BIOL 319 LAB PRACTICAL 2
1/352
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
353 Terms
Skeletal muscle cells...
make up about 70% of the cell mass of the body
- Muscles use chemical energy (ATP) to produce mechanical energy in directed movement
- Normally functioning skeletal muscle essential for all movement
Disease of muscle...
rare and mostly inherited (muscular dystrophies)
- trauma to muscle common
- commonly see patients with loss of muscle function as consequence of strokes damaging neurons in brain called upper motor neuron lesions
Muscle fibers = ___________
muscle cells
- prefixes for muscle = myo, mys, sarco
Three muscle tissue types
skeletal, cardiac, smooth
- Skeletal muscle = consciously controlled and voluntary, powerful compared to other muscle types and can rapidly contract, tires rapidly
- Smooth muscle = resides in walls of hollow organs, in-voluntary and not striated, contracts slowly and rhythmically to propel substances through channels of body
- Cardiac muscle = involuntary and has own intrinsic contraction rhythm which is altered by nervous control to meet bodies need for circulation
Excitability
All muscle cell membranes have electric charge differential which can be changed upon stimulation (neurotransmitter binding) to produce intracellular muscle response
Contractility
All muscle cells shorten when stimulated
Extensibility
All muscle cells can be stretched, sometimes even more so than their resting length
Elasticity
All muscle cells after being stretched can recoil to resting cell length
Muscles generate ________________
movement, such as bones or of fluids through the many tubes of body
- muscles keep us stationary to maintain posture and balance, why many exercise revolve around staying in one spot
Muscles also stabilize ________________
joints so that bones stay correctly in contact without slipping from correct position
- muscles are highly energetically active and thus also generate a lot of heat which contributes to the maintenance of a normal body temperature
Skeletal muscle structure
Connective tissue sheaths of skeletal muscle: epimysium, perimysium, endomysium
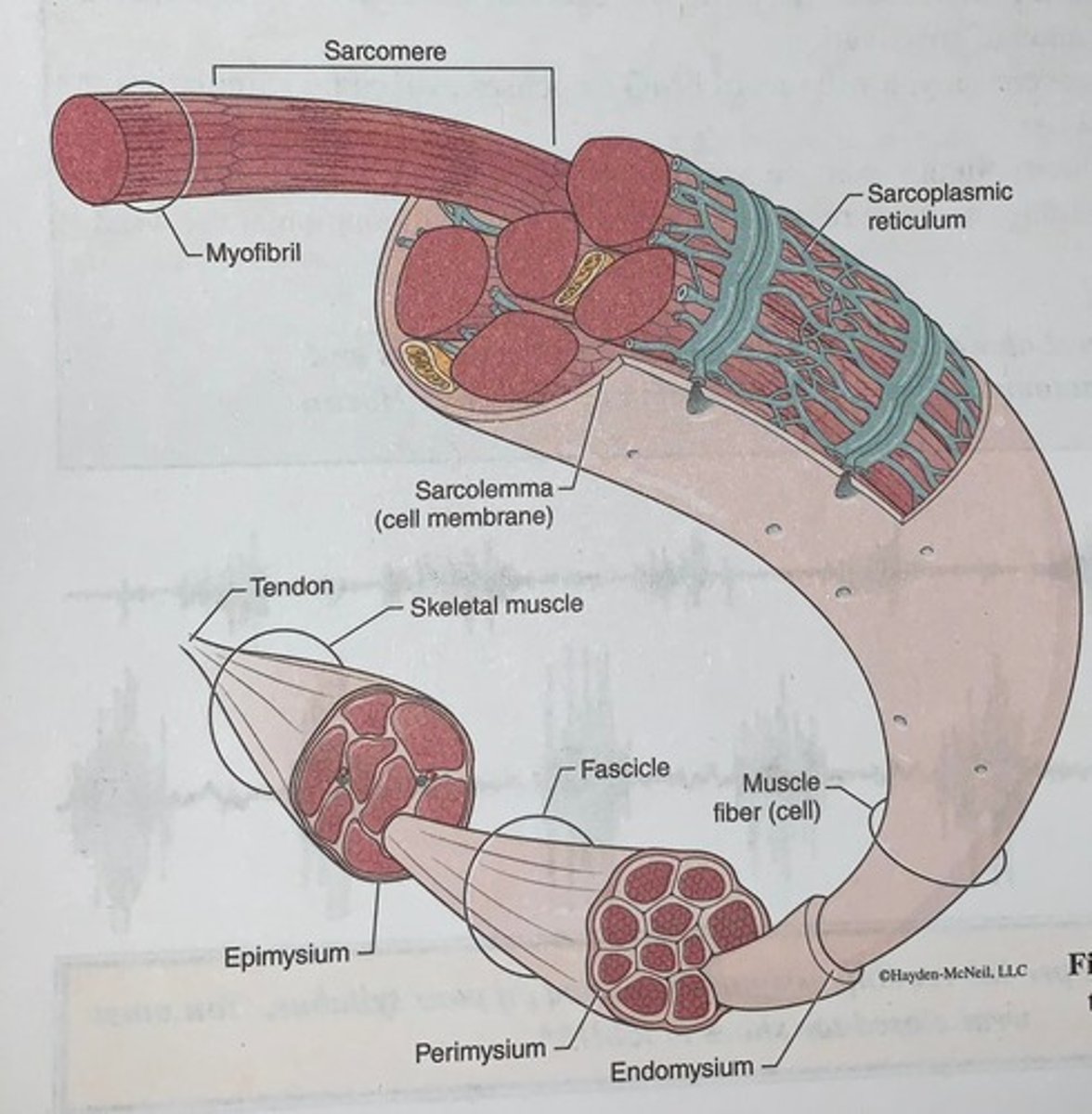
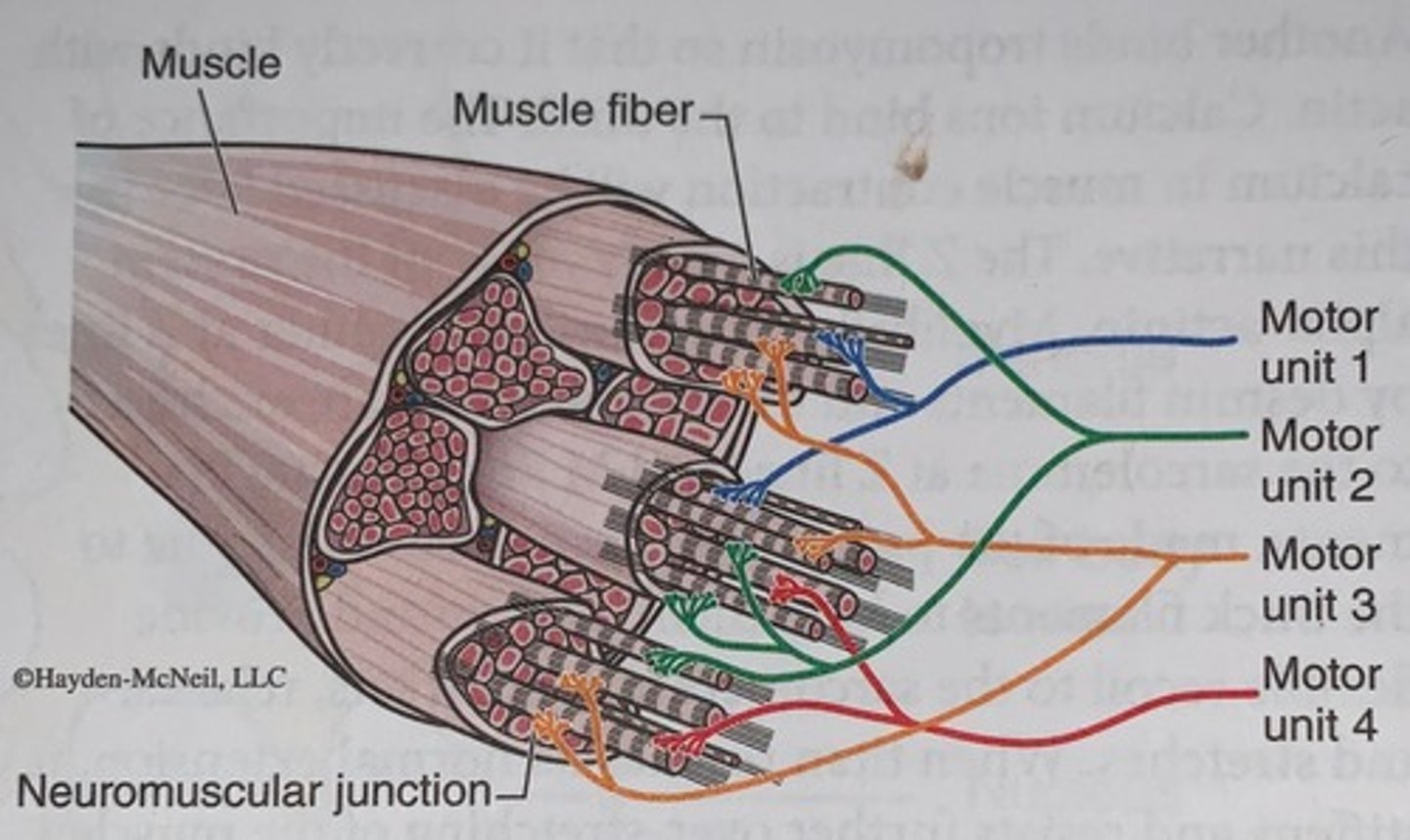
Components of a motor unit
motor unit consists of a motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates
Entire skeletal muscle...
