PHAR3911 - Kidneys
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
outline the excretory functions of the kidneys
excretion of metabolic waste (urea, creatine), bioactive substances (hormones, drugs) and toxins
outline the endocrine functions of the kidneys
erythropoietin (RBC production)
Renin (RAAS BP regulation)
Prostaglandins
outline the regulatory functions of the kidneys
water balance (urine)
electrolyte balance
outline the metabolic functions of the kidneys
activation of vitamin D
what is the anatomy of the kidney?
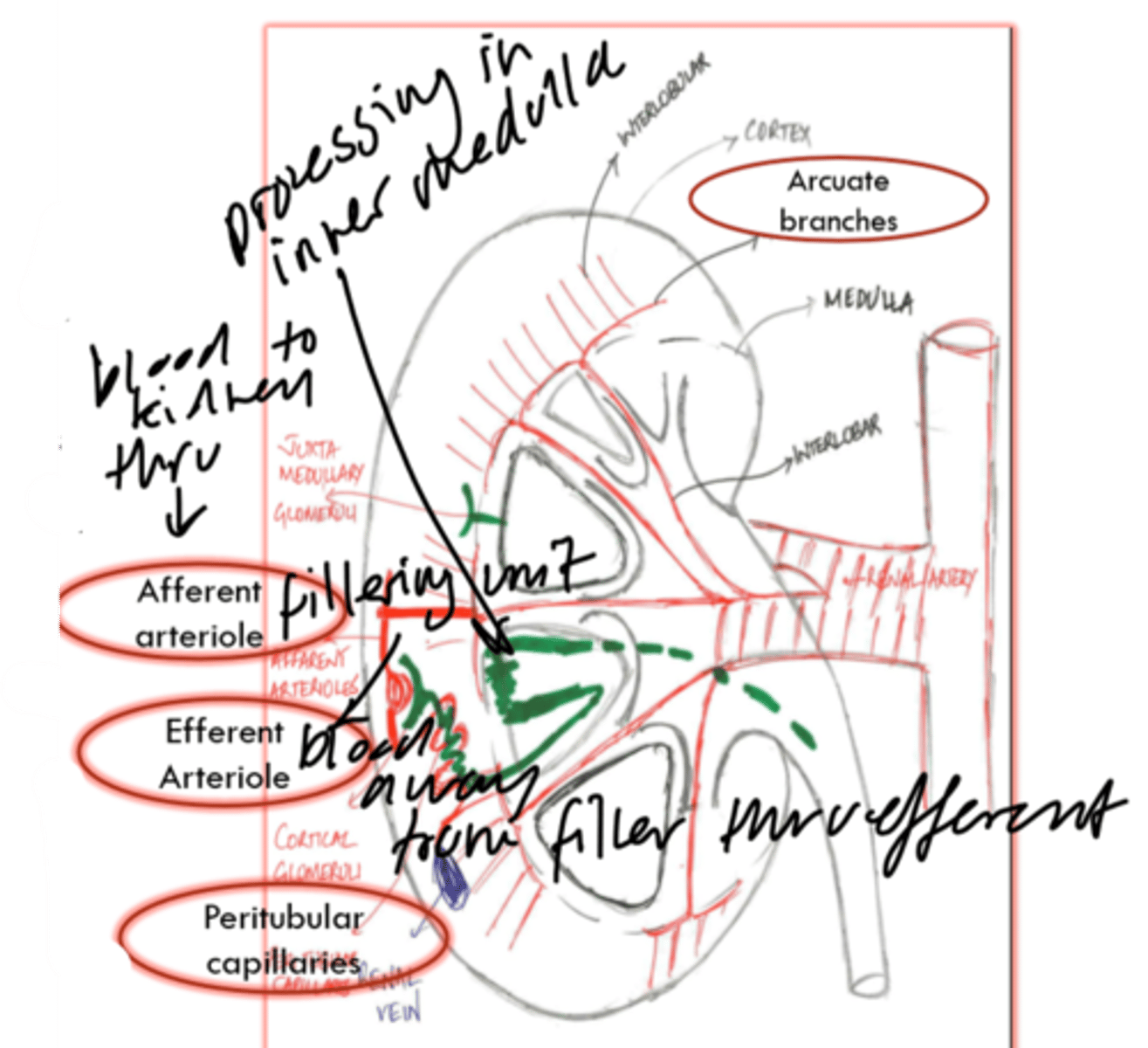
what is the filtration process of the kidneys?
