Ch9 Joints
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
joint definition
where two bones (or cartilage) come together to form a sometimes movable structure
articulation
3 functional classifications of joints — movement
synarthrotic
amphiarthrotic
diarthrotic
3 structural classifications of joints — tissue
fibrous
cartilaginous
synovial
synarthrotic joint
immobile or nearly immobile
strong articulation
where are synarthrotic joints found
bones protecting internal organs
fibrous sutures of skull
cartilaginous manubriosternal joint
amphiarthrotic joint
limited mobility
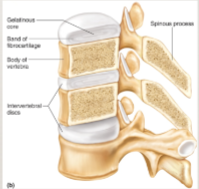
amphiarthrotic joint: vertebral joints
include the fibrocartilage discs
minor movement between joints is allowed
amphiarthrotic joint: pubic symphysis
right and left coxal bones articulate via pad of fibrocartilage
diarthrotic joint
freely moveable joint
all synovial joints are included here
most are found in appendicular skeleton
3 subclassifications of diarthrotic joints
uniaxial
biaxial
multiaxial
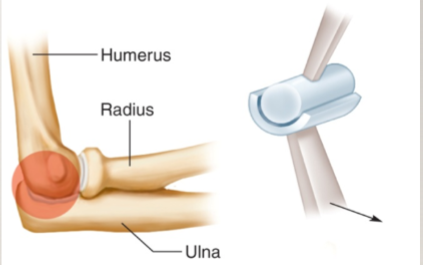
diarthrosis: uniaxial joint (and example)
movement on a single plane
humerus and ulnar articulation only allows flexion/extension
diarthrosis: biaxial joint (and example)
