CD 351 Exam 3
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
For students at the University of Alabama taking Hearing Science
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Psychophysics
How we perceive a physical stimulus
Psychoacoustics
How we perceive sound
The McGurk effect
A psychoacoustical phenomenon in which what we see clashes with what we hear
Scaling
The ordering of stimuli along some type of space
Threshold
The lowest sound that we can perceive
T/F: There is no absolute threshold
True
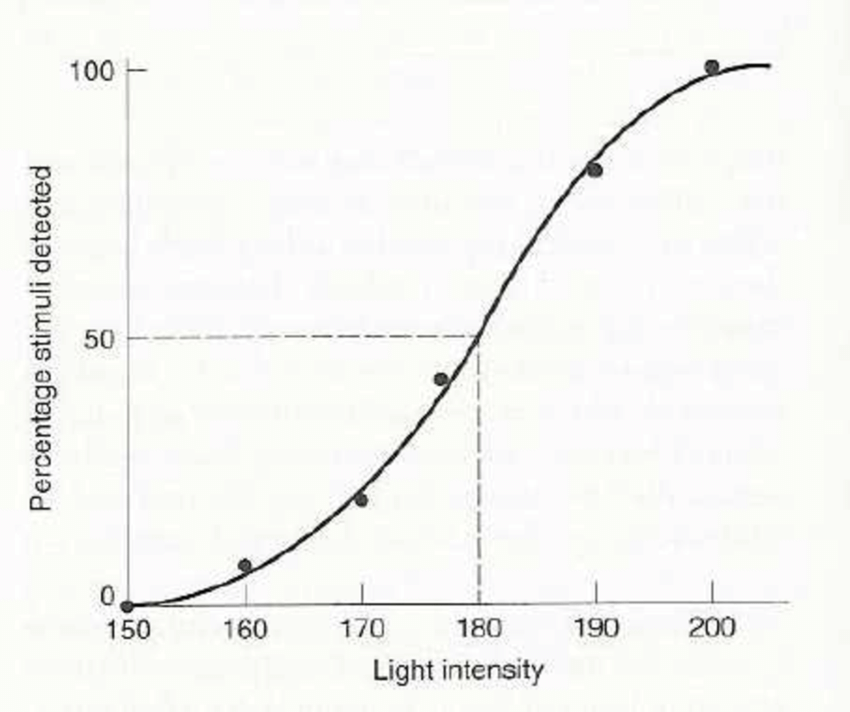
Method of Constant Stimuli
A phsycophysical method in which several stimulus levels are presented and each time the stimulus is heard is recorded.
Pros of Method of Constant Stimuli
Easy to administer
Can provide a precise estimate of the threshold if the step sizes are small
Cons of the Method of Constant Stimuli
You must know the approximate threshold of the listener in advance
Time may be wasted
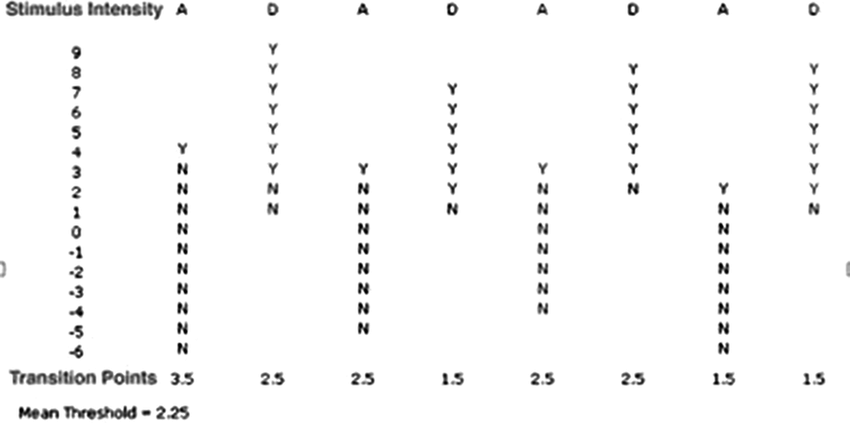
Method of Limits
A physcophysical method that starts where the tester thinks the listener will hear. The decibels will lower until the listener can no longer hear, and the process is repeated several times.
Pros of the Method of Limits
Efficient because we can focus the stimulation around the known threshold
Cons of the Method of Limits
False representation may cause errors in the estimation threshold
The listener may miss the true threshold if the step size is too big
Transition Point
The mean between intensities where a patient could and could not hear the stimulus.