occurs at glomerulus filter
small molecules able to pass through membrane
GFR indicates renal function
blood in urine indicates glomerular damage
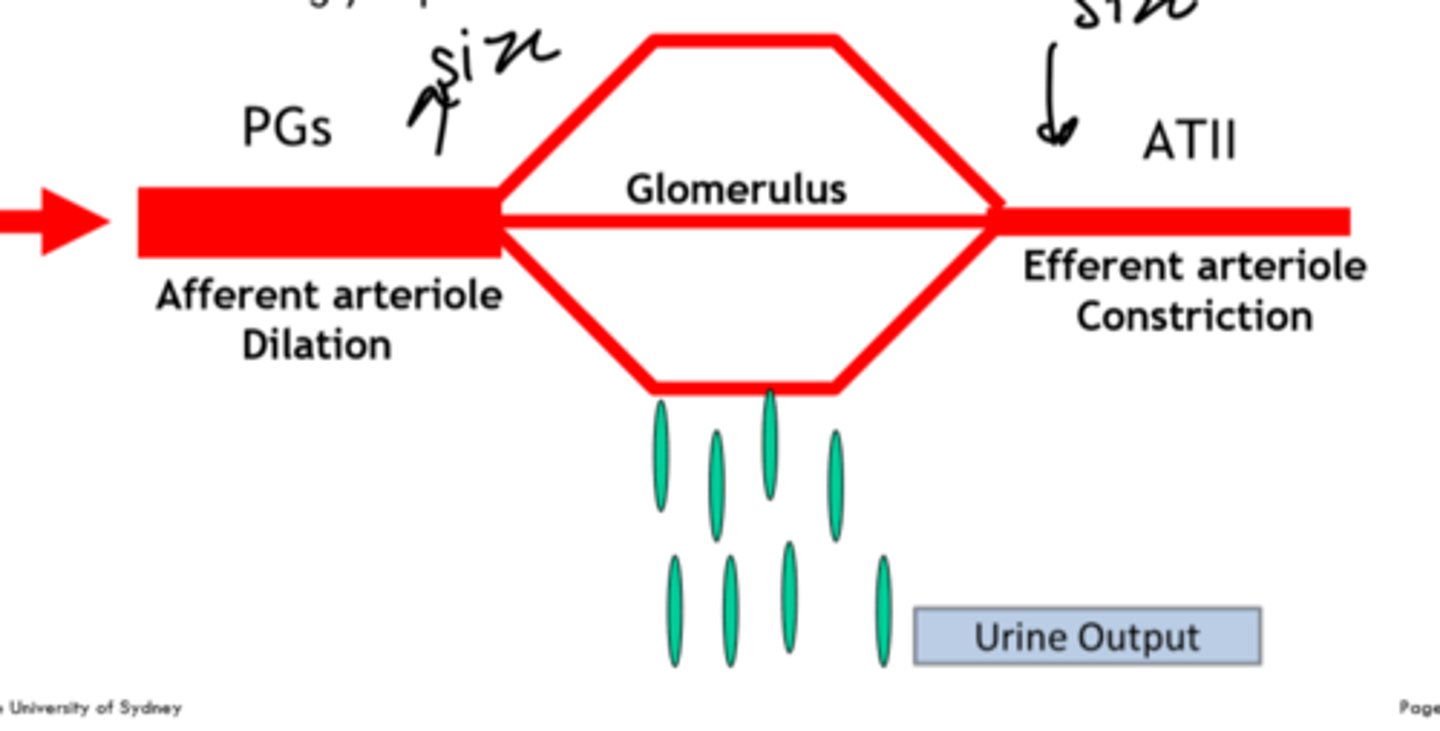
how are prostaglandins and Ang-II involved in filtration?
PG control size of afferent arteriole
AT-II control size of efferent arteriole
example: less salt = PG widens afferent Ang-II closes efferent
what are the THREE endogenous markers for kidney function?
