Metabolic Support of Photoreceptors - Ocular Physiology Spring 2025
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
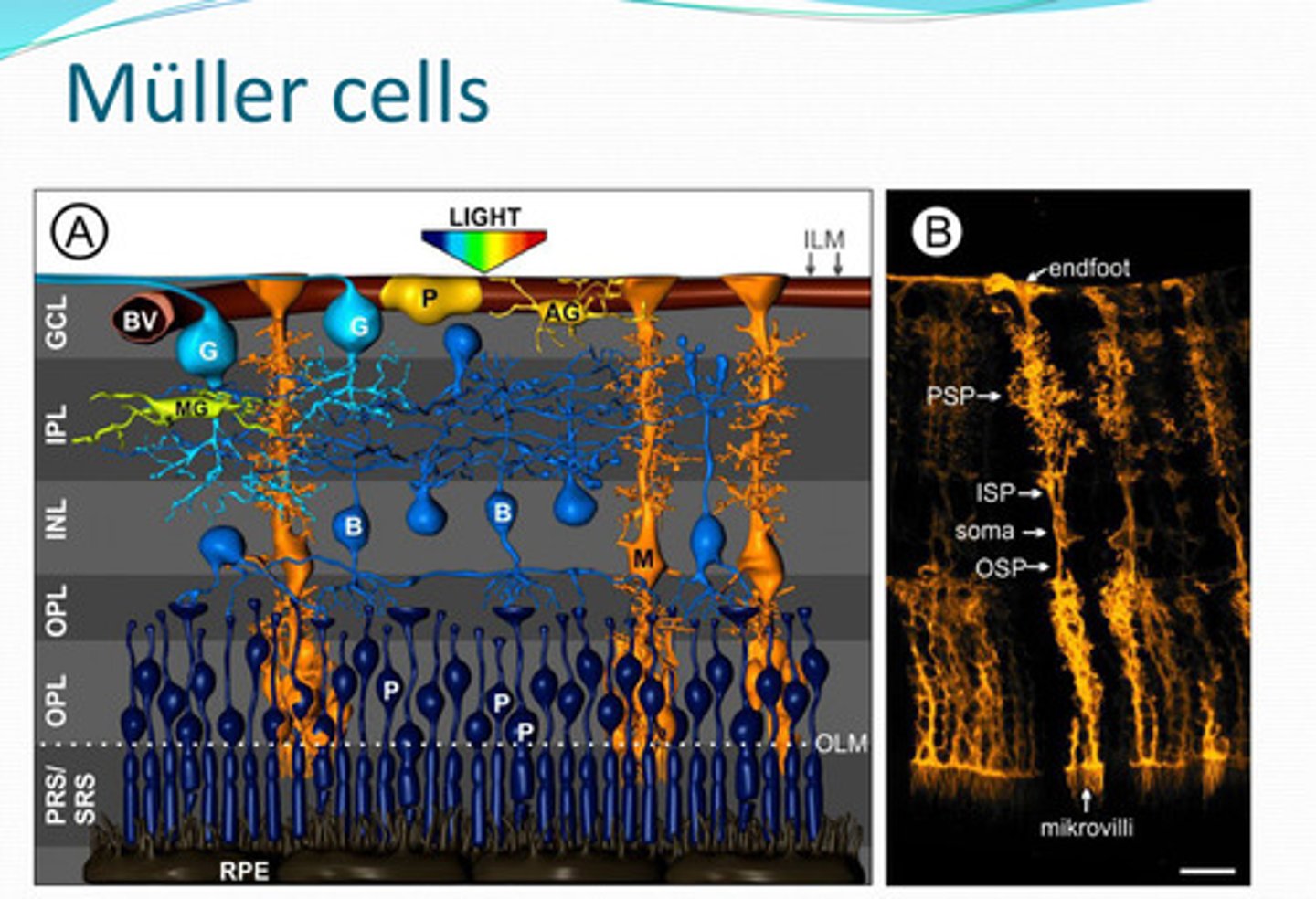
mueller cells
Cells that have a supportive function in the retina, regulate and maintains retinal vasculature, metabolism and transport of glucose, and helps protect the retina from oxidative stress
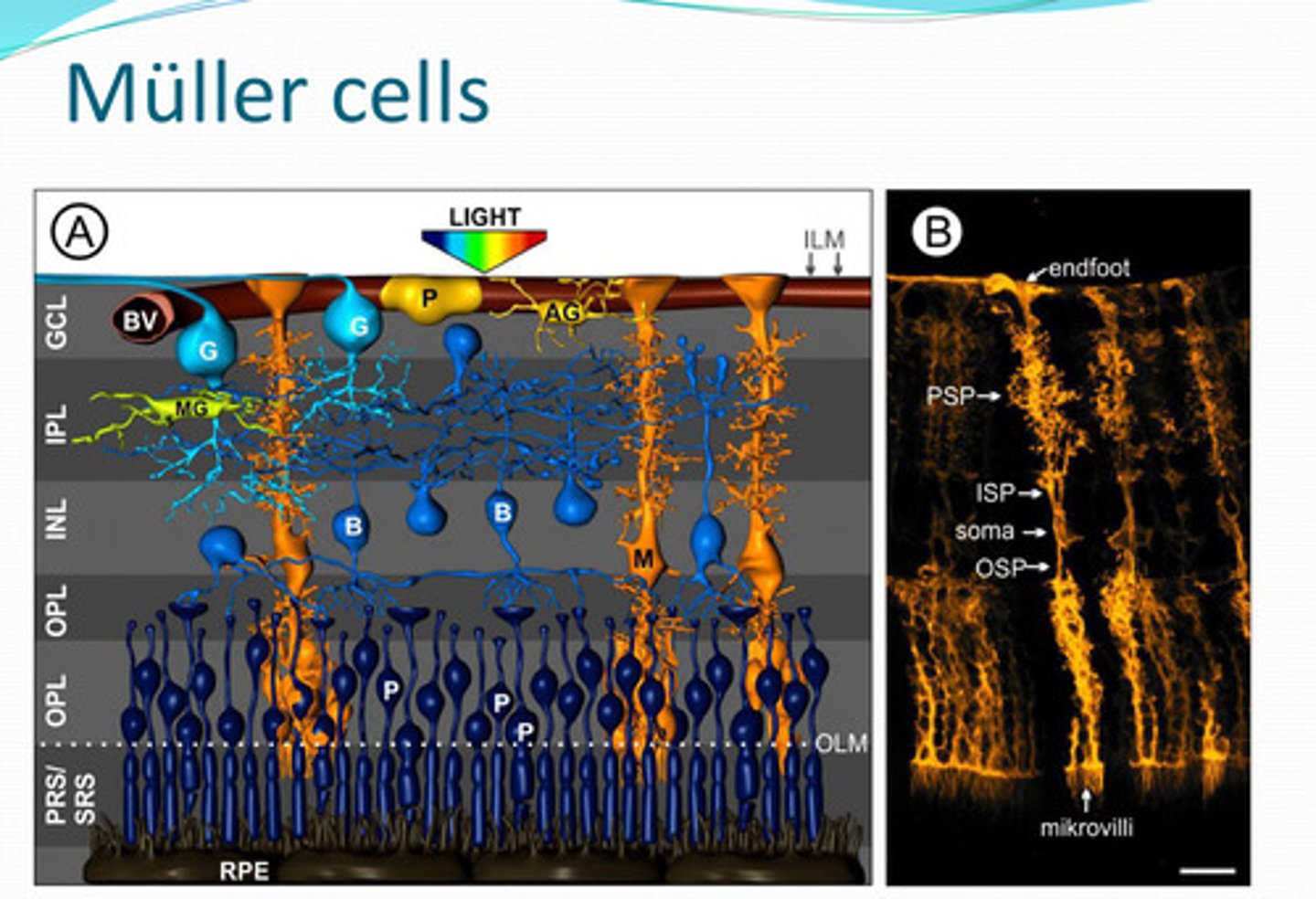
-regulates and maintains retinal vasculature
-metabolism and transport of glucose
-neurotransmitter metabolism
-helps protect the retina from oxidative stress (glutathione production)
-ionic/pH homeostasis
-K+/Cl-/water import & export
-CO2 regulation
-light conduit
What functions of the retina do Mueller cells support?
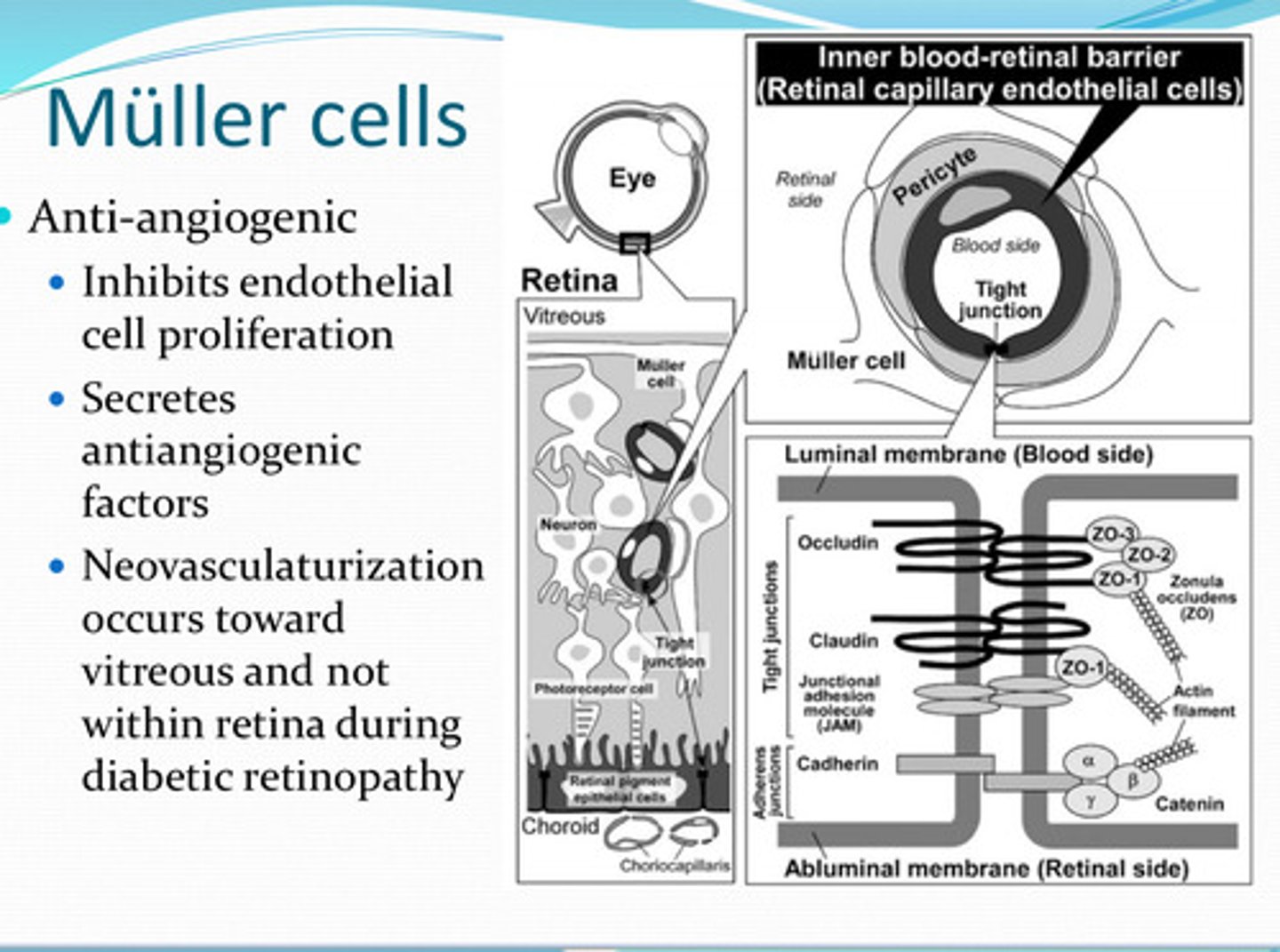
retinal capillaries
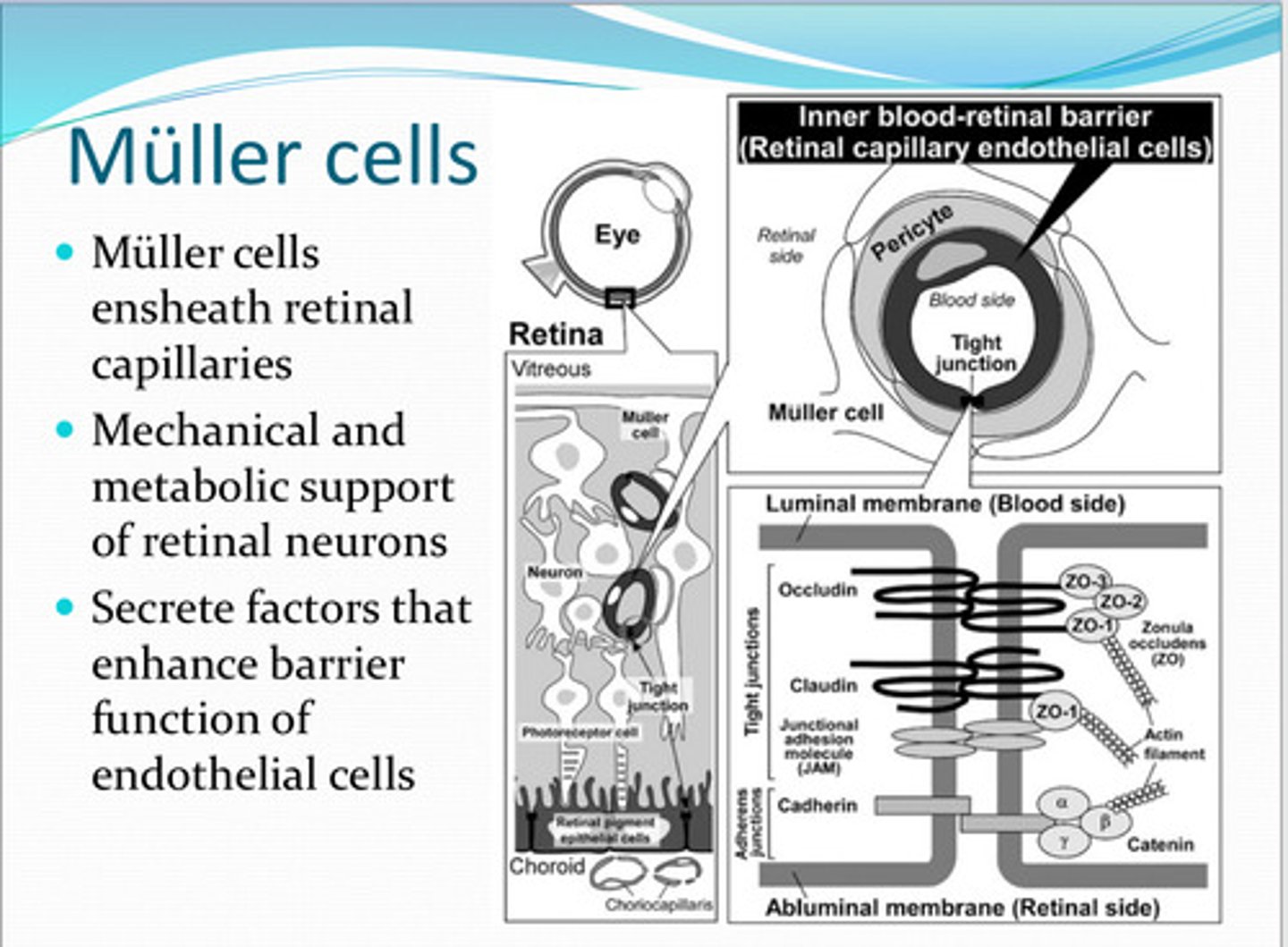
Mueller cells ensheath what?
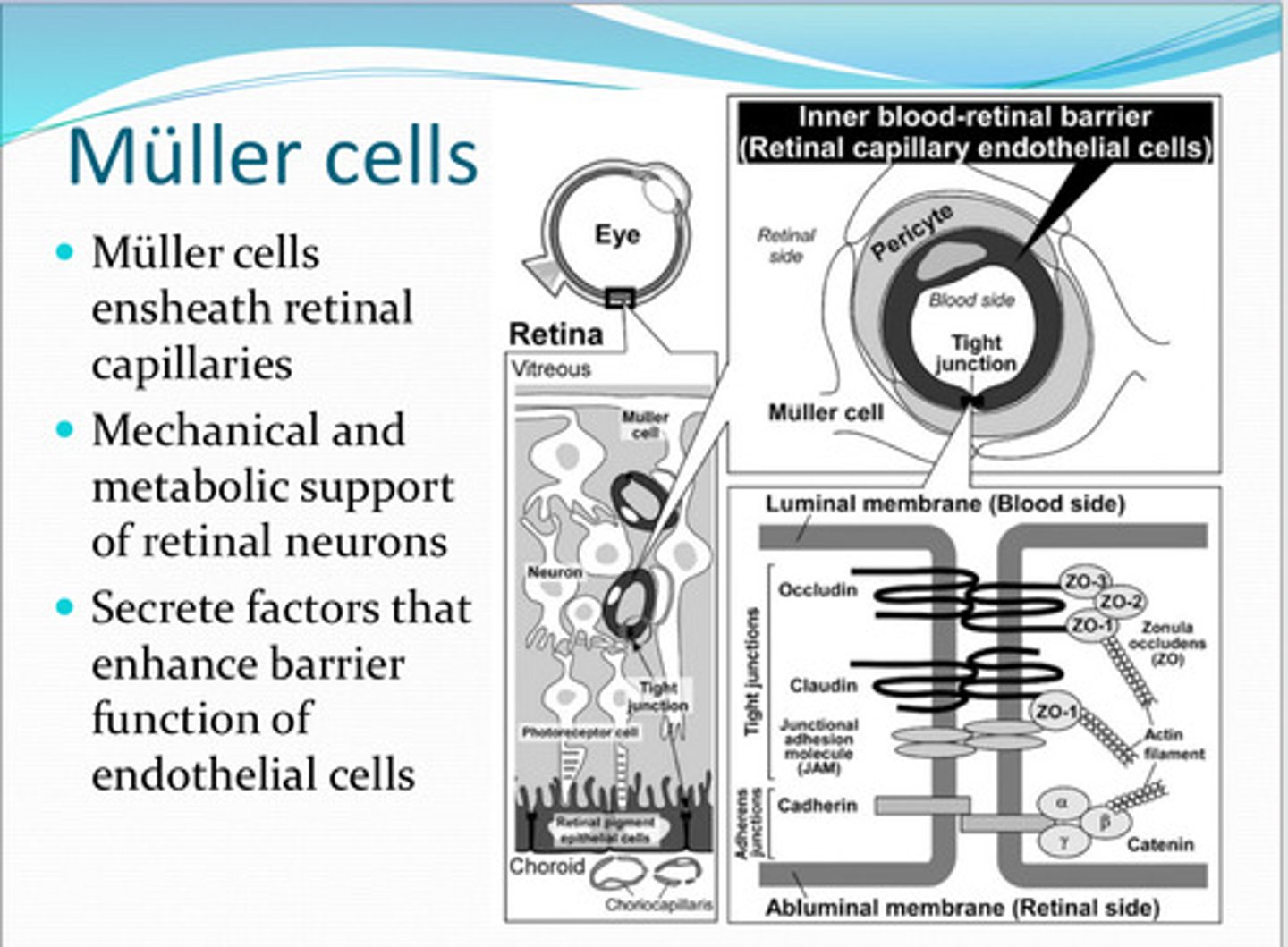
mechanical, metabolic
Muller cells have ____ and _____ support of the retinal nuerons
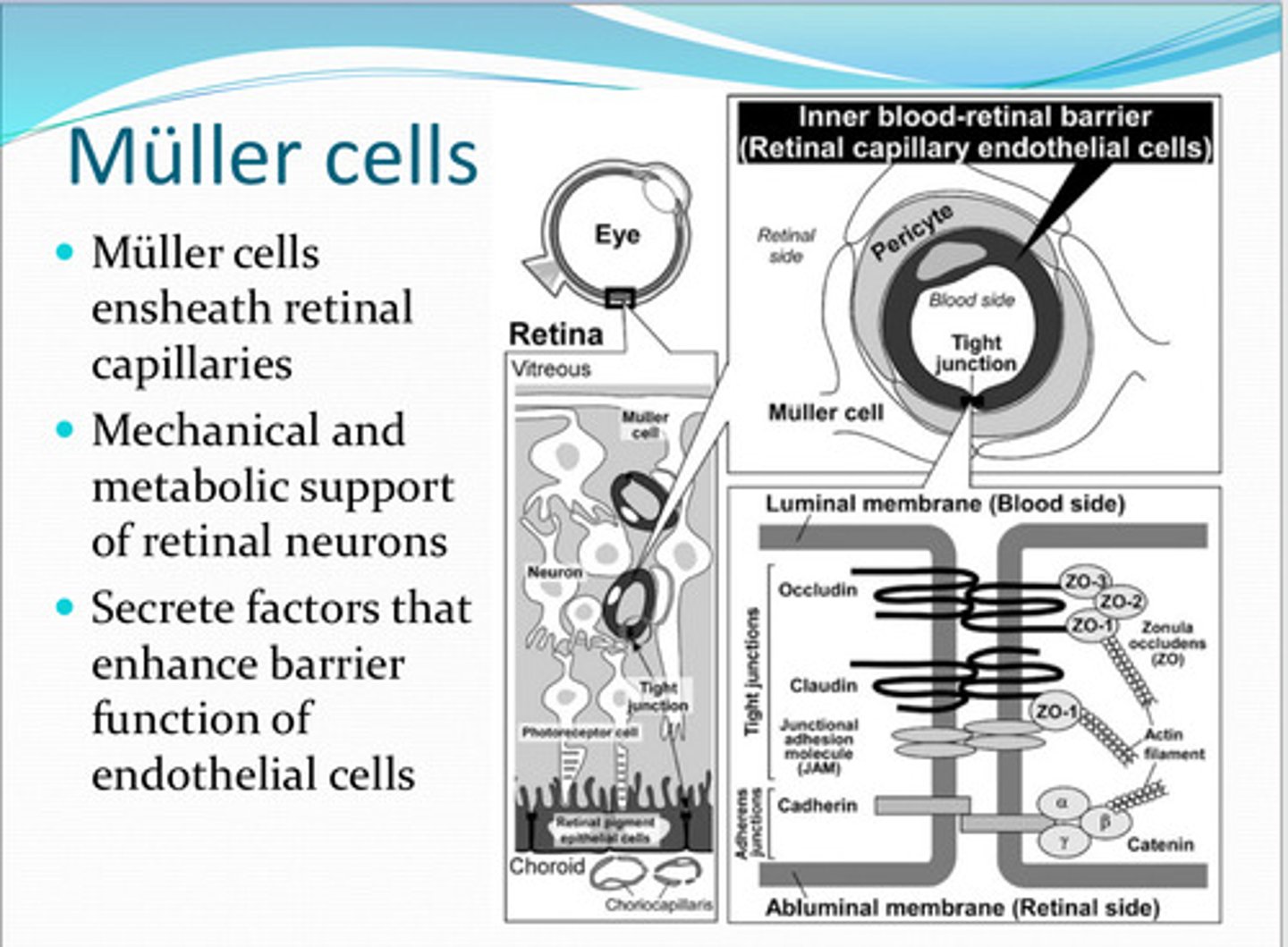
enhance barrier function of endothelial cells
Muller cells secrete factors that do what?
angiogenic
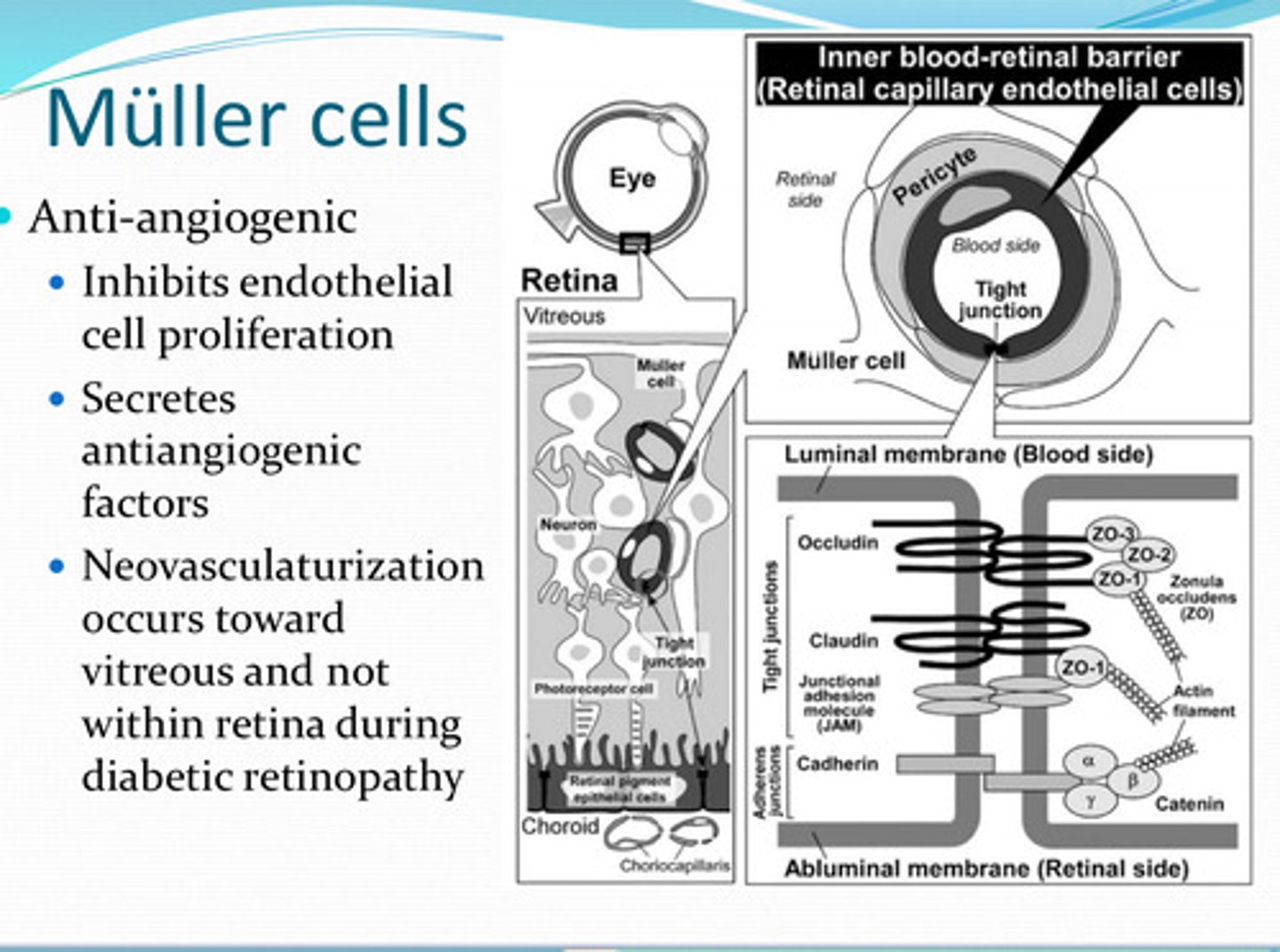
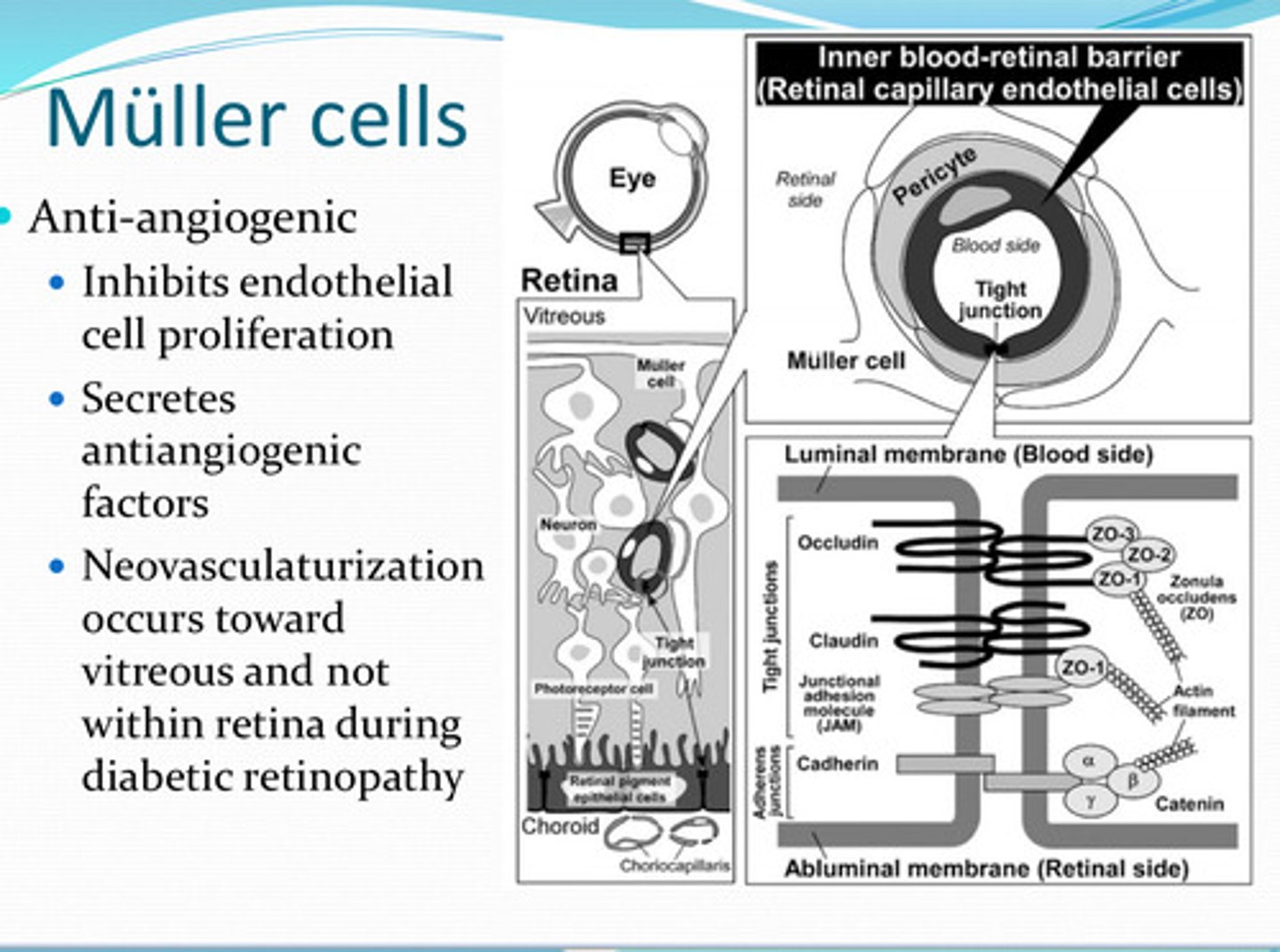
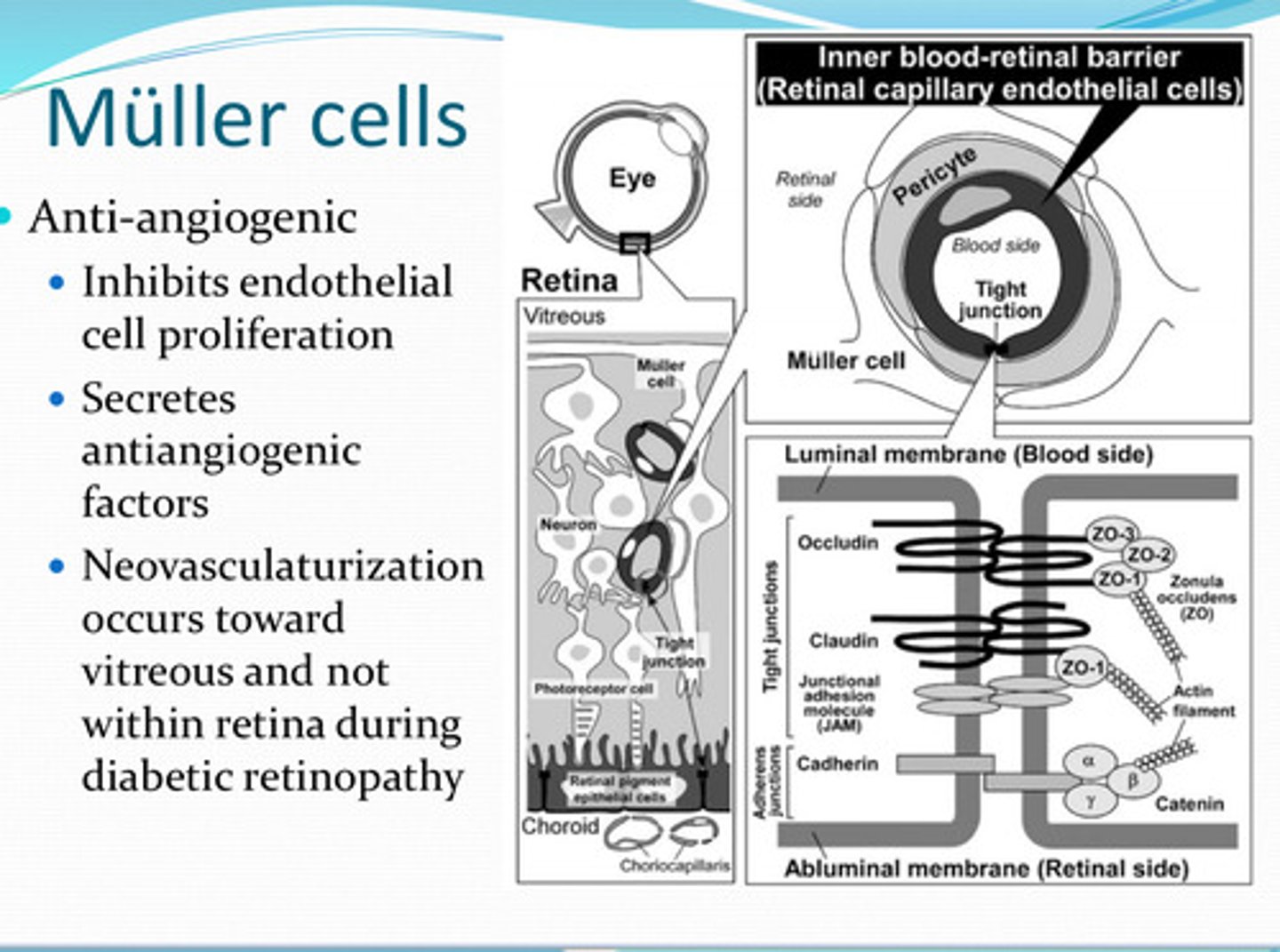
Muller cells are anti-________
endothelial cell proliferation
What do Muller cells inhibit?
anti-angiogenic factors
What do Muller cells secrete?
no -- neovascularization occurs toward the vitreous and not within the retina (even during diabetic retinopathy)
D/t the anti-angiogenic factors that Muller cells secrete, will neovascularization occur in the retina?
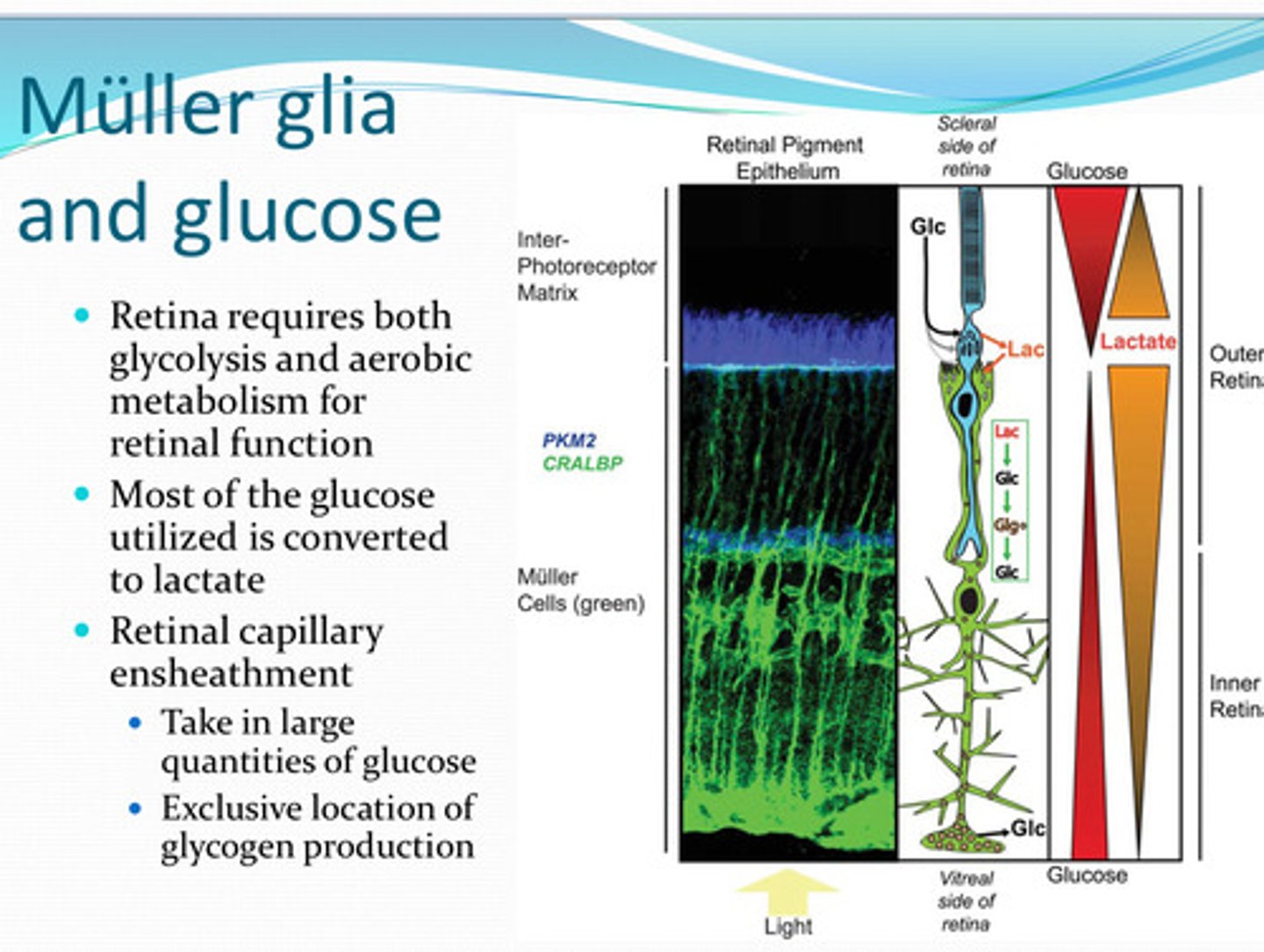
glycolysis and aerobic respiration
For retinal function, the retina requires both ____ and _____
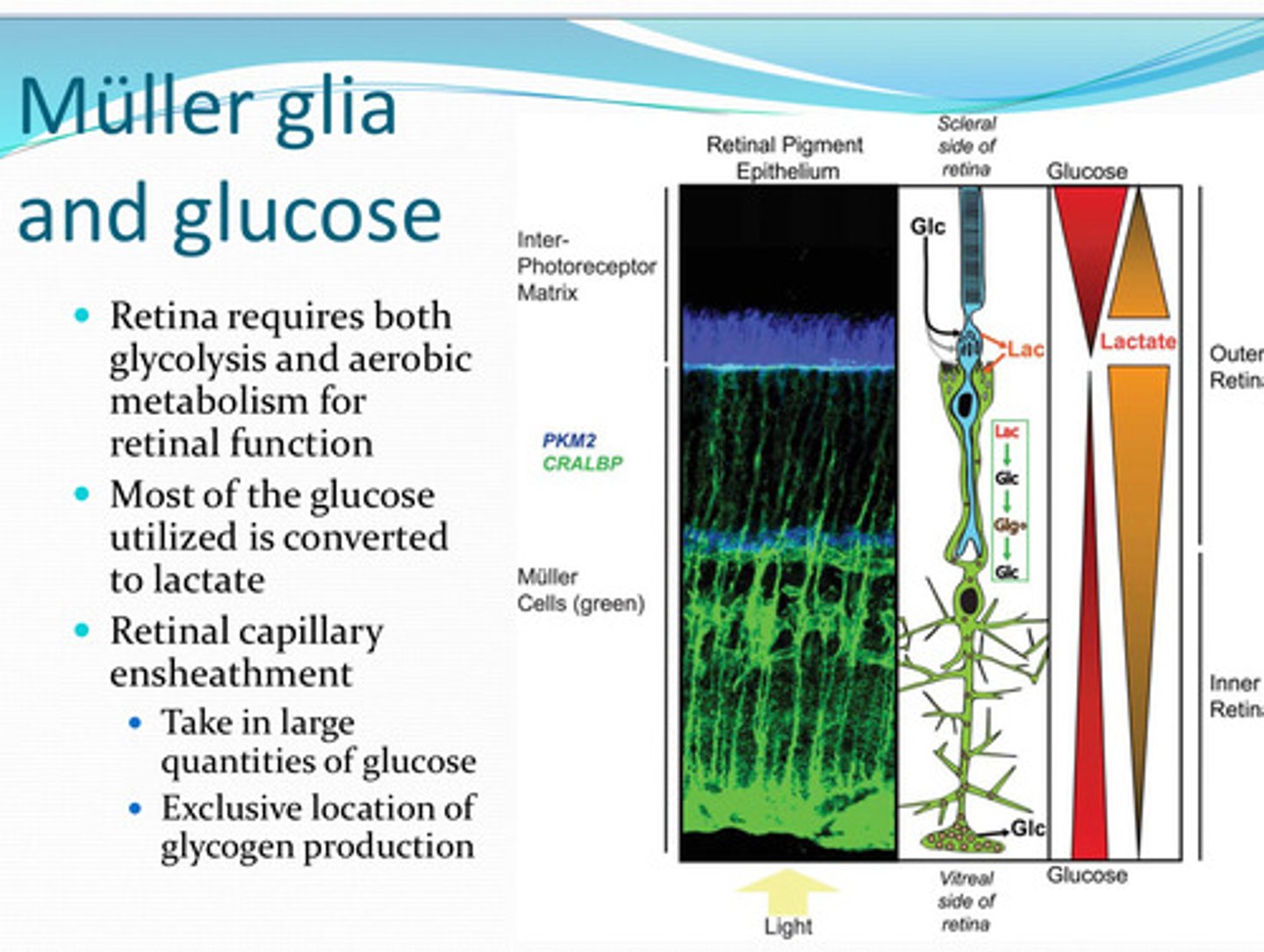
lactate
Most of the glucose utilized by the retina is converted to what?
