Geography AQA GCSE PAPER 1
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
Natural Hazard
A natural hazard is a natural process which could cause death, injury or disruption to humans, or destroy proprty or posesions.
Natural disaster
A natural hzard that has actualy happened
Geological hazards
Caused by kand and tectonic processes
Meteorological hazards
Caused by weather and climate
Factors affecting hazard risk
Urbanisation, poverty, development, climate change
Tectonic plates
Slabs of the Earth's crust
Continental crust
thicker and less dense
Oceanic crust
thinner and more dense
Tectonic plate movement
caused by convection currents underneath the Earth's crust
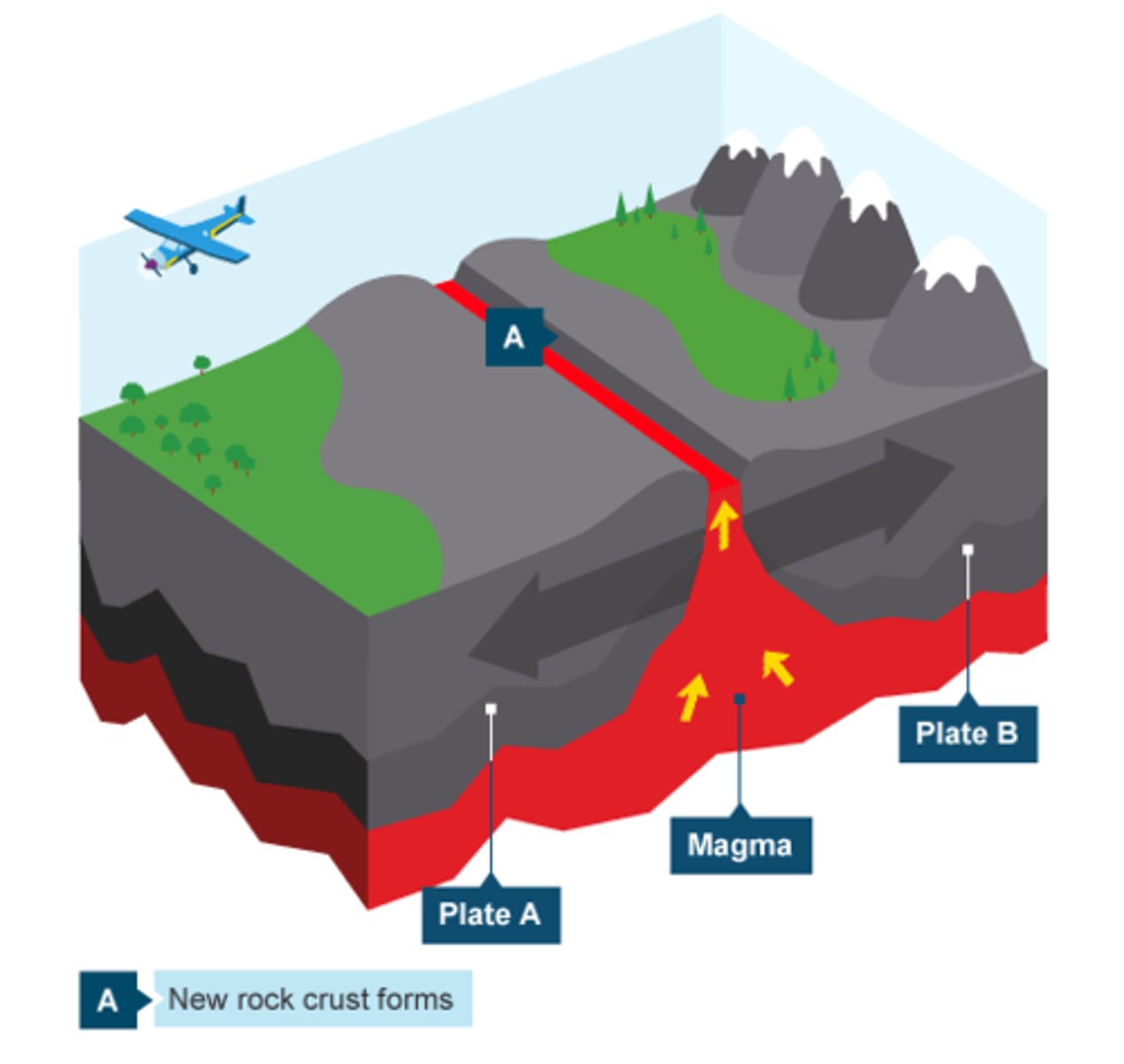
Destructive plate
Two plates moving towards one another, oceanic plate subducts under continental plate and friction causes melting of oceanic plate, triggers earthquake
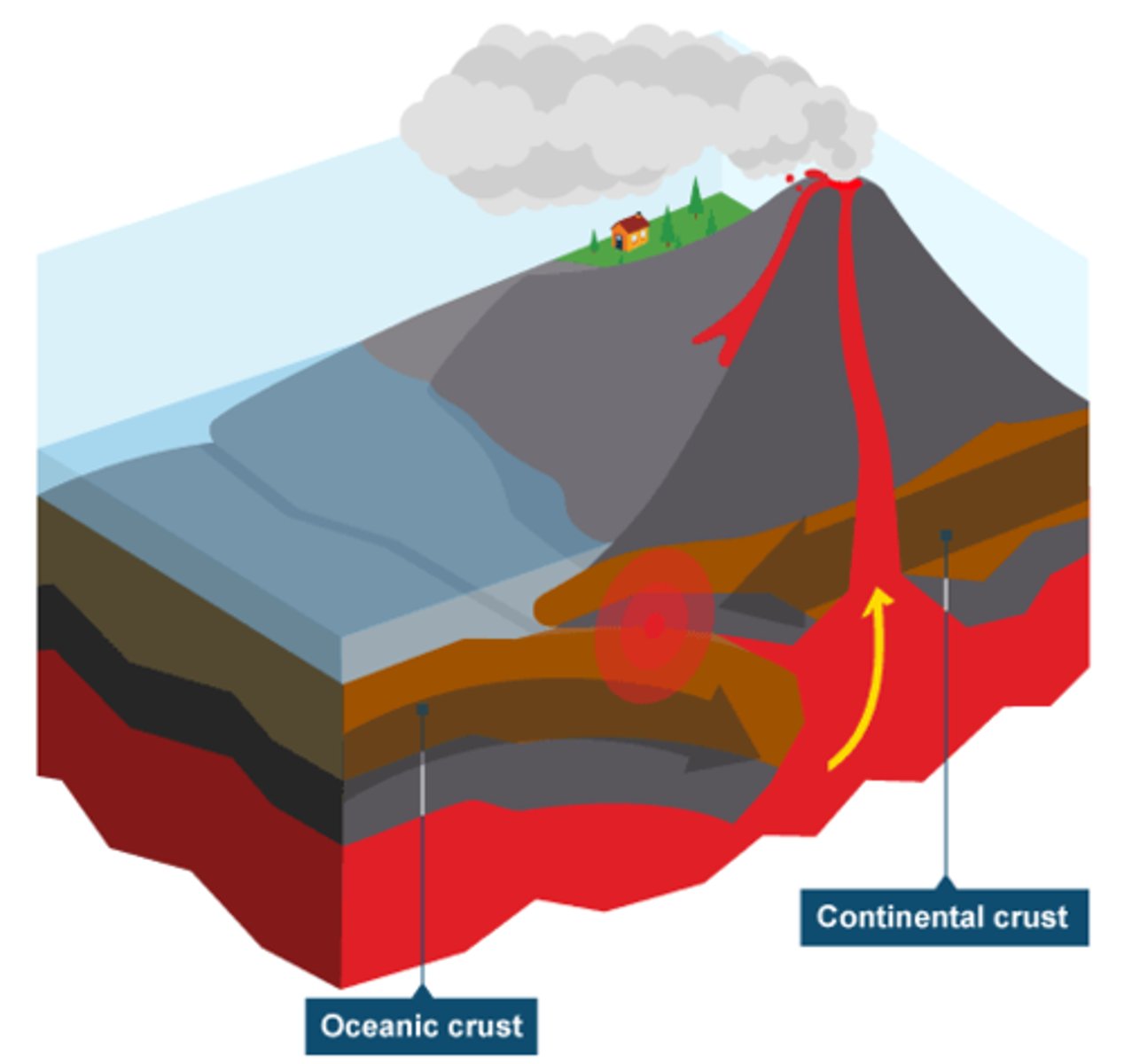
Constructive plates
Two plates move apart, magma forces way along gap and causes earthquake, erupted lava cools and forms volcano
Conservative plate
Two plates moving alongside, friction can send shockwaves causing earthquakes
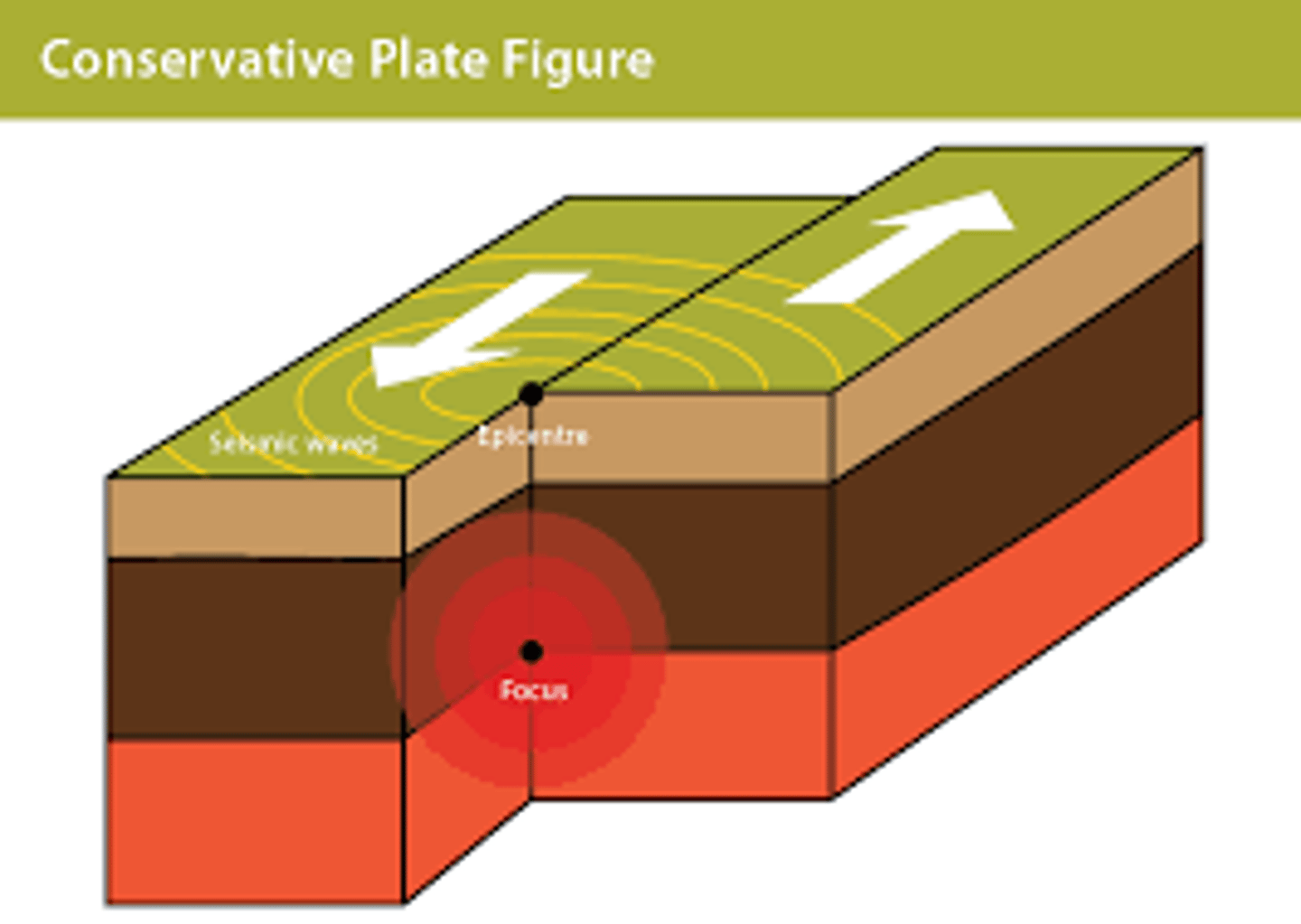
Earthquake causes
two plates 'jerking' past each other
the focus
the point in the Earth the earthquake starts
Epicentre
the point on the Earth' surface straight above the focus
Where are volcanoes found
At destructive and constructive plate marhgins
Where are earthquakes found
At all three types of plate margin
Earthquake Primary effects
buildings and bridges collapse
people are injured or killed
Roads are destroyed
Earthquake Secondary effects
Can trigger landslides, tsunamis = destruction
homeless can die from the cold
Leaking gas can start fires
Earthquake Immediate responses
Rescue people trapped by collapsed buildings and treat injured people
Recover dead bodies to prevent spread of disease
Foreign governments or charities may send aid workers, supplies , equipment or financial donations to the areas affected
