Neurocognitive Disorders
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Cognitive impairment
A decline in cognitive function including memory loss, decreased attention span, difficulty problem-solving, visuospatial difficulties, behavioral changes, learning/retention, judgement, reasoning
Delirium
What is characterized by an alteration in attention, consciousness, and cognition with a reduced ability to focus, sustain or shift attention - RAPID
cortical vs. subcortical mechanisms, ACh Drugs (reverse with pyridostigmine)
Pathogenesis for Delirium
elderly, inpatient (1/3), sick
What patient population is delirium common in?
fast and usually fluctuates, includes perceptual disturbances and a reduced ability to focus/maintain attention
How does delirium develop?
Drugs/alcohol (including withdrawals), infection (UTI), neurological disease (stroke, seizures), metabolic disturbances (hypoglycemic, hyperglycemic, electrolyte imbalance), medications
What are some causes of delirium?
Underlying neurological disorders (superimposed dementia (20-90%), stroke, parkinson), older age, sensory impairment
Risk factors for delirium
Short-term memory loss, anxiety, irritability, perceptual disturbances (hallucinations), psychomotor restlessness, sun-downing, Isn’t acting right
What are the symptoms of delirium?
Full head to toe - vitals, head, lung, chest, abdomen, GU, extremities, neuro, skin
Describe the physical exam for delirium
Sun downing
A phenomenon when patients have mild/moderate delirium at night that is more common in patients with dementia and characterized by increase confusion, disorientation, agitation, mood swings, hallucinations, paranoia, and difficulty sleeping
Distractibility
What is the HALLMARK of delirium
Distractibility, disorganized/tangential speech, drowsiness, lethargy, semi-comatose, Hypervigilance (EtOH or sedatives)
Clinical presentation of delirium includes disturbance of consciousness - what does that look like?
Decrease in level of functioning (unable to do tasks - need a baseline), dementia, perceptual disturbances, language difficulties
Clinical presentation of delirium includes change in cognition - what does that look like?
pacing, anxiety, rapid mood swings, hallucinations
The hyperactive symptoms of delirium are easiest to recognize but patients often refuse care → what does this look like?
inactivity, sluggish, drowsiness, dazed
The hypoactive symptoms of delirium are harder to recognize since patients often do not interact→ what does this look like?
CAM (confusion assessment method)
What assessment tool can you use for the diagnosis of delirium?
Acute onset + fluctuating course, Inattention, Disorganized thinking, Altered level of consciousness
What are the components of the CAM (must have the bold)?
Benzos, antihistamines, TCAs (amitriptyline), neuroleptics (clozapine), Parkinsons drugs (levodopa, amantadine), Anticholinergics, opioids (tramodol), sleeping aids, H2 blockers, steroids
What medications can cause delirium - STAR

CBC, CMP (calcium, glucose), UA with culture (Old lady UTIs ARE WACK), tox screen, B12, TSH/T4, ABG
84 y/o patient presents to the ER for AMS. Daughter reports that the patient has a PMHx of dementia, cirrhosis, and is currently on “So many medications I can’t keep up, you should have all of it.” Physical exam reveals inattention, disorganized thinking, and altered level of consciousness. What labs you want?
treatable medical illness/problem, no hx of trauma, no new focal neuro signs, patient is arousable and can follow simple commands
When should can you skip imaging in a delirious patient?
unknown cause, patient not improving with treatment of known
When is a head CT required for delirium (consider MRI if neg)?
Unknown cause with fever
When is a lumbar puncture required for delirium?
Excludes seizures, confirm metabolic/infectious encephalopathies
When is an EEG required for delirium?
Delirium tremens (alcohol withdrawal delirium)
A dangerous symptom of alcohol withdrawals that requires an ER trip characterized by tremors in the hands
ICU admit, Benzos (control agitation, prevents seizures), IV fluids, B1 (prevent werknicke’s encephalopathy)
Delirium tremens Treatment plan
Wernicke’s Encephalopathy
What type of delirium is characterized by a thiamine deficiency caused by EtOH usage (most common), malabsorption, dialysis, bariatric surgery, anorexia, AIDS, hyperemesis of pregnancy
Confusion, ataxia, horizontal nystagmus (Ophthalmoplegia)
Wernicke’s triad
Korsakoff syndrome
Wernicke’s encephalopathy + amnesia + grandiose story telling (confabulation)
BLAST the thiamine IV
Treatment plan for Wernicke’s
Dementia
A progressive decline in intellectual function WITHOUT disturbance in consciousness usually insidious and gradual in nature (usually no precipitating event)
3-15 years from onset to death
How does dementia affect life expectancy
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD - most common), Vascular dementia, frontotemporal dementia, Dementia with Lewy Bodies
Common causes of dementia
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD)
A progressive dementia with insidious onset characterized by atrophy of the cerebral cortex, beta amyloid plaques and Tau tangles
Loss of neurons and synapses and creation of neuritic plaques in the cerebral cortex and subcortical regions that leads to degeneration in the temporal, parietal, frontal cortex, and cingulate gyrus
Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease (AD)
Short term memory loss
What is the 1st and most prominent symptom of Alzheimer’s Disease (AD)
executive function, visuospatial function, language
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) presentation includes variable deficits in
Vascular Dementia
What type of dementia results from damaged blood vessels leading to a reduce in circulation (stroke, hemorrhage, stenosis, etc)
PMHx of CVAs, abrupt onset, step-wise/progressive accumulation of deficits (depends on location), focal neuro deficits, depression
Signs of Vascular Dementia
White matter hypersensitivities (MRI), White matter hypo-densities (CT)
What imaging changes will you see on MRI and CT for vascular dementia?