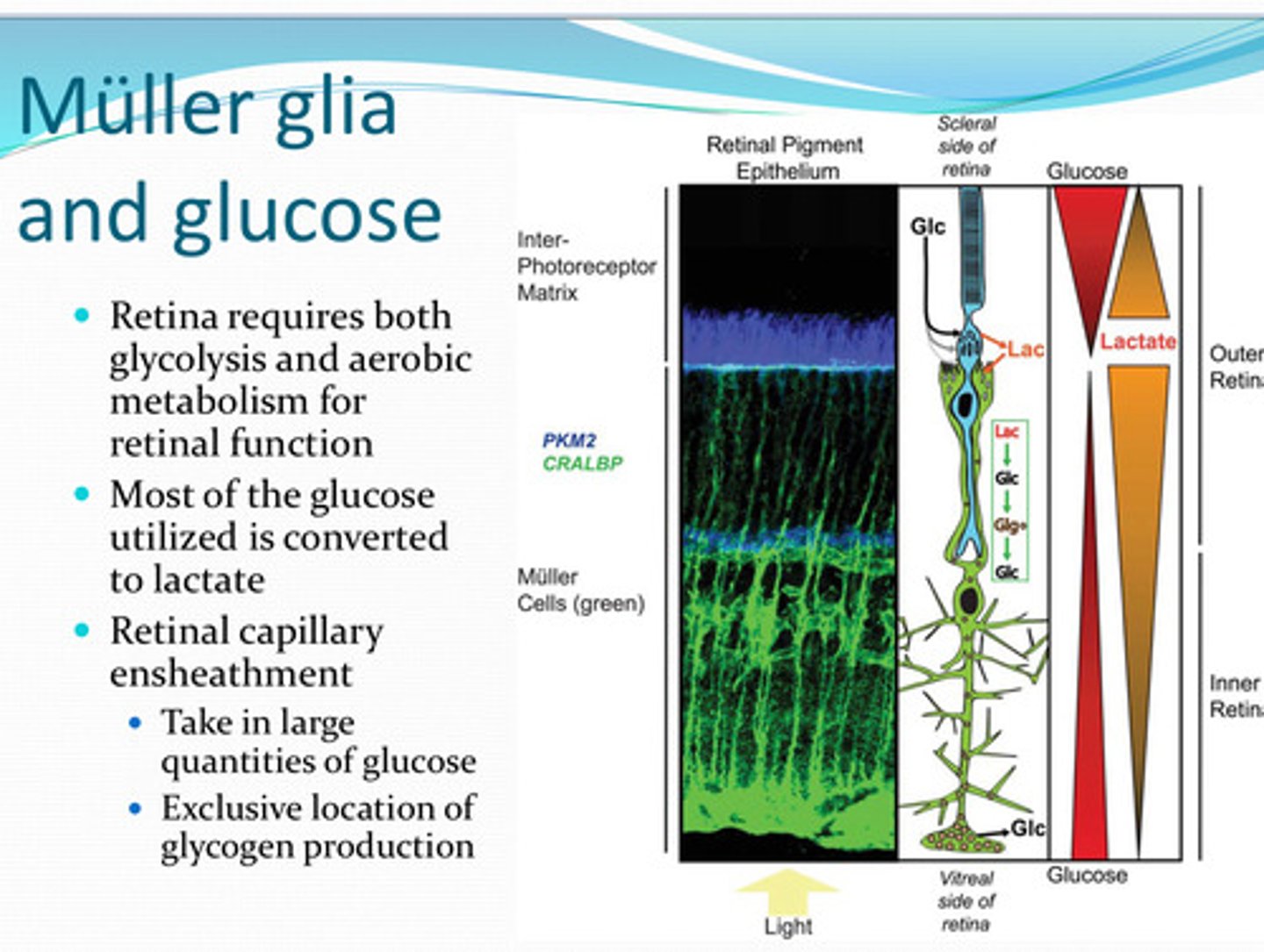
yes
Do the retinal arteries take in large amounts of glucose?:
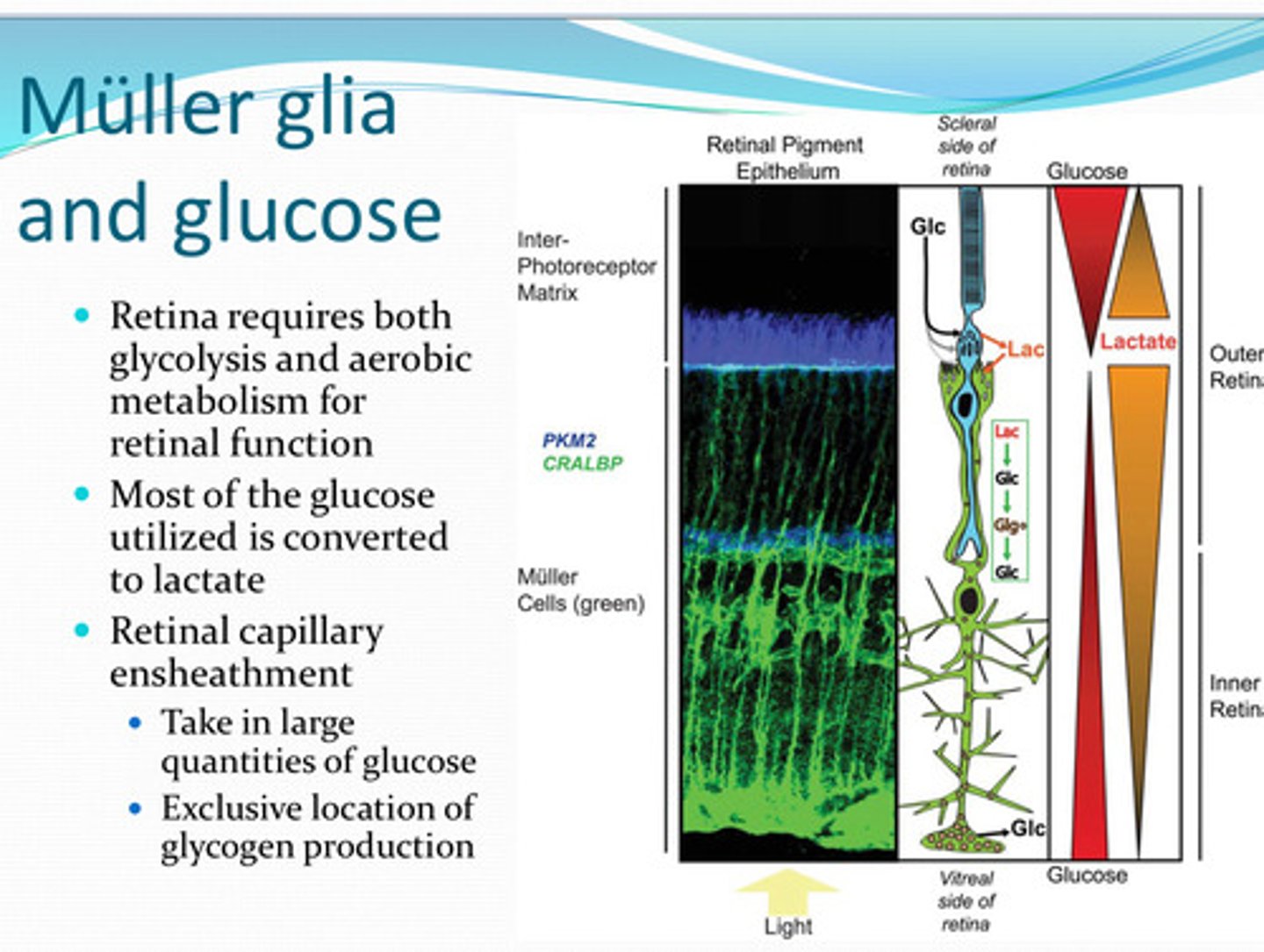
in the retina
What is the only location in the eye where glycogen is produced from glucose?
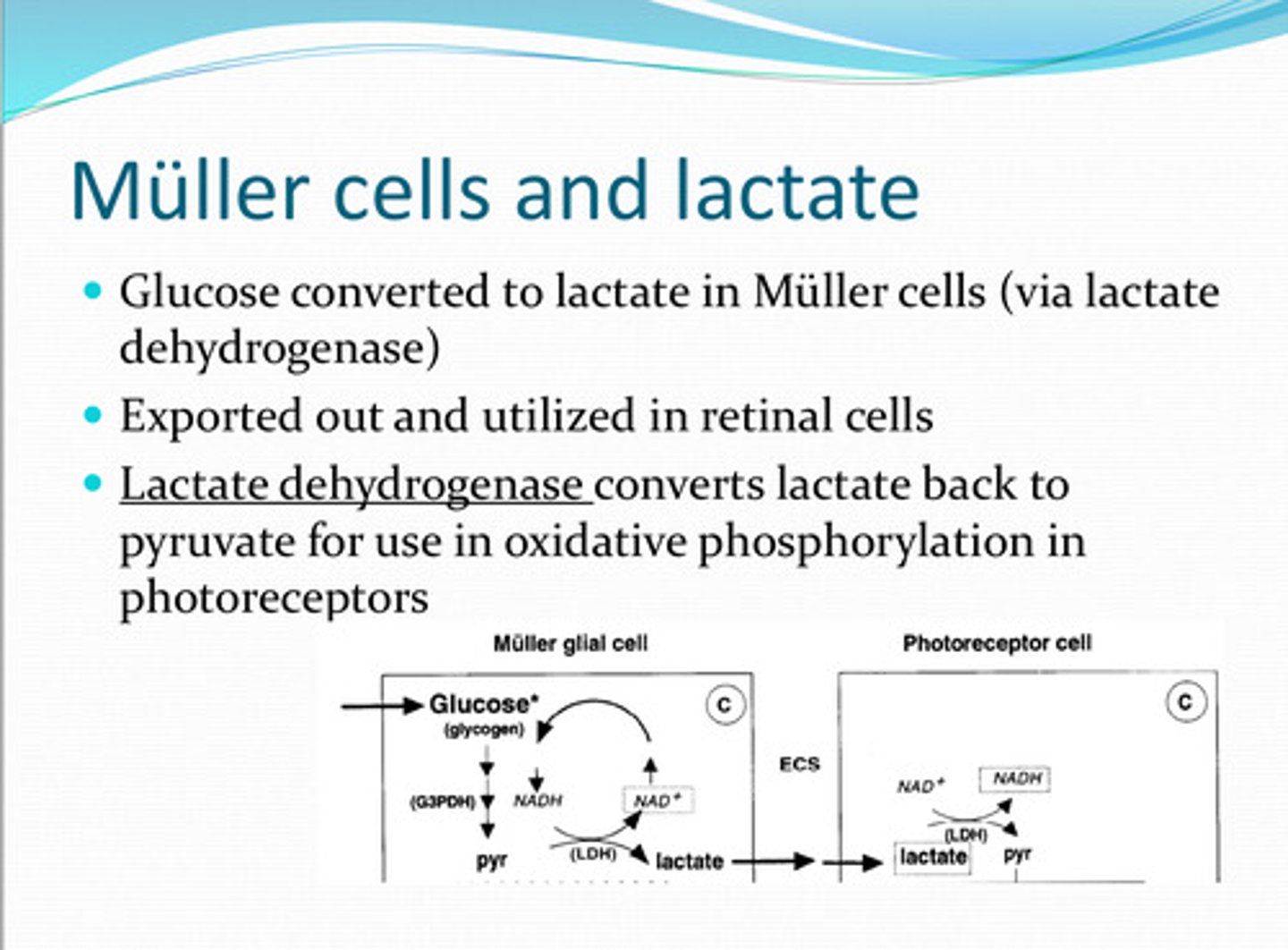
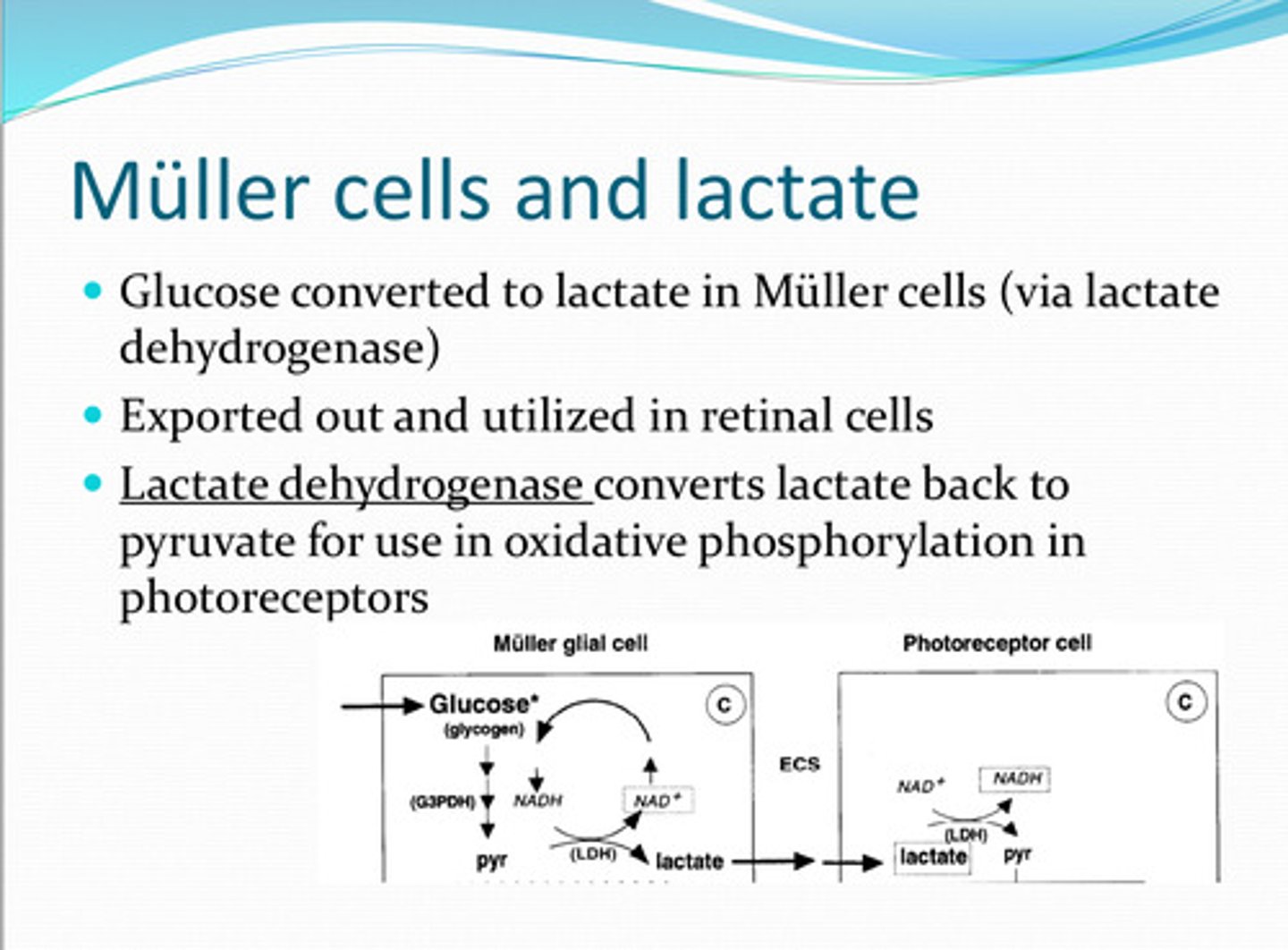
Muller
Glucose is converted to lactate in _____ cells
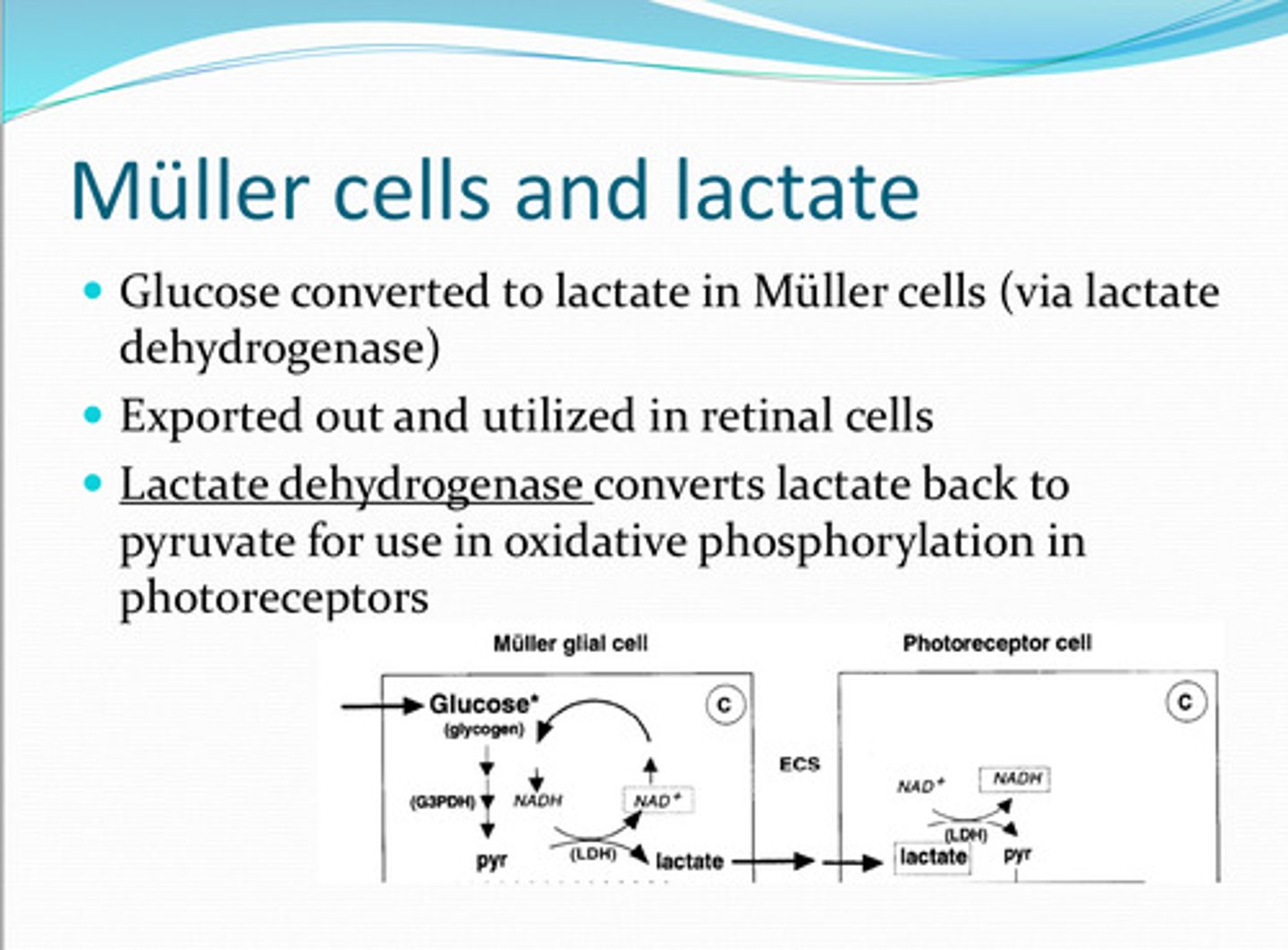
lactate dehydrogenase
______ converts the lactate back to pyruvate for use in oxidative phosphorylation in photoreceptors
yes
Glucose is converted to lactate in Muller cells. Is lactate also concerted to glucose in Muller cells?
converted to glycogen or transporter to inner retinal neurons
What happens to glucose in Muller cells?
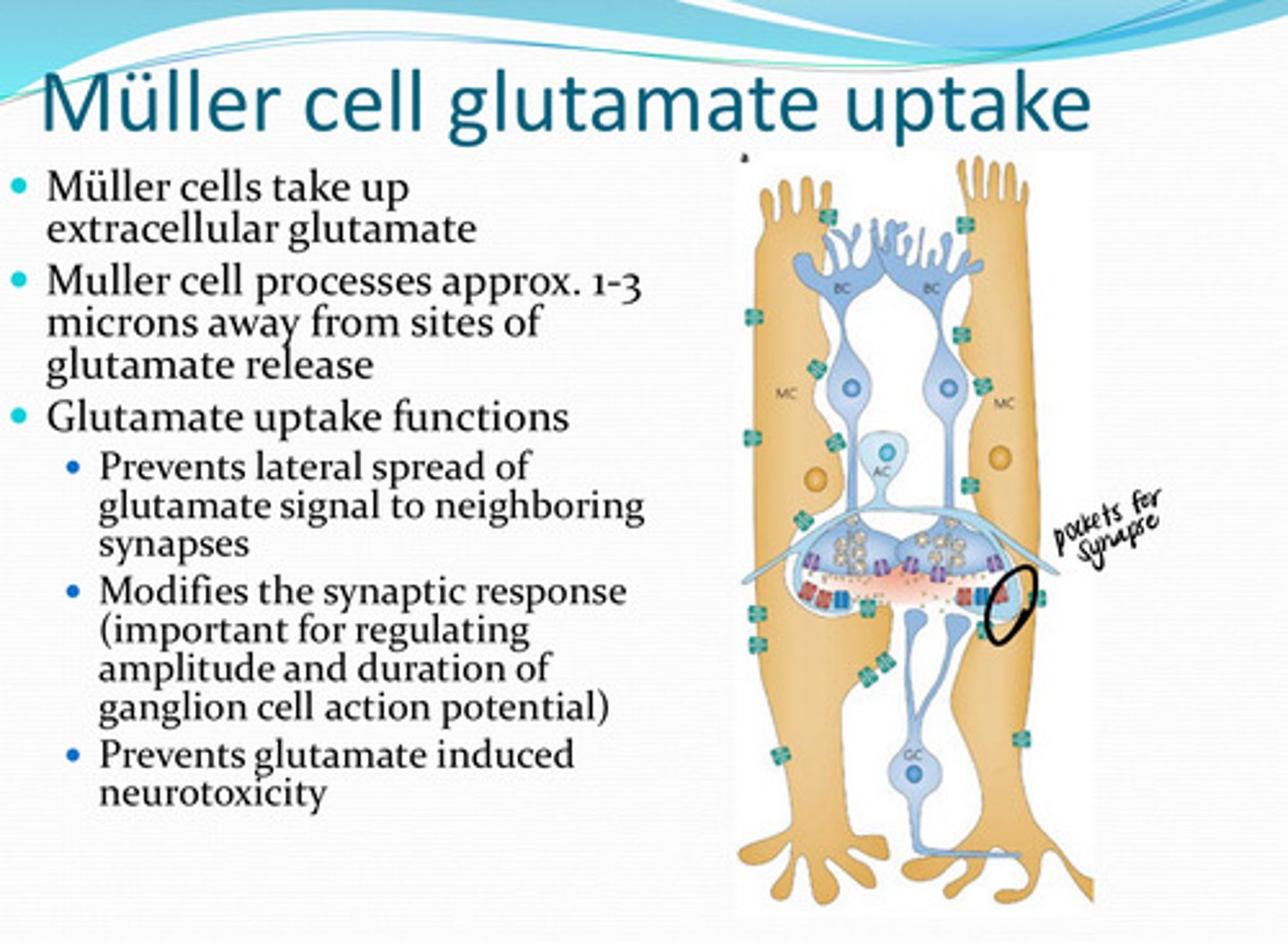
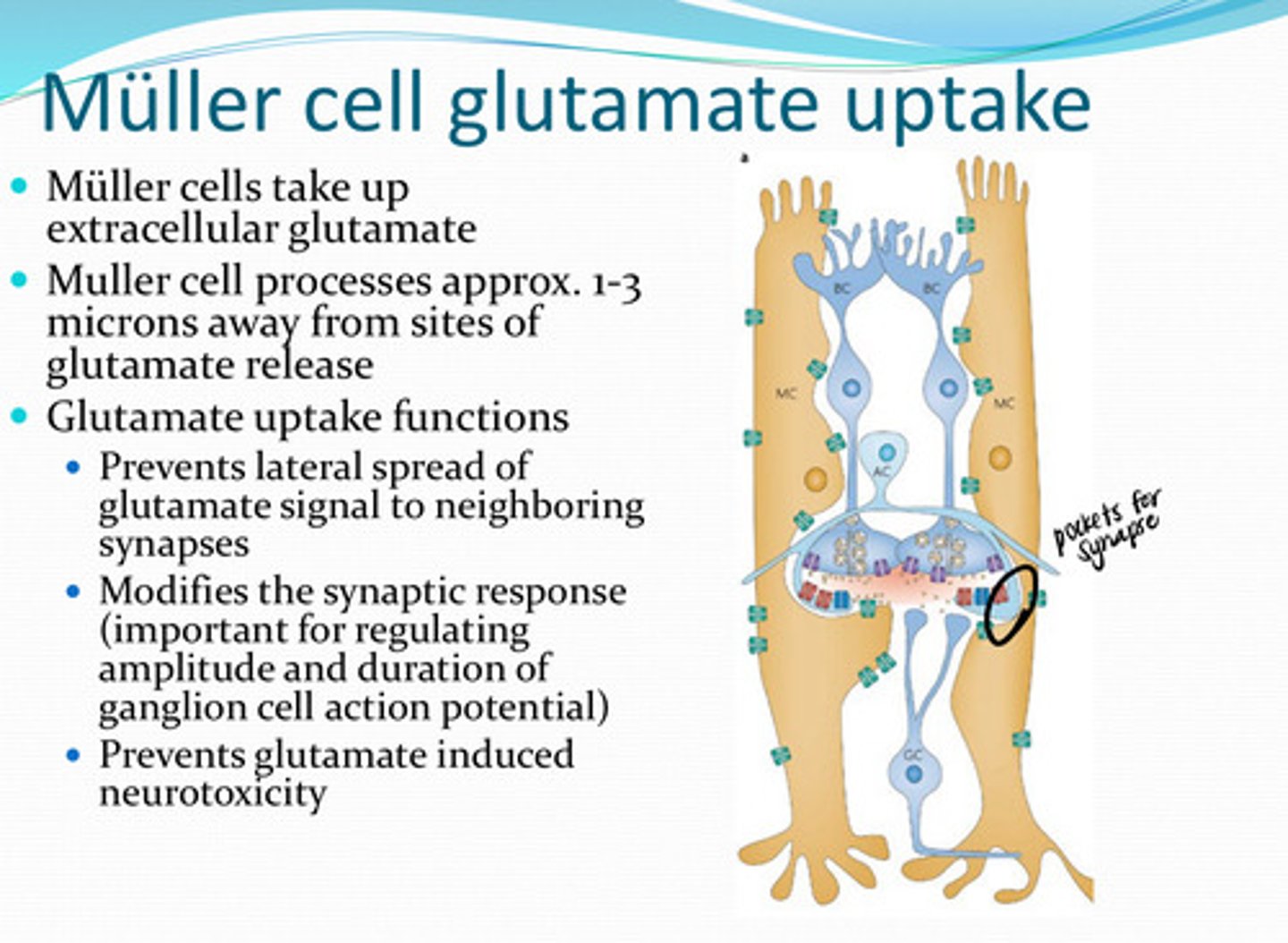
extracellular glutamate
Muller cells take up what?
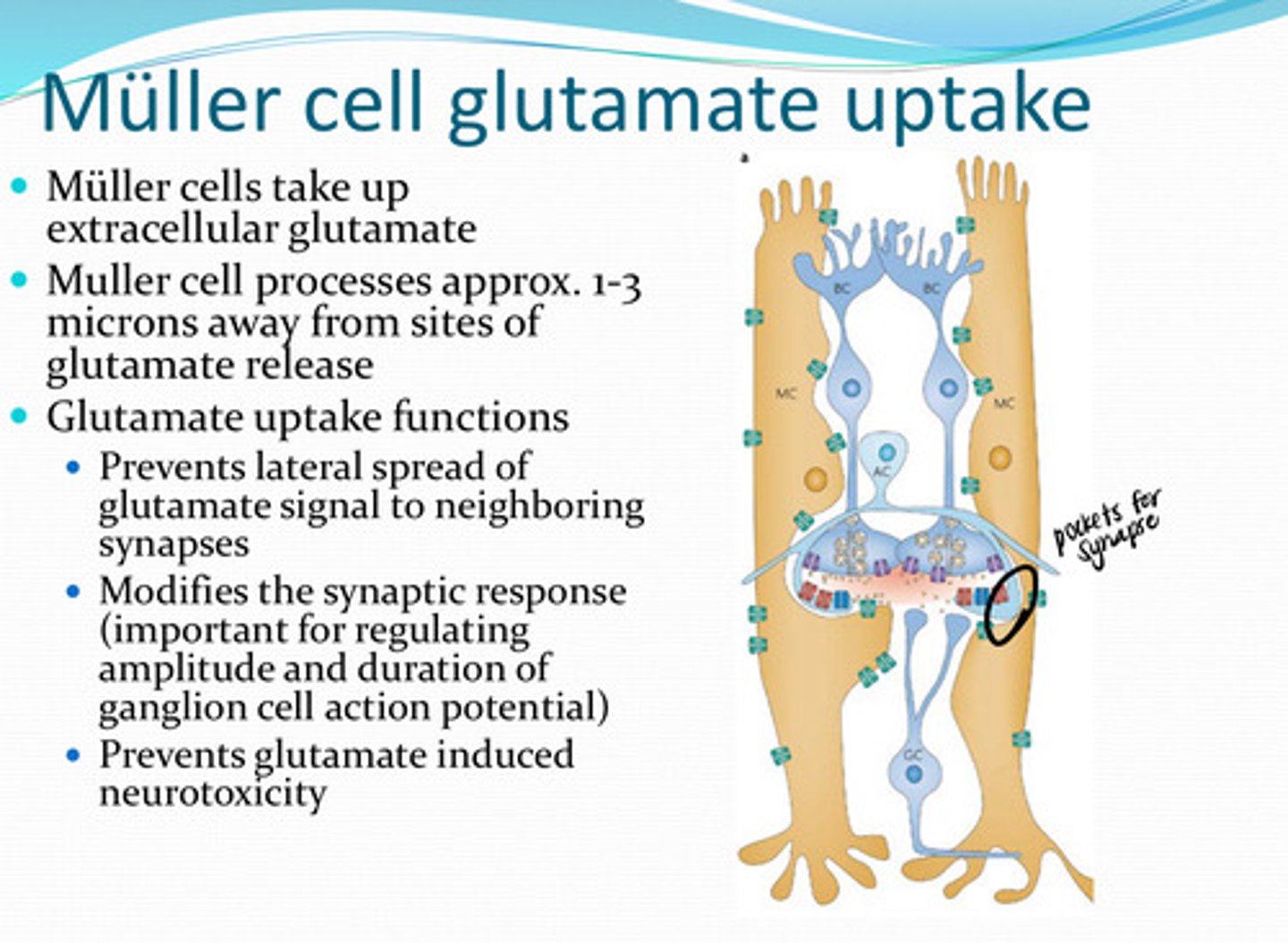
1) Prevents lateral spread of glutamate signal to neighboring synapses
2) Modifies the synaptic response (important for regulating the amplitude and duration of ganglion cell action potential)
3) Prevents glutamate induced neurotoxicity
What are the glutamate uptake functions of Muller cells? Why is this function important?
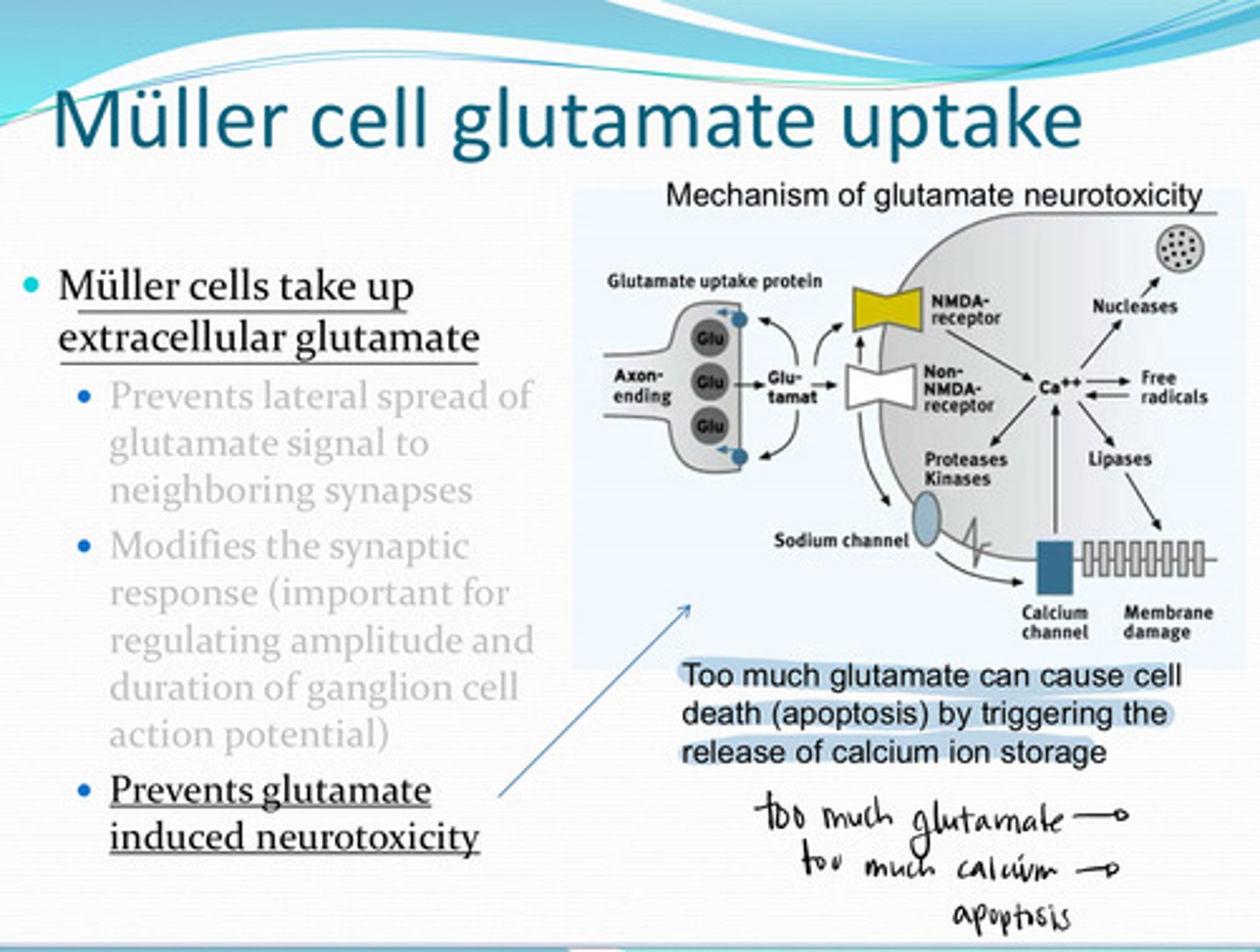
apoptosis (cell death) by triggering the release of calcium ion storage
Too much glutamate in the retina can cause what?
inner plexiform synapses
Muller cells take up a large percentage of the extracellular glutamate derived from __________
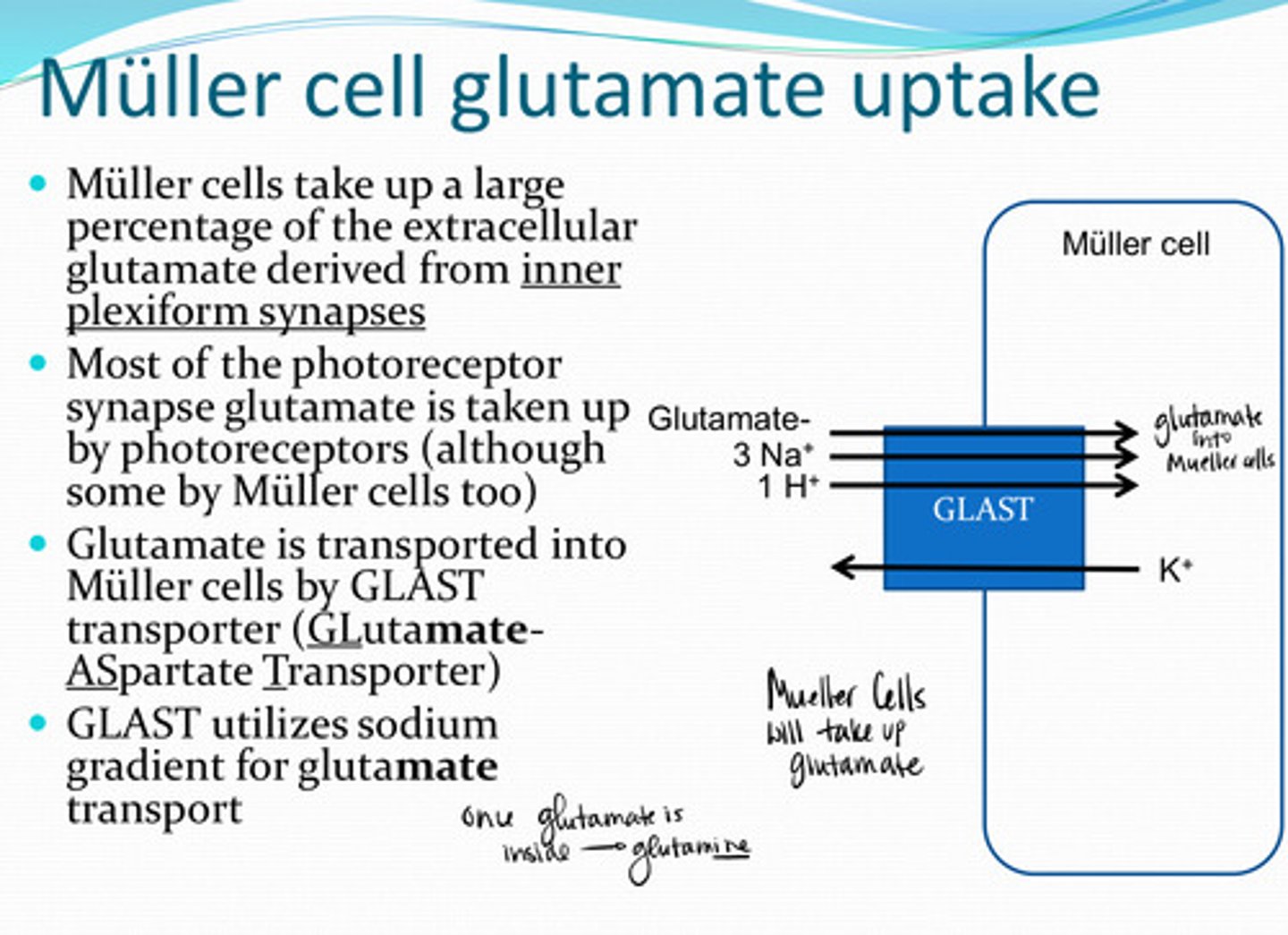
photoreceptors (although some by muller cells too)
Most of the photoreceptor synapse glutamate is taken up by what structure in the retina?