movement in two planes
metocarpohalangeal (knuckle) joint allows flexion/extension, but also lateral/medial movement

diarthrosis: multiaxial joint (and example)
movement along three axes
shoulder and hip joints allow anterior/posterior, medial/lateral, and rotation

fibrous joints
bones articulate via fibrous connective tissue
subclassifications of fibrous joints
suture
syndesmosis
gomphosis
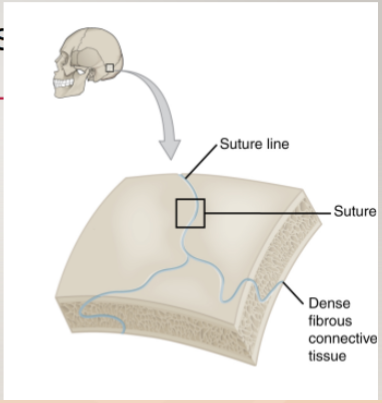
fibrous joints: suture
strong union between adjacent bones
typically classified as synarthrotic
think skull

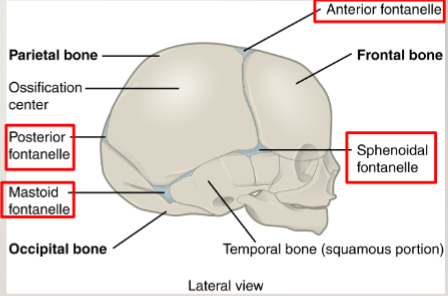
fontanelle
connective tissue between skull plates in infants
allows the skull to compress during birth
after birth they become sutures by ossification
synostosis
fusion of two or more bones into one bone
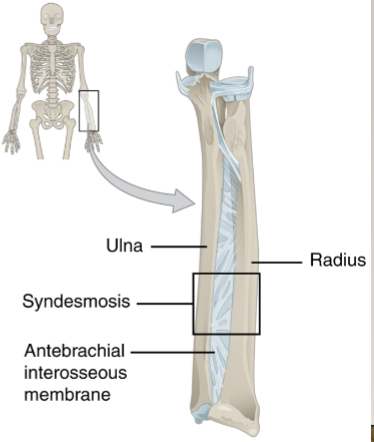
fibrous joints: syndesmosis
parallel bones are united by fibrous connective tissue
syndesmosis: interosseous membrane (and examples)
narrow or wide gap between parallel bones spanned by connective tissue
radius and ulna — allows for rotation
tibia and fibula — locks talus between tibia and fibula
fibrous joints: gomphosis
fibrous joint that anchors the root of tooth to bony socket in maxilla or mandible
called peg-and-socket joint