Earthquake Long term responses
Re-house people who have lost their homes
Repair or rebuild damaged buildings, roads, railways and bridges.
Reconnect broken electricity, water, gas, communication connections
Volcanoes Primary effects
Buildings and roads are destroyed by lava flows and pyroclastic flows.
Buildings may also collapse if enough ash falls onto them.
People & animals are injured/killed by pyroclastic flows, lava,falling rocks
Volcanoes Secondary effects
Mudflows form when volcanic material is mixed with water and landslides cause destruction, death & injury.
Tourism can be disrupted straight after and the eruption - but often it can increase afterwards with tourists interested in seeing volcanoes
Ash makes fields more fertile once it's broken down
Volcanoes Immediate responses
Evacuate people before the eruption if it was predicted or evacuate as soon as possible after direction starts
Provide temporary supplies of electricity gas and communication systems if regular supplies have been damaged
Foreign governments or charities may send aid workers supplies equipment or financial donations to areas affected
Volcanoes Long term responses
Repair and rebuild if possible or resettle affected people elsewhere.
Repair and reconnect damaged infrastructure (roads, rail, power lines and communication networks etc)
Improve, repair and update monitoring / evacuation plans
L'Aquila Italy HIC earthquake
On the 6th april 2009 a 6.3 earthquake struck L'aquila.
PE - Around 300 deaths mostly from collapsed buildings 1500 people were injured, 60,000 homeless.
SE -Aftershocks hampered rescue efforts and caused damage. Fires in some collapsed buildings caused damaged IR - Ambulances, fire engines, army were sent to attempt to rescue survivors. Cranes and diggers were used.
LTR - New settlements were built to accommodate over 20,000 residents that used to live in the damaged city centre. Most of the city centre is being rebuilt.
