Extraoral Radiology Review
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for Extraoral Radiology lecture review.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Extraoral Radiology
The study of areas that intraoral examinations do not include, visualizing the skull and facial structures, completing examination of jaws and other facial bones, and evaluating skeletal growth.
Screen and Film Specifications for Extraoral Radiography
Screen made of rare earth’s materials with a high/medium speed film. Film size: Lateral projection (13 x 18 cm). Cranium film (20 x 25 cm). Lateral mark to signal left or right.
X-Ray Machine Types for Extraoral Radiography
Conventional dental Rx, advanced panoramic machines, and machines developed specifically for extraoral Rx.
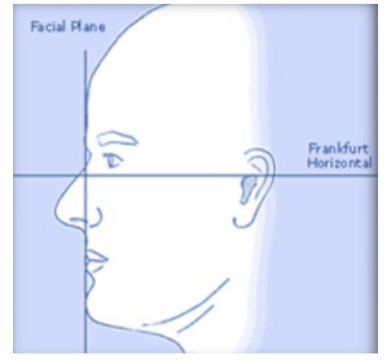
Frankfort Plane
Reference plane from the superior border of the external auditory meatus to the infraorbital border.
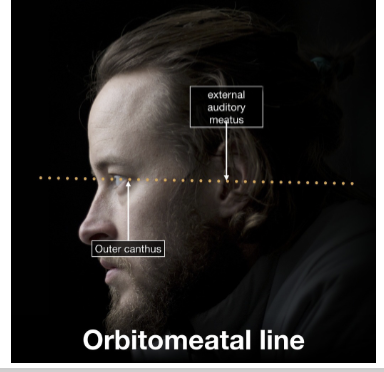
Canthomeatal Line
Reference line from the external auditory meatus to the outer canthus of the eye, at a 10º angle in relation with the Frankfort plane.
Posteroanterior Skull Projection Indications
Illness, trauma, or anomalies in the skull’s development. Evaluate progressive changes in the mediolateral skull dimensions (asymmetry). Evaluation of facial structures, including frontal and ethmoidal sinuses; nasal fossae, and orbits.
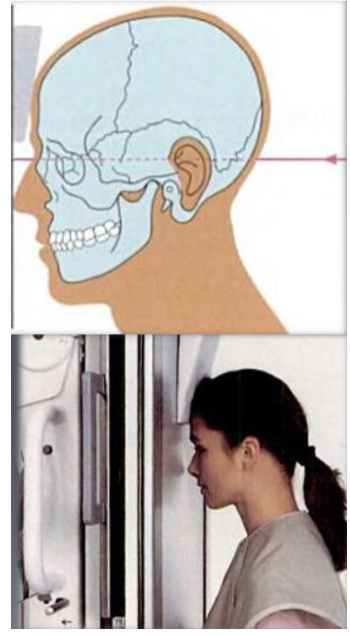
Posteroanterior Skull Projection - Head Positioning
Head centered, nose rests on sensor. Canthomeatal line parallel to the floor. Frankfort plane must be parallel to the floor for cephalometric applications. Superior border of petrosal sinus lined up with the lower third of orbit. Occlusal plane parallel to the floor.
Lateral Skull Projection Indications
Vertical and horizontal evaluation prior to orthodontic or surgical intervention. Assessment of facial growth and/or result of therapy. Assess skull fractures. Identify foreign bodies. Evaluate neoplastic changes. Evaluate air-fluid levels in sphenoid sinus. Airway evaluation.
Lateral Projection Head Position
Sensor placed vertically. Sagittal midline of the patient's head is parallel to the image detector. Head stabilized with Frankfort plane parallel to the floor. Sella turcica in profile. Temporomandibular joints are superimposed.
Waters’ Projection Indications
Best projection to study the maxillary sinus (sinusitis). Facial trauma (especially middle 1/3). Evaluation of odontoid process of the 2nd vertebrae (axis). Good view of mid-facial complex, mandible and condyles.
