IT 341 Final GMU
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
126 Terms
Converged Network?
A network where multiple types of traffic are all under one network
Benefits: Saves a lot of money and only one physical network to install and manage.
What is a Cisco Borderless Network?
Allows organizations to connect anytime anywhere with any type of secure device easily
unifies wired and wireless access(policy, access control and performance management)
networks services and endpoint services managed by an integrated management solution
Borderless switched networks are what 4 things?
Hierarchical-(Facilities understanding the role of each device at every tier)
Modular-(allows seamless network expansion and integrated services)
Resilient-(provides an always available network)
Flexible-(allows intelligent traffic load sharing
Converged networks that are part of organization have 3 parts...what are they?
Core - The center
Distribution - connection to the core
Access - Switches are used to connect to the distribution and give access to the users
Switched LANS allow for what/Role of Switched Networks?
Flexibility
traffic management
Features like: QoS, security, wireless and new tech support
Fixed vs modular vs stackable switch form factor?
Fixed - number of ports and abilities is set, no changes
modular - extra ports and other things can be added later
stack-able - switches are stacked a connected by cables to operate as one big switch
Switching General Concepts
Makes decisions based on?
Ingress port - where a frame enters the device.
Destination address
maintains a table that it uses to determine how it will forward traffic.
How does a switch learn what devices are on a network?
It builds a table called a MAC address or CAM table
This table saves the device port.
What does a switch do when it gets a frame that is not in the CAM table?
The switch floods all known ports except the one that they got the frame from. The correct port will accept the frame.
Switch Forwarding Methods
Store and forward
Cut-through
Store and forward vs cut-through?
- gets the entire frame and finds the CRC, if valid the frame is forwarded to destination address(error-checking,automatic buffering) Cisco's primary LAN switching method
- forwards the frame before it has been fully received. It at least reads the destination address(rapid frame forwarding)
fragment-free switching
a form of cut-through where the first 64 bytes are read and then it is forwarded.
Collision domain?
all ports belong to the same collision domain
all ports have a collision domain of their own
switch ports operate at full duplex( eliminates collisions, bidirectional) if connected to such device, and will operate at half duplex(collision domain,unidirectional) if connect to such devices
Broadcast Domain
a single domain formed by one switch, or multiple switches.
Too many will cause a lot of congestion.
How doe switches help alleviate network congestion? 3
segment the collision domains by port
provide full duplex links
buffer large frames
low per-port cost
port speed
fast internal switching
Switch Boot Sequence? (5)
1. POST (power-on-slef-test)
2. Run boot loader software
3. Boot loader does CPU initialization on a low-level
4. initializes the flash file system
5. Loads the IOS operating system
Recovering from a system crash
1. connect the PC to the switch console port
2. configure the terminal on the PC
3. disconnect the switch's power cord.
4. reconnect power cord right after, hold mode button
5. type switch at the command prompt to run the boot loader.
configure a switch
You will need the IP address(assigned to an SVI), subnet mask and the default gateway
1. conf t
2. interface vlan ...
3. ip addresss ...... subnet mask...
4. ip default gateway....
5. wr
show interface (interface_id) command
to check duplex and speed settings
fiber ports operate at one speed and are always full-duplex
What are the steps required to find a IOS image?
- Tries to boot with info already available in BOOT environment
- if not found, perform a top-to-bottom search through the file system
- IOS initializes the interface using the Cisco IOS commands from NVRAM
SSH(secure shell)
Provides an encrypted management connect, prefer to telnet.
Port Security
Controls the amount of Valid Mac address allowed to transmit information through switch port, by using static secure MAC ad(manual) or Dynamic secure MAC address(dynamically learned).
