Chemistry Reaction Mechanisms
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CHEM20018 UNIMELB
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Hell Volhard Zelinsky Reaction
a reaction of carboxylic acids which results in an alpha bromo carboxylic acid (Br is a good leaving group, so useful for SN2 reactions)
1) substitution of OH for Br to give an acyl bromide
Then, bromine will form C-Br bond on the alpha carbon of the acyl bromide
2) keto-enol tautomerism
3) bromination of the enol
4) hydrolysis of acid bromide to give the carboxylic acid (bromine will still be on alpha carbon, and thus be leaving group)
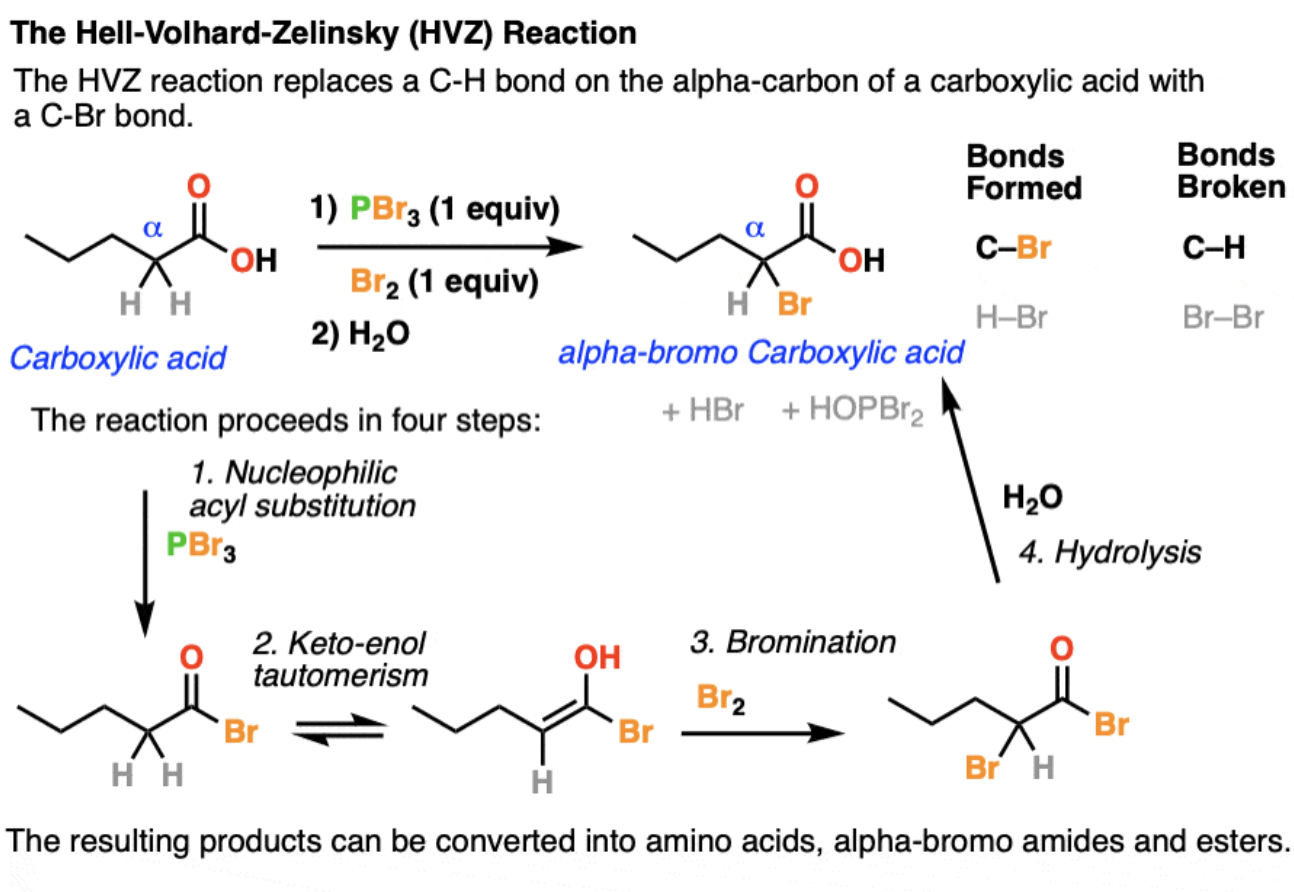
Tautomerism
A structural isomer that relates to movement of protons and double bonds to render the alpha carbon nucleophilic
Epimerization
An epimer is a distereoisomer that only differs at one stereocenter.
If a pure, optically active ketone is exposed to strong acid then a racemic mixture will be formed. This is because the enol intermediate is planar, and therefore achiral. When protonation occurs, there is equal likelihood for both the (R) and (S) enantiomers.