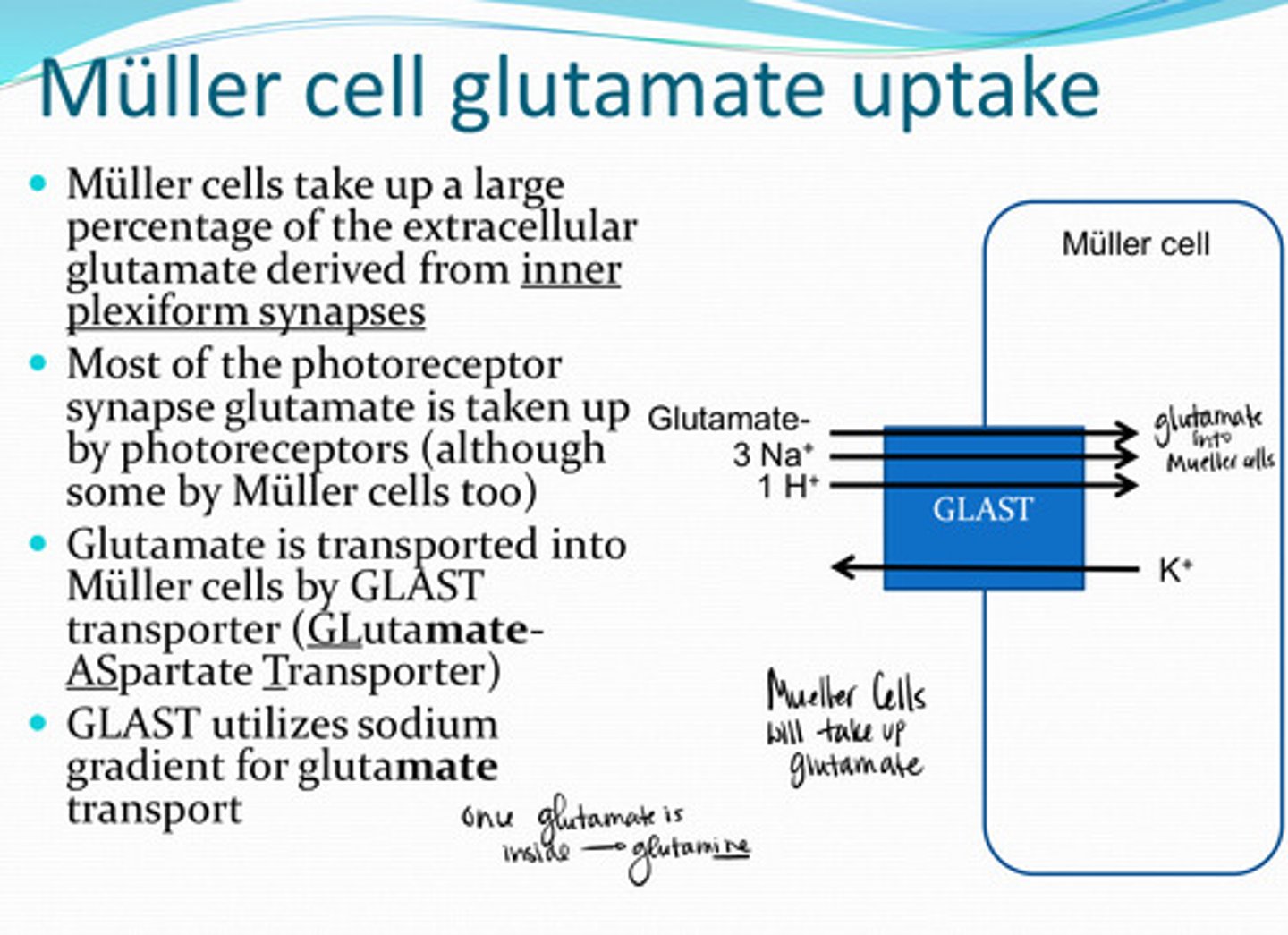
GLAST (Glutamate Aspartate Transporter)
Glutamate is transported into Muller cells by _____ transporters
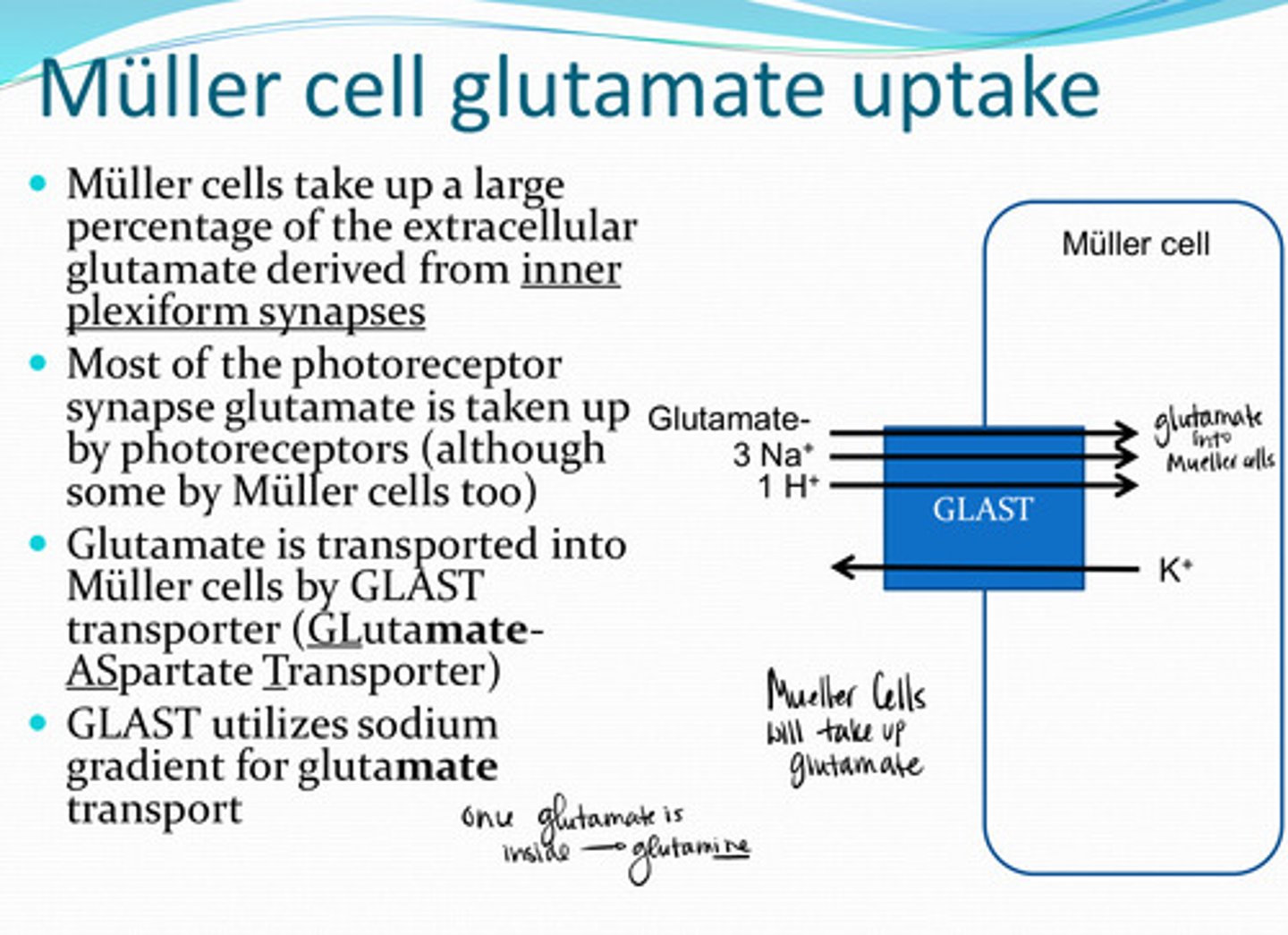
sodium
GLAST transporters utilize the _____ gradient for glutamate transport
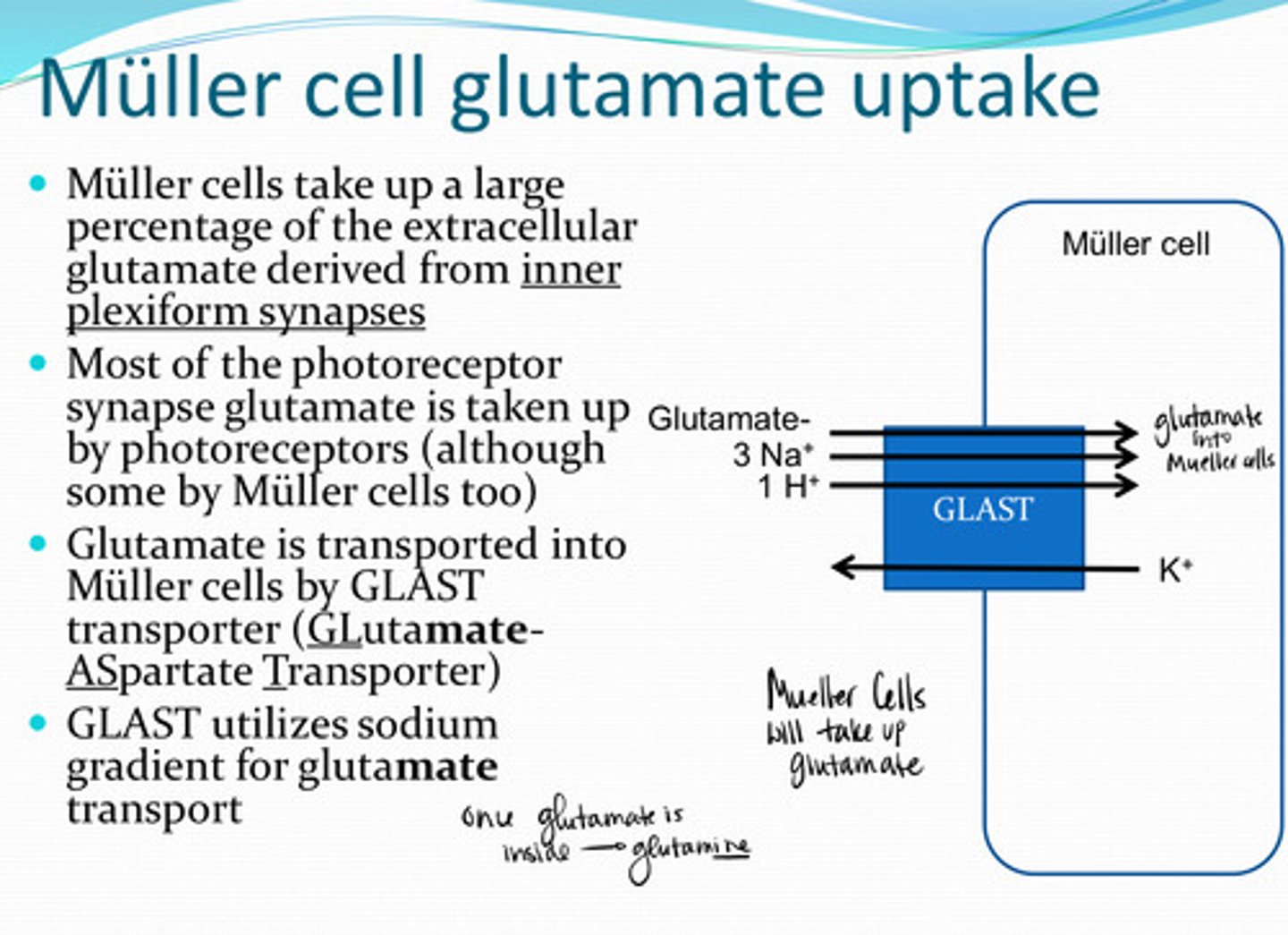
glutamine
Muller cells rapidly convert most of the glutamate to what?
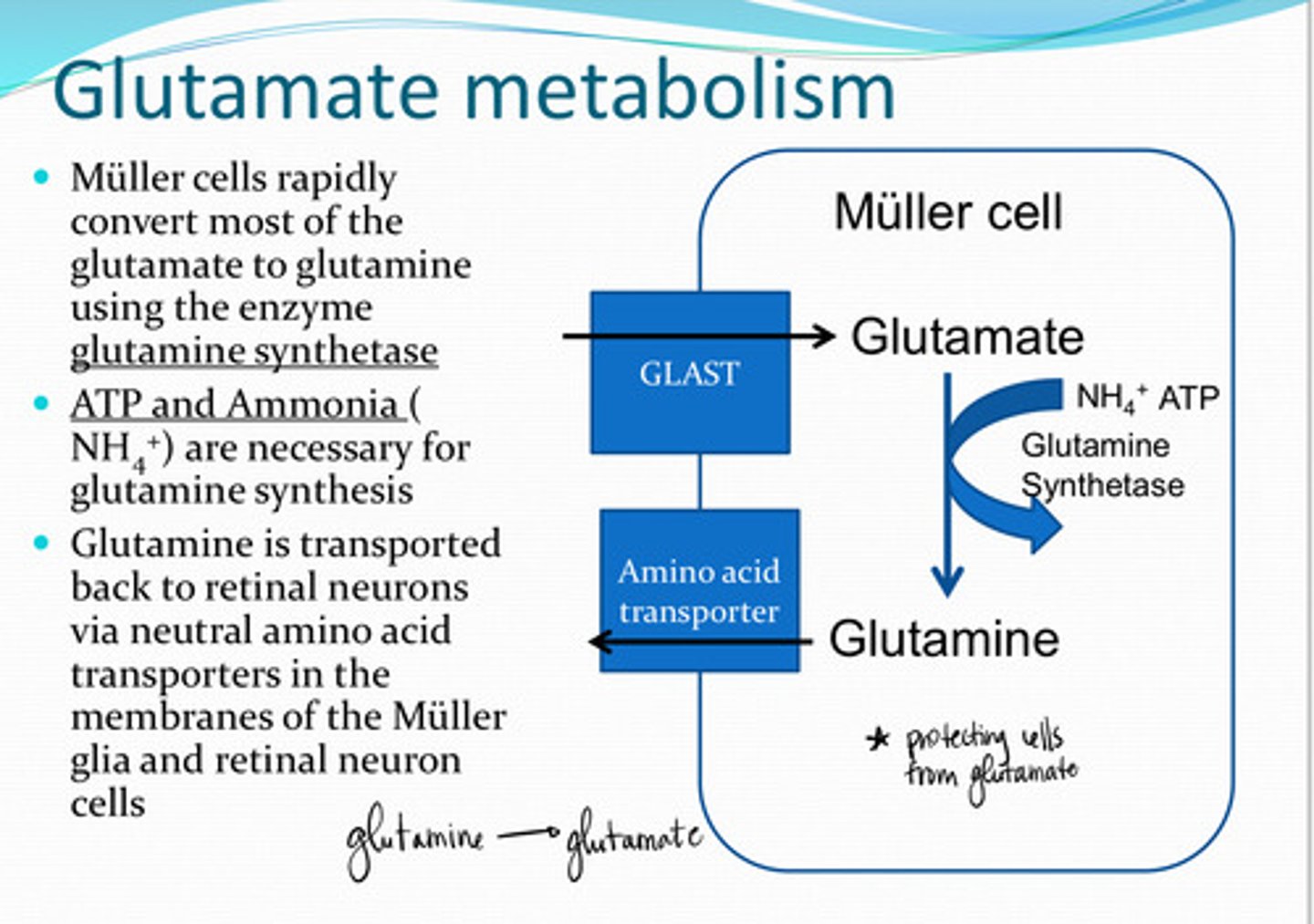
glutamine synthetase
Glutamate ---> glutamine in the Muller cells uses what enzyme?
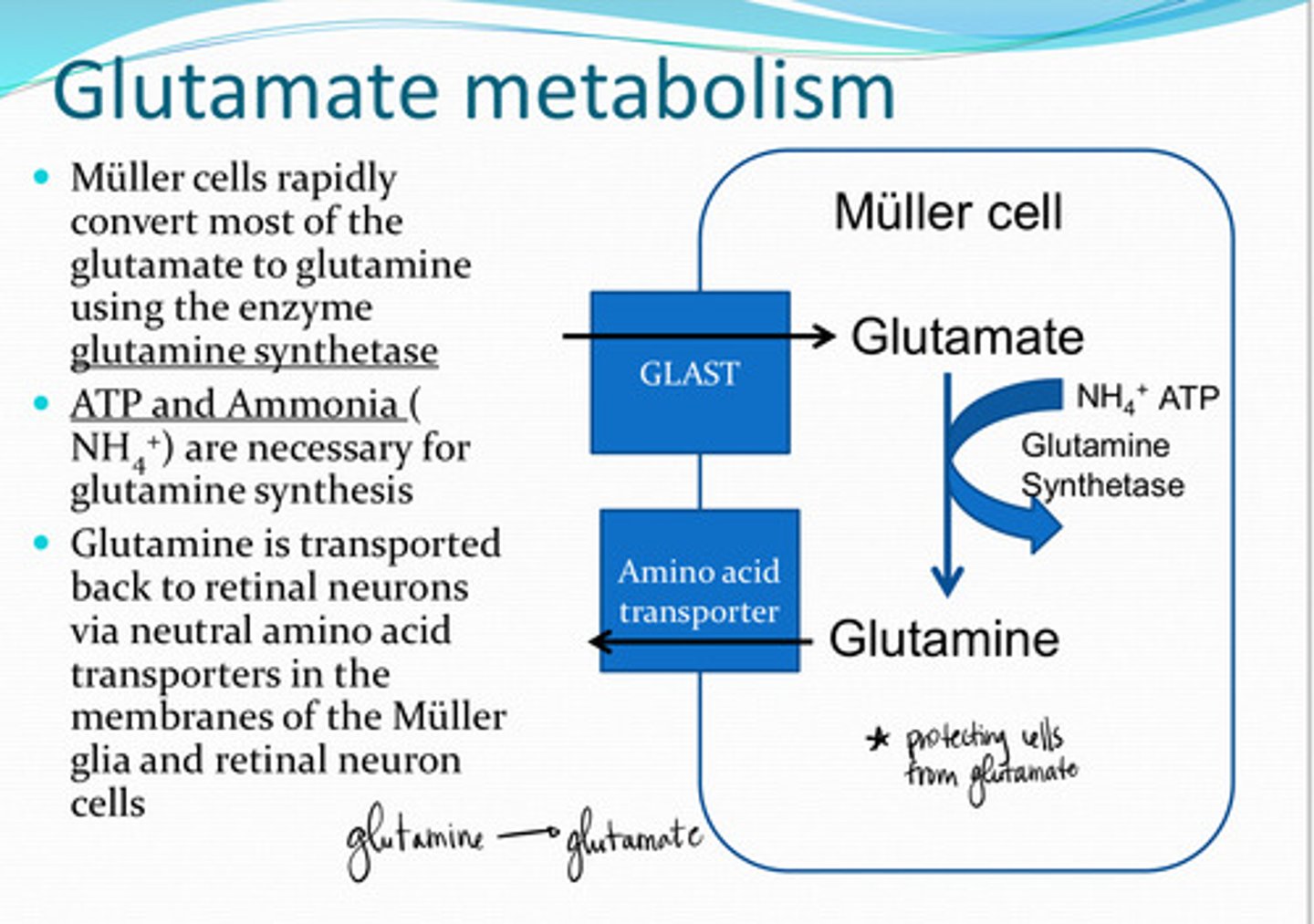
NH4+ (ammonia) and ATP
What 2 substances are needed for glutamine synthesis?
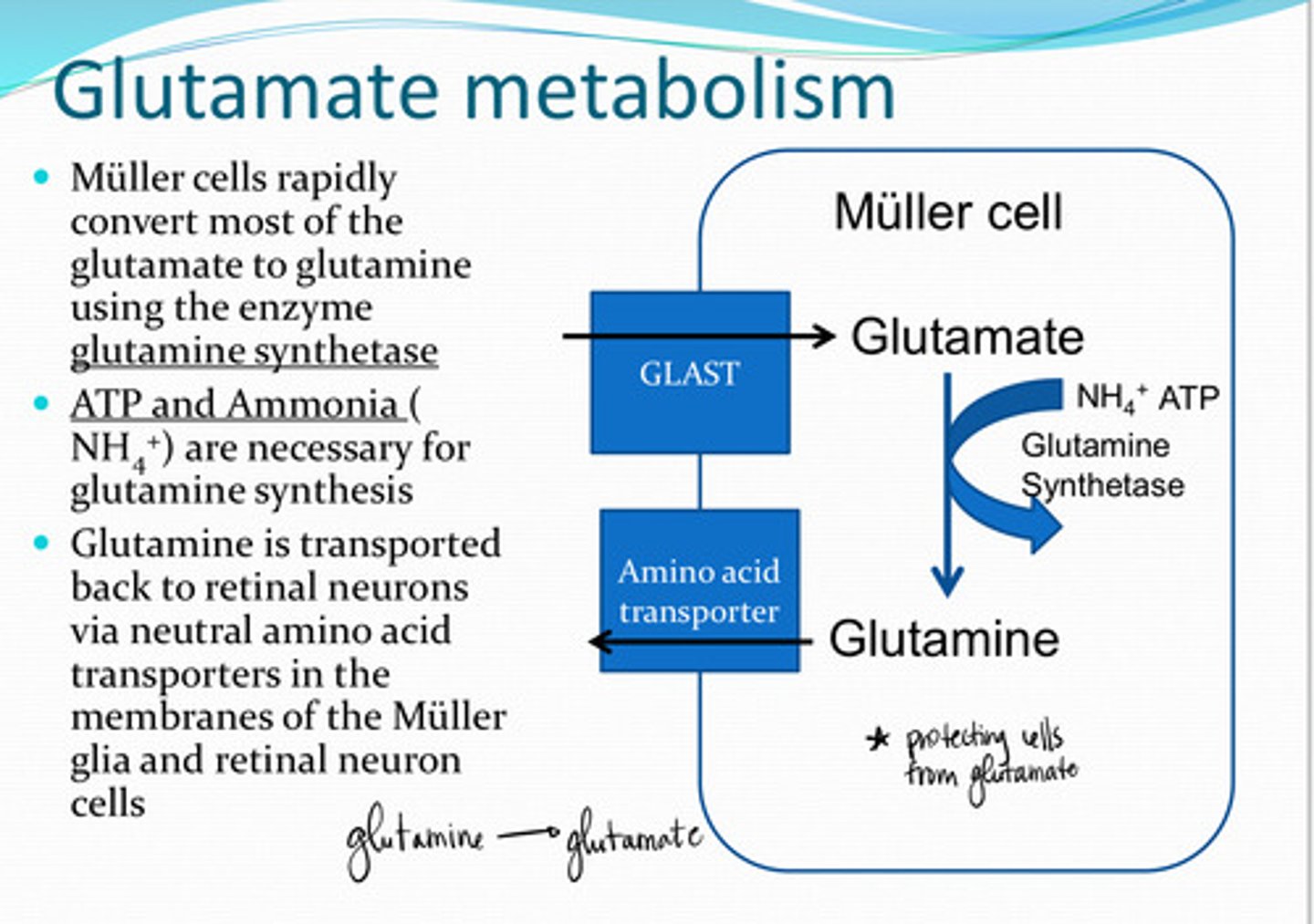
neutral amino acid transporters
Glutamine is transported back to retinal neurons via _______ transporters in the membranes of the Muller cell and retinal neuron cells
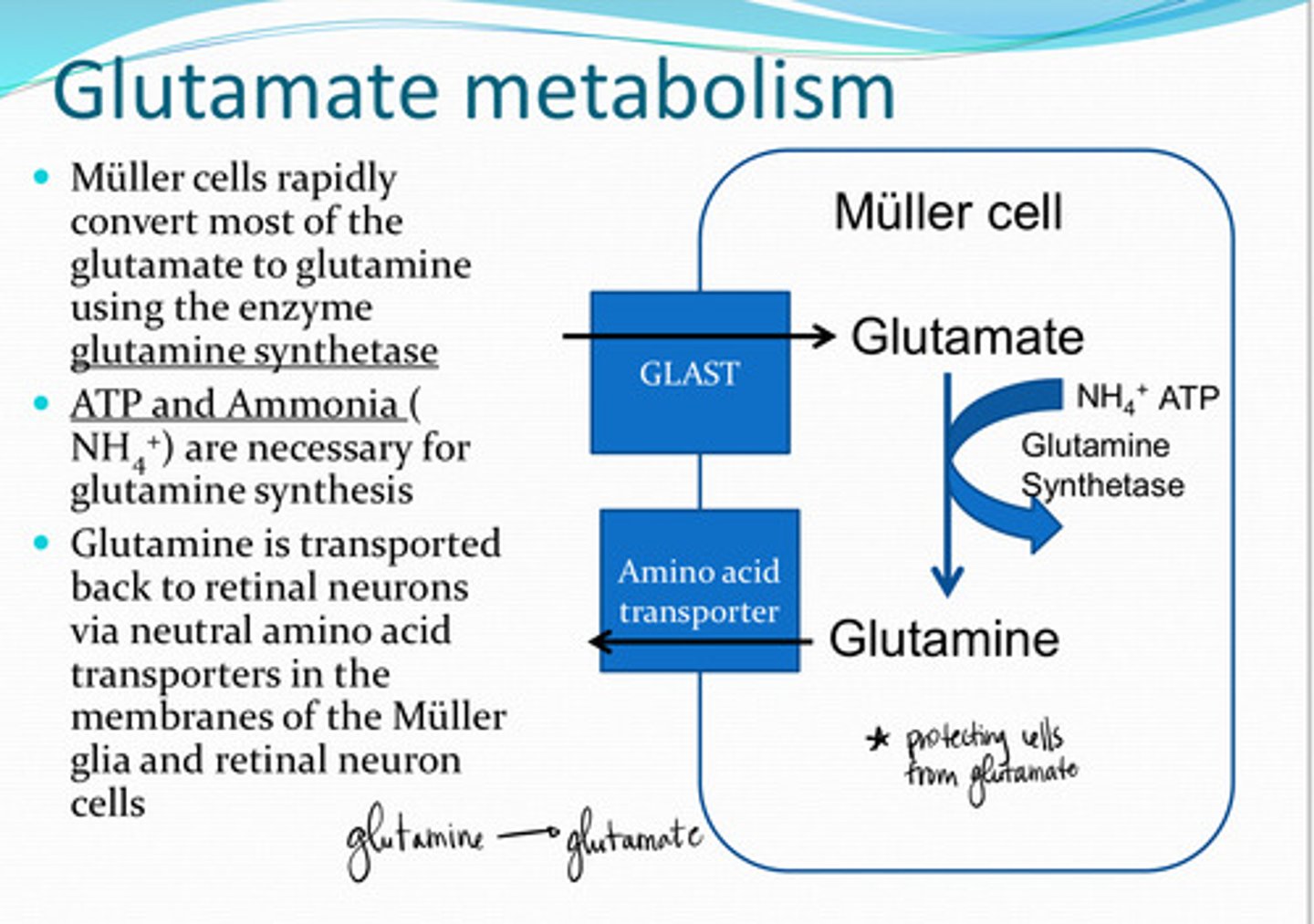
NH4+
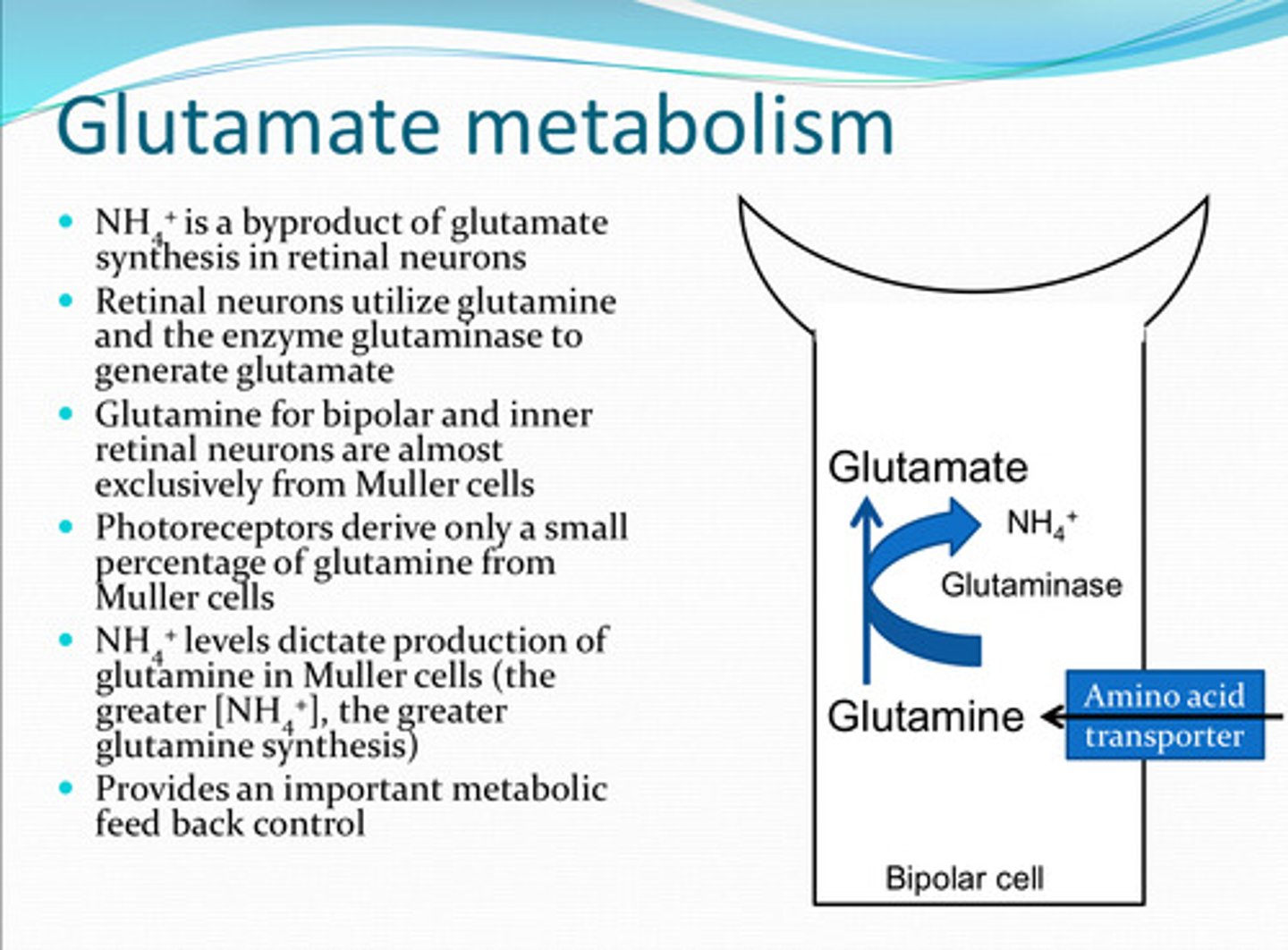
What is a biproduct of glutamate synthesis in retinal neurons?
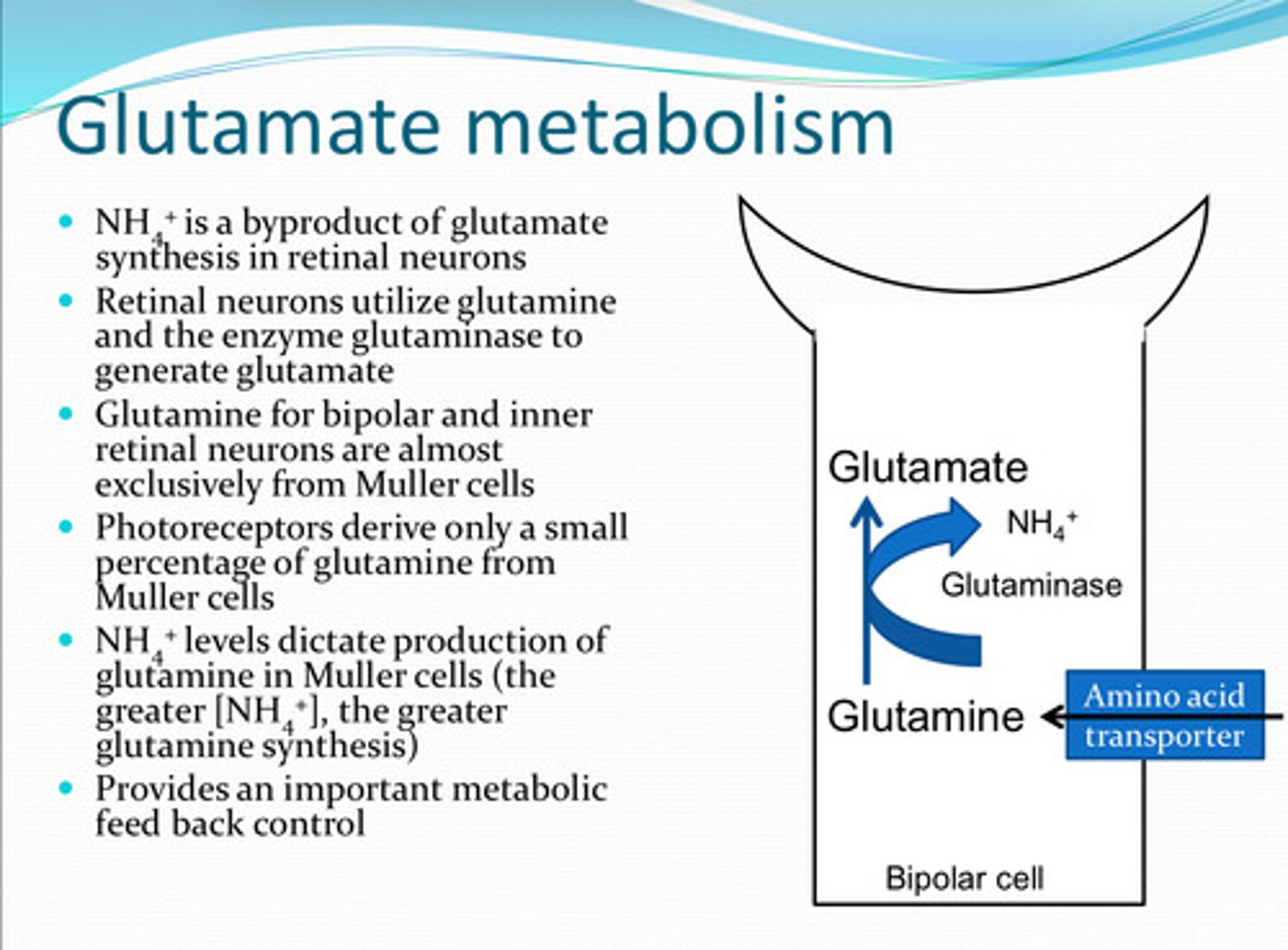
to generate glutamate
How do retinal neurons utilize glutamine and the enzyme glutaminase?
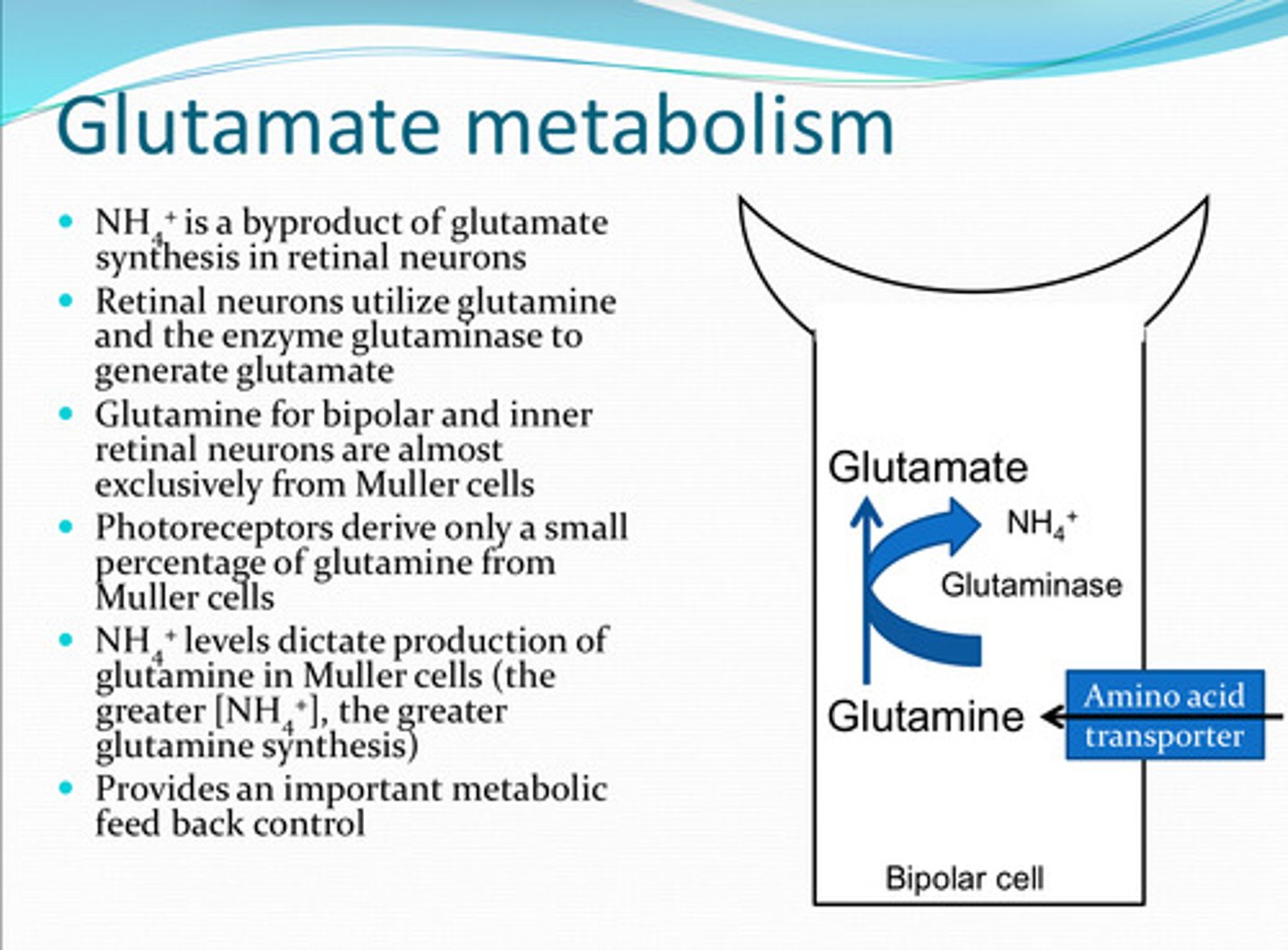
from Mueller cells
Glutamine in bipolar cells and inner retinal neurons is almost exclusively from what source?

