BIMM 120 Midterm 1
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Microbiology
study of microorganisms and microbes
Pathogen
disease-causing microorganism
Decomposition
breaking down of organic matter from dead organisms into forms which decomposers (e.g. saprophytic fungi) are able to process them
endosymbiont
in symbiotic relationship, lives within the body or cell of another organism
commensalism
relationship between organisms in which one organism derives benefit and the other is unaffected
Differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Denseness of eukaryotic DNA is higher than eukaryotes
Eukaryotic nuclear envelope keeps DNA organized, prokaryotic DNA floats in nucleoid
Membrane bound organelles in Euk, not in Prok
Eukaryotic chromosomes are typically linear, prokaryotic circular
No introns prokaryotes, present in eukaryotes
Transcription and translation coupled in prokaryotes, separate steps in eukaryotes
What is the relationship between the prokaryote/eukaryote distinction and the taxonomic category “domain?”
Prokaryote and eukaryote have a relationship with the taxonomic category “domain” in the sense that they are themselves domains. Life can be divided into three primary domains, archaea, prokarya, and eukarya.
Archaea are similar to bacteria since they are…
single celled
mostly have cell walls
non nuclear
extremely small (0.5-1 micron)
reproduce quickly ~20min
producers or consumers
possibly living in extreme conditions
Archaea are different from bacteria since they are…
highly genetically dissimilar
dissimilar in molecular makeup
different in cell wall, membrance, metabolic pathway structures
Are Archaea more closely related to bacteria or eukaryotes? How would you determine this?
Archaea are more closely related to eukaryotes than they are to bacteria. You may be able to determine this through sequencing of RNA/DNA genomes and looking for similarities, or you could look at details of the organisms and find similarities there. Eukaryotes and archaea have much more similar metabolic pathways than eukaryotes.
Bacteria
a member of a large group of unicellular microorganisms which have cell walls but lack organelles and an organized nucleus, including some that can cause disease.
Archaea
microorganisms that are similar to bacteria in size and simplicity of structure but radically different in molecular organization. Higher proportion of archaea are extremophiles, plasma membrane structure is very different from bacteria.
Protist
any eukaryote which is not a fungus, plant, or animal, which includes single celled or multicellular organisms (i.e. seaweed)
algae
single celled photosynthetic protist
protozoa
nonphotosynthetic single celled protist
fungus
eukaryote which secretes enzyme into the environment around it to digest food, absorbing nutrients
yeast
single celled fungus
virus
an infective agent that typically consists of a nucleic acid molecule in a protein coat, is too small to be seen by light microscopy, and is able to multiply only within the living cells of a host.
Example of Bacteria, Archaea, Protist, Algae, Protozoa, Fungus, Yeast, Viruses
E. Coli, Thermoproteota, Paramecium, Diatoms Paramecium, Ringworm, Bakers Yeast, Influenza
Are bacteria, archaea, protists, algae protozoa, fungi, yeast, viruses, single or multicellular?

Are bacteria, archaea, protists, algae protozoa, fungi, yeast, viruses, consumers or producers?
bacteria : both
archaea : no
protisits : both
algae : producer
protozoa : consumer
fungus : consumer
yeast : consumer
viruses : consumer
Earliest documented records of infectious disease
Earliest documented infections ~3800 bce, plague
1st Visualization of Microbes
Antony van Leeuwenhoek, 1676, first microscopes
First modern vaccination
Edward Jenner 1796, cowpox ulcer pus scratched into child’s arm for smallpox immunity
First recognition of disease spread by dirty hands
Ignaz Semmelweis 1846, maternity ward
Founders of Modern microbiogy
Koch and Pasteur
Pasteur, disproval of spontaneous generation - boiled broth in curved neck flask which let trapped air escape, allowing for dust and bacteria to collect away from broth. Broth was heated and cooled slowly to sterilize, remained sterile until put into contact with bacteria and dust
Koch, postulates -
1. in all cases of disease, microbe must be found
2. microbe must be able to be isolated from host
3. microbe must be able to reinfect a different host, show same characteristics of disease
4. microbe must then be re-isolated again from reinfected host
First discovery of antibiotic
alexander fleming, 1928, penicillin
First eradication of disease
1977, smallpox
Virus, Bacteria, Eukaryotic Cell sizes

Resolution definition
ability of a microscope to distinguish details of a specimen or sample
resolution requirements
adequate contrast between light and dark
wavelength of light is smaller than object
adequate magnification
Limit of resolution
smallest distance over which two points can be distinguished as separate
light interactions with matter
absorb, refract, reflect, scatter
reason for immersion oil
so light isn’t lost at the glass oil interface
brightfield
utilizing simple stains like crystal violet, methylene blue, carbol fuchsin
Negative staining looks like darkfield, all of background is stained but sample is not!
phase contrast
slows the speed of the incident light, retarding the phase in a way that causes destructive interference between wavelength of speciment and wavelength of light. Results in being able to see live transparent organisms that have been darkened
DIC
phase contrast but with polarized light
Darkfield
utilizes only scattered light to visualize organisms. specimen is obliquely lit, and may allow view of much smaller objects
transmitted electron microscopy
transmitted electrons emitted and detected by fluorescent screen
scanning electron microscopy
scattered electrons are detected, 3D image
what is needed for proper resolution?
adequate contrast, magnification, and wavelength of light smaller than object
what do eukaryotes and prokaryotes have in common?
eukaryotes and prokaryotes…
have DNA
have ribosomes
have plasma membrane
have cytoplasm
have motor elements like flagella
coccus

coccobacillus

vibrio

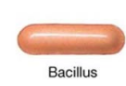
bacillus
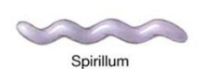
spirillium
spirochete

Prokaryotic Plasma membrane is a…
fluid mosaic. proteins are half the weight of the plasma membrane. receptors for environmental conditions, nutrient transport, secretion pores, ETC and ATP synthase, and pathogenic virulence factors are all in the plasma membrane
Plasma membrane
unsat = loose, sat = tighter, hopanoids can form even tighter membranes at high temperatures. Archaea have even more methods to conserve membrane integrity at high temperatures like making tetraether lipds to make a monolayer, or cyclizing isoprene to increase membrane stiffness
cell walls
help maintain shape, resist osmotic pressure, resist harsh conditions