Cell Biology-AP Bio Full Set Diagram | Quizlet
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
Selective Permeability
Allows some substances to cross more easily than others
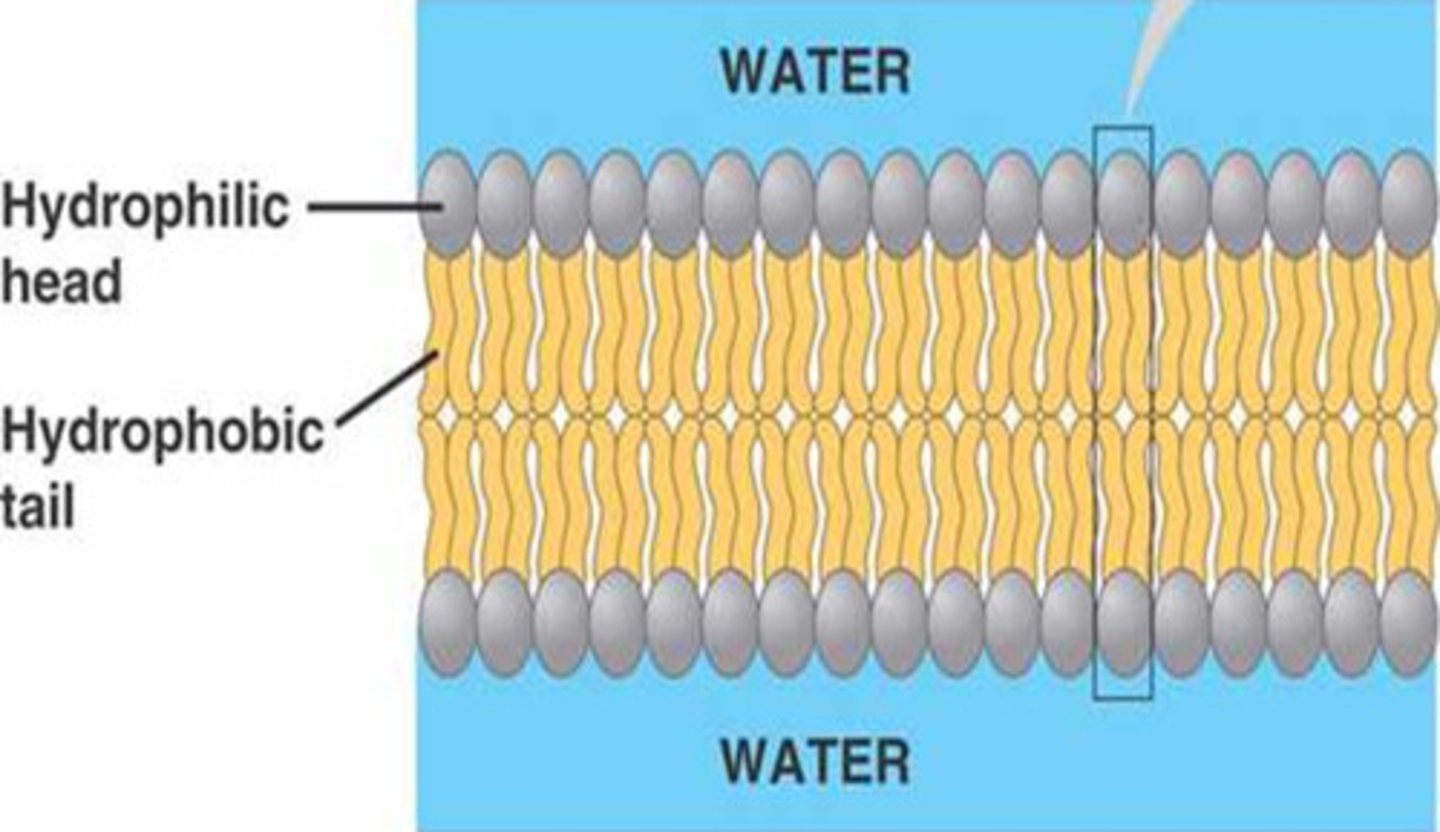
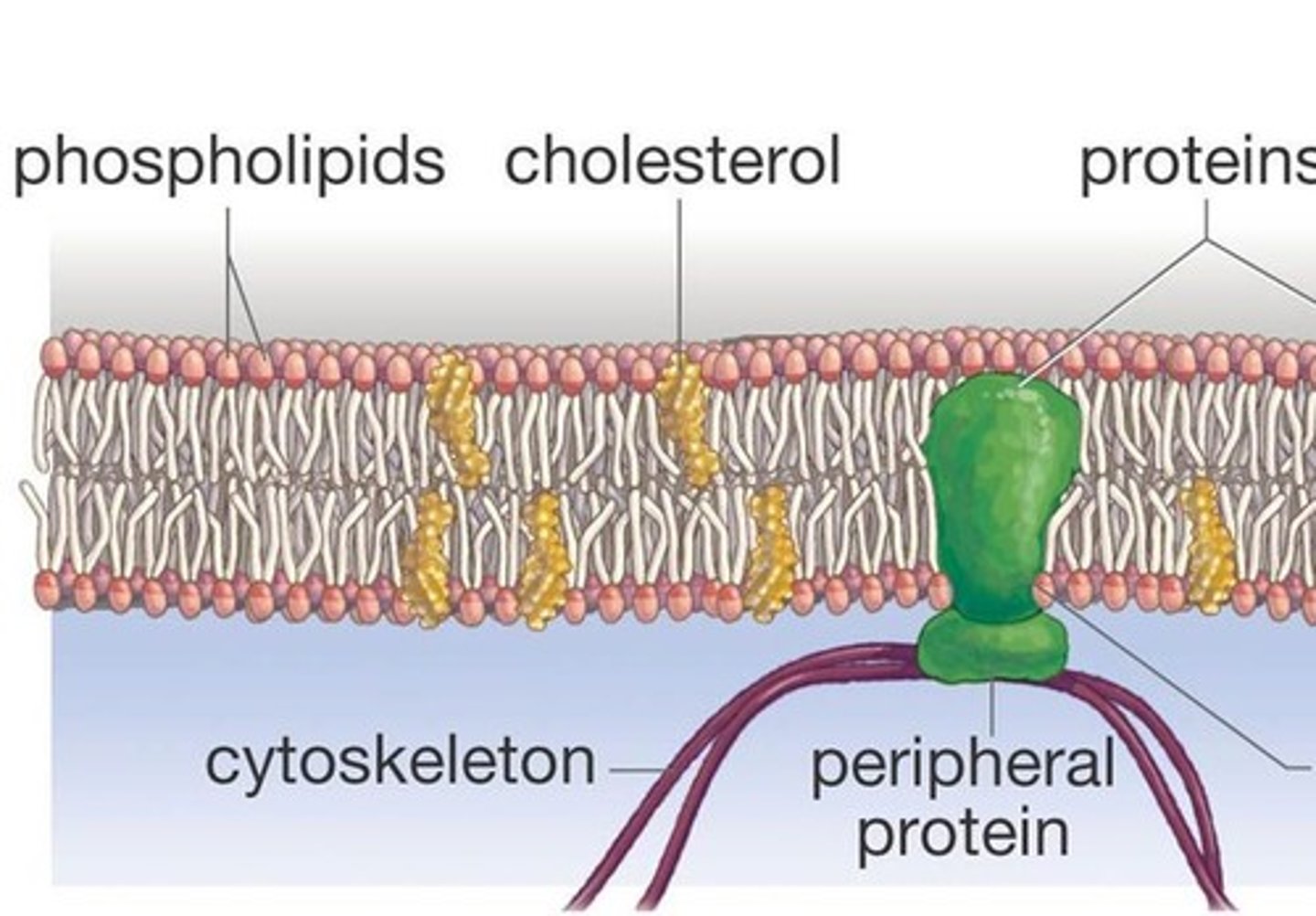
phospholipid bilayer
a double layer of phospholipids that makes up plasma membranes
Integral Membrane Proteins
Proteins that extend through the phospholipid bilayer. Has regions that are both polar and non polar (ampipathic)