small
Photoreceptors derive a (large/small) amount of glutamine from Muller cells
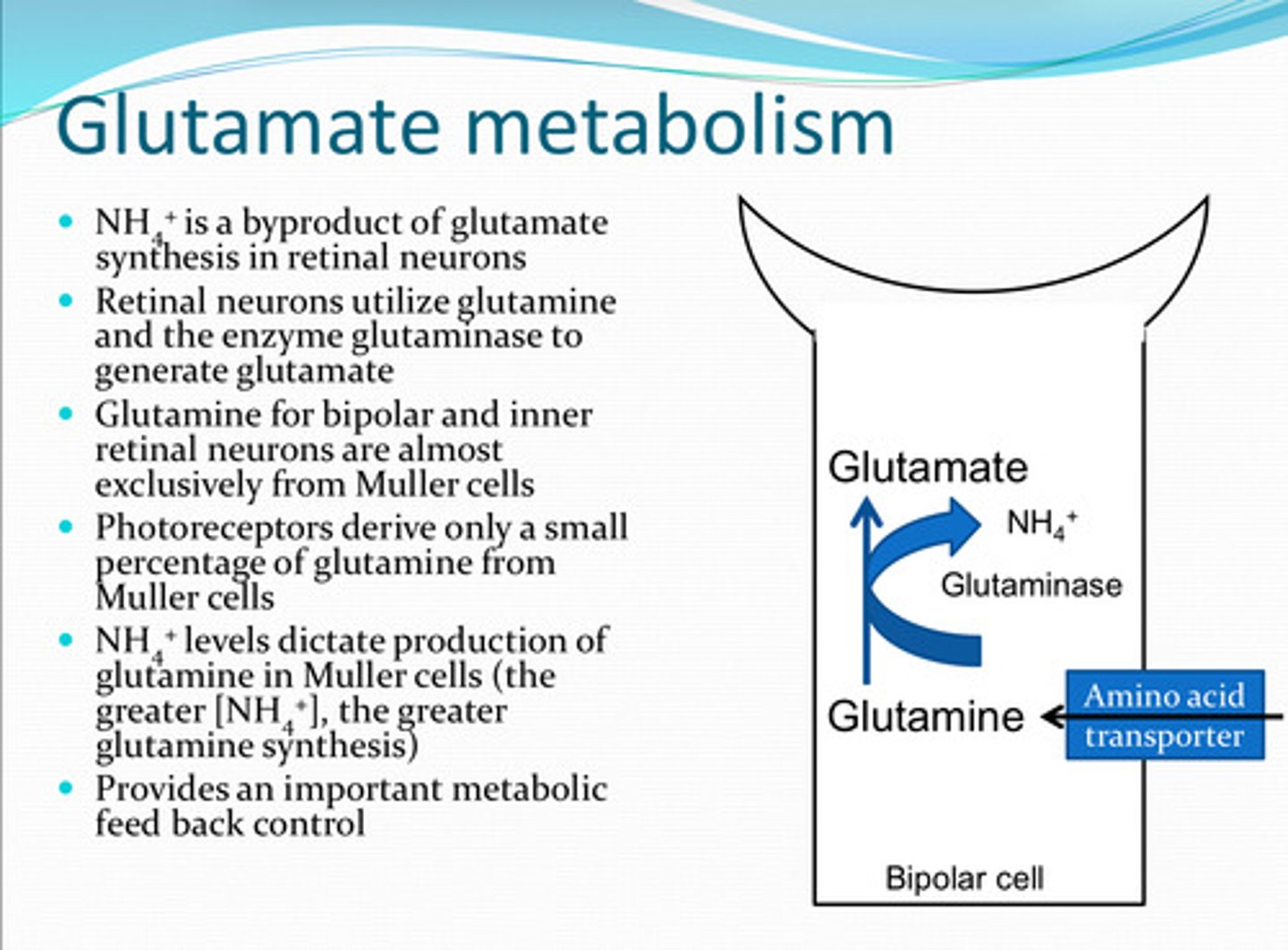
glutamine in Muller cells
**increase in NH4+ = increase in glutamine synthesis
NH4+ levels dictate production of what?
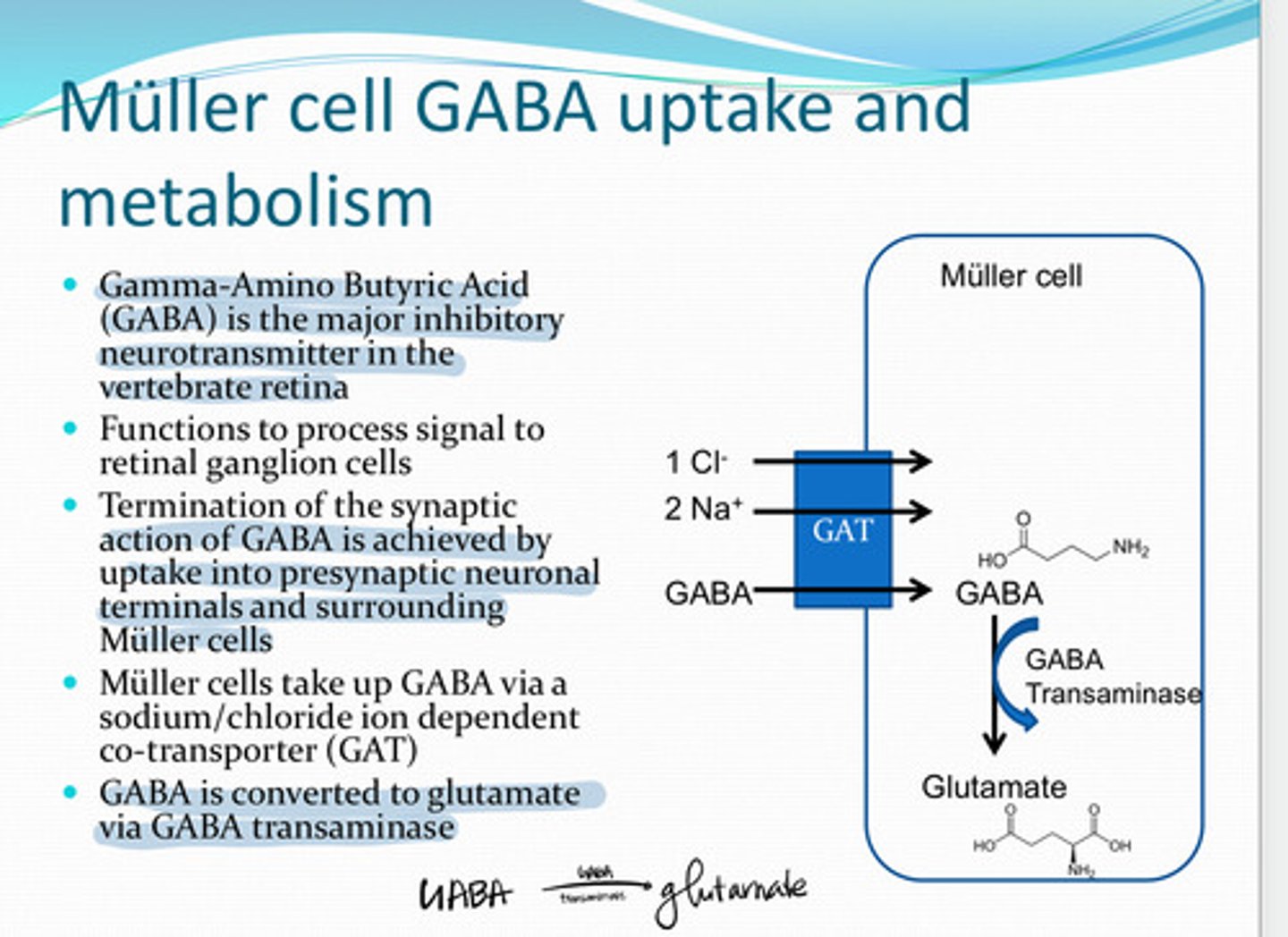
GABA (Gamma Amino Butyric Acid)
The major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate retina
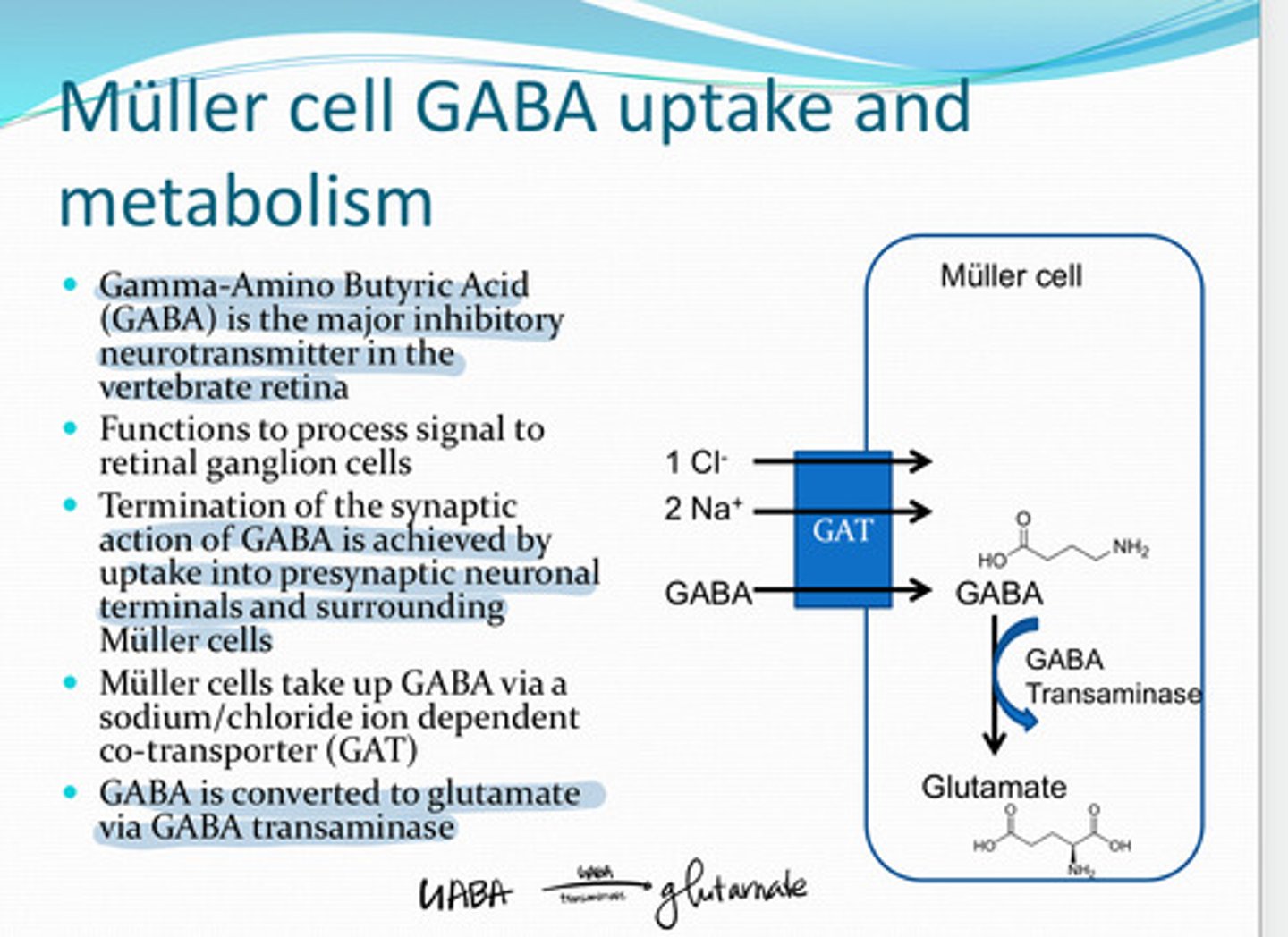
to process signal to retinal ganglion cells
What is the function of GABA in the retina?
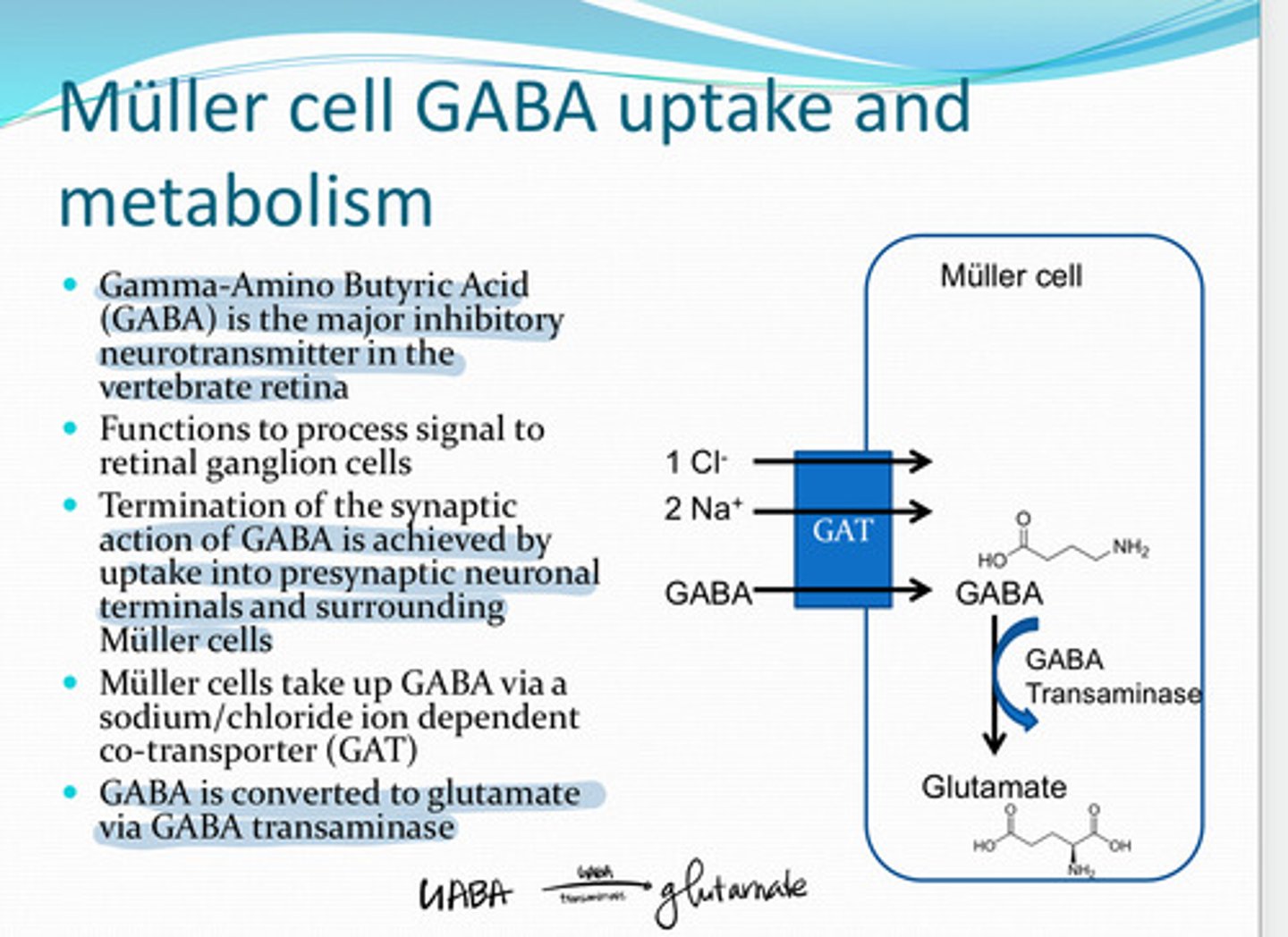
via a Na+/Cl- ion dependent co-transporter (GAT)
How do Muller cells take up GABA?
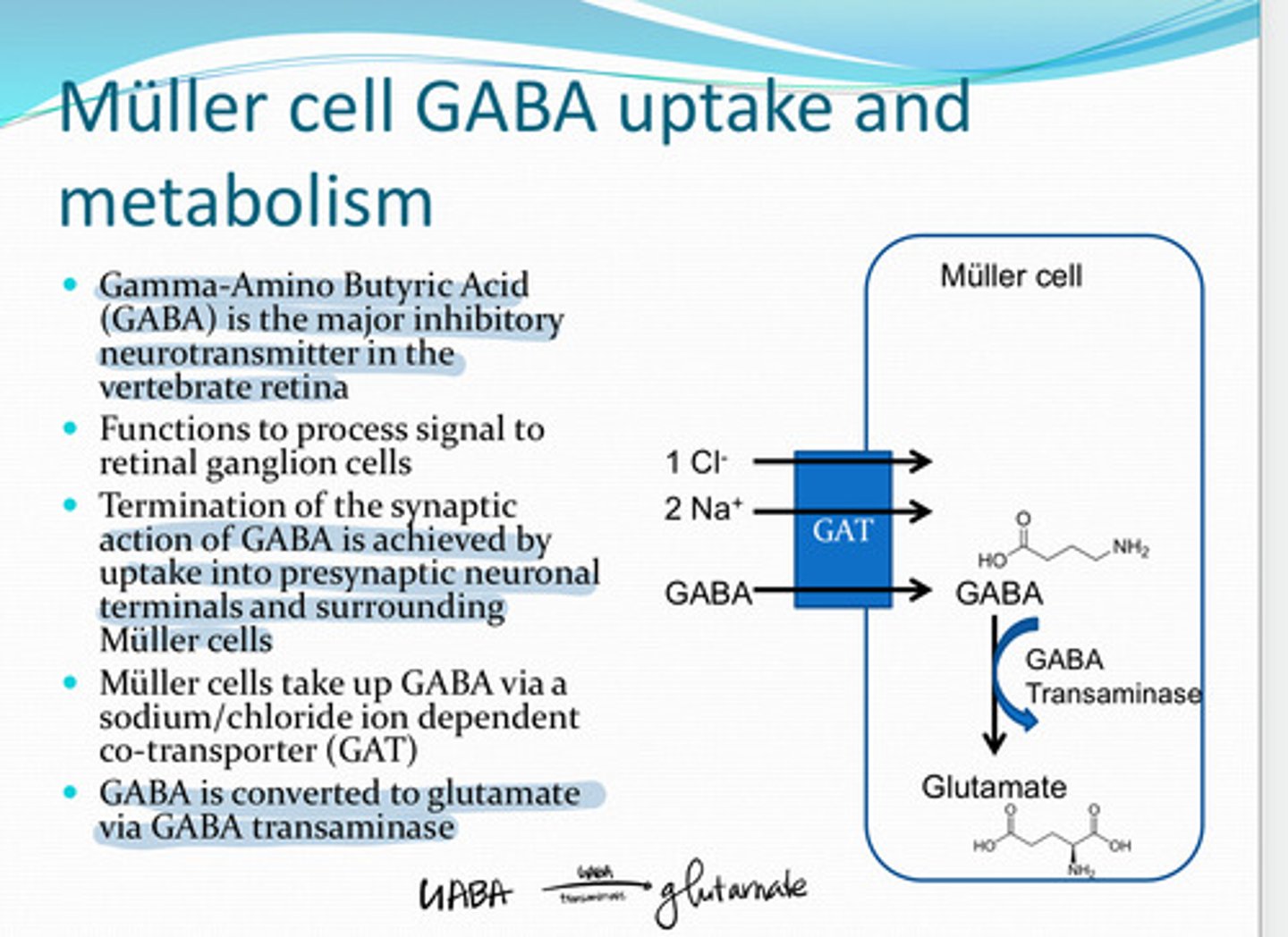
glutamate
GABA is converted to ______ in the Muller cell via GABA transaminase
The Inner blood retinal barrier
What is necessary to maintain a stable ionic environment to ensure proper function of the specialized environment of the retina?
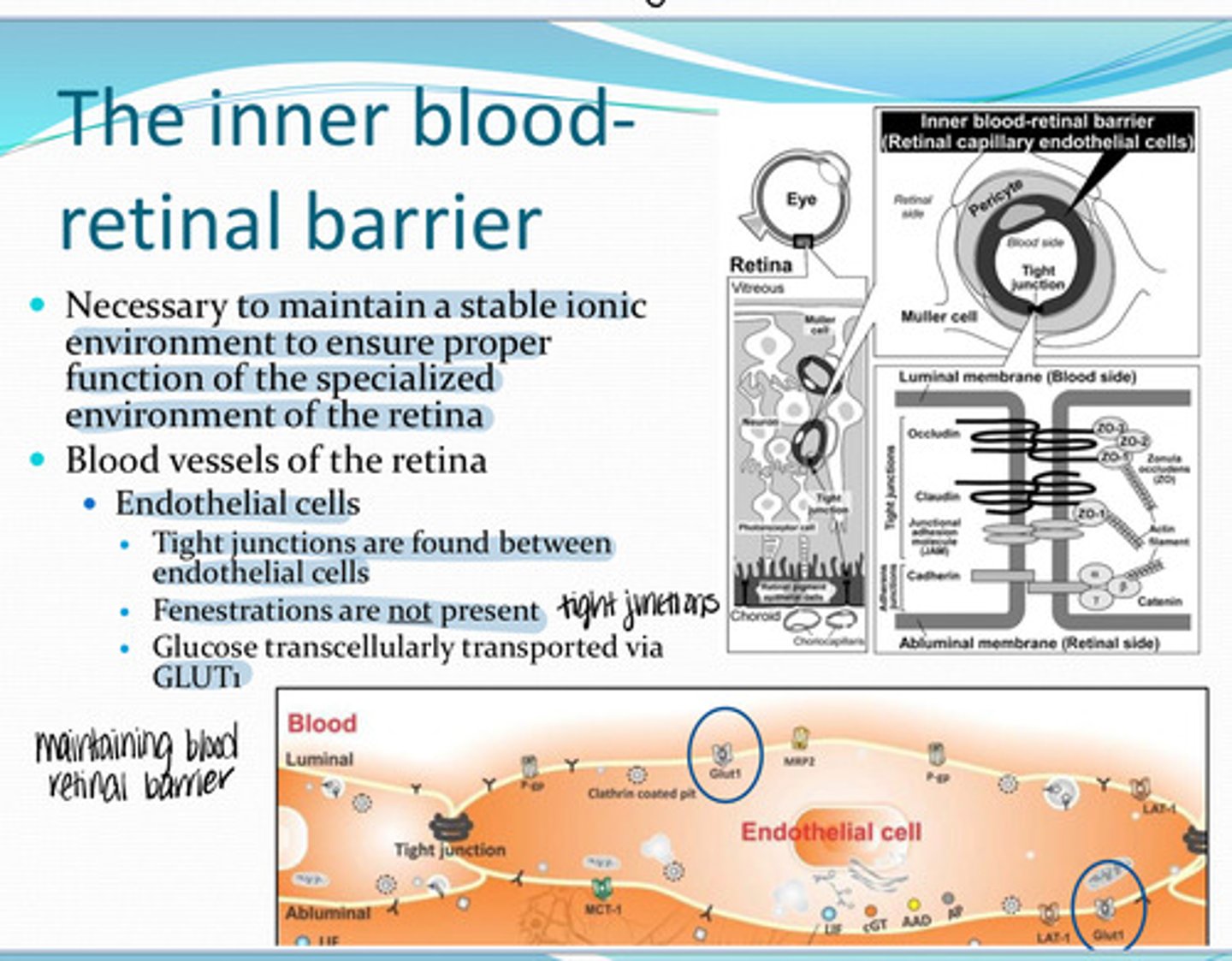
Endothelial cells
Where are blood vessels present in the retina?
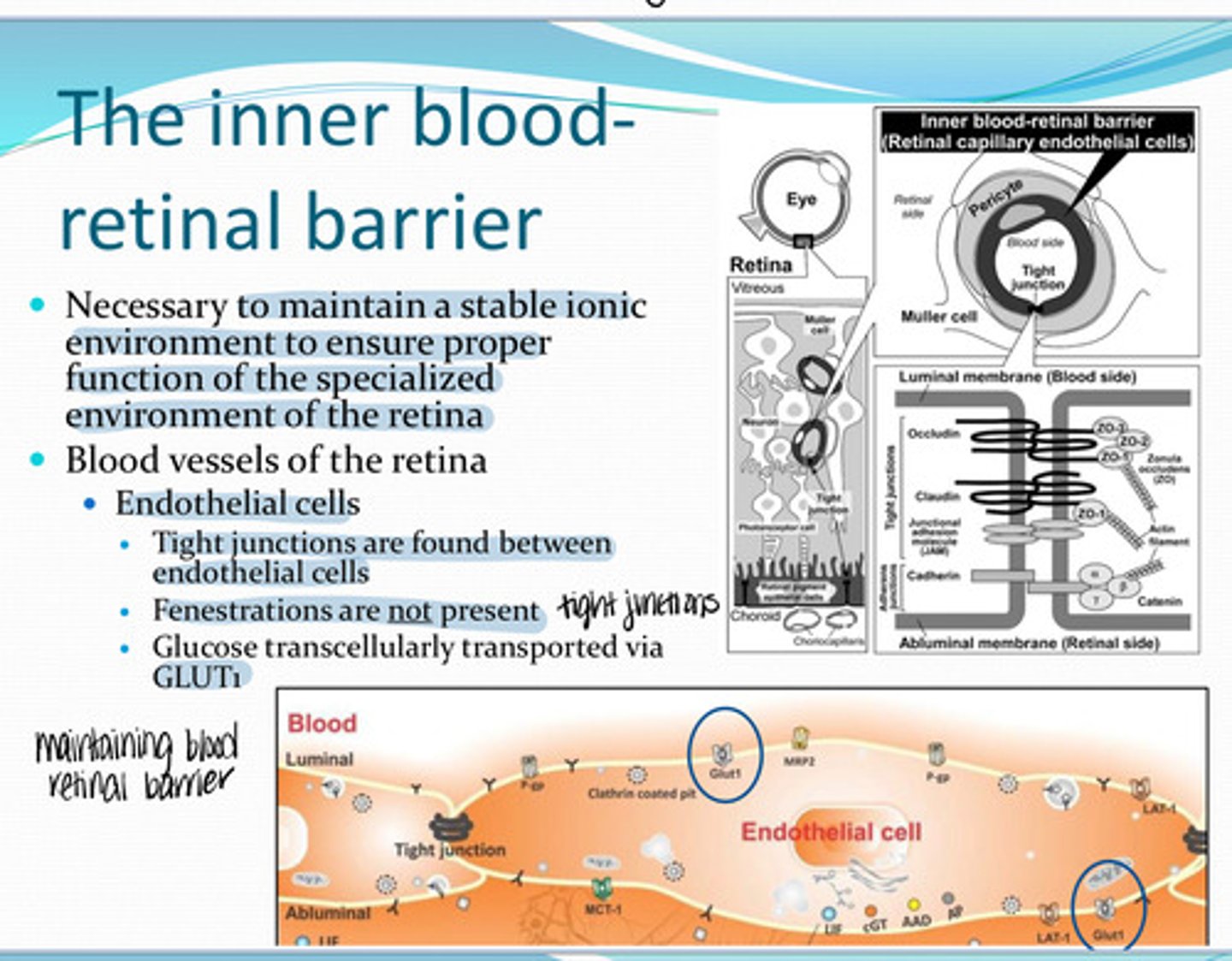
no fenestrations -- tight junctions are found between the endothelial cells
Are there fenestrations of the retinal endothelial cells where blood vessels are present in the retina?
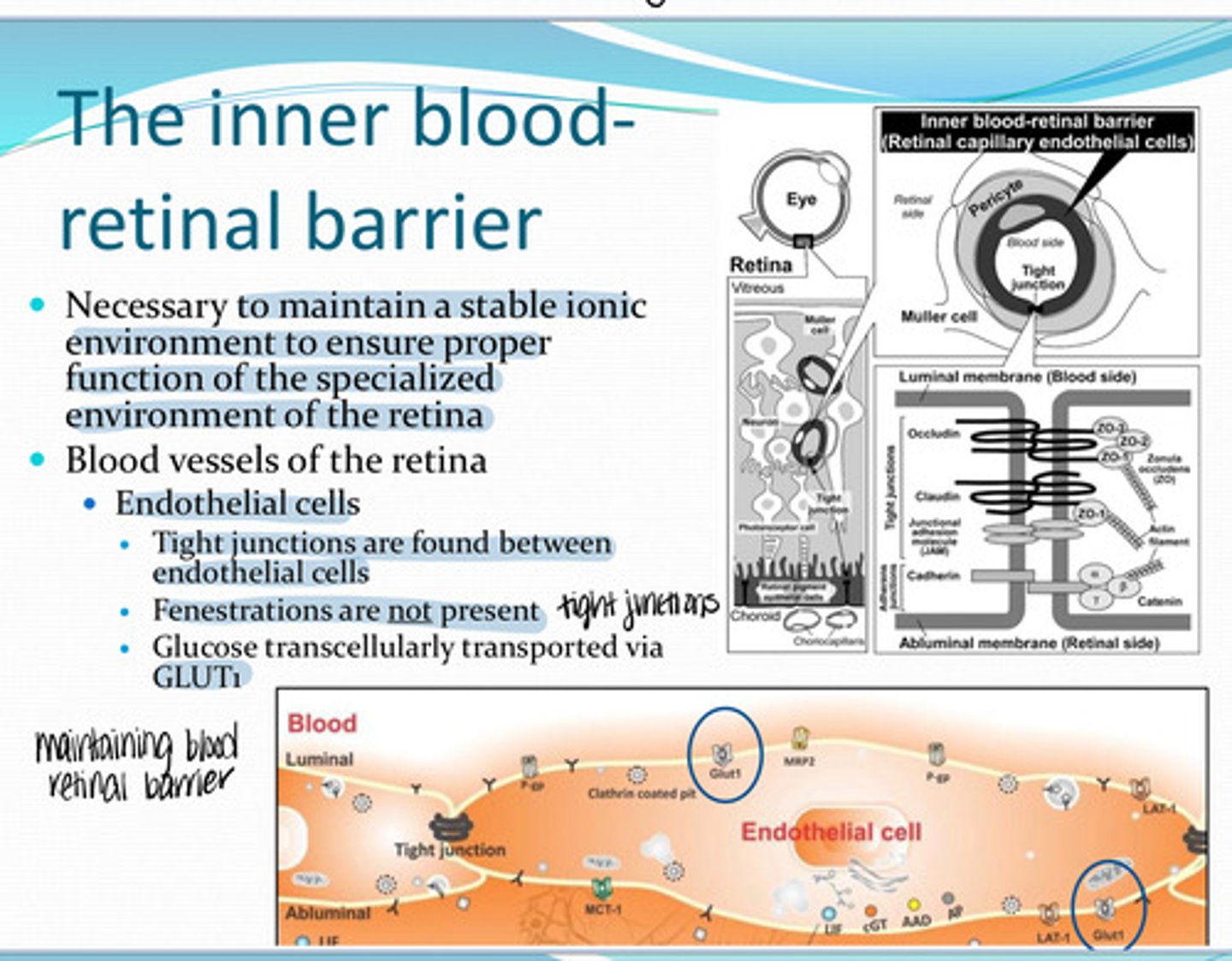
GLUT1 -- transcellularly
In the endothelial cells of the retina, glucose is transported via _______
yes
Do the retinal arteries have a distinct structure?
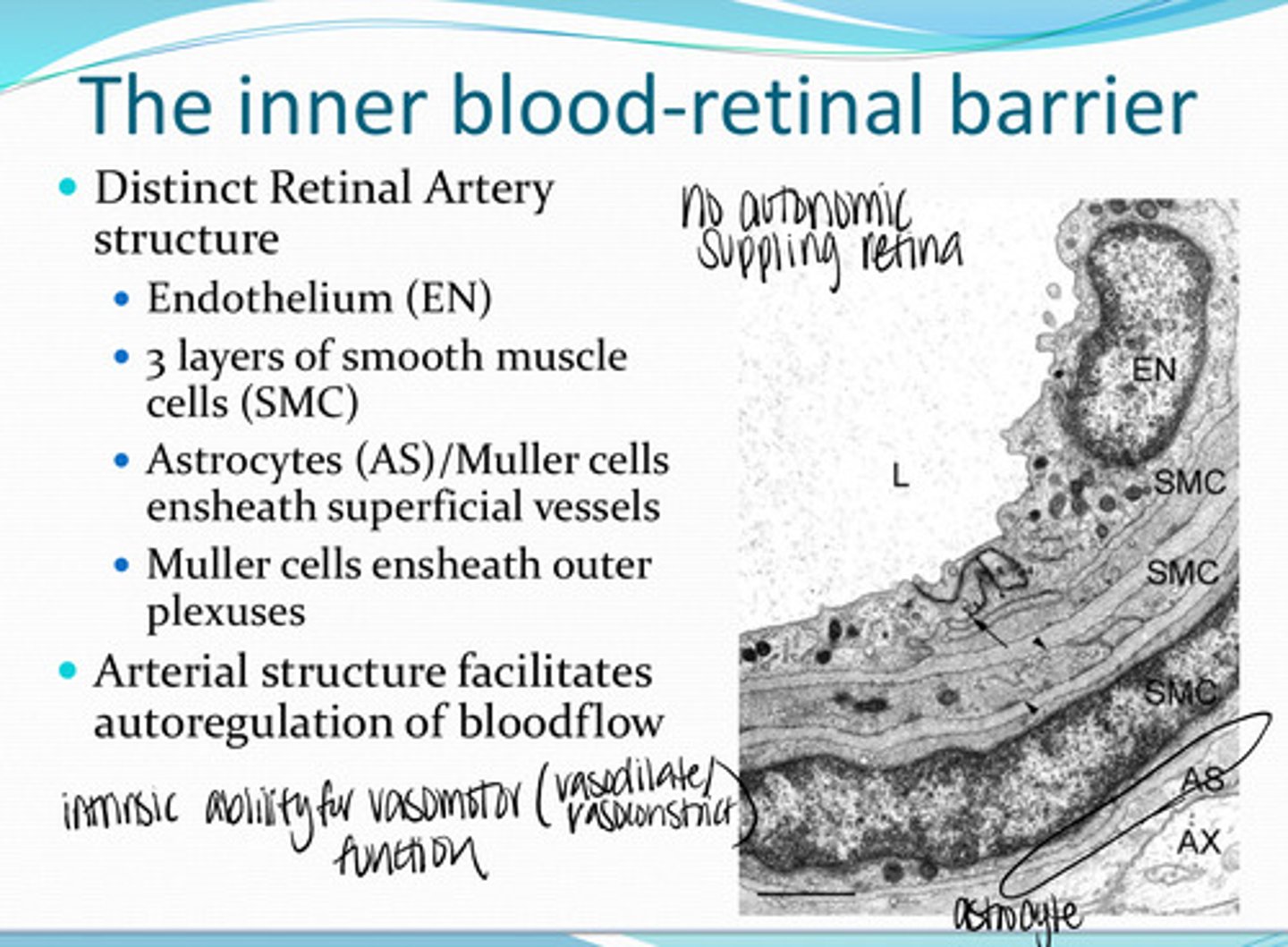
-endothelium
-3 layers of smooth muscle cells
-astrocytes/Muller cells ensheath the superficial vessels
-muller cells ensheath outer plexuses
What structures compose the Retinal Arteries?
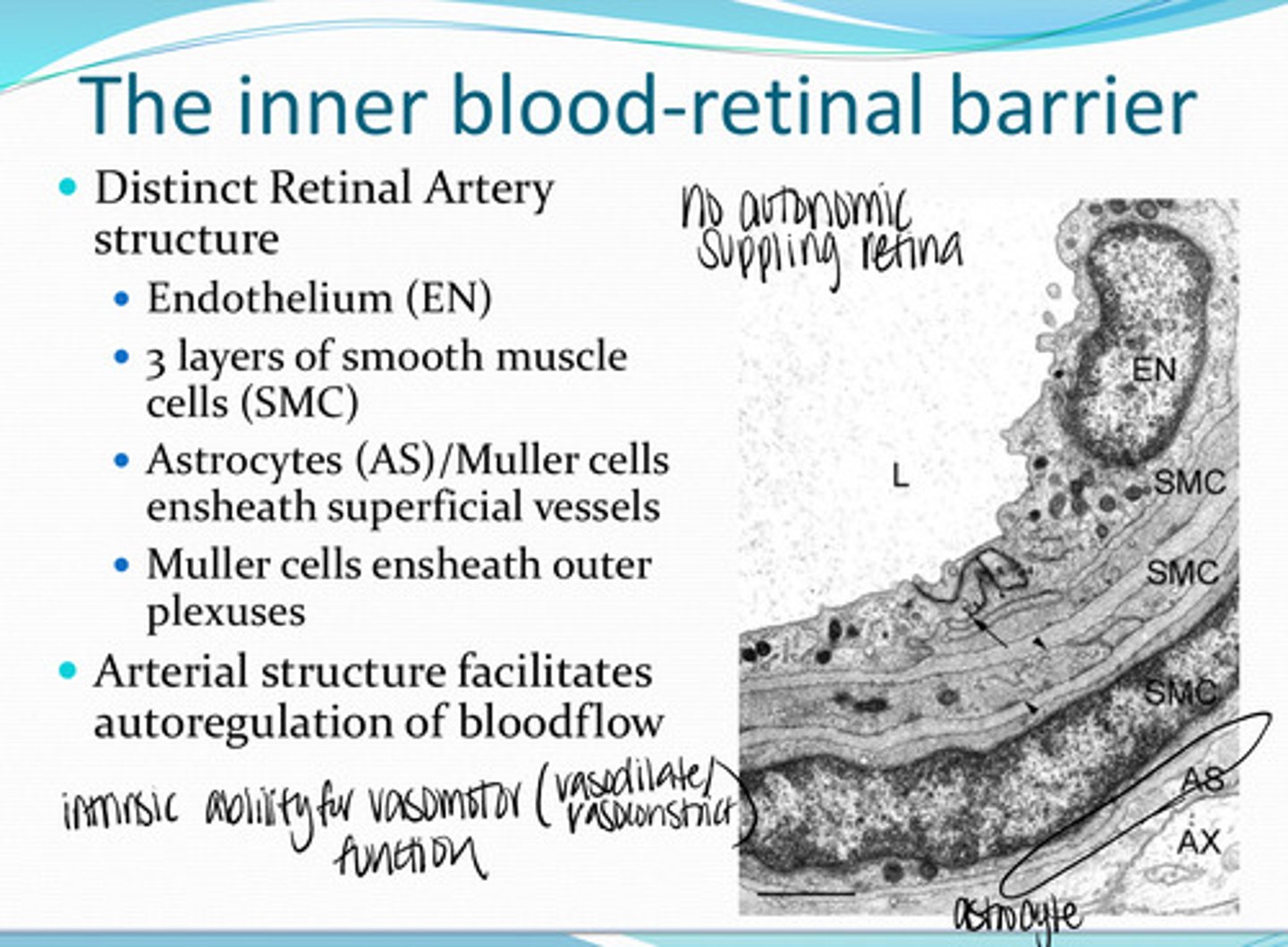
bloodflow (intrinsic ability for vasoconstriction and vasodilation)
The arterial structure of the retina facilitates autoregulation of what?