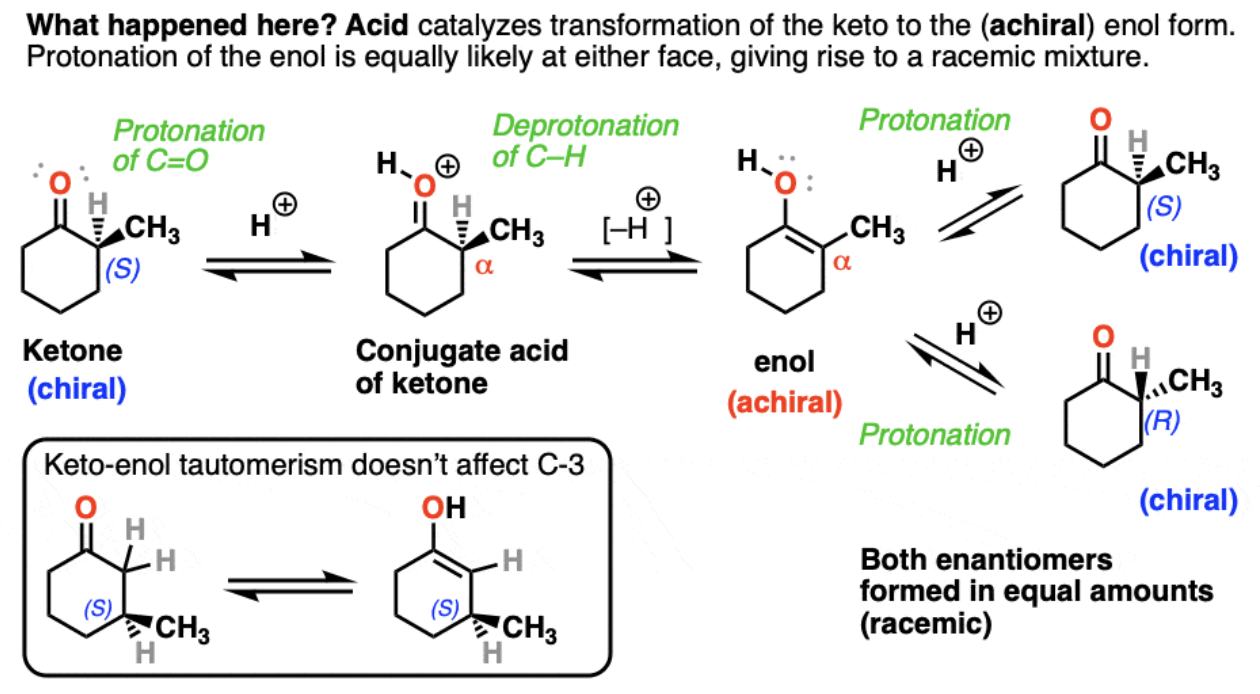
Halogenation of Ketones
Strong acid + Ketone + Halogen = alpha-halo ketone
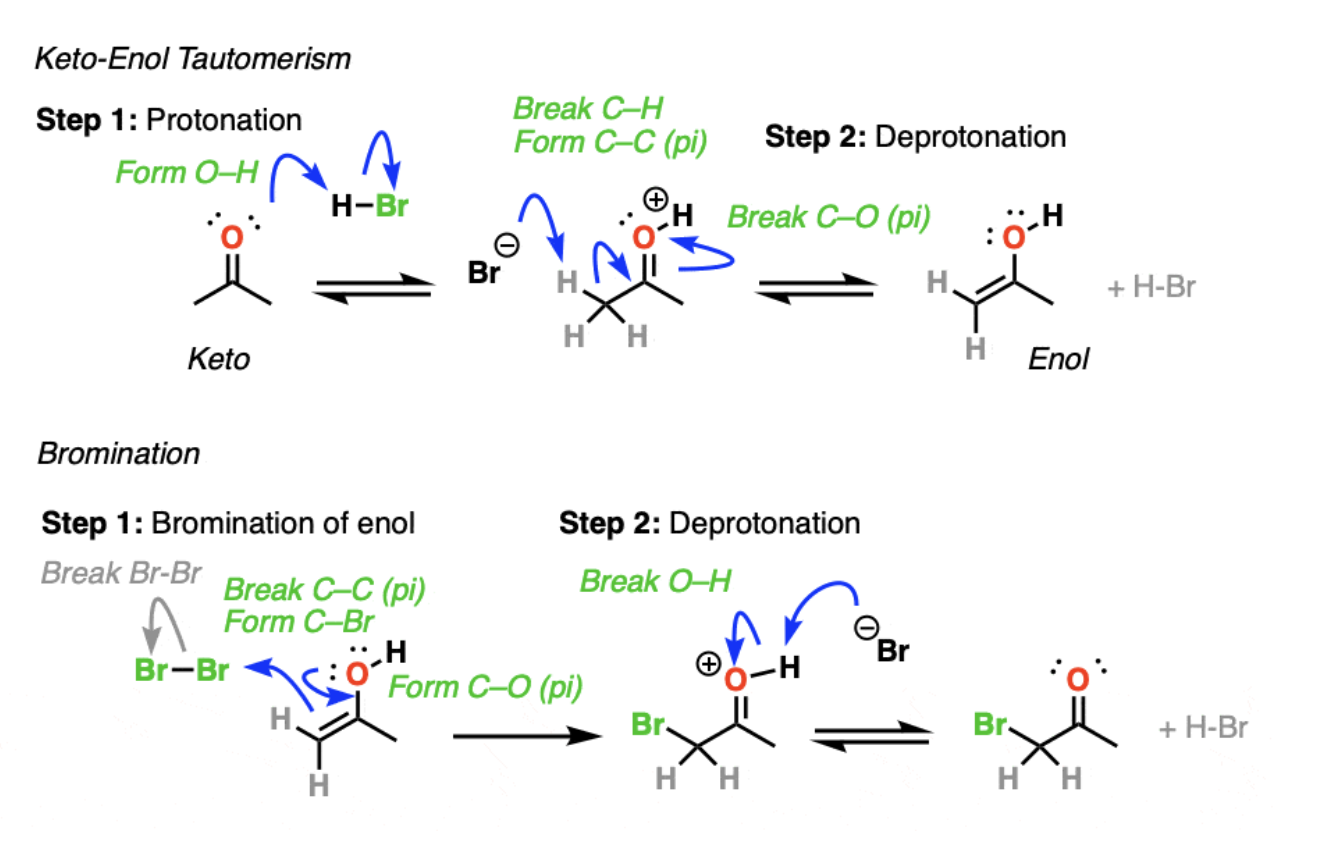
1) undergo enolization
2) then bromination
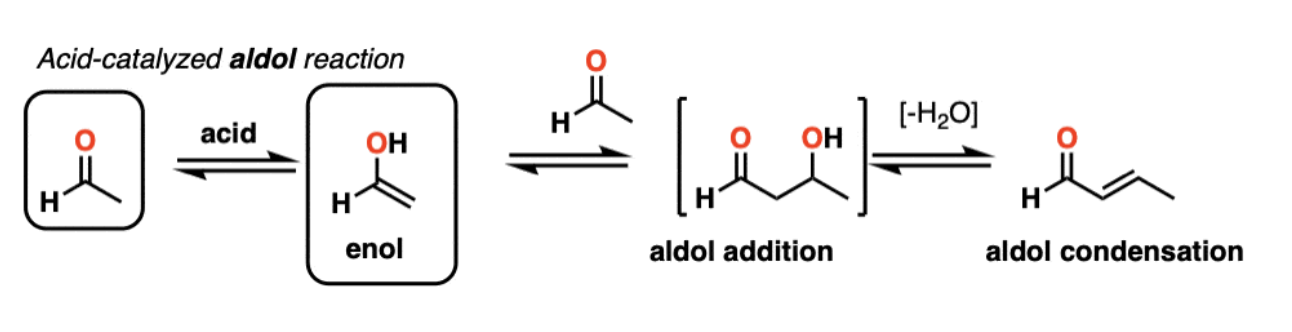
Acid-Catalyzed Aldol Reaction
ALMOST always results in a condensation product
1) Acid catalyzes keto-enol tautomerism
