Nucleic acids
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
DNA and RNA are both types of what
nucleic acids
DNA and RNA are both important (-)-(-) molecules
important infomation carrying molecules
DNA holds (-) info found in all living cells
genetic infomation 0 the instructions an organism needs to grow and develop from a fertilised egg to a fully grown adult
DNA and RNA are ***** made from nucleotides
polymers
what is the role of RNA
transfers genetic infomation from the DNA to the ribosomes. Ribosomes read the RNA to make polypeptides(proteins) in translation.
what are ribosomes made from
Ribosomes themselves are made from RNA and proteins
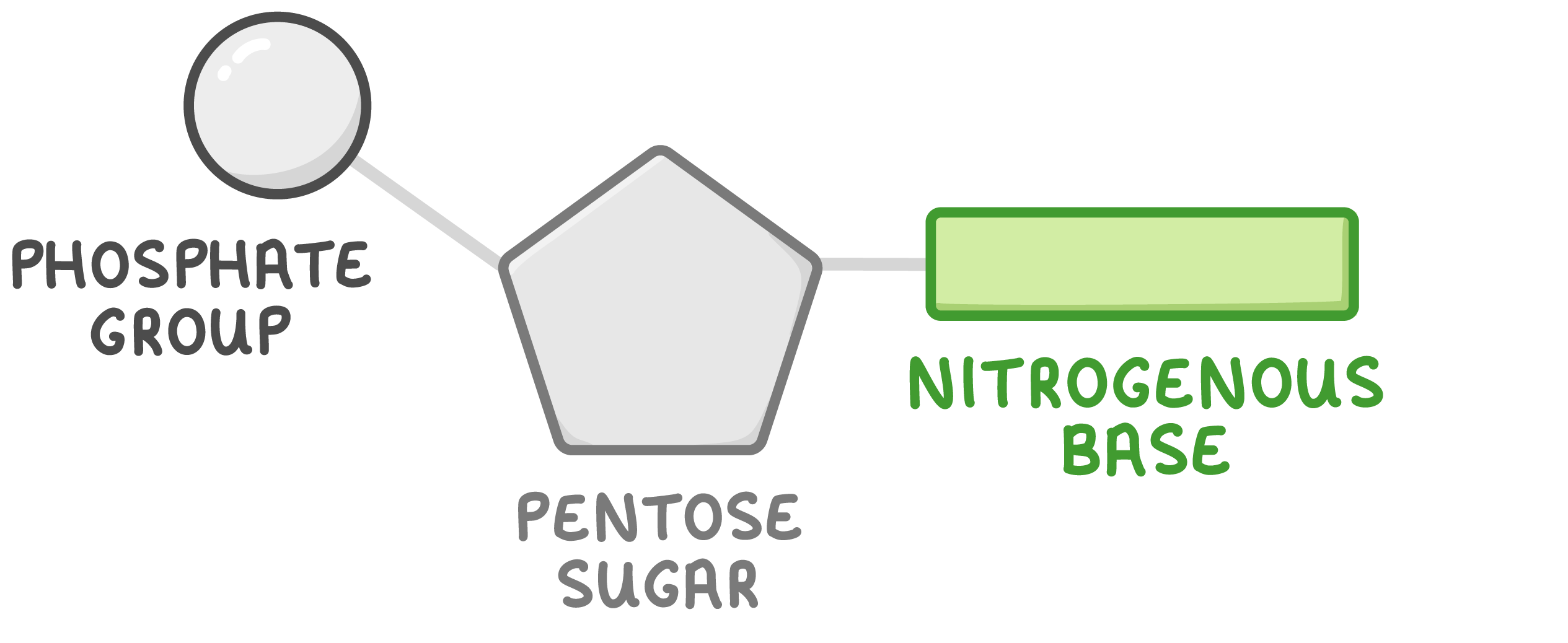
desribe the structure of a nucleotide
pentose sugar- contains 5 carbons
nitrogen-containing organic base 9organic means containing carbon) - contains carbon and nitrogen. thymine, guanine, adenenine, cytosine
phosphate group- contains phosphate
nucleotides are monomers and can join to form dimers (dinucleotides) andpolymers (polynucleotides)
draw a nucleotide
list the components of a RNA nucleotide
Ribose - A pentose sugar.
