Unit 6 Vocab
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms

Emission Spectra
The range of light (or electromagnetic radiation) emitted by an atom or molecule when its electrons fall from a higher to a lower energy level.
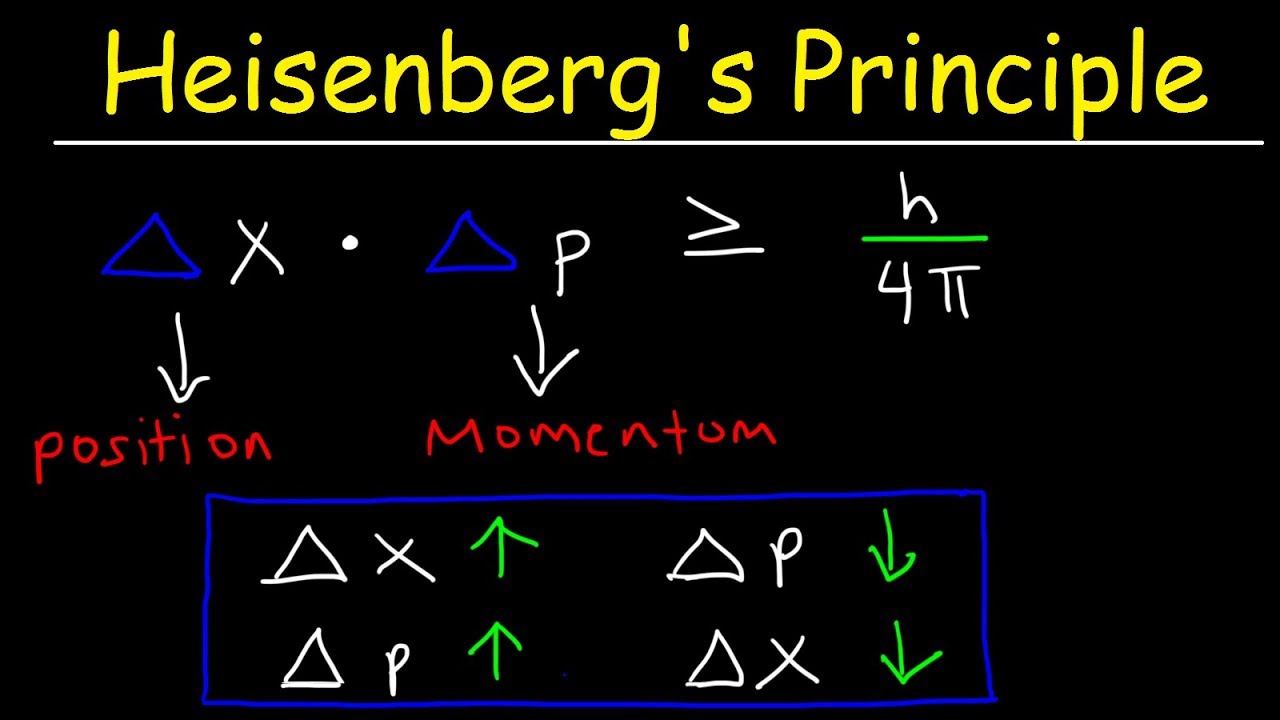
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
A quantum physics rule stating that it's impossible to know both the exact position and exact momentum of a particle at the same time.
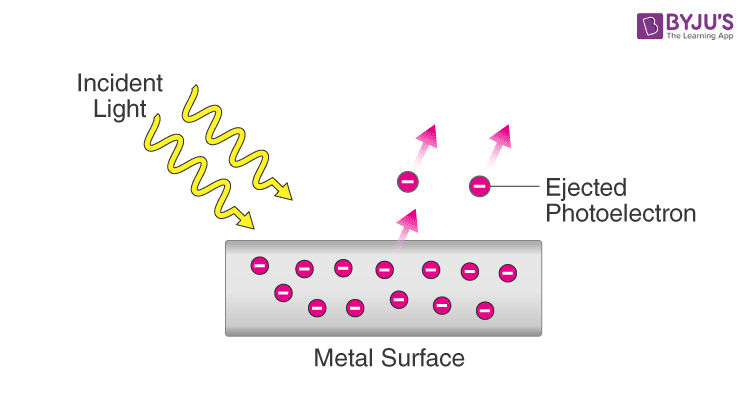
Photoelectric Effect
When light hits a metal surface and causes electrons to be ejected from that surface.
