Biology Lab exam #2
1/169
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
170 Terms
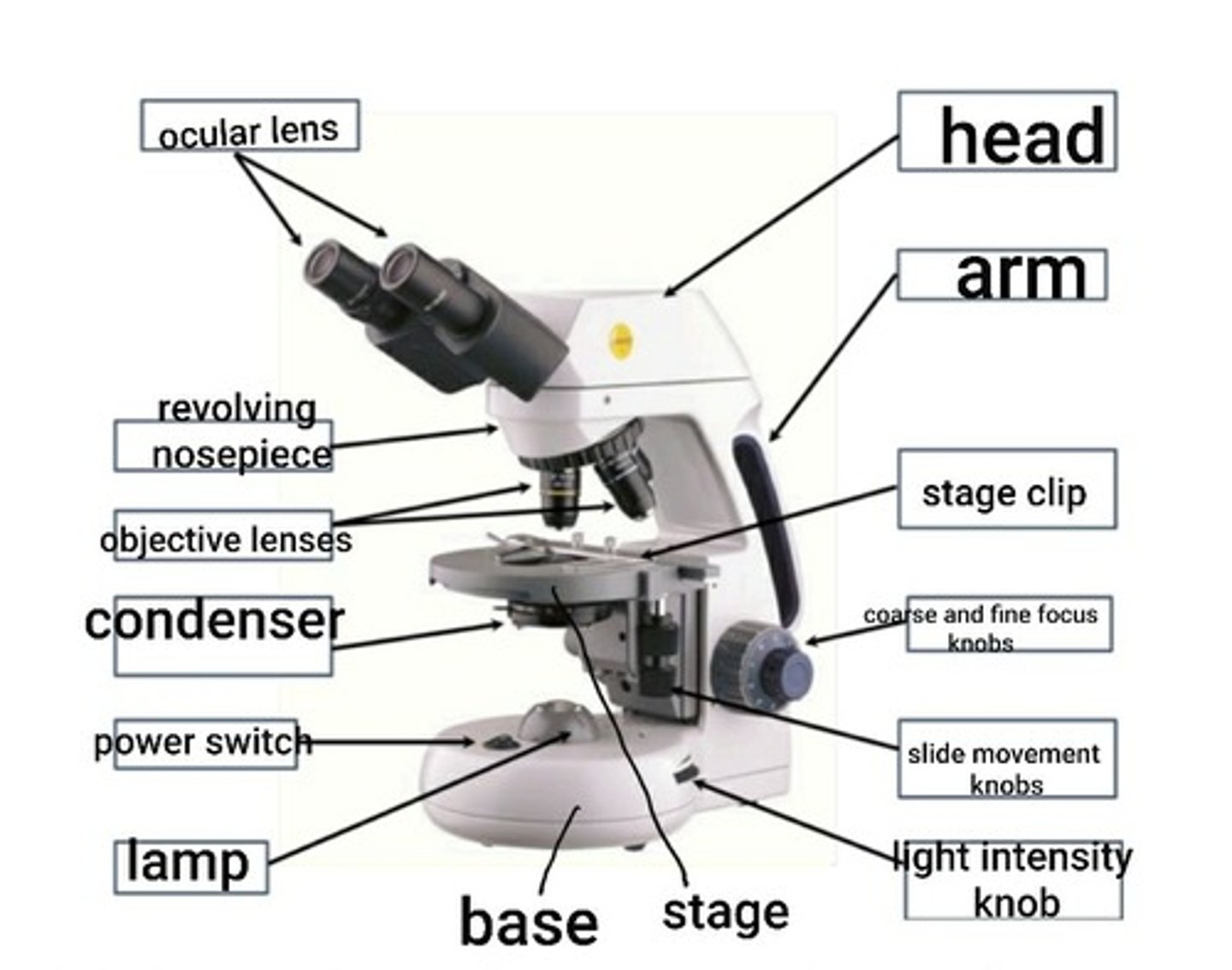
head of microscope
supports the objective lenses and ocular lenses
ocular lens (eyepiece)
This is the lens you look through to view the specimen. The ocular lens magnifies the specimen. It has a magnification of 10X.
binocular microscope
a light microscope that has two ocular lenses
Monocular microscope
A light microscope that has only one ocular lens
interpupillary distance
distance between eyepieces
pointer
in the eyepiece and can be used to point to a specific object in the field of view
field of view
the circle of light you see when looking into the microscope
objective lenses
the four lenses located on the revolving nosepiece. Include the 4X scanning lens, 10X low power lens, 40X high power lens, and 100X oil immersion lens.
arm
supports the stage and condenser lens
condenser lens
focuses light from the lamp through the specimen. height can be adjusted by an adjustment knob.
iris diaphragm
controls the amount of light passing through the specimen. It is located in the condenser. Improves contrast and detail of image.
light intensity knob
controls the amount of light allowed to pass through the lens. Does not improve contrast or detail.
stage
Supports the slide being viewed
clip
Holds the slide in place
Slide movement knobs
move the slide across the stage
coarse focus knob
moves stage up and down at low power
fine focus knob
brings an object into focus at high power
base
a stand for the microscope that houses the lamp.
General rules for microscope use
1. carry the microscope with 2 hands (one under the base and the other on the arm).
2. adjust the microscope for your personal use. never push or pull the microscope across the table. pick it up to move it.
3. check the lenses. only use lens paper and lens cleaner to clean the lens.
4. Be careful with water. It can damage the microscope.
5. Don't force it. If a part will not move any farther dont force it.
total magnification
objective lens x ocular lens
what happens to the working distance and the field of view as magnification increases?
they decrease
start with what power lens?
the lowest power (4X scanning lens)
Where do you start the stage once it is mounted and you rotate to the scanning lens?
the stage should be at its highest position so you can lower it with the coarse and fine focus knobs until it is in focus. Bringing the stage toward the object can damage the slide or objective lens.
use only what focus with high power objective lenses?
fine focus knob
Is the image right side up or upside down when looking through the microscope?
upside down
when you move the slide away from you does the image move away from you or towards you?
towards me
when moving left or right what happens to the image?
it moves in the opposite direction.
Parfocal
lens that stays in focus when magnification/focal length is changed
depth of field
the distance between the nearest and the furthest objects that give an image judged to be in focus in a camera.
working distance
distance between objective lens and specimen
only use oil with what lens?
oil immersion lens (100X)
rules for retiring a microscope
1. clean the oil immersion lens with lens cleaner and lens paper if it was used.
2. reduce light intensity to lowest level.
3. lower stage to lowest position.
4. turn revolving nosepiece so 4X lens is in place.
5. loosen the head screw and reposition the head and eyepieces from the viewing position to the storage position then tighten the screw.