Ghorka Nepal LIC earthquake
On the 25th April 2015 a 7.8 struck Ghorka Nepal
PE - Around 9,000 deaths, mostly from collapsed buildings Tens of thousands of people were injured, 1,000,000 homeless. SE - Triggered an avalanche on Mt Everest killing 13. Tourism stunted which was a good source of income for the country. rice fields destroyed which was their primary food supply IR - Uk £5 million on resources to help immediately, 135,000 people given immediate aid such as supplies and shelter LTR - rehousing schemes, internationally more than 255,000 people helped
Why people live near tectonic hazards
They have always lived there / They are employed in the area. /The soil around volcanoes is fertile as it's full of minerals makes it good for growing crops, attracting farmers / Volcanoes are tourist attractions.
managment strategies
Monitoring , Prediction, Protection, Planning
monitoring
seismometers and lasers to monitor earth movements can be used in early warning systems. scientists can use tell tale signs that come before a natural hazard
prediction
predictions aren't reliable but by monitoring the movement of tectonic plates they can forecast which areas will be affected, if it is predicted areas can be evacuated saving lives
protection
buildings can be designed to withstand an earthquake by using reinforced concrete or with foundations that absorb the energy, buildings can be strengthened, auto shut off switches to electricity water and gas to prevent fires
planning
emergency services trained for the event, educate people so they know what to do, plan evacuation routes, stockpile emergency supplies
Tropical storms
Tropical storms develop when the sea temperature. Is 27* or higher and when the wind shear between higher and lower parts of the atmosphere is low. Warm, moist air rises and condensation occurs. This releases huge amounts of energy which makes the storm powerful. The rising air creates an area of low pressure, which increases surface winds. Tropical storms move towards
the west.
features of a tropical storm
Tropical storms are circular in shape , hundreds of km wide and usually last 7-14 days. They spin counterclockwise in the northern hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere.
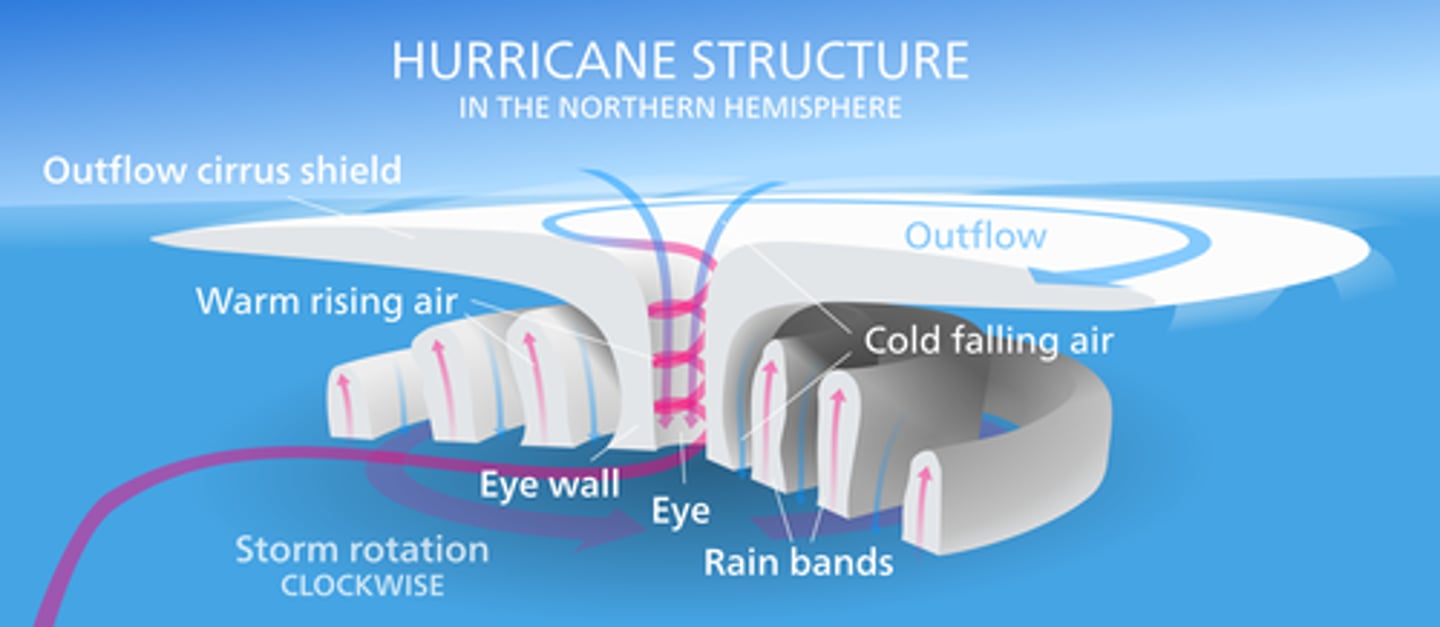
Tropical storm Primary effects
Buildings and bridges are destroyed
Rivers and coastal areas flooded
People drown, or are injured / killed by debris
Tropical storm Secondary effects
People are left homeless, which can cause distress, poverty, ill health or death due to lack of shelter. There is a shortage of clean water and lack of proper sanitation- this makes it easier for diseases to spread.
Business are damaged or destroyed causing unemployment.
Tropical storm Immediate responses
Evacuate people before the storm arrives
Rescue people that have been cut off by flooding and treat injured
Tropical storm Long term responses
Repair homes or rehouse people that have been displaced
Repair or replace damaged infrastructure.Repair and improve flood defence systems e.g levees and flood gates
Typhoon Haiyan
Typhoon Haiyan struck The Phillipines in south-east Asia in November 2013. category 5 storm one of the strongest recorded with 313km/h winds
PE - More than 7000 people were killed, 1.9 million made homeless, 30,000 fishing boats destroyed.
SE -, 6 million lost there jobs there were no fishing boats which is generally the main source of income in a family,
IR - essential supplies provided to over 800,000 people
LTR - reparations costing £4.55 billion
Uk weather hazards
Thunder, Rain, Wind, snow and ice, hail, drought, heatwaves.
November & December 2010
A period of heavy snow and cold weather across uk from 25.11.10 - 26.12.10 because of cold air from northern Europe and Siberia caused two long periods of cold with a brief thaw in between.
Climate change evidence
Ice and sediment cores - ice sheets are made up of layers of ice - one is formed each year. Scientists drill into ice sheets to get long cores of ice. By analysing the gases trapped in the layers of ice they can tell what temperature was each year, Temperature records, Pollen analysis, Tree rings - as a tree grows it forms a new ring each year - the tree rings are thicker in warmer and wet conditions.
Natural causes of climate change
Orbital changes, Major volcanic eruptions, solar output
Huaman causes of climate change
Burning fossil fuels, Cement production, Farming: farming of livestock produces lots of methane because of the large quantities of cows, Deforestation: When trees and plants are chopped down, they stop taking in C02. Carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere when trees are burnt as fuel or to make way for agriculture.
eviromental effects of climate chnage
Warmer temperatures are causing glaciers to shrink and ice sheets like greenland to melt. The melting of ice means that the water stored on land as ice returns to the oceans. This causes sea levels to rise, Sea ice is also shrinking leading to loss of polar habitats, Rising sea levels means low-lying and coastal areas, like the maldives, will be flooded regularly. Coastal erosion will increase as sea levels rise and some coastal areas will be submerged completely, so habitats will be lost.
social effects of climate change
In some places deaths due to heat have increased - but deaths due to cold have decreased.
Some areas could become so hot and dry that they are difficult or impossible to inhabit. Low-lying coastal areas could be lost to the sea or flood so often that they could become impossible to inhabit. This could lead to migration and overcrowding in some areas.
Global ecosystems
An ecosystem is a unit that includes all the biotic (living) parts (e.g animals and plants ) and the abiotic (non living parts (e.g the soil and climate) in a specific area. There are multiple ecosystems - Grassland, Tundra, Temperate deciduous forest, Rainforest, Desert and polar.