such as gastrocnemius, is an organ and made up of more than just muscle fibers
- Entire muscle will also have within it nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissue, nerves and blood vessels enter muscle near its center and then branch through the muscular running through connective tissue sheaths (epi, peri, endomysium)
- Skeletal muscle not autorhythmic
Tendons
are connective tissues that attach muscle to bone, connective tissue sheaths of muscle are continuous with each other and with tendons to transfer the force of contracting muscle fibers to the structure (such as bone) to be moved
Muscles have ___________
actions, origins, and insertions (AOI), bone or structure that is moving is the insertion while the bone or structure that mostly does not move is the origin, Muscle attachments can be direct or indirect
Direct attachment
If periosteum or perichondrium is fused with the muscles epimysium
Indirect attachment
are more durable and small and more common, tendon or aponeurosis is an example of an indirect attachment,
Tendons are mostly _____________
collagen and rope-like extensions of a muscle's connective tissue while an aponeurosis is similar except sheet-like
- indirect attachments can even blend into the fascia of other muscles to form an attachment
- because tendons are so fibrous and tough they can be small and pass around friction points like boney projections or joints
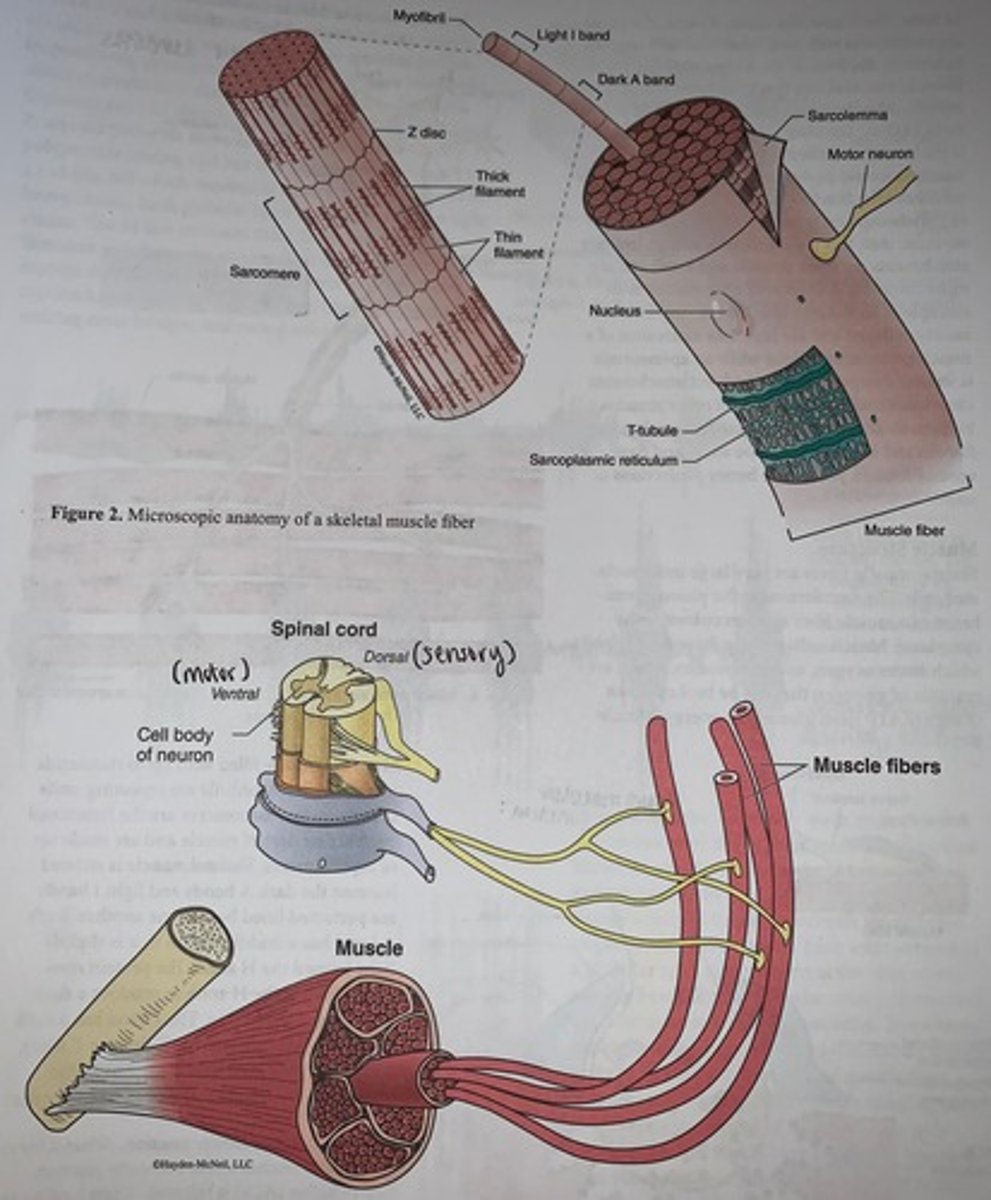
Skeletal muscle fibers are very large _________________ cells
multinucleated
- sarcolemma is the plasma membrane of a muscle fiber and sarcoplasm is cytoplasm
- muscle cells contain lots of myoglobin, which stores oxygen
- glycosomes which are granules of glycogen that can be broken down to supply ATP from glucose for energy
Muscle fibers are mostly filled with ________________
up to thousand of myofibrils
- myofibrils are repeating units of sarcomeres
- sarcomeres are the function contracting unit of muscle and are made up of myofilaments
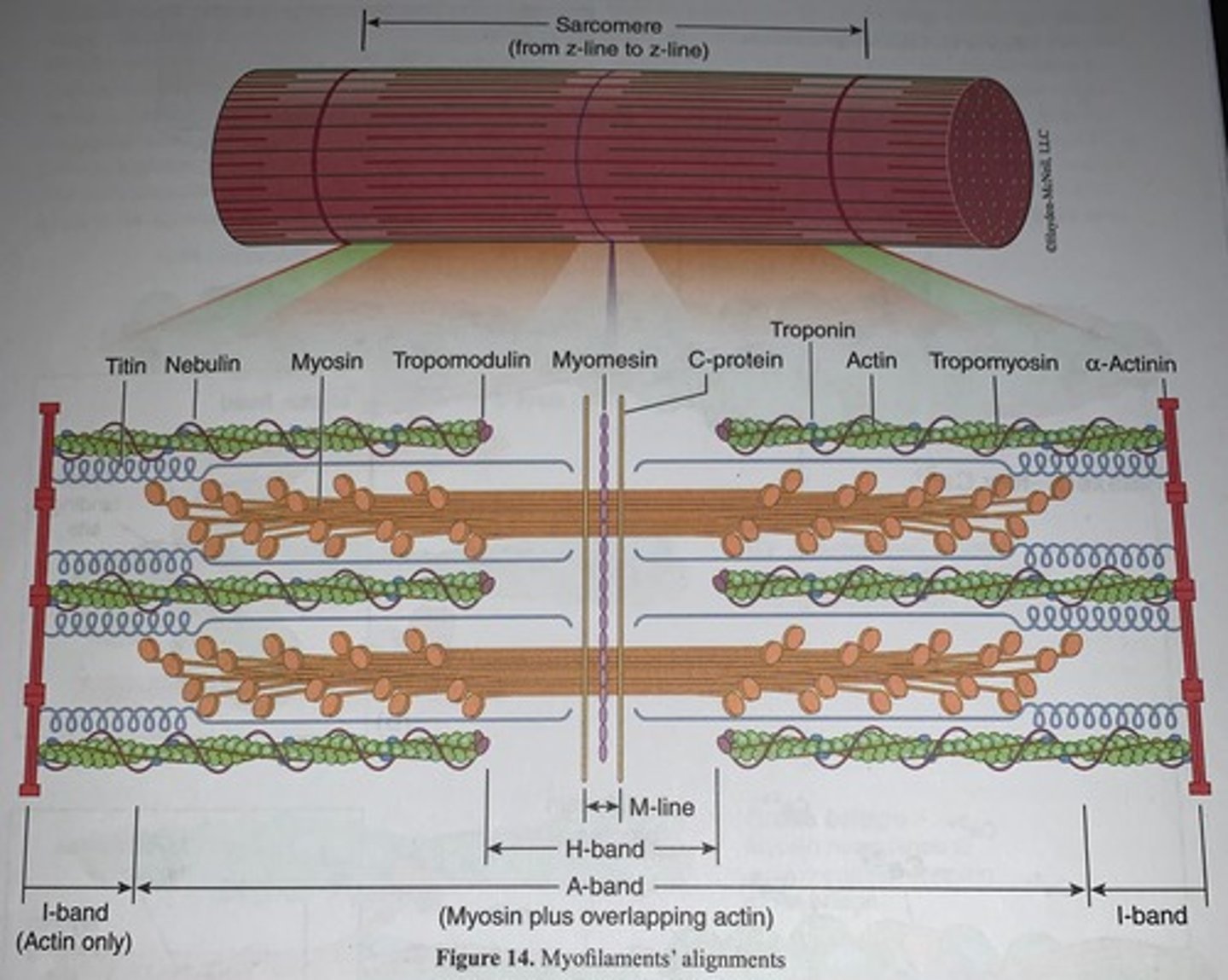
Skeletal muscle is striated because ___________________
the dark A bands and light I bands are perfected lined beside one another
- each A band has a middle region that is slightly light termed the H zone
- protein myomesin bisects the H zone to produce a dark line termed the M line
- the I band has dark midline region termed the Z line (or Z disc)
Sarcomere runs from _________
Z line to Z line
- Another way to state this would be to say that sarcomere runs from each half I banned to half I band with an A band in the middle
Myofilaments
which are mostly actin and myosin with other proteins such as tropomyosin, arrangements in the muscular fiber render the above characteristics skeletal muscle anatomy
Thick filaments
contain myosin and run length of the A banned
- myosin molecule made of four light and two heavy polypeptide chains and has two globular heads hinged to rod-like which consists of helix of two polypeptide heavy chains
- each globular head associates with two light chains
M-line connects ____________
thick filaments
- thick filaments only have myosin heads in areas where actin and myosin overlap
- when muscle contract the globular myosin heads link thick and thin filaments together making cross bridges and swivel as motors to create force that shortens the sarcomere
- each thick filament can contain over 300 myosin molecules
Thin filaments
which contain actin are more lateral and connect at the Z line
- thin filament consists of helix of two actin subunit stands plus tropomyosin and troponin
- each actin subunit is globular actin and contains active sites where myosin heads attach
- globular actin polymerized together is termed filamentous actin
Tropomyosin
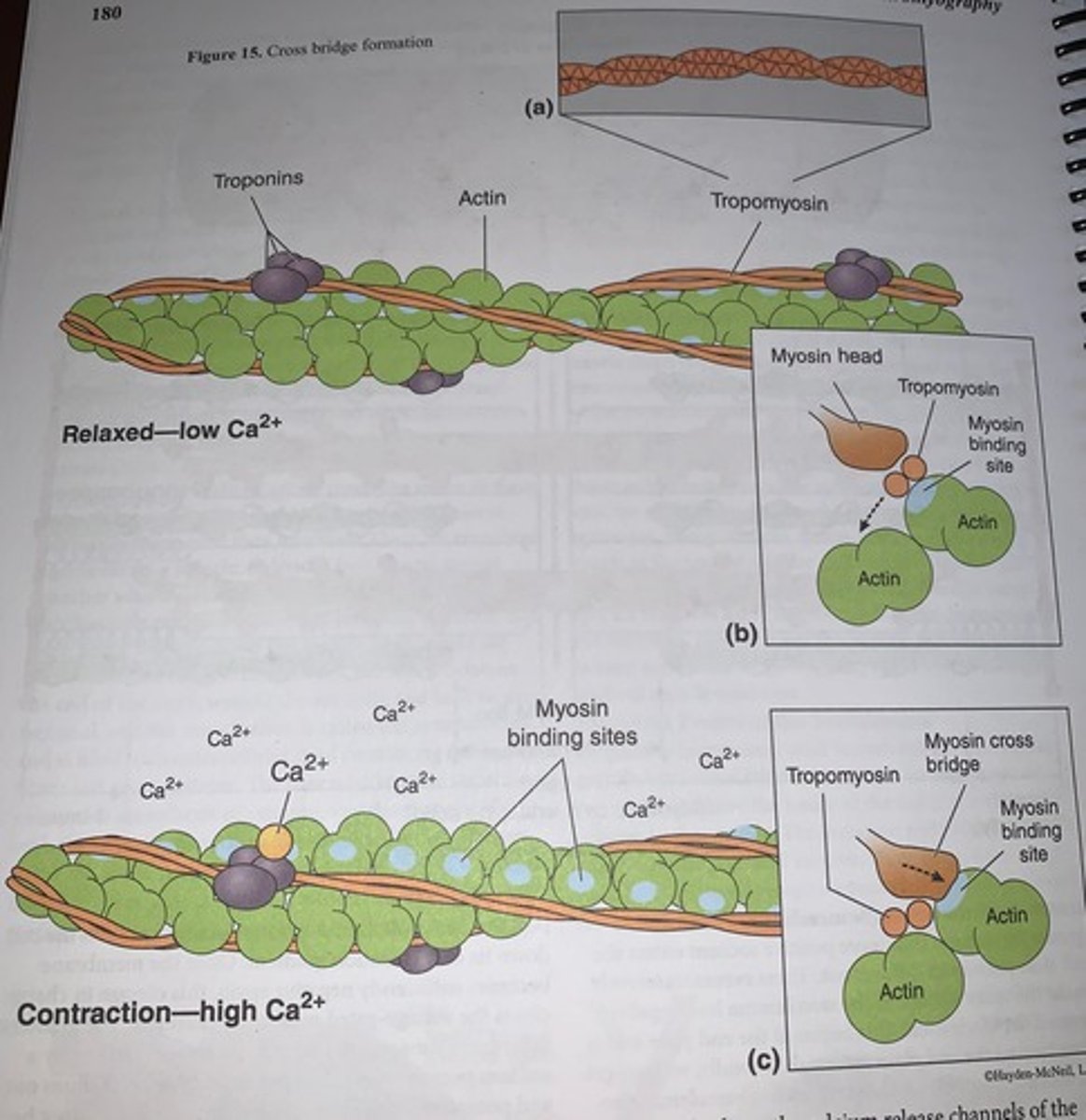
forms a polypeptide strand that spirals around actin to reinforce it, in relaxed muscle fiber tropomyosin blocks actin's myosin-binding sites
Troponin
is composed of three globular polypeptides each of which have different function
- one polypeptide is inhibitory and binds actin
- Another binds tropomyosin so that it correctly binds with the actin
- calcium ions bind to the third
Z line
is mostly made up of the protein alpha-actinin
- myofibrils are connected together at Z lines by desmin filaments and the myofilaments are anchored to the sarcolemma at Z-lines and M-lines
- elastic filaments made of the protein titin run from the Z line to the thick filaments to hold them in place and provide flexible recoil to the sarcomere as it contracts, relaxes, and stretches
When Titin reaches its normal extension...
