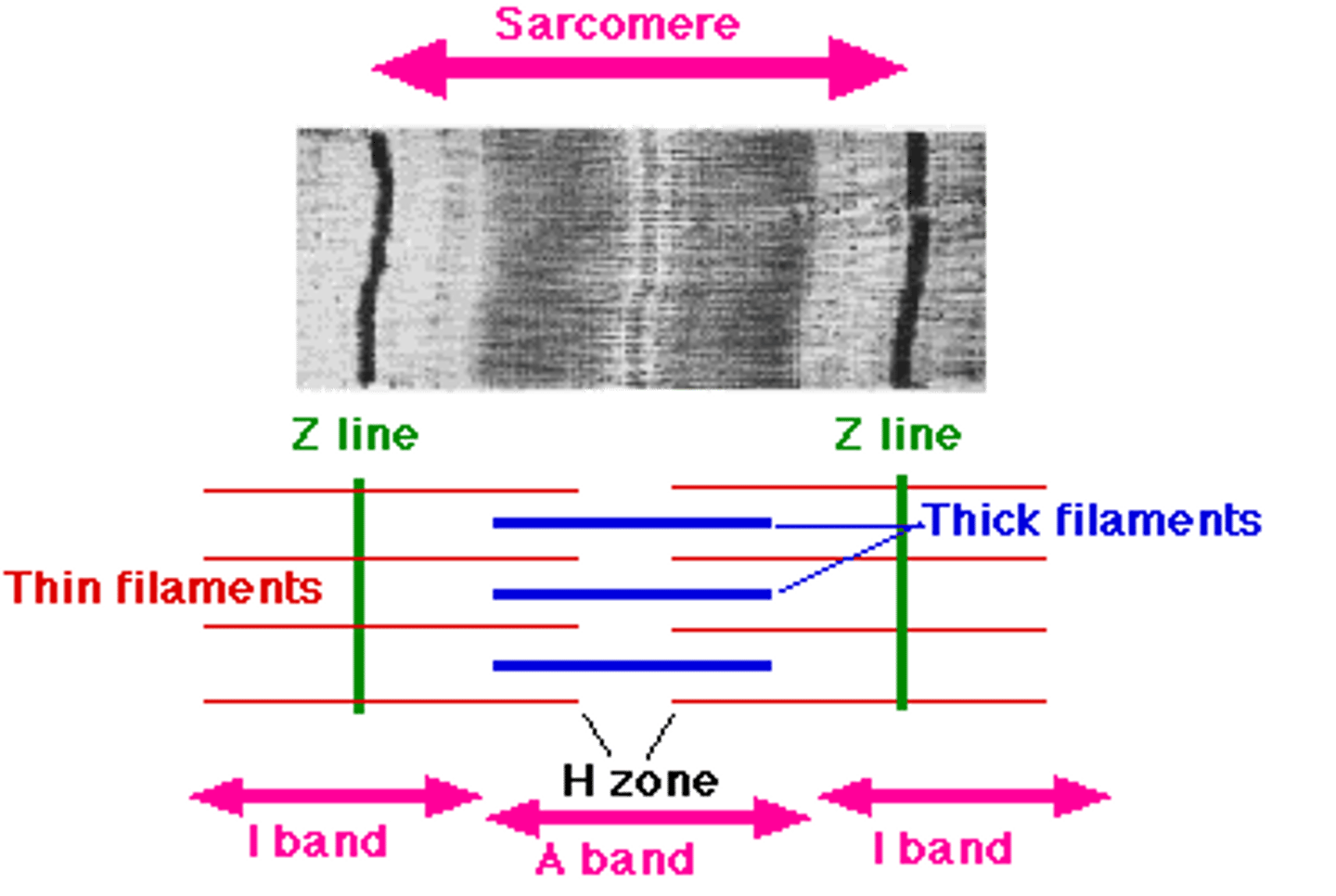
Structure of muscles
each muscle fiber contains many microfibrils
each divided along its length into repeating units called sacromeres
General definition of joints
Areas where two or more bones join together
Describe muscle contraction