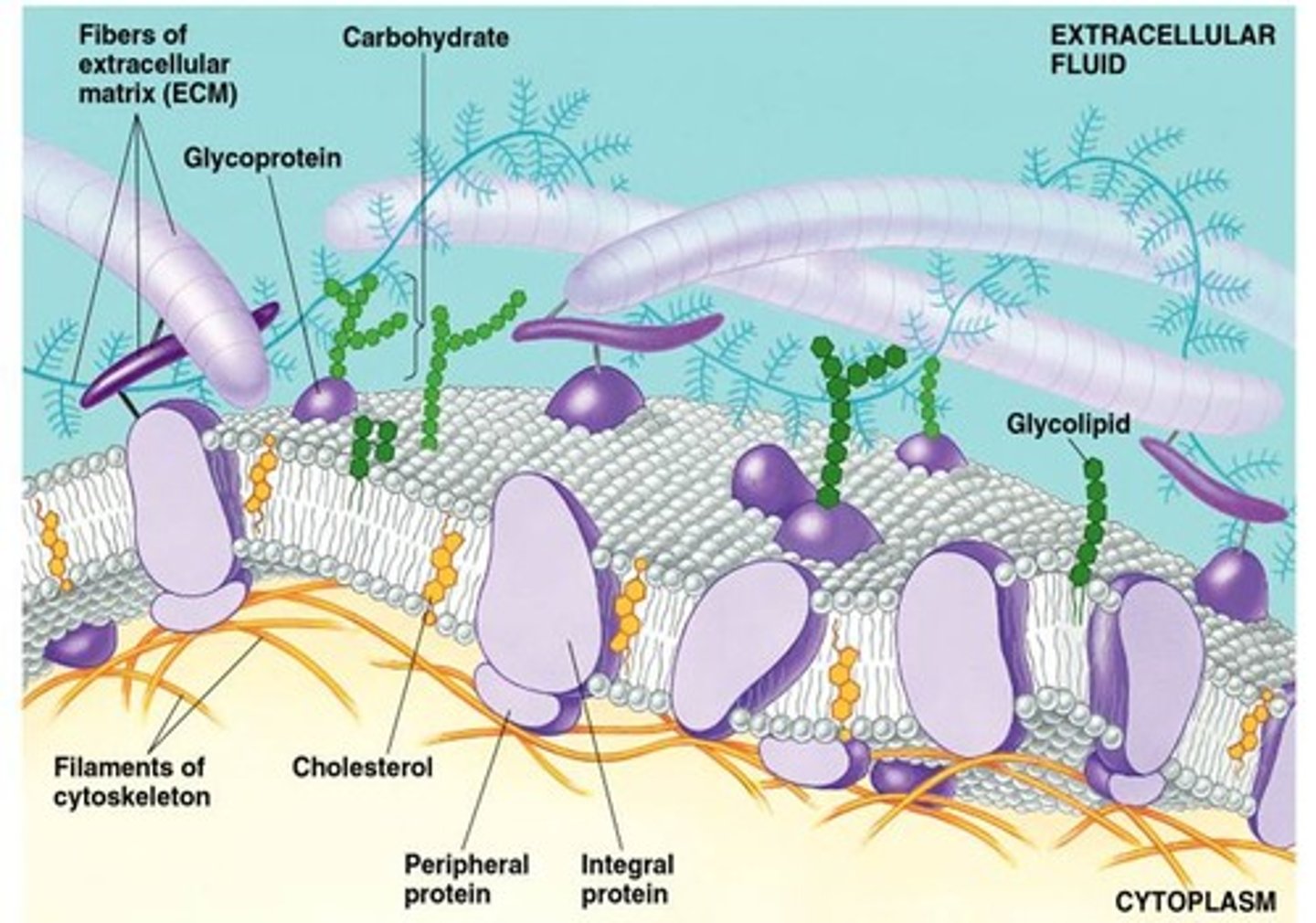
Peripheral Proteins
A protein loosely attached to the surface of a membrane
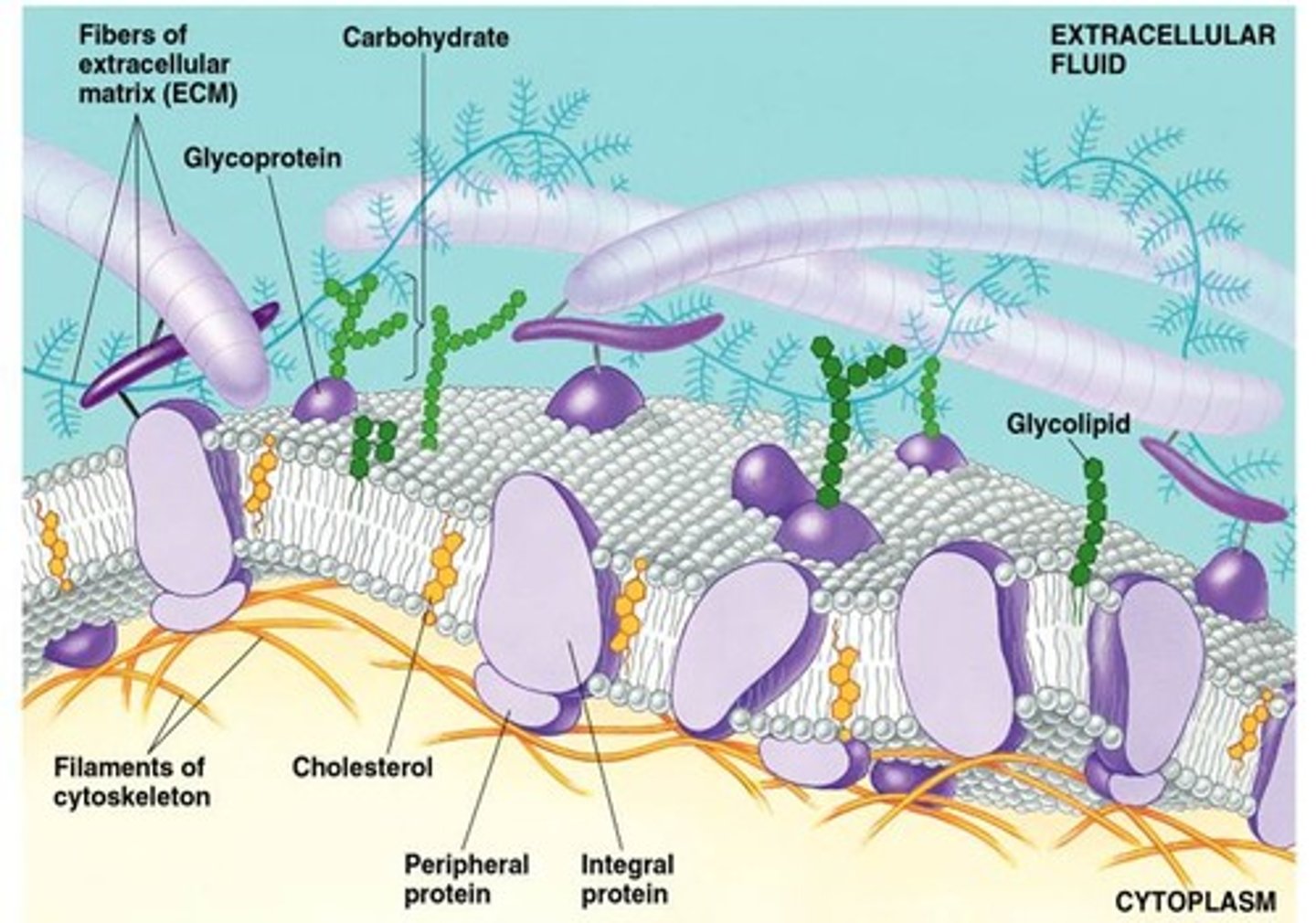
Glycoproteins
proteins that have carbohydrates covalently bonded to them
cholesterol
steroid present in the plasma membranes of animal cells. A large amount of this in a phospholipid bilayer at High Temperatures reduces membrane fluidity, but at Lower Temperature prevents the membrane from solidifying.