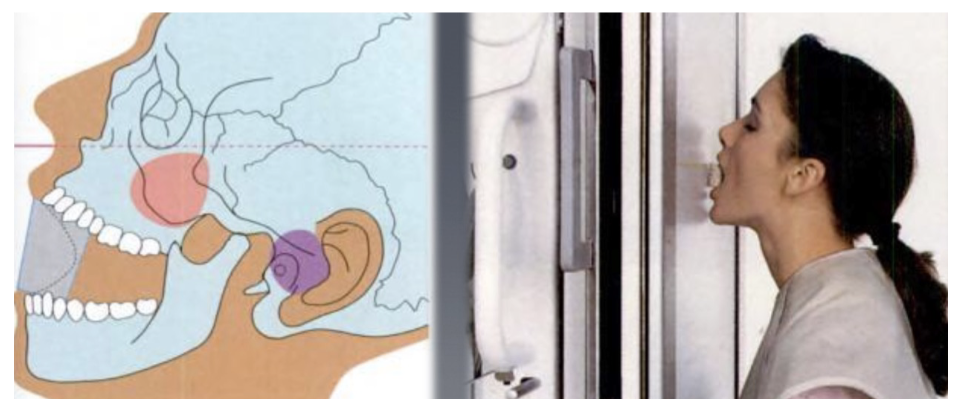
Waters’ Projection Head Position
Sensor is placed vertically. Patient’s face is facing the sensor. Chin is raised until the mento-mandibular line is perpendicular to the sensor. Canthomeatal line is 37-40º from receptor.
Reverse Towne’s Projection Indications
To study coronal aspect of the mandibular condyles, rami, posterior wall of maxillary sinus, nasal septum, and styloid process. Useful in suspected fractures of the mandible. Shows medial displacement of the condyle.
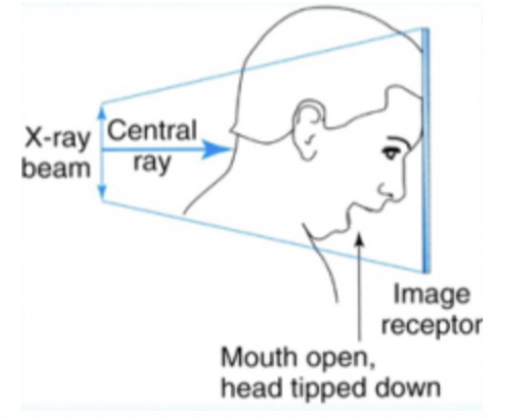
Reverse Towne’s Projection Head Position
Patient facing the sensor. Mid-Sagittal plane is aligned perpendicular to the midline of the sensor. Patient’s chin is tucked down to bring the head down 30º. Patient must open mouth as much as possible to visualize the condyles.