A, U, G, or C base - Adenine, URACIL , guanine, or cytosine.
A phosphate group
list the components of a DNA nucleotide
Deoxyribose - A pentose sugar.
A, T, G, or C base - Adenine, thymine, guanine, or cytosine.
A phosphate group
what type of bond is formed when nucleotides join together to form POLYNUCLEOTIDES (also name the reaction)
a phosphodiester bond is formed (consisting of a phosphate group and two ester bonds)
the nucleotides join by a condensation reaction between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the sugar of another
what is the name of a chain of sugars and phosphates
sugar-phosphate backbone
describe the structure of DNA(strands, bonds between where?, direction of strands,carbons)
two DNA polynucleotide strands would round each other to forma double helix
held by hydrogen bonds between complementry base pairs
the strands are antiparallel (opposite directions)
one strand is 5’ to 3’ and the other is 3 to 5 (refers to the carbon number on the deoxyribose sugar
name wich nitrogenous bases bond pair with eachother. what does this ensure
adenine-thymine
cystosine-guanine
ensures accurate replication and stability of DNA as there are always equal ammounts of adenine and thymine in a DNA molecule and equal ammounts of cytosine and guanine
how many hydrogen bonds form between A and T
2
how many hydrogen bonds form between C and G
3
how does the stucture relate to the function of DNA
Stable due to the strong, covalent phosphodiester bonds in the sugar-phosphate backbone.
Complementary base pairing allows for accurate replication.
Hydrogen bonds between bases allow easy strand separation for replication and transcription.
Compact structure fits inside the nucleus while storing a vast amount of genetic information.
DNA is an important biological molecule. Describe its structure and explain how this structure allows it to carry out its function. (6 marks)
DNA is a polymer of nucleotides.
Each nucleotide contains a phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogenous base
DNA is double-stranded and forms a double helix. This gives DNA a compact structure which fits inside the nucleus while storing a vast amount of genetic information.
The sugar-phosphate backbone is joined by phosphodiester bonds, giving DNA structural stability.
Complementary base pairing occurs (A-T, C-G), which ensures accurate replication.
The two strands run antiparallel (one runs 5’ to 3’, the other 3’ to 5’), allowing enzymes like DNA polymerase to function correctly.
Hydrogen bonds between complementary bases allow strand separation, which is important for DNA replication and transcription.
the relative simplicity of DNA led many scientists to doubt that it carried (-) (-)
genetic code
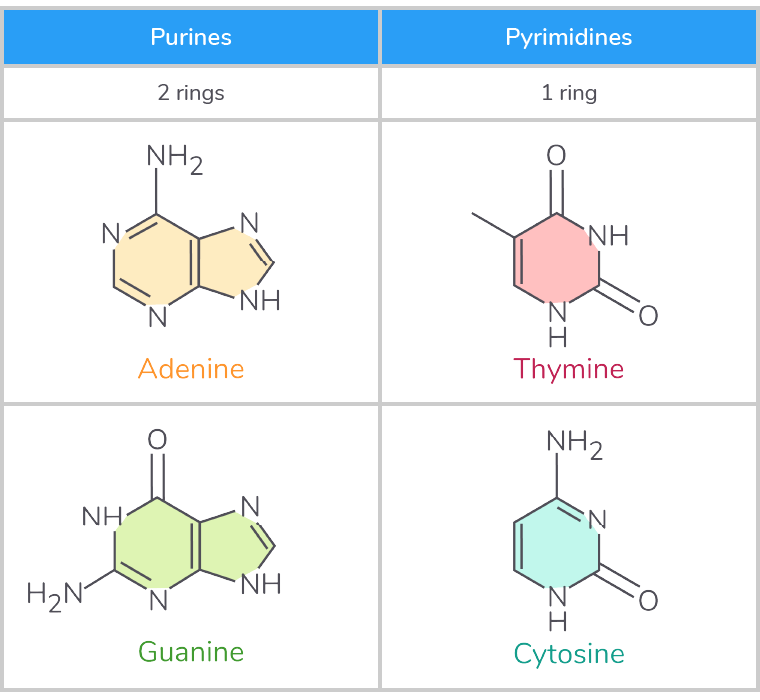
off spec but useful- what are purines and pyrimidines
Purines - These are larger bases that contain two carbon ring structures (A and G).