Concentration Gradient
a difference in the concentration of a substance across a space
Diffusion
the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, so that they spread out evenly reaching equilibrium
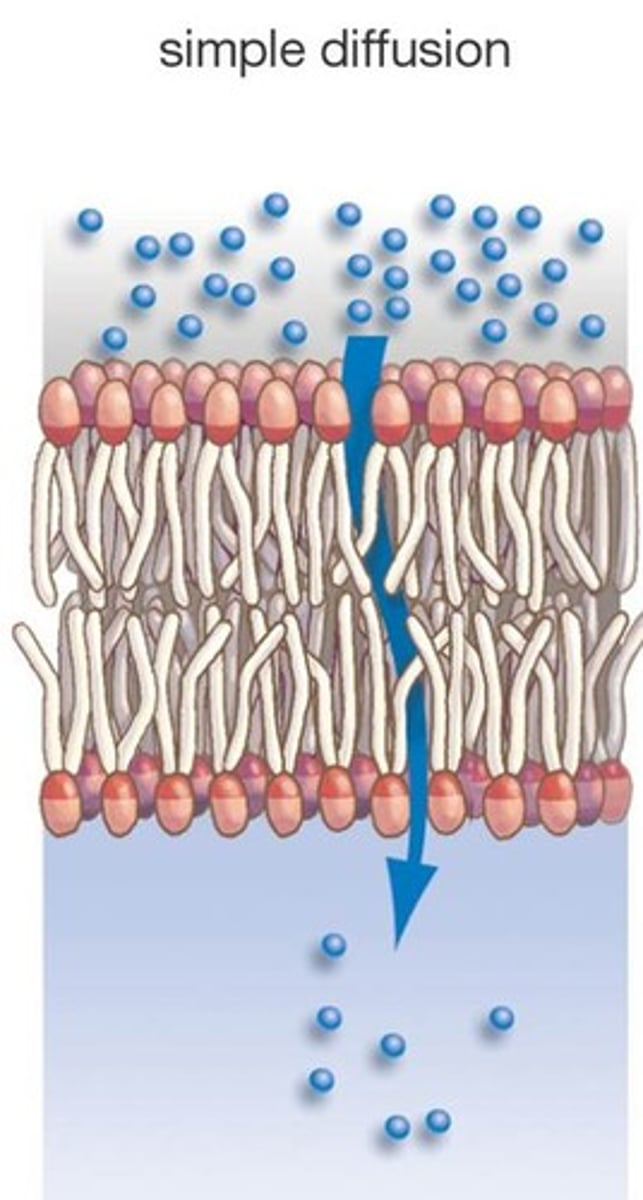
Osmosis
The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane
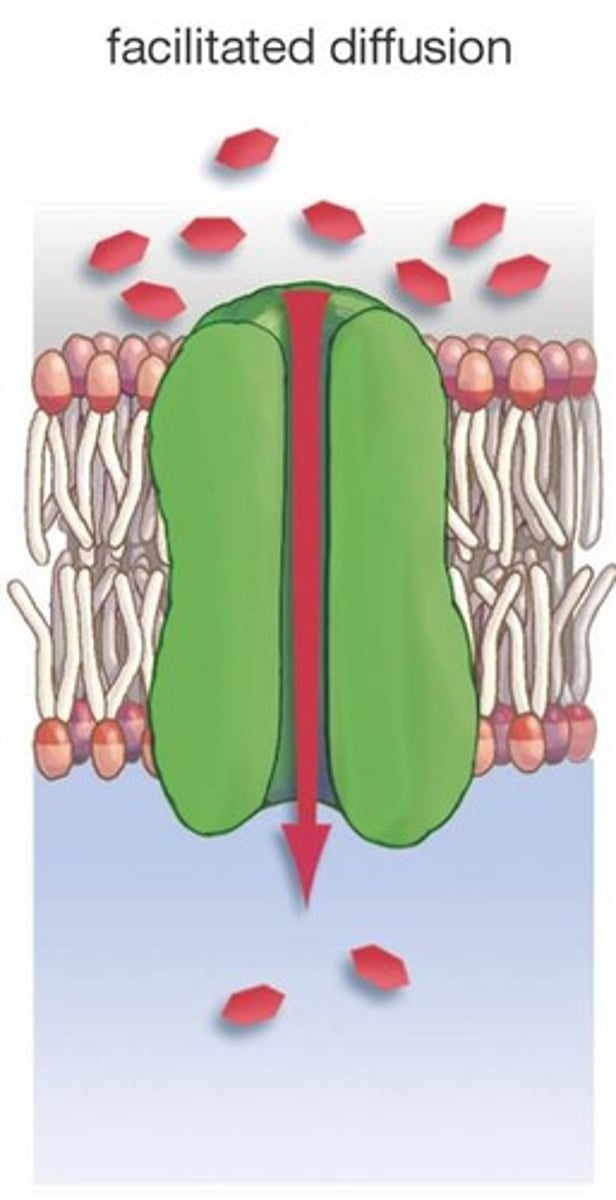
Transport Proteins
proteins that help to transport substances across cell membranes
Aquaporins
Channel proteins that help massive amount of water pass through the membrane; a lot in our kidneys
Passive Transport
movement of materials through a cell membrane without using energy
Isotonic
a solution whose solute concentration equals that inside a cell; the cell will not change

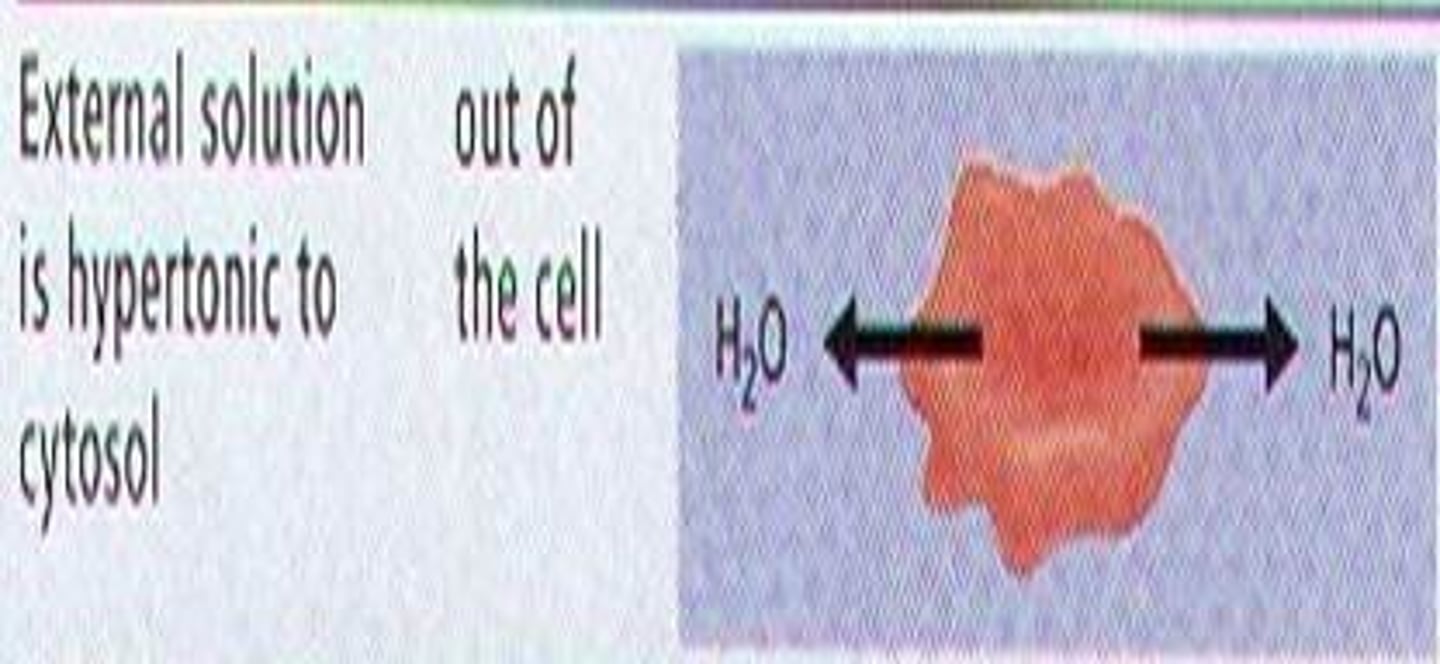
Hypertonic