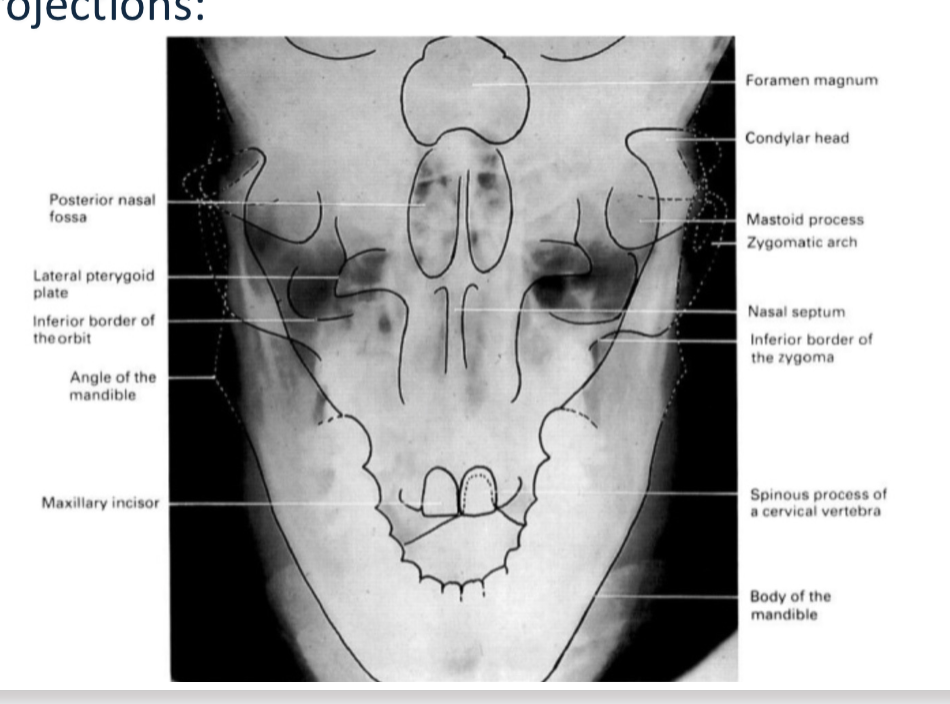
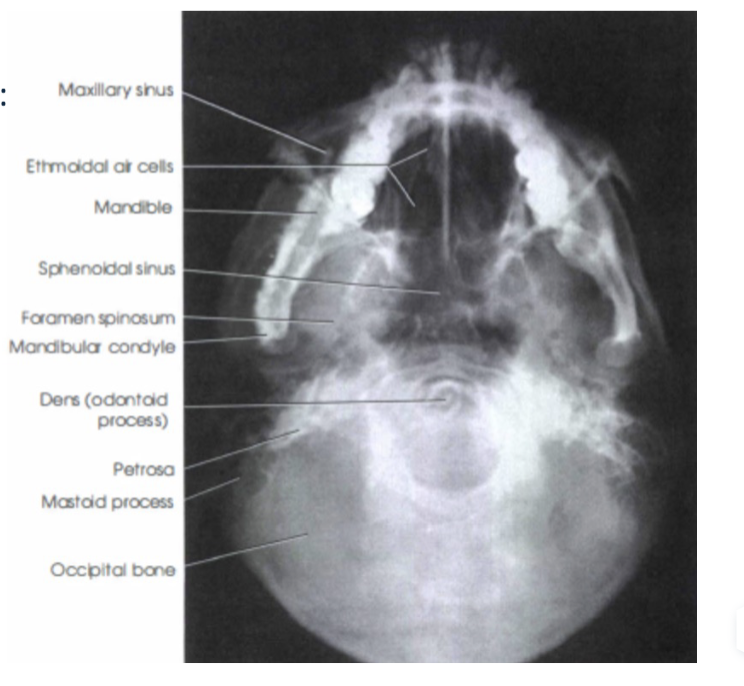
Submentovertex Projection Indications
Used to assess potential pathology, trauma, or disease progression to the base of the skull like in foramen ovale, foramen spinosum, and sphenoid sinus. Assessment of facial asymmetry. Determine angulation of condylar heads compared to the cranial base. Detect fractures in zygomatic process.
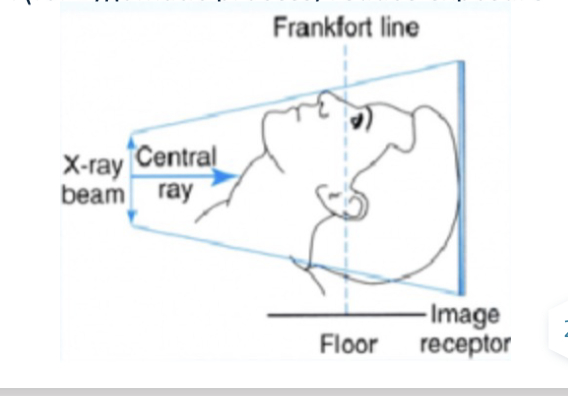
Submentovertex Projection Head Position
Sensor is placed vertically. Patient extends head and neck backwards so that the Frankfort line is perpendicular to the floor and parallel to the sensor plane.