2) acid protonates the oxygen of an aldehyde or ketone
resulting conjugate acid is a much better electrophile!
3) addition of the enol to the protonated aldehyde or ketone
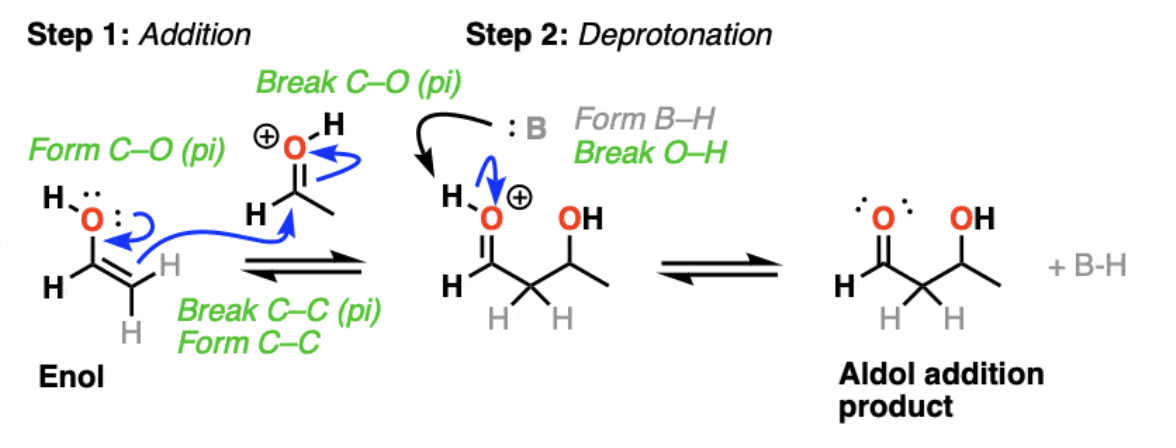
4) Protonation of the hydroxyl group ‘pushes' out the water to form an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound.