the solution with the greater concentration of solutes than that inside the cell; the cell will lose water to its environment--> Cell will shrivel up
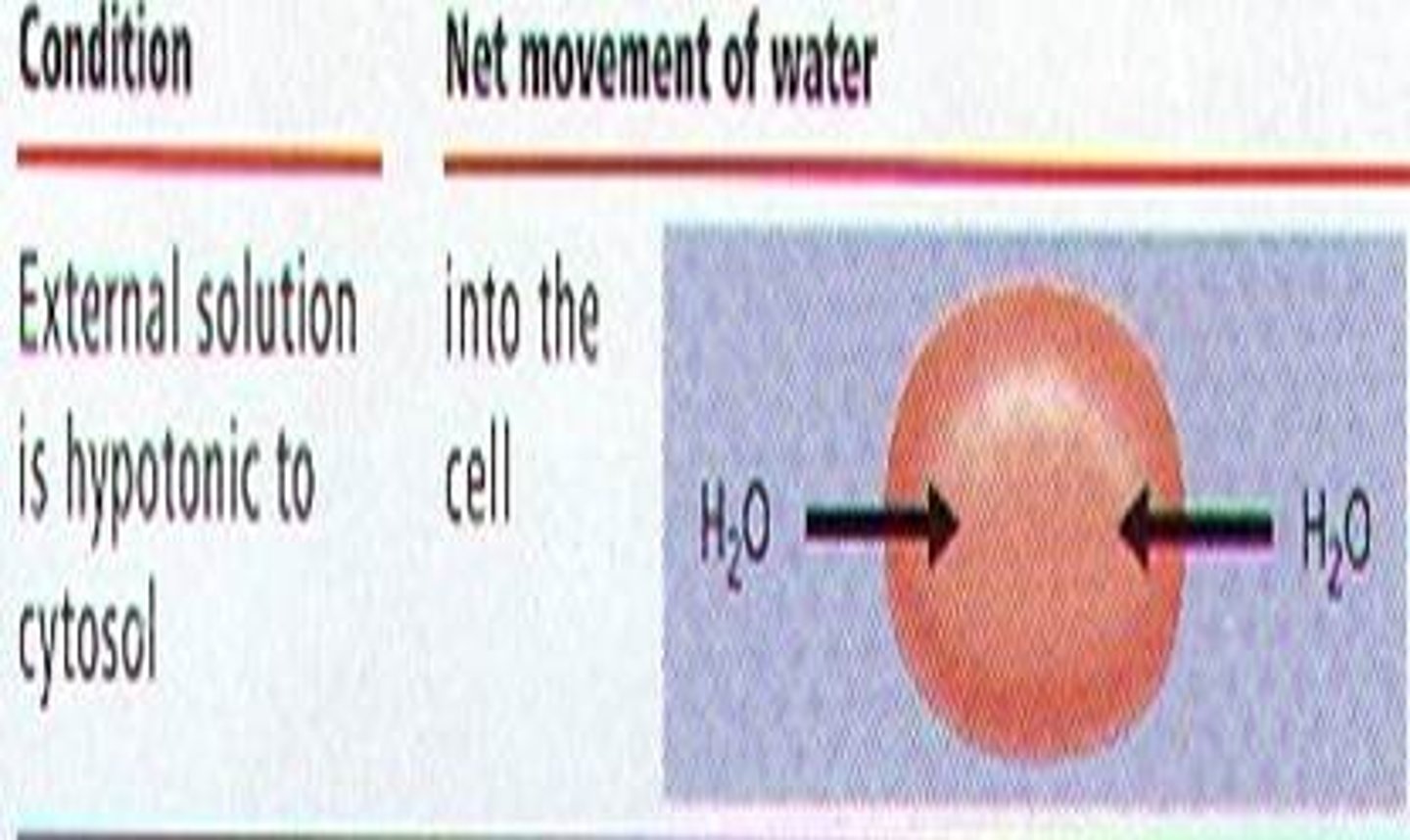
Hypotonic
the solution with the lower concentration of solutes than that inside the cell; water will enter the cell -> Cell will swell and burst
Osmoregulation
The control of water balance
Turgid
Very firm (healthy state), especially for plant cells
Plasmolysis
As a plant cell shrivels its plasma membrane pulls away from the wall
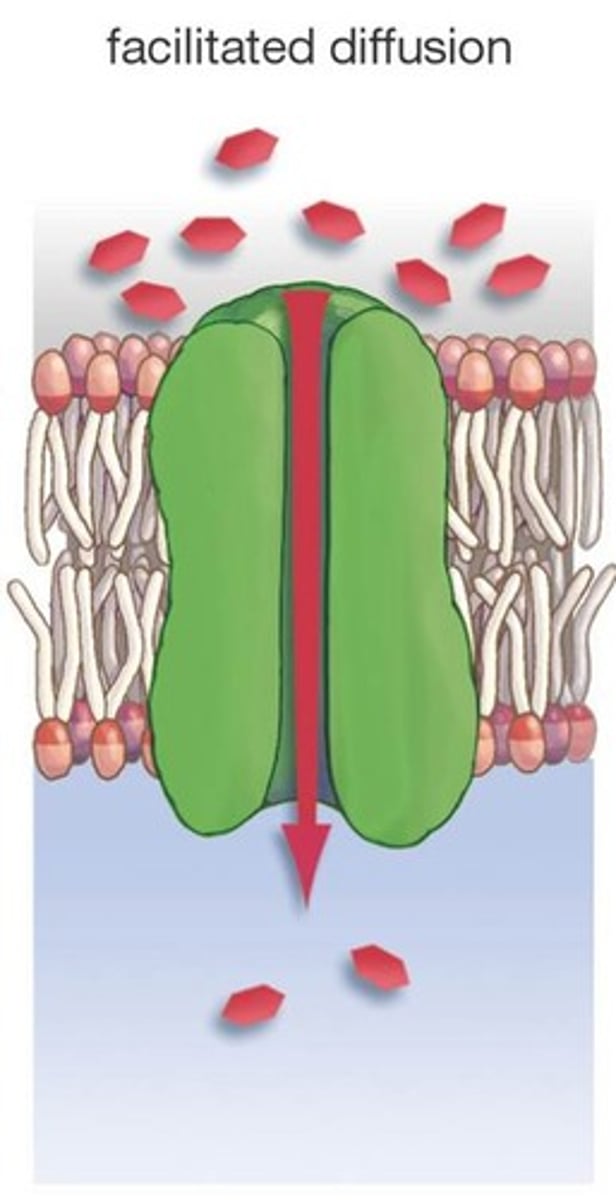
Facilitated Diffusion
passive transport of ions or polar molecules across a plasma membrane by transport proteins
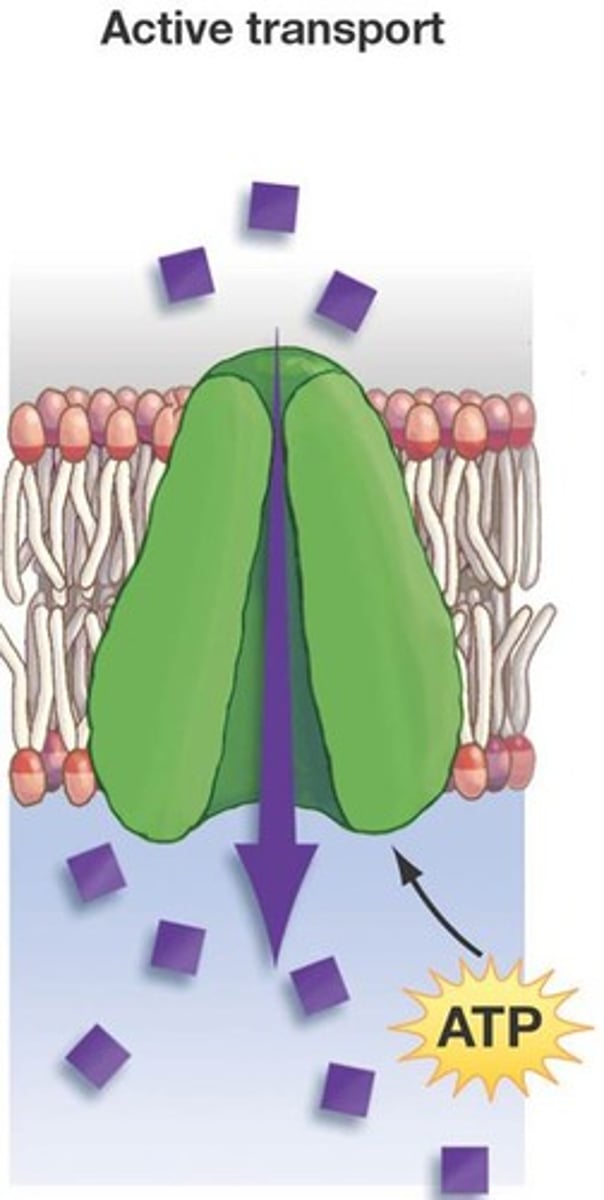
Active Transport
transport of a substance through a cell membrane against the concentration gradient; requires energy