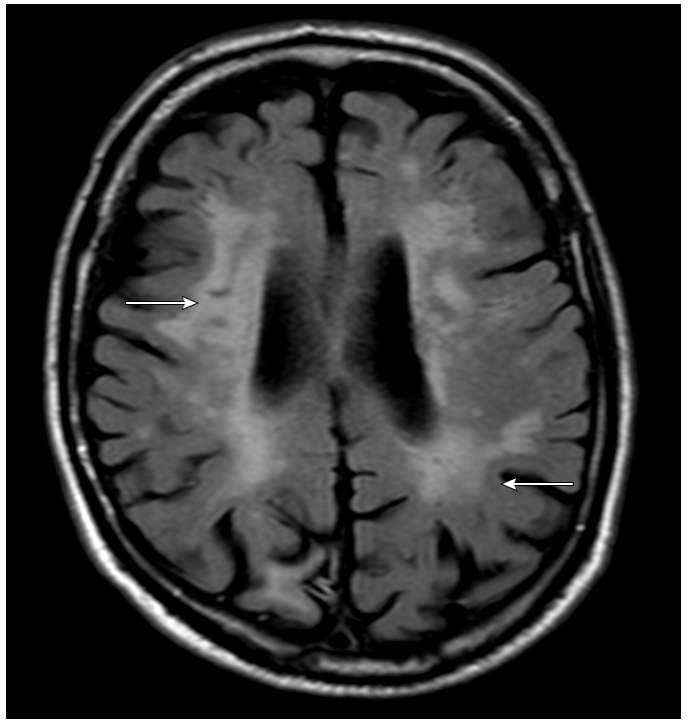
Decreased concentration, forgetfulness, slowed thinking
Subcortical symptoms of Vascular Dementia
abnormal gait, focal weakness, dyscoordination
Motor symptoms of Vascular Dementia
Hx of psychiatric illness (40%), autosomal dominant pattern (10-25%)
Quirks of Frontotemporal dementia
Abnormal protein inclusions in the cytoplasm/nuclei of neuronal/glial cells, Loss of neurons, myelin and astrocystic gliosis in the frontal and temporal lobes
Pathogenesis of FTD
Tau, TAR-DNA binding protein 43
Which proteins aggregate in Frontotemporal dementia
Behavioral (50/50 protein, psychosis), Non-fluent aphasia (70% tau, language), Semantic dementia (100% TDP-43, language)
What are the variations of Frontotemporal dementia
Disinhibition - Kissing, touching, socially inappropriate, Hyperorality (snacking), compulsive behaviors (hoarding)
Hallmark of the Behavioral variant of FTD (most common type)
difficulty producing the sound (articulatory difficulty)
Hallmark of Progressive Non-Fluent Aphasia variant of FTD
impaired single-word comprehension and object naming in the setting of preserved fluency, repetition, and grammar (trouble matching words with what they mean)
Hallmark of Semantic variant of FTD
Dementia with Lewy Bodies
An abnormal collection of alpha-synuclein protein in the neurons in the brain cortex (anterior frontal lobe, temporal lobes, cingulate gyrus, insula)
Motor deficits similar to parkinson’s, AD symptoms, visual hallucinations, fluctuating delirium, visuospatial/executive cognitive disfunction, psychiatric disturbances
Symptoms of Dementia with Lewy Bodies
Short-term memory loss, Word finding difficulty, Visuospatial dysfunction, Executive dysfunction, apathy
General presentation of Dementia
Frontal, subcortical
Executive dysfunction and apathy are associated with damage in what area
Right parietal lobe
Visuospatial dysfunction is associated with damage in what area
Temporal parietal junction of the left hemisphere
Word finding difficulty is associated with damage in what area
Hippocampus
Short term memory loss is associated with damage in what area
Fam hx, chronic illness (especially vascular), head trauma, female
Risk factors for dementia
education, ongoing intellectual stimulations
Protective factors for dementia
ADLs, amount of decline, risk factors, ability to be a reliable historian, speech, depression
What do you need to find out when collecting a hx on a patient with dementia?
occult medical illness, underlying neurological condition (do a neuro exam), exclude treatable conditions, evaluate self care
What do you need to find out when collecting a physical exam on a patient with dementia?
Quick screen patients older than 70 (3 simple nouns, clock, 3 simple noun recall), MMSE if there’s any deficit, Full neuropsych
What are some screening tools for dementia?
MRI
Which imaging is preferred for dementia to r/o CVD, tumor, or structural abnormality
PET (radiolabel beta-amyloid)
Which imaging can help differentiate between AD and FTD
B12, FT4/TSH, RPR, CBC, CMP, CSF (beta amyloid decrease, tau increase)
Labs for Dementia
aerobic exercise, mental stimulation, cannot regain lost skills
Gameplan for dementia - non pharm
Cholinesterase inhibitors (donezepil, rivastigmine, galatamine)
Gameplan for dementia - pharm 1st line for AD and DLB (DOES NOT PREVENT PROGRESSION OR TREAT FTD)
Memantine (AD, DLB - no FTD), SSRI (No paroxetine), Trazodone for the insomnia (other meds can cause delirium), Methylphenidate (for apathy - may cause agitation), Delusions (resperidone, olanzapine, quetiapine - may increase fall risk)
Gameplan for dementia - pharm
r/o delirium if patient is agitated/impulsive, behavioral interventions (reorientation, distraction, mental stimulation, exercise, sleep), Benzos may worsen agitation, maximize cognitive and behavioral therapies, Stop driving
Safety concerns for dementia
prions (jakob-creutzfeldt is common), infections, toxins, neoplasms, autoimmune
If the dementia is rapidly progressive like weeks to months → what gets added to the differential
MRI, spinal tap with CSF, basics, thyroid panel, RPR, HIV, lyme, serology, rheumatology labs
Workup for rapidly progressive dementia