6.unplug electrical cord and fold it neatly and secure it with the tie. 6. use two hands to carry the microscope.
what never to do with microscopes
1. do not turn on the light switch until the light intensity is at its lowest level. because you could burn out the bulb.
2. never use the coarse ficus with any objective lens above 10X.
3. never slide the base of the microscope across the table.
4. ise only lens paper to clean the ocular and objective lenses. never use Kim wipes or paper towels because they are too abrasive for the lenses.
5. never leave oil on a lens. clean it.
Parts of a microscope blank picture
labeled parts of microscope
how can fungi be distinguishes from bacteria?
fungi has a fuzzy appearance to its colony because of a mass of filaments called hyphae that creates a network called a mycelium.
form, elevation, and margin of bacteria colony (blank)

answer to form, elevation, and margin of bacteria colony

form
the shape of a whole colony.
Elevation
shape of colony as it rises from the plate when viewed side on.
margin
the shape of the colony's edges
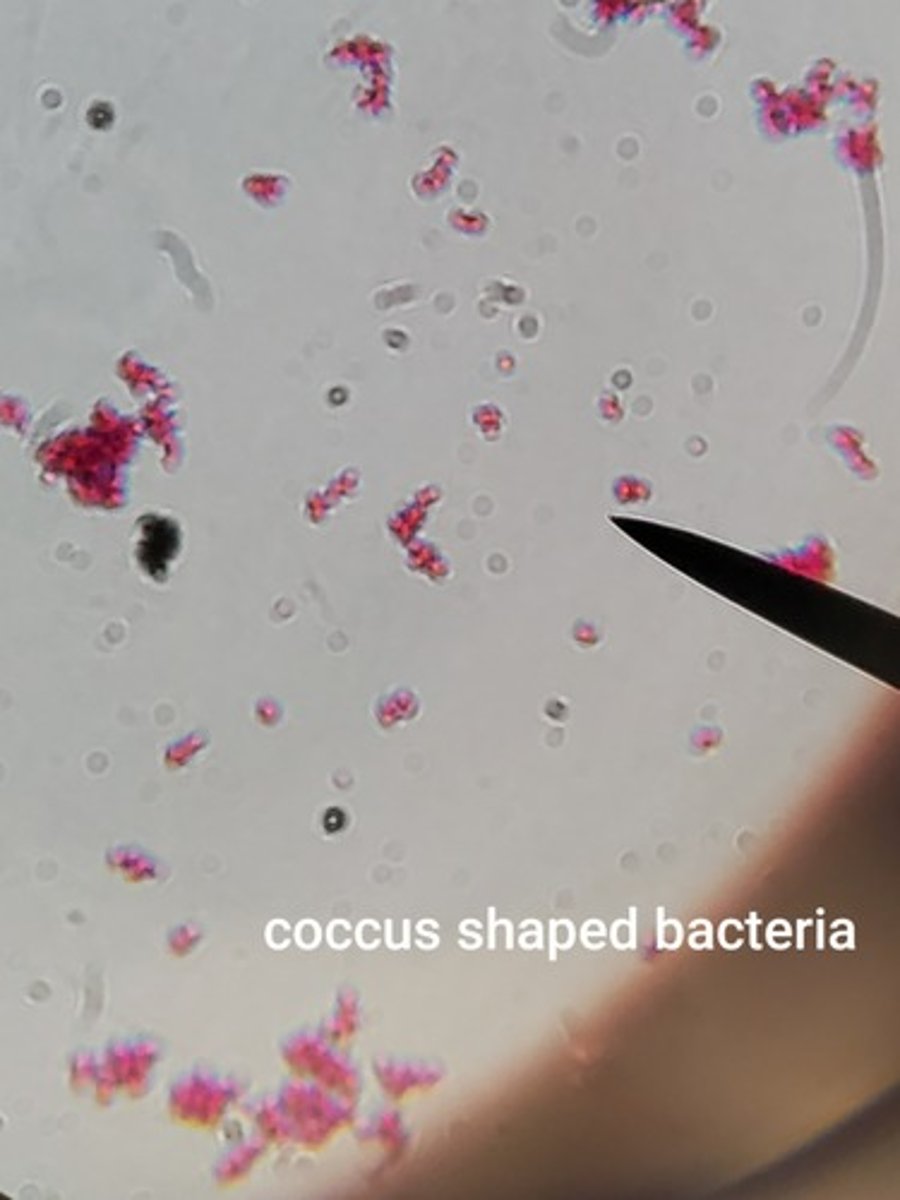
coccus bacteria
spherical
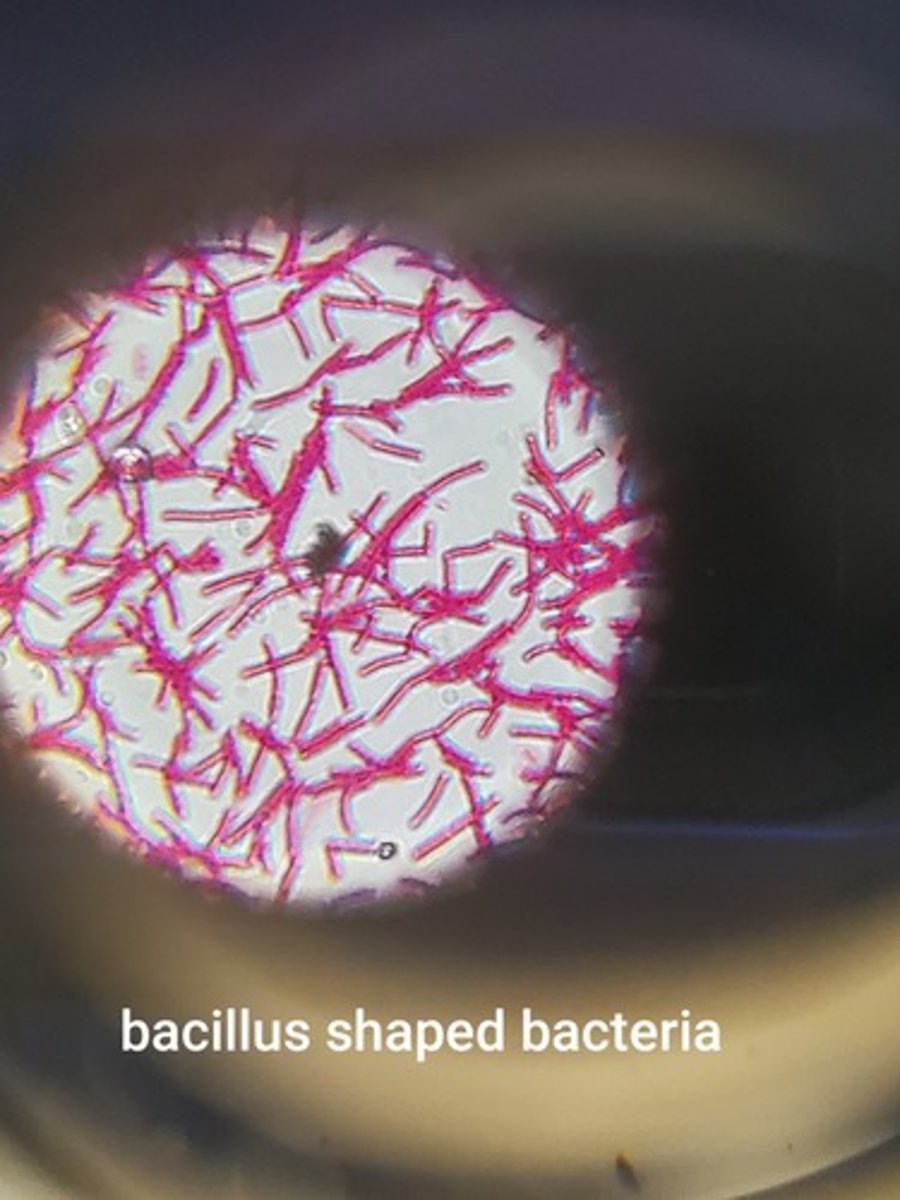
bacillus bacteria
rod shaped
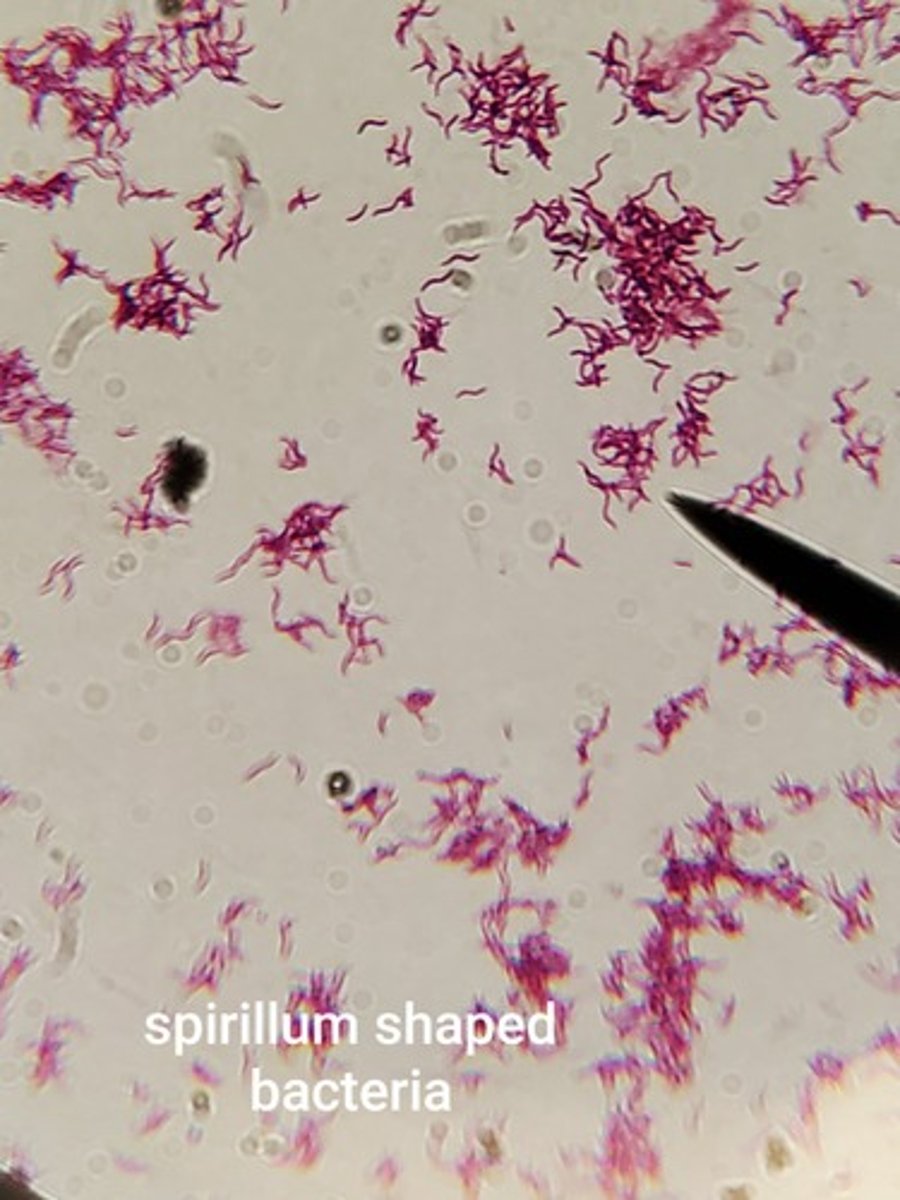
Spirillum Bacteria
spiral or corkscrew shaped
Gram-negative bacteria
1. more complex cell wall
2. thin peptidoglycan cell wall layer
3. outer lipopolysaccharide wall layer
4. retains safranin
5. appears pink or red
Gram-positive bacteria
1. simple cell wall
2. thick peptidoglycan cell wall layer
3. no outer wall layer
4. retain crystal violet/iodine
5. appear blue or purple
Gram staining procedure
-Dye: crystal violet 1 minute then rinse with deionized water
-Mordant: Gram's iodine 1 minute and pour off stain
-Decolorizer: 95% ethyl alcohol 15 seconds then rinse
-Counterstain: safranin stain 1 minute then rinse and let air dry.