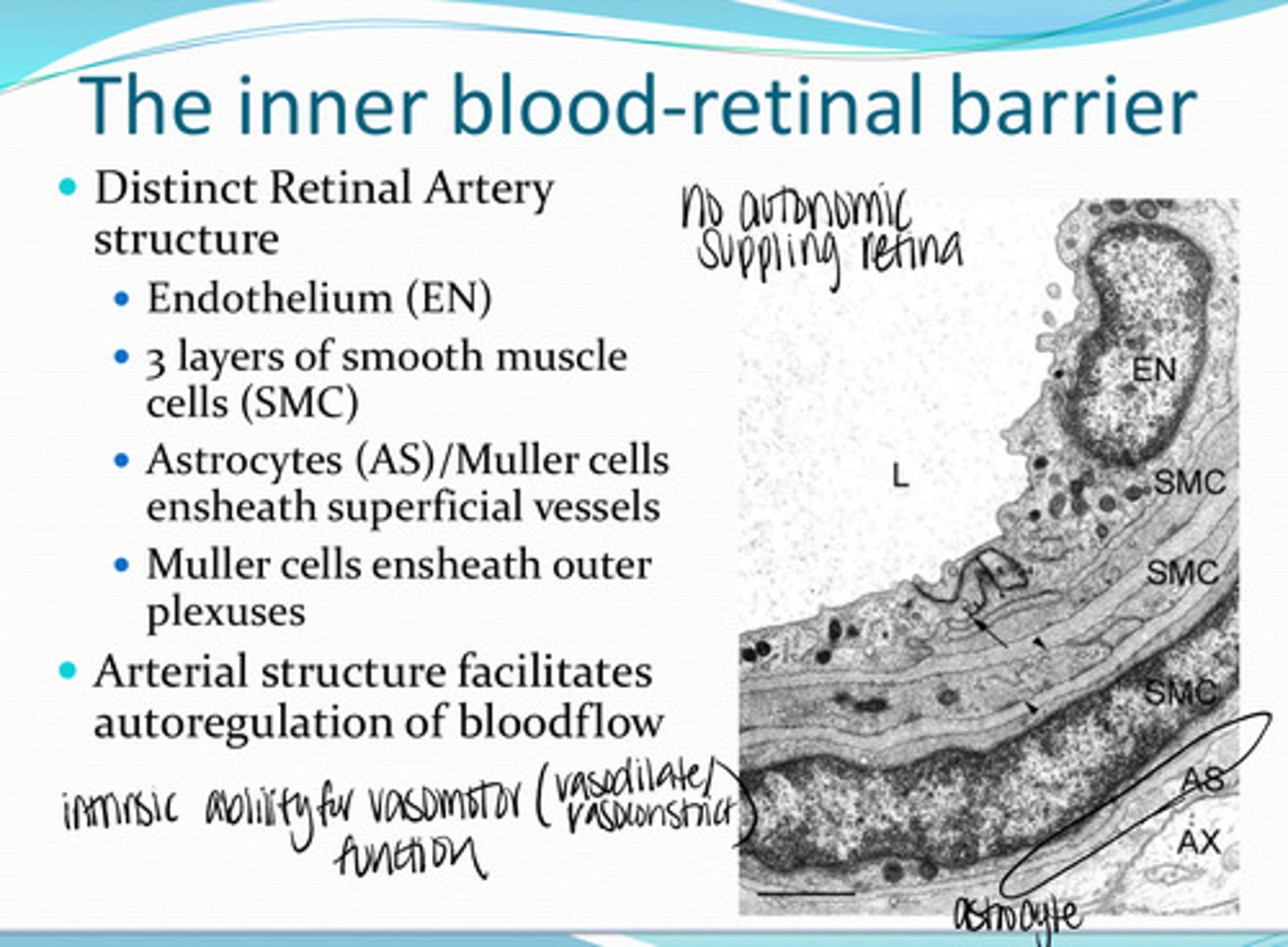
no
Is there any autonomic supply to the retinal blood vessels?
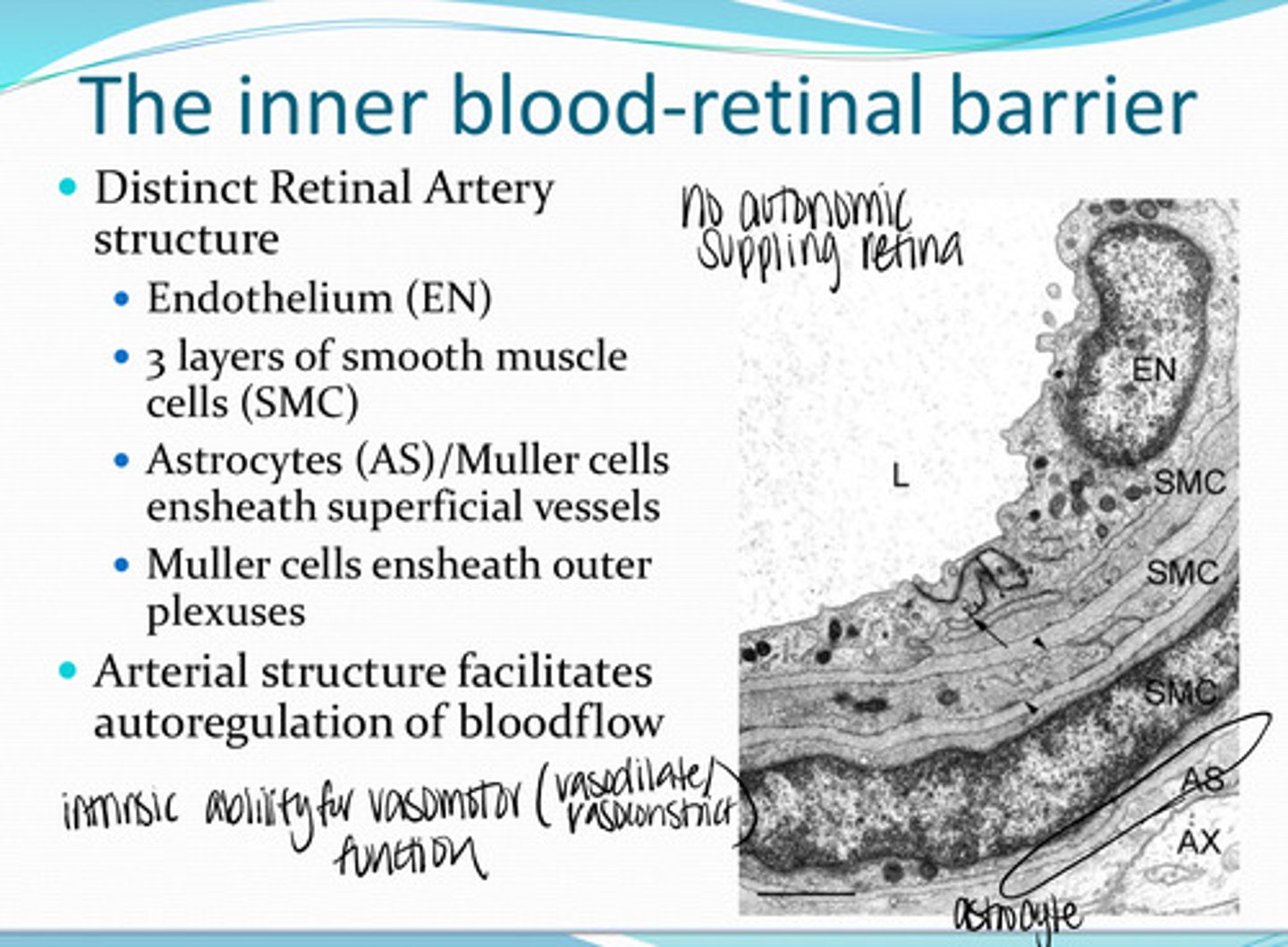
necessary to maintain a stable ionic environment to ensure proper function of the specialized environment of the retina
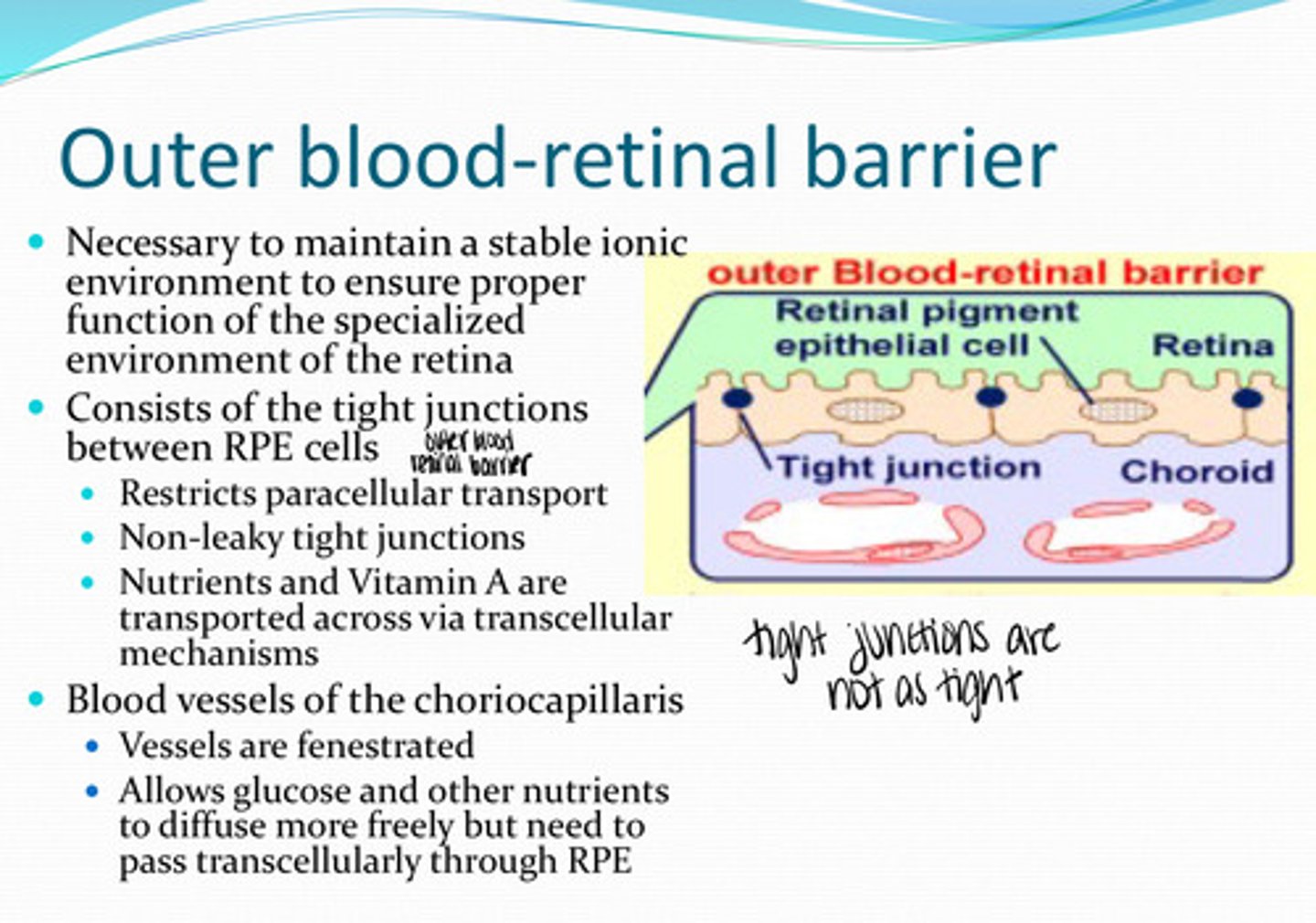
What is the outer blood retinal barrier necessary for?
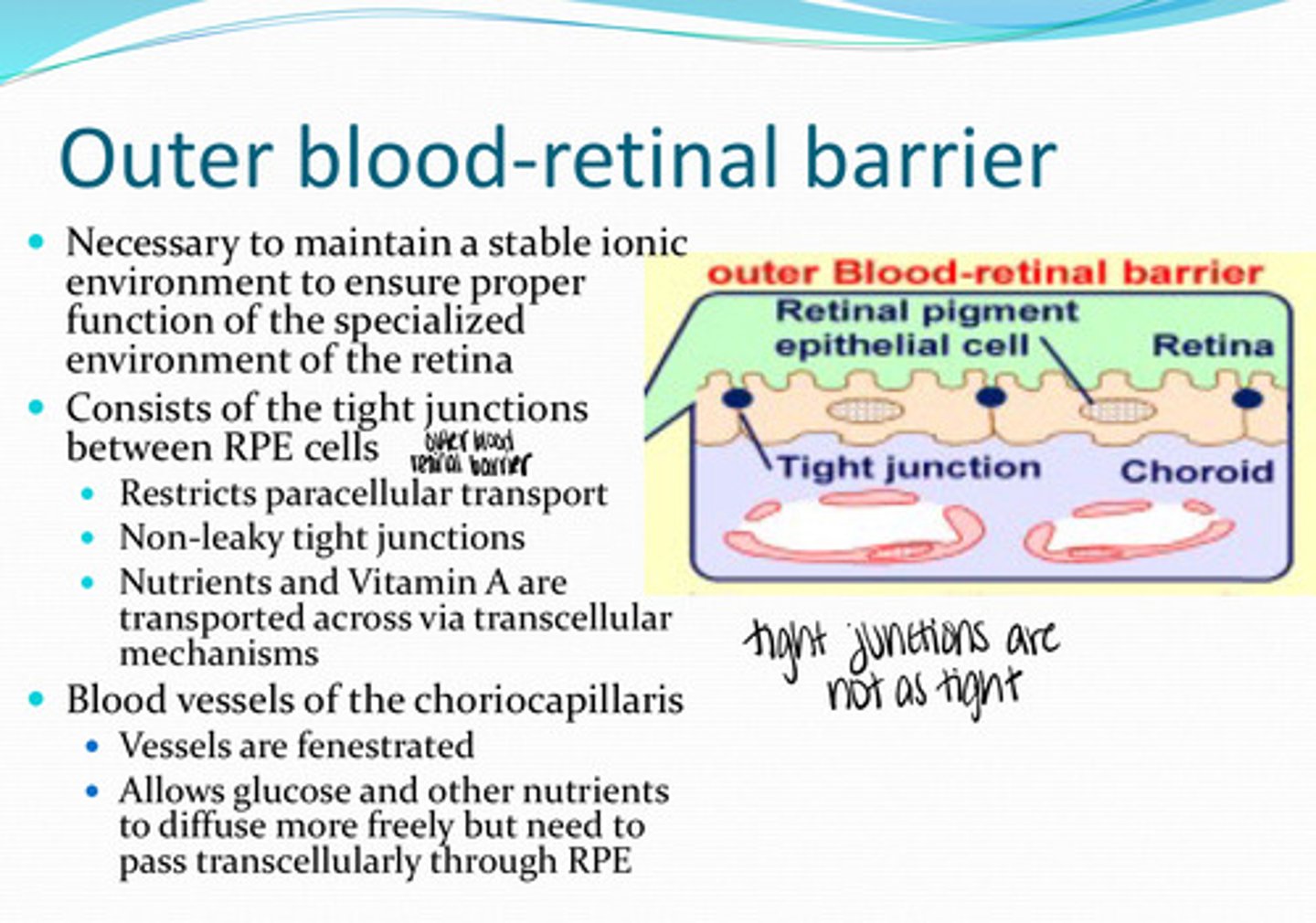
tight junctions between the RPE cells
What does the outer blood retinal barrier consist of?
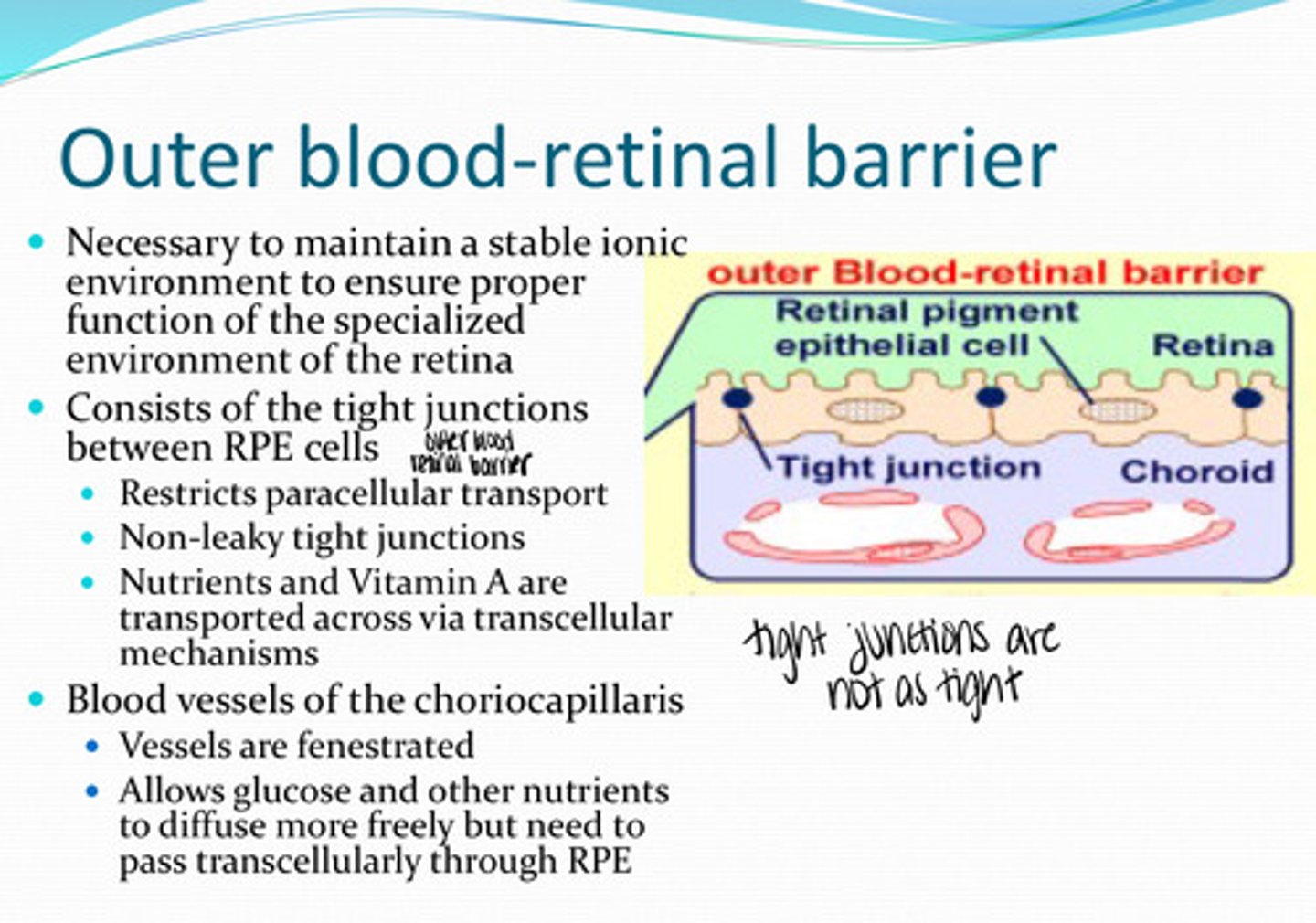
no -- non-leaky tight junctions are present
Is there any paracellular transport between RPE cells?
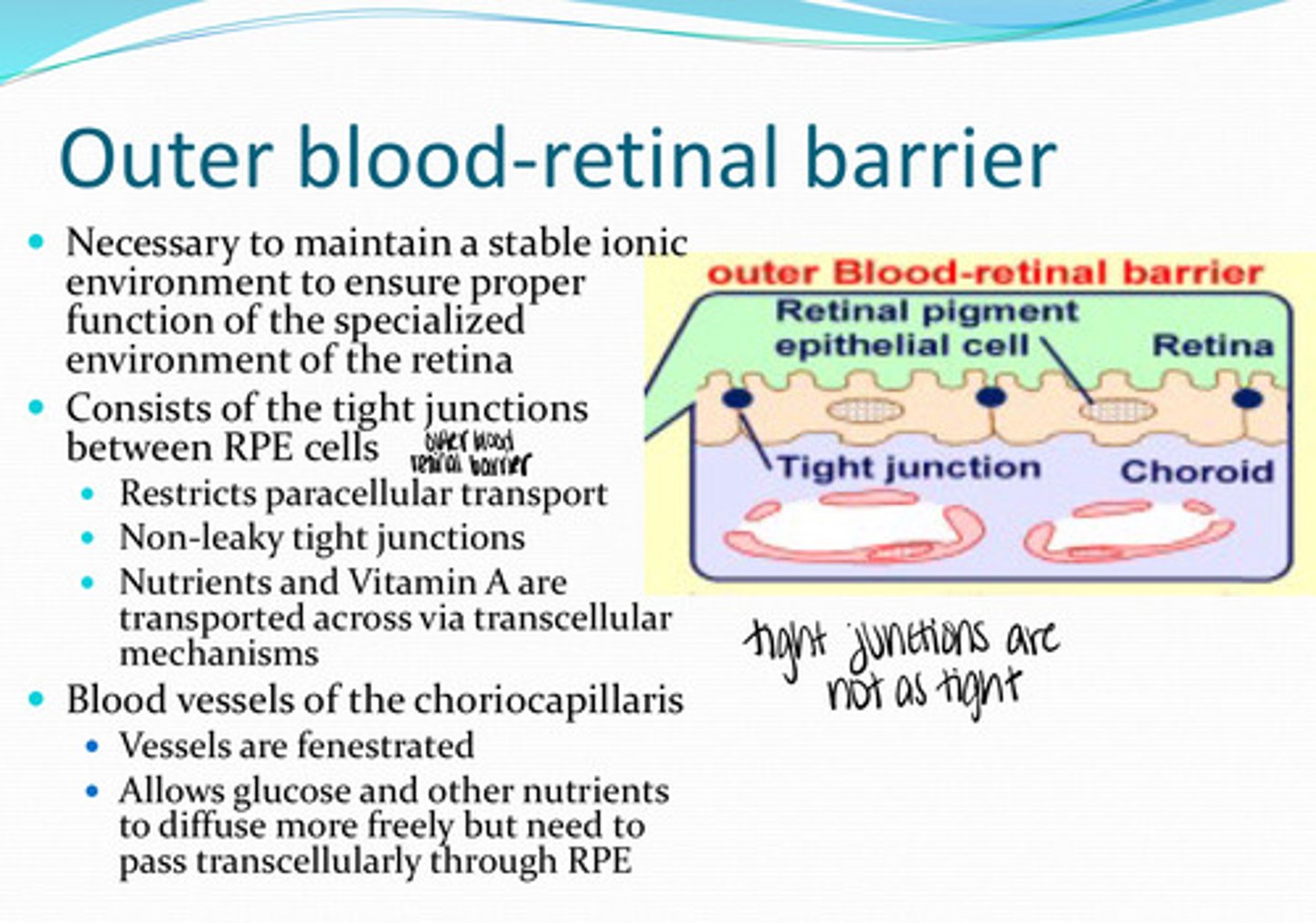
nutrients, vit A
What is transported transcellularly across the RPE membrane?
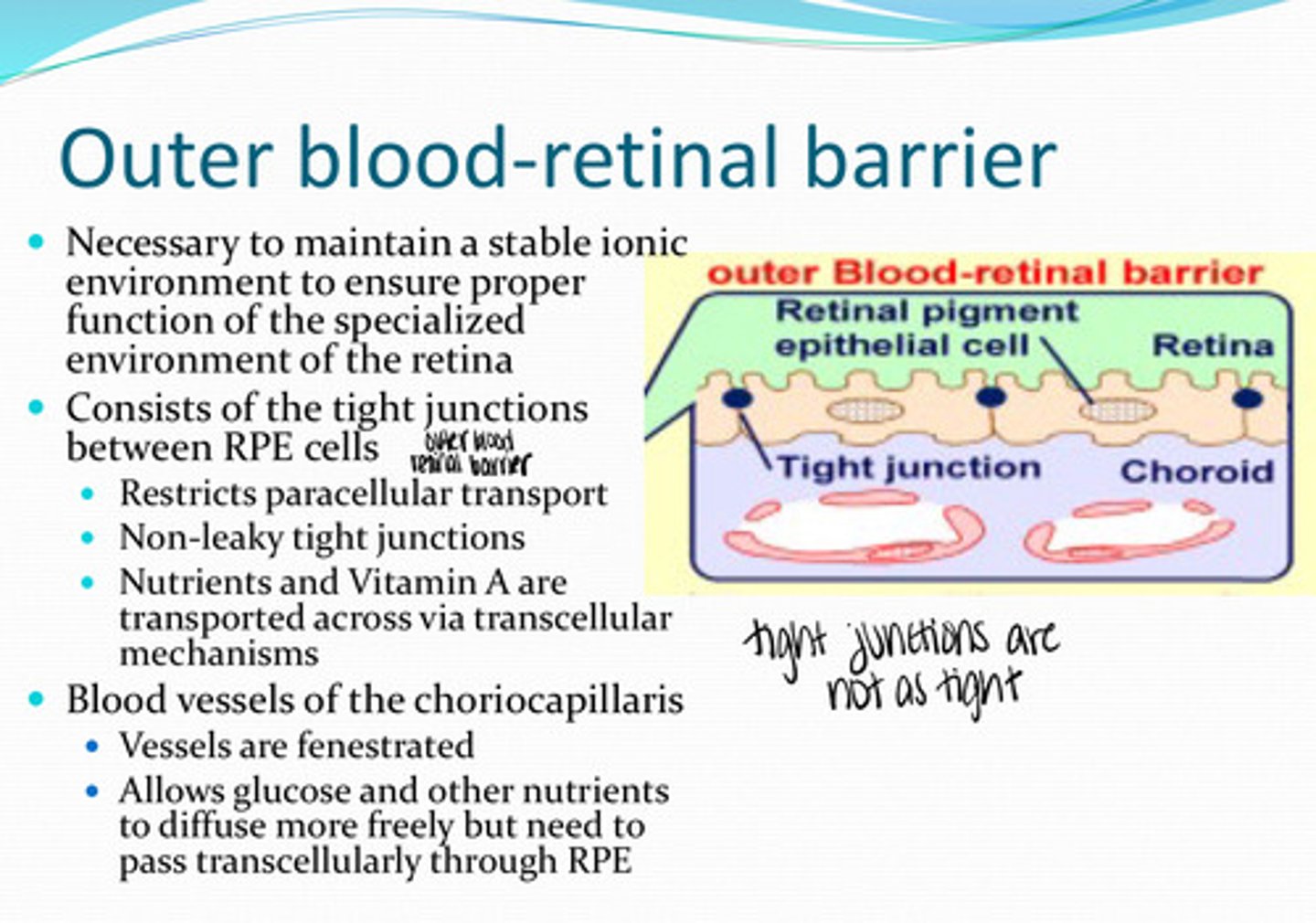
yes
Are the blood vessels of the choriocapillaris fenestrated?
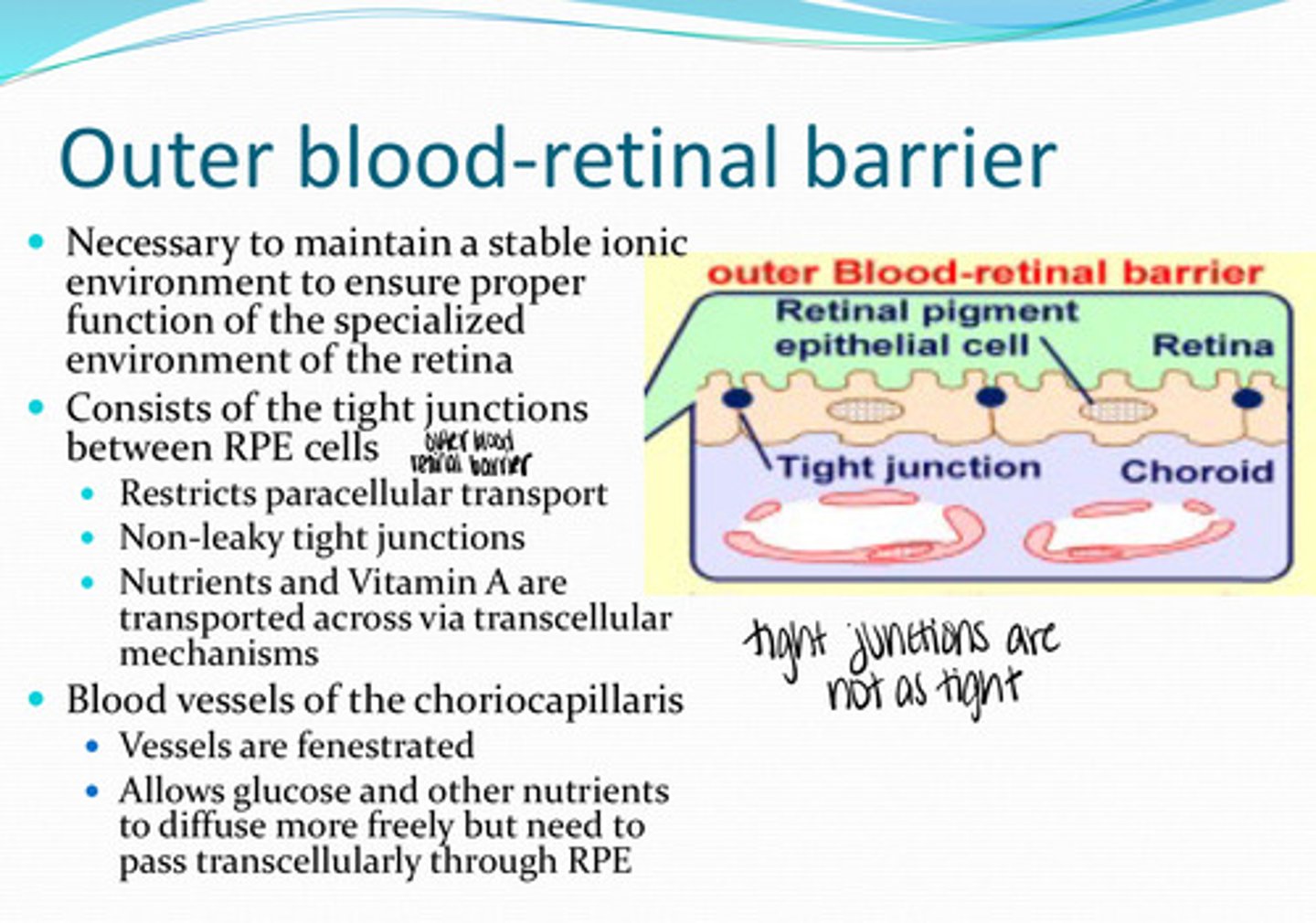
allows glucose and other nutrients to diffuse more freely but need to pass transcellularly throught the RPE
What is the importance of fenestrated choriocapillaris blood vessels?
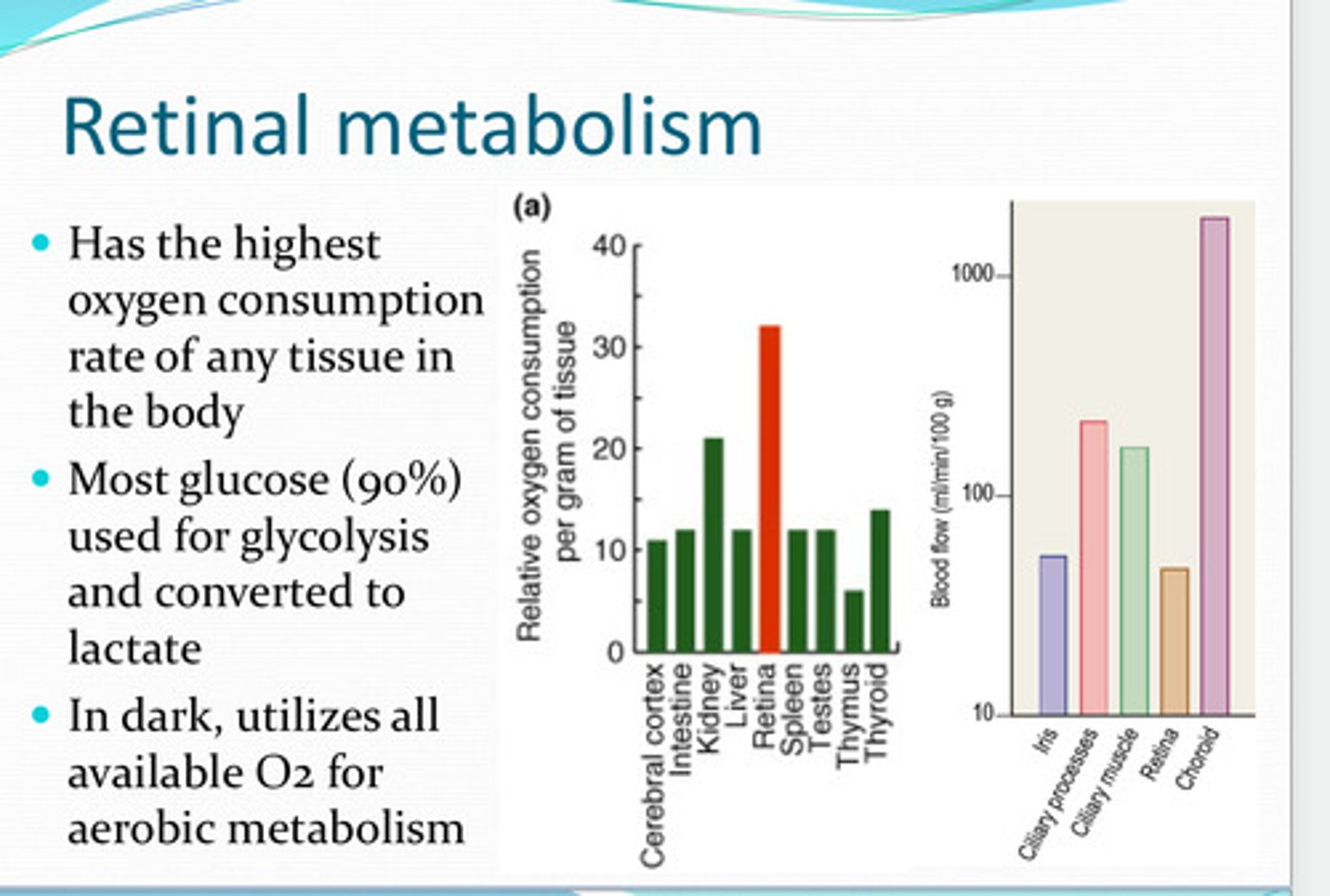
retina
What has the highest O2 consumption rate of any tissue in the body?
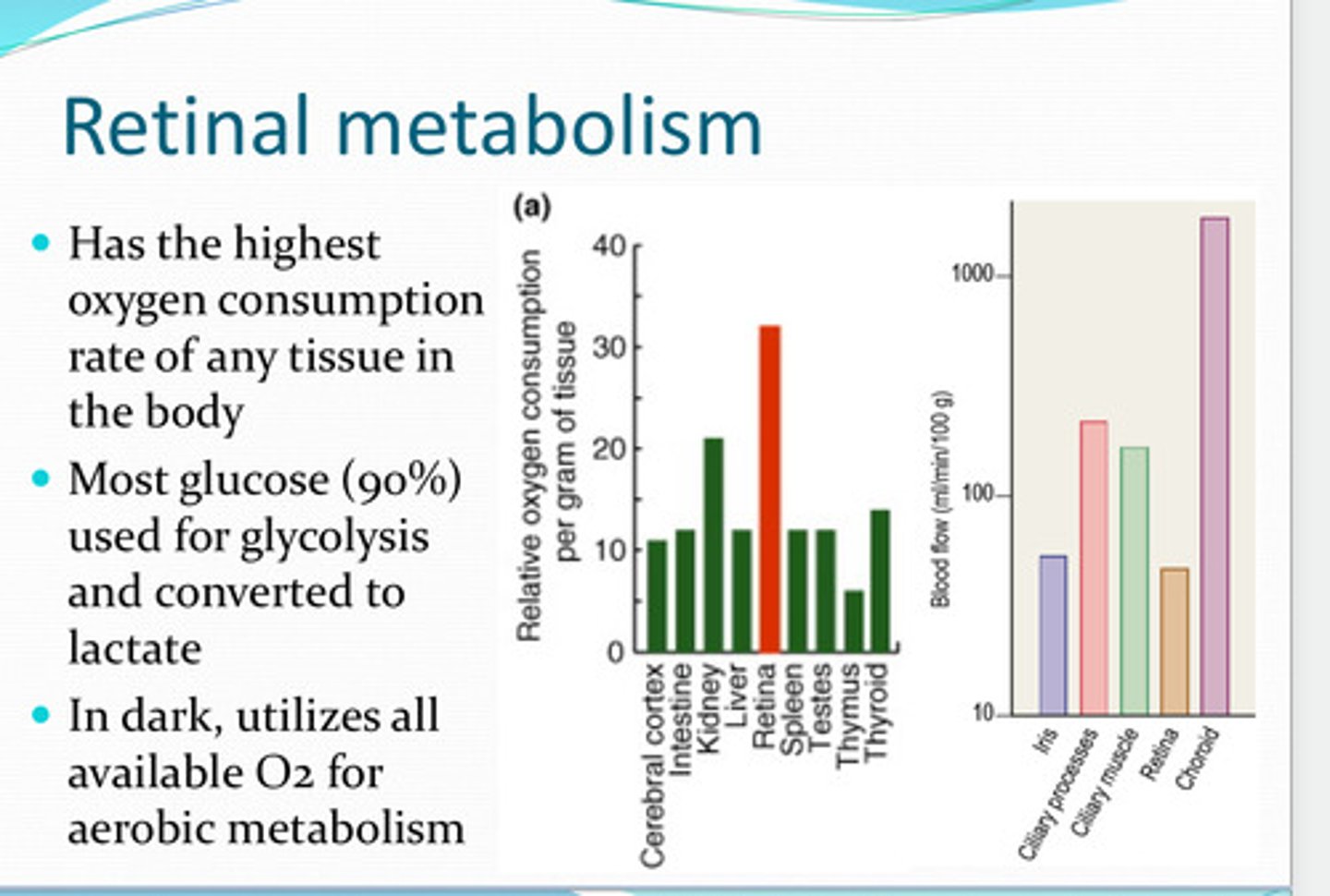
used for glycolysis and converted to lactate
Most glucose of the retina is used for what? Converted to what?
