Variations in Sexual Development
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
What are the genes affecting gonadal differentiation?
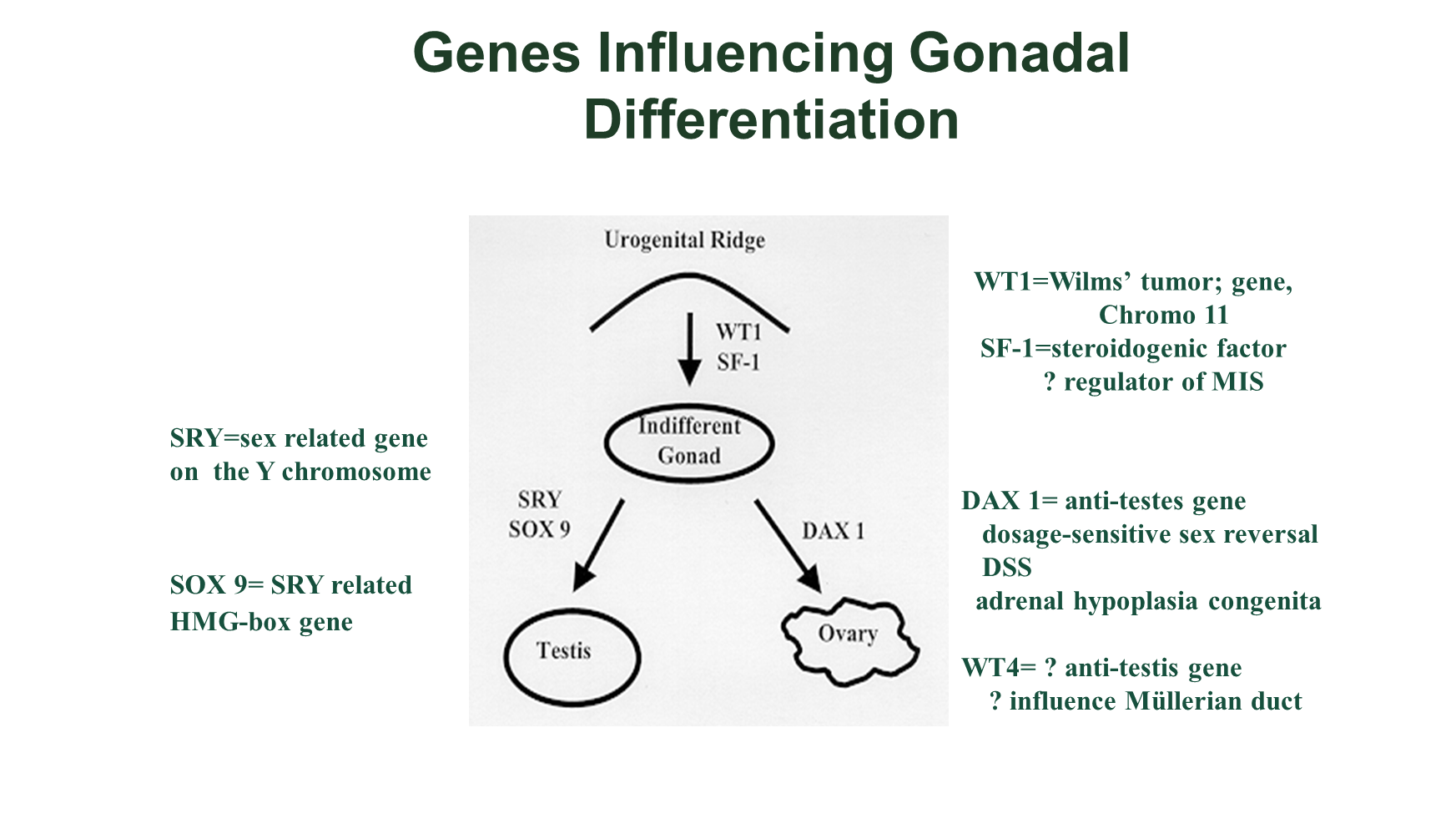
Gonadal differentiation occurs at the urogenital ridge in response to the Wilms Tumor Gene (WT1) and Steroidogenic Factor (SF1) into a indifferent gonad
1) In response to the SRY and SOX9 gene the indifferent gonad can develop into Testis
2) In response to the DAX1 gene the indifferent gonad can develop into the ovaries
How do the testes and ovaries develop?
1) The testes will develop in the presence of a Y-chromosome Testis Determining Factor beginning at the 6th week
→ causes the differentiation into Sertoli Cells and Leydig cells
→ Sertoli cells will secrete anti-Mullerian hormone causing Mullerian duct regression
→ Leydig Cells producing testosterone allows for the progression of the Wolffian duct to form the male internal genitalia
2) The ovaries develop in the absence of Testis Determining Factor and is considered the default pathway
→ in the absence of anti-Mullerian hormone the Mullerian ducts will progress forming the female internal genitalia
How do hormones influence external genitalia development?