- examine under oil immersion lens
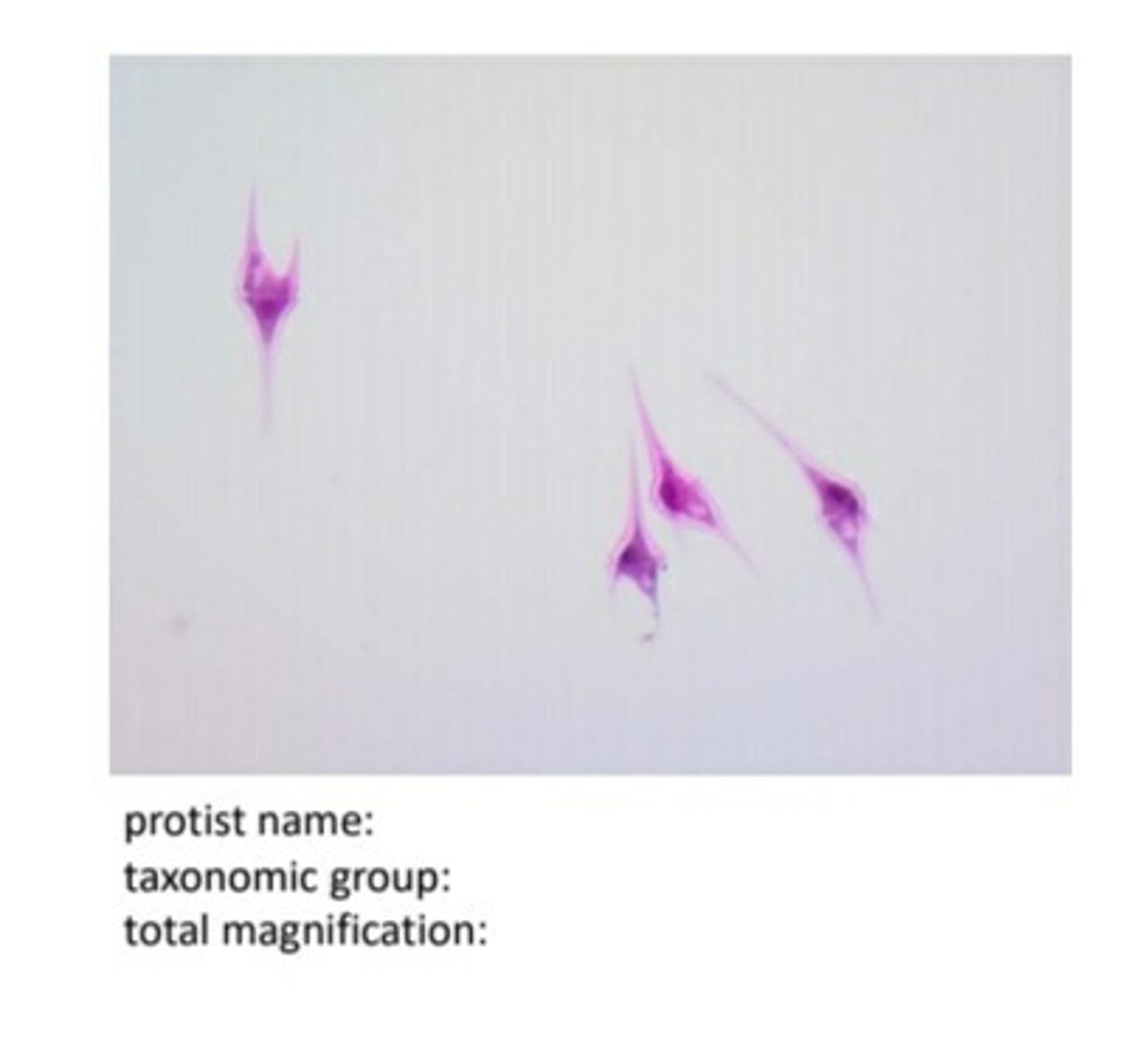
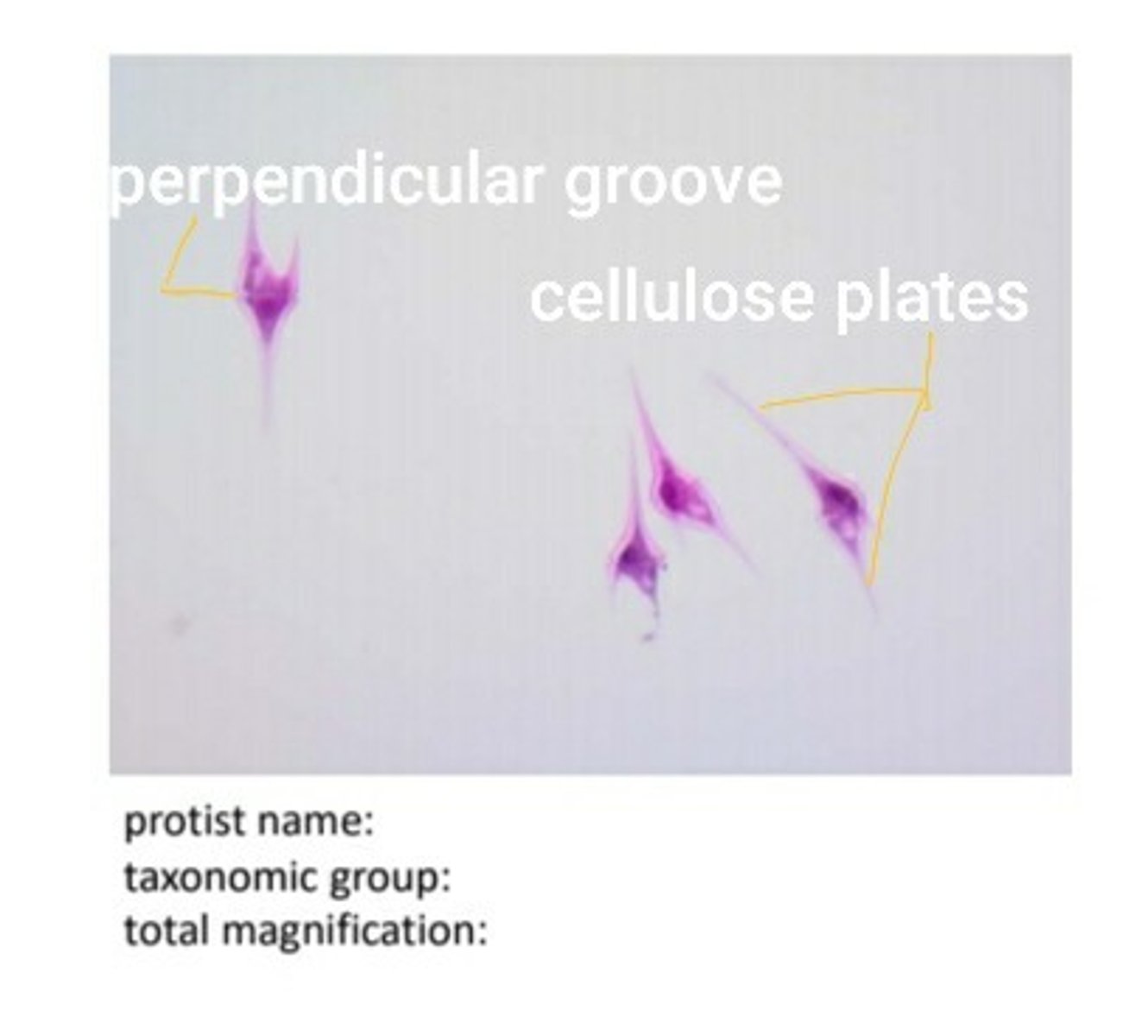
Dinoflagellates
Euglenozoa (Euglena)

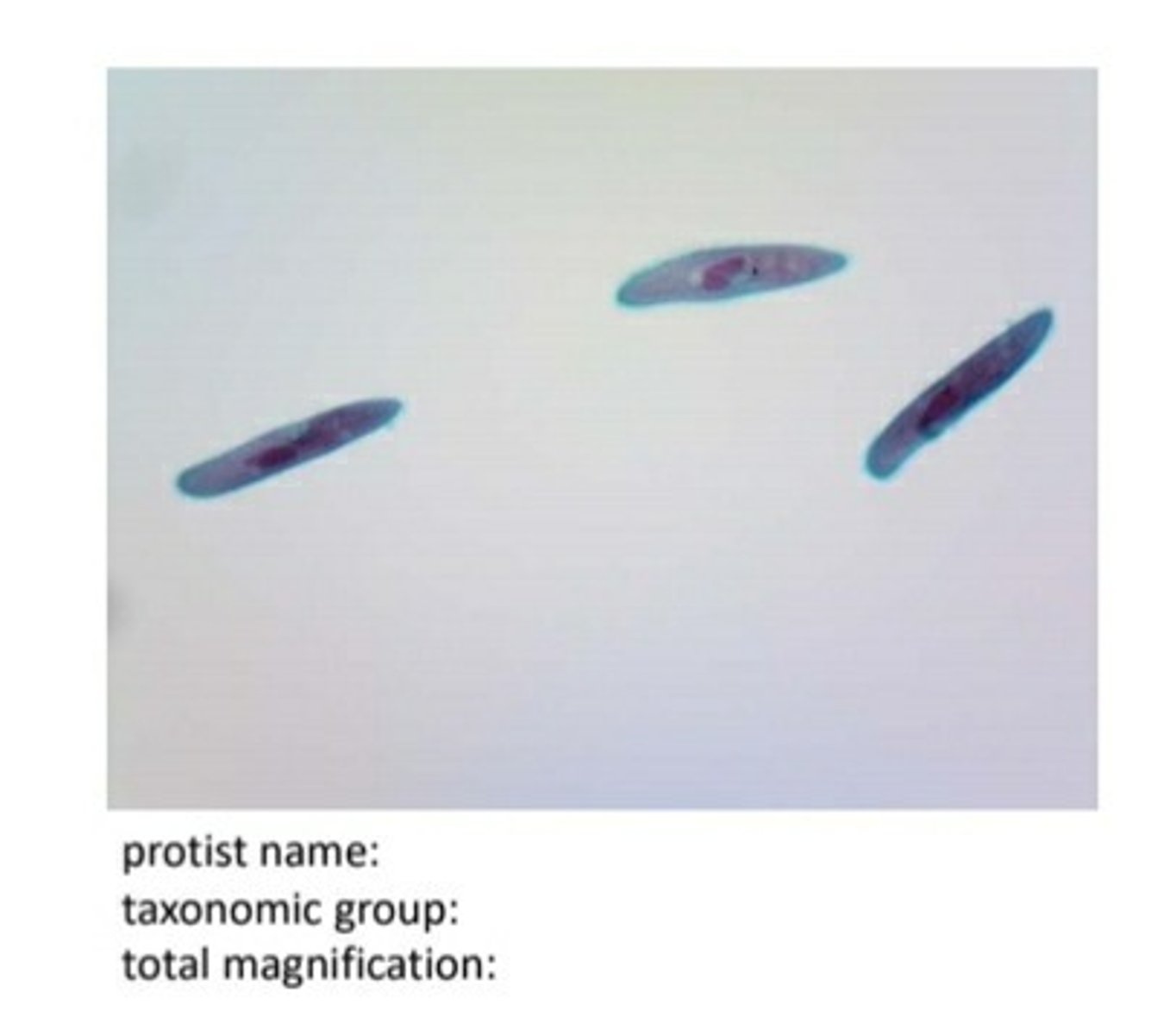