it stiffens and resists further over-stretching of the muscle
- dystrophin links thin filaments to the sarcomere and when aberrantly or deficiently expressed leads to the Pathology muscular dystrophy
- in cross-section, three thick filaments surround each thin filament and 6 thin filaments surround each thick filament
The tubing within muscle is also very important for ___________________
contractility
- in muscle smooth endoplasmic reticulum becomes very elaborate and is termed sarcoplasmic reticulum
- each myofibril is surrounded by interconnecting sarcoplasmic reticulum
- at the A band I band junction the sarcoplasmic reticulum forms large perpendicular cross channels called terminal cisterns which are always found in pairs
Mitochondria and glycogen granules are...
highly abundant near the sarcoplasmic reticulum
- the sarcoplasmic reticulum controls calcium levels within the sarcoplasm and stores and releases calcium to control muscle fiber contraction
Also at the A band I band junction...
elongated tube extensions of the sarcolemma dive deeply into the cell and are termed T-tubules
- T tubules + terminal cisterns and on either side is called a Triad
- when a nerve stimulates a muscle and electrical signal travels down the sarcolemma and since T tubules are just two extensions of the sarcolemma
- the electrical signal can best be carried deep into the muscle to every sarcomere
The electrical signal causes _________
the release of calcium from the terminal cisterns which leads to contraction
- both the T tubules and the terminal cisterns of the sarcoplasmic reticulum have integral membrane proteins that protrude into the space between these structures
- these integral proteins of the T tubules function as voltage sensors while the integral proteins of the terminal cisterns create gated channels for the release of calcium
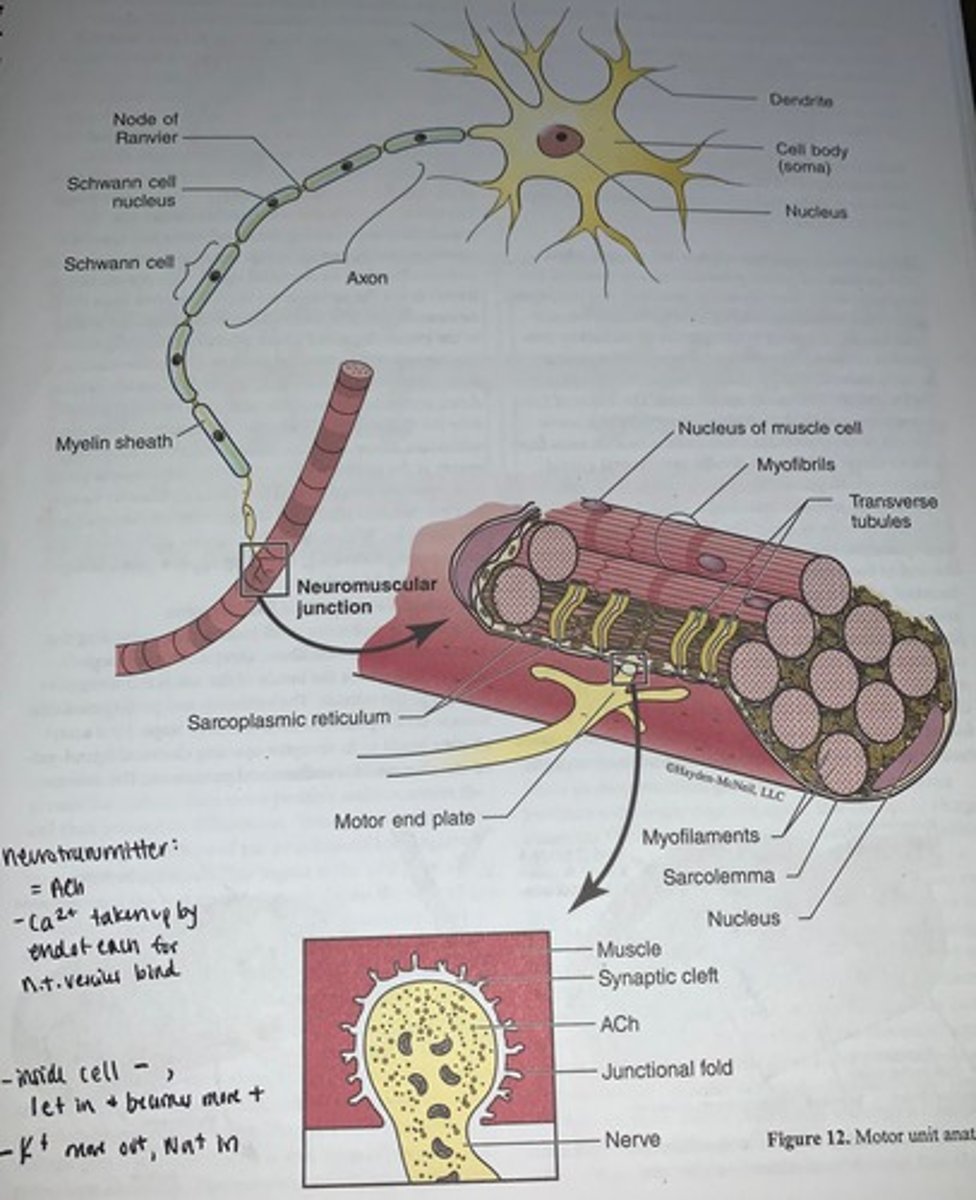
Motor neurons
connect to muscle fibers via neuromuscular junctions
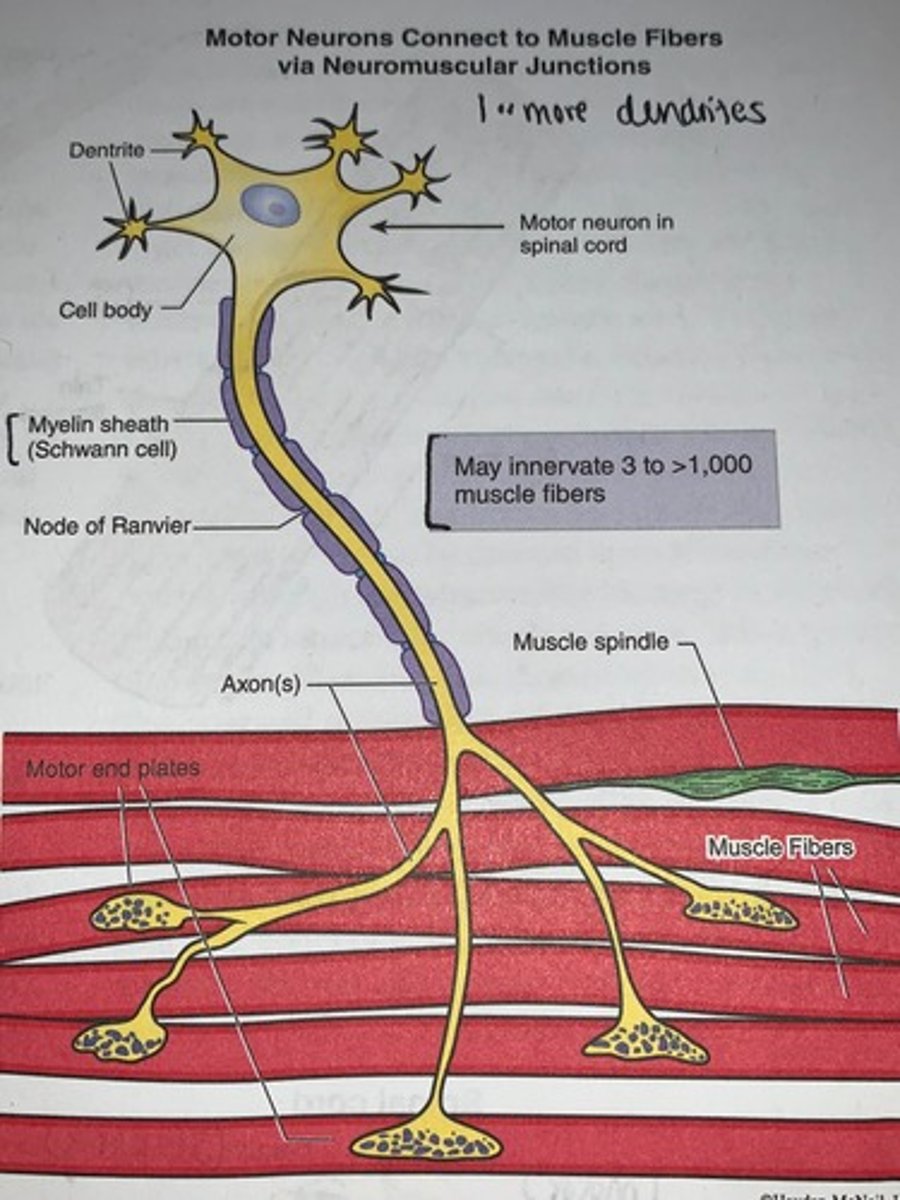
Neuromuscular junction
when a nerve impulse reaches a neuromuscular junction, acetylcholine (ACh) is released
- upon binding to sarcolemma receptors, ACh causes a change in sarcolemma permeability leading to a change in membrane potential
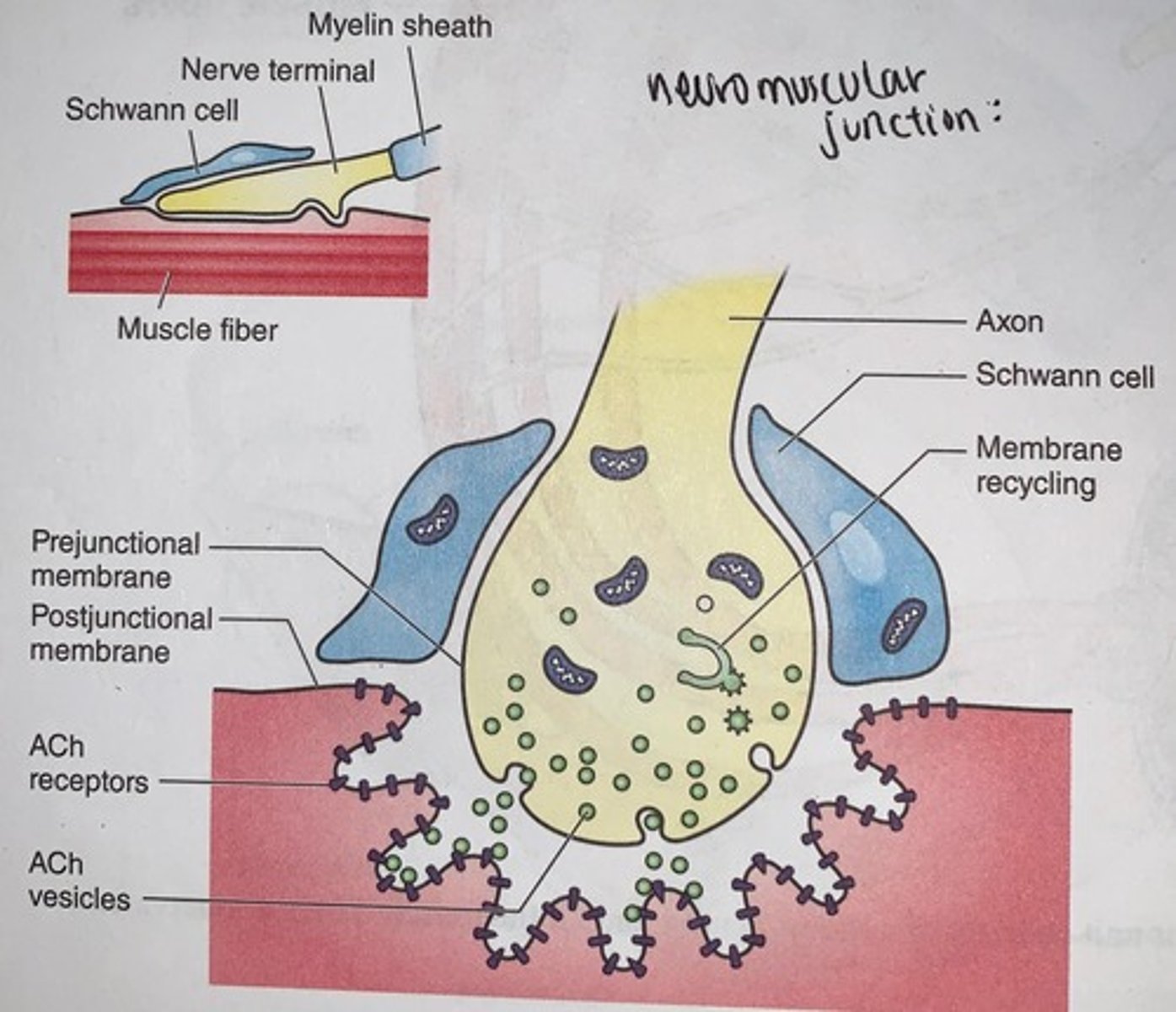
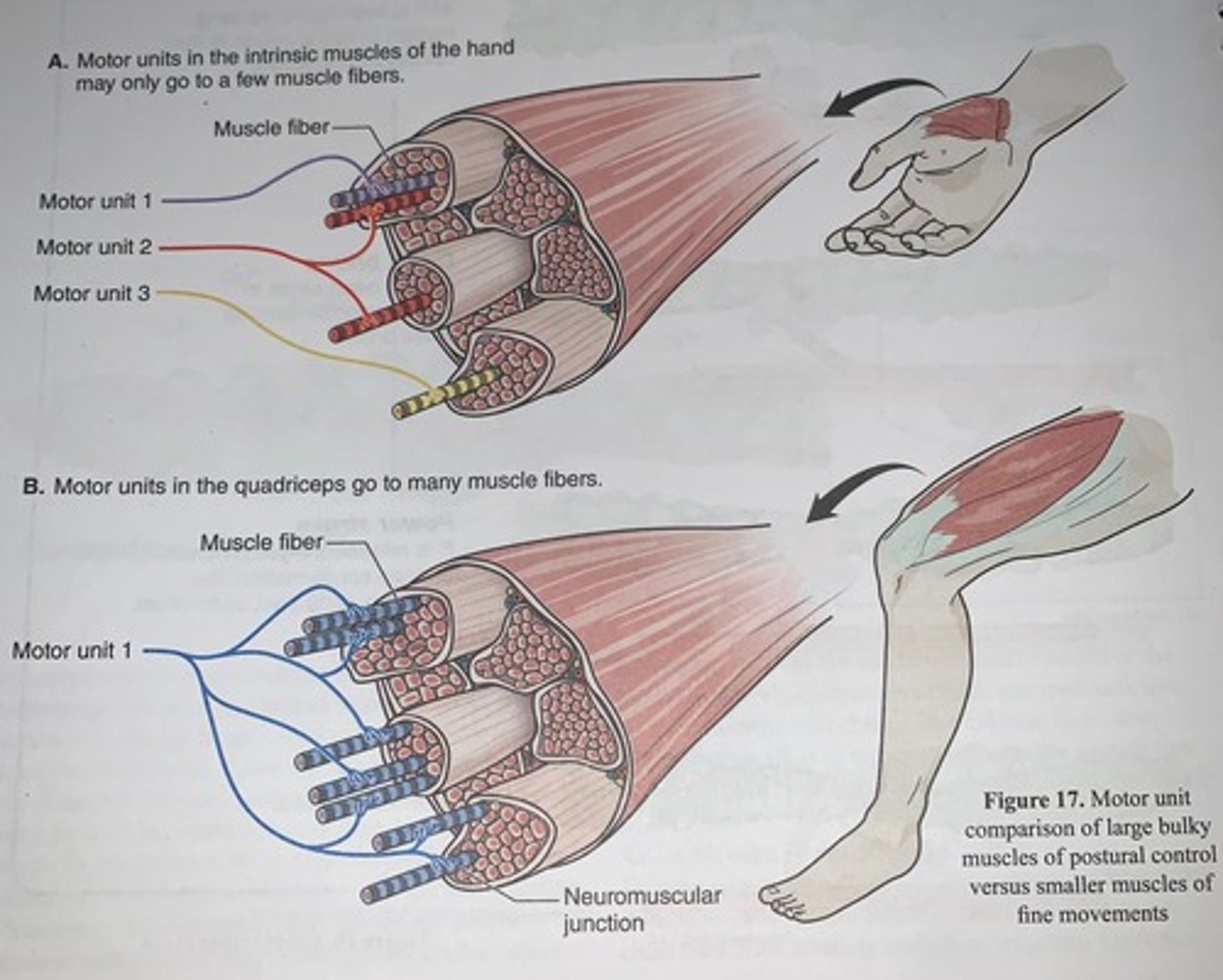
Skeletal muscle motor units