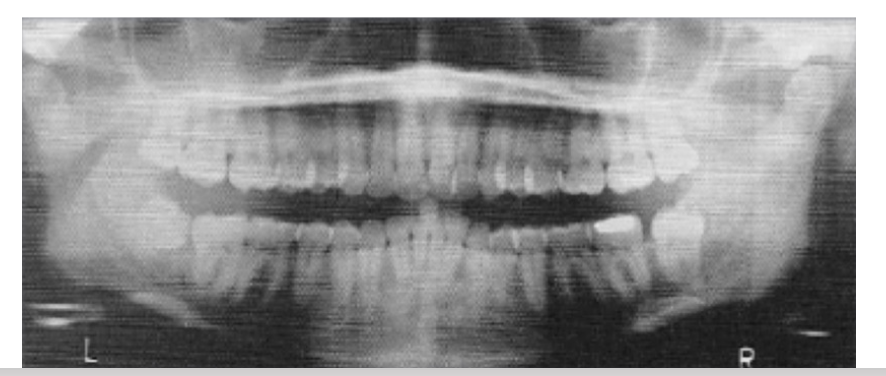
Panoramic Radiography
A radiologic technique that provides a 2D overview of the jaws and surrounding structures, frequently indicated to evaluate unerupted third molars, orthodontic treatment, tooth development, developmental abnormalities, trauma, large lesions, etc.
Advantages of Panoramic Radiography
Broad anatomical coverage, low radiation dose (similar to 4 bitewings), short imaging time, relatively comfortable, screening and educational tool.
Indications for Panoramic Radiography
General / Initial screening (lower resolution, lower radiation), Trauma evaluation (except anterior regions), Third molar assessment, dental/developmental control, Orthodontic Assessment, in patients unable to have intraoral explorations
Disadvantages & Limitations of Panoramic Radiography
Lack of detail due to resolution, superimposing structures, focal trough, artifacts, cost of equipment, patient movement causes distortion, geometric distortion, requiring follow-up intraoral exam and possible x-ray
Focal Trough
A three-dimensional curved zone, or “image layer,” where the structures lying within this zone are reasonably well defined on the final panoramic image.
Wrong patient positioning may result in alteration of size
⬩ More lingual -> closer to the beam -> magnification.
⬩ More vestibular -> minimization.
Panoramic Rx Patient Positioning
Remove metal objects. Place lead apron. Patient should be standing or sitting with a straight position. Patient should bite the bite-block with anterior teeth (focal trough). Frankfort plane is parallel to the floor and midsagittal plane perpendicular to it. Inform the patient that the machine will move around their head. Ask the patient to stay still during the exposure and place tongue against the palate.
Upwards Inclined Chin in Panoramic Radiography