ciliates (paramecium)
dinoflagellates label perpendicular groove and cellulose plates
Diatoms (unicellular)
diatoms filamentous
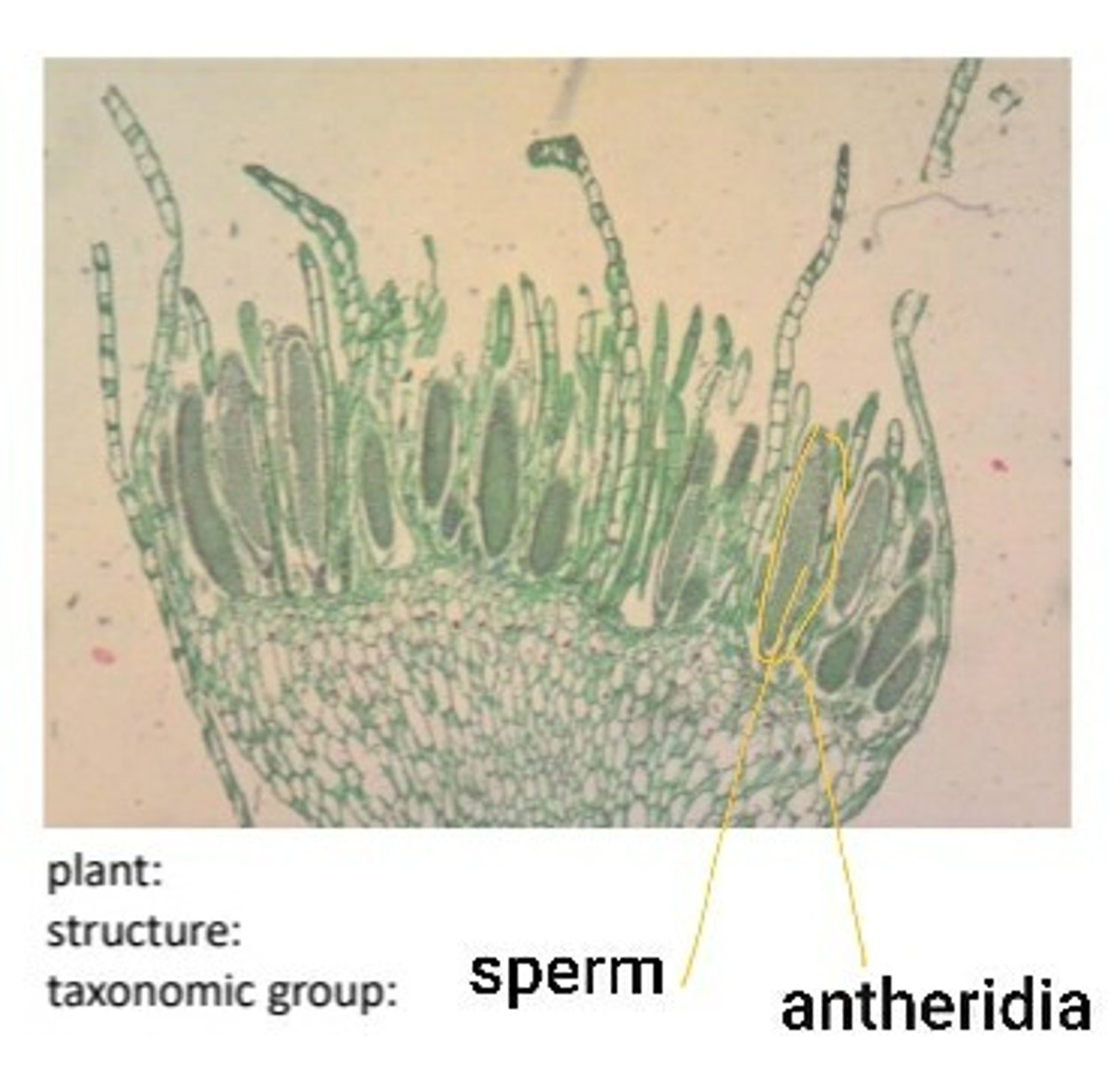
plant:mnium
structure:protonema