four representative motor units are illustrated, each compromising a motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates
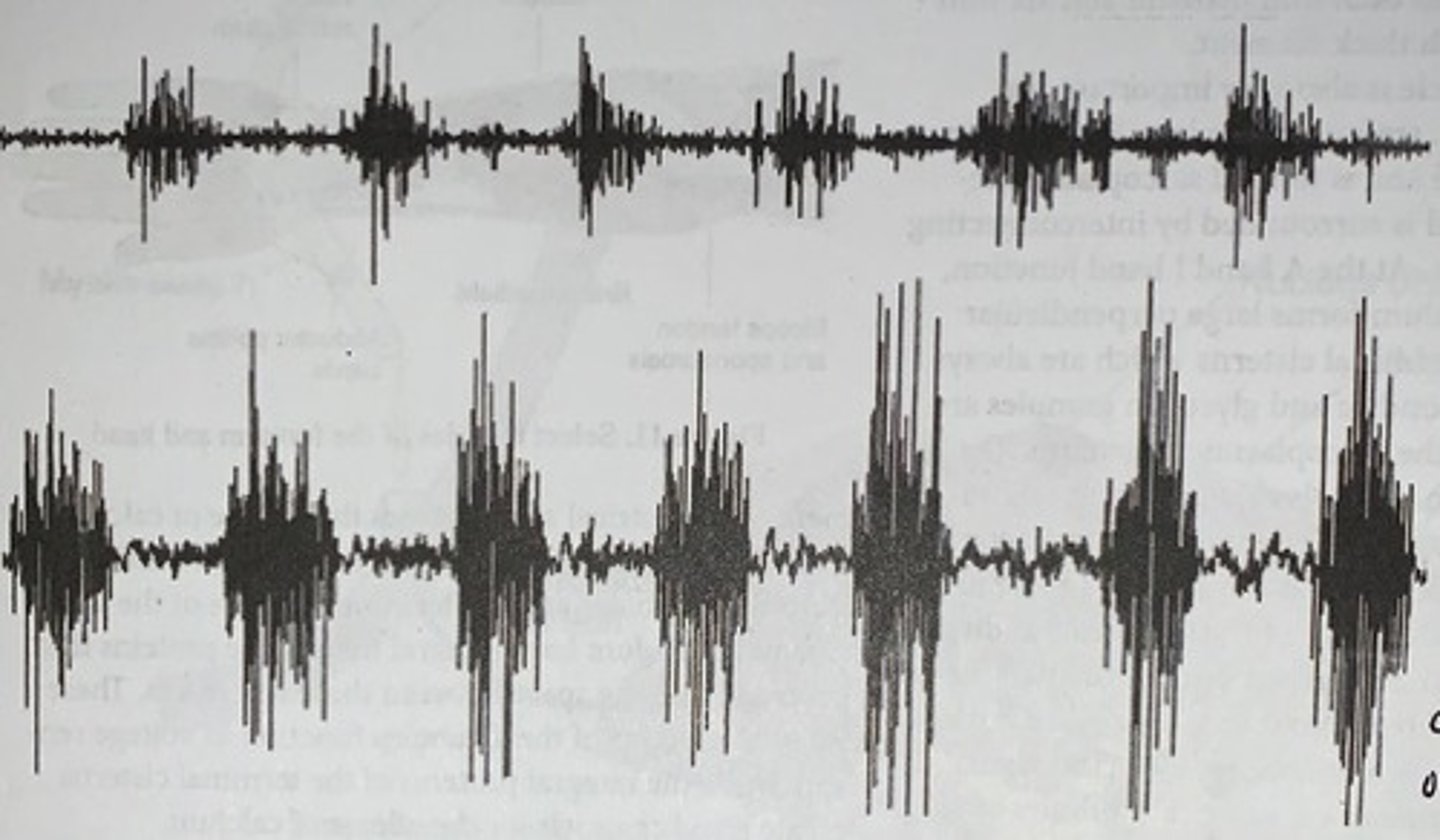
Electromyograms
recorded from a small (top) and large (bottom) muscle
- the magnitude of the electrical signal reflects the number and size of motor units activated
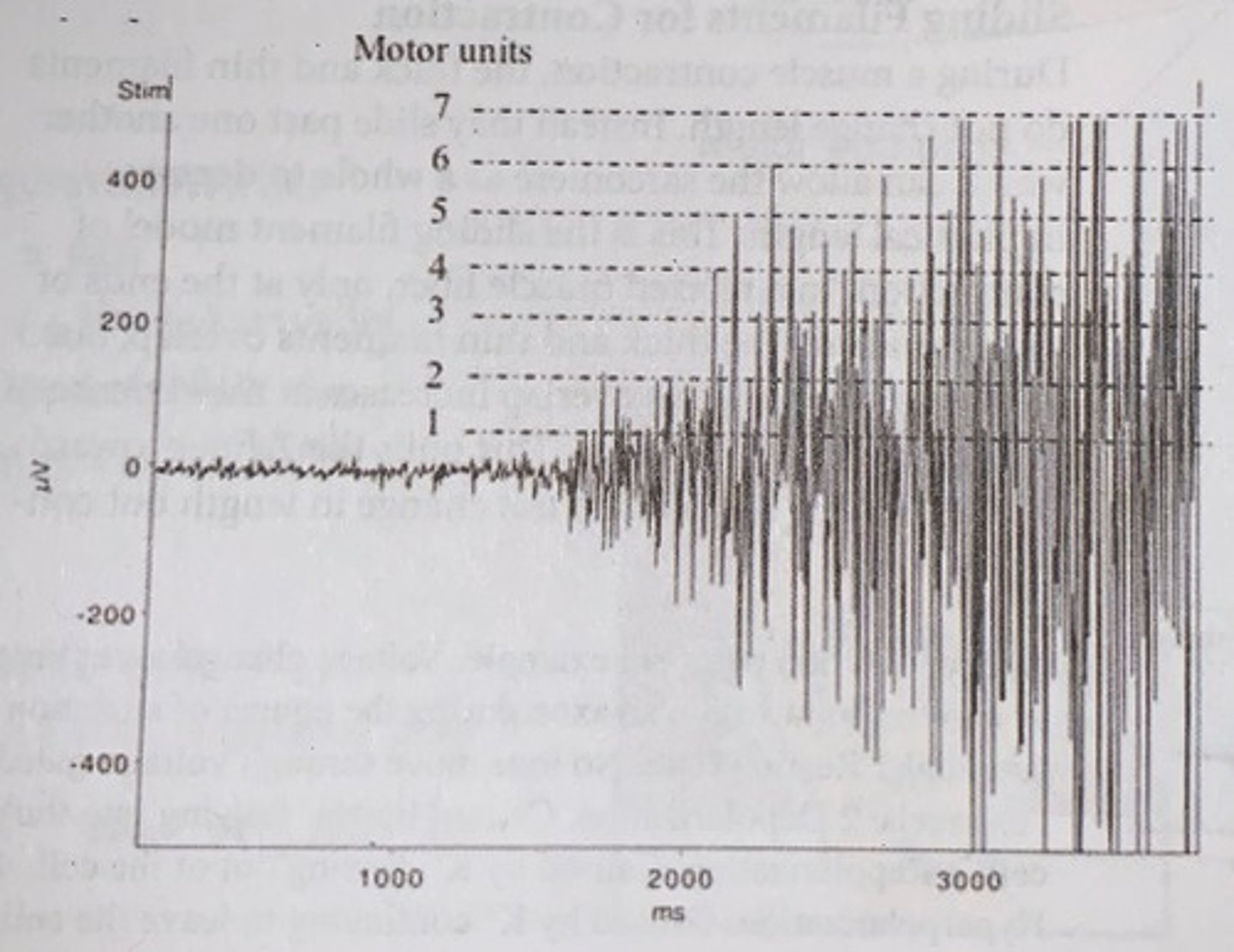
How to count motor units on a graph
recall the size principle that smaller motors are always recruited first
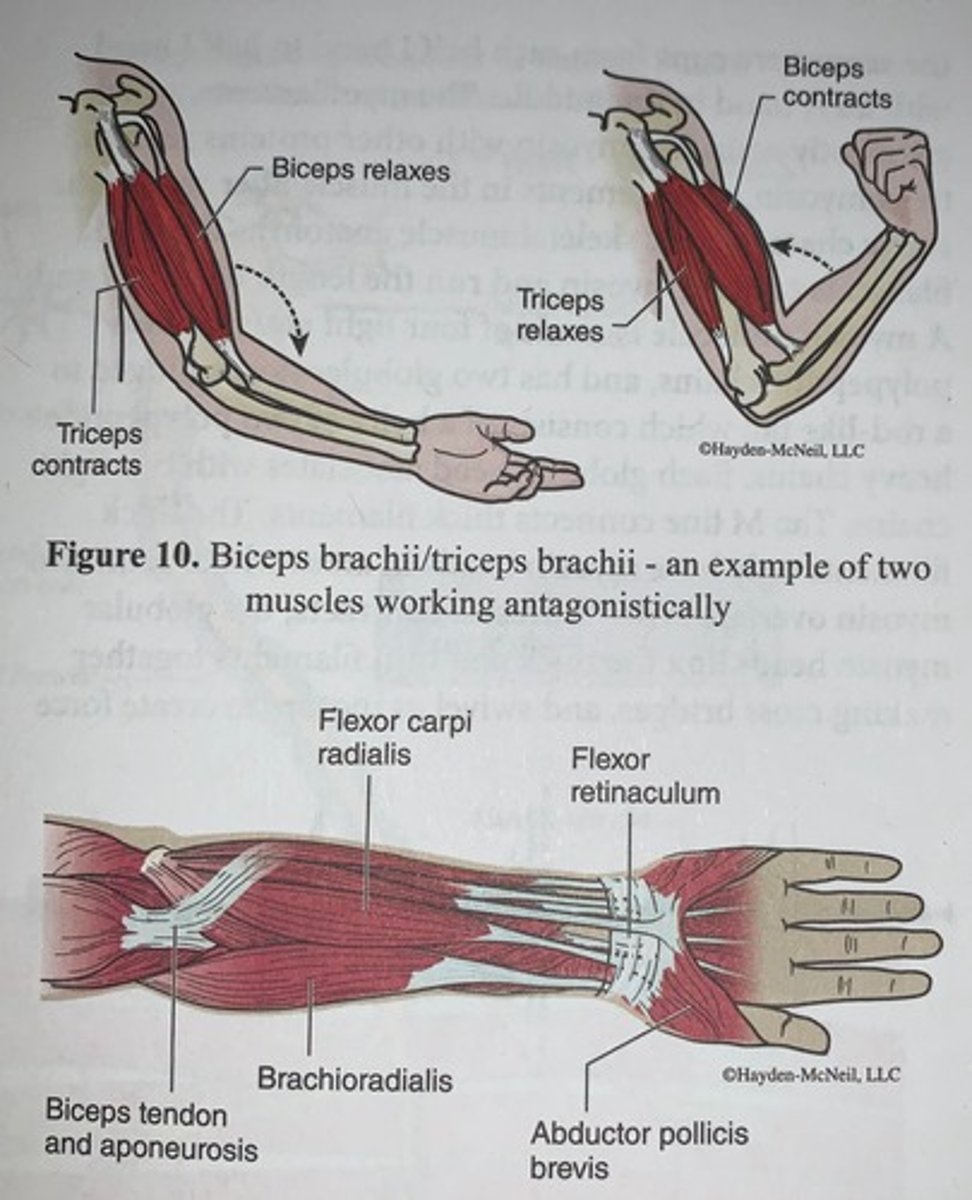
Select muscles of the forearm and hand
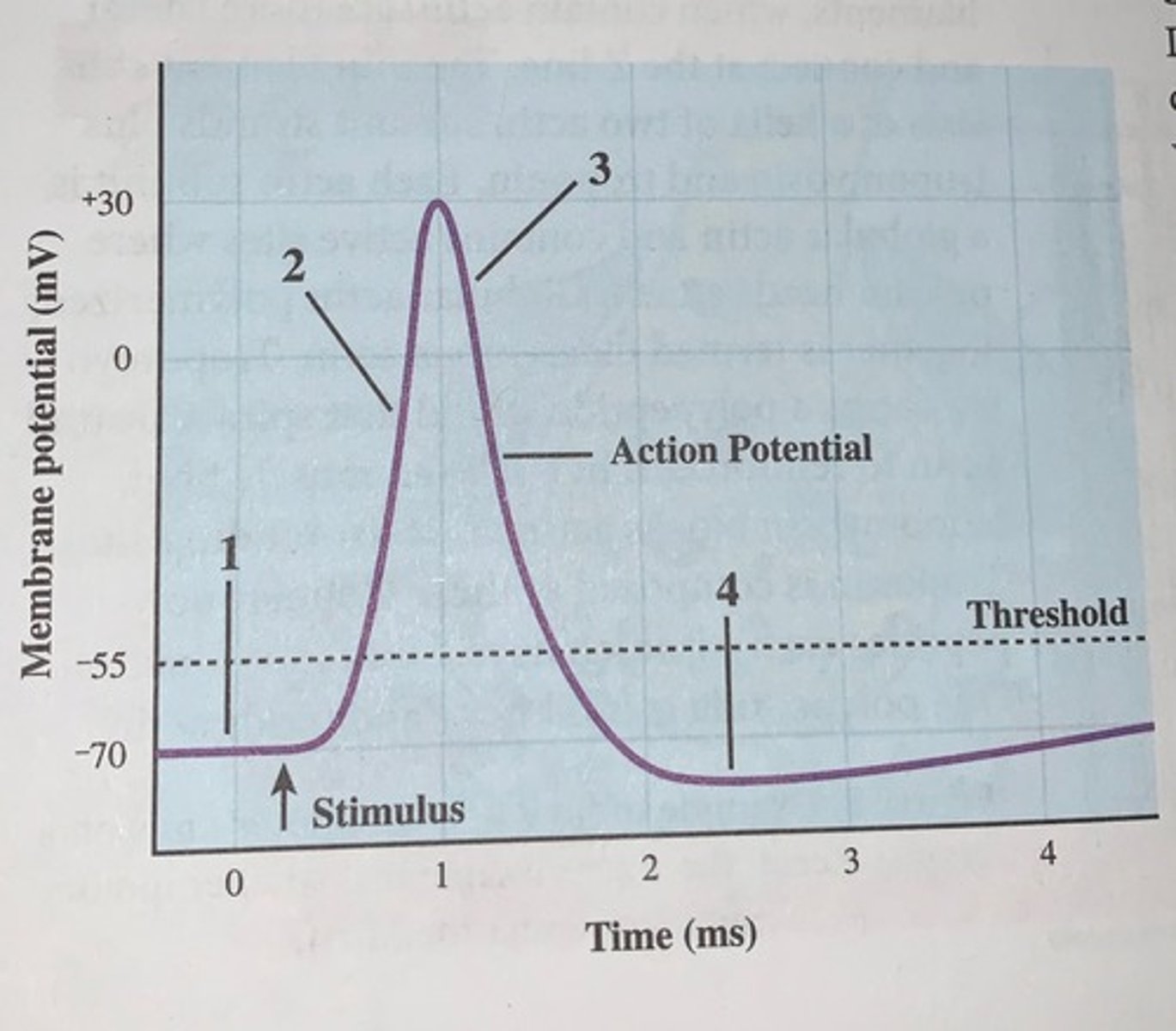
Action potential example
voltage changes over time at a given point inside an axon during the course of an action potential
1. resting state = no ions move through voltage-gated channels
2. depolarization = caused by Na+ flowing into the cell
3. repolarization = caused by K+ flowing out of the cell
4. hyperpolarization = caused by K+ continuing to leave the cell
During a muscle contraction...
the thick and thin filaments do not change length
- instead they slide past one another which can allow the sarcomere as a whole to decrease in physical length
- this is the sliding filament model of contraction
In a relaxed muscle fiber...