Port Security Violation Modes
Protect
Restrict
Shutdown(default)
Whats NTP protocol
Network time protocol - uses to synchronize the clocks of computer systems data networks
Split into a client and server
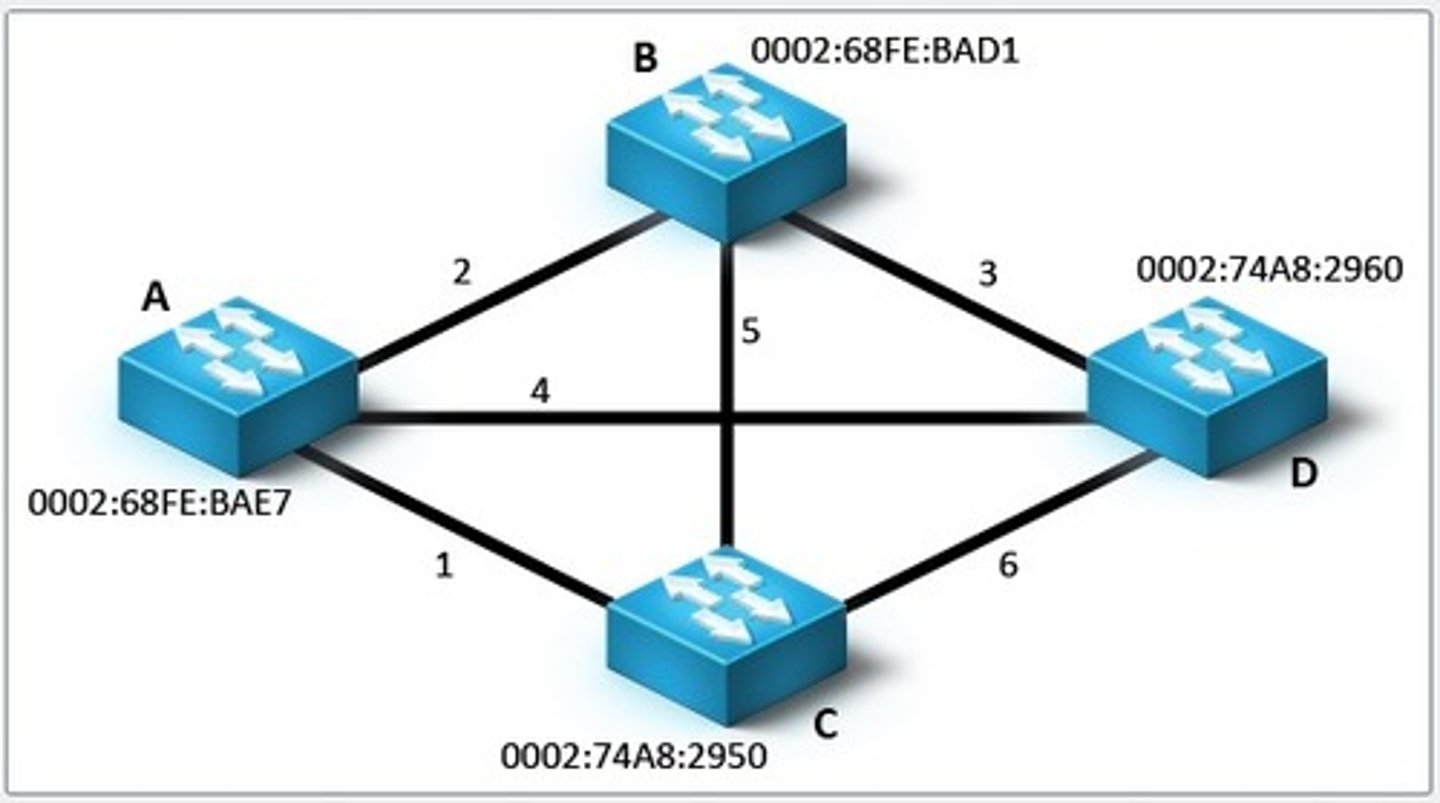
What is a VLAN?
Logical partition of layer 2
multiple VLANs can exist
each has its own broadcast
separate LAN devices, user and devices don't matter.
How do you pass packets from VLAN to VLAN?
isolated, unaware of each other
so you must use a router to pass packets.
Benefits on a VLAN?
- groups of secure information can be separated from the rest of the network(better security)
- cost reduction
- small broadcast domains
- Better IT efficiency since users can be grouped by requirements
Types of VLANs and what they do?