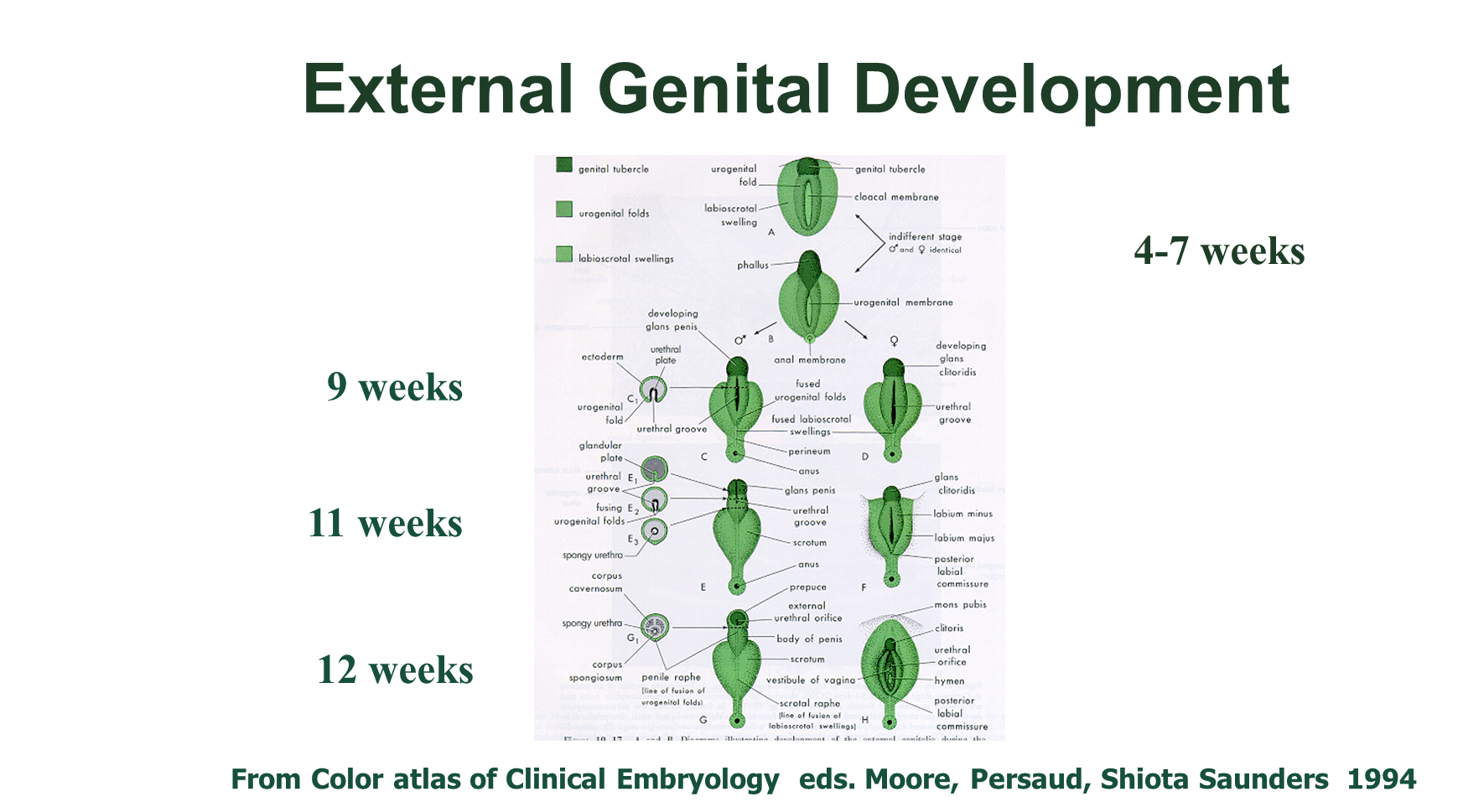
Occurs at the 9th week
1) DHT or Dihydrotestosterone promotes the development of male external genitalia
2) Estrogen is not required for female development of the internal and external genitalia
What are disorders of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia?
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia is a group of autosomal recessive disorders of adrenal steroid synthesis
→ Results in an inability to produce Cortisol, causing increased levels of ACTH which get shunted to adrenal androgen production
Subdivided into female virilization or a female that is male presenting
1) 21-hydroxylase deficiency
→ patients are XX but present as males, and will be hyperpigmented and salt wasting (excrete too much sodium)
2) 11B-hydroxylase deficiency
→ patients are XX, but present as hyperpigmented males and are hypertensive
Subdivided into male underdevelopment or a XY patient that is female presenting
1) 17a-hydroxylase deficiency
→ patients are unable to produce all forms of adrenal hormones including androgens
→ results in an under-virilized male
What is Pure Gonadal Dysgenesis? What is a common example?
Pure Gonadal Dysgenesis are groups of sexual development disorders characterized by streak gonads (failed gonad development), absent sex hormones, and normal Mullerian structures
1) Example is Turner Syndrome where a patient only has one X chromosome
→ present as female, but lack gonads and sex hormones
→ will have a short stature and a wide chest
What is Ovotesticular Diversity?
Patients with ovotesticular diversity will have both ovarian and testicular tissue
→ patients will be more male presenting