periodontal ligament
short bands of dense connective tissue fasten tooth within gomphosis joint
cartilaginous joint calssifications
synchondrosis
symphysis
cartilaginous joints: synchondrosis
bones joined by hyaline cartilage
permenant vs temporary synchondrosis example
sternocostal joint vs epiphyseal plate
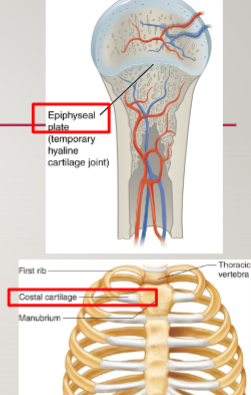
epiphyseal plate
area of actively growing cartilage and bone during adolescence
fuses to a synestosis during adulthood
cartilaginous joints: symphysis
fibrocartilage joins bones
resistant to pulling and bending bc of collagen fibers
amphiarthrotic
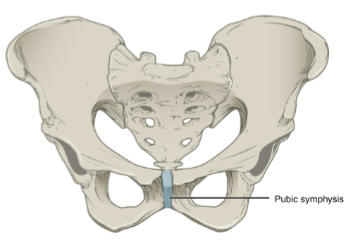
examples of symphysis joints
intervertebral discs
pubic symphysis
manubriosternal joint
synovial joints
have a joint cavity
articulating joints are not directly connected
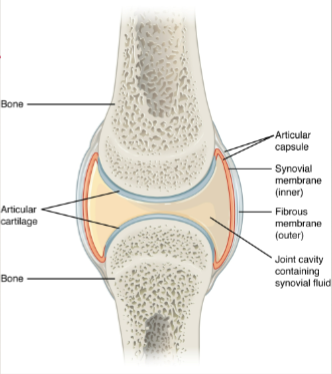
synovial joints: articular capsule
fibrous structure attached to each bone outside of articulating surface
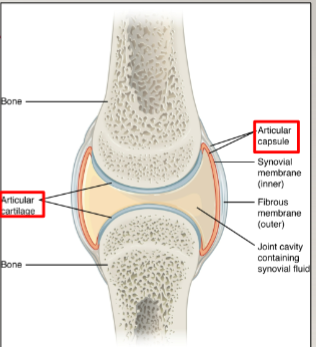
synovial joints: articular cartilage
thin layer of hyaline cartilage that covers articulating surface of each bone
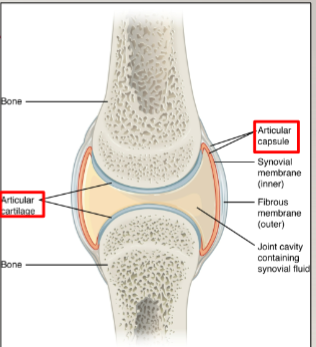
synovial joints: synovial membrane
lines inner surface of articular capsule and secretes synovial fluid for lubrication

