AP human geography Unit 2
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Overpopulation
When people exceed the capacity of the environment to support life at a decent standard of living.
Ex: If a country is overpopulated, it can cause a lack of resources needed for survival.
Census
An important data source for population geography.
Important for planning and services
helps understand demographics because it provides essential data on race and sex to understand a community
Non - participation
A census may be inaccurate due to this because homeless or people living in a country illegally will not be included in the data.
Sampling
Identifies detailed characteristics of people and is useful for an accurate count.
Ecumene
A portion of Earth’s surface where people are forever settled. such as South Asia, East Asia, Southeast Asia, and Europe.
Physiological density
number of people per unit of farmable land
*can be used to see which countries/regions rely on farming and agriculture the most
Doubling time
The numbers of year needed to double the population assuming a constant natural rate of increase
*important to measure and plan for the future
Arithmetic density
Total number of people in a country/region divided by land area
*can be an important source for measuring the population
NIR (natural increase rate)
The percentage by which a population grows in a year
*can be used to plan for the future because too more or too less people can have consequences.
Agricultural density
The ratio of the number of farmers to the amount of farmable land
*can be used to measure economic development.
TFR (total fertility rate)
The average number of children a woman has through her child bearing years.
*can be used to measure size of population
Demography
The spatial distribution of race, gender, health, fertility, and age.
*can be used for a census
CDR (crude death rate)
Total number of death per year for every 1000 people alive in society.
*can be used to measure life expectancy
CBR (crude birth rate)
Total number of birth per year for every 1000 people alive in society.
*Measure high and low birth rates and plan accordingly.
Zero Population Growth (ZPG)
When the CBR declines to the point where it is equal to the CDR and the NRI is 0
Industrial revolution
A time period where farming became more efficient, Goods became cheaper, and wages increased
*important for economic growth
Medical revolution
Advancements in Medicine, such as vaccines and through technology and have diffused around the world.
*improved life expectancy.
*the cure to COVID - 19
Demographic Transition Model (DMT)
The changes of population through society from high and low CBR and CDR and high and low NRI.
*It can be helpful to understand the economic development of a country/region
*Geographers can use it to better understand what effect the population will cause
Elderly Support Ratio
The number of working age people divided by # of people 65 or older
*can be useful to understand economic development.
Infant Mortality Rate (IMR)
number of deaths of infants under 1 year of age compared with total live births
*can help with understanding healthcare issues
Dependancy ratio
Numbe of people too old or too young to work compared to the number of people in their productive years.
*is helpful in understand the state of employment and economic development.
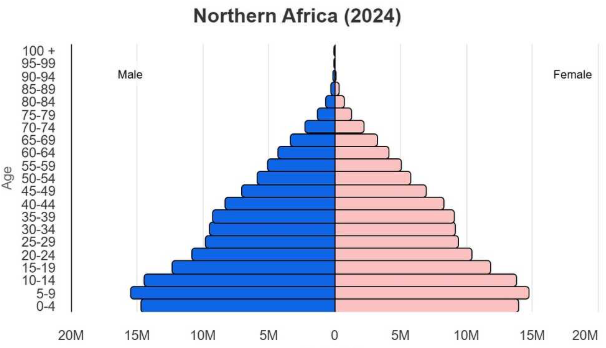
Population pyramid
A bar graph used to represent people base on their age and gender.
Boy = left side Girls = right side Base (0-4 yrs) Top (old people)
Important for planning and services if there are a lot of old people more health care if lots of young people lots of employment
Maternal Mortality Rate
total number of female deaths per 100,000 live births due to pregnancy and childbirth complications.
Sex ratio
The number of males for every 100 females in the population
Epidemology
The branch of science that is concerned with the distribution and control of dieseases within the population
*can help us understand how a virus is diffusing and how to stop it
*people wearing masks to try and prevent the spread of COVID-19
Pandemic
The spread of a disease over a wide geographical area, affecting a large portion of the population.
*COVID-19
Epidemiological transition
Distinctive health threats in each stage of the DMT.
*can help us understand the healthcare needs of population based on their age
Stage 1 (DMT)
CBR + CDR are very high and the NIR is nearly zero.
Stage 2 (DMT)
CBR is high, CDR is very low, and NRI high.
Stage 3
CBR starts to plummet and CDR stays low, NIR is still good but slowing down.
Stage 4
CBR + CDR are both very low and the NIR is near zero.
Stage 5
CBR drops below the CDR and NIR become NDR because population declines.
Malthusian theory
The idea that the population is growing faster than our food supply.