Tropical rainforests
The climate is the same all year round and there are no defined seasons.It is hot (temperatures and generally between 20 - 28*C. Rainforests are believed to contain more animal species than any other ecosystem. The soil is not very fertile as heavy rain washes the nutrients away. The rainforest is home to many people that have adapted their lifestyle to living there over many generations. Most trees are evergreen (i.e. they don't drop their leaves in a particular season) to take advantage of the continual growing season.
Plant adaptations to the rainforest
Climbing plants, such as lianas, use the tree trunks to climb up to the sunlight.
Plants drop their leaves gradually throughout the year meaning that they can go on growing all year round.
The rainforest has four distinct layers of plants with different adaptations. For example the plants in the highest layer (emergents) only have branches at their crown (where most sunlight reaches them) and the plants in the under canopy have large leaves so that they can absorb as much light as possible, as there is only a small amount that is available.
animal adaptations to the rainforest
Many animals spend their entire lives high up in the canopy. They have strong limbs so that they can spend all day climbing and leaping from tree to tree e.g. howler monkeys.
Some animals have flaps of skin that enable them to glide between trees, e.g. flying squirrels. Others have suction cups for climbing e.g. red eyed tree frogs.
Some birds have short, pointed wings so that they can easily maneuver between the dense tangle of branches in the trees, for example the Harpy Eagle has a short wingspan.
deforestation
The removal of trees from forests is called deforestation. It's happening on a huge scale in tropical rain forests. Reasons - Population pressure: As the population in the area increases, trees are cleared to make land for new settlements.
Mineral extraction: Minerals (e.g. Gold and iron ore) are mined and sold to make money.
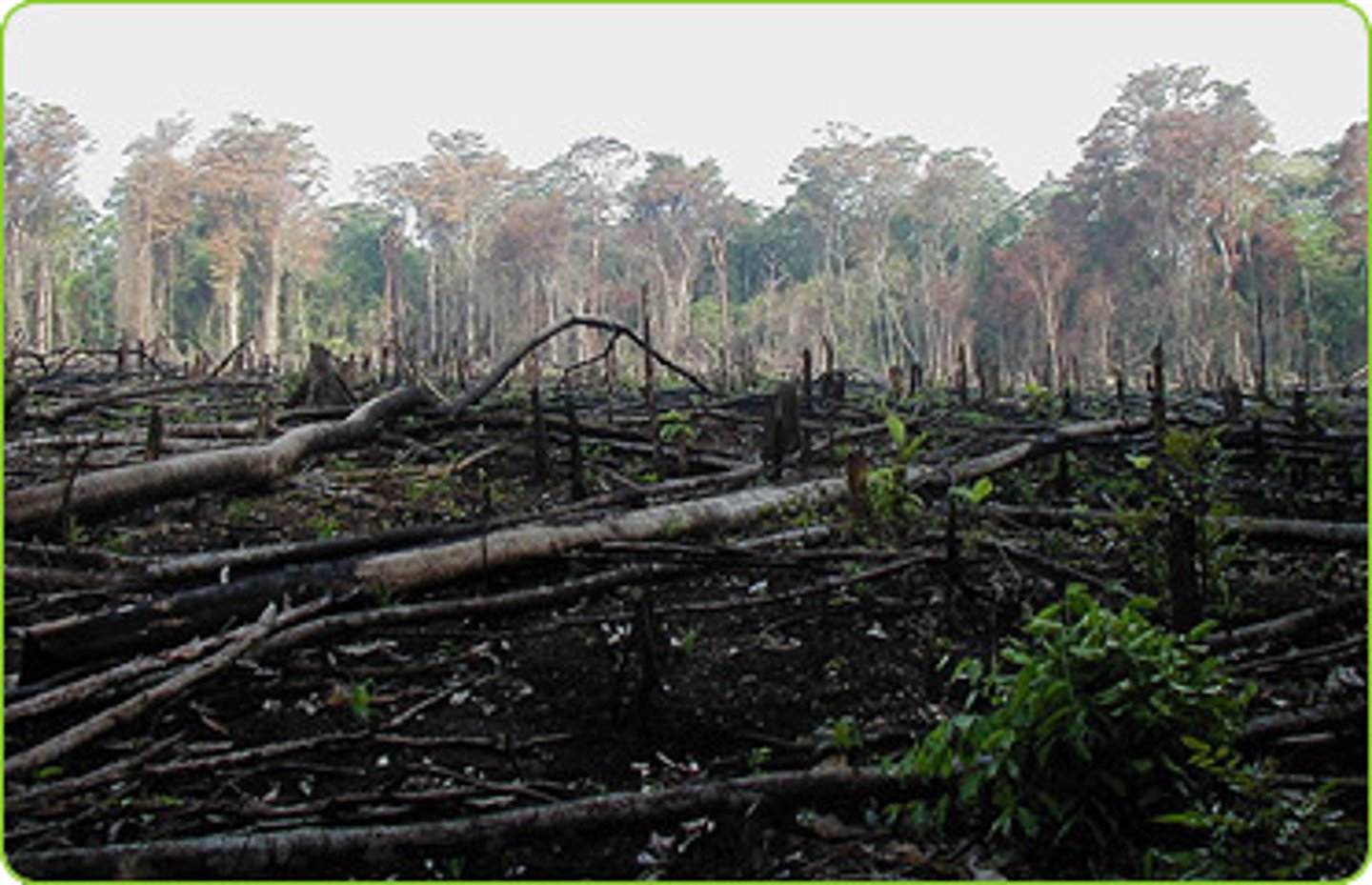

imapcts of deforestation
With no trees to hold the soil together, heavy rain washes away the soil. This can lead to landslides and flooding.The livelihoods of people can be destroyed - deforestation can cause the loss off the animals and plants that they rely on to make a living. Many people work in the industries that cut down trees. If there were to be a law placed on the ban of deforestation then all of the employees will lose their job.
managing the rainforest
It is important to protect the rainforest in order to preserve its biodiversity - maintaining a high diversity of animals and plants is valuable to people and the environment. to do this replanting, selective logging and ecotourism takes place.
Hot deserts
Many people living in the desert grow few crops where there are natural springs or wells to supply water, usually in the desert fringes.Insidious people are often nomadic, Hot deserts contain animals adapted to survive in the harsh environment, Soil is usually shallow with a coarse, gravelly texture, There's very little rainfall- less than 250mm per year.

Plant adaptations to the desert
Plant roots are either long to reach deep water or spread out wide near the surface to catch as much water as possible when it rains.
Many plants e.g. cacti are succulents. They have large fleshy stems for storing water and thick waxy skin to help reduce water loss (water loss from plants is called transportation) some also have sharp spines and toxins to stop animals stealing water from them.
Some plants have small leaves or spines - this gives them a low surface area , reducing the rate of transpiration
animal adaptations to the desert
Being nocturnal means that an animal can stay cool in burrows during the day or sit still in the shade whilst it is hot out, for example the fennec fox. Desert animals also have long lips or ears providing them with a large surface area to loose hear from.
Lizards and snakes are able to tolerate high body temperatures e.g. iguanas can survive up to temperatures of 42*C
desertiication
Desertification is the degradation of land so that it becomes more desert-like - it becomes drier and less productive. A third of the world's land surface is at risk of desertification, particular at the margins of deserts. Soil erosion is a key part of desertification. Soil that is exposed is easily removed by wind or water. Nutrients in the soil are lost making the soil unproductive. Eventually the ground becomes sandy, dusty, stony or just bare rock.
reducing desertification
Water management, tree planting, soil management, using the correct technology.
mechanical weathering
The type of weathering in which rock is physically broken into smaller pieces (without changing its chemical composition)
Chemical weathering
The process that breaks down rock through chemical changes
Mass movements
The shifting of rocks and loose materials down a slope. It happens when the force of gravity acting on a slope is greater than the force supporting it
Three processes of erosion
Hydraulic action, abrasion,attrition
Hydraulic action
When waves crash against rock and compress the air in the cracks, putting pressure on the rock.