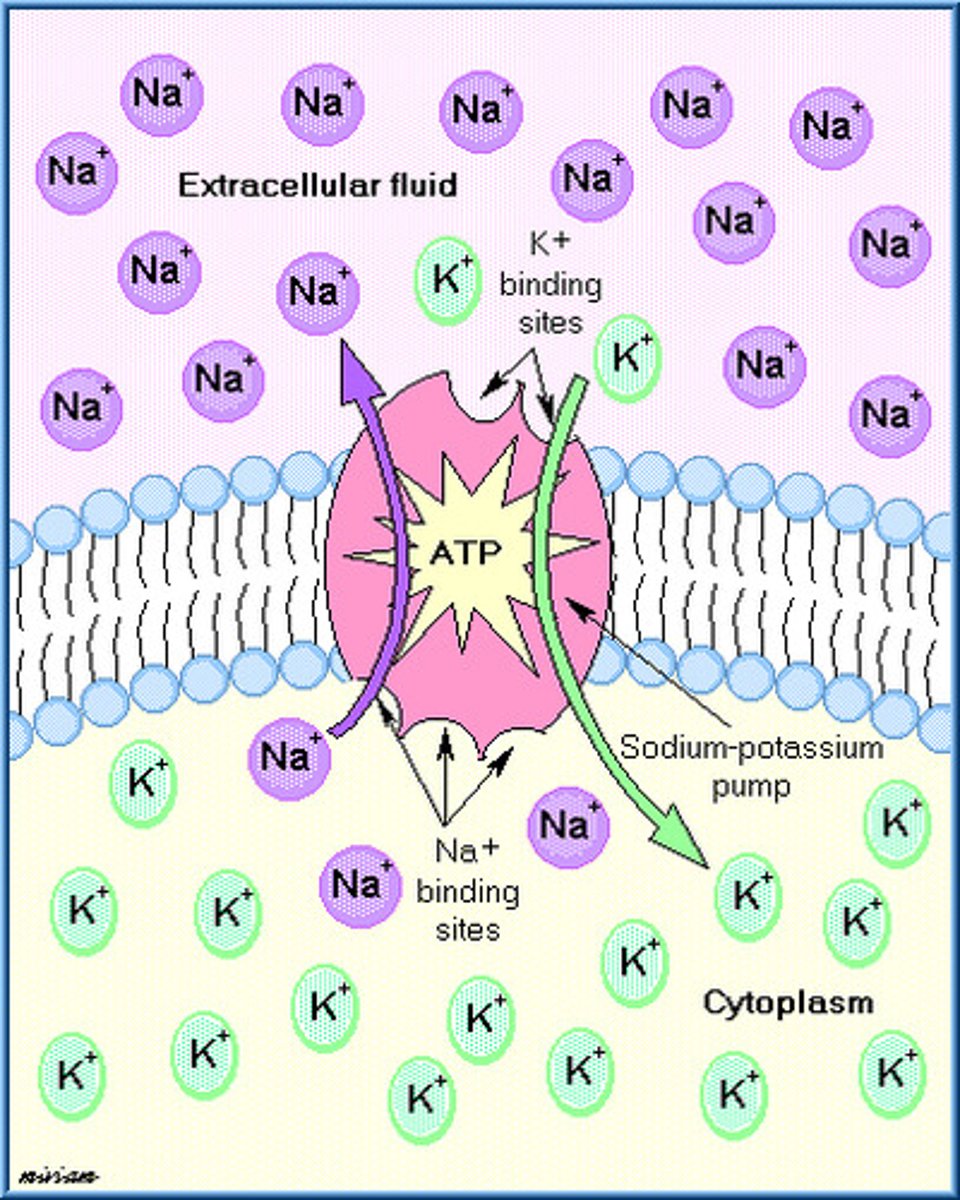
Sodium-Potassium Pump
a carrier protein that uses ATP to actively transport sodium ions out of a cell and potassium ions into the cell
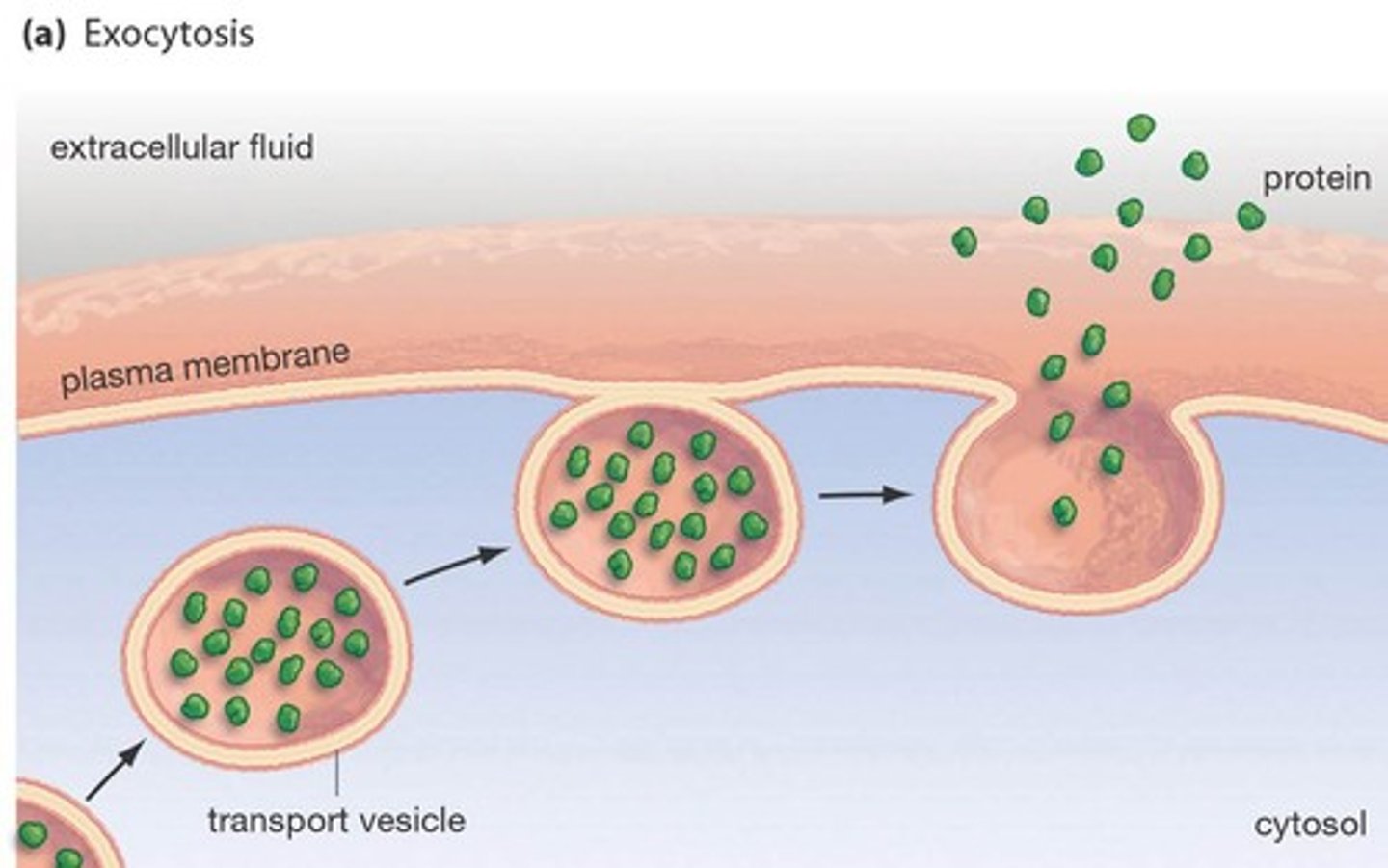
Exocytosis
process by which a cell releases large amounts of material by vesicles
Endocytosis
the movement of a substance into a cell by a vesicle
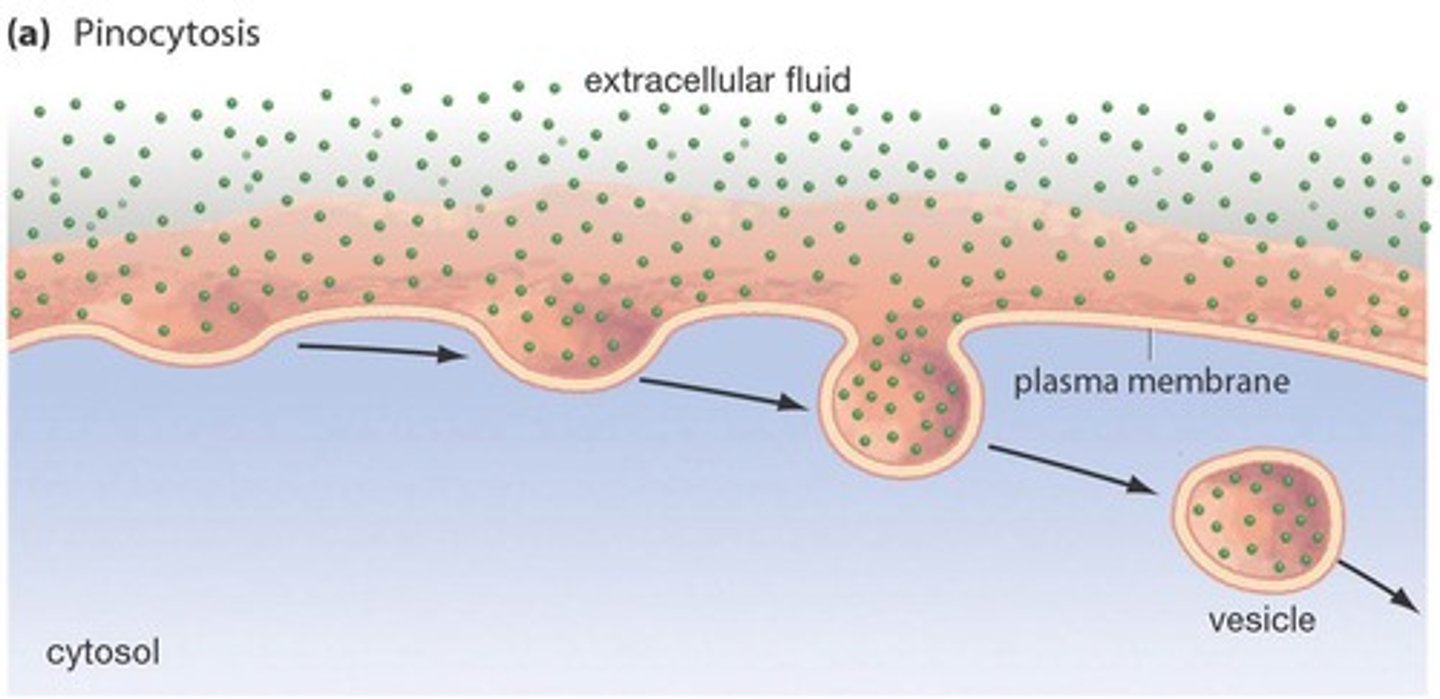
Pinocytosis
cellular drinking
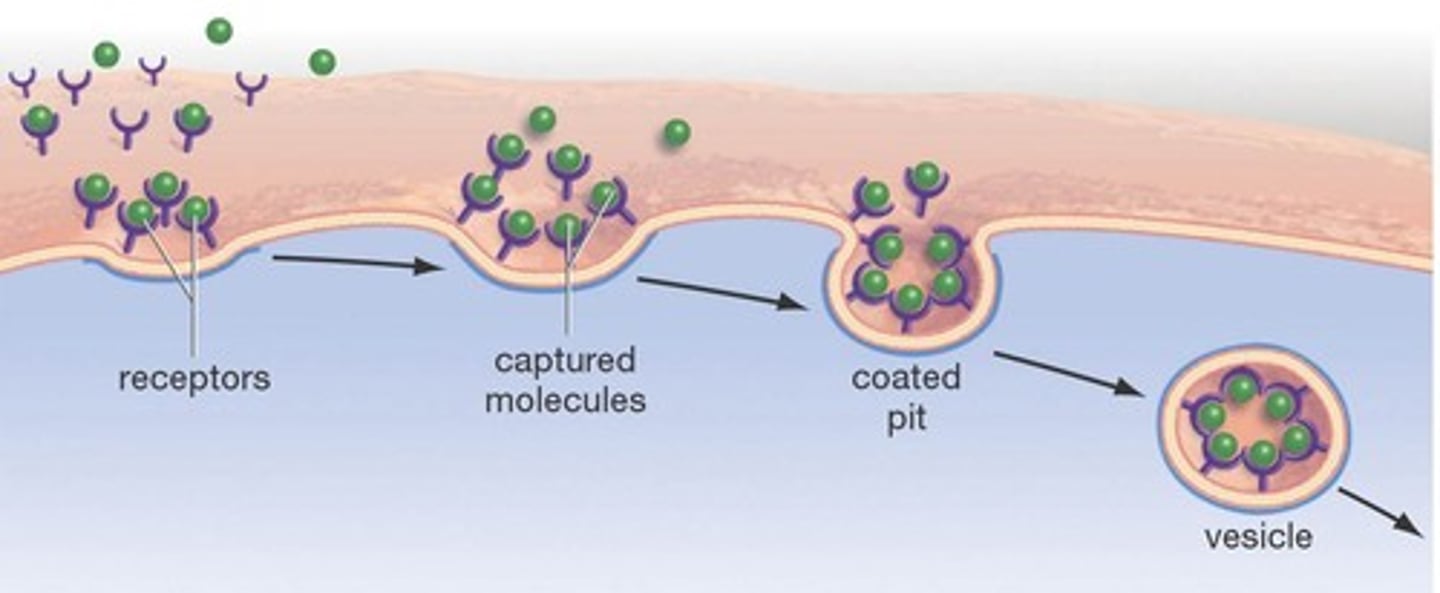
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
Taking in large amount of specific substances by binding to receptors, which form vesicles and are then taken in by the cell
osmotic pressure
The force required to resist the movement of water by osmosis. Osmotic pressure is a measure of the concentration of a solution. A solution that is highly concentrated has a strong tendency to draw water into itself, so the pressure required to resist that movement would be high. Thus, highly concentrated solutions are said to have high osmotic pressures.
water potential
The physical property predicting the direction in which water will flow, governed by solute concentration and applied pressure.
water potential equation
water potential = solute potential + pressure potential
solute potential
This measurement has a maximum value of 0; it decreases as the concentration of a solute increases.
solute potential equation
Ψs = -iCRT
pressure potential
This measurement has a minimum value of 0 (when the solution is open to the environment); it increases as pressure increases.
