Lecture 1: Proper Sample Storage & Submission
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What are the three blood sample types?
whole blood, serum, plasma
What sample type represents an unspun, non-clotted sample, ±anticoagulant?
whole blood
What sample type is the fluid fraction of whole blood obtained from an anticoagulated sample?
plasma
What sample type is the fluid fraction of whole blood obtained from a clotted sample?
serum
What sample type is used for a CBC?
whole blood
What sample type is used for chemistry?
plasma or serum
What does a plasma sample have that a serum sample lacks?
buffy coat
What is the buffy coat in a plasma sample?
WBCs
Serum = plasma - __________?
fibrinogen
What are the three layers of a plasma sample?
blood plasma, buffy coat (WBCs), RBCs
What are the layers of a serum sample?
serum, clot
What may cause hemolysis in a blood sample?
traumatic venipuncture or plunging syringe when filling collection tubes
Why should blood samples be transferred into tubes promptly?
coagulation
Traumatic venipuncture may introduce hemolysis and/or artificially reduce __________.
platelet counts
What blood tubes should you fill last and why?
purple top tubes to avoid EDTA contamination
What must be done when filling anticoagulant tubes?
ensure proper volume and prompt, gentle tube inversion for mixing
What are the three types of anticoagulant tubes?
EDTA, heparin, citrate
What blood tube prevents coagulation by chelating calcium?
EDTA- purple top
How does a heparin (green top) blood tube prevent coagulation?
inhibits coagulation by potentiating antithrombin
What is a purple top tube used for and why?
CBC, it is gentler on cells
What is a green top tube used for?
plasma biochemistry
What is a blue top tube used for?
coagulation testing
How does a citrate (blue top) tube prevent coagulation?
reversibly prevents coagulation by weakly chelating calcium
What are the two types of plain tubes?
red and white top
What blood tube is species dependent clotting time prior to centrifugation and used for serum biochemistry?
red top
What is a tiger top tube?
serum separator tube
How does a tiger top tube work?
contains gel with intermediate density between cells and serum or plasma
upon centrifugation, the fluid fraction will be separated from cell fraction, preventing leeching of certain analytes into the cell fraction
How long must a tube with clot activator with gel be allowed to let clot for?
30 mins
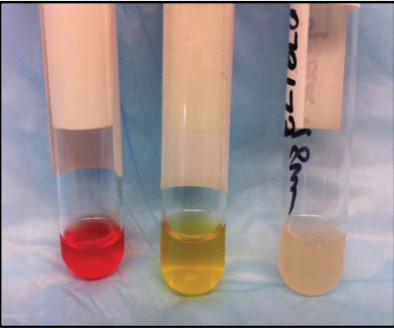
What issue occurred in each of these samples?
R: hemolysis
M: icterus
L: lipemia
What effect does hemolysis have on the appearance of a plasma/serum sample?
results in free hemoglobin and subsequent red discoloration
What effect does lipemia have on the appearance of a plasma/serum sample?
results in a lactescent appearance (milky)
What effect does icterus have on the appearance of a plasma/serum sample?
represents elevated bilirubin and yellow discoloration
Why should small animal patients ideally be fasted for blood draws?
lipemia
True or false: large animal plasma and serum naturally have a moderately yellow appearance.
true
What effect does in vitro hemolysis have on CBC results?
falsely decreases PCV, HCT, and RBC
What effect does in vitro or in vivo intravascular hemolysis have on CBC results?
falsely decreased PCV, HCT, and RBC
MCHC falsely increased
ghost erythrocytes from intravascular hemolysis may be falsely counted as platelets, increasing PLT
refractometric protein becomes difficult to read
What effect does in vitro or in vivo intravascular hemolysis have on chemistry results?
spectrophotometric interference and inhibition of chemical rxns
increase in intra-RBC analytes (K, phosphorus, ALT, LDH, Mg)
minimal to mild increase in CK enzymatic activity
What effect does in vitro or in vivo intravascular hemolysis have on electrophoresis results?
severe hemolysis can cause beta globulin spikes
What effect does interference from lipemia have on CBC results?
falsely increases HGB and subsequently MCHC
large lipid aggregates may be falsely counted as platelets, increasing PLT, or potentially leukocytes, increasing WBC
falsely increase refractrometric protein
What effect does interference from lipemia have on chemistry results?
spectrophotometric interference
proportional decrease in Na & Cl, slight decrease in K
What change in plasma/serum appearance can lipemia promote?
in vitro hemolysis
Why should samples with interference from lipemia be refrigerated?
to precipitate out the lipid, allowing collection of less lipemic serum/plasma
What effect does interference from icterus have on CBC results?
little to no effect
What effect does interference from icterus have on chemistry results?
marked to severe hyperbilirubinemia falsely decreases biuret total protein and creatinine, respectively