- Data VLAN = user generated traffic
- Default VLAN(VLAN 1)= all switch ports are part of this VLAN after boot
- Native VLAN = used to carry untag traffic that does not originate at a VLAN port
- Management VLAN = used for managing the switch with SSH, Telnet, HTTP
Voice VLANs?
Sometimes called VoIP - very demanding
supports time-sensitive voice traffic
transmission priority
VLAN Trunks?
Carries multiple VLANs
established between two switches so devices on the same VLAN ca communicate
IEEE 802.1q - popular VLAN trunk protocol
How can you control broadcast domains?
VLANS can be used to control the spread of broadcast domains because they have a broadcast domain of their own
Help control the reach of broadcast frames
Frame tagging
when a VLAN identification header is added to a frame
Tagging Ethernet Frames?
This occurs when a frame tag is added to a frame with the proper VLAN identification.
Switches add the frame and remove the frame when its its time to forward
Frames belonging to the native VLAN are?
Not tagged since this is the default VLAN
What is the default native VLAN on a cisco router?
VLAN 1
What happens if a frame is sent to a switch that has no ports on a native VLAN and no trunk links to any other VLANs?
The frame is dropped since it has no where to go
VLANs are split into two categories? what are they?
Normal Range VLANs
Extended Range VLANs
Normal Range VLANS?
numbered 1 to 1005
conf stored in flash memory
VTP used to managed VLAN between switches
Extended Range VLANs?
numbered 1006 to 4096
conf stored in the NVRAM
VTP not used or learned
Creating VLANs
SW1#conf t
SW1(config)#vlan 10 SWI(config)#name firstvlan
end
VLANs are often associated with what?
an IP address, so IP address outside of a certain range often don't connect correctly
all devices in a VLAN must be in the same IP network
What does "switchport trunk allowed vlan" do?
command that specifies which VLANs are allowed in a trunk link
Inter-VLAN routing
layer 2 switches cannot forward traffic between VLANs without the assistance of a router
Inter-VLAN Routing Options
Legacy inter-VLAn routing
Router-on-a-Stick
Layer 3 switching using SVIs
Legacy Inter-VLAN Routing
Different physical router interfaces are connected to different physical switch ports, where each switch port is configured with a different VLAN.
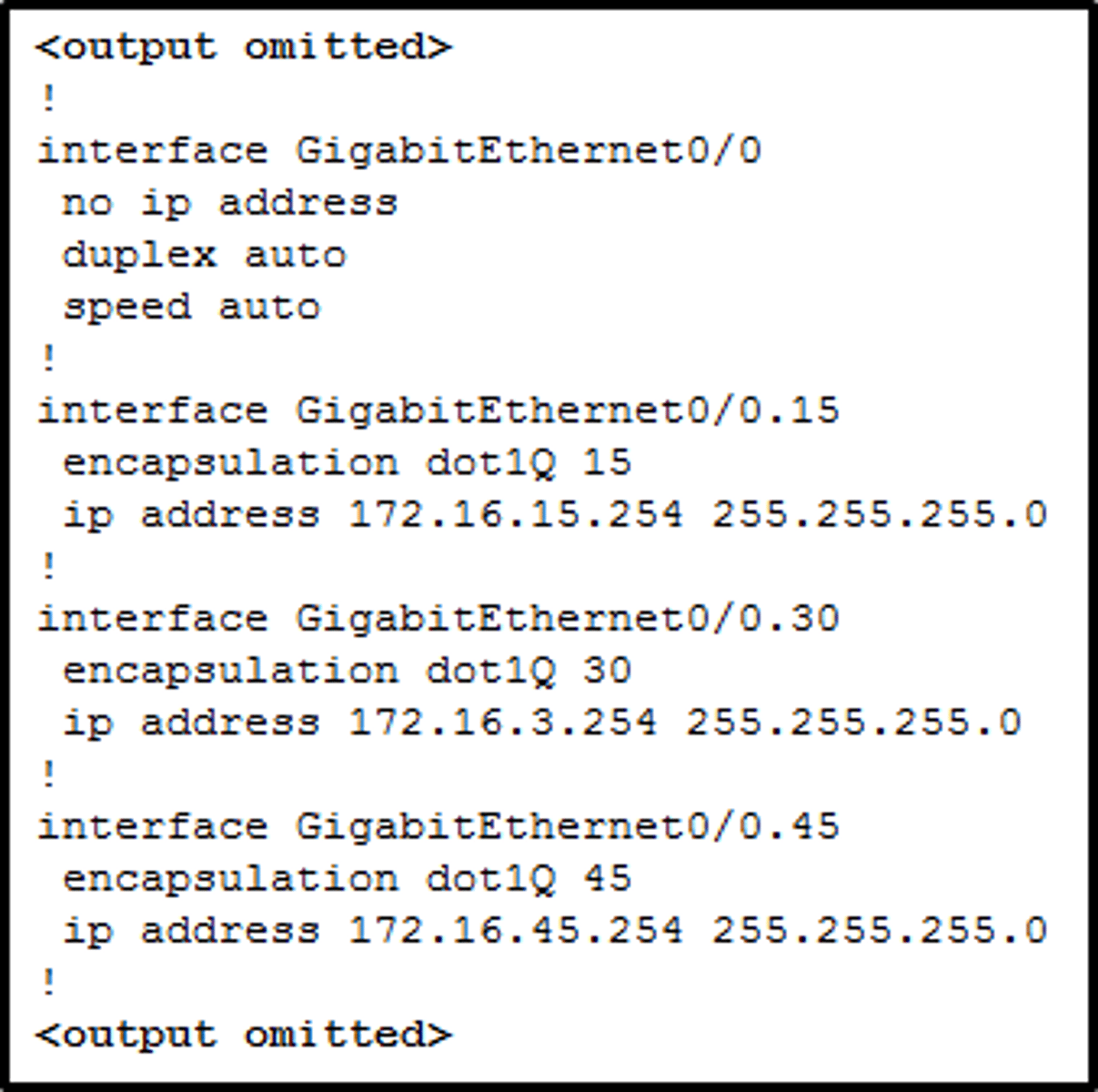
router on a stick inter-VLAN routing