taxonomic group:bryophyte
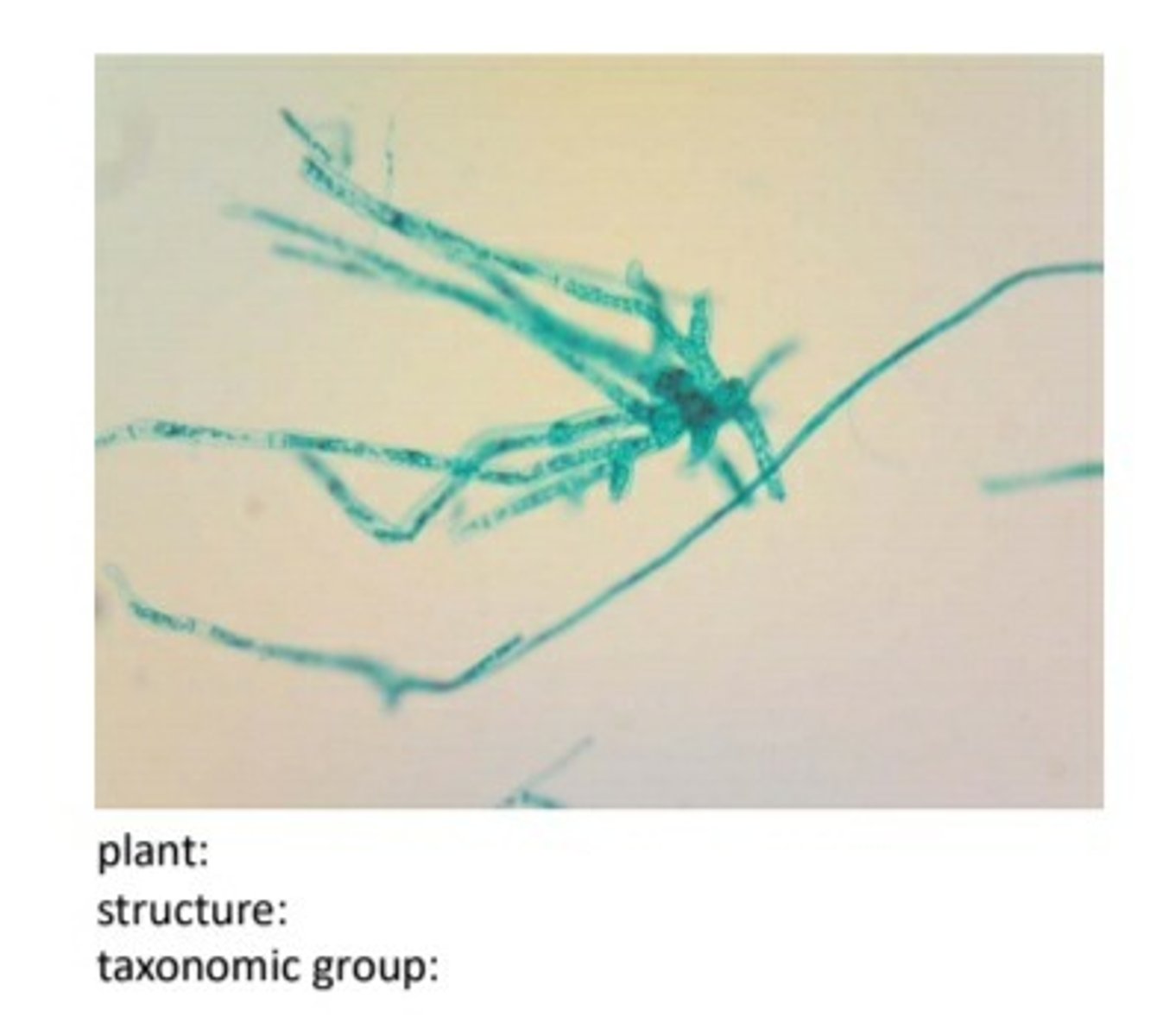
unlabeled male gametophye for mnium protonema bryophyte. (label the sperm and antheridia)
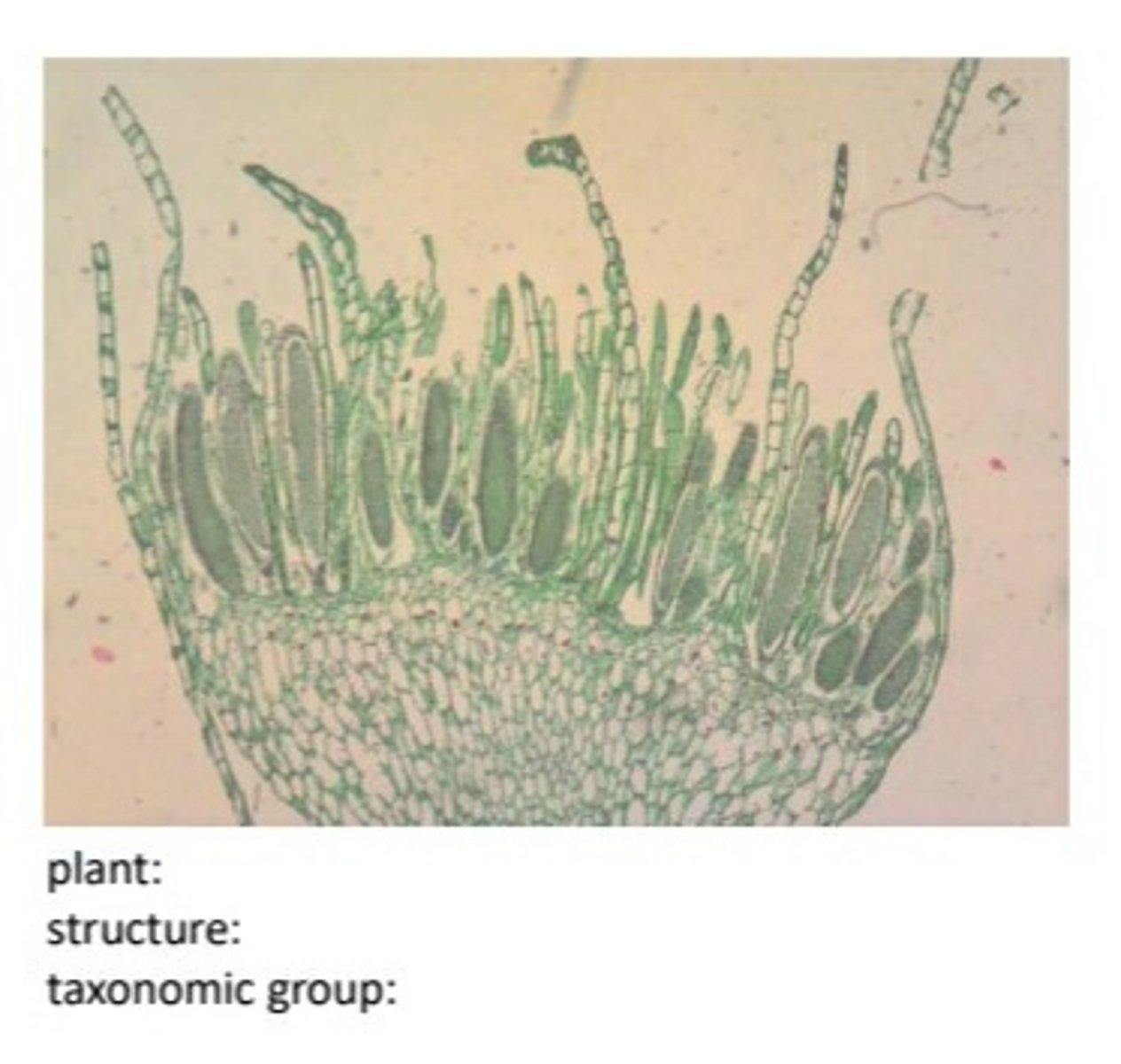