Quantum
The smallest possible amount of something, often referring to energy in quantum physics.
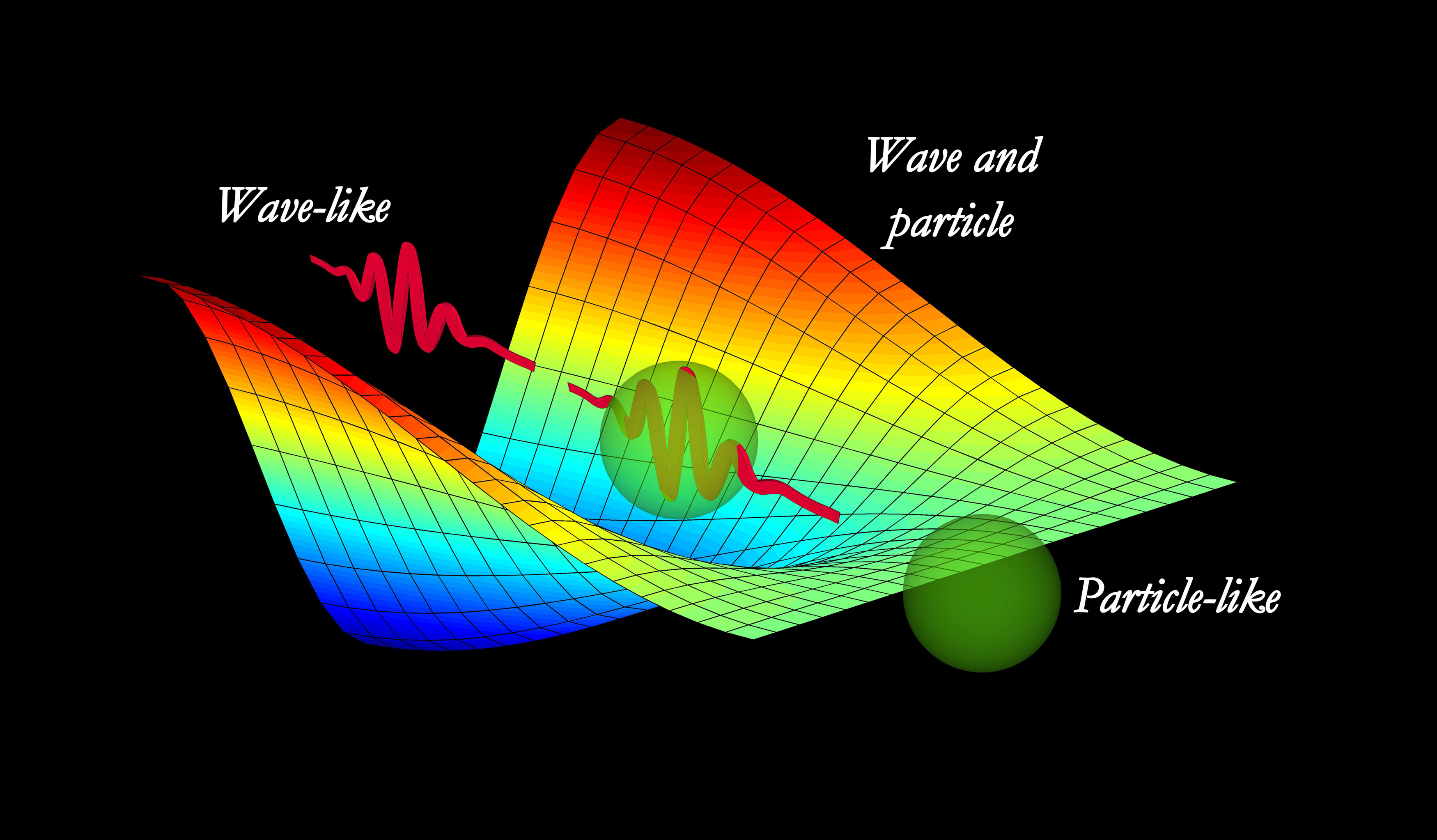
Wave-Particle Duality
The idea that particles like electrons and photons behave both like waves and like particles.