ligament classifications
extrinsic ligament
intrinsic ligamen
intracapsular ligament
extrinsic ligament (and example)
located outside of joint capsule
ex. patellar ligament
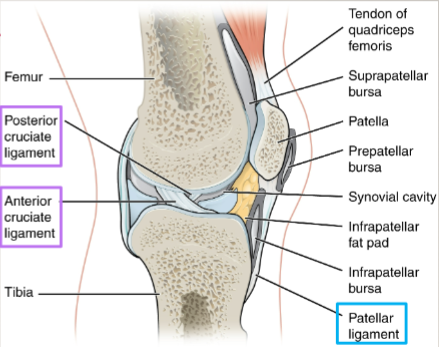
intrinsic ligament
fused to or incorporated into wall of articular cappsule
intracapsular ligament
located inside articular capsule
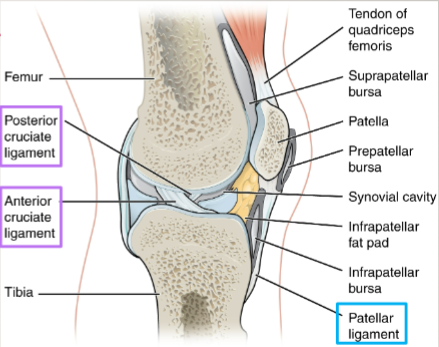
tendon
dense connective tissue that attaches muscle to bone
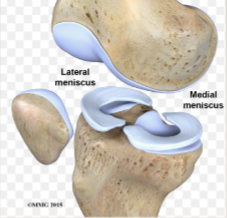
articular discs // meniscus
may help join bones together
provides cushioning and shock absorption
bursa
thin connective tissue sac with lubricating fluid
located outside of synovial joint
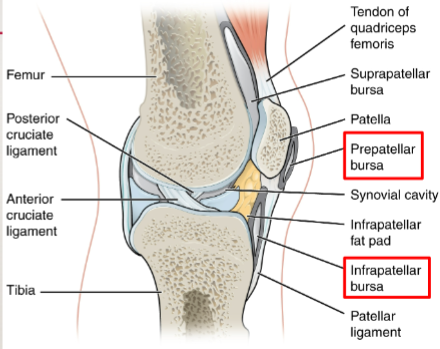
where can you find bursas
where skin, ligaments, muscles, and/or tendons rub against each other
bursa classifications
subcutaneous bursa (patellar)
submuscular bursa (trochanteric)
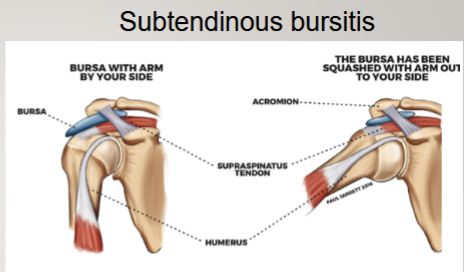
subtendinous bursa (subacromial)
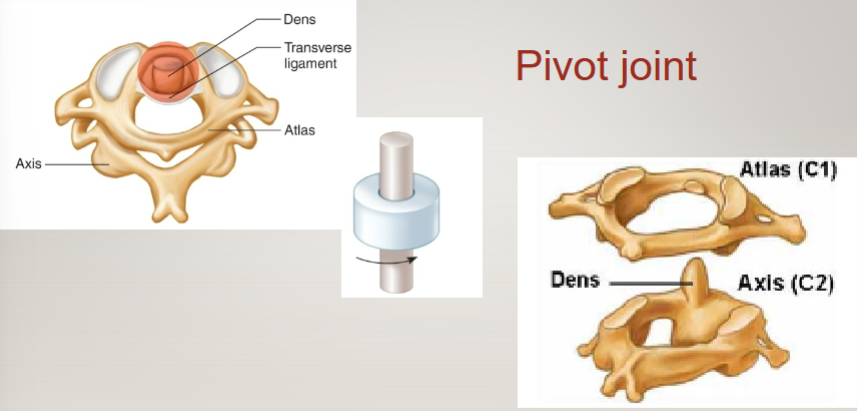
example of pivot joint
C1 and C2 with the dens
synovial joint: shoulder joint
ball and socket
tendons of several muscles blend with fibrous layer of joint capsule to form rotator cuff