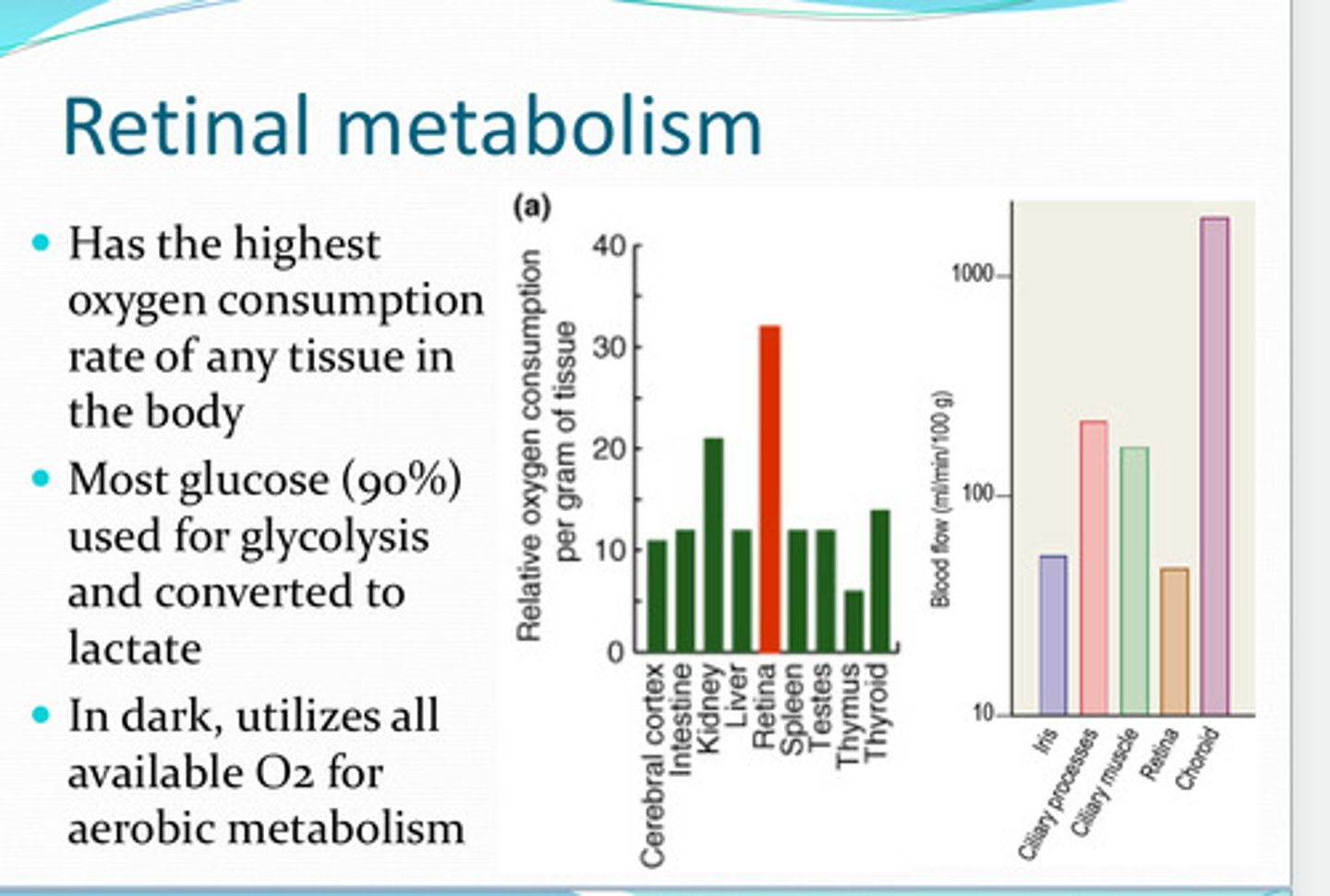
yes, utilizes all available O2 for aerobic respiration
In the dark, does the retina utilize its O2?
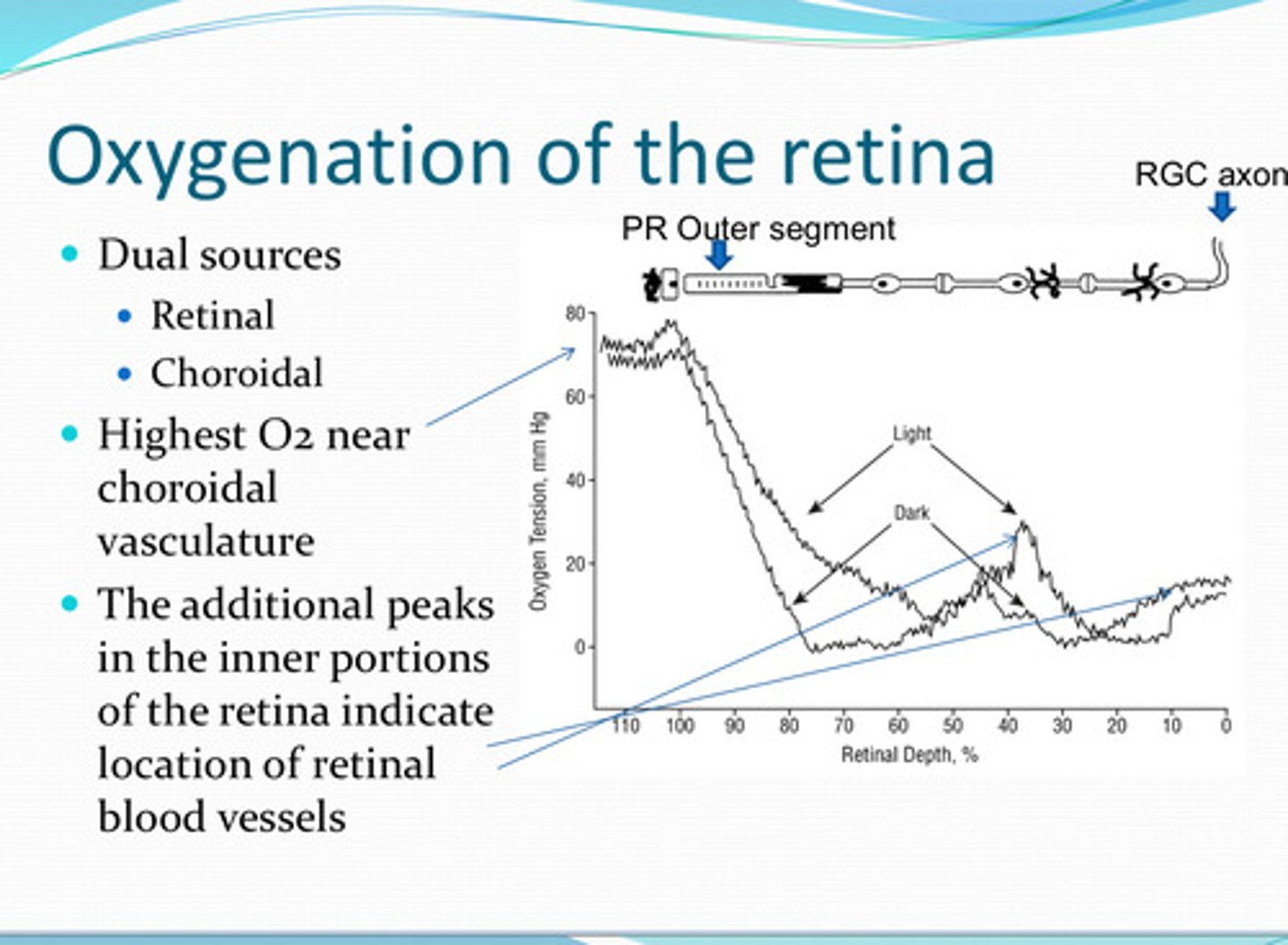
-retinal vessels
-choroidal vessels
Where is the oxygen supply for the retina from?
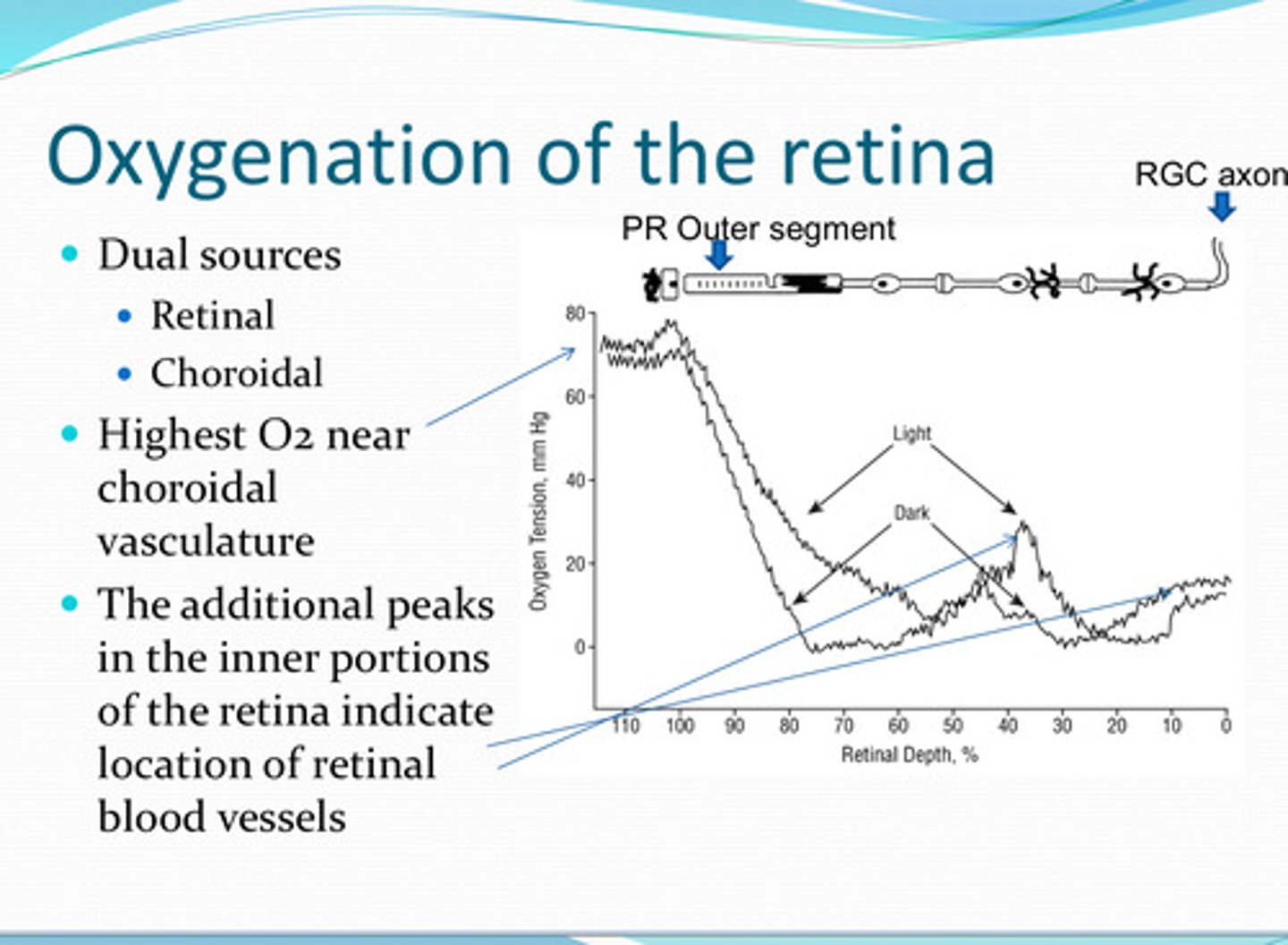
near the choroidal vasculature
Where is the highest pO2 in the retina?
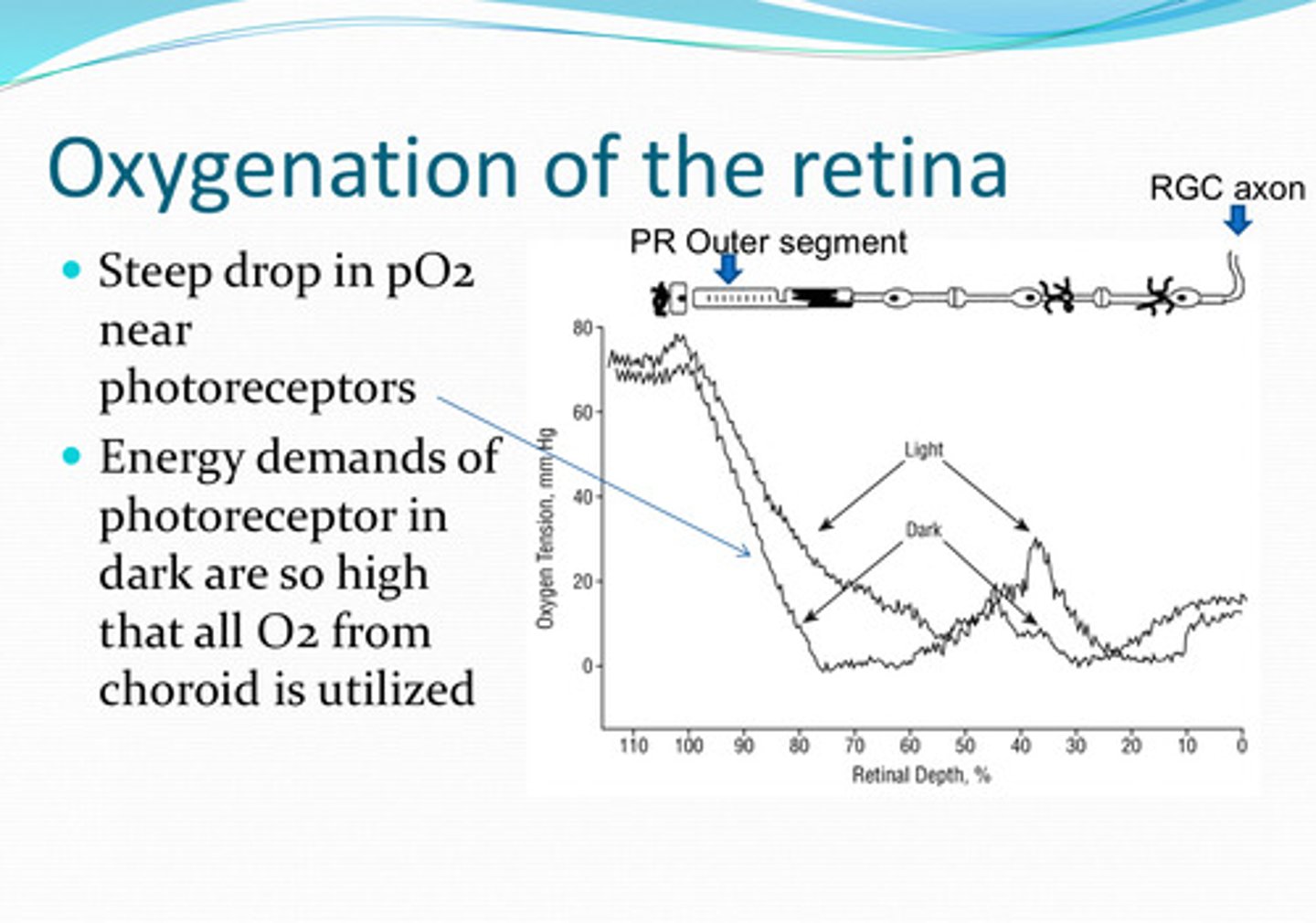
near the photoreceptors
Where is there a steep drop in pO2 in the retina?
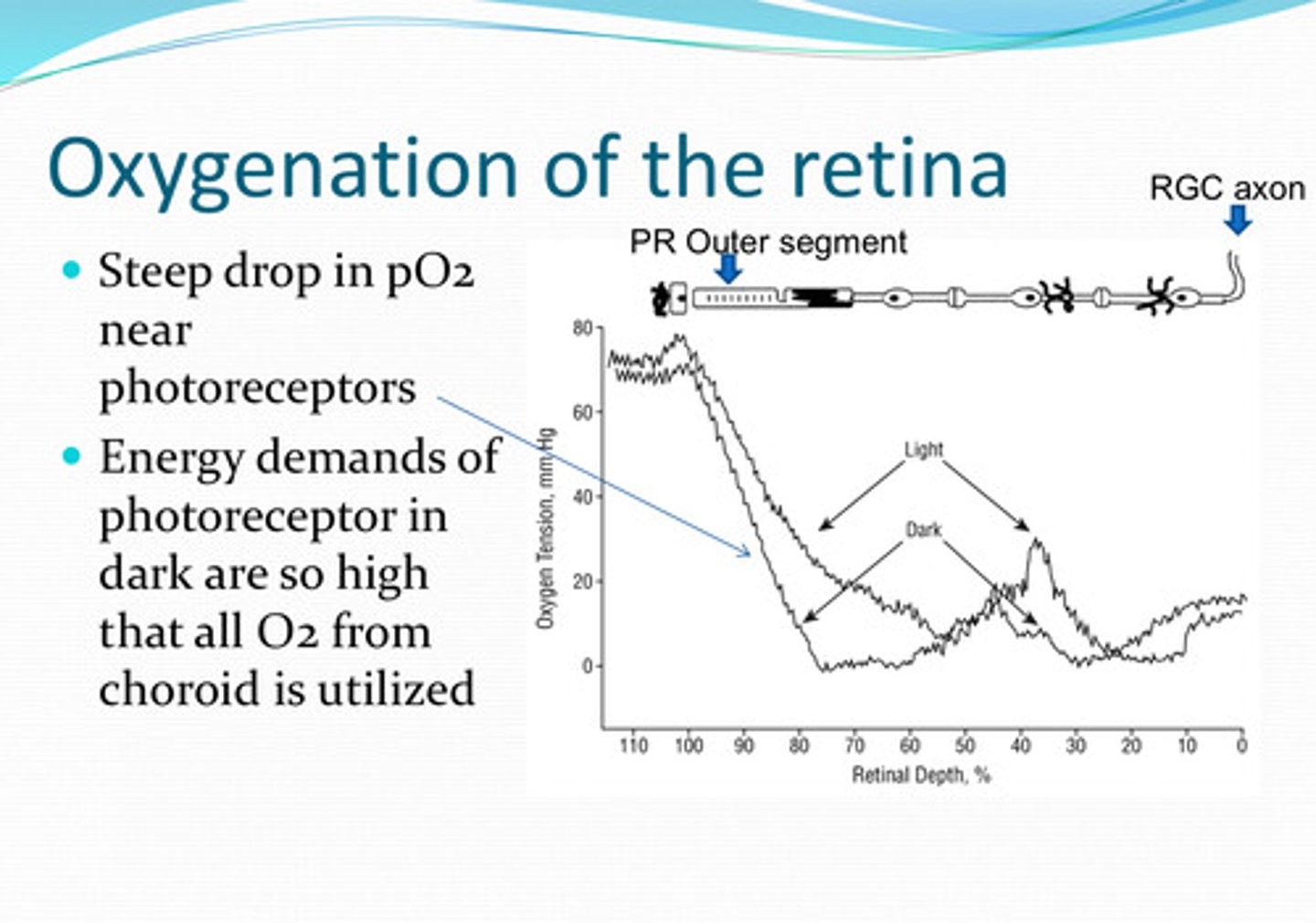
energy demands of photoreceptors are so high that all O2 from the choroid is utilized
Why is the pO2 low near the photoreceptors?
true
True or False:
O2 levels in the retina change with light conditions
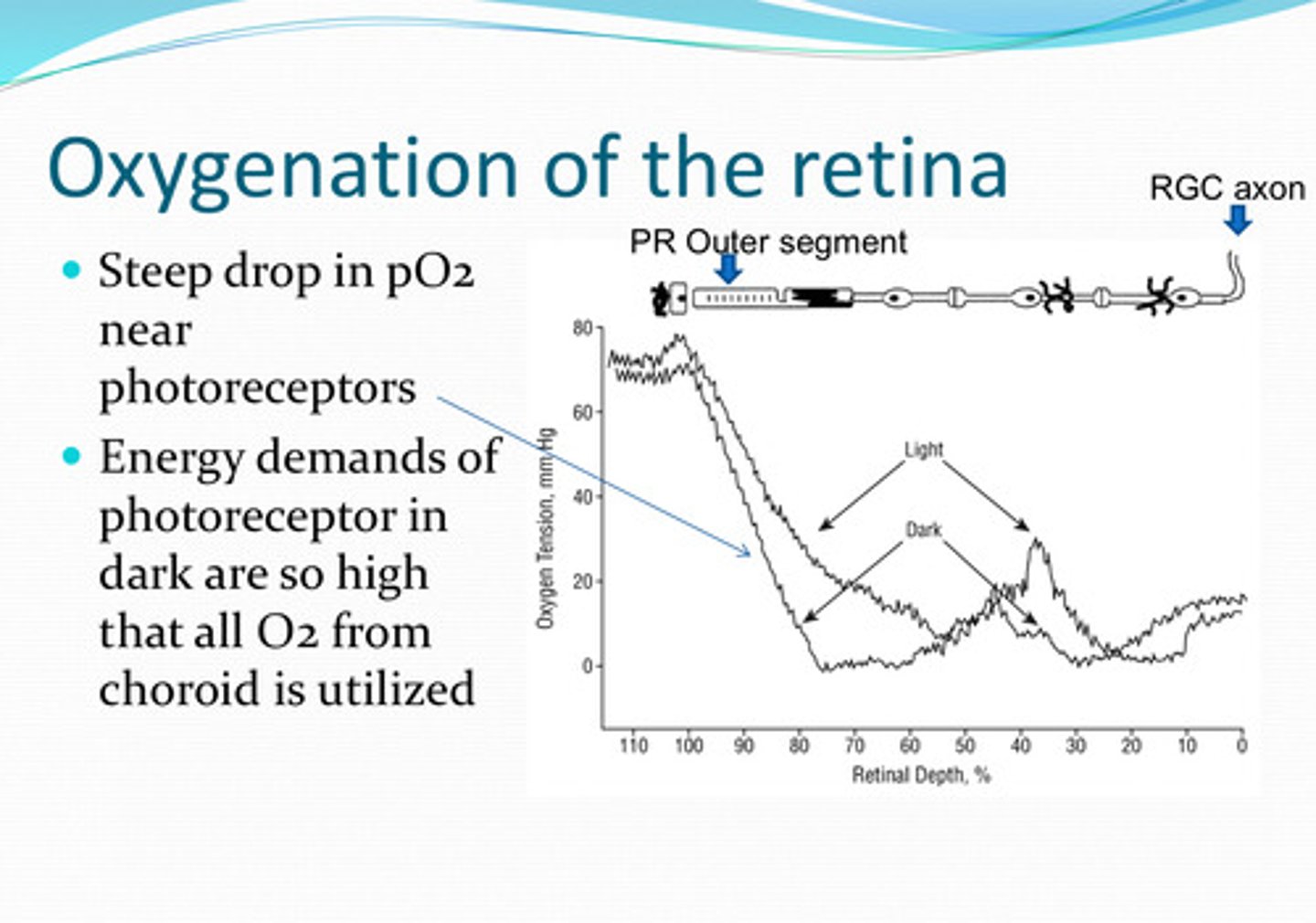
less O2
Will the retina need more O2 or less O2 in the light?
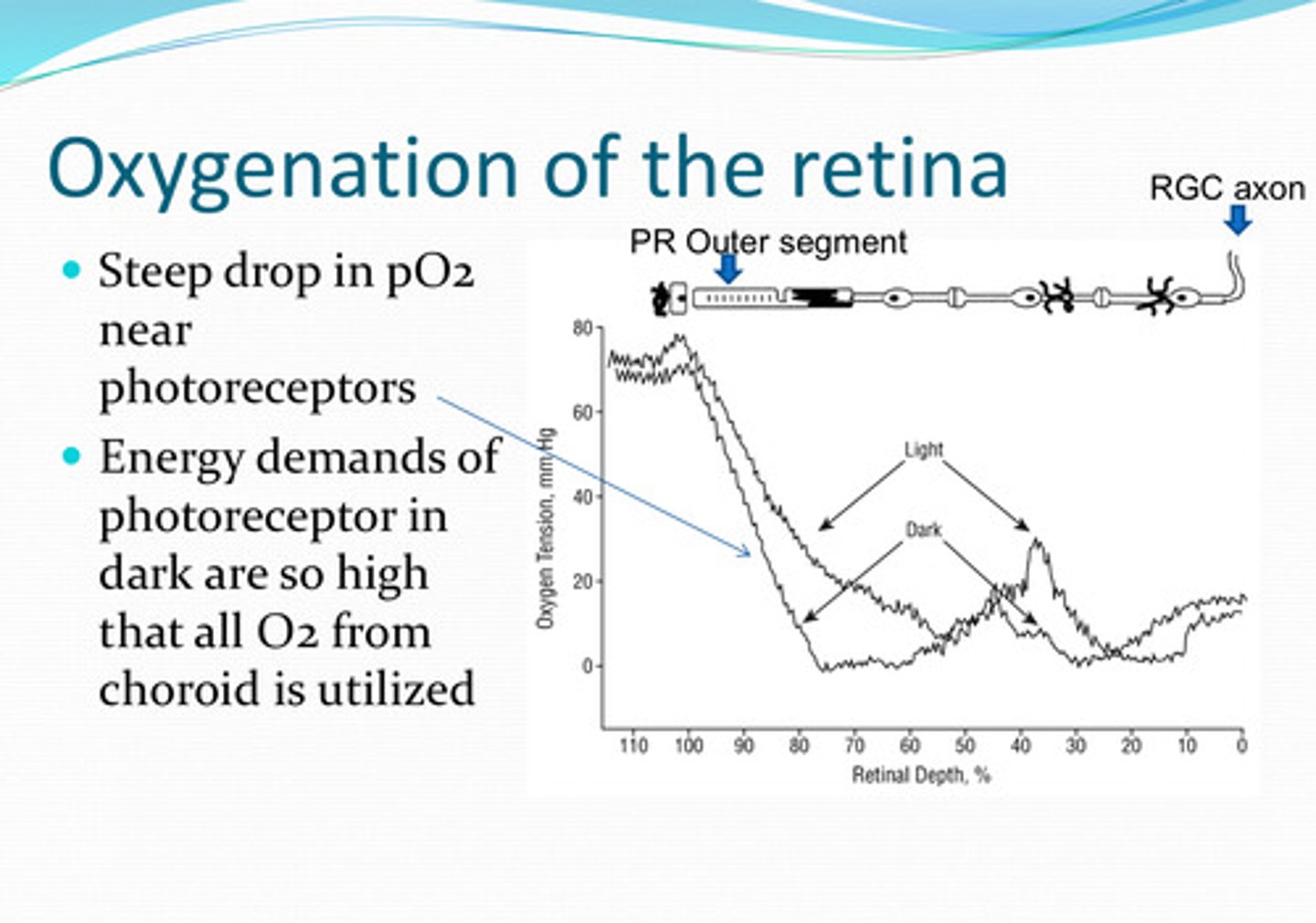
more O2
Will the retina need more O2 or less O2 in the dark?
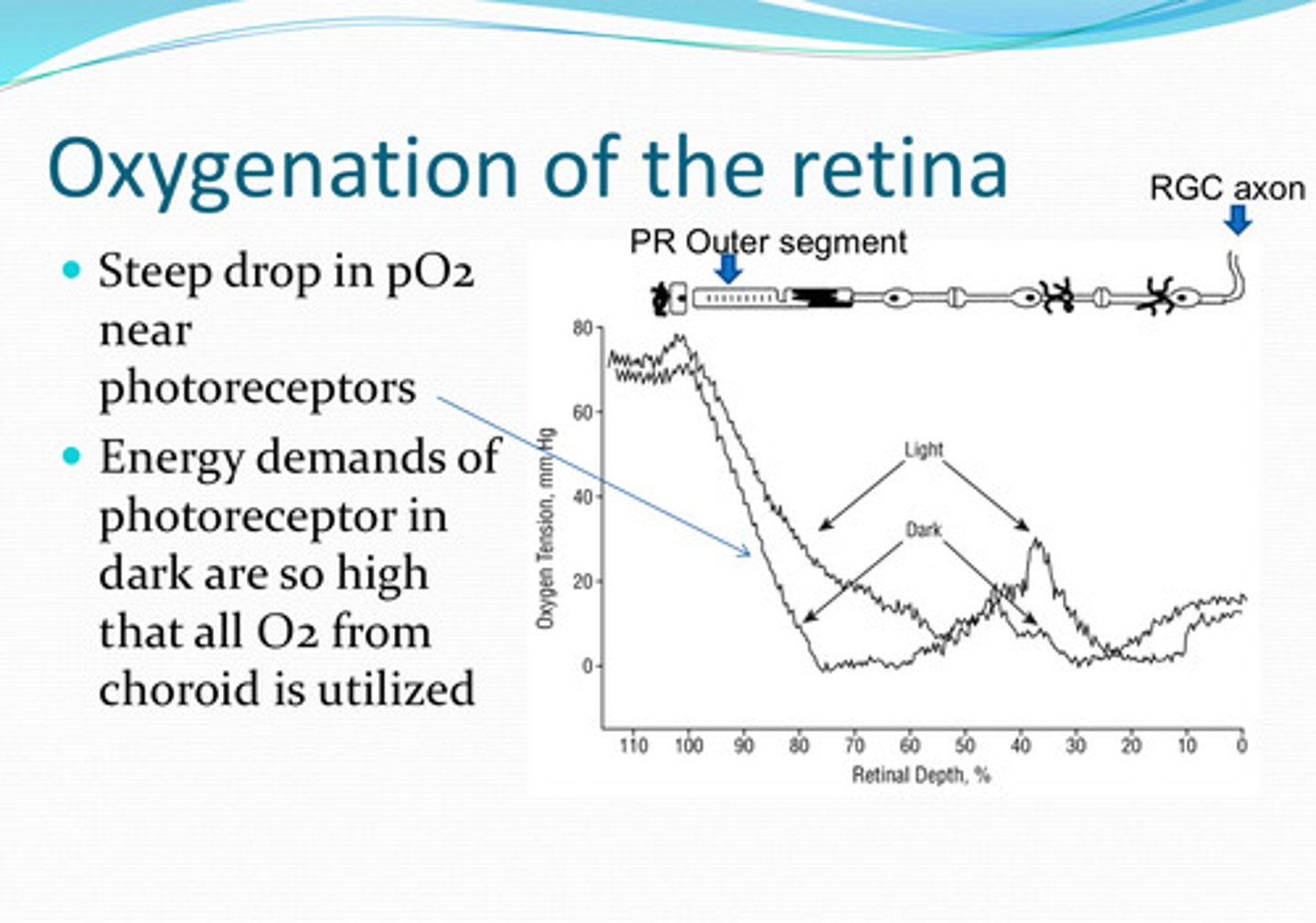
Higher rate of aerobic metabolism in the dark
Why does the retina need more O2 in the dark?
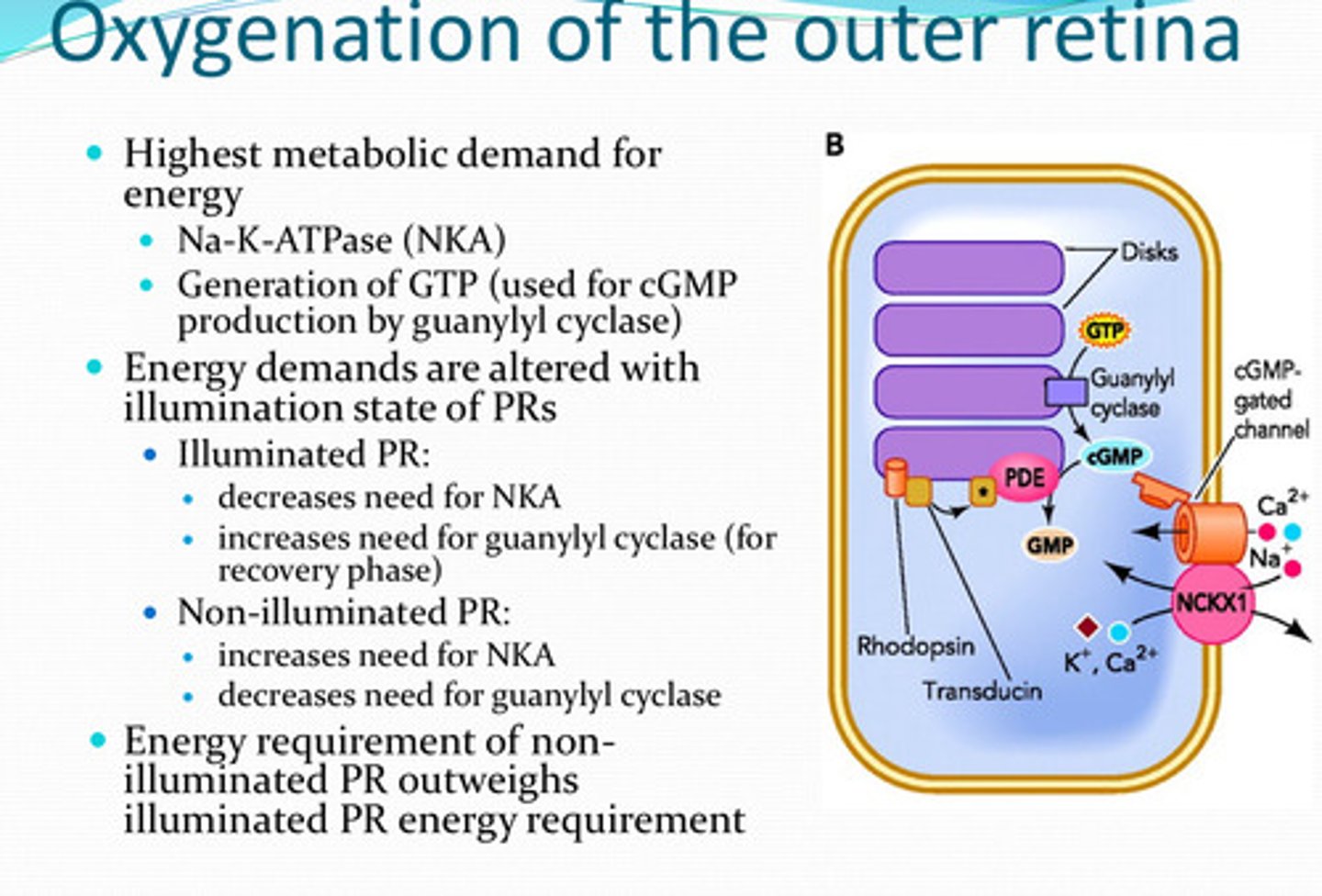
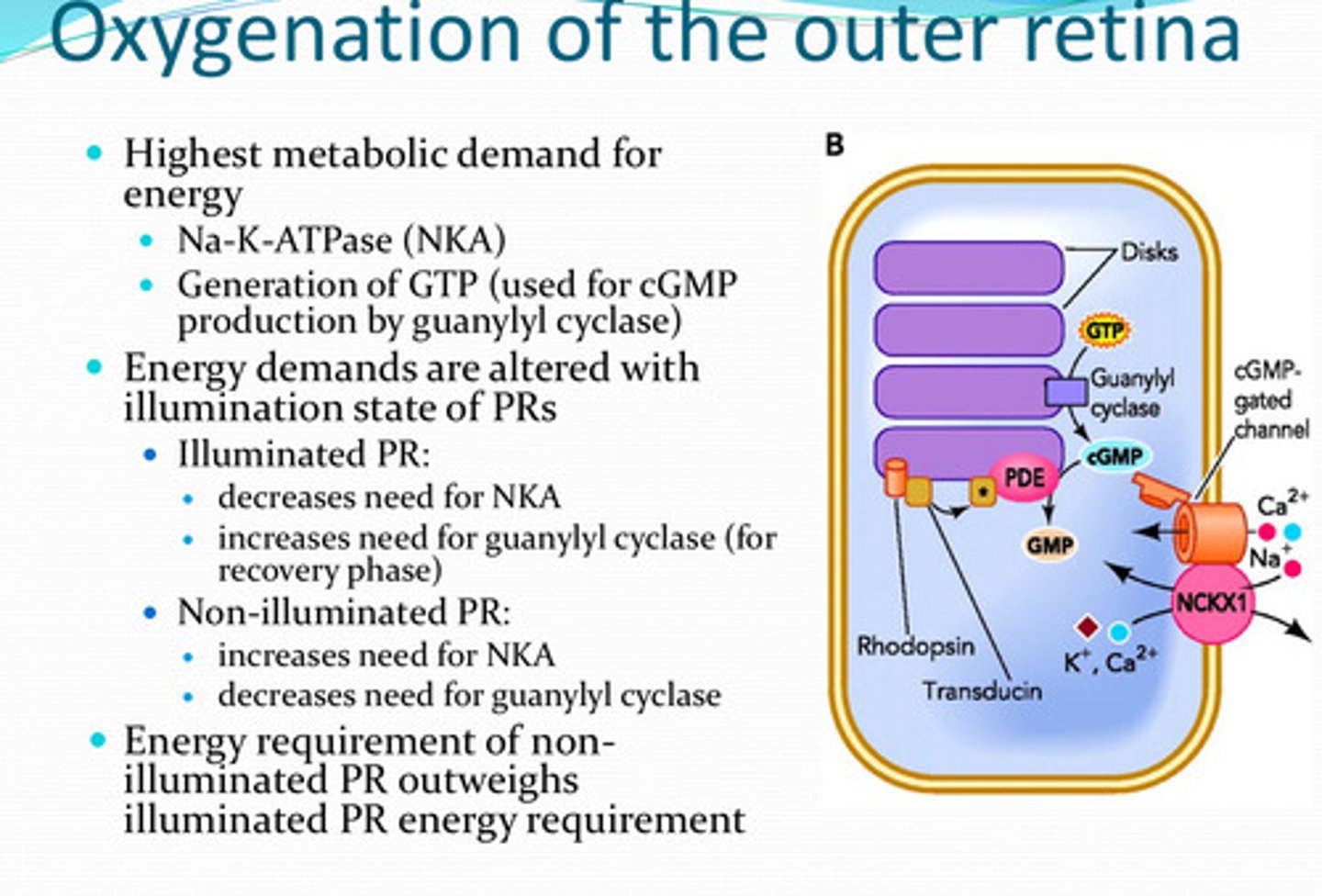
-NKA
-generation of GTP (by guanylyl cyclase)
What process(es) have the highest metabolic demand for energy in the retina?
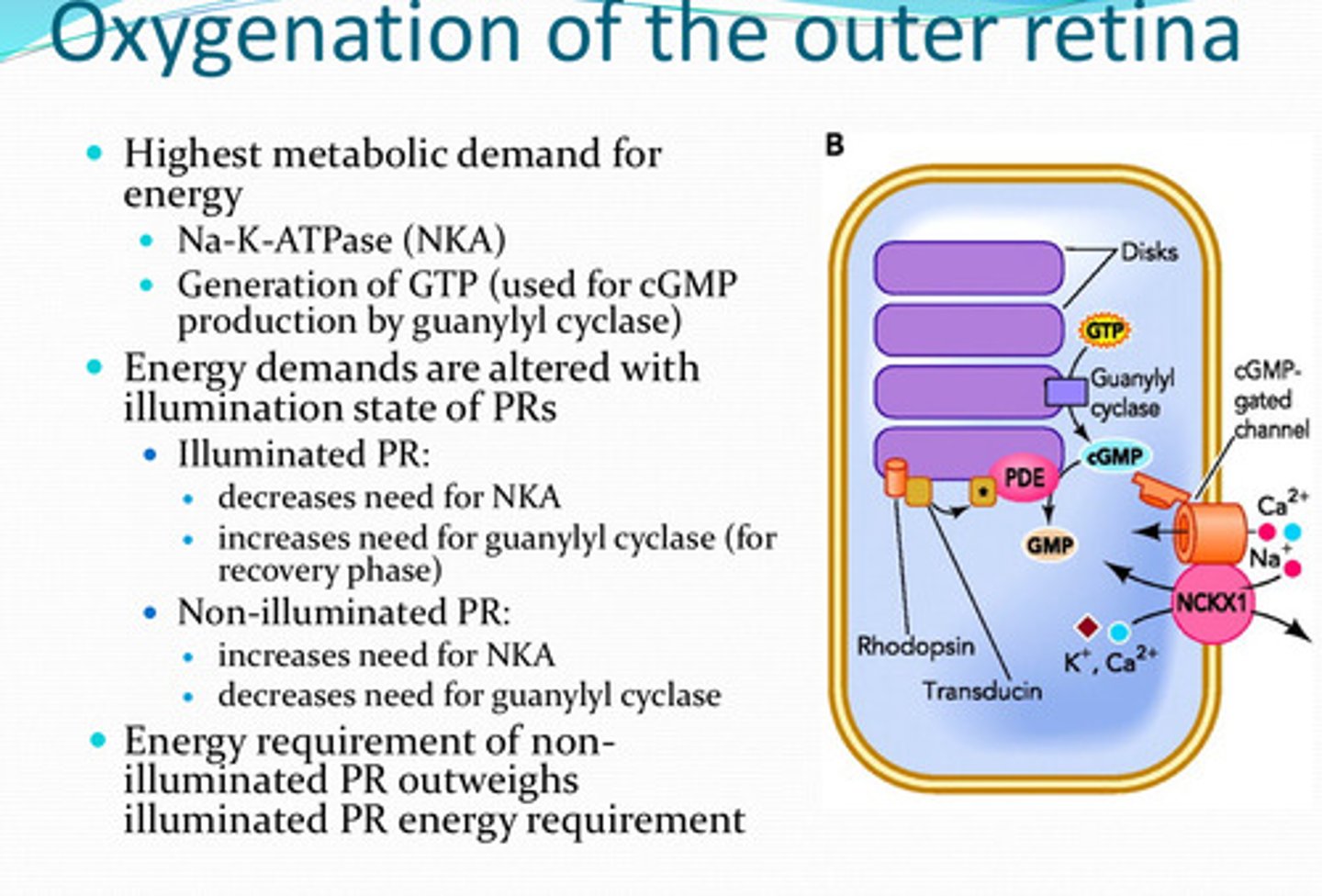
yes
Is the energy demand of the retinal cells altered with illuminated states of the photoreceptors?