Pyrimidines - These are smaller bases that contain one carbon ring structure (T and C).
describe RNA stucture
a single stranded polynucleotide chain which is much shorter
uracil in RNA replaces what base in DNA
thymine
what type of replication does DNA undergo and what does mean and this ensure
semi-cnservative replication- meaning half the strands in each new DNA molecule are from the original DNA molecule.
This ensures genetic continuity between generations of cells (i.e the cells producedby cell divison inherit their genes from their parent cells
describe the process of semi-conservative DNA replication
the double helix unwinds as DNA helicase causes strands to seperate/ breaks H- bonds between complementry base pairs
Free nucleotides are attracted to exposed bases on template strands
Complementry / specific base pairing
DNA polymerase joins nucleotides together (on the new strans) by making phosphodiester bonds in condensation reactions
the replication is semi conversative / new DNA molecules contain one old strand and one new strand
name the two enzymes involed in DNA replication and what they do
DNA helicase - breaks the hydrogen bonds between the complementry bases to seperate the two strands
DNA polymerase - joins adjacent nucleotides together by making PHOSPHODIESTER bonds in condensation reactions- this requires ATP
If an inhibitor of DNA polymerase were introduced into a cell, what would be the effect on cell division?
Cell division would stop as DNA replication cannot occur.
This is because DNA polymerase cannot join nucleotides together and the new DNA strands will not form.
Why does DNA polymerase move in opposite directions along the two strands?
The two strands in DNA are antiparallel (they run in opposite directions). DNA polymerase is an enzyme with a specific tertiary structure and a specifically shaped active site. It can only attach new nucleotides at the 3’ end of a DNA nucleotide. This means it can only move in the 5’ to 3’ direction.
what did Watson and Crick discover
the double helix structure and the semi-conservative model of DNA replication which was validated by the Meselson and Stahl experiment
what is the conservative and fragmented or dispersive replication
conservative- one entirely new DNA molecule is amde, and the original remains intact
fragmented or dispersive - DNA strands are mixtures of old and new DNA
Describe Meselson and Stahl’s experiment (1958)
context: bacteria will incorperate nitrogen into the bases in their DNA.
they used the bacterium E. coli and different isotopes of nitrogen to determine the correct model of DNA replication
Growing Bacteria in Heavy Nitrogen (15N):
E. coli was first grown in a medium containing only the heavy isotope of nitrogen (15N), which was incorporated into their DNA.
This made the DNA denser.
Switching to Light Nitrogen (14N):
The bacteria were then transferred to a medium containing only the lighter isotope of nitrogen (14N) and allowed to replicate once.
Centrifugation to Analyse DNA Density:
DNA was extracted and centrifuged to observe its position in the test tube.
It does this by spinning the extracted DNA at high speed. Causing the DNA to collect in different areas, depending on the density.
After one round of replication in 14N:
DNA formed a single intermediate band in the centrifuge tube.
This disproved the conservative model, as there was no fully light (14N) or fully heavy (15N) DNA.
This supported the semi-conservative replication model, as the DNA consisted of one original (15N) strand and one newly synthesised (14N) strand.
After two rounds of replication in 14N:
Two distinct bands were observed
One intermediate density consisting of one original (15N) strand and one newly synthesised (14N) strand.
One less dense band that consisted of two strands containing 14N.
Final Conclusion:
The experiment provided strong evidence that DNA replication occurs via the semi-conservative model.