Abrasion
The grinding away of rock by other rock particles carried in water, ice, or wind
Attrition
Eroded particles in the water smash into each other and break into smaller fragments. There edges also get rounded off as they rub together
The waves that carry out erosion processes are called
Destructive waves
Destructive waves are
High and steep and have a high-frequency
the backwash is more powerful than the swash
meaning material is removed from the coast
Destructive waves
large waves that carry sand and other material away in the backwash and REMOVE MATIERAL
Transportation
Is the movement of material by either longshore drift, traction, saltation ,suspension or solution
Material is transported along coasts by a process called
Long shore drift
long shore drift
The prevailing wind (the direction the wind ususally blows from) causes waves to approach the coast at an angle. The swash carries the sand and pebbles up the beach at the same angle (usually 45º). The backwash, however carries the material back down the beach at right angles (90°) as this is the steepest gradient.
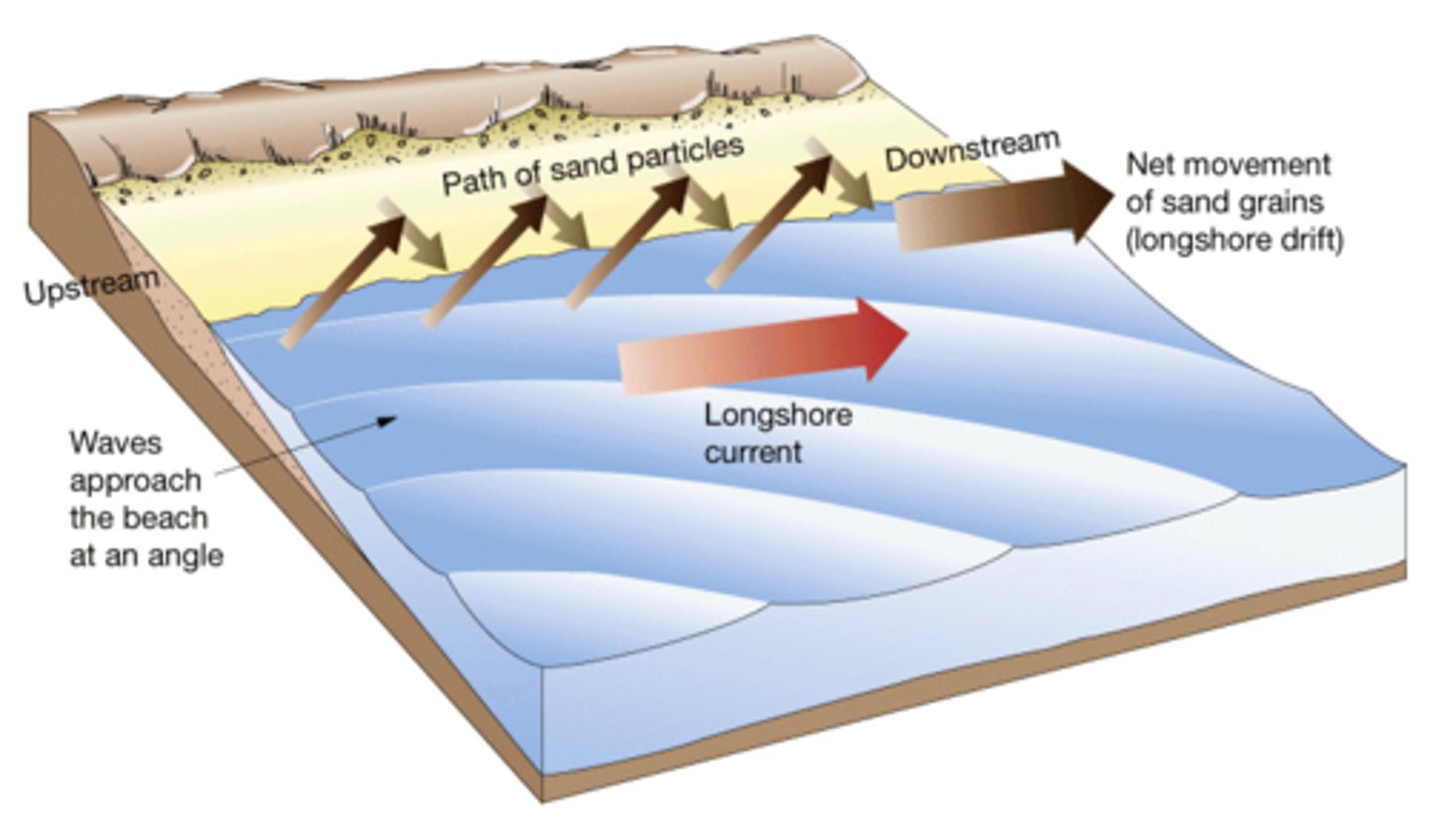
The four processes of transportation are
Traction
Saltation
Suspension
Solution
Traction
Large particles are pushed along the seabed by the force of water
Saltation
Small pebbles and stones are bounced along the river bed
Suspension
Small particles are carried along by the water
Solution
Soluble materials dissolve in water and are carried in the sea
Deposition
When material being carried by the sea water is dropped on the coast
Constructive waves are
Low and long
The swash is more powerful and the backwash is weaker
It carries material up at the beach and doesn't take a lot of material back down the beach
Constructive waves
waves that carry and deposit sand and other materials
Holderness coast
Mappleton is a small village that could become lost to the sea. The road running through it, the B1242 links towns along the coastline and would have been lost to coastal erosion if protection measures were not put into place. So, blocks of granite were brought in and placed along the cliff base and 2 rock groynes were put into place to trap sediment moving because of longshore drift. However there are now problems further down the coast at great cowdens farm.