Cell Theory
all cells are cells/made up of cells
all cells come from cells
concentration gradient
difference in the concentration of a substance from one location to another (ex. difference in concentration on the inside of a cell versus the outside)
Basic Cell feature
plasma/cell membrane-phospholipid bilyaer
liquid layer-cytosol/cytoplasm
chromosomes (genetic material)
ribosomes
Concentration
A measurement of how much solute exists within a certain volume of solvent
Prokaryotic Cells
no membrane around nucleus
no membrane bound organelles
nulceoid
cytoplasm bound by plasma membrane
cotransporter
protein that moves two or more molecules through a cell membrane by secondary active transport
Nucleoid
area of any cell where DNA chills
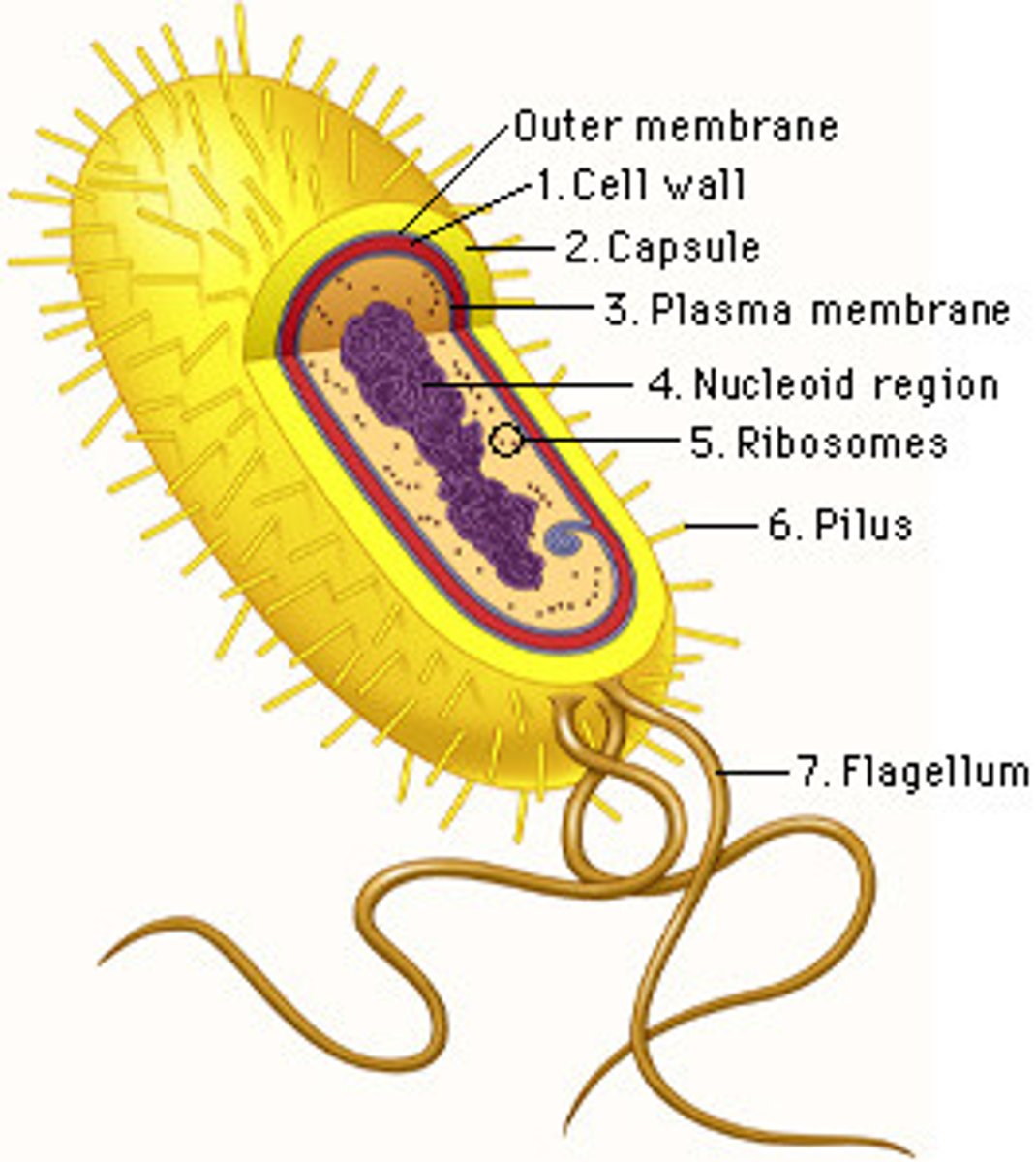
Prokaryotic features
cell wall without cellulose
sometimes have an outer capsule
ribosomes
nucleoid
may be moble with flagella
Eukaryotic Features
DNA in nucleus bounded by membrane nuclear envelope
organelles membrane bound
Larger
TERM
Plasma/Cell Membrane
DEFINITION
selectibe barrier allows certain amount of oxygen, nutrients, and waste in and out
double layer of phospholipids
Surface Area and Volume
surface area increases squared while volume increased cubed (volume increases faster than surface area)
Cell size is limited by
surface area because the cytoplasm needs to be near the plasma membrane for diffusion
Flagellum
single tail that causes motion and direction parallel to length
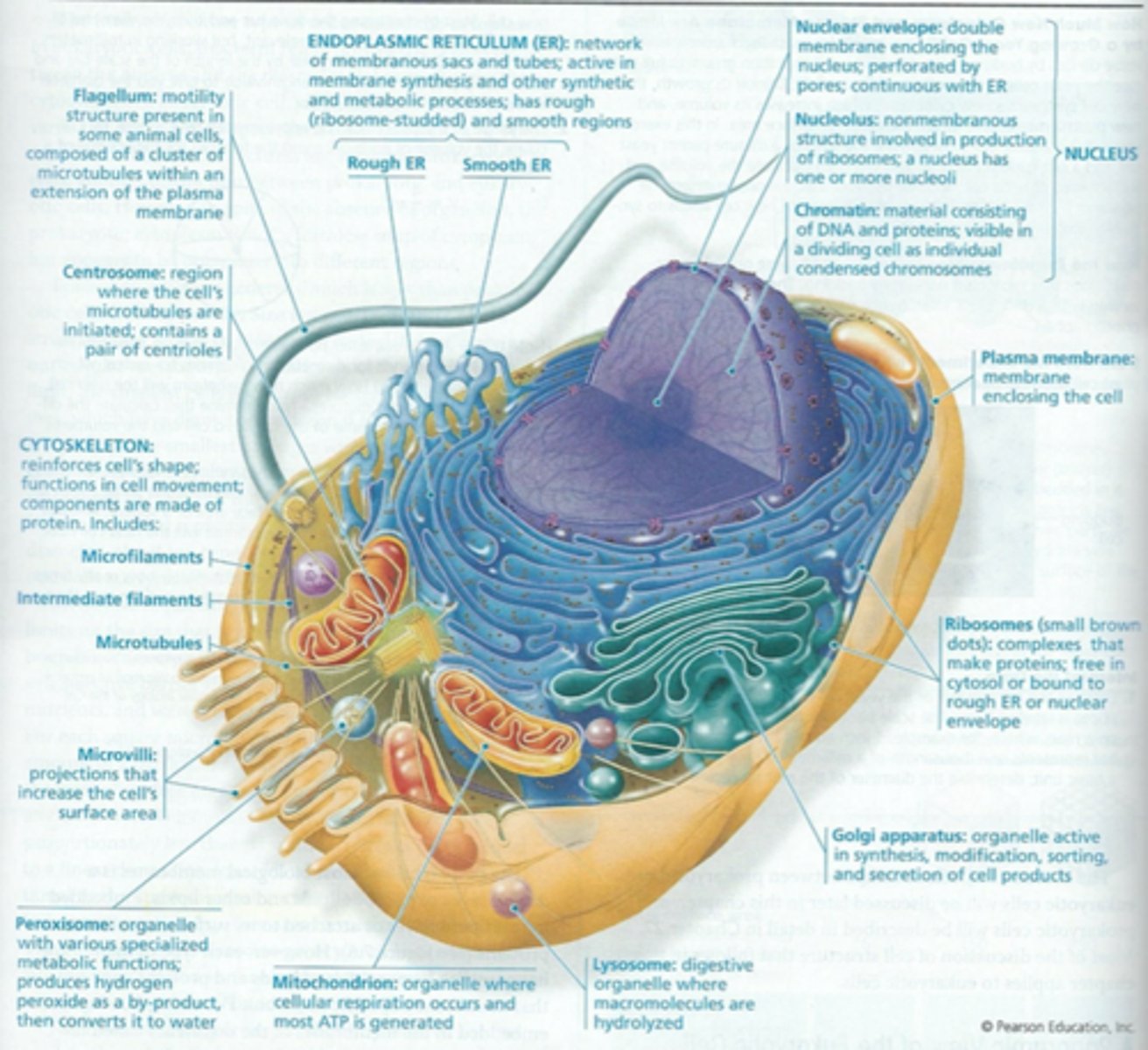
TERM
Smooth ER
DEFINITION
does lipid synthesis
metabolizes carbs
detoxifies drugs and poisons
stores calcium ions
TERM
Rough ER
DEFINITION
when protein released into lumen of space in Rough ER
chaperons and ribosomes control folding and it gives protein environment to develop
TERM
Nucleolus
DEFINITION
area in nucleus where DNA is that makes ribosomes
appears through EM
area of densely stained granules and fibers
adjoining part of chromatin
TERM
Ribosomes
DEFINITION
where mRNA goes into cytoplasm attracts ribomsomes
makes proteins
produced as 2 different subunits that come together at mRNA
TERM
Golgi Apparatus
DEFINITION
shipping and receiving center, looks like ER, notifies proteins of ER, sorts and packages materials into transport vesicles, manufactures certain macro molecules, consists of membranes
TERM
Mitochondrion
DEFINITION
Cell organelle that converts the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use. Contains DNA. Where ATP synthesis takes place
Plant Cells
have cell walls, chloroplast, plasmodesmata, central vacuole, multi-cellular, auto-trophic, make sugar using sunlight
Nucleus
where most DNA in Eukaryotic Cells is located
the control center of the cell
Free Ribosomes
not bound to ER
proteins produced here usually stay in cell
attached ribosomes
bound to ER
proteins that are produced here usually secreted
secretes glycoproteins, protein movement because of transport vesicles, it is a membrane factory
Vesicle
small compartments that move things around
small organelle that contains and transports materials (like proteins) within the cytoplasm.
Trans Face
shipping side of Golgi
Lysosomes
Golgi produces it
An organelle containing digestive enzymes (hydrolytic)
Acidic inside (low pH)
Abundant in cells like white blood cells
housekeeper, gets rid of old organelles
Transport Vesicle
can stay in cell and become lysosome or merge with membrane to release contents outside
Phagocytosis
some cells can engulf food particles then lysosomes merge with food vacuoles and break it down. Not possible if cell wall present.
Vacuoles
other compartments not as directed as vesicles
diverse maintenance compartments
large vesicles from ER and Golgi
selective in transporting solutes
Central Vacuole
it is in a plant, fills up with water to get bigger, helps maintain turgor pressure
Mitochondria
in most eukaryotic cells
cellular respiration
enveloped by double membrane
has free ribosomes and circular DNA
can reproduce on own
Endosymbiosis Theory
Eukaryotic came about from prokaryotic living inside another prokaryotic