A single physical interface on the router connects to a trunk port on a switch and routes traffic between multiple VLANs on a network.
verify sub interface configurations
show vlan
show ip route
What is routing? (Basic level)
connetcs one network to another and determines how to efficiently move traffic between networks
LANs
Ethernet networks that contain PCs, printers and servers.
WANs
used to connect networks over large geographical areas
What are some things routers can do?
- use static and dynamic routing to build routing tables
- determine the best path for a packet
- encapsulate the packet and forward it
Static assigned IP addresses?
manually assigned IP address, subnet mask and default gateway
used for servers or printers where you need to always no the destination
Dynamically assigned IP addresses?
IP info is assigned by the DHCP
this is how most hosts work
Steps to configure a basic router? (4)
- name the device
- secure management access
- configure the banner
- save the config
"show ip interface brief" command
You can see a summary of which interfaces you have on your router
show ip route
Displays the contents of the IPv4 routing table stored in RAM.
What is AD (Administrative distance) and is it better to have a lower or higher number?
- this is the distance from the router to the device or function
- the lower the AD the closer. For example, an AD of 0 would mean that something is directly connected.
What is the routing table and what does it store?
- file stored in the RAM that contains info like...
directly connected routes,
remote routes,
next hops or networks
What does "show IP route" do?
display the routing table contents like
local route interfaces
directly connected interfaces
static routes
dynamic routing protocol
What is inter-VLAN routing?
The process of forwarding network traffic from one VLAN to another through a router
VLANs cannot forward traffic even if they are not the same switch without some sort of assistance
What is router on a stick?
one of the routers interfaces is configured as a 802.1Q so it can read VLAN tags. Subinterfaces are created for each VLAN with an IP address.
Members on that VLAN use that subinterface IP address as the default gateway
What does VLAN trunking do? (Use of multiple VLANs out)
This allows many VLANS to use just one physical port on the switch to connect it to the router rather than multiple.
ICMP echo request is?
a may of pinging a device to see if it is connected and working properly.