Infectious disease
part of stage 1 and 2. *animal attacks , parasitic diseases.
Chronic disease
Heart cancer, diabetes, flu, extended life expectancy due to medical advancements. part of stage 3,4, and 5
Neo-Malthusian
Population growth, if unchecked, will outpace resources and lead to disaster
Migration
Permanent move to a new location
*important for decreasing overpopulation
*I move to the US from India
Emigration
Leave your origon country to settle in another
*emphasized origon country
*decreases overpopulated areas
Mobility
All types of movement from one place to another.
*form of relocation diffusion
Circulation
Short term, repetitive movements, on an annual, weekly, monthly basis.
*establishes a routine
*going to the temple once a week
Net migration
the difference between the total numbers of immigrants coming into the country and the told number of emigrants leaving a country
*can be helpfulto understand economic development
Immigration
moving into a new country
*emphasizes the destination
*increases population
Postive net migration or net in migration
when the number of immigrants exceeds the number of emigrants
negative net migration or net out migration
The number of emigrants exceed the number of immigrants
International migration
Permanently moving from country to another
*moving from India to the US
*can decrease and increase population
Migration transition
Changes in society that are comparable to the DMT
*it can be used to measured what stage a country in
also useful for measuring economic development
Forced migration
You are COMPELLED to migrate due to economic or environmental reasons.
*war
Voluntary migration
You CHOOSE to leave for economic or environmental reasons.
*job opportunities.
Internal migration
Permanent move with in a country
*moving from Illinois to Indiana for a job
Interregional
moving from one region of a country to another
*leave a rural area to move to a urban area
Intraregional migration
Movement within a region.
*Moving from the city to the suburbs to start a family.
Counterurbanization
When people immigrate into rural areas more than emigrate out of it.
*People might do so if they don’t like the rapid pace, hustle, and the noise of the city and prefer peace and quiet.
Remittance
When a portion of the money you make from working in another country is transfered to someone from the country you emigrated from.
*people do it because they are poor and need to provide
*generates money for the economy because you need to pay to transfer money
*high in South and East Asia
Intervening obstacle
When political or environemental features hinder migration.
*The Trump Adminiistration deploying ICE troops all over the country to round up and deport immigrants legal and illegal.
Desertification
Dry/Drought like conditions due to human actions.
*high in Africa, causes reliance on government and international organizations for things like water.
Floodpain
An area subject to A LOT of flooding.
*Water is up to peoples stomach when walking outside and people are driving vehicles that are halfway in the water.
*common in Jakarta
Asylum Seeker
Someone who has migrated to another country with hopes of being recognized as a refugee.
*can be provided with shelter, food, and water,
Internally displaced person (IDP)
Someone who has migrated for fear of persecution/violence but not across international borders
Pull Factor
Something that causes you to move to a new location.
*job opportunities
Refugee
Forced to migrate to avoid armed conflict and violence.
*Syrian refugees from the civil war.
Push factor
Something that causes you to move out of your present location.
“lack of job opportunities and war.
Unauthorized Immigrant
Someone who enters country without legal documents.
Quota
Maxium limit on the number of people who can immigrate to the United States in a 1 year period.
*passes by Congress to decrease population growth and decrease job competition
Brain Drain
Large scale emigration by talented/skilled people
*increases workforce productivity and economic development in destination country
Chain migration
When someone migrates to a specific location because their relatives or people with the same nationality migrated there previously.
*these factors can help a person get settled easier and if chain migration continues for a few years in the destination country it can increase workforce productivity and economic development.
Guest worker
Someone who temporarily immigrates to a country from a poor country for job opportunities.
*common in the 1960’s and 1970’s in Germany
Circular migration
When someone leaves their country temporarily to go to their host country for work on a daily, monthly, weekly, or annual basis.
*increases workforce productivity and economic development in destenation country.
Ravenstien laws of migration (not in order)
Most of the time people migrate for economic reasons
People migrate within a short distance instead of a long distance
Most migrants are indivduals (not familes) and are adult males
Every migration flow has a counter flow
Migrants who travel long distances usually travel to big city destenations
Urban residents are less migratory than inhabitants of rural areas.
Transhumance
Herd animals have moved from highlands to lowlands between seasons.
requires a lot of space and is an example of seasonal mobility
*sheep
Step migration
Person migrates slowly in small steps.
Ex: Rural to small town to city to suburb
Transnational migration
When you migrate from one nation to another but still maintain the culture from your origon country.
*Dual citizenship and Remittance