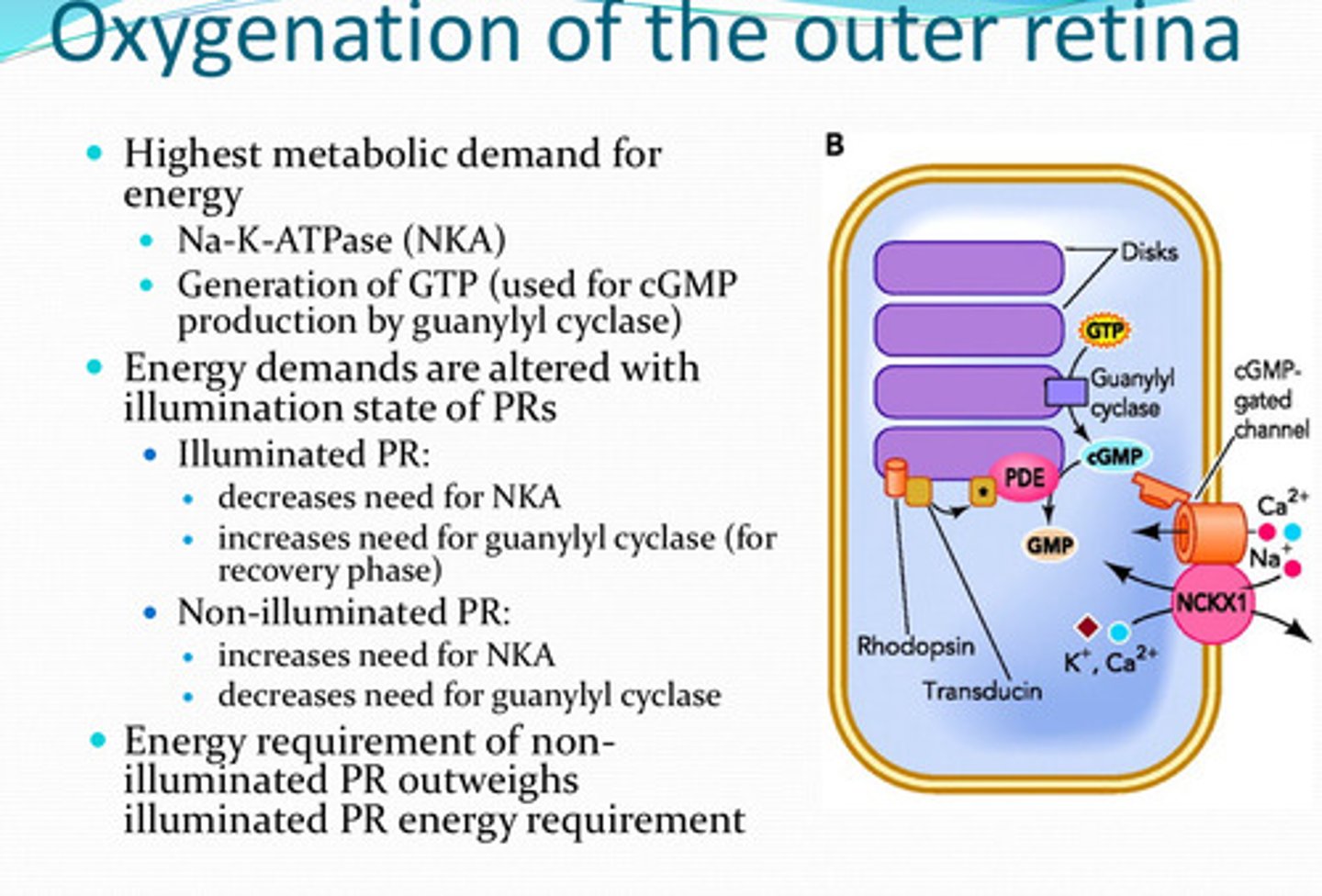
decreased
With illuminated photoreceptors, is there an increased or decreased need for NKA?
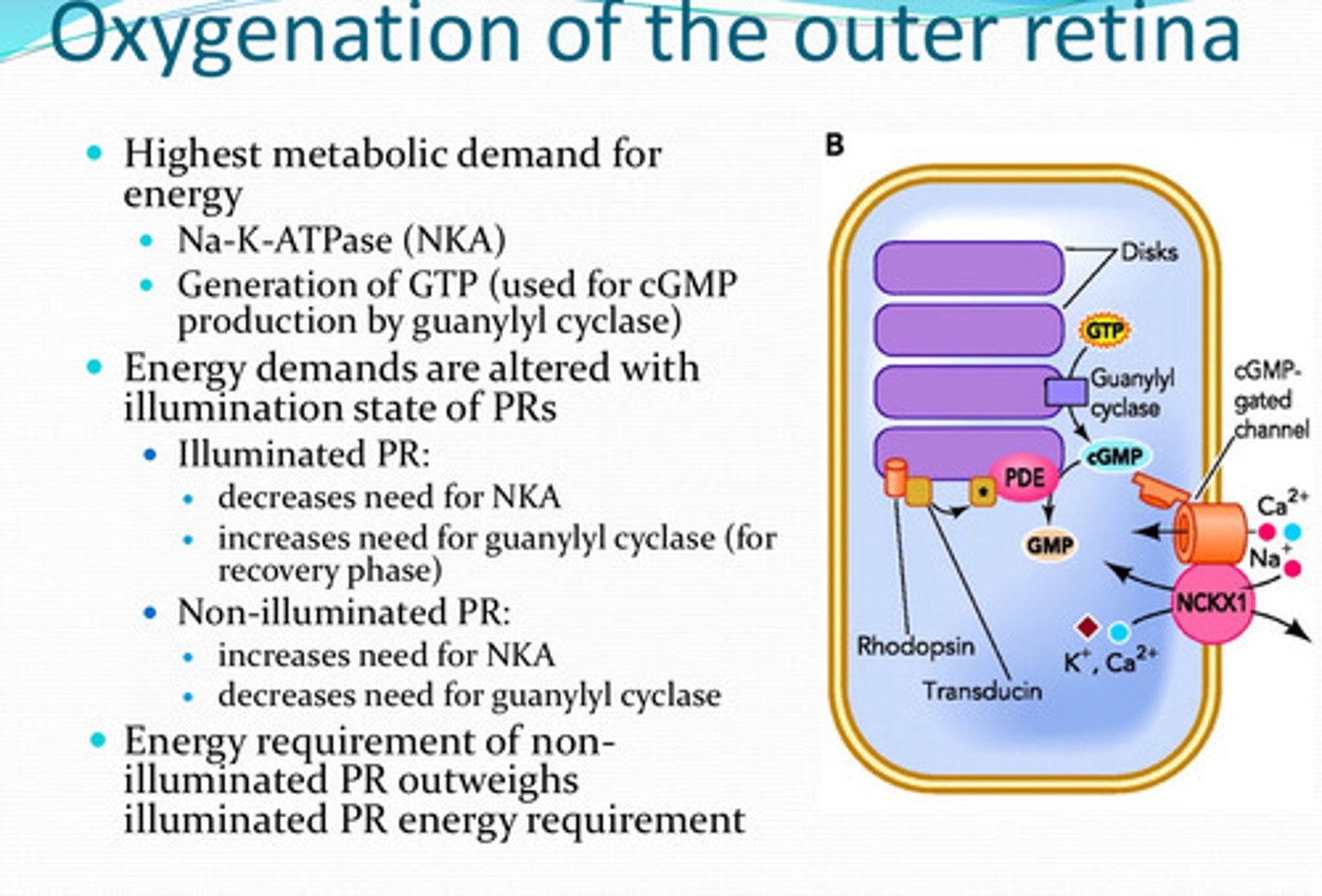
increased
With non-illuminated photoreceptors, is there an increased or decreased need for NKA?
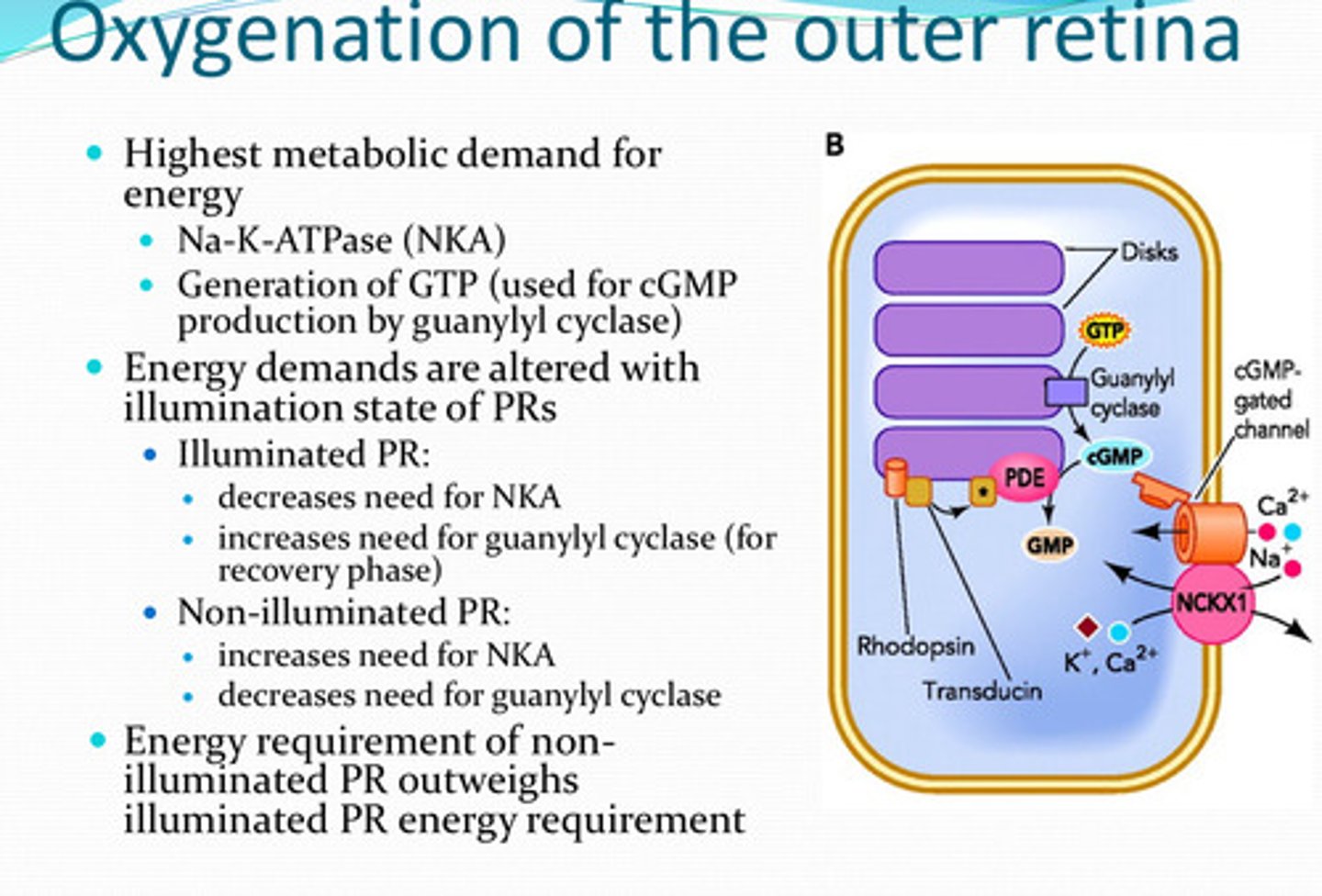
increased (for the recovery phase)
With illuminated photoreceptors, is there an increased or decreased need for guanylyl cyclase?
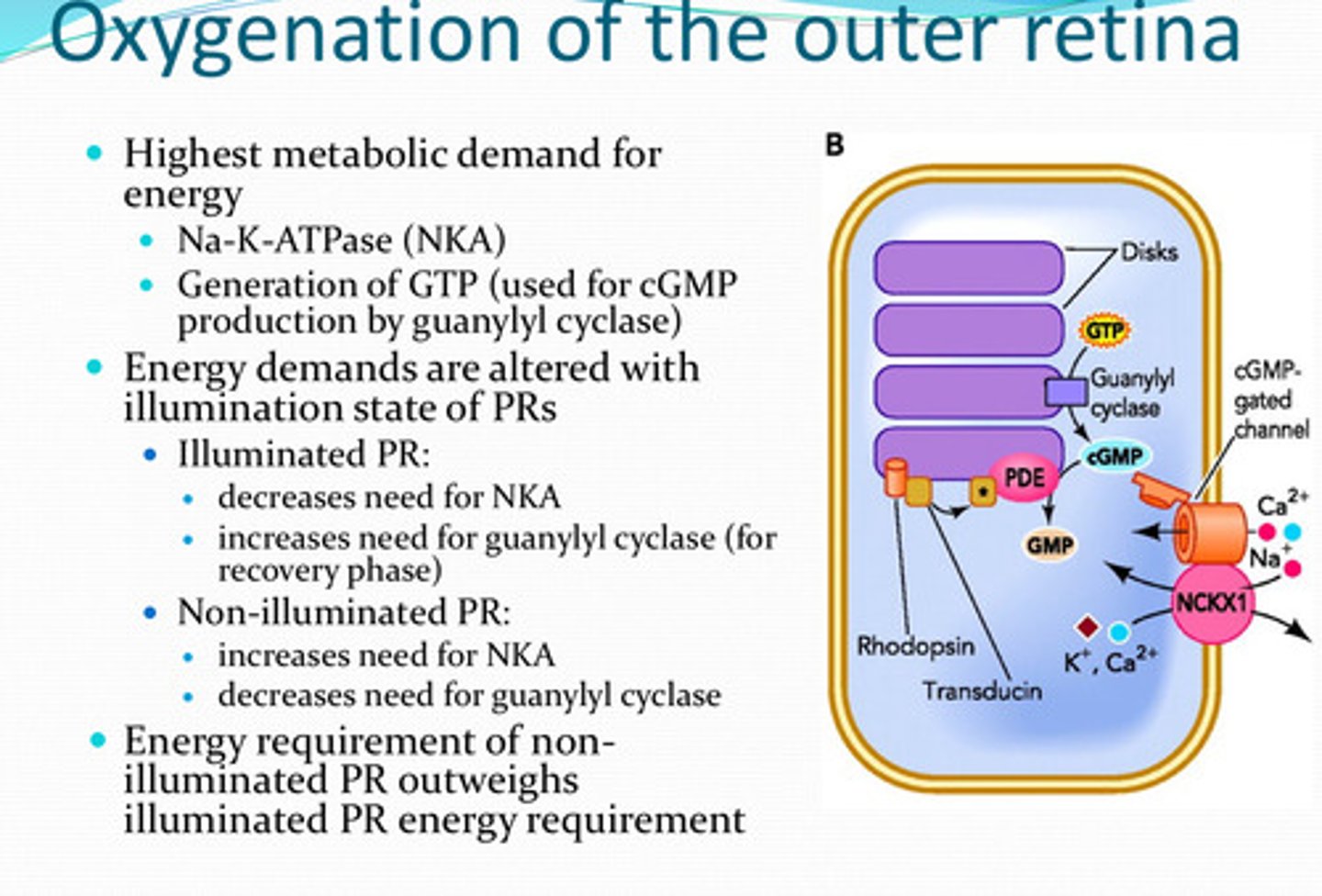
decreased need
With non-illuminated photoreceptors, is there an increased or decreased need for guanylyl cyclase?
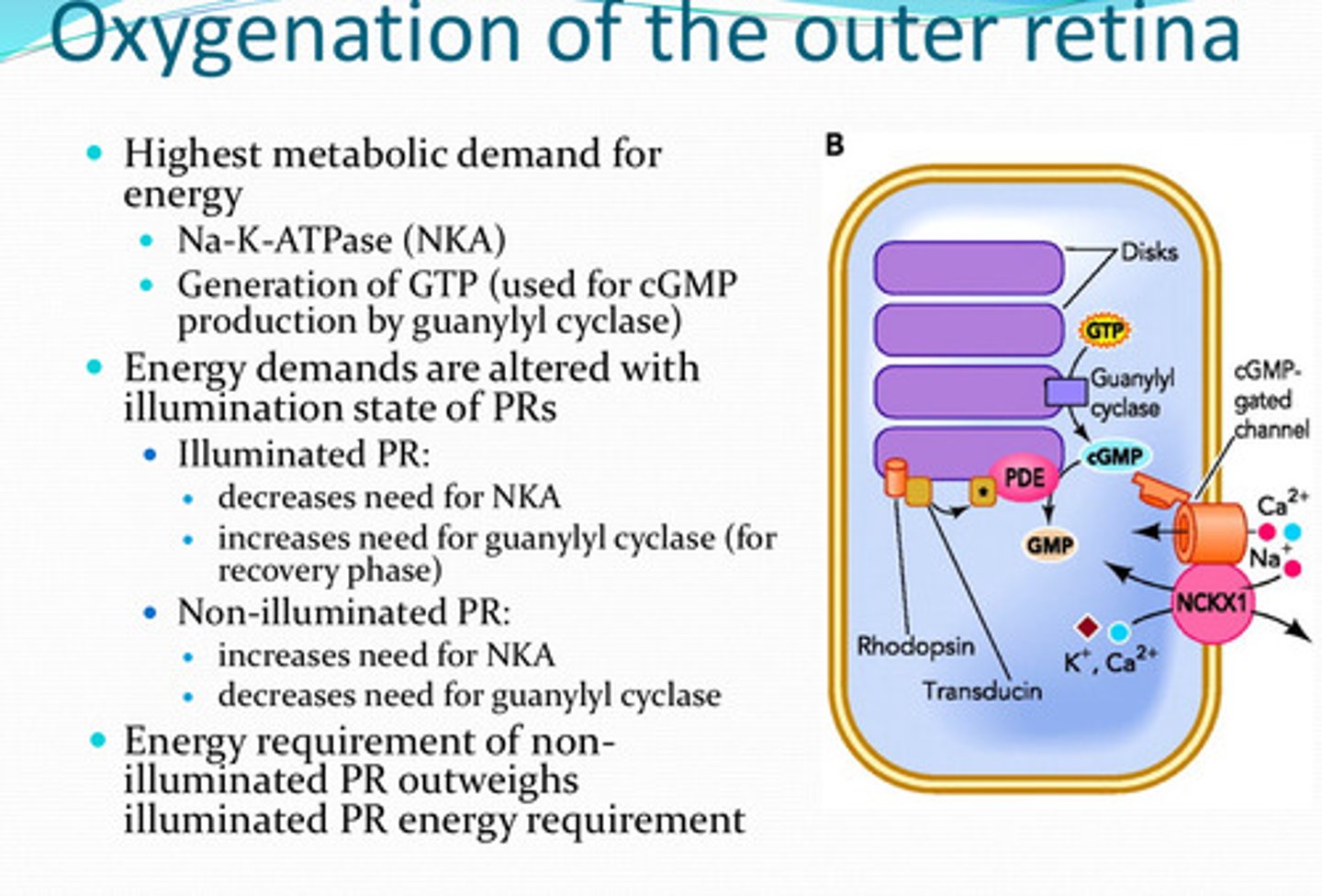
non-illuminated PR; illuminated PR
The energy requirement for ______ outweighs the energy requirement for ______
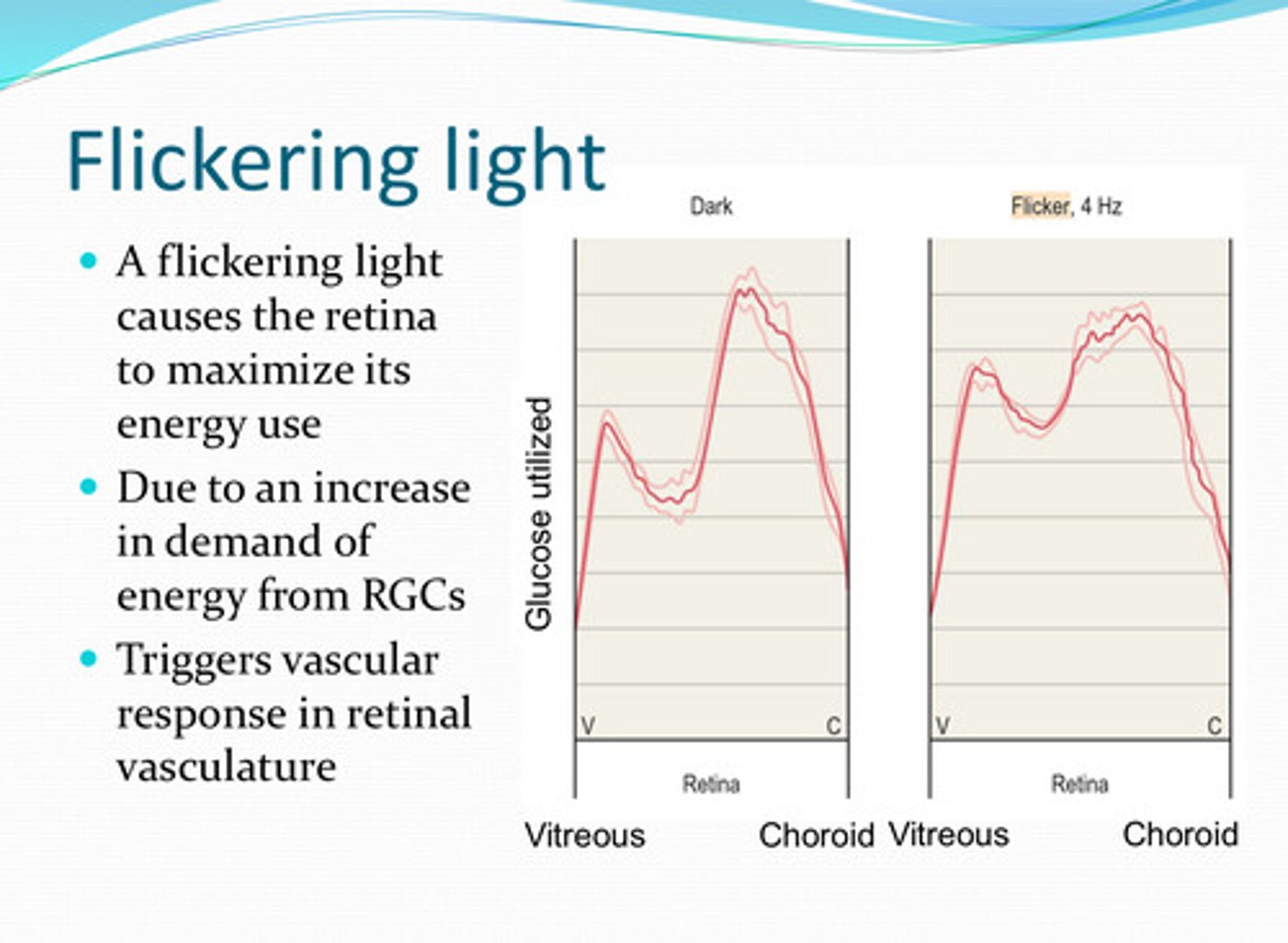
flickering
A _____ light causes the retina to maximize its energy usage
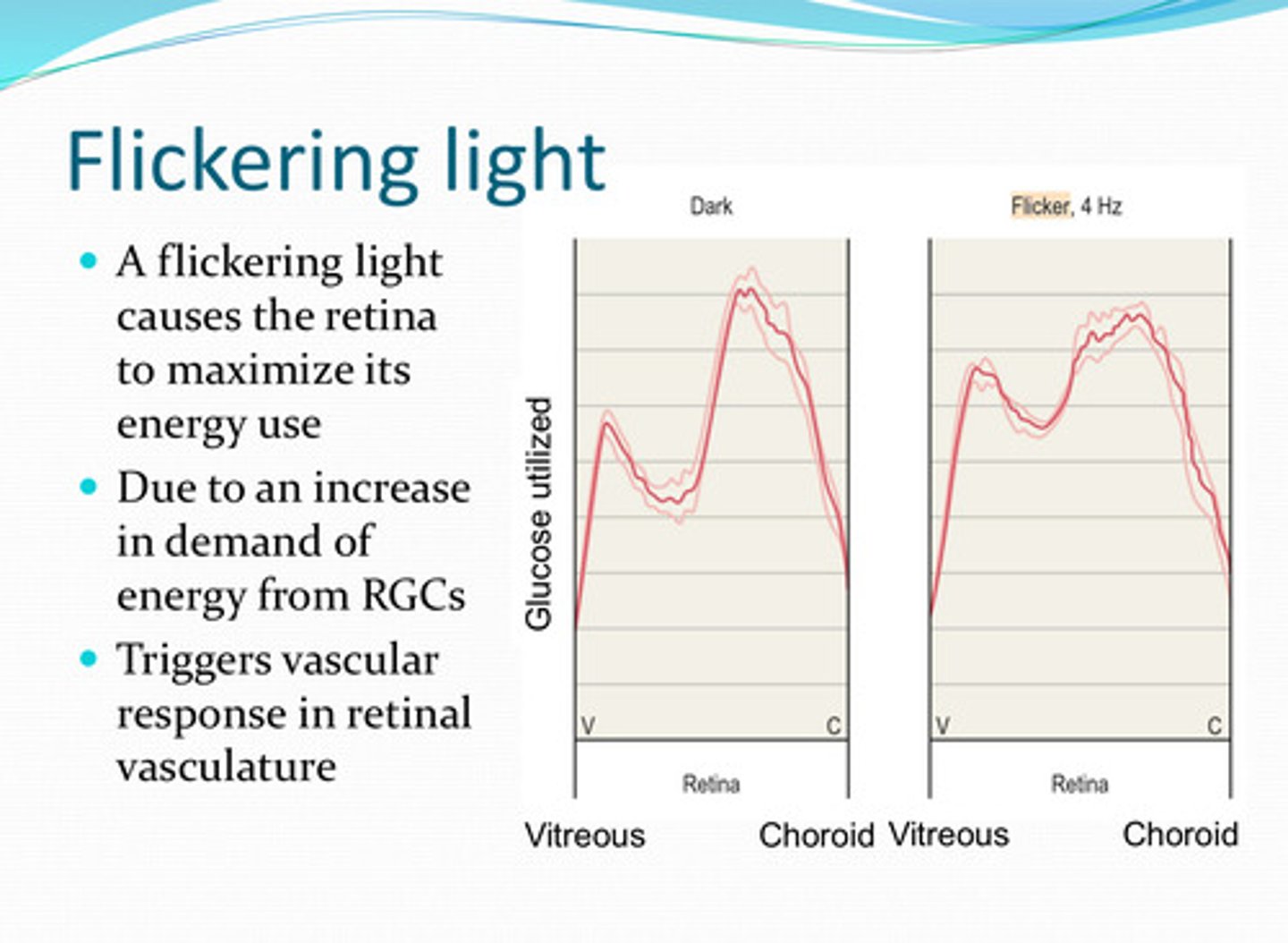
an increase in demand of energy from the RGCs, triggers vascular response in retinal vasculature
Why does a flickering light cause the retina to maximize its energy usage?
no
Is there neural innervation of the retinal vasculature or optic nerve head vessels?
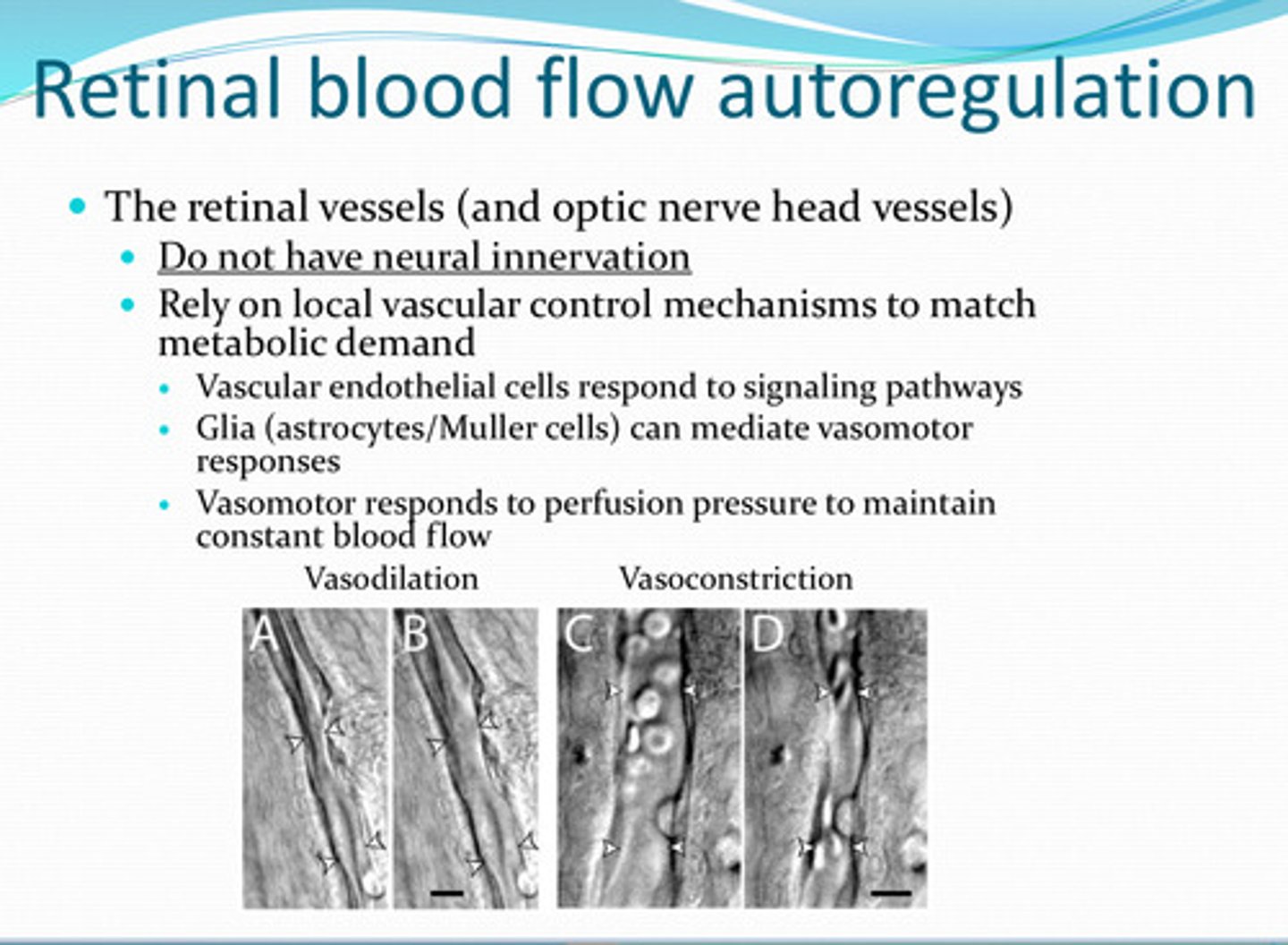
rely on local vascular control
What do the retinal vasculature or optic nerve head vessels rely on to match metabolic demand?
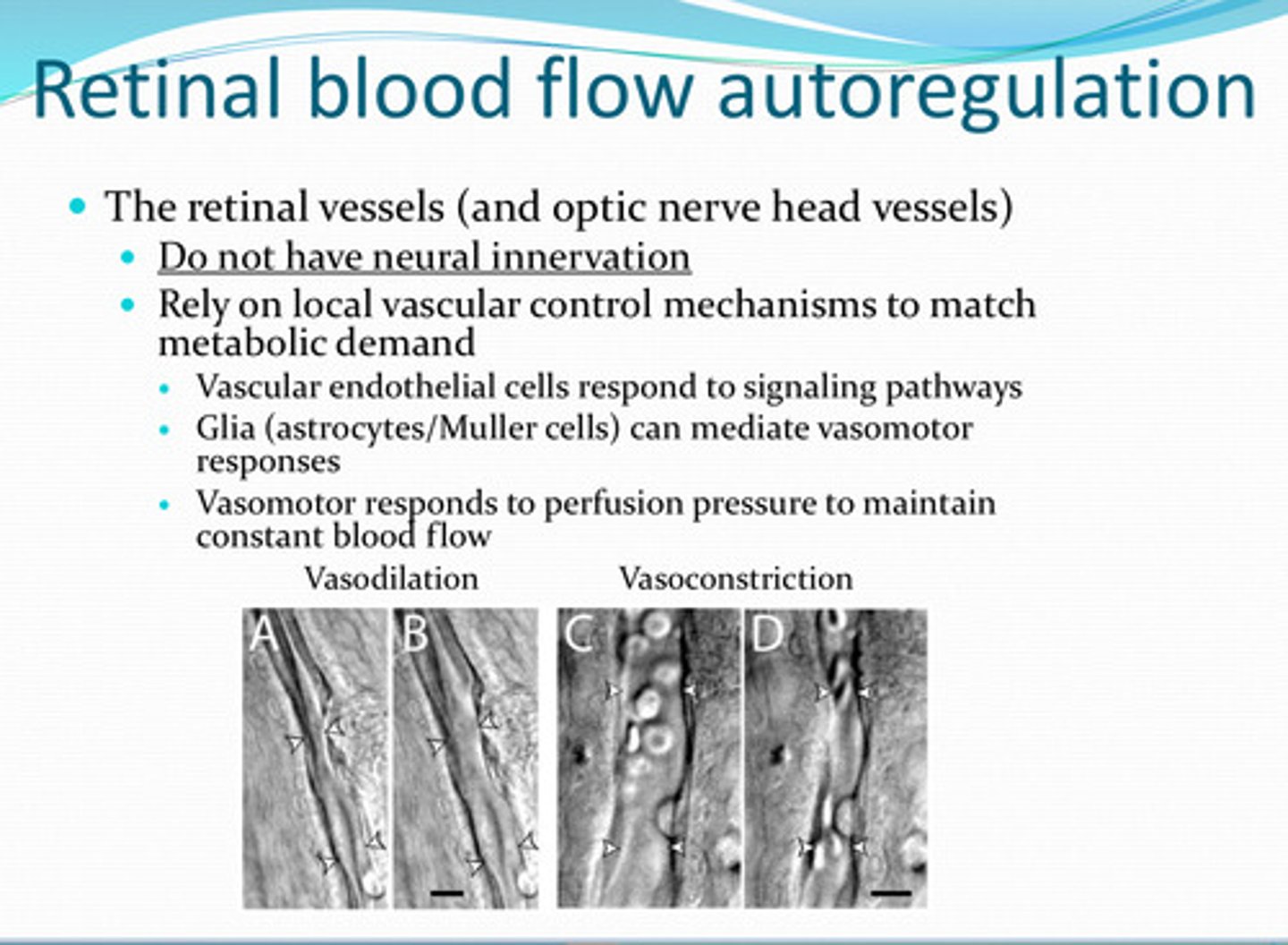
signaling pathways
Vascular endothelial cells of retinal vasculature and optic nerve head vessels respond to what?