label the antheridia and sperm on male gametophyte for mnium protonema bryophyte
amoebozoa (amoeba)

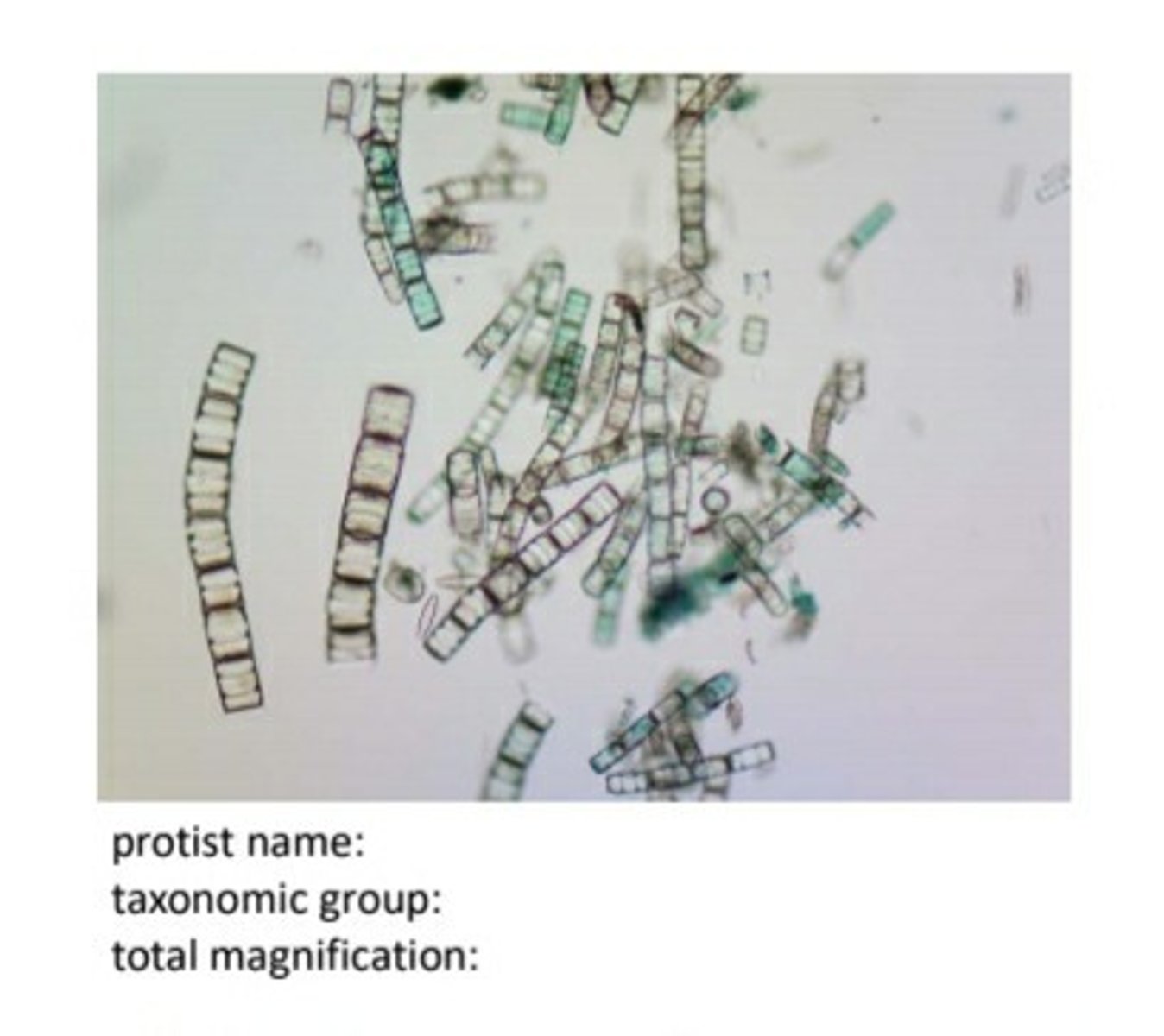
blue-green algae (oscillatoria) 100X
not actually a protist. now a bacteria.