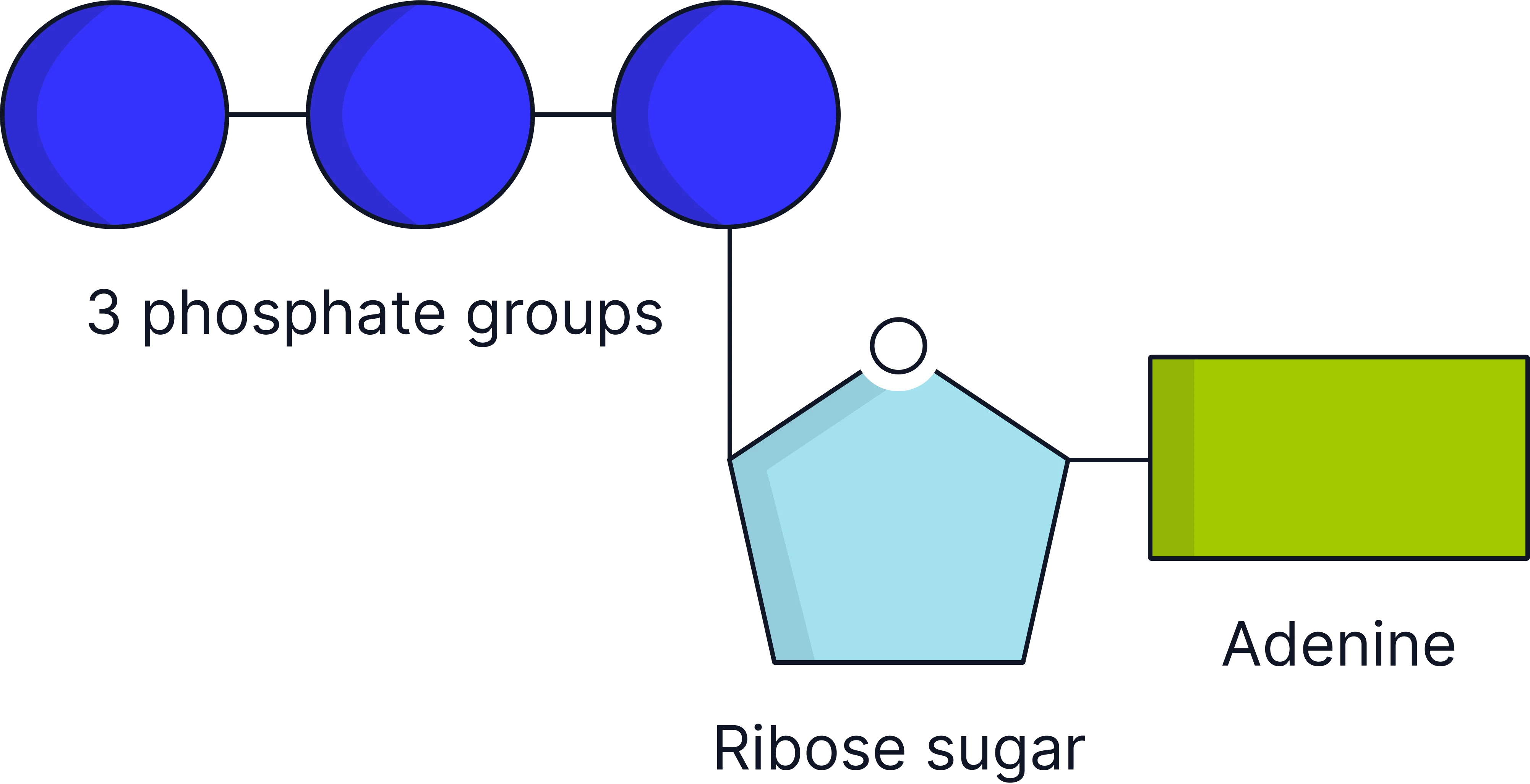
how is ATP similar and different to RNA molecule
They both contain ribose sugar.
They both contain a nitrogenous base.
They both contain a phosphate group.
ATP always has the base adenine whereas RNA nucleotides can contain adenine, cytosine, guanine or uracil.
ATP has 3 phosphate groups whereas RNA nucleotides have 1 phosphate group.
ATP is a ***** derivative
nucleotide
describe the structure of ATP
Adenine – nitrogenous base.
Ribose – a pentose sugar.
Three phosphate groups – key to energy storage and release.