Cross profile
The side to side cross-section of a river channel and/or valley
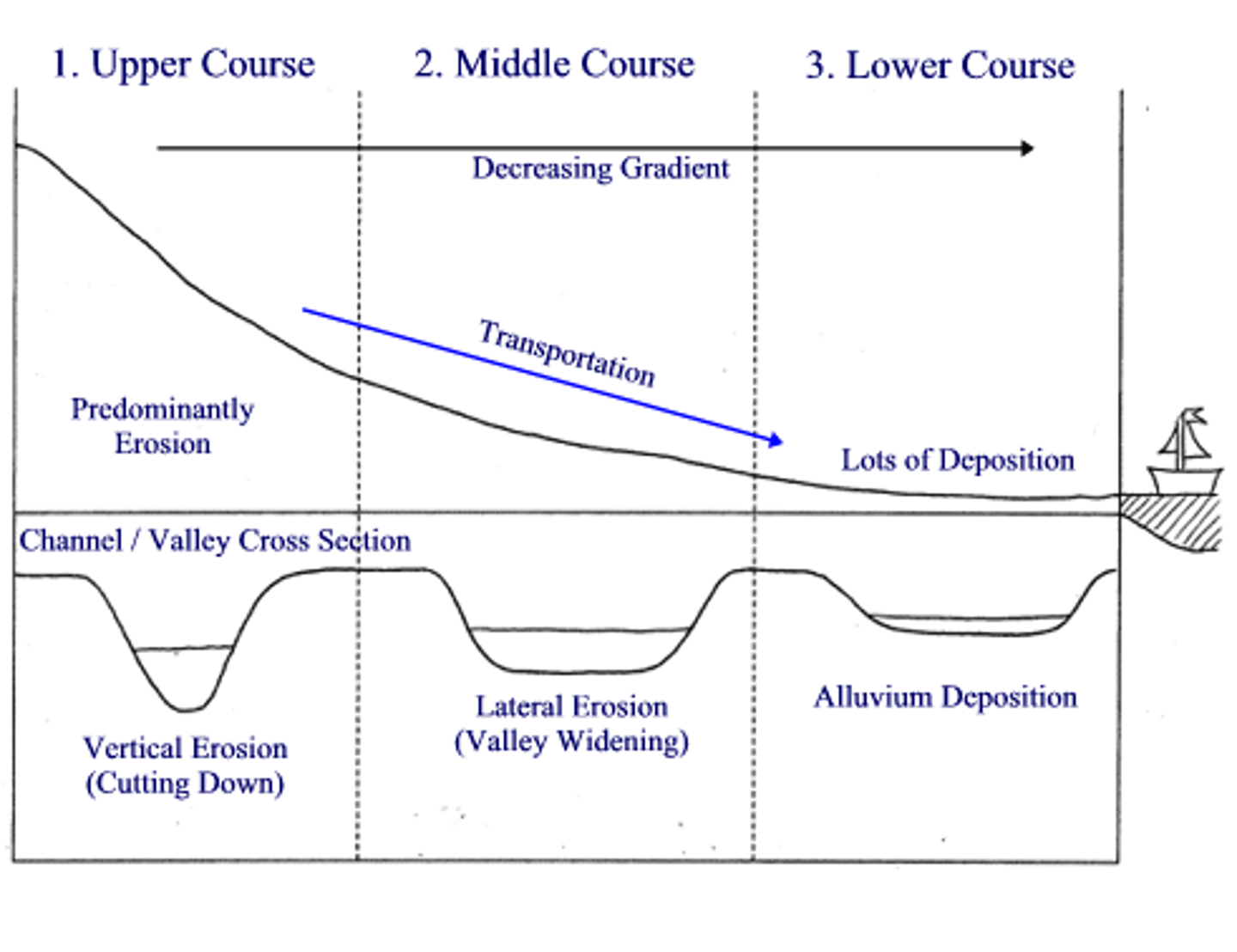
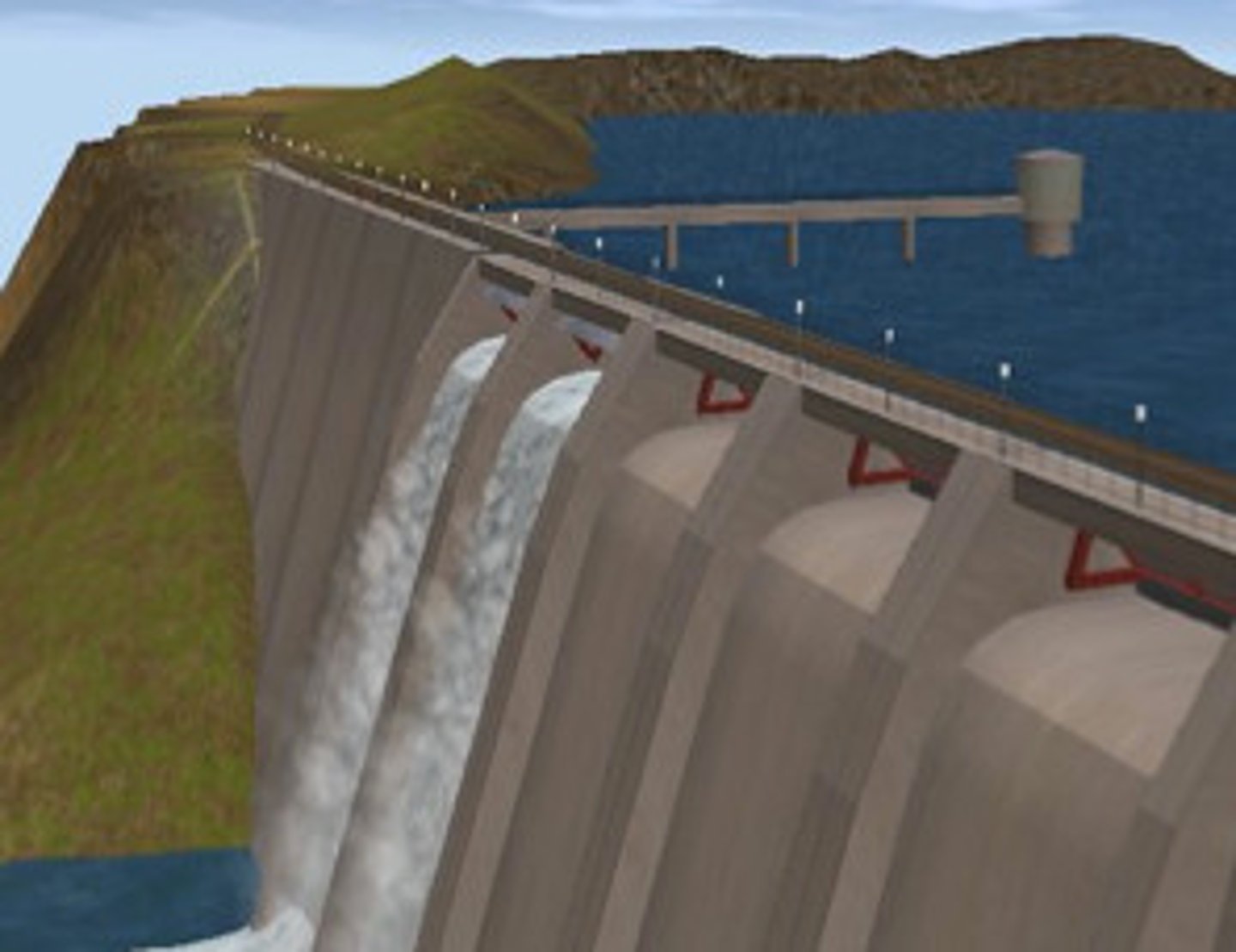
Dam and reservoir
A barrier(made on earth, concrete or stone) built across a valley to interrupt river flow and create a man‐made lake(reservoir) which stores water and controls the discharge of the river

Discharge
The quantity of water that passes a given point on a stream or river‐bank within a given period of time
Embankments
Raised banks constructed along the river; they effectively make the river deeper so it can hold more water. They are expensive and do not look natural but they do protect the land around them

Estuary
The tidal mouth of a river where it meets the sea; wide banks of deposited mud are exposed at low tide

Flood
Occurs when river discharge exceeds river channel capacity and water spills out of the channel onto the floodplain and other areas
Flood plain
The relatively flat area forming the valley floor on either side of a river channel, which is sometimes flooded.