Occlusal plane will be flat or inverted, resulting in distortion of mandible, and a radiopaque shadow of the hard palate on the apices of maxillary teeth.
Downwards Inclined Chin in Panoramic Radiography
Overlapping teeth, mandibular symphysis inferior border might not be visible, and both condyles appear over the upper limit of the image.
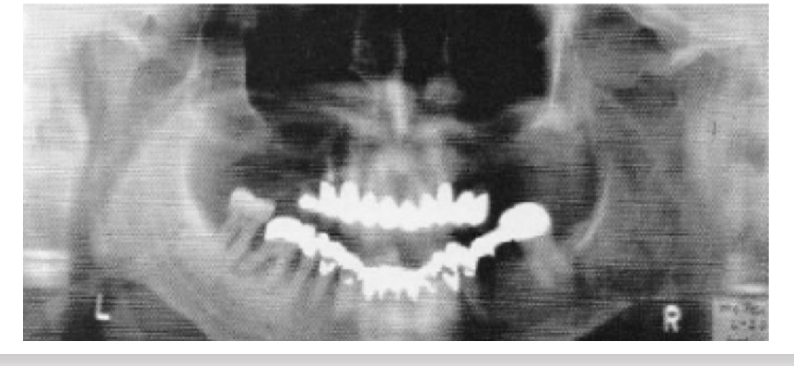
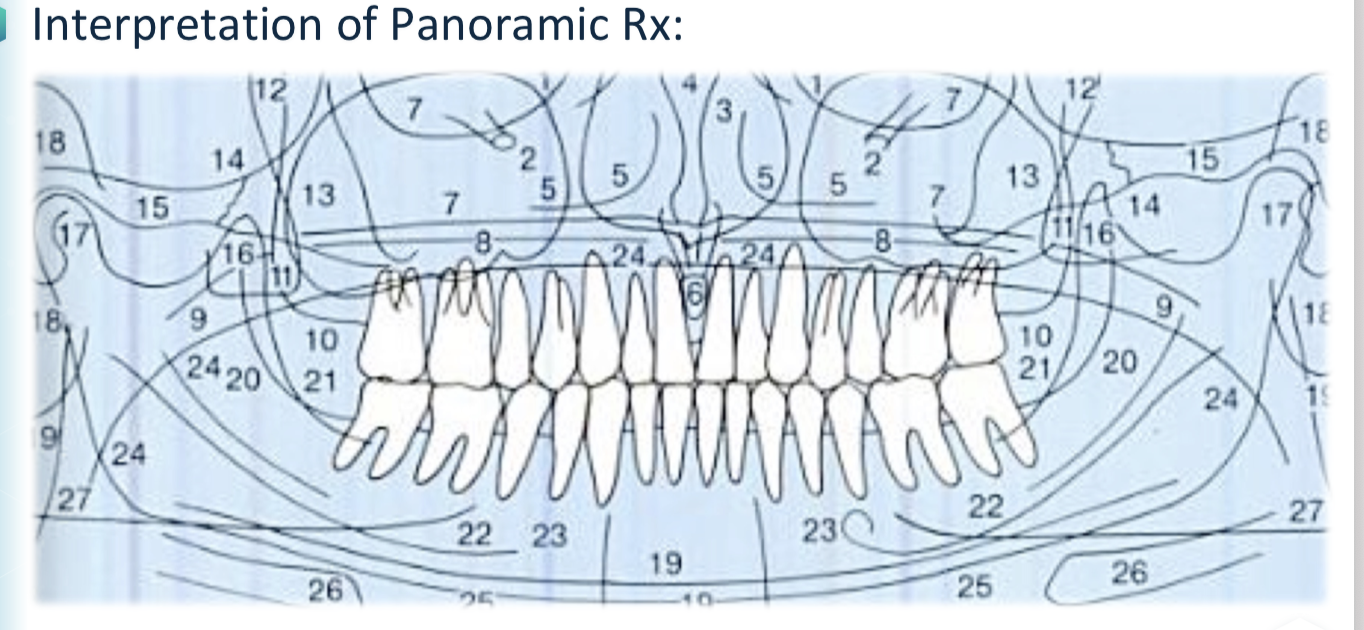
Panoramic Radiography - Mandible Ramus Identification
Superiorly the condyle is located, along posterior border of the ramus to the mandibular angle, in addition to Posterior border of the nasopharynx, Ear-lobe, Soft palate, Tongue dorsum, and a “Ghost Shadow” opposed to the mandible.
Panoramic Radiography - Body of Mandible Identification
From the mandibular angle to the symphyseal region, with Cortical bone of the lower border of the mandible, homogenous density and >3 mm thick. Evaluate Trabecular bone, Midline (radiopaque), Inferior alveolar (mandibular) canal, and Mental foramen.
Panoramic Radiography - Maxilla Identification
Cortical outline. Study the posterior border of the maxilla, the pterygomaxillary fissure and the tuberosity. Evaluate trabecular bone. Nasal septum. Evaluate maxillary sinuses for Borders and cortical bone, Symmetry of size and density, and Presence of fluids, cysts, etc.
Panoramic Radiography - Zygomatic Bone Identification
Zygomatic process (above 1st and 2nd maxillary molars) and Lower border of zygomatic arch. Caution: The temporo-zygomatic suture may resemble a fracture line.
Panoramic Radiography - Soft Tissue Identification
Tongue, Lip outline, Soft palate, Posterior border of the oropharynx & nasopharynx, Nasal septum, Ear-lobes, Nose, Nasolabial folds, and Radiolucent shadow of airway.
Panoramic Radiography - Dentition Evaluation
Evaluate teeth and surrounding bone, noting Proximal surfaces overlap. Caries or periodontal pathology require intraoral projections. Major caries or periapical lesions may be visible.