Base-catalyzed Aldol Reaction
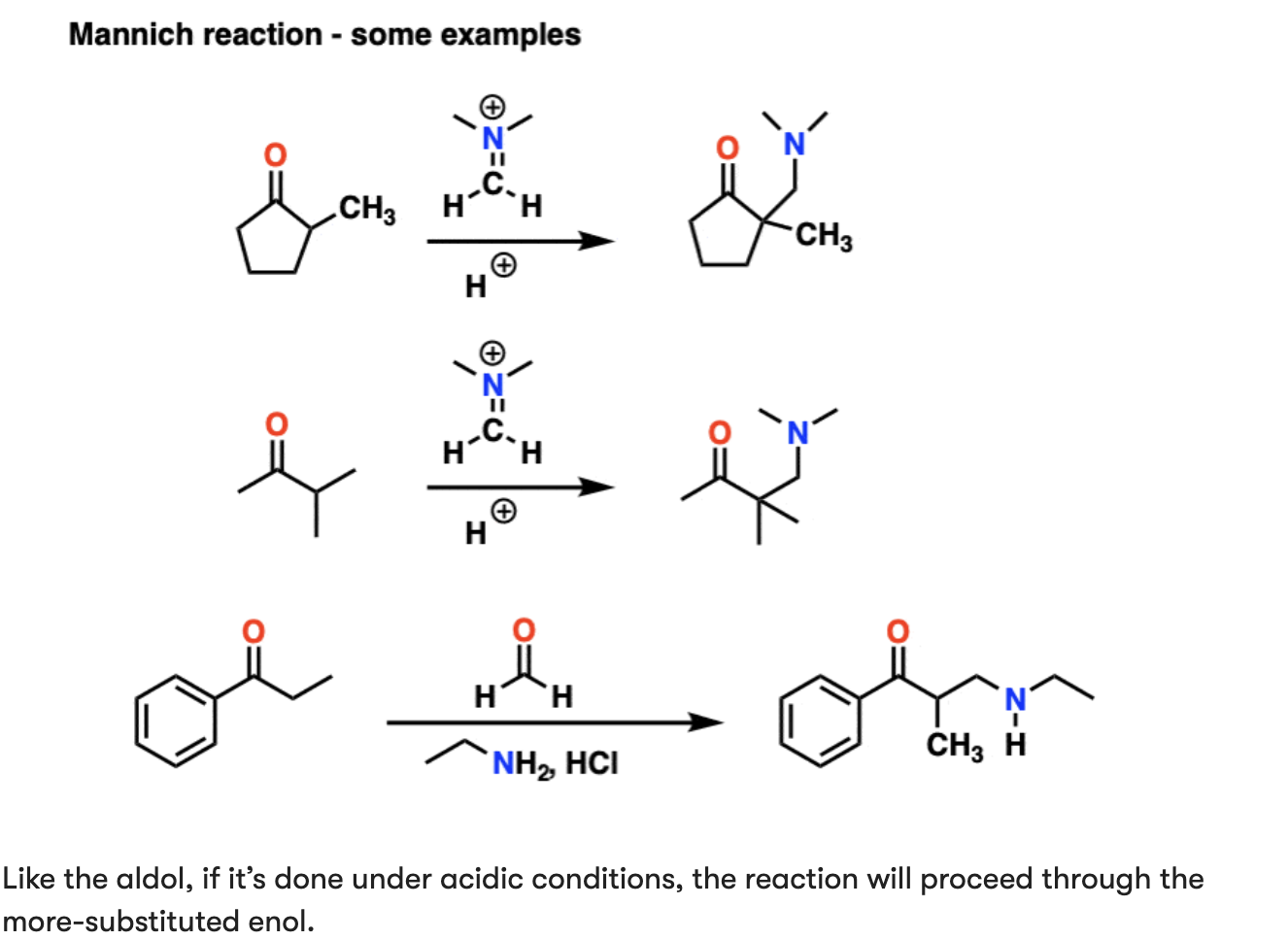
The Mannich Reaction
Similar to aldol reaction, but electrophile is a C=N bond instead of C=O
Positively charged iminium ion electrophile
1) formation of the enol tautomer
2) addition to the iminium ion
The Claisen Condensation
Ester (2 equivalents) is treated with a Base (1 equivalent) => Product is a ‘beta-keto’ ester (ketone located 2 carbons away from the ester carbonyl
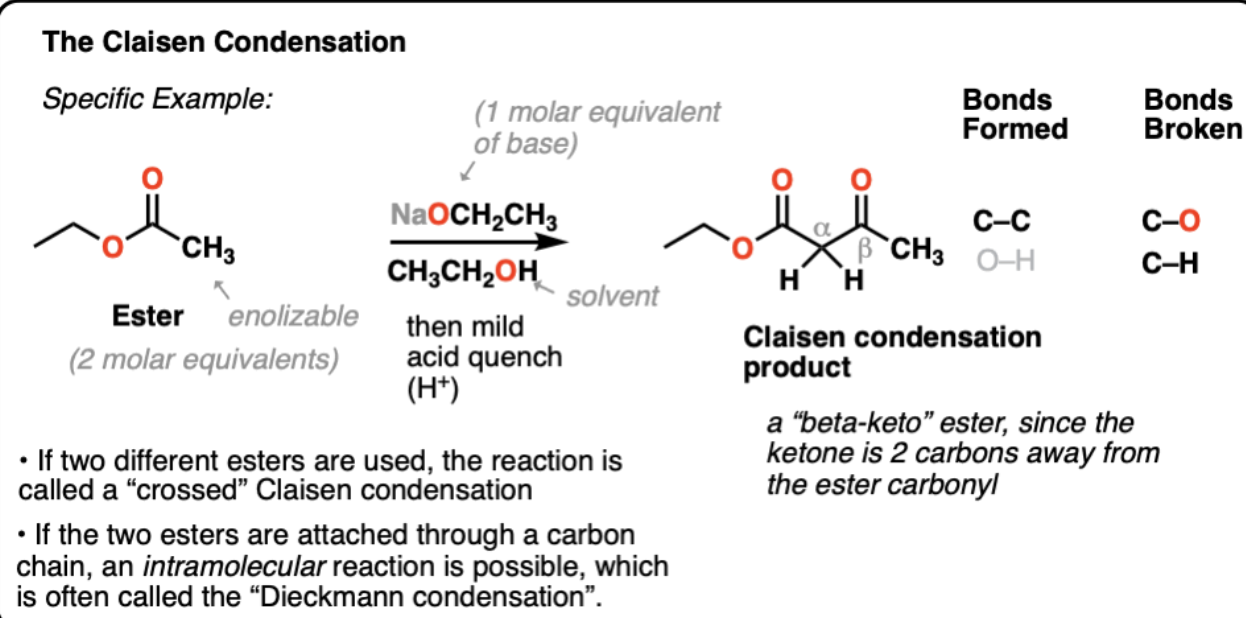
1) Deprotonation of Ester alpha-carbon => Enolate
2) Nucleophilic Acyl Subsitution (form C-C b/w enolate and ester, break C=O on ester, form C-O)
3) Elimination of extra C-O into C=O
4) Deprotonation → enolate of beta keto ester → Must be quenched with mild acid.
CROSSED CLAISEN CONDENSATION (joins two different esters but one is non-enolizable)