only at the ends of the A bands do the thick and thin filaments overlap but during contraction this overlap increases at the expense of the H Zone and the I bands
- this pulls the Z lines toward the M line and the A bands do not change in length but consecutive A bands become closer together as the muscle fiber shortens
- This is accomplished upon nervous stimulation of the muscle leading to increased sarcoplasmic calcium concentrations and latching of the thick filaments to myosin-binding sites of the thin filament actin
- sliding occurs as the myosin powerstrokes, releases, attaches again, and then repeats these steps
Skeletal muscles do the majority of the work for locomotion in support...
of the animal skeleton
- each muscle is made up of individual muscle fibers (muscle cells) organized in fascicles
- skeletal muscles contract when a motor nerve stimulates an electrical action potential (muscle potential that originates at the neuromuscular junction) that propagates along the sarcolemma leading to brief rises and intracellular calcium resulting in completion of excitation-contraction coupling
Somatic (voluntary) motor neurons...
activates skeletal muscle
- the cell bodies of these neurons are located in the brain or spinal cord
- the axons of these neurons are usually bundled together to form a nerve and run to the muscle they innervate
Once an axon from a nerve enters a muscle...
it divides into several axonal branches which serve the muscle fibers
- each muscle fiber has only one neuromuscular junction or motor end plate about halfway down the muscle fiber where the nerve communicates to the muscle
- space between the end of axon term the synaptic end bulb or axon terminal and the muscle fiber is called the synaptic cleft and is filled with extracellular fluid containing collagen fibers and glycoproteins
Mound-like axon terminals contain...
an abundance of synaptic vesicles that are filled with neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh)
- the sarcolemma at the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) is greatly folded to form a junctional folds which function to increase surface area for an abundance of acetylcholine receptors
When a nerve action potential traverses the axon and reaches the axon terminal...
(depolarization of the axon due to sodium influx) depolarization of the axon terminal membrane lead to a calcium influx in the axon terminal which in-turn leads to the synaptic vesicles fusing with the axon terminal membrane to release acetylcholine into the synaptic cleft
- in this way the electrical signal traveling down the nerve is converted to a chemical signal
- the acetylcholine diffuses across the synaptic to bind to the acetylcholine receptors on the junctional folds of the sarcolemma
Activation of the acetylcholine receptors opens...
channels that allow sodium influx into the muscle fiber depolarizing the sarcolemma and causing a muscle action potential
- in this way the chemical signal is converted back to an electrical signal
- this depolarization travels down the sarcolemma in all directions from the neuromuscular junction in down the T-tubules to lead to the event discussed above where is calcium released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum leads to the muscle contraction
- acetylcholinesterase in the synaptic cleft quickly breaks down acetylcholine to acetic acid and choline to terminate the signal thus allowing for fine control of muscle activation
Many diseases, toxins, and drugs...
interrupt events at the neuromuscular junction, myasthenia gravis is an example where in this disease acetylcholine receptors are deficient likely due to autoimmune destruction of the receptors
- symptoms of this disease include difficulty talking and swallowing, drooping upper eyelids, and generalized muscle weakness
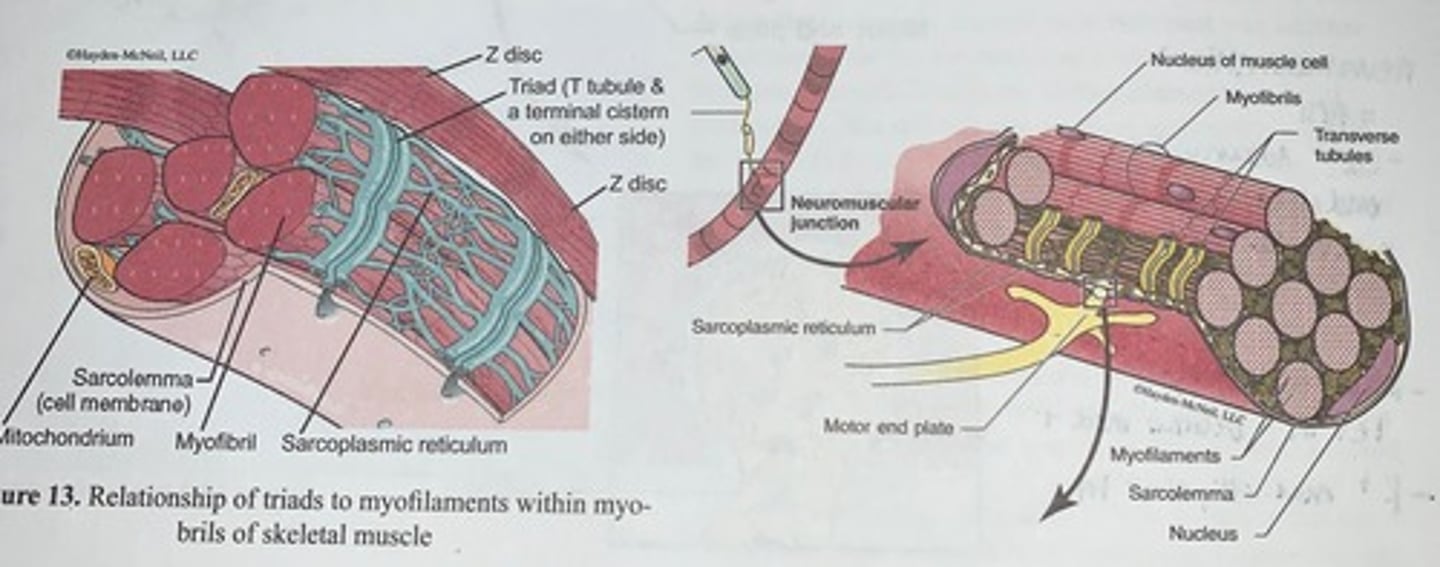
Relationship of triads to myofilaments within myofibrils of skeletal muscle
Motor unit anatomy
Myofilaments' alignments
All plasma membranes of all human cells...
including the sarcolemma of muscle fibers carry a resting charge or polarization where the inside of the cell is more negative relative to the outside, the initiation and propagation of a muscle action potential involves three steps:
First step:
acetylcholine binds to a receptor opening chemical ligand-gated ion channels for sodium and potassium
- a concentration difference across the membrane of these ions is greater for sodium thus more positive sodium enters the cell and potassium diffuses out
- these events transiently make the inner surface of the sarcolemma less negative = depolarization
- this begins at the end plate and is thus termed the end plate potential
Second step:
voltage-gated sodium channels on the surrounding sarcolemma respond to the change in charge and open allowing positive sodium to enter down its electrochemical gradient
- once a threshold potential is achieved the voltage change in the membrane becomes sufficient to open for the voltage-gated sodium channels and spread the signal in the form of a depolarization wave along the sarcolemma term a muscle action potential
Third step:
once the voltage becomes sufficiently less negative, this change in charge closes the voltage-gated sodium channels and open voltage-gated potassium channels
- the membrane then becomes more negative and repolarizes as positive potassium exits the cell down its concentration gradient
- once the membrane becomes sufficiently negative again at this change in charge closes the voltage-gated potassium channels
- the gradient differences for sodium and potassium are restored by a sodium potassium ATPase pump that moves sodium out and potassium in
- while repolarizing the cell cannot be stimulated again until the membrane is sufficiently negative
- this is termed the refractory period
The electrical events leading to the muscle contraction...
happen very transiently fast but the consequential contraction may last for more than 100 times the duration of the electrical signal
- the muscle action potential travels along the sarcolemma and down the T-tubules where the depolarization causes voltage-sensitive tubule proteins to undergo a change in shape which leads to opening of calcium release channels in the terminal cisterns
Calcium moves into the sarcoplasm where it...
removes inhibitory action of the tropomyosin as calcium binds to troponin causing the troponin to change shape which moves tropomyosin away to expose the binding active sites for myosin on the actin thin filaments
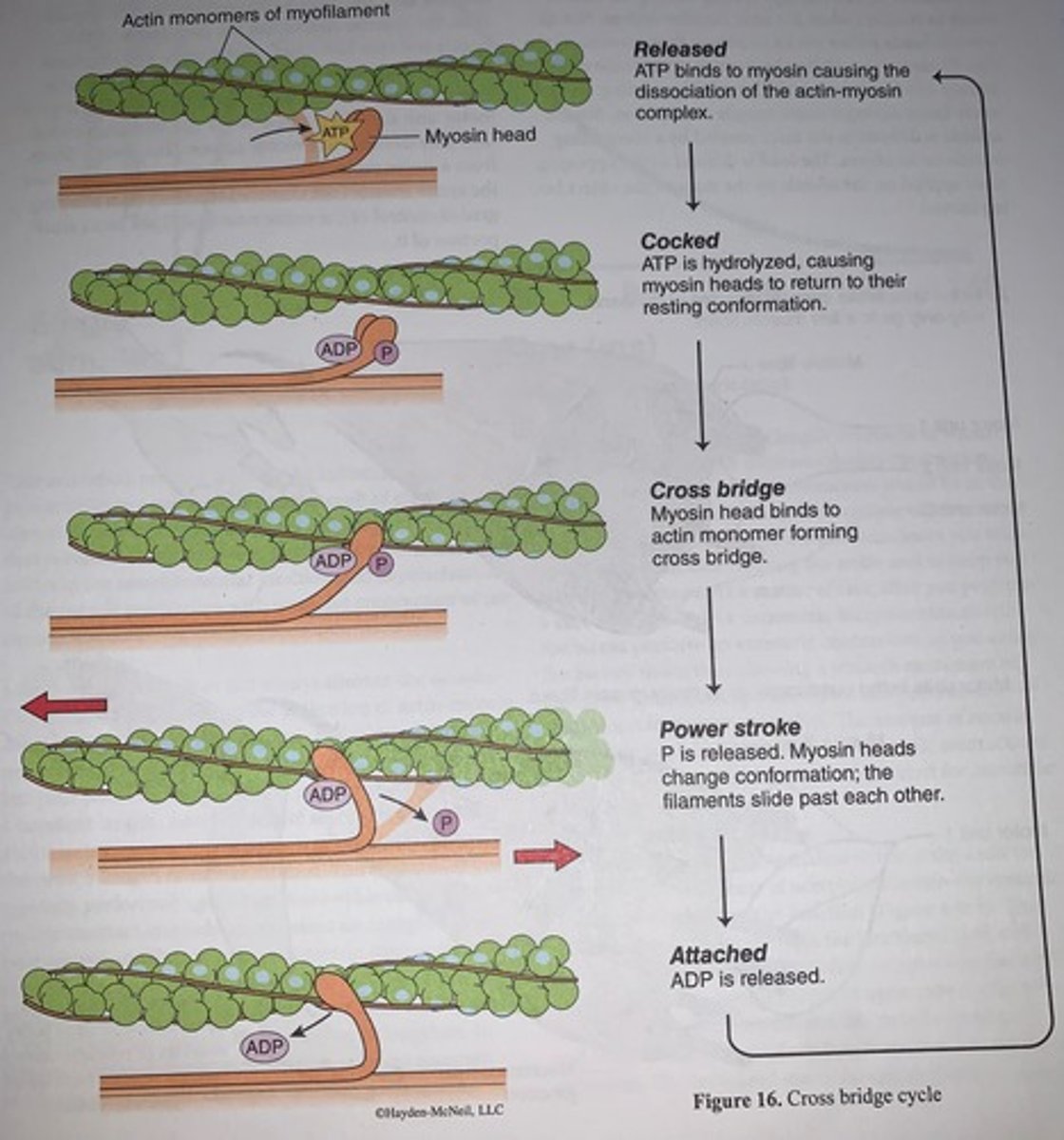
Myosin binds and cross bridge cycling commences...
the events from the stimulation of the muscle by the nerve to the contraction of the muscle are collectively referred to as excitation-contraction coupling
- when the membrane repolarizes the voltage sensitive tubule proteins regain their resting configuration which consequently closes the calcium release channels of the terminal cisterns
- calcium is actively pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum
- once calcium levels drop the inhibitory effect of tropomyosin is restored such the actin myosin no longer cross bridge leading to muscle relaxation
Tropomyosin physically blocks the _____________
myosin binding active sites on actin when intracellular calcium is low
- as calcium levels rises intracellularly it binds to troponin
- once two calcium ions bind to troponin and undergoes a change in shape which then forces tropomyosin to change position into the actin helix groove thus unblocking the myosin binding sites on actin
- myosin binds to actin, the power strokes occur as phosphate and ADP are released from the myosin head allowing the myosin to swivel or stroke from its high energy conformation to a lower energy state
This pulls the actin filament toward the ________________
M line
- ATP then binds to the myosin head causing the myosin head to detach (as a side note, this is the stage where rigor mortis takes over in the decease)
- if ATP is not present then the muscles will become stiff because actin and myosin cannot detach and do not detach until the muscles proceeded to degrade
- it takes time for rigor mortis to set in because after an animal passes away it takes some time for ATP to dissipate within the muscle fibers)
The next step in cross bridge cycling occurs as the...
ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP in phosphate which repositions the myosin head to its high energy "cocked" position
- the myosin binds to actin and the cycle repeats until either ATP is depleted or intracellular calcium is decreased
- when nerve impulses arrive at the muscle in rapid succession intracellular calcium quickly elevate and is sustained leading to another contraction before the muscle was completely relaxed
- this next contraction will best be stronger and/or more sustained
Myosin heads stay in their high energy conformation at...
the cessation of the cross bridge cycling leaving the muscle ready to contract when the next impulse arrive
- not all myosin heads powerstroke in unison thus preventing the thin filament from sliding backwards when some of the myosin heads are detached
- cross bridge cycling occurs many times during a single muscle contraction
Muscle tension
defined as the force exerted by a contracting muscle on an object
- load is defined as the opposing force applied on the muscle by the mass of the object being moved
Each individual muscle fiber is innervated by...
a branch of a motor axon
- under normal circumstances a neuronal action potential activates all the muscle fibers innervated by the motor neuron and it's axonal branches
- the motor neuron together with all of the individual muscle fibers that it innervates is termed a motor unit
Motor units vary greatly in size from...
just a few muscle fibers innervated by a single neuron (small motor unit) up to thousands (large motor unit)
- the smaller the muscle unit the finer the control of movement in that muscle
- muscles controlling the movement of the fingers and eyes have smaller motor units
- those controlling large limb muscles have very large motor units
Most muscle consists of a range of motor unit sizes...
regardless of the size a motor unit only contains one motor neuron
- the muscle fibers from a single motor unit are typically spread throughout the entire muscle (not clustered together) thus allowing graded control of the entire muscle and not just a small portion of it
This action process involves the initiation of an action potential...
(either voluntary or as a result of electrical stimulation of a peripheral nerve), conduction of the action potential along the nerve fiber, release of neurotransmitter at the neuromuscular junction and depolarization of the muscle membrane with resultant contraction of muscle fibers
Muscle contraction does not always ____________
shorten the muscle
- contraction really refers to the activation of actin-myosin cross bridges
- muscle contraction can either be isotonic or isometric
Isometric exercises:
the muscles contract but your joints do not move in muscle fibers maintain a constant length
- another way of saying this is that an isometric contraction muscle tension increases but the muscle length remains constant
- these exercises are typically performed against an immovable surface
- isometric contractions help us maintain an upright balanced posture and stabilize joints
- in isometric contractions the thin filaments do not move while the cross-bridges of form to generate force
Isotonic exercises:
a body part is moved in the muscle fibers shorten or lengthen
- isotonic contractions muscle tension remains constant but the muscle length changes
- isotonic contractions are concentric if the muscle length decreases or eccentric if the muscle length increases during contraction
- an example of concentric contraction would be in the biceps while curling a barbell
- an example of eccentric contraction would be in a calf muscles as you walk uphill to prevent over rotating the ankle to keep you stable as you move, after you perform a curl with a barbell (a concentric biceps contraction) the biceps perform an eccentric contraction as you swing the barbell down this allowing a smooth movement of the elbow joint both up and down and prevents the elbow joint from over-extension
- the amount of muscle shortening is typically measured for isotonic contractions while increasing muscle tension is measured for isometric contractions
Cross bridge formation
Cross bridge cycle
Motor unit comparison of large bulky muscles of postural control versus smaller muscles of fine movements
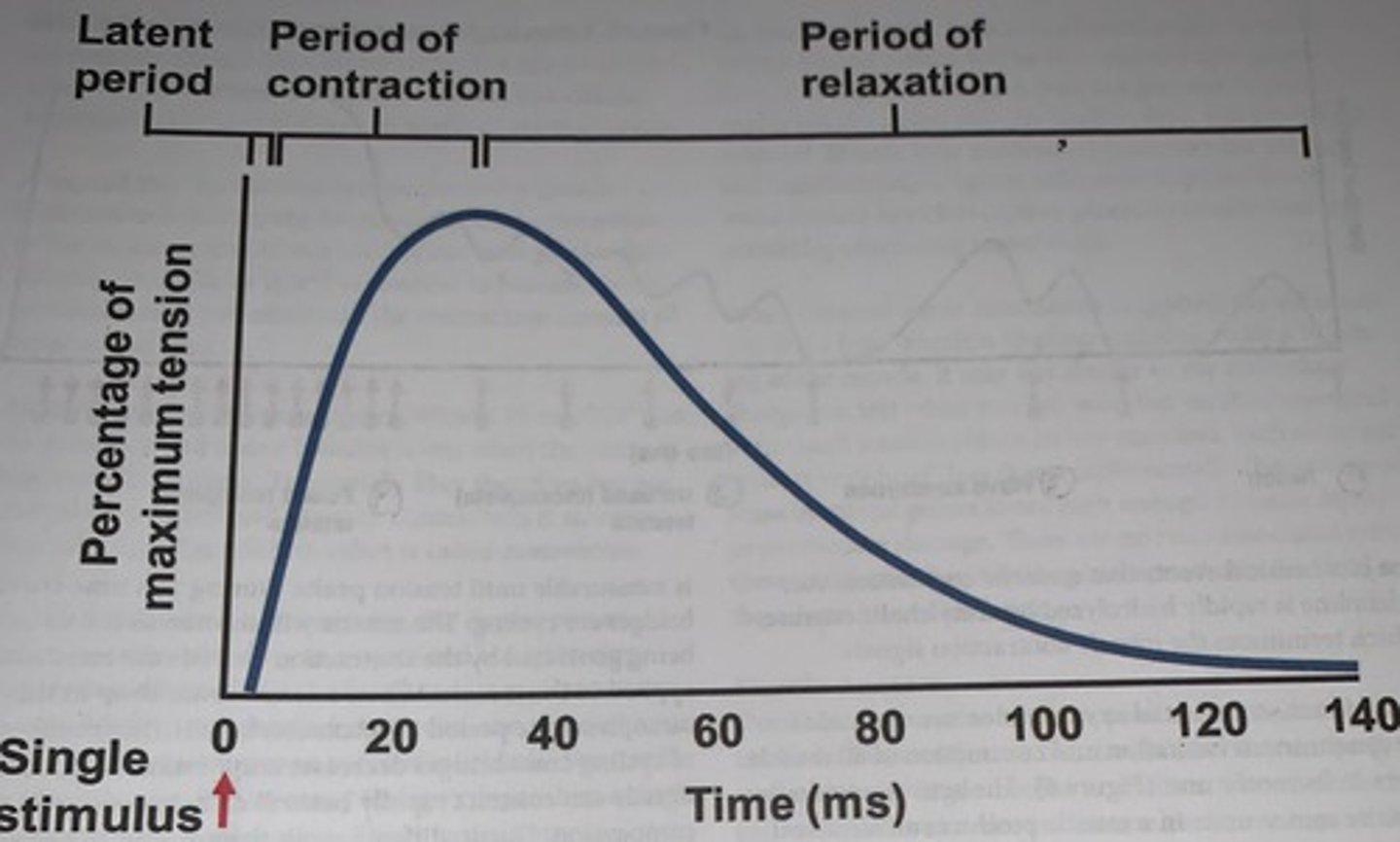
Myogram showing the three phases of an isometric twitch
Action potentials arriving at the axon terminal trigger...
the release of acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft of the neuromuscular junction
- the acetylcholine diffuses through the junctional cleft in fine to the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on the motor end plate
- the bound receptors often cation-selective ion channels which depolarizes the muscle in plate and leads to the release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Increased cytosolic calcium sets in motion...
the biochemical events that underlie contraction
- acetylcholine is rapidly hydrolyzed by acetylcholinesterase which terminates muscle contraction signals
Single action potential in one motor neuron lead to...
the synchronous excitation and contraction of all muscle fibers and its motor unit
- the activation of one or more motor units in a muscle produces an electrical event that is often sufficiently large to be detectable with electrodes applied to the skin surface
- such an extracellular recording of the electrical activity in a whole muscle is called Electromyogram (EMG)
- in the EMG you are observing a compound muscle potential (CMP): the sum of the electrical activity of many individual muscle fibers all firing at once
- the magnitude of the CMP reflects the number of motor units activate
An action potential in a motor neuron induces...
an action potential in the muscle fibers it innervates by releasing the neurotransmitter acetylcholine in the neuromuscular junction
- this muscle action potential causes a brief increase in the intracellular concentration of calcium ions and activates the contractile molecular machinery inside the fiber
This requires the use of intracellular supplies of ____________
ATP as the energy source
- the result is a brief contraction called at twitch
- a muscle twitch is a motor unit reaction to a single action potential of its motor neuron
- every twitch is made up of three parts or periods: the latent period, the period of contraction, and the period of relaxation, excitation-contraction coupling occurs during the latent period which only lasts a few milliseconds after stimulation
- cross bridges are beginning to form but measurable tension has not been achieved
- the greater a load that is applied to a muscle the longer the latent period will be
- the period of contraction last from once tension is measurable until tension peaks
- during this time cross bridges are cycling
The muscle will shorten as the force being generated by the contraction exceeds...
the resistance applied to the muscle, when calcium levels drop in the sarcoplasm of the period of relaxation begins
- the number of cycling cross-bridges decreases and tension declines
- a muscle can contract rapidly but will relax more slowly in comparison
- due to differences in the enzyme composition and metabolic properties of different muscles in the body, some muscles will twitch and relax more rapidly (such as the lateral rectus eye muscle) then other slower muscles (such as the soleus calf muscle)
A whole muscle is controlled by...