Muscle contraction Is caused by interactions of thick and thin filaments
Thin filament (actin) is attached to Z line
Thick filaments (myosin) is "hanging" in the middle
When myosin attaches to actin it pulls strings of actin toward each other
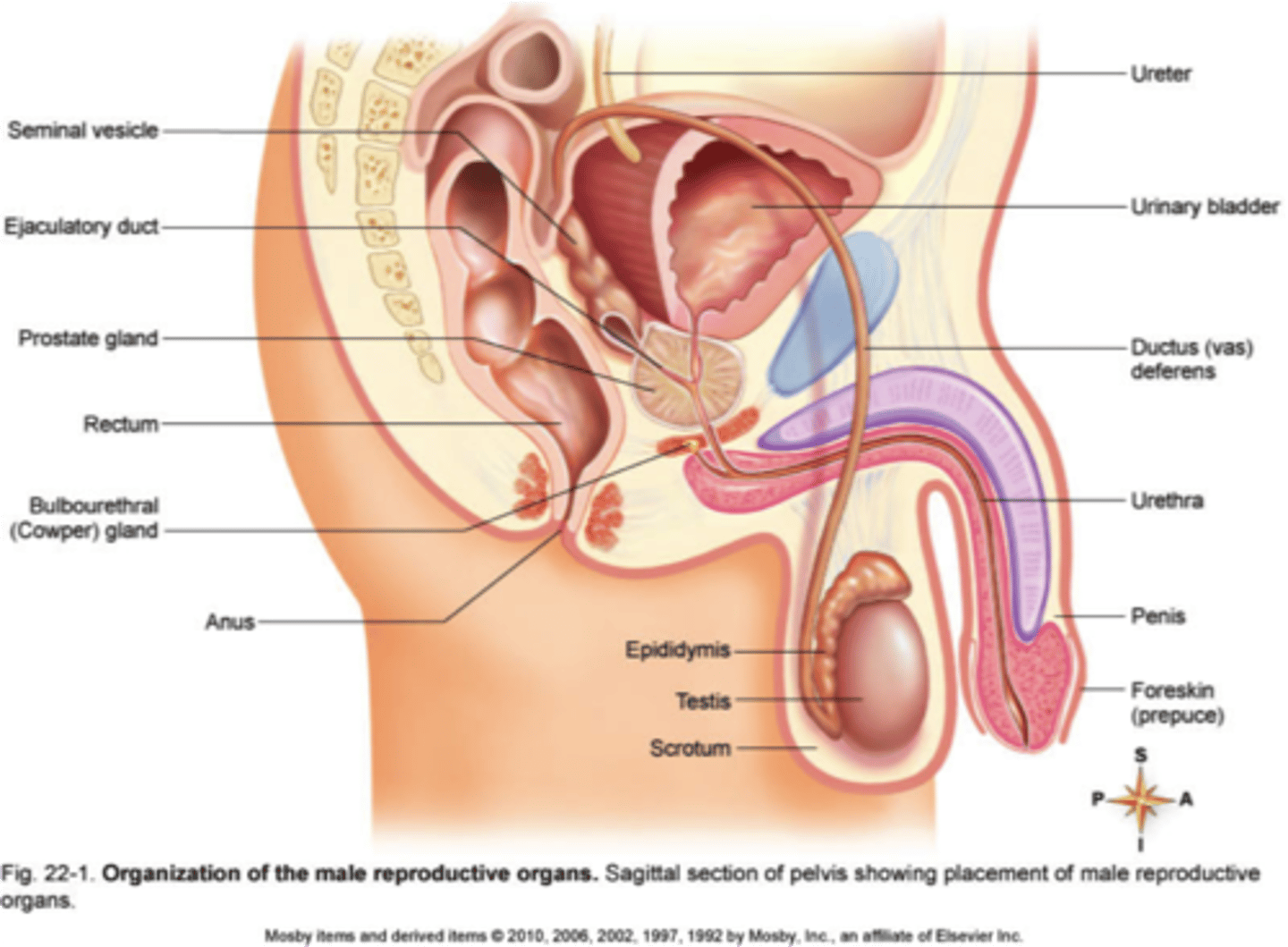
Parts of the male reproductive system