inside gets safe place host gets a cell good a making energy
chloroplasts made the same way as Mitochondria
Chloroplasts
capture light energy, contains DNA
has three chemical environments
1. stroma
2. between bilayers
3.thylakoid
Chlorophyll
pigment that captures light energy and changes it into chemical energy
Peroxisomes
oxidation organelle bounded by a single membrane
produces hydrogen peroxide by combining hydrogen with oxygen; hydrogen peroxide eventually gets turned into water
Cytoskeleton
network of fibers in cytoplasm
protection from compression
support
many organelles are bound to it
organizes cell
motility-reacts with motor proteins like Dynien an Actin
Track along which motor proteins move
microtubule
Microtubules
hollow made of tublin protein
easily assembled and disassembled
biggest fiber
protection of crushing, compressing
very important in shaping cell in animal cells
guide movement of organelles and vesicle help with movement of cilia and flagella
centrosome
where centrioles are located in a non cell division
has triplets of microtubules around a hollow center
located in the cytoplasm and near the nucleus
the microtubule organizing center
Cilia
The hairlike projections on the outside of cells that move in a wavelike manner
protists have it
Microfilaments
solid rods smallest of cytoskeleton
made up of Actin
Changes in cell shape
cell motility
muscle contractions
keeps microvilli in shape
cahnges in shape of myosin causes filaments to move
extracellular matrix (ECM)
The meshwork surrounding animal cells, consisting of glycoproteins, polysaccharides, and proteoglycans synthesized and secreted by the cells.
Cell Wall
primary cell was is made first
secondary cell wall made last and is inner wall
Organelles
membrane enclosed structures within eukaryotic cells can be seen with LM
examples of prokaryotes
bacteria and Archea
Examples of eukaryotes
protists, animal, plant, fungi
Cytoplasm
interior of cell region between nucleus and plasma membrane in Eukarotic
Plasma Membrane
functions as selective barrier that allows passages of enough oxygen nutrients and wastes to serve the cell
Microvilli
increase surface area without increasing volume
Nuclear Envelope
encloses nucleus seperating its contents from cytoplasm, double membrane lipid bilyaer with proteins
has pore structures
Endomembrane System
regulates protein traffic and performs metabolic functions in cell
includes nuclear envelope ER Golgi lysosomes vesicles, vacuoles, plasma membrane
Endoplasmic Reticulum
extensive network of memranes
Functions of Smooth ER
synthesis of lipids, metabolism of carbs, detoxification and storage of calcium ions
(oils phospholipids steroids)
Functions of Rough ER
glycoproteins are proteins that have carbs covalently bonded to them most common secretory proteins
Cis Face
near ER transport vesicles move materials into this place
Number of Mitochondria correlates to...
cells level of metabolic activity
Mitochondrial Matrix
enclosed by inner membrane contains different enzymes mitochondrian DNA and Ribosomes as well as enzymes
Centrosomes
in animal cells microtubule grow out of it, near nucleus considered microtubule organization center
compression resisting
Centrioles
composed of nine sets of triplet microtubles in a ring
ampipathic
a chemical having both polar and
nonpolar parts
9 + 2 arrangement
major portion of each flagellum and motile cilium contains 9 pairs of microtubules that form a circle around 2 lone microtubules in eukaryotes. Associated with eukaryotic flagella and motile cilia
Diffusion of ions
- uses a concentration gradient (chemical), and/or an electrical gradient
- produced by a difference in charge between two adjacent areas
- ions will be attracted to opposite charge
- electrochemical gradient
nuclear lamina
A netlike array of protein filaments lining the inner surface of the nuclear envelope; it helps maintain the shape of the nucleus.
Plasmodesmata
channels through cell walls that connect the cytoplasms of adjacent cells
fluid mosaic model
model that describes the arrangement and movement of the molecules that make up a cell membrane