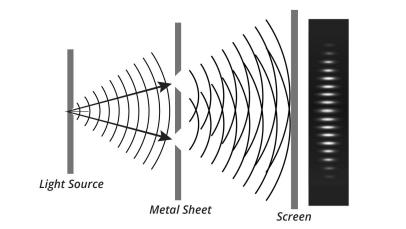
Double Slit Experiment
A famous experiment showing that light and particles can act like waves, creating an interference pattern when passed through two slits.
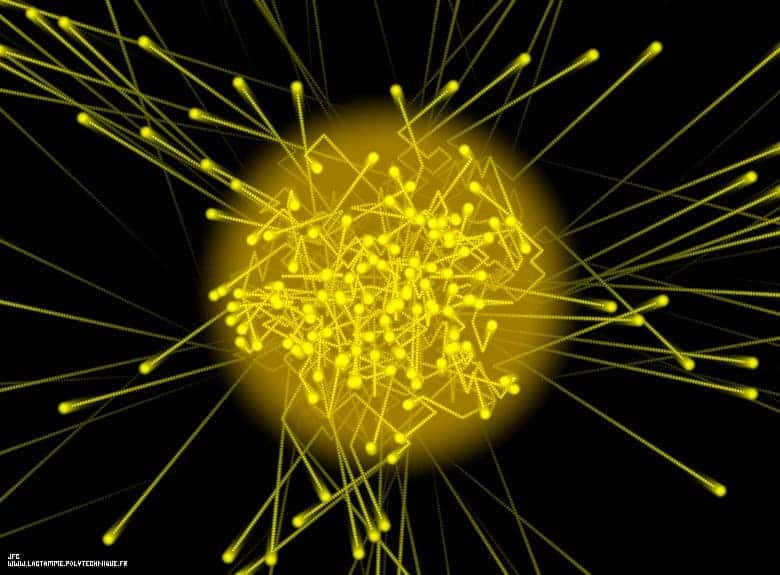
Photons
Tiny particles of light that carry energy but have no mass.

Cyber Security
The practice of protecting computers, networks, and data from unauthorized access or attacks.
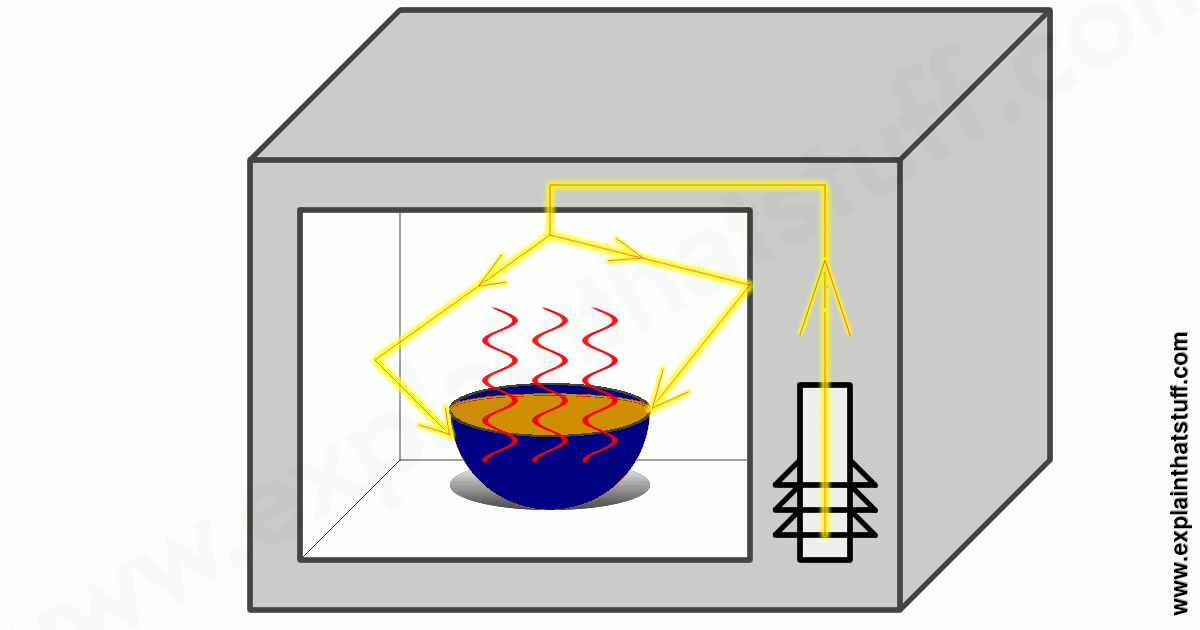
Microwaves
A type of electromagnetic wave with longer wavelengths than infrared light, used in cooking and wireless communication.
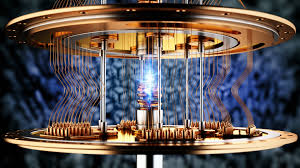
Quantum Computing
A new type of computing that uses quantum bits (qubits) to perform complex calculations much faster than traditional computers.

