ACERIP Study Materials: Basics and Wellness in Emergency Medical Services
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Emergency
someone's well-being is at risk, not necessarily life-threatening
Describe the beginning of EMS
- 1940s/50s
- Started in funeral homes
- Black men were first
- Always improves post war
Highway Safety Act of 1966
required each state to establish a highway safety program that met prescribed federal standards and included emergency services
"White papers" for EMS, why EMS is under Dept. of Trans.(though most of country includes them in fire dept.)
white papers
an authoritative report or guide that addresses important issues in an industry and offers solutions
4 parts of an EMS system
access, care, transport, facility
Describe the access portion of EMS
PSAP (911) answered by EMDs (emergency medical dispatchers, may provide limited verbal instructions to patient)
Describe the care portion of EMS
Main job is to stabilize on scene and provide life-saving care to prevent injury (do not harm)
Describe the transport portion of EMS
- provide medical care en route
- every call gets a ticket (report)
- document ALL belongings
- Take note of meds, do not take meds
Trauma center levels
1) all care
2) initial care
3) assessment/resuscitation
4) basic life support
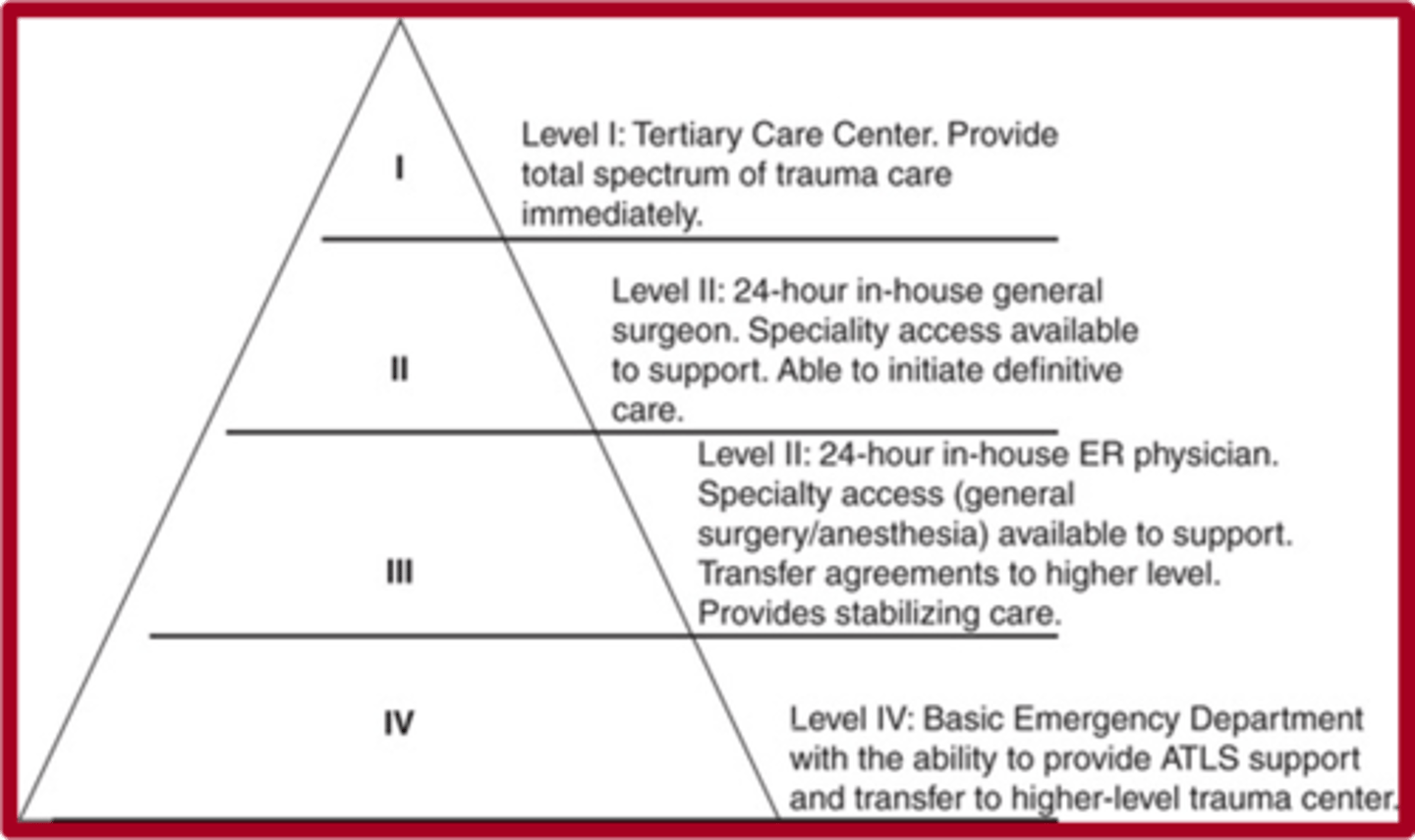
level 1 trauma center
- all types of trauma 24/7
- lots of research
- includes specialty hospitals
level 1 trauma centers in triangle
UNC and Duke
Hierarchy of EMS positions
Paramedic > AEMT > EMT > EMR
EMR (emergency medical responder)
- first on scene (typically fire dept.)
- only immediate care

EMT (Emergency Medical Technician)
- Stabilize non life-threatening injuries
- Control life-threatening situations
- certified by state

AEMT (Advanced EMT)
- IVs, more meds, & airway techniques
- some EKG stuff

Paramedic (EMT-P)
- all the basic EMT duties + in-depth assessment provision of - advanced cardiac life support & EKG interpretation
- intubation
#1 priority of EMT care
yourself (make sure you, your partner, and bystanders are safe at all times)
Most common dangerous situations
inebriation, domestic dispute, traffic
BSI (Body Substance Isolation)
Assumes that all substances are infectious
Medical director
- physician who authorizes or delegates to the EMT the authority to provide medical care in the field
- can revoke local not state credentials
On-line medical direction
Orders from the on-duty physician given directly to an EMT in the field by radio or telephone (ex. using unprescribed meds)
Off-line medical direction
Written protocols and standing orders issued by the Medical Director that allow EMTs to give certain medications or perform certain procedures without speaking to the Medical Director or another physician.
Acute stress response
- during/immediately after
- mainly anxiety symptoms
- sudden, unexpected catastrophic events
Delayed stress response
- long after
- PTSD symptoms
Cumulative stress response
- from constant high-stress
- burnout
How do you respond to hostile grief
empathetically, never reactively
maintain dignity, communicate, no false assurances, show respect, allow expression, comfort them