Malonate Chemistry
synthesis of carboxylic acids using diethyl malonate
diethyl malonate is easily fully deprotonated (using weaker/ cheaper bases)
1) Deprotonate with base (EtO-) and alkylate (R-X)
2) Saponify with hyroxide to give carboxylate
3) Treat with acid (H+) and heat to evolve CO2
(monosubstituted malonate can be alkylated a second time)
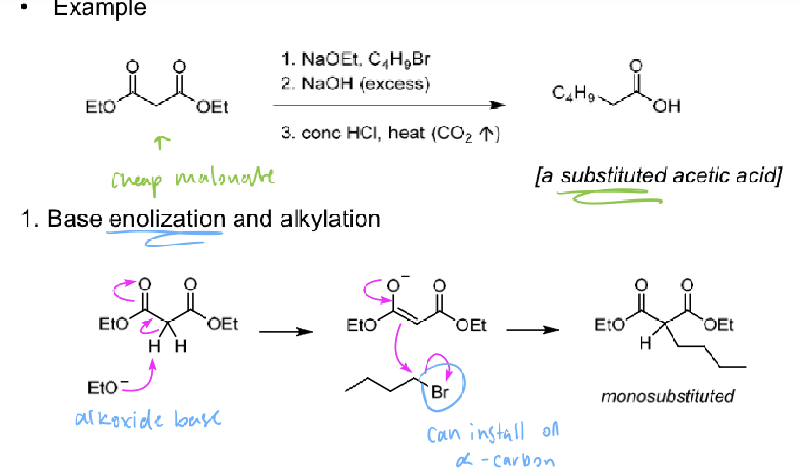
ANY a- or a,a- disubstituted acetic acid can be made using malonate chemistry (retrosynthesis too)
Acetoacetate Chemistry
Ethyl acetoacetate + weak base + brominated addition → Methyl Ketone (a ketone where a methyl group is attached to the carbonyl group)
1) base enolization and alkylation
2) ester hydrolysis to give acid
3) thermal decarboxylation of keto-acid
can perform retrosynthesis!!