Creatine
Urea
Albumin and blood (glomerular -ve -> disease/ damage can neutralise -> -ve albumin normally rapelled now pass thru -> 3m = damage often CKD)
what are the main factors influencing serum creatinine?
age (old have lower)
gender (female have lower)
malnutrition (lower)
medications (trimethoprim increases)
what is acute kidney injury?
abrupt decline in renal function leading to increase in serum concs of urea, creatine, and other substances
reversible if identified early
what are the THREE ways of acquiring AKI?
Community-acquired (elderly)
Hospital-acquired (surgery or drug-induced)
ICU-acquired (septic shock)
what is the main biomarker and mortality risk of AKI?
biomarker is GFR
24-48 hours delay between damage/cell death to see increased serum creatine from reduced GFR
what is the Dx criteria for AKI?
increase serum creatine >25umol/L within 48 hours
OR
increase 1.5x baseline 7days prior
OR
significant reduction in output
what are the THREE categories of AKI?
1. pre-renal (organ before kidney e.g heart not enough blood)
2. intra-renal (direct kidney tissue damage)
3. post-renal (obstruction of urethra)
how does ACEI + NSAID combination affected patients with kidney stress?
NSAIDS block action of PG
ACE1/ARB block action of Ang-II
can lead to renal failure
what are the clinical manifestations of AKI?
hypertension, oedema, n/v, dark urine
what are the key aspects of AKI prevention?
identify high-risk patients
fluid therapy
stop nephrotoxic drug therapy until kidneys are normal (SADMAN)
monitor renal function
adjust doses
what are they key steps to treatment of pre-, intra-, and post- renal AKI?
Pre-renal: remove offending medication
Intra-renal: fluids, remove medication, wait for recovery
pot: relieve obstruction
what are the THREE steps Hyperkalaemia (K+>6.5mmol/L) Tx?
1. calcium gluconate to stabilize
2. insulin (carry K+ back into cells)
3. ion exchange resin hemodialysis
define Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
kidney damage
GFR <60ml/min for 3 months
long term preventable health condition
typically asymptomatic until most of function lost
what are NINE risk factors for CKD?
1. diabetes
2. uncontrolled hypertension
3. CVD
4. Family Hx
5. obesity
6. smoking
7. >60
8. ATSI
9. AKI Hx
what are the TWO main causes of CKD?
Diabetes (T2D)
Hypertension
how is CKD linked to CVD?
causes vasoconstriction -> exacerbate hypertension
pressure on heart -> CVD
what are FIVE non-pharmacological management strategies for CKD?
1. smoking cessation
2. diet (limit salt)
3. alcohol limit
4. physical activity
5. weight management
how to preserve renal function in CKD patients?
manage hypertension with ACE or ARB (Ramipril) and or CCB (amlodipine)
what is the Tx and link between lipids and CKD?
CKD can alter lipid metabolism -> increase LDL, TG, VLDL
Tx: if pt >50 years old + GFR >60 = statin OR <60 = statin + ezetimibe
if pt <50 = statin
how to manage Na+ balance in CKD patients?
diuretics -> inhibit sodium reabsorption -> reduce risk of retention -> oedema
thiazides (idapamide) or loop (frusemide) or K+ sparing (spironolactone) risky
limit salt intake
how to manage metabolic acidosis in CKD patients?
acid-base balance hindered by CKD
sodium bicarbonate (SodiBic)
how to manage pruritis in CKD patients?