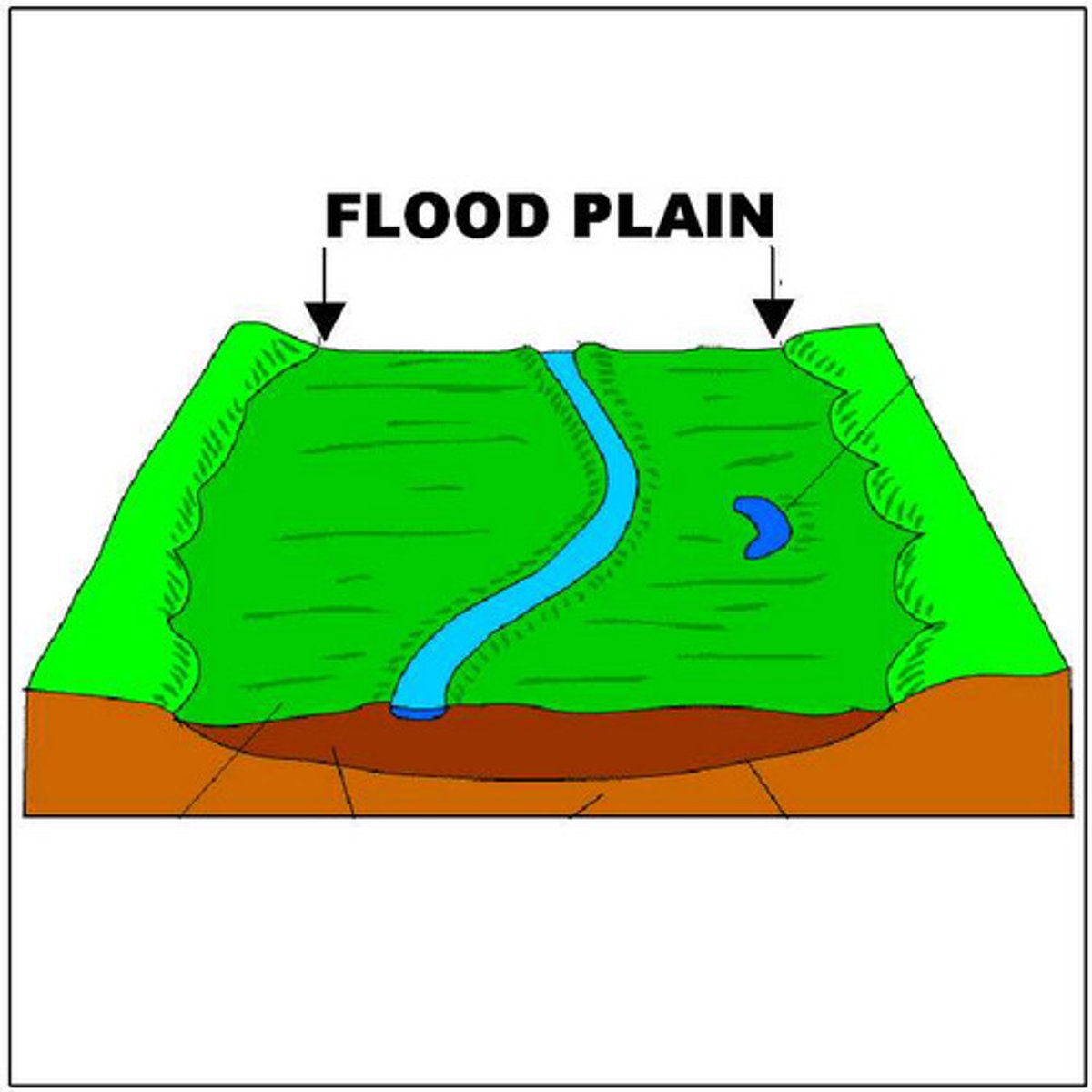
Flood plain zoning
This attempts to organise the flood defences in such a way that land that is near the river and often floods is not built on. This could be used for pastoral farming, playing fields etc. The areas that rarely get flooded would therefore be used for houses, transport and industry
Flood relief channels
Building new artificial channels which are used when a river is close to maximum discharge. They take the pressure off the main channels when floods are likely, therefore reducing flood risk
Flood risk
The predicted frequency of floods in an area
Flood warning
Providing reliable advance information about possible flooding. Flood warning systems give people time to remove possessions and evacuate areas.
Fluvial processes
Processes relating to erosion, transport and deposition by a river
Gorge
A narrow, steep sided valley, often formed as a waterfall retreats upstream.
Hard engineering