*ethyl acetoacetate can be made by Claisen Condensation of Ethyl Acetate
The Michael Reaction
Conjugate Addition of enolate + a,B-unsaturated carbonyl → 1,5-dicarbonyl
1,5 dicarbonyls are super useful intermediates for heterocycles
1,2 Addition → very reactive nucleophiles (H-, CH3-,MeMgBr, LiAlH4 etc.) KINETIC PRODUCT
1,4 Conjugate addition (adds to beta carbon) (e.g. enolates, amines, thiolates, enamines etc.) THERMODYNAMICALLY STABLE
1) deprotonation to form an enolate
2) conjugate addition of the enolate to the alkene (in 1,4 will add to the beta-carbon)
3) protonation = new enolate (C-C single bond and broken C=C bond)
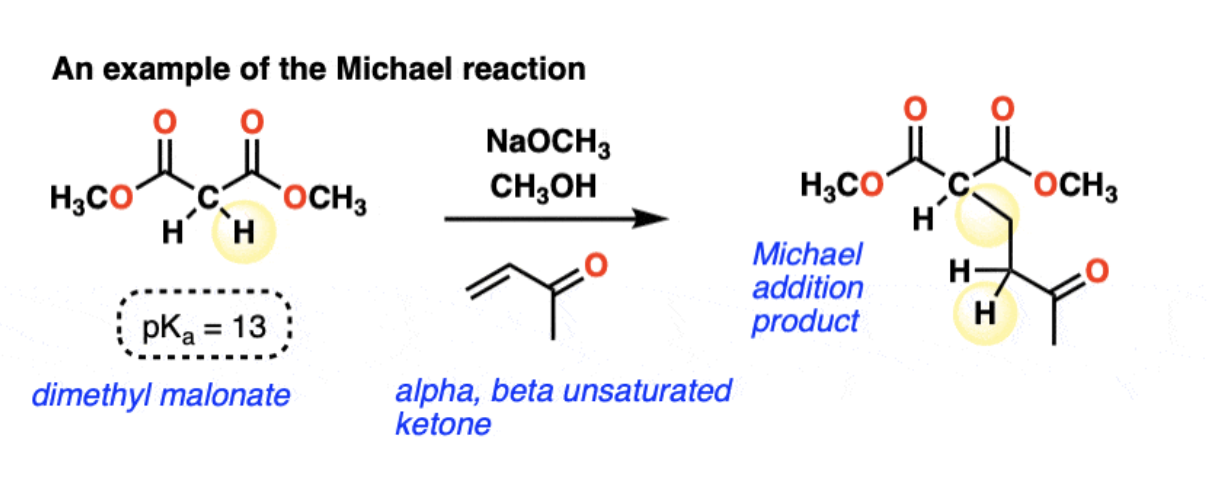
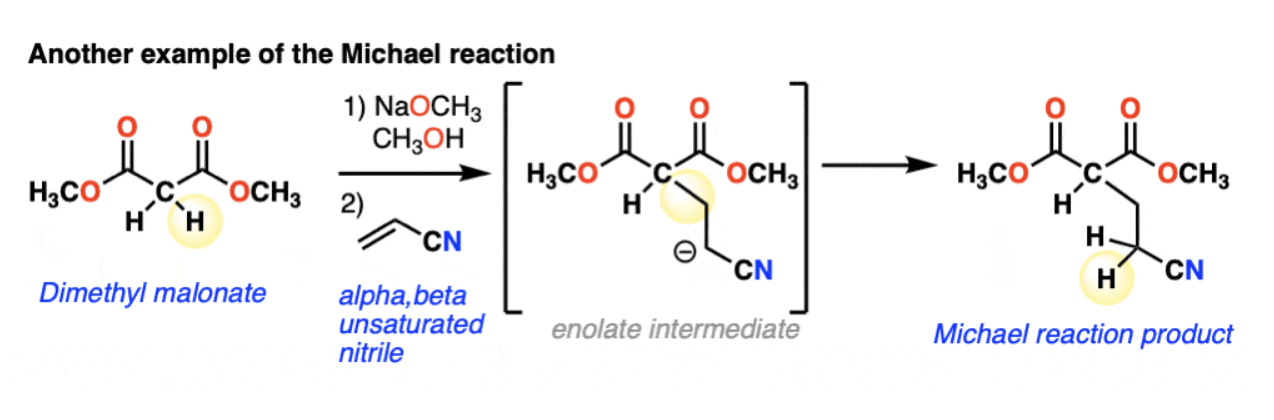
→ Retrosynthesis: Number from 1 carbonyl to other, disconnect C2-C3 bond and add H to C2.