Radio Telescope
A device that uses antennas to detect radio waves from space, helping astronomers study stars, galaxies, and other cosmic objects.
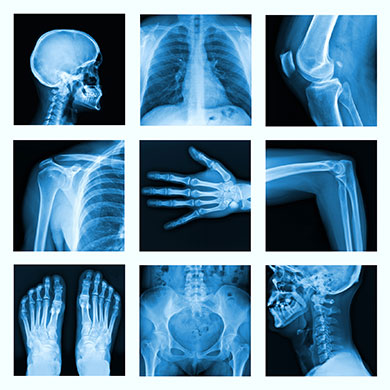
X-Rays
High-energy electromagnetic waves used in medicine to view inside the body and in astronomy to observe high-energy space objects.
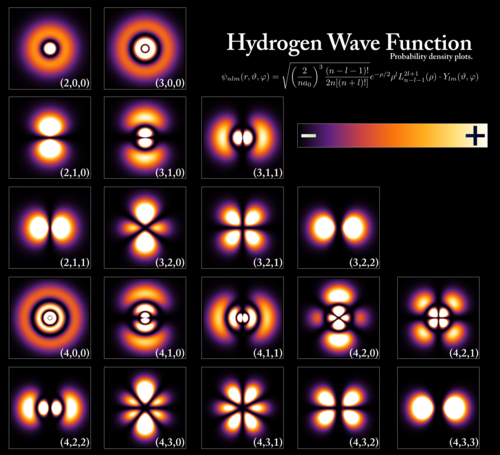
Quantum State
A complete description of a quantum system, including information about all its possible measurable properties.Q
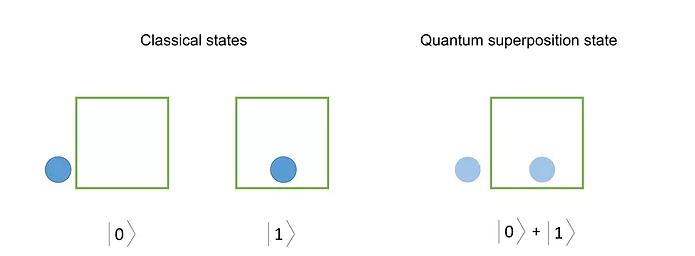
Quantum Superposition
A principle in quantum mechanics where a particle can exist in multiple states at the same time until it is measured.