the firing up of motor axons
- these motor nerve control movement in a variety of ways to produce smooth strength graded muscle responses
- one way in which the nerve system controls a muscle is by adjusting the number of motor axons firing
- thus controlling the number of twitching muscle fibers
- this process is called recruitment
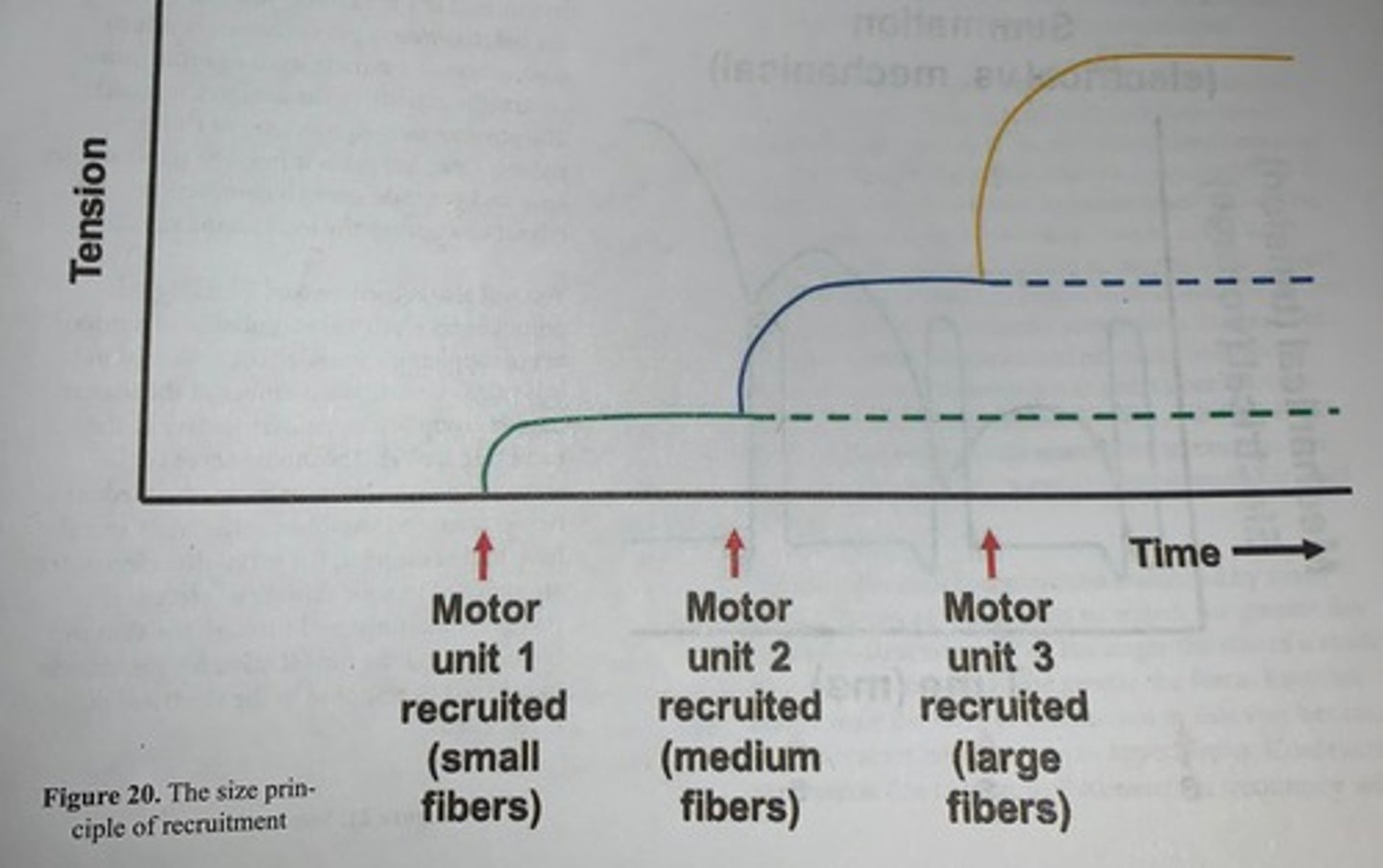
A threshold stimulus is achieved when...
the stimulus is just strong enough to generate an observable contraction
- as stimulus strength increases so does the muscle contraction until a maximum contraction is reached at which a maximal stimulus stimulates the muscle to contract with as much force as possible and higher stimuli do not increase the strength of contraction
- this stepwise but smooth increase and strength of contraction with strength of stimulus is due to the physiological property called the size principle in which the central nervous system signals small motor units as the stimulus increases until no more motor units are available to be recruited Comet low threshold easy excitable motor neurons control smaller motor units and high threshold
- at least excitable motor neurons can control large motor units
- the size principle explains how the same muscle can control fine delicate movements and also perform powerful heavy maneuvers
A second way the nervous system controls a muscle contraction is...
to vary the frequency of action potentials and the motor axons
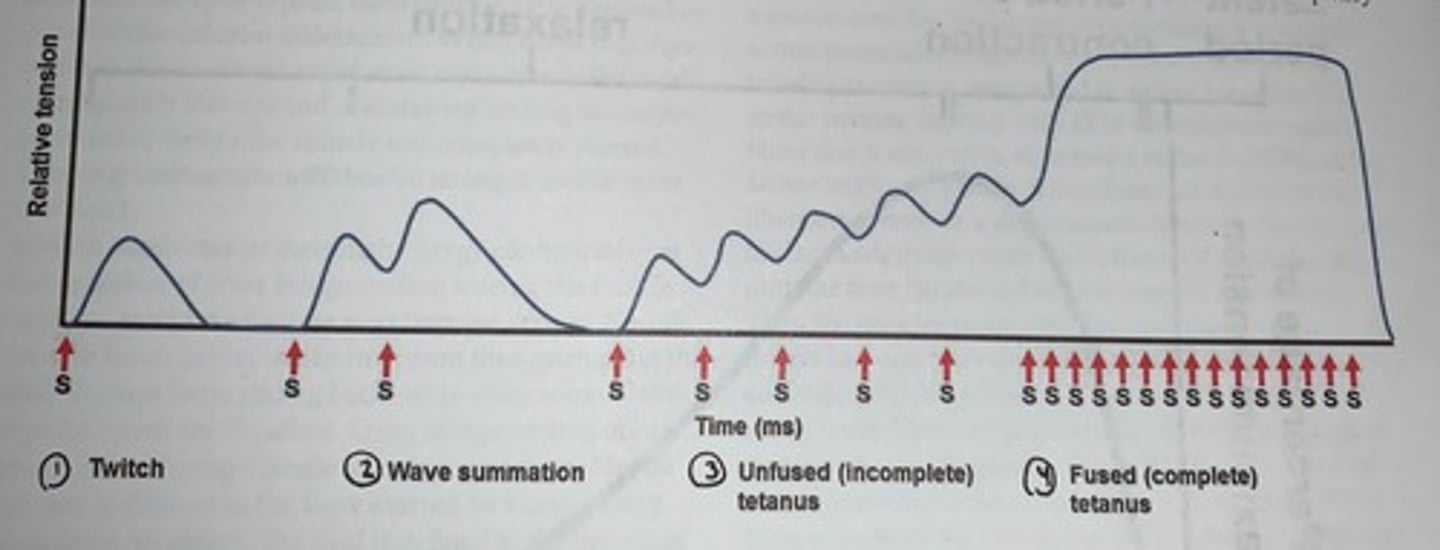
- at stimulation intervals greater than 200ms intracellular calcium is restored to baseline levels between action potentials and the contraction consists of separate twitches
- at stimulation intervals between 200 and 75ms calcium in the muscle is still above baseline levels when the next action potential arrives
- the muscle fiber therefore has not completely relax in the next contraction is stronger than normal
- this additive effect is called summation
At higher stimulation frequencies the degree of summation increases...
reading to a sustained but quivering contraction referred to as unfused or incomplete tetanus
- at even higher stimulation frequencies the muscle has no time to relax at all between successive stimuli
- the result is a smooth contraction many times stronger than a single twitch: a tetanic contraction
- this muscle is now in a state of complete or fused tetanus
Skeletal muscle also maintains a baseline tone in which...
even a relaxed muscle will be in a state of slight contraction
- this slight contraction does not give rise to movements but does keep muscles healthy, firm, and primed respond
- muscle tone additionally generates are posture and stabilize joints
- spinal reflexes in response to activated muscle stretch receptors generates muscle tone by activating alternating motor units
When external nerve stimulation is applied...
the volunteer will feel a brief pinch, a tingling sensation, with a twitching of the muscle
- it may feel similar to the static discharge you feel when you rub your feet on the carpet and then touch a metal object
- in our exercises each electrical pulse is brief (less than a millisecond)
- the voltage of these electrical pulses is not high enough to cause injury or permanent damage
- there are no risks associated with the small currents
- nothing is inserted into the skin so there is no risk of infection
Muscle's response to changing stimulation frequency
Size principle of recruitment
The skeleton provides both ______________
support and articulation for the body
- bones adjacent to other bones have uniquely crafting interacting joints (or articular surfaces) on each end which allow and almost frictionless movement of the adjacent bones through a narrowly directed range of motion
- joints act as pivot points for motion when skeletal muscle either connected directly to bone are connected to strong bundles of collagen fibers called tendons contracts
Two or more muscles usually work ____________
antagonistically
- in this arrangement as one muscle contracts and shortens its antagonist relaxes and elongates
Electromyography is a technique that measures the ______________
electrical activity of muscles and nerves controlling their muscles
- the data recorded in an electromyogram (also known as an EMG or myogram)
- there are two methods of recording: needle electrodes inserted through the skin into the muscle or electrodes placed on the skin surface
The size and shape of the waveform measured provides...
information about the ability of the muscle to respond when the nerves are stimulated
- in the clinical setting EMG is most often used when people have symptoms of weakness and examination shows and impaired muscle strength
- it can cause help to differentiate muscle weakness caused by neurological disorders from other conditions
The EMG provides a deception of _______________
the timing and pattern of muscle activity during complex movements
- the raw surface EMG signal reflects the electrical activity of the muscle fibers active at that time
- motor units fire asynchronously and it is sometimes possible with exceedling weak contraction to detect the contributions of individual motor units to the EMG signal
- as the stretch of the muscular contraction increases the intensity of action potentials increases and the raw signal at any time may represent the electrical activity of perhaps thousands of individual fibers
The raw EMG signal during voluntary contractions may...
be processed in various ways to indicate the intensity of EMG activity
- in the method used hear the negative growing portions of the EMG are inverted in then the whole signal is integrated in such a way as to smooth out individual spikes and make the time course of changing activity much clearer
In this part of the exercise you will examine coactivation:
a phenomenon in which contraction of a muscle leads to some minor contractile activity in the antagonist muscle
- the physiological significance of this is not entirely clear but it likely helps to stabilize the joint in generate smooth contractions and relaxation against the load on the muscle
You will also record evoked EMG signals produced by...
electrical stimulation of motor nerve supplying a muscle
- the abductor pollicis brevis muscle is a member of the thenar muscle group on the palmar surface of the hand
- the motor nerve to the abductor pollicis brevis muscle (the median nerve) is easy to stimulate at the wrist and elbow
- in this exercise flat metal disc electrodes are attached to your skin, brief electrical pulses are administered through the skin to the nerve
- and the time it takes for the muscle to contract in response to the electrical pulse is recorded
The speed of the response is dependent on ______________
the conduction velocity
- in general the range normal conduction velocities will be approx 50 to 60 meters per second
- however the normal conduction velocity may vary from one individual to another and from one nerve to another
Nerve and muscle disorders cause the muscles _____________
to react in abnormal ways
- measuring the electrical activity in muscles and nerves can help detect the presence
- location and extent of diseases that damage muscle tissue (muscular dystrophy) or nerves (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Lou Gherig's disease)
- in the case of nerve injury the actual site of nerve famae can often be located
- in clinical setting EMG and nerve conduction studies are usually done together