Give C3-C4 becomes a double bond
Retrosynthesis Summary
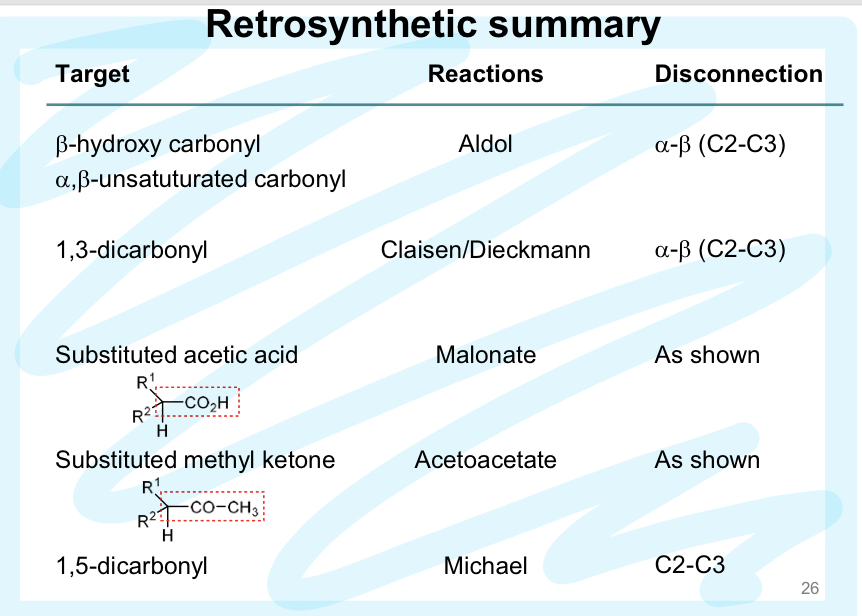
The Betti Reaction
Mannich- Type reaction with phenols → Betti Base PRACTICE EXAMPLES OF THESE
Kiliani- Fischer Ascent
→ Extends sugars by one carbon. Mix of stereo isomers (~equal)
1) Formation of cyanohydrin (e.g NaCN, KCN etc.)
2) Hydrolysis of the cyanohydrin (results in carboxylic acid)
3) Reduction to aldose
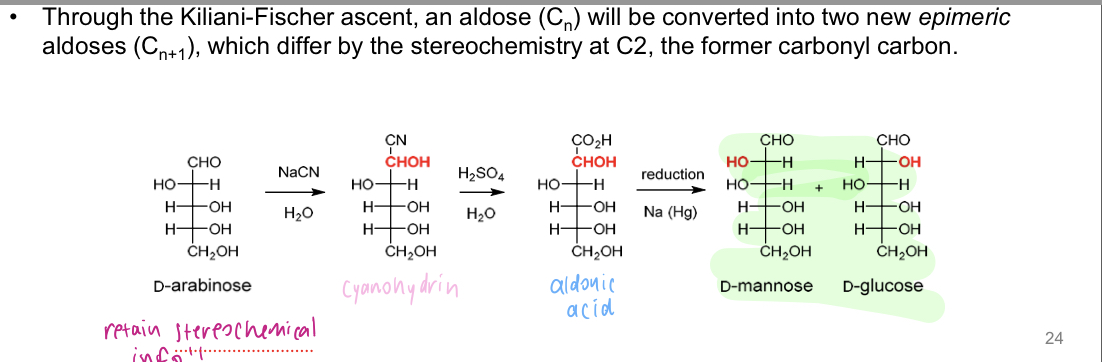
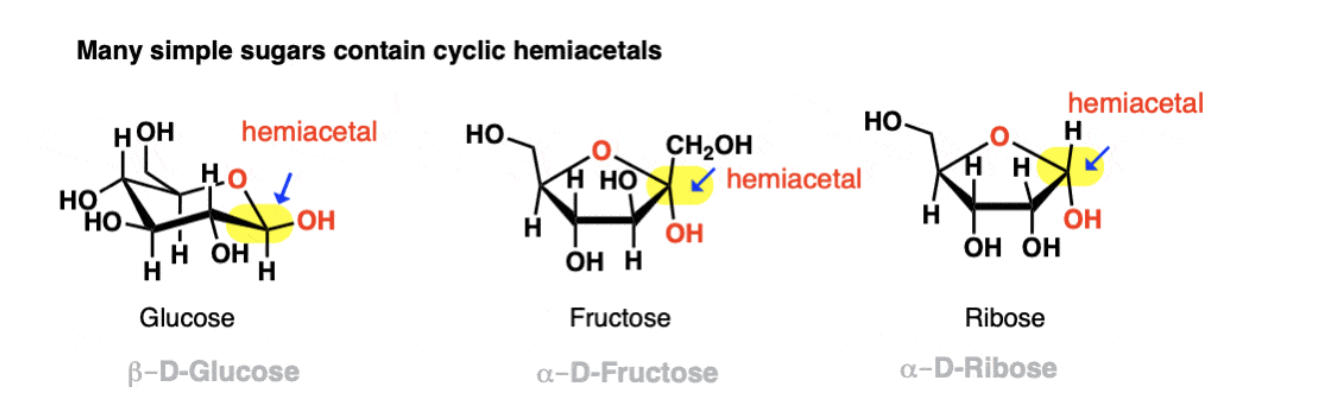
Hemiacetal and acetal formation
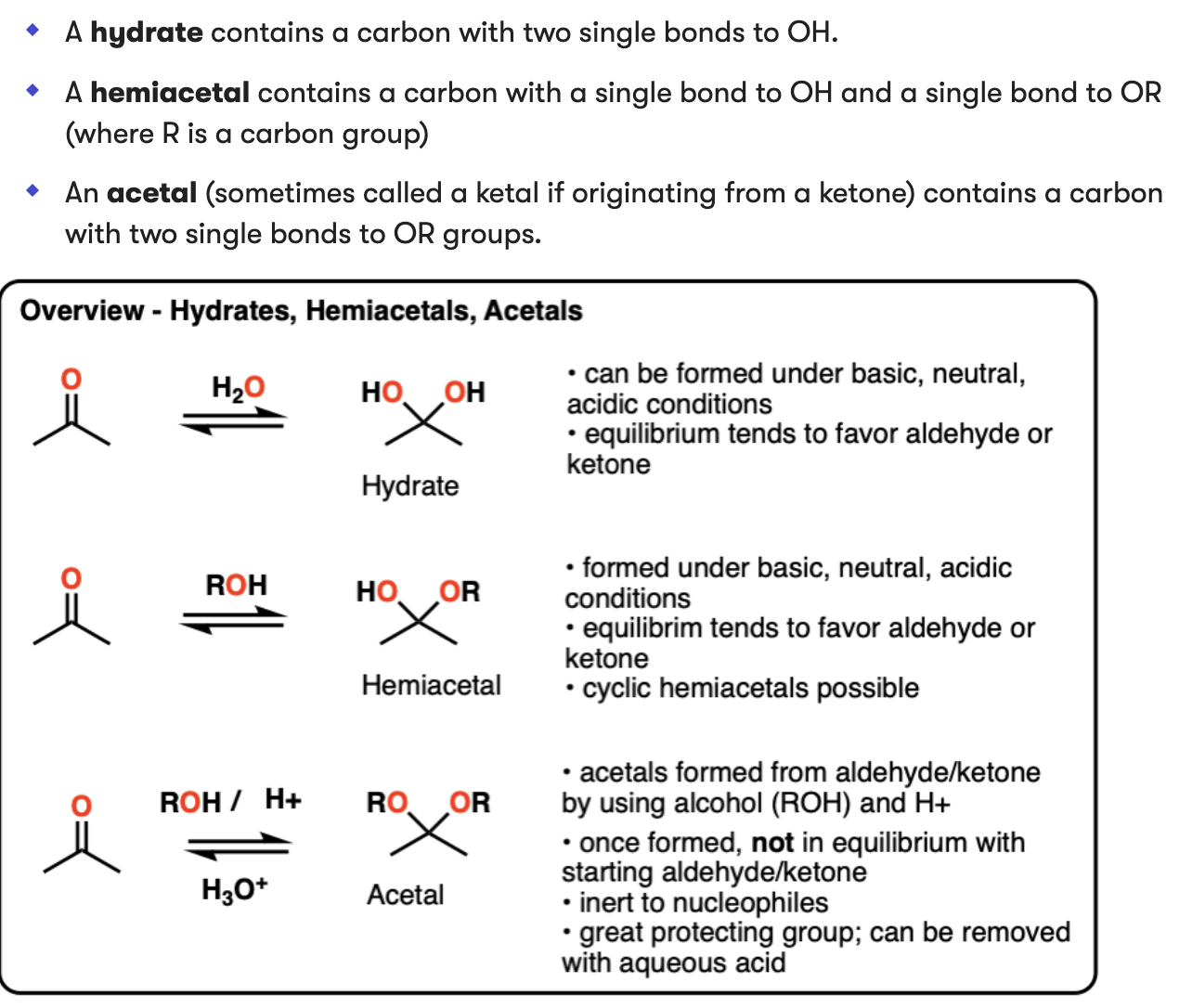
Hemiacetals exist in equilibrium with respective aldehydes and ketones.
C=O is broken, OH-OR attach to Carbon
This can also occur intramolecularly if an alcohol and aldehyde/ ketone are present on the same molecule
Acetals are “locked” and can only be converted back with an aqueous acid
1) Protonation of OH group
2) Elimination of H2O
3) Addition of R-OH across C=O
4) Deprotonation of base O-H resulting in R-(2RO)-C
P A D P E A D.
Anomeric Carbon
The anomeric Carbon can form and break acetals
Di- and Polysaccharides
Monosaccharides can be connected through their respective anomeric centers. (glycosidic/ acetal formation)
AMYLOSE = Starch, helix of ~300-3000 alpha-D-glucopyranose residues.
CELLULOSE = plant startch, 1,4 linkage of beta-D-glucopyranose