Involves the building of entirely artificial structures using various materials such as rock, concrete and steel to reduce, disrupt or stop the impact of river processes
Hydraulic action
The force of the river against the banks can cause air to be trapped in cracks and crevices. The pressure weakens the banks and gradually wears it away
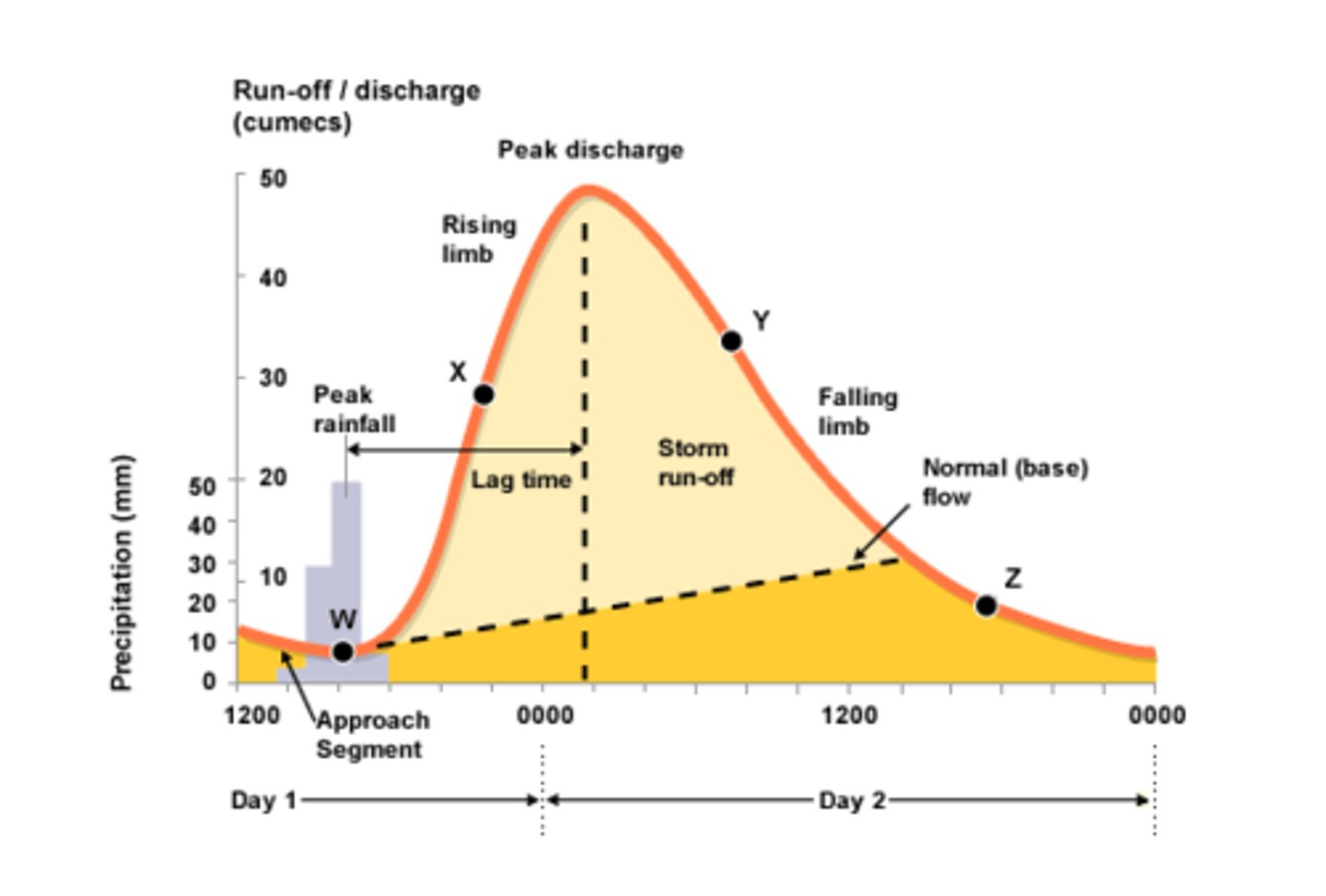
Hydrograph
A graph which shows the discharge of a river, related to rainfall, over a period of time
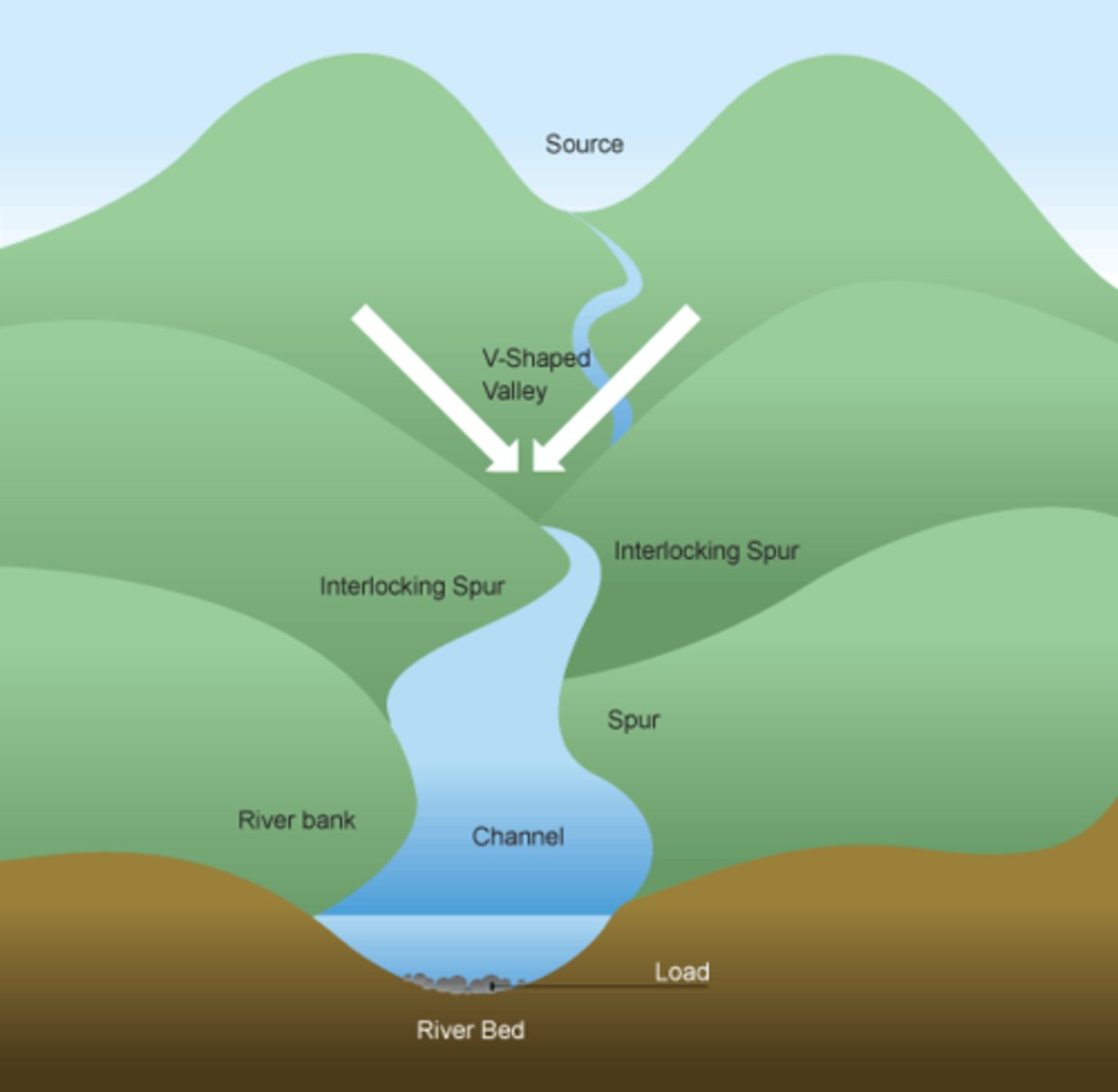
Interlocking spurs
A series of ridges projecting out on alternate sides of a valley and around which a river winds its course
Lateral erosion
Sideways erosion by a river on the outside of a meander channel. It eventually leads to the widening of the valley and contributes to the formation of the flood plain

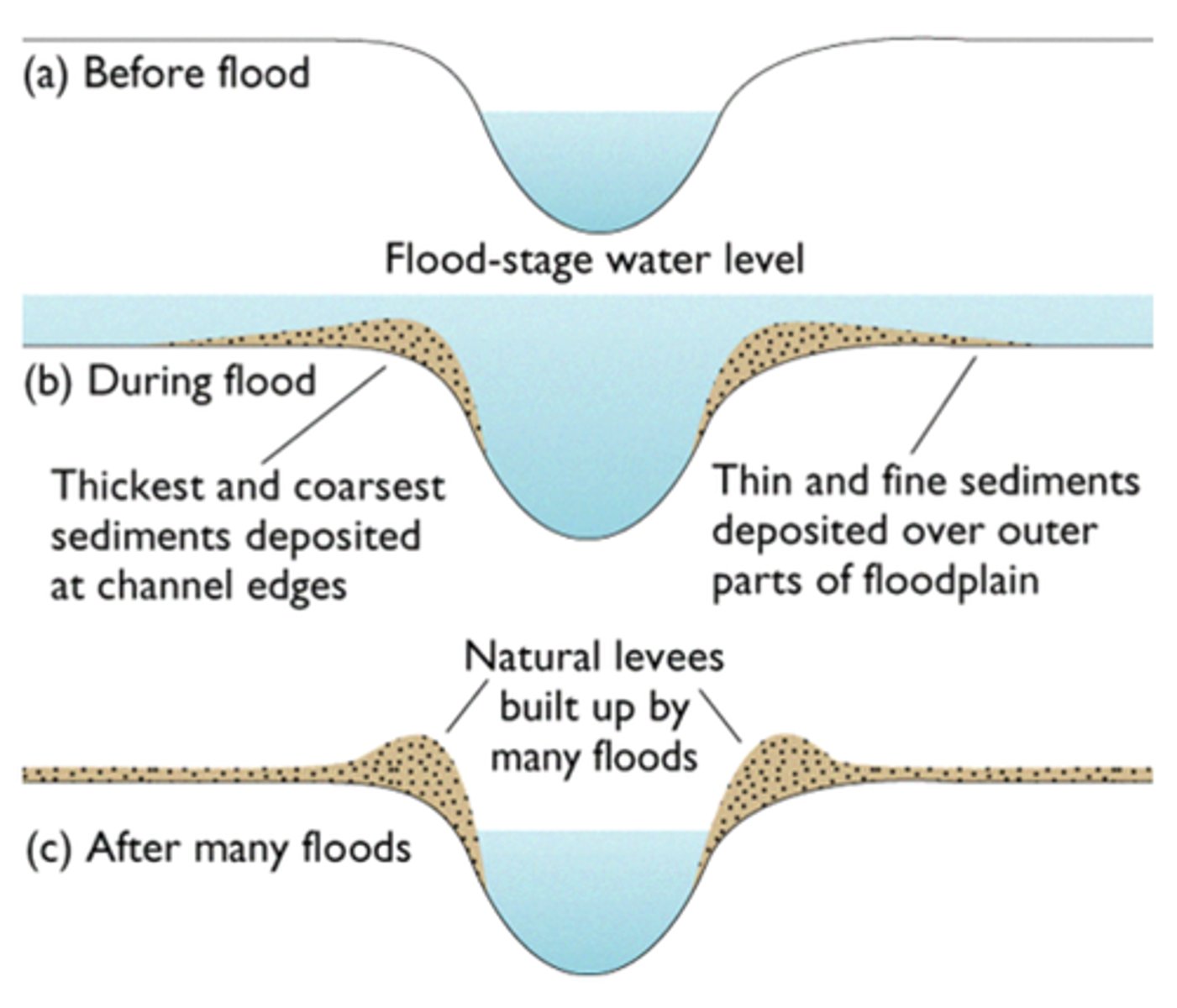
Levees
Embankment of sediment along the bank of a river. It may be formed naturally by regular flooding or be built up by people to protect the area against flooding