Mood Disorders
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
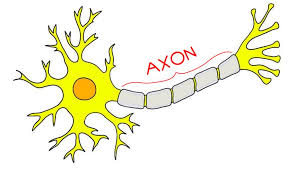
Axon
Long threadlike part of a nerve cell along which impulses are conducted from the cell body to other cells
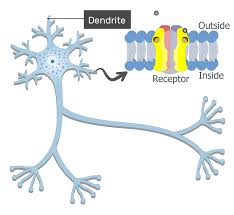
dendrite
A short branched extension of a nerve cells, along which impulses recived from other cells at synapses are transmitted to the cell body
Neurotransmitter
A chemical substance that is released at the end of a nerve fiber
Dopamine
neurotransmitter (nerve messenger) and hormone in the brain and body, act as a chemical messenger that influences reward
Norepinephrine
Chemical that acts as a neurotransmitter (nerve messenger) and a hormone, helps body stay alert
5-HT
Serotonin, a chemical that acts as both a neurotransmitter in the brain and a hormone, regulating moode, sleep, appetite (feelings of well being)
MAO
Monoamine Oxidase, an enzyme on the outer mitochondrial membrane that breaks down neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and adrenaline; it regulates their levels in the brain and body
Transporter
A specialized protein embedded in a cell’s membrane that selectively moves ions, small molecules (like nutrients or neurotransmitters), and even larger substances across the membrane
Reuptake
The process where neurotransmitters (chemical messengers) are actively transported back into the neuron that released them
Synthesis
The process of building or creating complex molecules from simpler ones, often using enzymes, essentially “putting things together”
Enzyme
A biological catalyst, usually a protein, that speeds up specific chemical reactions in living organisms without being used up
Rate limiting
the slowest stage in a metabolic pathway, or series of reactions that dictates the overall speed
Tryptophan
An essential amino acid, a vital building block for proteins, but also crucial as a precursor for important
Tyrosine
A crucial, non-essential amino acid (protein building block) that serves as a precursor for vital neurotransmitters (dopamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine)
Substance P
an 11 amino acid neuripeptide curcial for transmitting pain signals, inflammation, and emotional responses
Hashimoto’s disease
A chronic autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system mistakenly produces antibodies and immune cells that attack and destroy the thyroid gland