blue-green algae (oscillatoria) 400X

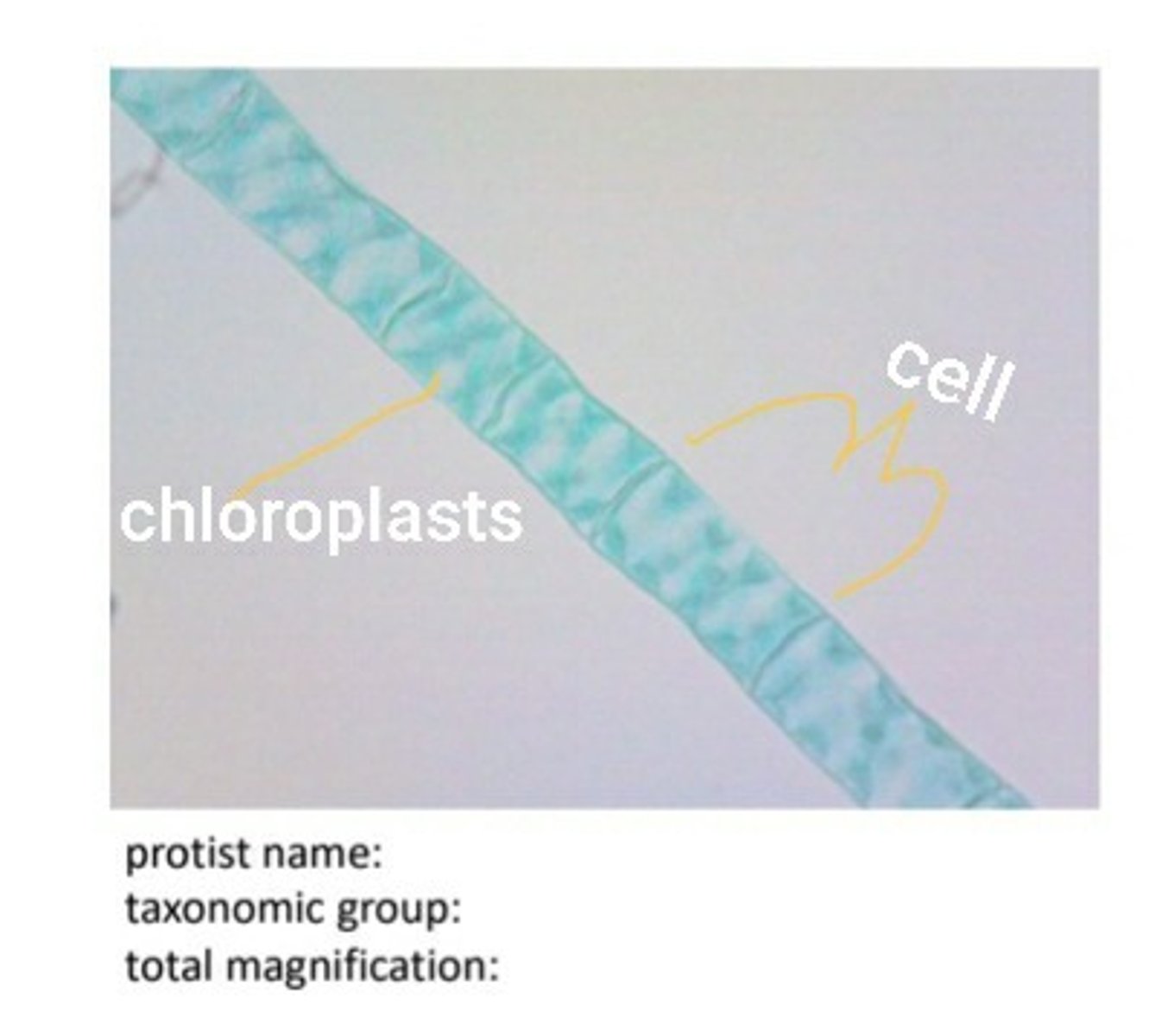
Green Algae: Spirogyra 100X

Green Algae: Spirogyra 400X

spirogyra label chloroplasts and cell
amoeba label pseudopodia

taxonomic groups of protists and examples
1. Euglenozoa-Euglena
2. Ciliates-Paramecium
3. Dinoflagellates
4. Diatoms
5. Amoebazoa-Amoeba
6. Blue-green algae
7. Green algae-Spirogyra
euglenozoa (euglena) locomotion
flagella
Euglenozoa (Euglena) nutrition
mixotrophic
Euglenozoa (Euglena) cell number
unicellular
euglenozoa (euglena) cell surface
plasma membrane
ciliates (paramecium) locomotion
cilia
ciliates (paramecium) nutrition
heterotrophic
ciliates (paramecium) cell number
unicellular
ciliates (paramecium) cell surface
cell membrane
ciliates (paramecium) special characteristics
-macronucleus and micronucleus
-posterior and anterior contractile vacuoles to maintain osmotic balance
dinoflagellates locomotion
flagella
dinoflagellates nutrition
photoautotrophic
dinoflagellates cell number
unicellular
dinoflagellates cell surface
cell wall
dinoflagellates are responsible for what 2 things?
red tide and bioluminescence
Diatoms locomotion
nonmotile
diatoms nutrition
photoautotrophic
diatoms cell number
unicellular
diatoms cell surface
exoskeleton of double shells of silica
Amoebozoa: Amoeba locomotion
amoeboid motion/pseudopodia
amoebazoa (amoeba) nutrition
heterotrophic
Amoebozoa: Amoeba cell number
unicellular
Amoebozoa: Amoeba cell surface
plasma membrane with amorphous body- no defined body shape
blue-green algae (oscillatoria) locomotion
glide (actually bacteria not protists)
blue-green algae (oscillatoria) nutrition
photoautotrophic
blue-green algae (oscillatoria) cell number
unicellular filamentous
blue-green algae reproduction
fragmentation in which filaments break off the original mat and start a new colony
Green Algae: Spirogyra locomotion
nonmotile
Green Algae: Spirogyra nutrition
photoautotrophic (same pigments as plants)
Green Algae: Spirogyra cell number
mostly unicellular
Green Algae: Spirogyra cell surface
cell wall
Paramecium shape
extended oval
Alternation of generations takes place in what 4 groups?
1. Phaeophyta
2. Rhodophyta
3. Clorophyta
4. Embryophyta
Explain alternation of generations
- the cycle of life has to go through a haploid and diploid phase
-the sporophyte generations is always diploid and makes spores via meiosis (diploid to haploid)
-the gametophyte generation is always haploid and mitosis produces gametes (sperm and eggs)
-gametrs come together via fertilization to create a zygote then it grows into an adult sporophyte (diploid) via mitosis.
what process produces the sperm and egg in plants?
mitosis
what process produces the spores in plants?
meiosis
in which structure of a plant does fertilization take place?
archegonia