Mean threshold value
The mean of all transition points
Modification of Limits
A shorter version of the method of limits that is typically done in a clinic
Method of Adjustment
A psychophysical method in which the listener turns a dial back and forth until they cannot hear the stimulus anymore several times.
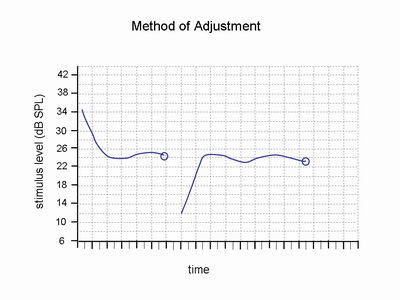
Békésy Tracking
When the intensity increases as the subject pushes a button and the intensity decreases as the subject releases the button. The midpoints correspond to the 50% point.
Pros of the Method of Adjustment
Offers the patient control over the situation
Easy and simple
Cons of the Method of Adjustment
The results can be unreliable
Does not have the highest confidence in accuracy
Response Bias
When the patient will only respond to a stimulus under certain conditions
What are the two reasons a listener may answer incorrectly on the Method of Limits test?
Anticipation (they’re expecting the stimulation)
Habituation (they’re used to answering for the stimulus)
Why would a listener answer incorrectly on the Method of Adjustment test?
Perseveration in the response
Catch Trial
When a tester does not play a stimulus and watches to see if the listener responds.
Pros of a Catch Trial
Simple
Provides information about bias
Provides some information about how reliable the threshold is
Cons of a Catch Trial
Does not provide a way to “adjust” the threshold to correct for any biases
Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Analysis
The assumption that when you are close to a threshold, sometimes “no sound” sounds like something. Used to train military personnel for radars.
Hit
When there is a stimulus present and it is heard
Miss
When there is a stimulus but it is not heard
False Alarm
When there is no stimulus present but something is heard
Correct Rejection
When there is no stimulus but nothing is heard
What are the optimal answers for a ROC trial?
Hit and correct rejection
ROC curve
A response bias test in which the stimulus changes, but the way that a listener responds to it changes
Conservative Listener
“Only indicate you heard something if you are 100% certain.”
Liberal Listener
“Indicate that you heard something when you feel like it’s correct.”
Two-Alternative Forced Choice (2FAC)
A response bias test that involves two intervals: one without sound and one with sound. The listener is asked to pick which trial had sound.
The most common method for studying hearing sensitivity is ___.
A mix of 2FAC and adaptive method
Masking
A change in the threshold for a stimulus caused by the presentation of another stimulus
Quiet Threshold
The absolute threshold for the signal presented alone
Masked Threshold
The absolute threshold for signal when presented with a masker
Amount of Masking
The difference between a quiet threshold and a masked threshold
Simultaneous Masking
When the masker and signal overlap in time
Simultaneous masking is a ___ correspondence ratio
1:1
True Simultaneous Masking
When the signal is presented in the middle of the masker
Forward Fringe Masking
When the signal and the masker are on at the same time, but the signal stops first
Backward Fringe Masking
When the masker comes on first, followed by the signal. They both stop at the same time.
Simultaneous Noise Masking
When the signal is the tone and the masker is the noise
The higher the noise on a broadband graph, the ___ the frequency is affected.
more
The curve on a broadband noise making graph is the ___
Threshold of audibility curve
T/F: Frequency does make a difference on broadband noise making
False
Parameter
The spectrum level of noise
Simultaneous Narrowband Masking
When the signal is higher in frequency, the Amount of Making is generally greater because more frequencies are engaged on the basilar membrane.
As the signal gets closer to the masker in time, the masker becomes more ___.
Effective
The masker is more effective as the threshold goes ___.
Up
There is a decrease in the threshold as a signal gets ___ from the masker in time
farther away
When the masker and the signal are ___ in frequency, the masker is more effective
closer together
Tone-on-tone masking
When the masker is fixed in frequency and sensation level. The signal frequency and level varies
Beats
When the signal and the masker are very close in frequency (usually < 10 Hz)
T/F: At a high level, the high frequency masker will not mask a low level frequency well
True
T/F: At a low level, the low frequency masker will not work better than a high level, high frequency masker.
False
Combination Tones
A phenomenon where two loud tones are sounded together and a third tone is heard that is not actually present in audible sounds.