derived demand
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
what is derived demand?
derived demand means that a factor of production is not demanded for tis own sake but for the goods and services that it is used to produce
what are factors of production?
factors of production are the elemnts needed by a buisness to produce goods and services eg land,labour,capital an denterprise
show the affect of lithium due to an icnrease in demand for mobile phoens
If demand for mobile phones increases this causes an increase in the quantity of mobile phone supplied (movement along the supply curve). This will cause an increase in the demand for mined lithium. This leads to a higher price for lithium and therefore an increase in the quantity of lithium supplied (movement along the supply curve).
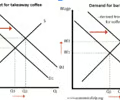
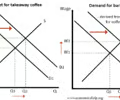
explain the effect of an increase in takeaway coffee sales on the demand for baristas, the wages of baristas and the number of people working as baristas
If demand for takeaway coffee increases (shift in right in demand) this causes an increase in the quantity of takeaway coffee supplied (extension in the supply curve). This will cause an increase in the demand for baristas (shift to right in demand) as more coffee needs to be made faster leading to higher wages for baristas and therefore an increase in the number of people working as baristas (extension in the supply curve) as mroe people willing to work as baristas.
main differnece between the labour market and the other markets
-The supply of labour comes from people/individuals/ households
-The demand for labour comes from businesses So we can see how the Demand of Labour varies with wage We can also see how the Supply of Labour varies with wage
what will firms prioritise whiel buyign factros of production?
Firms try to prioritise the factors of production which give them the lowest cost for each revenue-want to maximise outpur an dminimise cost. They depend on:
-Productivity of the factor available. Better quality resources tend to demand a higher price due to their high productivity.
-The cost of the factor: the higher the cost of factor of production the lwoer theri emand. eg is labour costs are relatively high compared to the cost of capital then workers might be replaced by amchinery and technology. The demand for capital depends on the cost of borrowing money- higher interest rates icnrease the cost of financial capital itnensive production
-availability of different factors: the greater the availaibilty of land, labour and capital the lower their costs tend to be and hence the higher their demand. The greater the quanitity of a factor of production the lwoer its cost.
Firms use all 4 factors of production, explain what might affect their decision about how much of each they use.
-Land: How expensive the land is and if it's suitable for building the factory on and weather they can build their factory upwards with lots of levels.
-Labour: if labour are skilled,readily available and don't require training and the wages they are willing to work at.The demand for the product and if lots of labour are needed to increase supply.
-Capital: how expensive the capital is to buy and how long it takes to be produced and how easy it is to move to factory/deliver
-Enterprise:How expensive they are,weather they are skilled and useful
what is training?
action of teaching or learning practical skills or behaviours. Requires basic education.
what is education?
acquiring basic knowledge through a process of receiving instruction.
how will education,training and experience impact productivity?
-It will make them more skillful and productive as they are more knowledgeable on how to do their job efficiently -Highly trained workers are highly productive as they are already trained so no time will be wasted learning how to do their jobs, know how to work efficiently -experienced workers are more efficient and less likely to make mistakes and so waste less resources-know how to handle accidents and situations better
factors besides derived demand that affect the demand for labour?
-demand for final product, right shift of supply for product causes right shift in demand for workers
-availability of substitutes including machinery: will decrease demand for workers, also makes demand more elastic
-productivity of workforce which depend on skills ie education of workers
what are labour intensive industries?
in laboru intensive industries the cost of labour is porportionately higher than the cost of other factors of production eg accountancy, real estate services and toursim. Labour intensive production processes tend to be sued to produce individual or personalsied products
why may firms choos eto invest in labour intensive production?
suitable for producing more customised products
Personalised service & unique products so can charge higher prices
Highly skilled & specialised workers woudl mean high quality products
More flexibile to meet changing levels of demand eg can hire more temporary workers and lay off workers
Risk of break down, repairs & maintenance
-May be because there is an abundance of labour and so the cost of labour is relatively cheap-labour intensive production particularly associated wiht countries which have a alrge population
disadvanateg of labour intensive
-can be expesnive. Hiring highly skilled and experienced workers results in higher costs of production adn so higher prices charged to consumers
what is capital intensive production
in capital intensive industries the sue and cost of capital is more prominent than that of any other factor of productione g car manufacturing. Need a lot of money to fund thri acitivites which can act as a barrier ot entry sicne its expensive for new firms to enter industry
advanatges of capital intensive production?
-labour being repalced by machienry may lead to more efficent an dproductive process of production as machinery able to work continuously without taking breaks. Can benefit in form of technological eocnomues of scale by icnreas their outpur and productivity levels by mass producing products so unit costs fo production are relatively low.
-can benefit by using mass production techniques such as automation which enables mroe outpur in less time. Unit costs of production are therefore low
-Less risk of human error-machienry more accurate then humans in prodcution process
-Less expensive as less staff required
disadvanateg of capital intensive
-however intiial cost of obtianing equiptment and continuel cost of running (eg maintenance) it may be high
-capital machienry generally seen as a long term investment but over a period of time the machinery and equipment will wear out an dwill need replacing. This wearing out is known as depreciation
-reliance on assembly lines means any breakdown will cause major problems for the buisness
factors affecting chossing between capital and labour intensive production
The cost of labour compared to the cost of capital- capital tends to be cheaper due to mass production methods). Choose cpaital intensive methods if laboru costs are high and vise vera
The size of the market - capital intensive for mass market products, labour intensive for more personalised items like a tailored suit, wedding dress
The firm’s objectives - if the goal of the business operating in mass markets is to make profit then capital intensive is the best as unit costing will be much cheaper, if a more unique product and service is the goal then labour intensive is better or if want to operate on a smaller scale.
Increase in demand for bottled water and the affect on the wages of bottled water production workers.:
An increase (shift to the right) in the demand for bottled water will cause and an increase or (shift to the right) in the demand for production workers in bottled water plants. This will lead to excess demand in the market for bottled water production workers. Firms will need to increase the wages they offer to employees to attract extra workers. This will cause an extension along the supply curve for bottled water employees. This will result in a new equilibrium at Q1/W1 where wages are higher and the number of workers is higher.
what is wage elasticity of supply of labour
The wage elasticity of supply of labour is the sensitivity of the supply of labour to a change in the wage rate.
what si elasticity of supply of labout like?
-In short term: always inelastic -in long term: always elastic -jobs requireing lots of skills: inelastic as its hard ot increase supply in short term -jobs requiring few skills are likely to be more Elastic-easy to increase supply short term-widely available -jobs with high levels of job satisfaction are likely to be relatively -Elastic- as a lot of people want to work so high supply
what is elastic demand for labour
The responsiveness of the demand for labour to a change in the wage rate of labour.depend on Wages proportion of total costs Ease of substitution of capital (or other factors) PED of product produced
what is elasticity of demand for labour like:
-If firms produce a product which is inelastic they can easily pass rising costs to consumers. This is likely to make wages higher and demand for labour more inelastic
-If firms have easy options to mechanise production demand for labour is more likely to be (called ease of factor substitution) elastic -If wage costs are low as a percentage of total cost demand for labour tends to be more Inelastic -In the very short-term firms find it hard to change production methods so demand will be more inelastic