synovial joint: elbow joint
two articulations
hinge between trochlea of humerus and trochlear notch of ulna
plane between capitulum of humerus and fovea of radius head
pivot joint of radial head on ulna
knee joint
largest and most complex synovial joint
condyles of femur and tibia
allows some rotation
hip joint
ball and socket joint
head of femur + acetabulum of hip bone
flexion vs extension
angle between two body parts is decreased vs increased

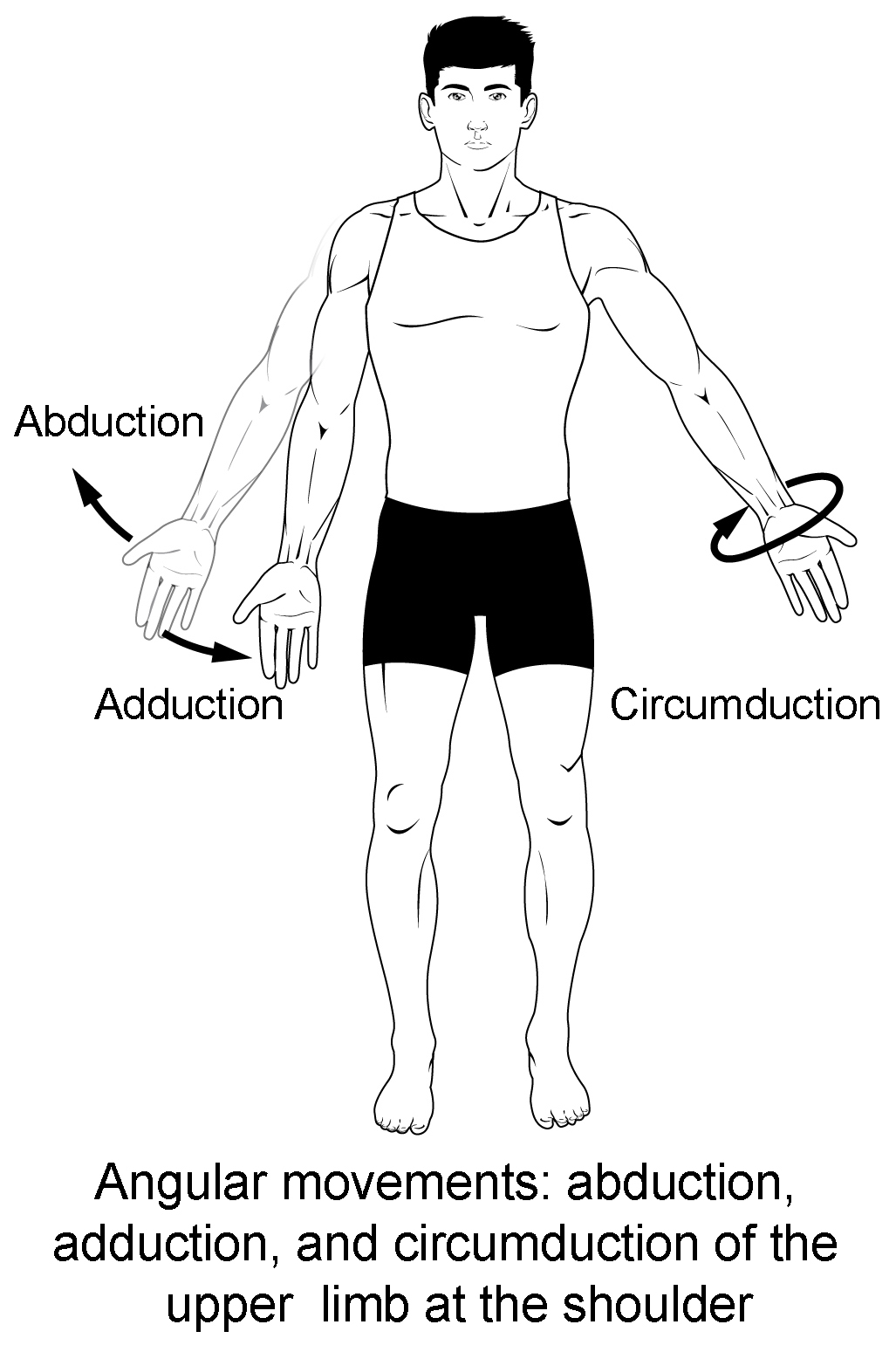
abduction vs adduction vs circumduction
movement away from midline vs toward midline vs combined
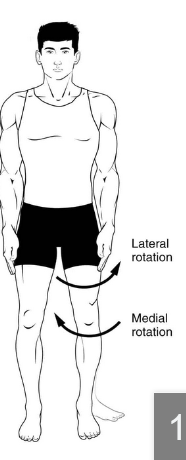
lateral vs medial rotation
synonymous with external vs internal rotation
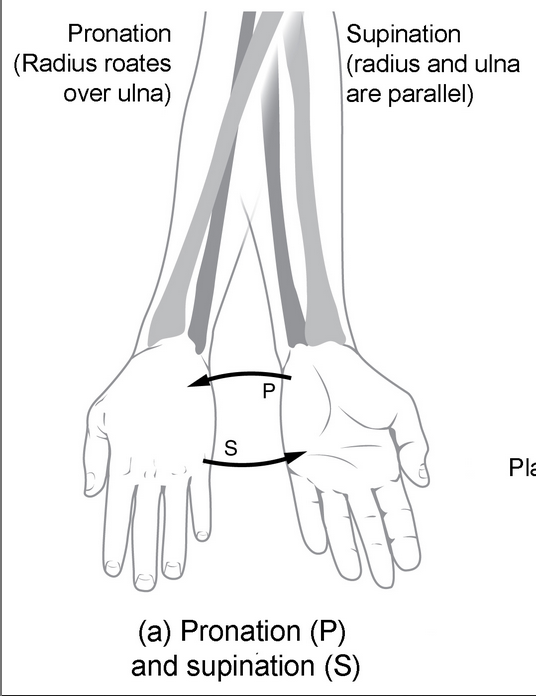
supination vs pronation
palms up vs palms down
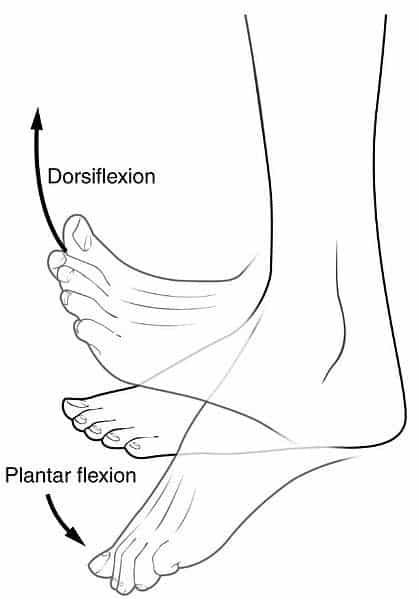
plantar flexion vs dorsiflexion
toes down vs toes up (ankle movement)
inversion vs eversion
sole of the foot toward the midline vs away from the midline

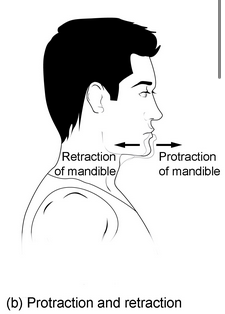
retraction vs protraction
posterior vs anterior movement
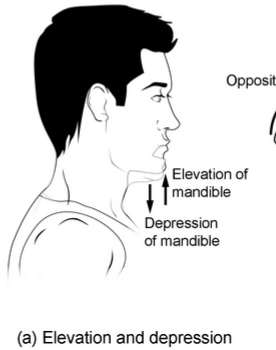
elevation vs depression
superior vs inferior movement
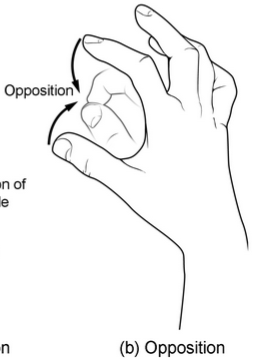
opposition
thumb and finger pads join