Tracert?
utility used to confirm that a pouting path took place between two devices
Two ways routers can learn about remote networks?
Manually - entered manually into the routing table
Dynamically - automatically learned using the dynamic routing protocol
directly connected entries
Route source
Destination network
outgoing interface
remote network entries
route source
destination network
administrative distance
metric
next hop
route timestamp
outgoing interface
Static routing advantages over dynamic?
- Not advertised over the network, so better security
- use less bandwidth and dont use CPU cycles to calculate communication routes
- the path a static route uses to send data is known
Static routing disadvantages?
- initial config and maintenance is time-consuming
- config can have errors
- admin is needed to maintain route info
- doesnt scale well with a growing network
- requires knowledge of the whole network for implementation
When should you use static routes?
- small networks with not alot of growth
- routing in a stub network
- using a single default route
- connect to a specific network
- provide a backup route incase the primary route fails
-summarizes routing table entries
Whats a stub network?
- is a network accessed by a single route and it has no other neighbors
Summary Static Route
multiple static routes all using the same exit interface or next-hop IP address
destination networks must be contiguous
What is a default static route?
a route that matches all packets(used when a packet doesn't have a specific route)
a route that all IP packets are sent to that a routing table doesn't not already know
is a route with 0.0.0.0/0 as its destination
default static route used...
when connecting a edge router to a service provider network.
when connecting a stub router
A Next-Hop creates one of three routes types, what are they and what does each one do/know?
Next-hop route - only the next -hop IP address is specified
Directly connected static route - only the router exit interface is specified
Fully specified static route - the next hop and exit interface are specified
troubleshoot a missing route
ping
traceroute
show ip route
show ip int brief
show cdp neighbors detail
What are the purposes of dynamic routing protocols?
- discover remote networks
- maintaining updated routing info
- best path to destination
- ability to find next best path
dynamic protocol uses
good for large networks
help network administrator manage the network
main components of dynamic routing
data structures
routing protocol messages
algorithms
Advantages to dynamic routing?
- share info about remote networks
- determine best path/ update routing table
- dynamic routing requires less overhead
- less work for admin to config and maintain
- independent of network size
Disadvantages of dynamic routing?
- part of a routers resources (CPU) are dedicated for protocol operation
- more complex to implement
- less secure
- route depends on topology
When is a network completely converged?
- When all routers on the network have complete and accurate info
What is convergence time?
time it takes for routers to share info, find best paths and update routing table
Speed of propagation?
amount of time it takes for router in a network to forward routing info
IGP? (Interior Gateway protocol)
Used for routing inside of a network group
EGP? (Exterior gateway protocols)
Used for routing between LAN, protocol used for the internet
What does distance vector mean?
distance refers to how far
vector refers to the direction
so its how far the connection is going and in what direction
RIPv1
First generation legacy protocol
RIPv2?
Simple distance vector routing protocol
automatically summarizes networks at major network boundaries.
IGRP?
First gen cisco protocol (not used anymore)
EIGRP?
New and advanced version of vector routing
How does a distance vector work?
use routers as sign posts along the way to the final destination
How does a link-state router work?
No sign posts, makes a complete map of the network topology using link-state information
Types of Link-State protocols?
OSPF( routing protocol) and IS-IS(provider network)
link-state protocols advantages
each router builds its own topological map
immediate flooding of LSPs
hierarchical design
link-state disadvantages
maintaining a link-state and SPF tree requires more memory
more cpu processing
What does a classful routing protocol do? What problems does this create?
- doesnt send subnet mask info in updates(RIPv1, IGRP)
- cannot provide CIDR info, when this was creates network were only class A
Which routing protocols are bad? Which are good?
BAD: RIPv1 RIPv2 IGRP
Good: EIGRP OSPF IS-IS
routing protocol metrics
a metric is a measurable value given by the routing protocol to routes based on their usefulness
RIPv1 vs RIPv2?
Both: uses hop count as a metric, max of 15 hops, then dies, updates every 30 seconds
RIPv1: updates at 255.255.255.255
everything else is not supported
RIPv2: updates at 224.0.0.9
Everything else is supported