often in stage 4 and 5
emollients
avoid soaps
primrose oil
UVB therapy
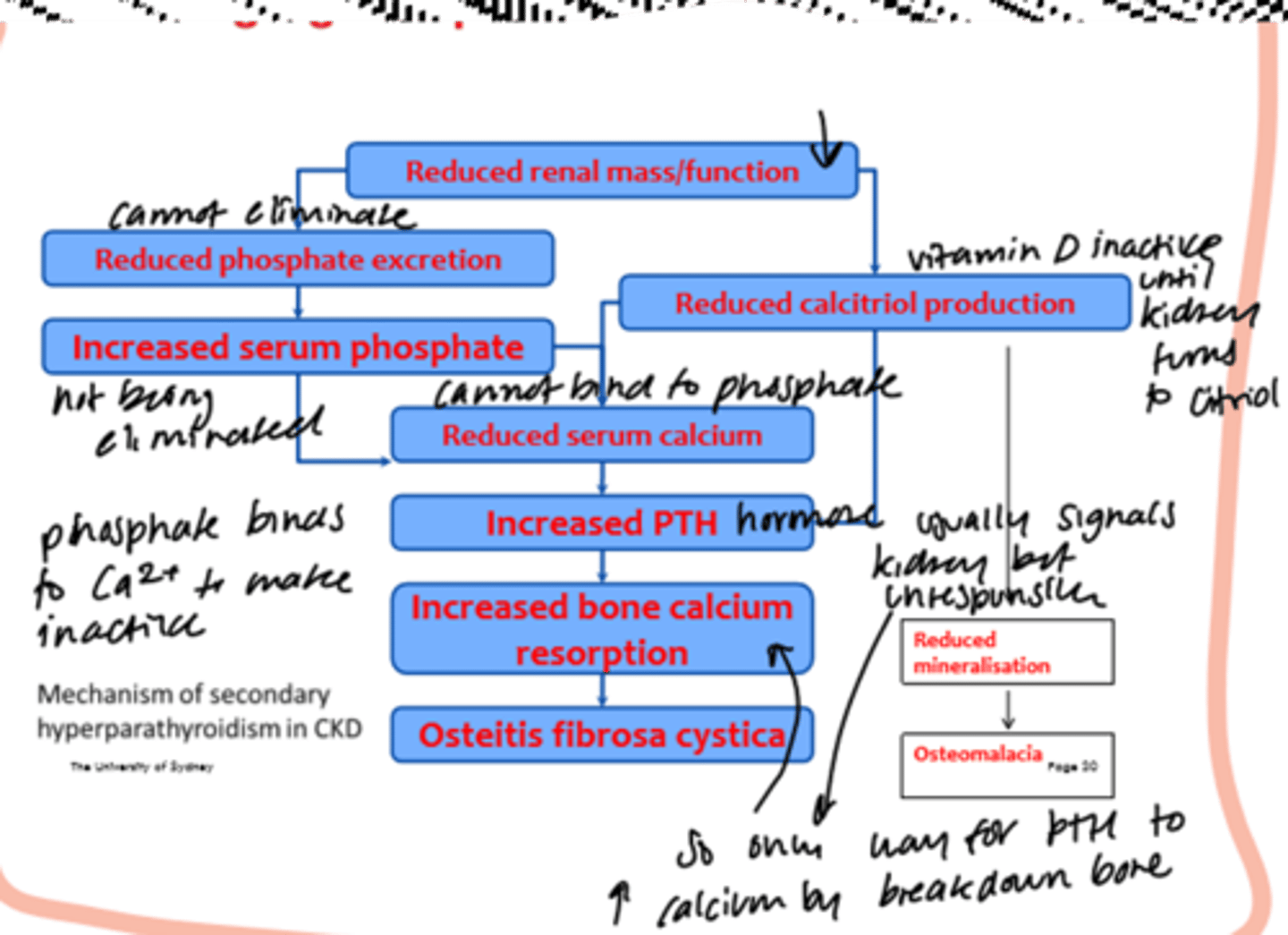
how to manage vit D and phosphorus metabolism issues in CKD patients?
kidney involved in bone metabolism (phosphate excretion, vit D activation) -> risk of bone diseases (osteoporosis)
Tx:
1. phosphate (diet + binding agents)
2. calcium
3. vitamin D
how to manage anemia in CKD patients?
caused by reduced EPO synthesis and iron absorption
Tx: iron supplement -> target Hb 100-115g/L -> decrease morbidity
SE: increase blood viscosity -> increase BP -> CV risk
what are the THREE Tx options for End-Stage Kidney Disease (ESKD)?
1. Renal Replacement Therapy (dialysis)
2. Transplant
3. supportive care
how to determine whether dialysis should be initiated?