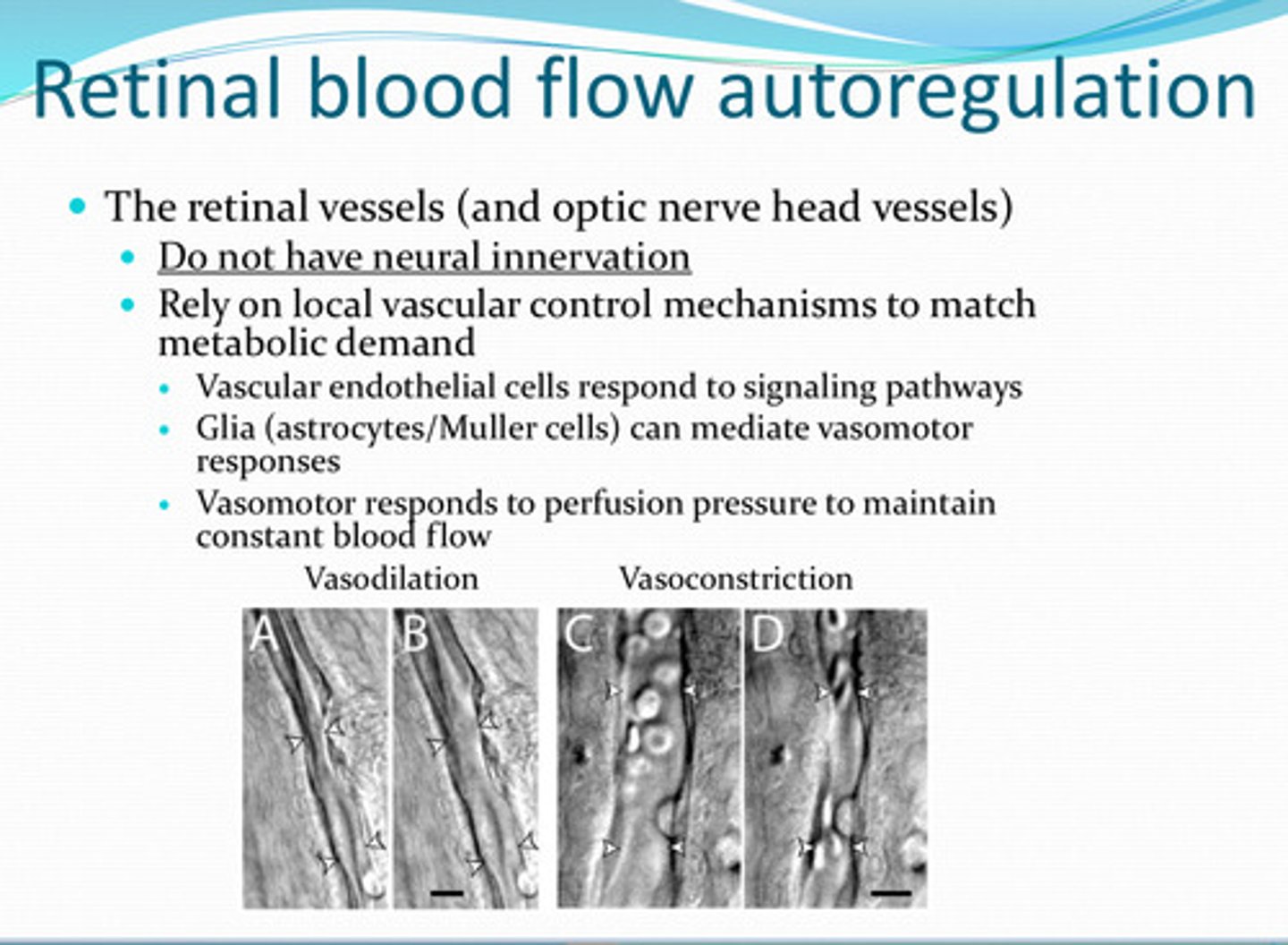
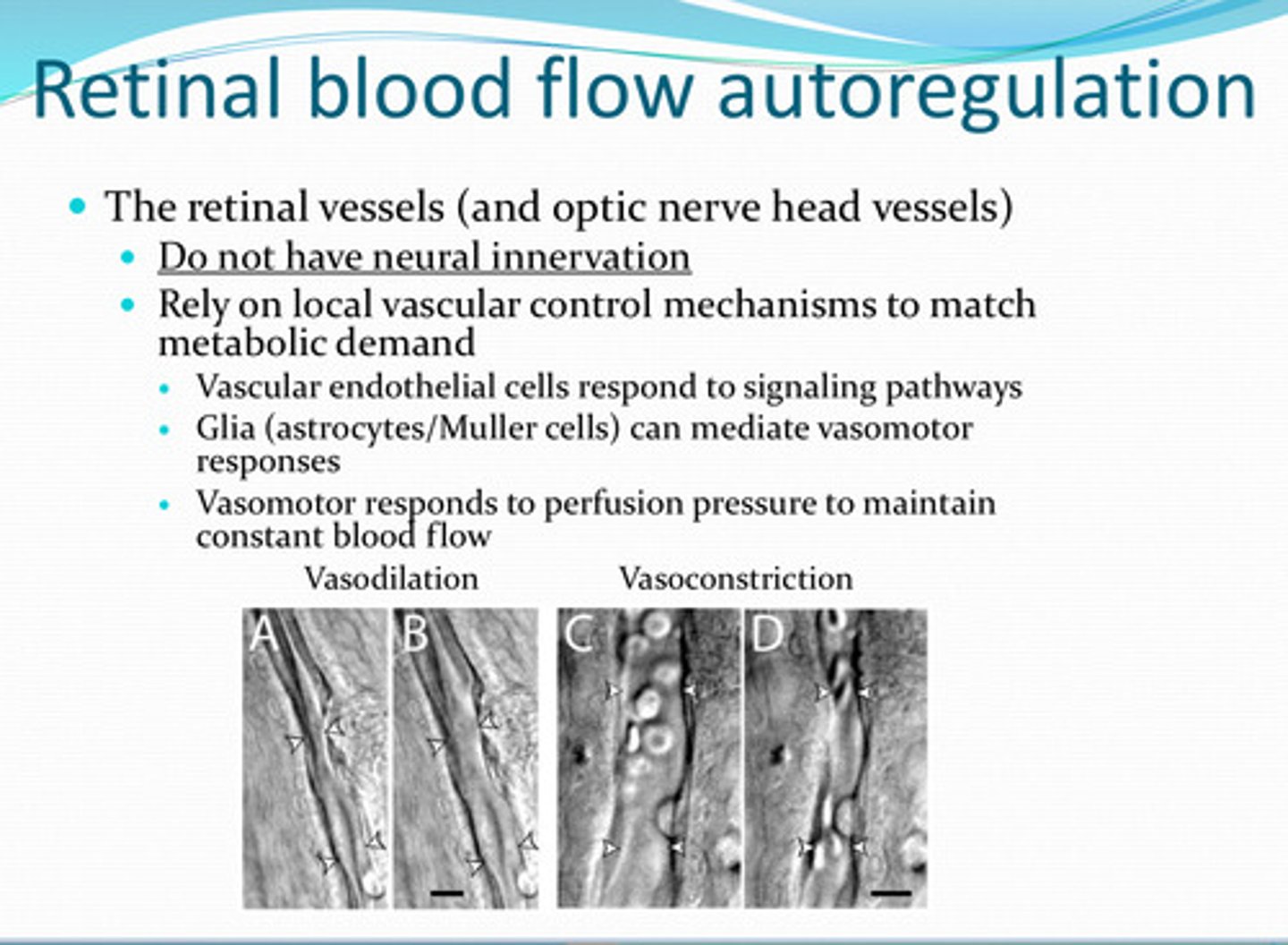
glia (astrocytes/muller too)
______ can mediate vasomotor responses in retinal vasculature
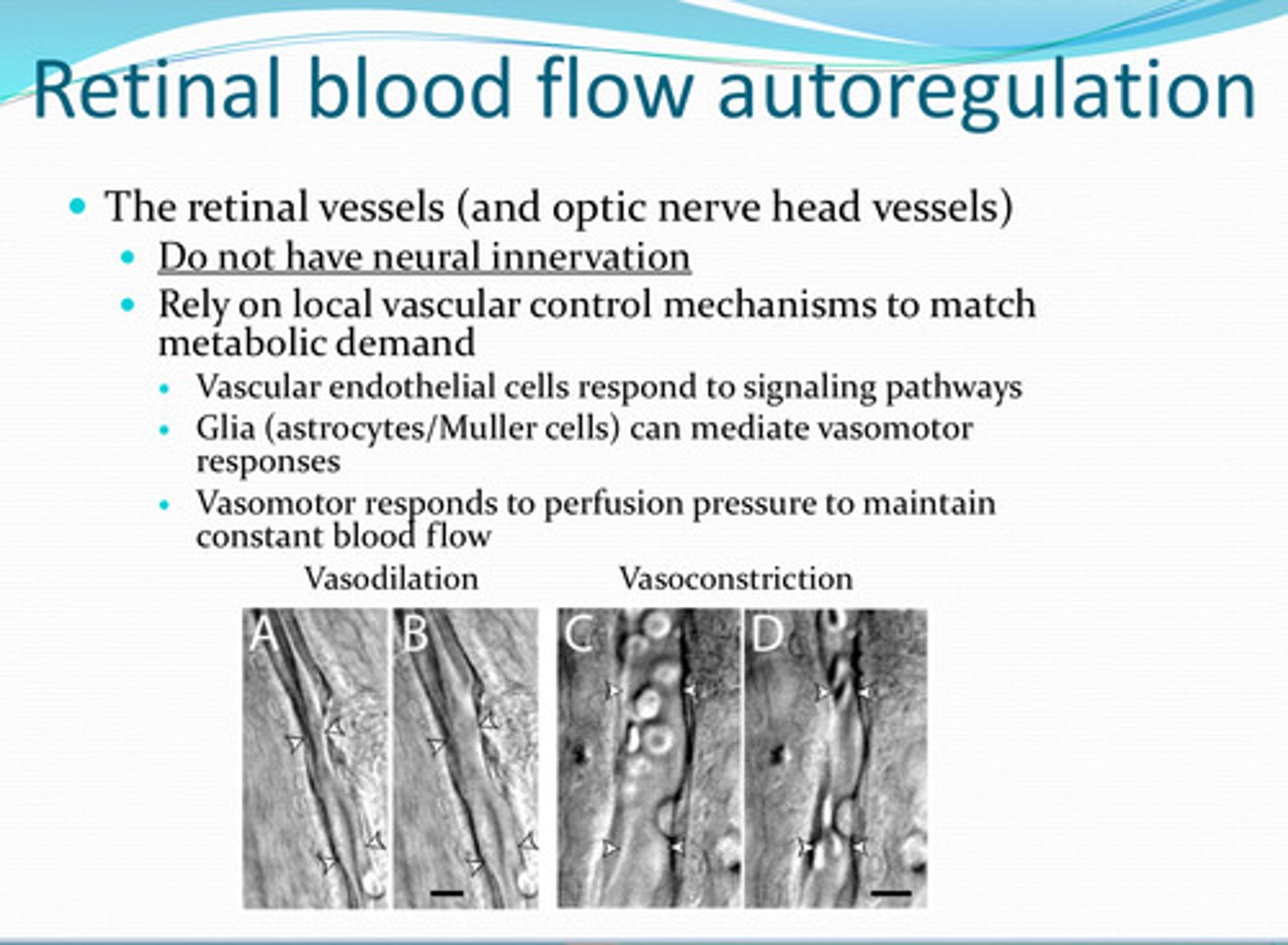
perfusion pressure -- to maintain constant blood flow to retina and optic nerve
What does the vasomotor system of the retinal vasculature and optic nerve head vessels respond to?
outer
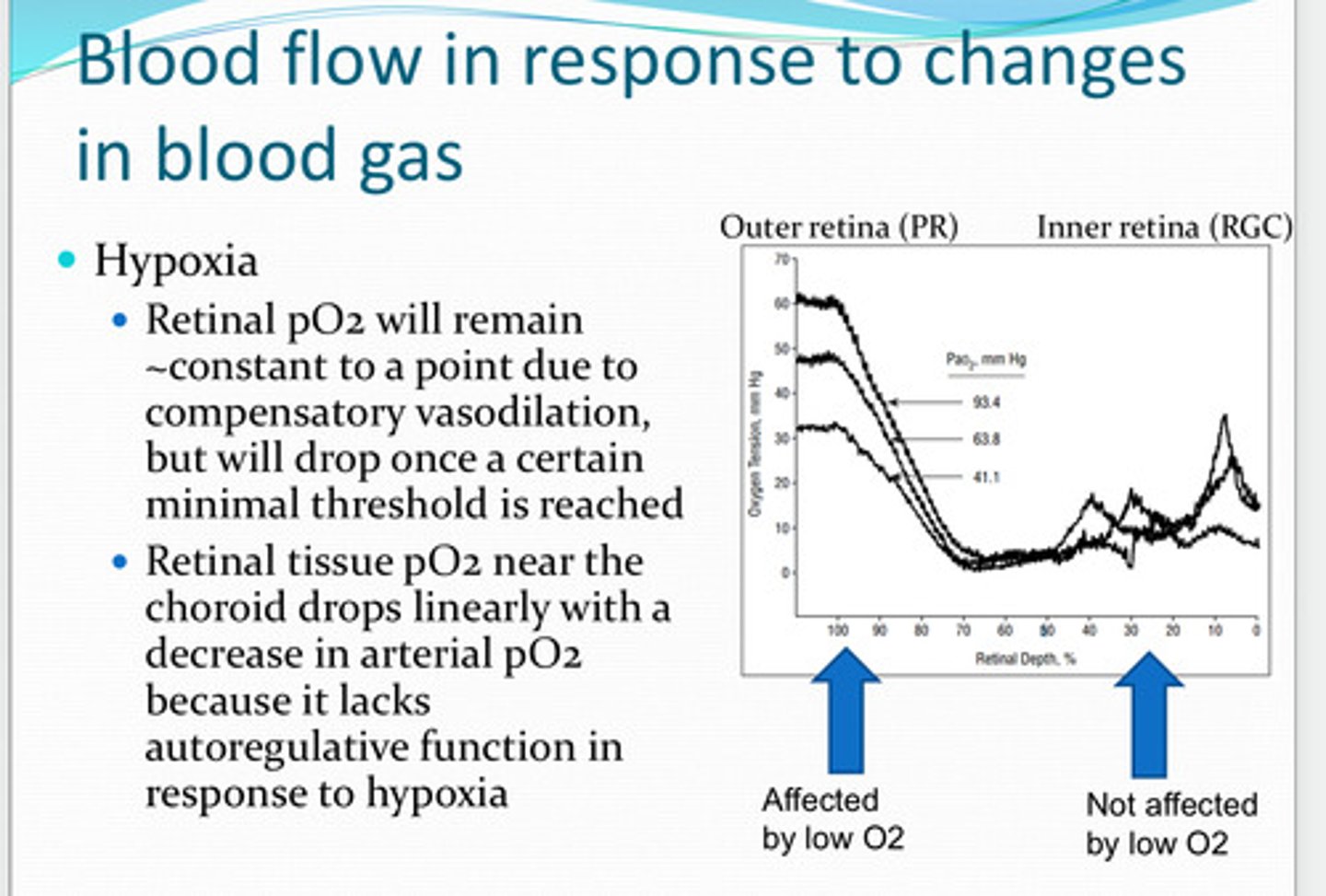
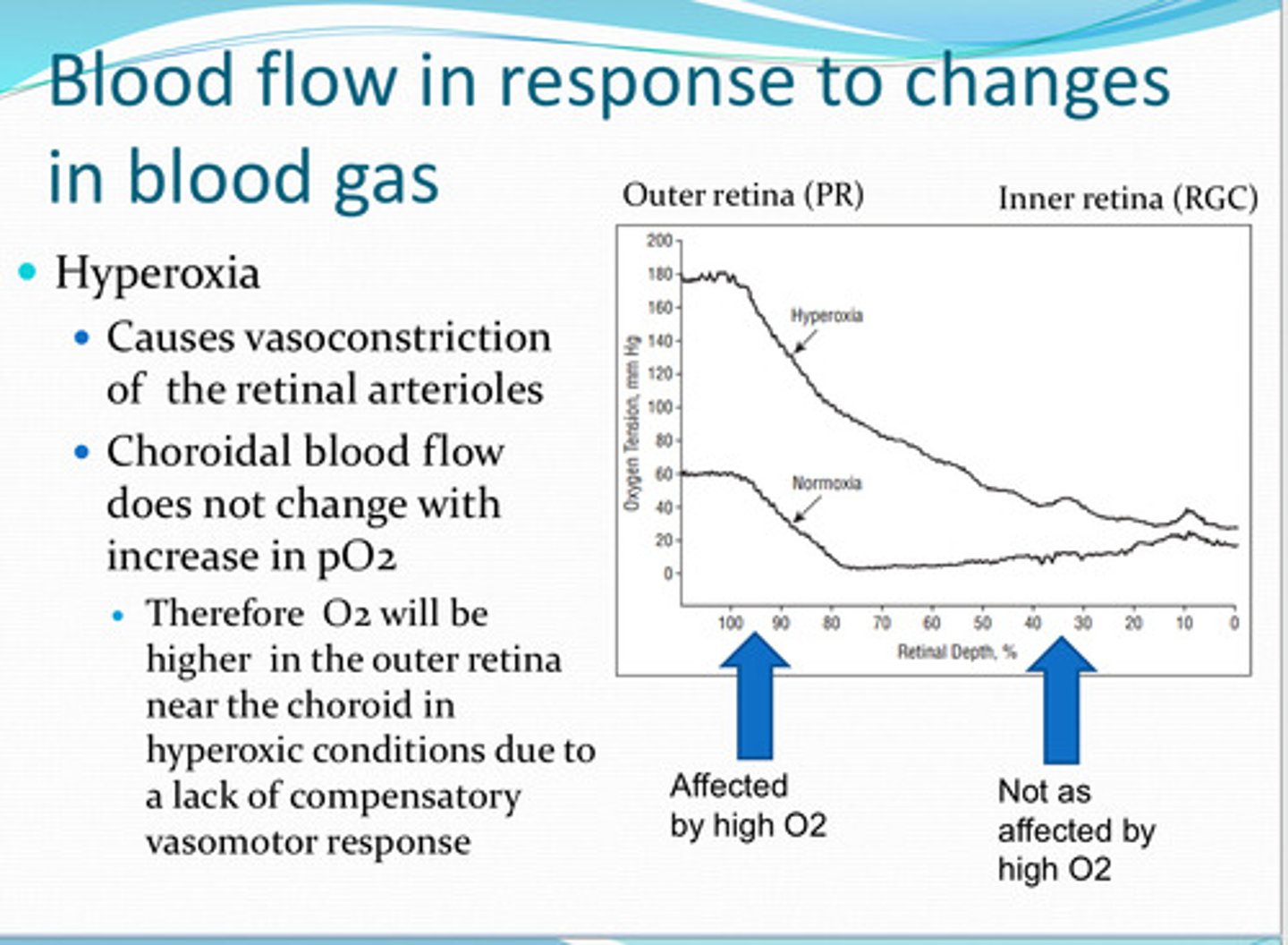
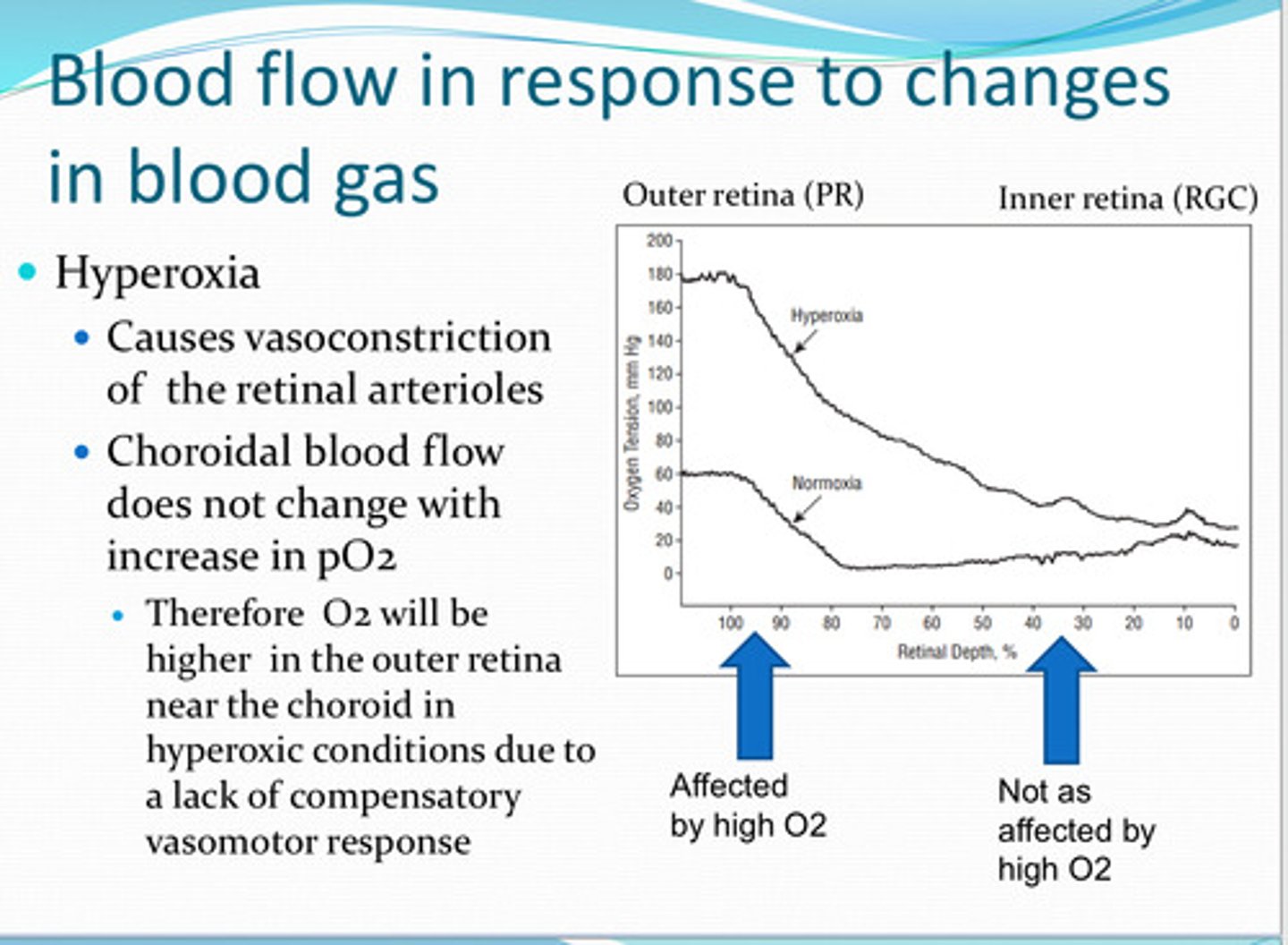
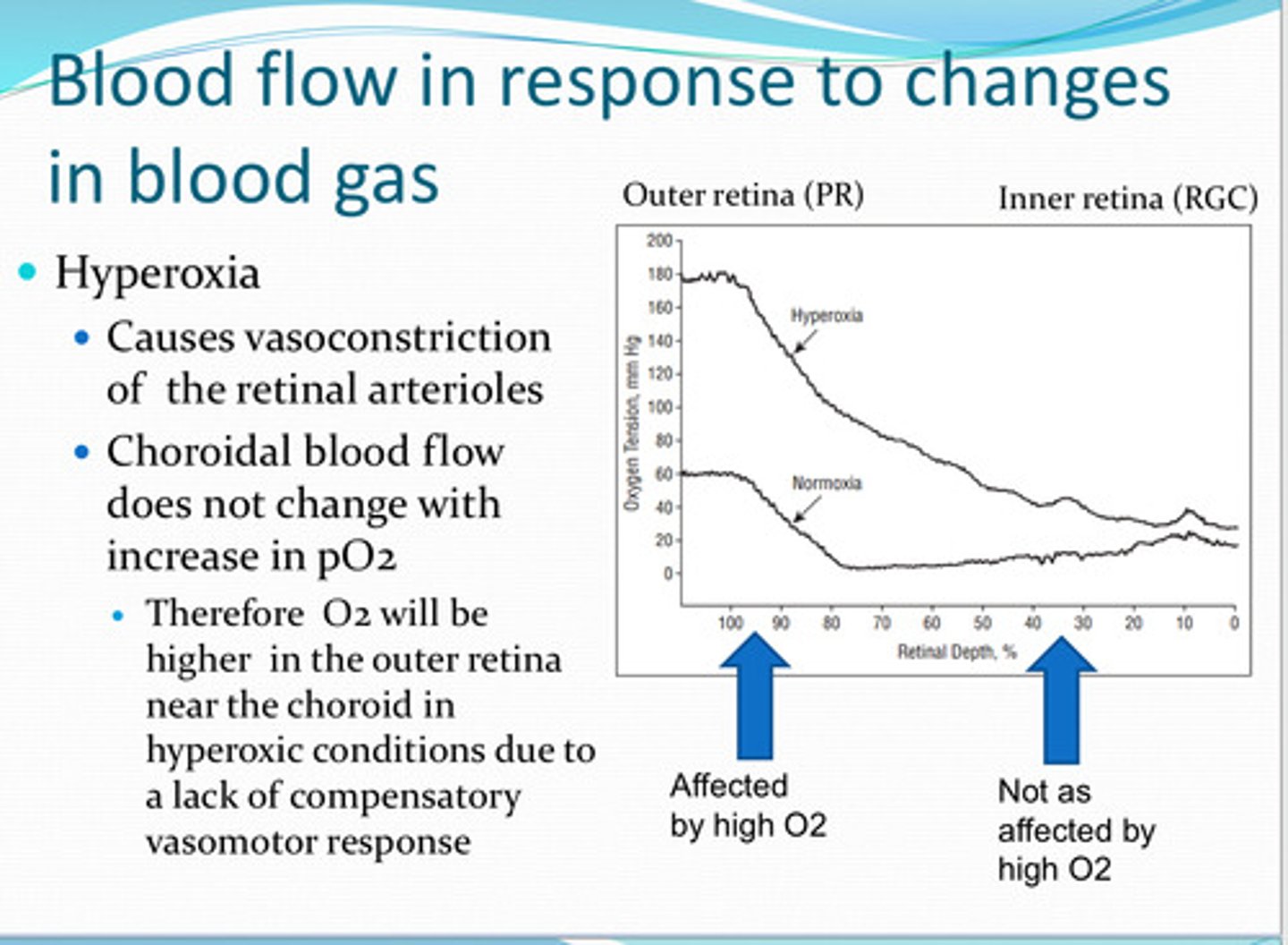
reduction in blood oxygen preferentially affects the ____ retina
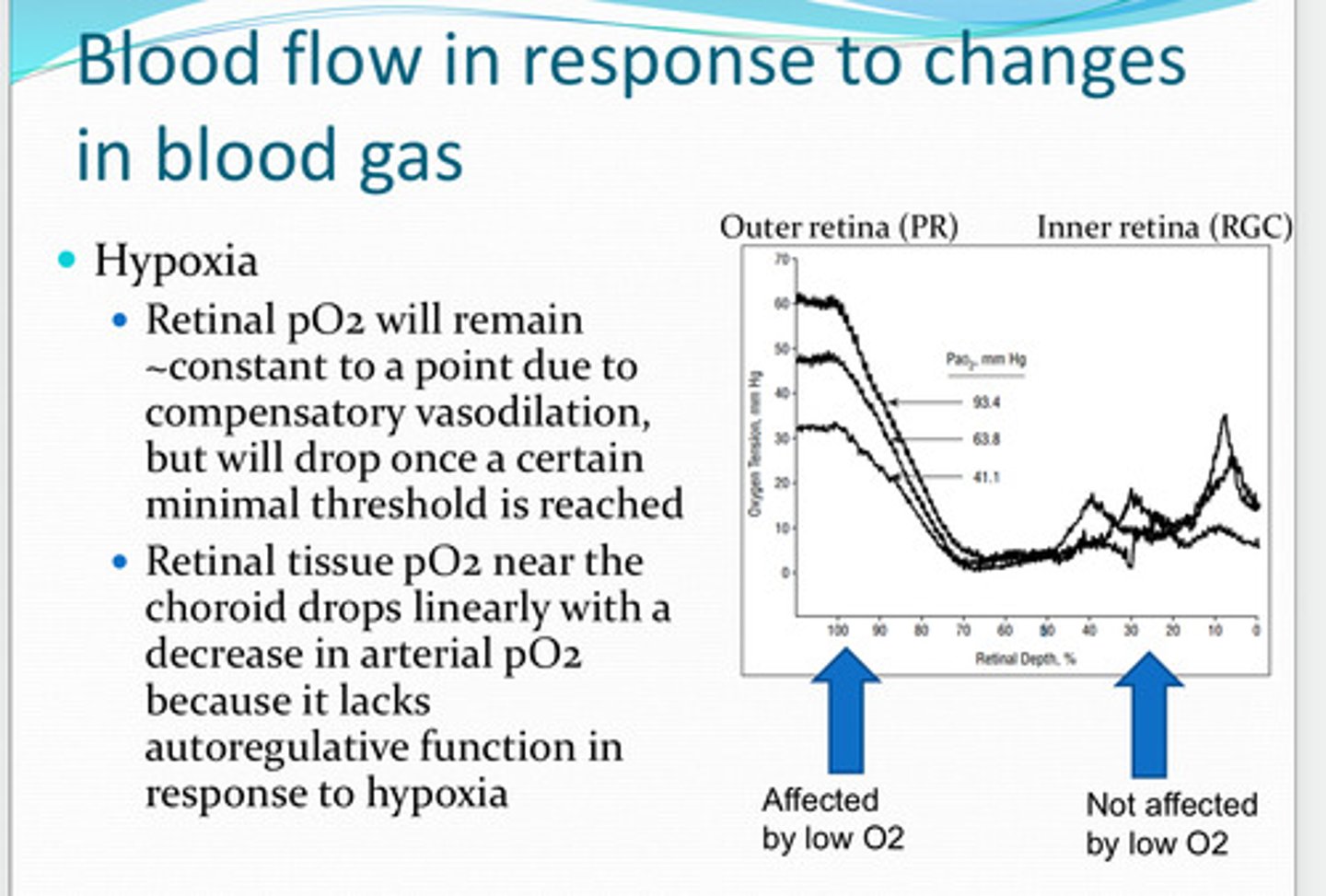
causes vasodilation in the retinal vessels and increases blood flow due to release of retinal lactate and endothelium derived nitric oxide
Hypoxia of the retina causes what?
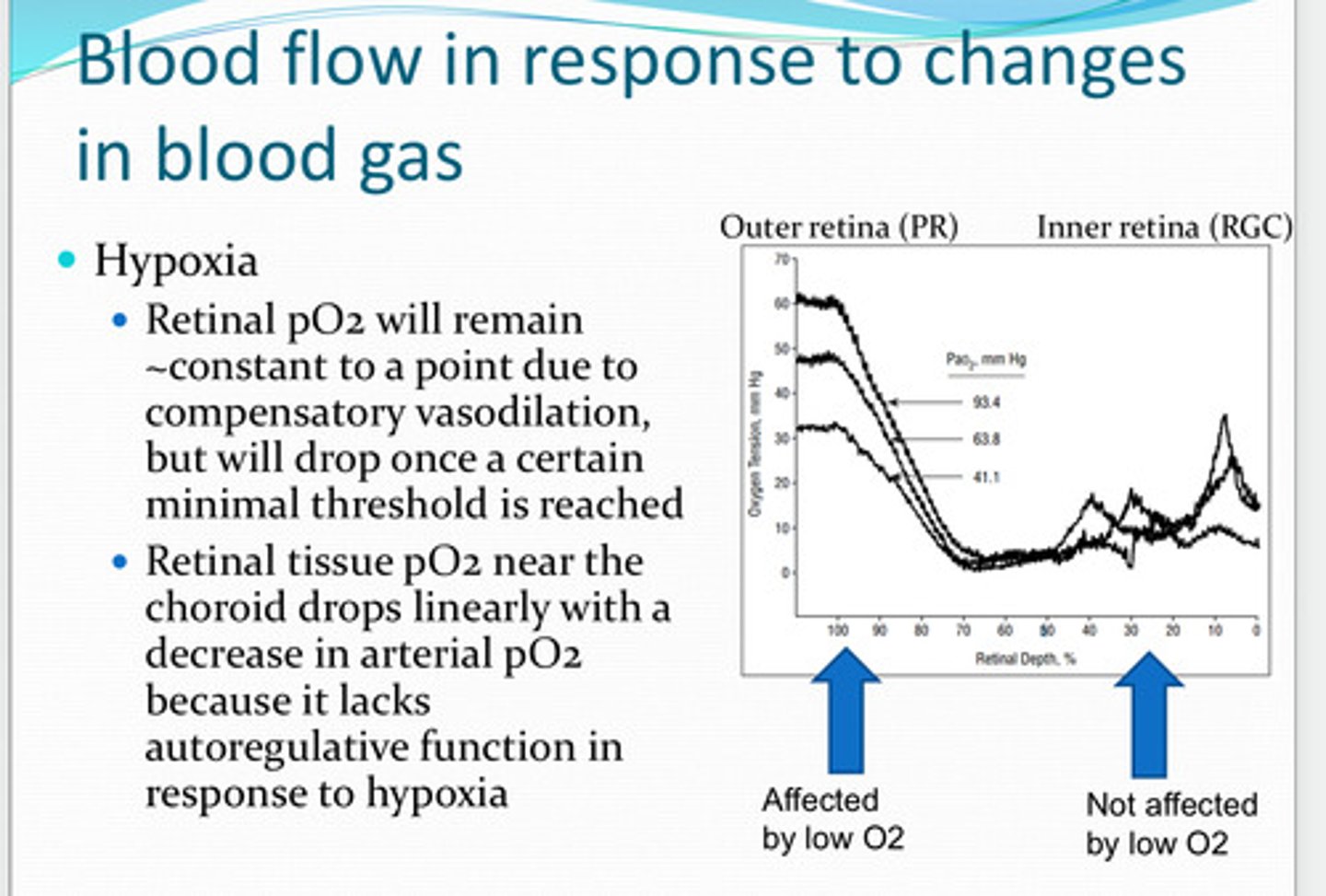
retinal pO2 will remain about the same to a point due to compensatory vasodilation. it will drop once a certain minimal threshold is reached
With hypoxia, will pO2 remain about the same? Why? When will pO2 drop?
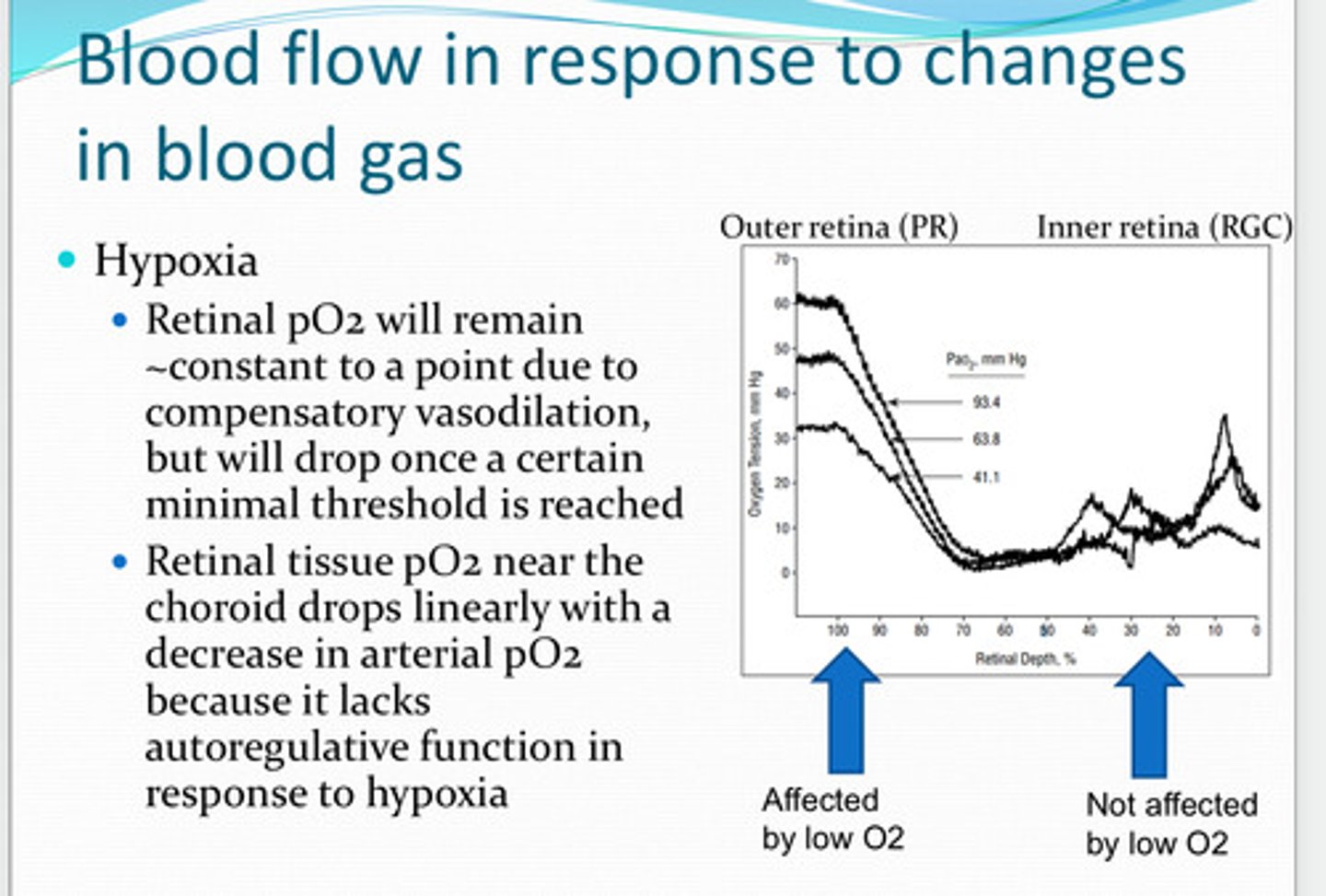
choroid
retinal tissue pO2 near the ____ drops linearly with a decrease in arterial pO2 because of the lack of autoregulation function in response to hypoxia
vasoconstriction
Hyperoxia causes ____ of the retinal arterioles
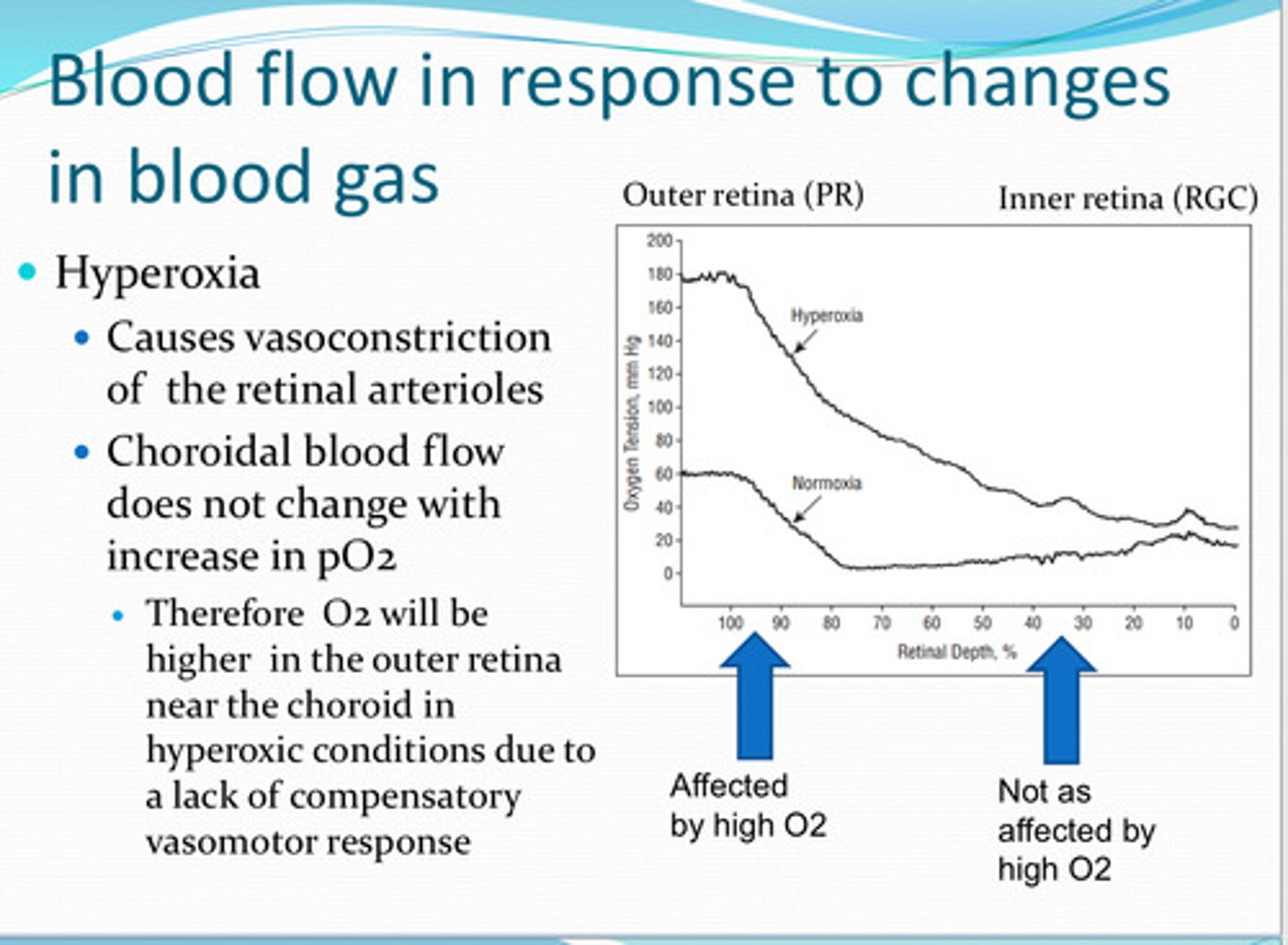
no -- therefore O2 will be higher in the outer retina near the choroid in hyperoxic conditions due to a lack of compensatory vasomotor response
does the choroid blood flow change with increase in pO2 in the retina?
-nitric oxide (NO)
-prostaglandins (PG)
-lactate (stimulating the release of NO and PGs)
What substances play a role in tone relaxing (vasodilation) of retinal blood vessels?
-endothelin-1 (ET-1)
-pericytes express endothelin receptors and respond to ET1 and contract retinal arterioles
What substances play a role in tone contracting (vasoconstriction) of retinal blood vessels?
sympathetic
_____ stimulation reduces choroidal blood flow
-mediated by vasoconstrictive alpha-receptors in smooth muscle cells
-stimulated by the neurotransmitter neuropeptide Y (NPY), a vasoconstricting neurotransmitter
Why does sympathetic stimulation reduce choroidal blood flow?
parasympathetic
_____ stimulation increases choroidal blood flow
-mediated by vasodilation
-stimulated by acetylcholine, vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP), PACAP, and NO
Why does parasympathetic stimulation increase choroidal blood flow?