A - acidosis
E - electrolyte imbalance (K+)
I - intoxicants
O - overload
U - uremia (sickness)
GFR 15mL/min or less
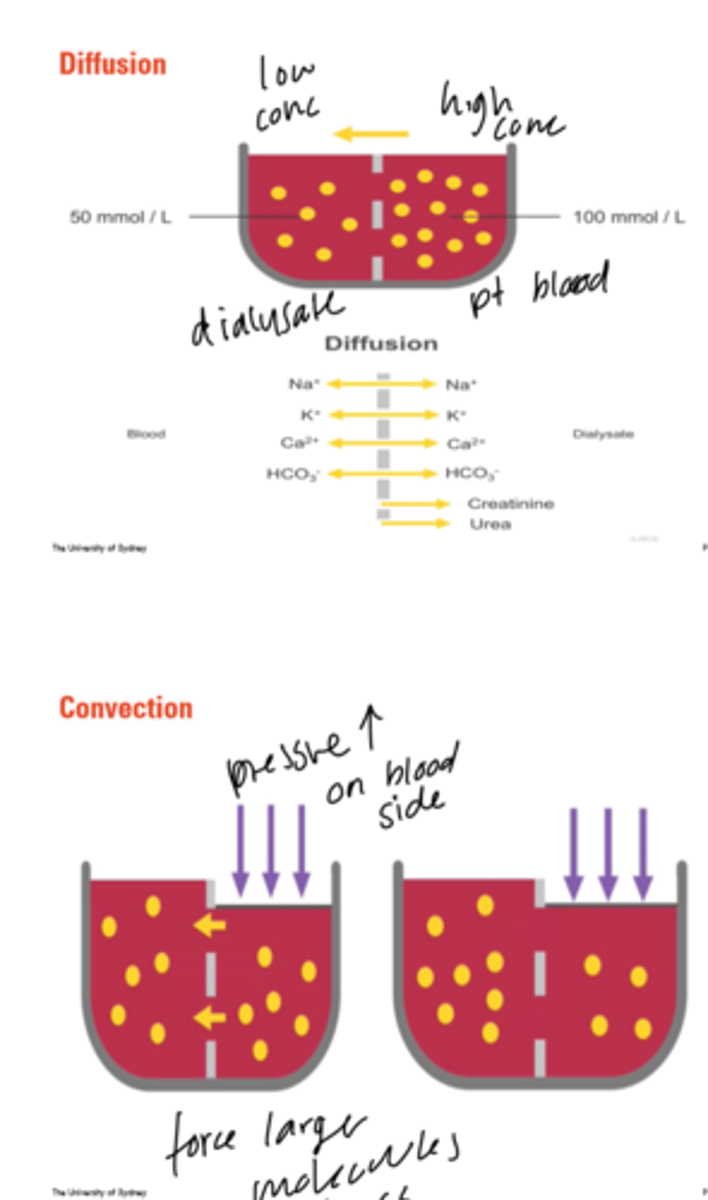
what are the two processes that make up dialysis?
diffusion and convection
what are the TWO modalities of dialysis?
1. peritoneal dialysis (PD) - catheter in abdomen multiple times a day
2. hemodialysis (HD) - blood through machine multiple times a week (4-6h at least 3 times)
what is an AV fistula in hemodialysis?
surgical connection of veins in the arm
allows blood flow >400 mL/min
high pressure fast flow facilitates dialysis
what are the pros and cons of hemodialysis?
pros: 3 treatments per week, no at home equipment
cons: travel, restricted diet, infection risk
what are the TWO methods of peritoneal dialysis?
CAPD
APD (overnight)
what is the process of peritoneal dialysis?
drain
flush
fill
dwell
what are the pros and cons of peritoneal dialysis?
pros: flexible with lifestyle, can be asleep, can travel
cons: permanent catheter, infection risk, weight gain
how is drug dosing affected by dialysis?
drugs that are likely to be cleared by the dialysis should be dose afterwards to avoid Tx failure
what are the benefits and side effects of renal transplantation?
benefit: extend life, improve QOL
side effects: immunosuppression, infection risk, long term cancer risk
what are the THREE risk factors of drug-induced kidney disease (DIKD)?
1. CKD Hx
2. Elderly
3. Infection/ critical illness
what are the FOUR classes of drugs that can worsen renal function?
1. Diuretics
2. ACE/ARB
3. NSAIDs
4. Antihypertensives
what are THREE classes of drugs that cause direct nephrotoxicity?
1. antimicrobials (amp-B, gentamicin)
2. anticancer (methotrexate)
3. Immunosuppressants (cyclosporin)